Similar presentations:
Intro to international relations (class 9)
1.
PLS 150 INTRO TO INTERNATIONALRELATIONS
DR MAJA SAVEVSKA
Assistant Professor
Department of Political Science and International Relations
SSH | Nazarbayev University
Office: 8.502
Email: maja.savevska@nu.edu.kz
30-11-22
Intro to IR
Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan
2.
Week NineMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (10
min)
• Interactive
Activities
3.
Current Events4.
RecapWhat does the Heckscher-Ohlin theory predict
about trade? What will a country export most?
What are the two alternative approaches to
explaining trade preference formation?
5.
Issue AreasTrade
Globalization of Production and FDI
Monetary Affairs
Development and Inequality
6.
Globalization“Accelerating set of processes involving
flows that encompass ever greater number
of the world’s spaces and the lead to
increasing integration and interconnectivity
among those spaces” (Ritzer 2009:1).
7.
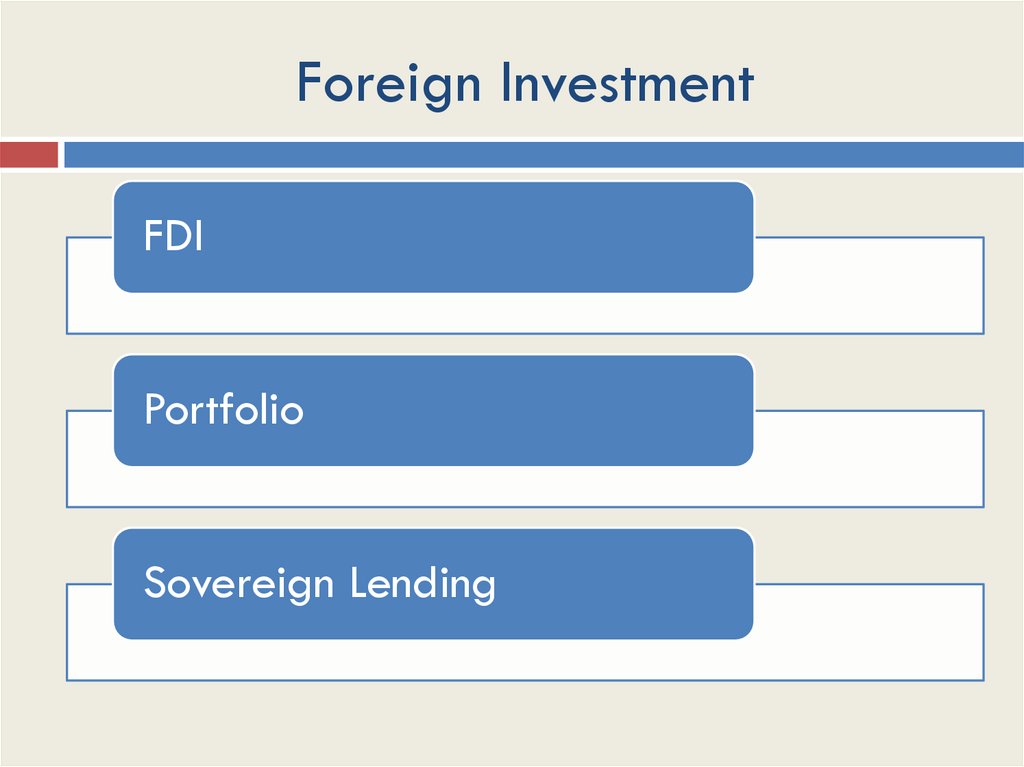
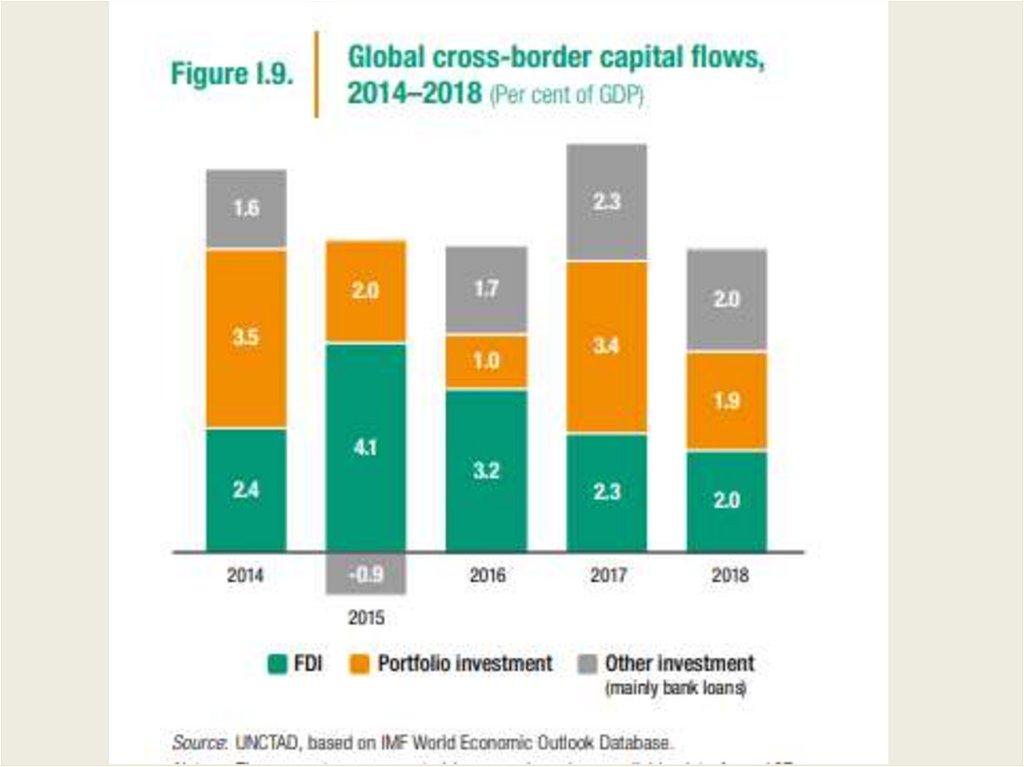
Foreign InvestmentFDI
Portfolio
Sovereign Lending
8.
