Similar presentations:
Intro to international relations (class 8)
1.
PLS 150 INTRO TO INTERNATIONALRELATIONS
DR MAJA SAVEVSKA
Assistant Professor
Department of Political Science and International Relations
SSH | Nazarbayev University
Office: 8.502
Email: maja.savevska@nu.edu.kz
30-11-22
Intro to IR
Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan
2.
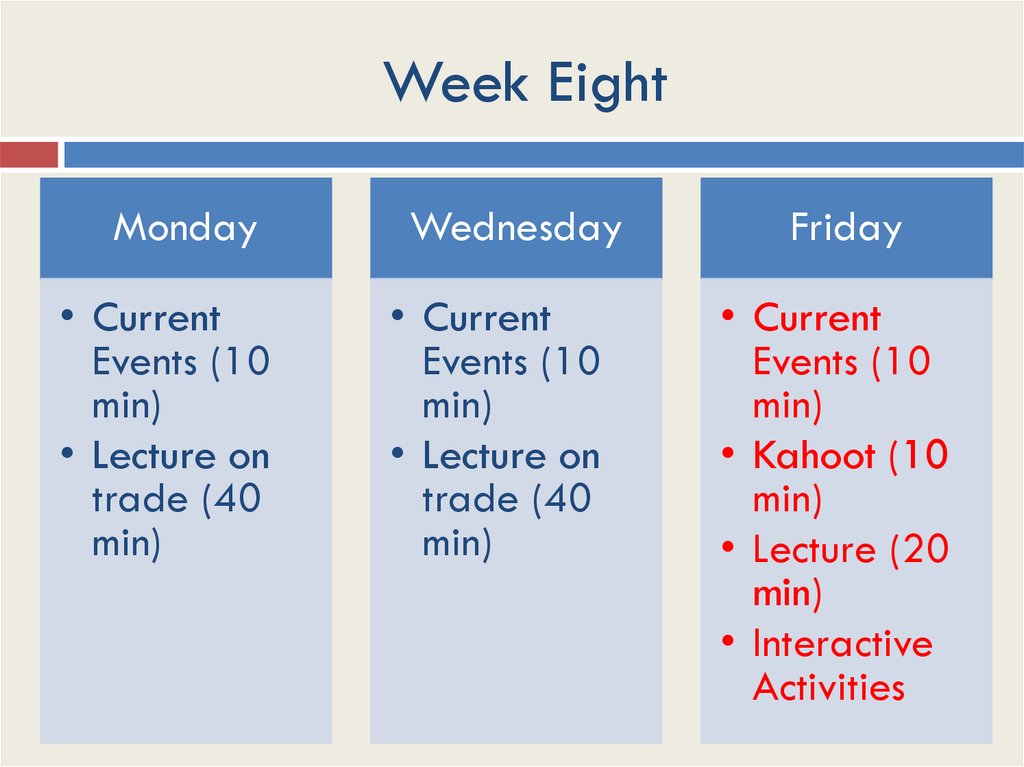
Week EightMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (20
min)
• Interactive
Activities
3.
Current Events4.
AnnouncementYou have to choose a paper topic by the end of
week 9
You have to declare your topic via Moodle
Choose any weekly topic
5.
Issue Areas in IRSecurity
International Political
Economy
6.
Issue AreasTrade
FDI and Globalization of Production
Monetary Affairs
Development and Inequality
7.
8.
9.
10.
TradeExchange of goods and services
Domestic trade
Wholesale and retail
International trade
Across borders
11.
Why Should Countries Trade?Economic Case
Makes them better off
Production Possibility Frontier
Opportunity costs:
The value foregone in order to make one product rather
than another
12.