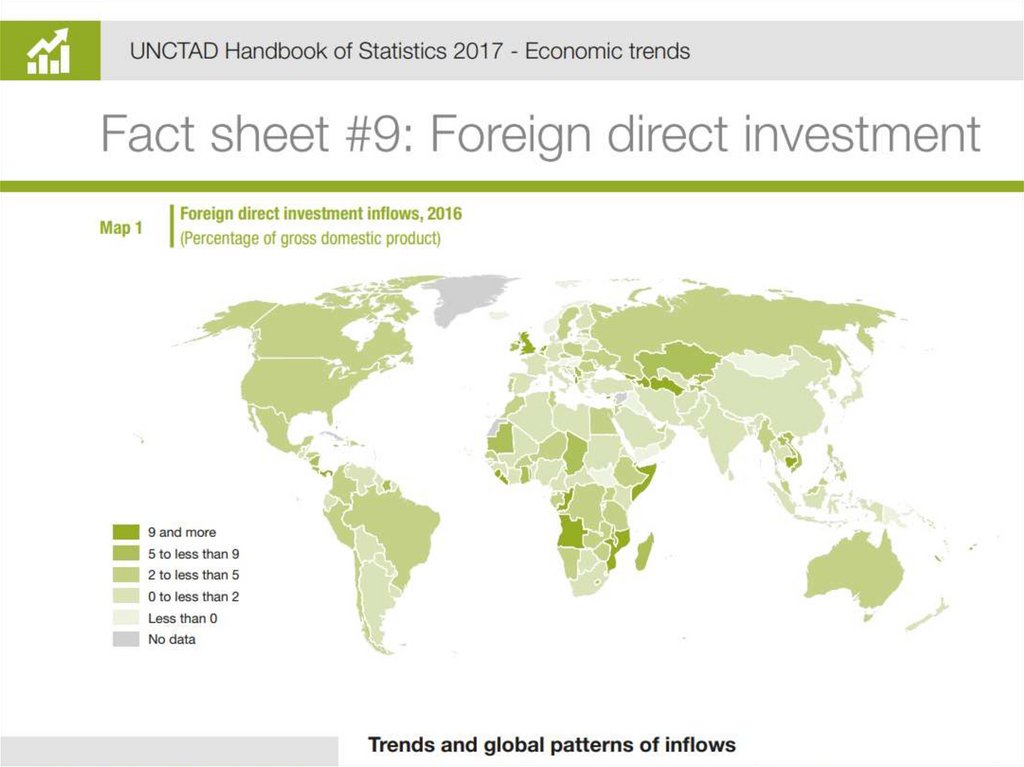
Foreign InvestmentForeign Direct Investment
Investment abroad
Managerial control
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
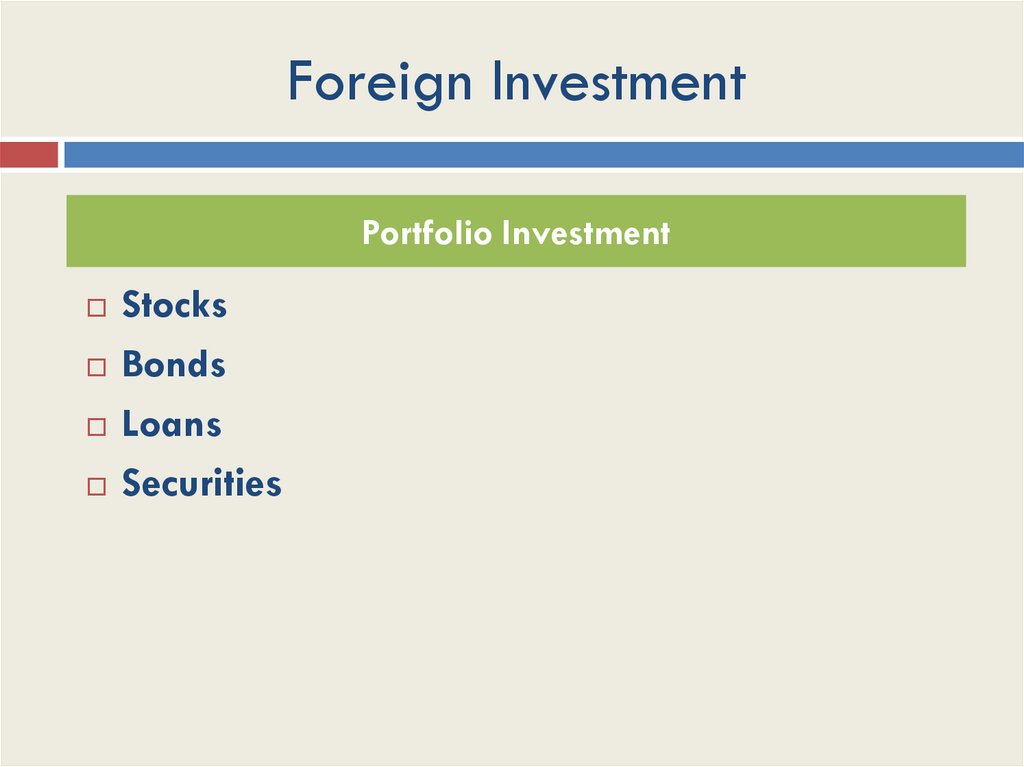
Foreign InvestmentPortfolio Investment
Stocks
Bonds
Loans
Securities
14.
Foreign InvestmentSovereign Lending
Loans to governments
Private investors
Public:
IMF
Bilateral
Concessional
15.
16.
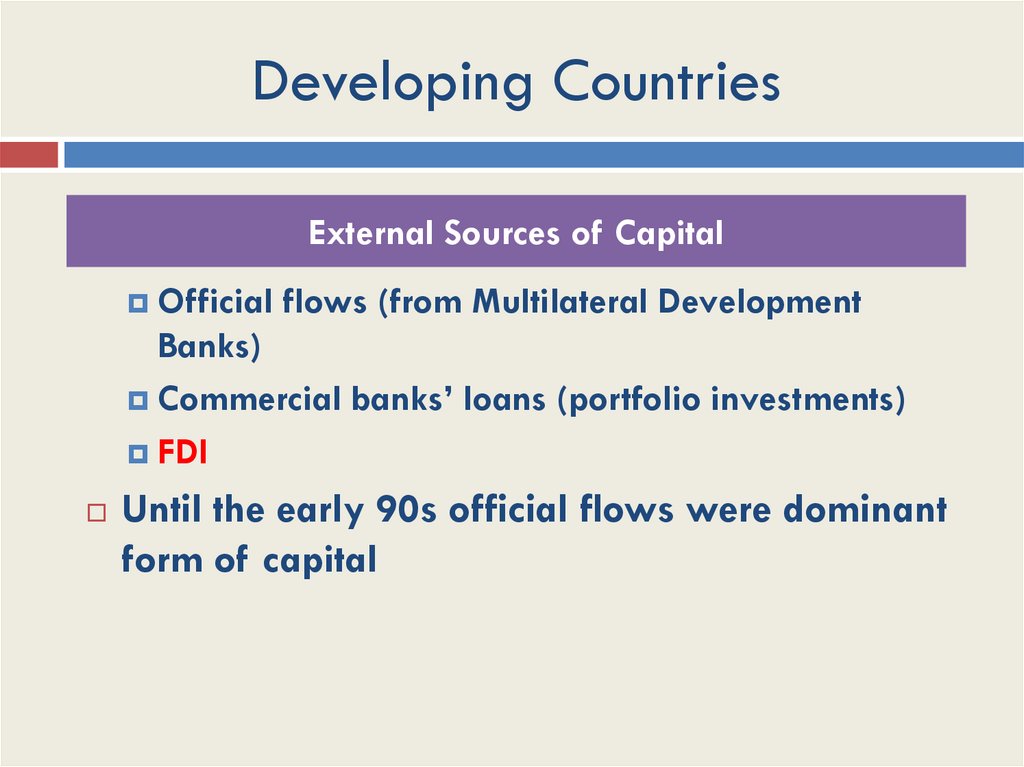
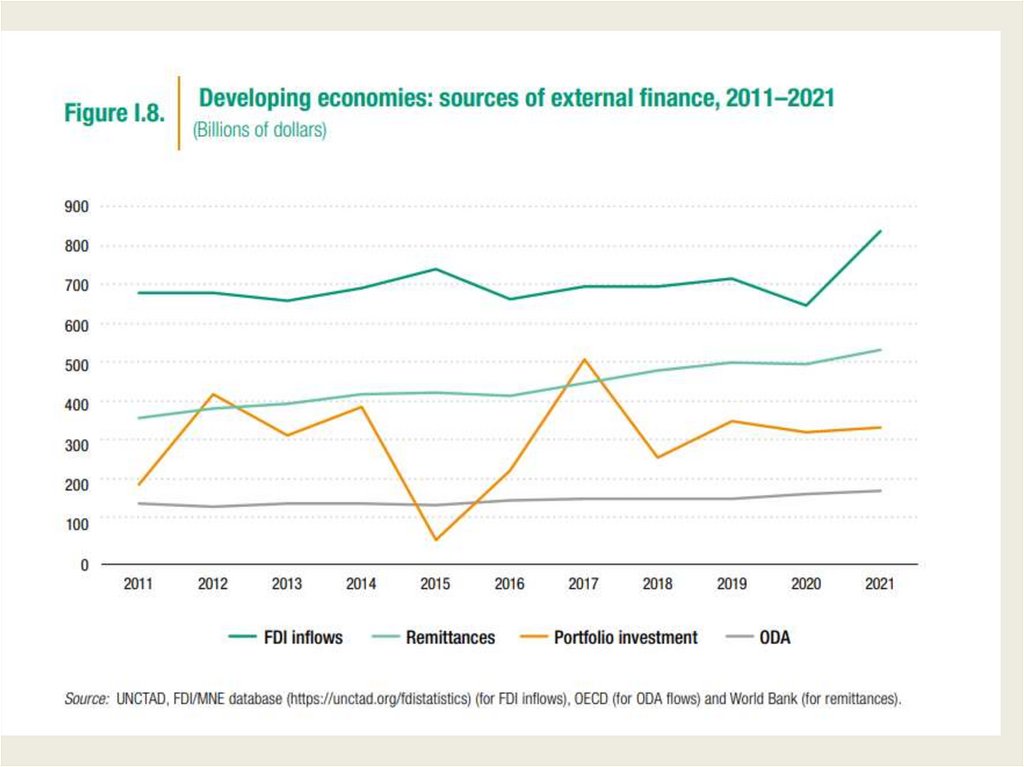
Developing CountriesExternal Sources of Capital
Official flows (from Multilateral Development
Banks)
Commercial banks’ loans (portfolio investments)
FDI
Until the early 90s official flows were dominant
form of capital
17.
18.
Week NineMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (20
min)
• Interactive
Activities
19.
Current Events20.
Foreign InvestmentWhy Invest?
Common interests:
Profit for investors
Access to finance for recipients
21.
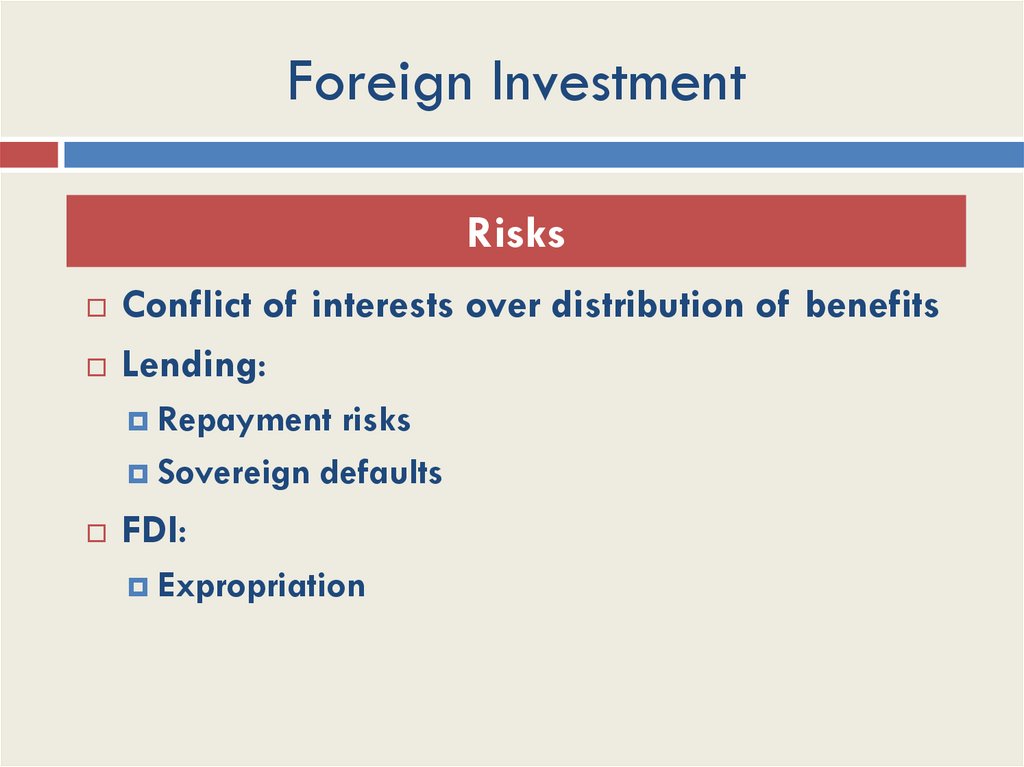
Foreign InvestmentRisks
Conflict of interests over distribution of benefits
Lending:
Repayment risks
Sovereign defaults
FDI:
Expropriation
22.
Foreign Investment: LendingDebtor-Creditor Relationship
Solutions to information asymmetry problems:
International Organizations
BIS
IMF
World Bank
23.
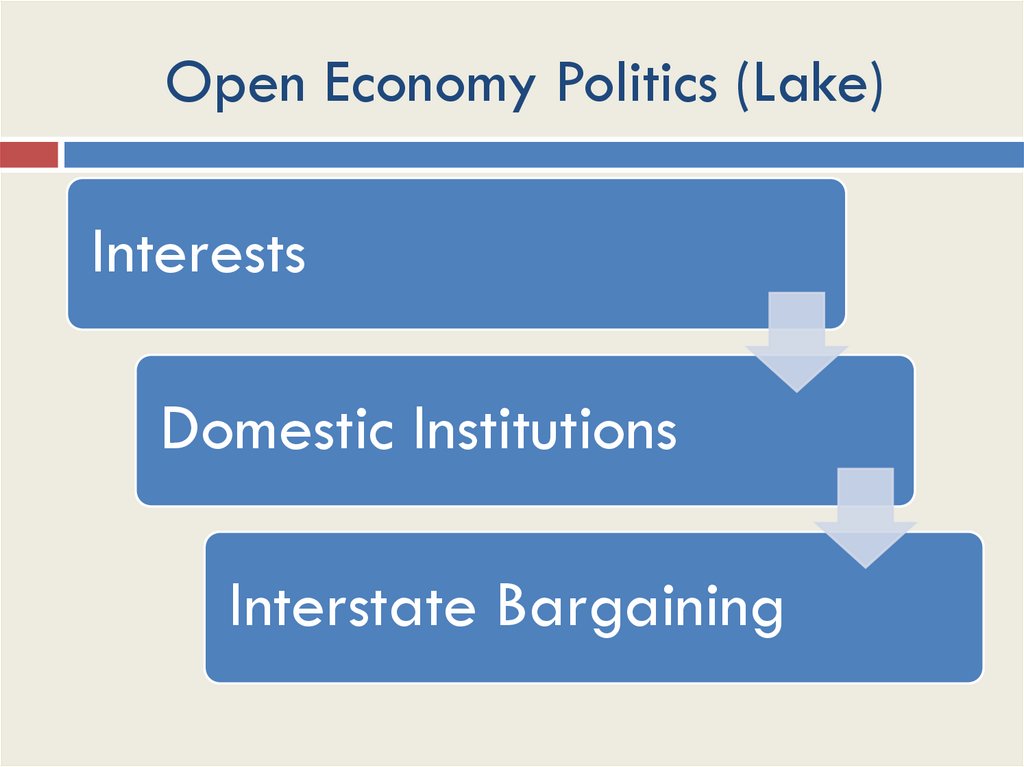
Open Economy Politics (Lake)Interests
Domestic Institutions
Interstate Bargaining
24.
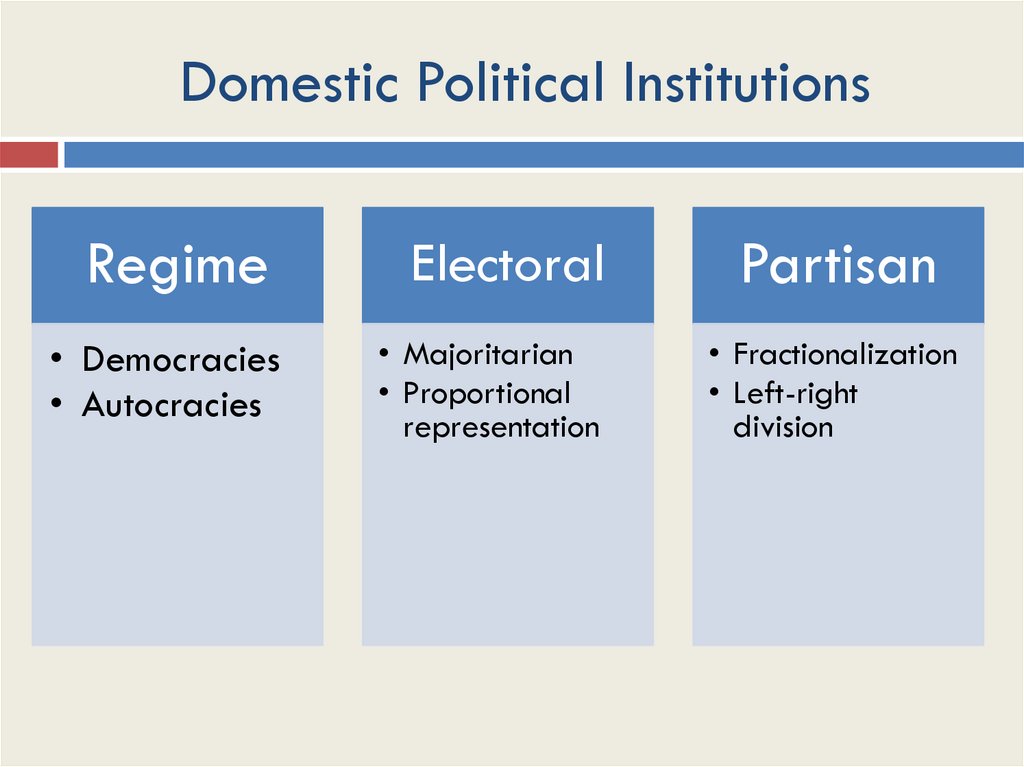
Domestic Political InstitutionsRegime
Electoral
Partisan
• Democracies
• Autocracies
• Majoritarian
• Proportional
representation
• Fractionalization
• Left-right
division
25.
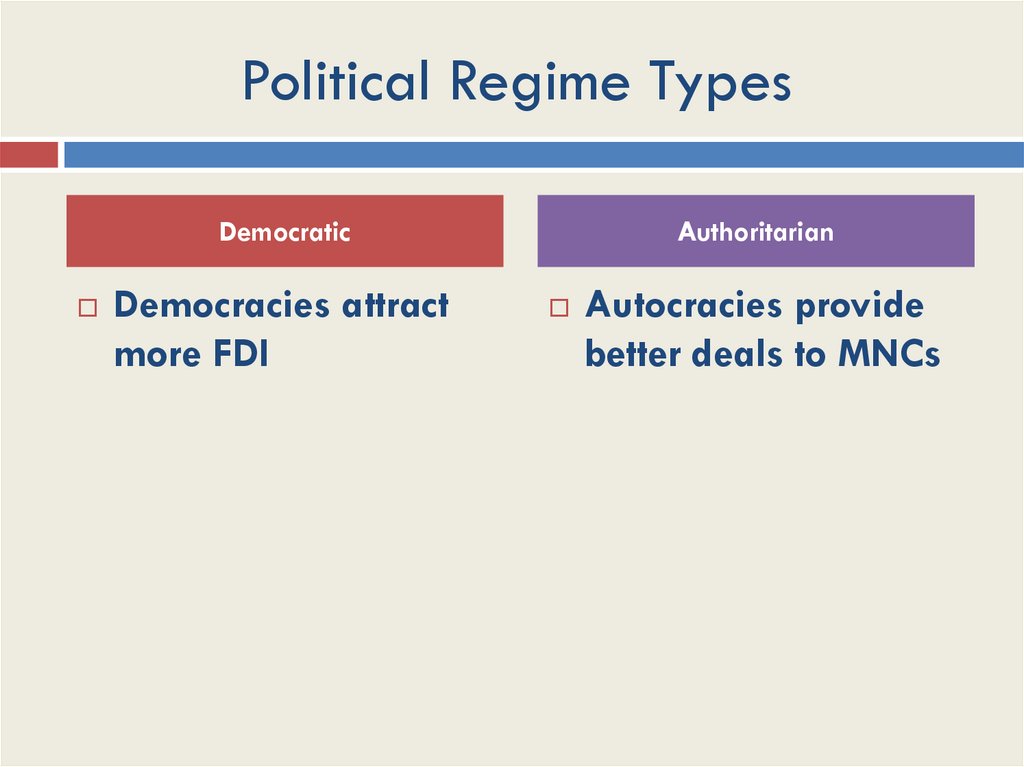
Political Regime TypesDemocratic
Democracies attract
more FDI
Authoritarian
Autocracies provide
better deals to MNCs
26.
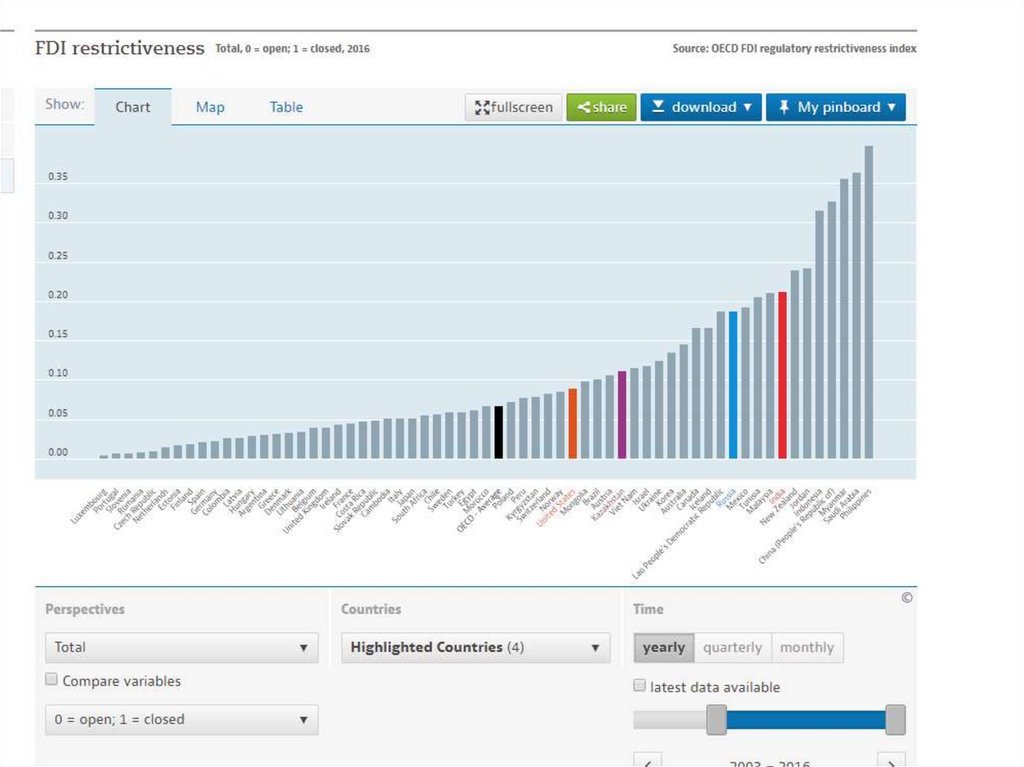
International Investment RegimeLevel of Institutionalization
Protection of investment under international
law
Absence of multilateral organization
BITs:
Example of measures:
Regulation of expropriation
Preference of local companies vs. foreign
Fair and equitable treatment of foreign investors
27.
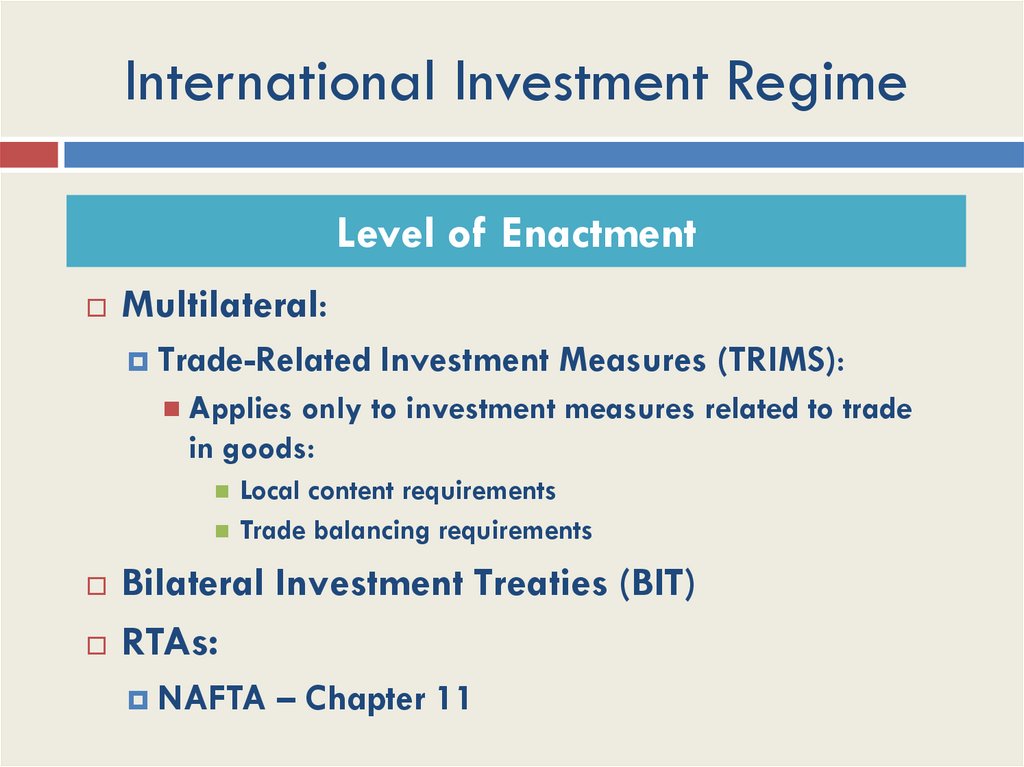
International Investment RegimeLevel of Enactment
Multilateral:
Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS):
Applies only to investment measures related to trade
in goods:
Local content requirements
Trade balancing requirements
Bilateral Investment Treaties (BIT)
RTAs:
NAFTA – Chapter 11
28.
Week NineMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
finance (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (20
min)
• Interactive
Activities
29.
Current Events30.
Kahoot!31.
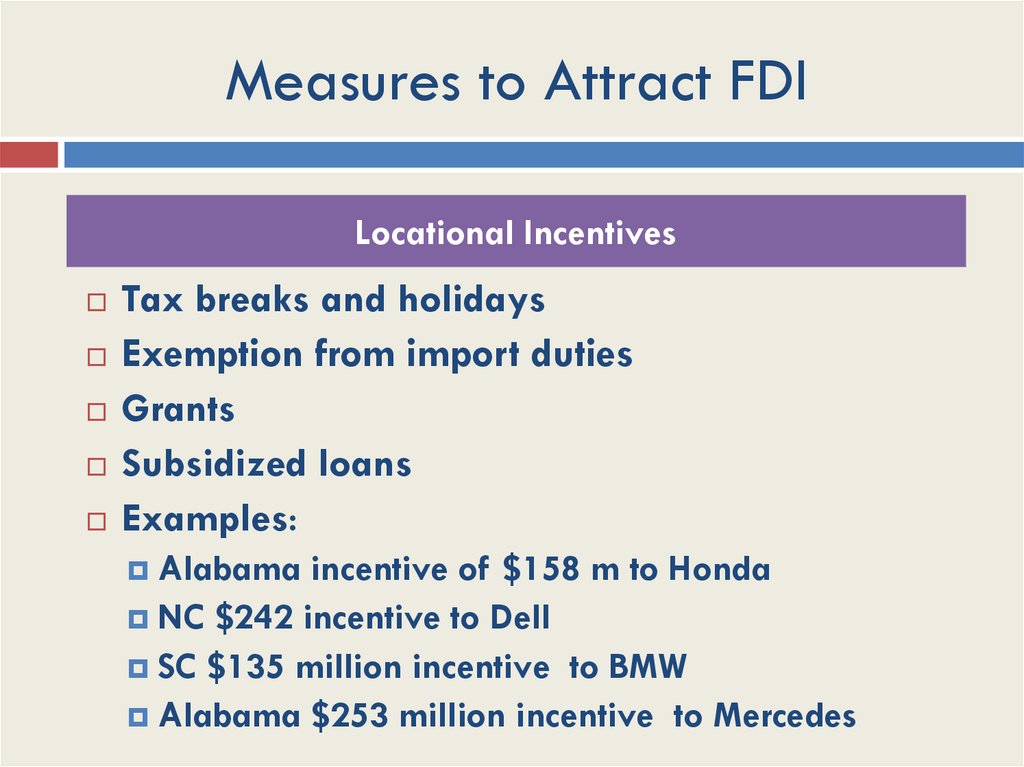
Measures to Attract FDILocational Incentives
Tax breaks and holidays
Exemption from import duties
Grants
Subsidized loans
Examples:
Alabama incentive of $158 m to Honda
NC $242 incentive to Dell
SC $135 million incentive
to BMW
Alabama $253 million incentive to Mercedes
32.
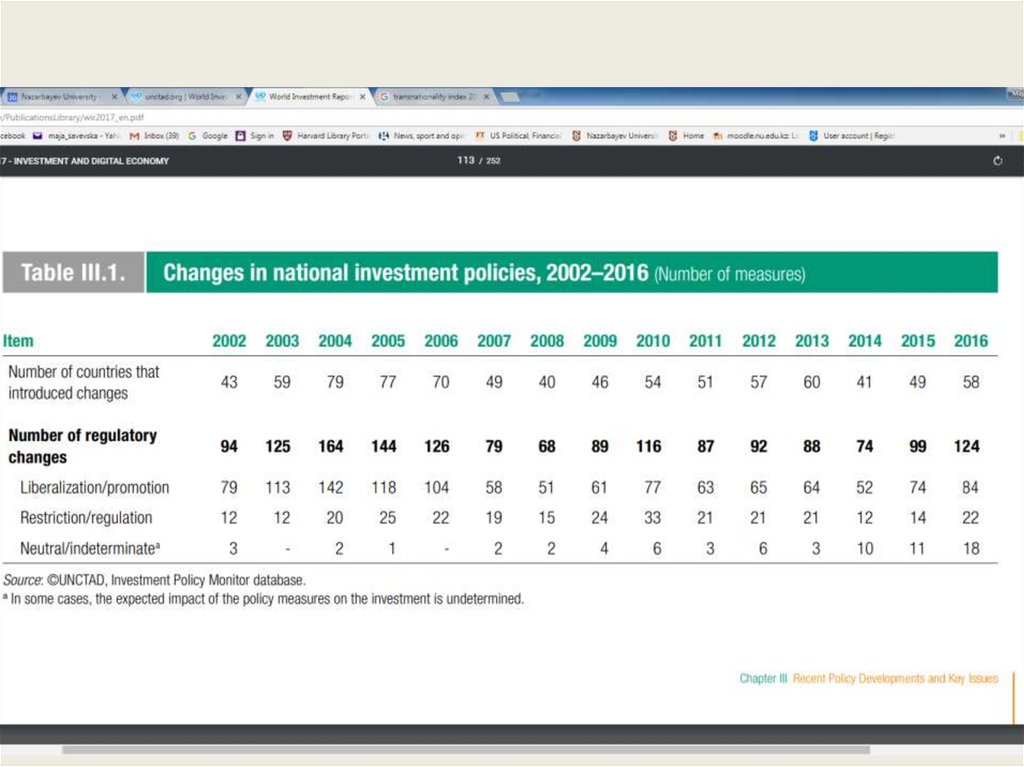
DataUNCTAD
Between 2000 and 2010 UNCTAD documented a total of
1944 investment-related regulatory changes
85% were liberalizing investment
15% were investment restrictive
33.
34.
35.
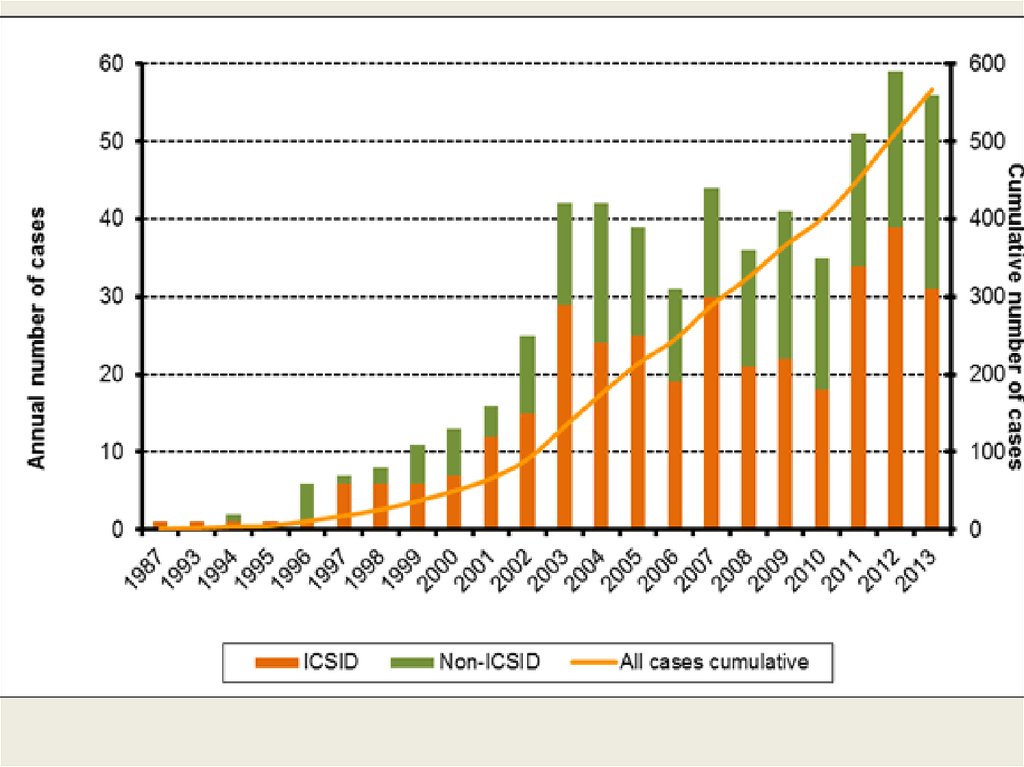
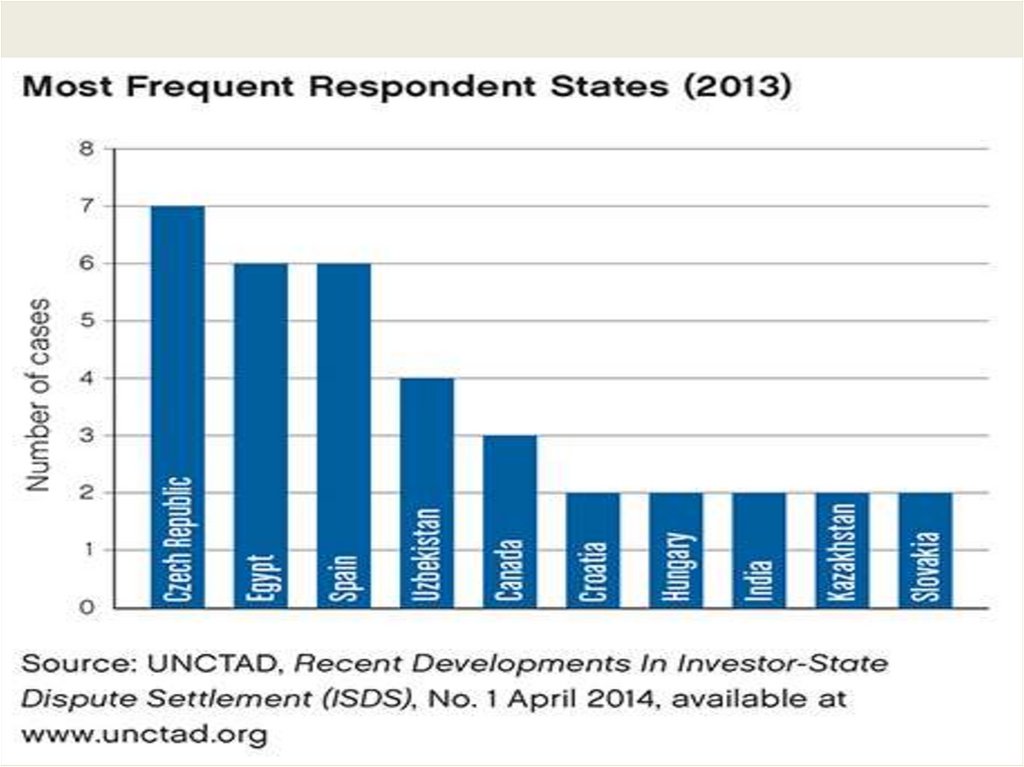
International Investment RegimeEnforcement Mechanism
Investor-State Dispute Settlement mechanisms
Judicial review
Ex: International Centre for the Settlement of
Investment Disputes (part of World Bank Group)
36.
37.
38.
Exercise IInvestment
UNCTAD’s investment hub
Find Kazakhstan data about how many BIT it
has signed and how many Treaties with
Investment Provisions (TIP).
How many BITs and TIPs in total in the world?
http://investmentpolicyhub.unctad.org/ISDS
39.
Exercise IIInvestment
UNCTAD’s investment hub
Explore the Investment Policy Monitor
Explore the Investment Law Navigator
Choose few countries and see the type of
measures they implement
40.
Exercise IIIInvestment
UNCTAD’s investment hub
Find Kazakhstan data about investor-state
dispute settlements
http://investmentpolicyhub.unctad.org/ISDS
41.
Q&ADr Maja
Savevska
Thank you for your attention





















 economics
economics








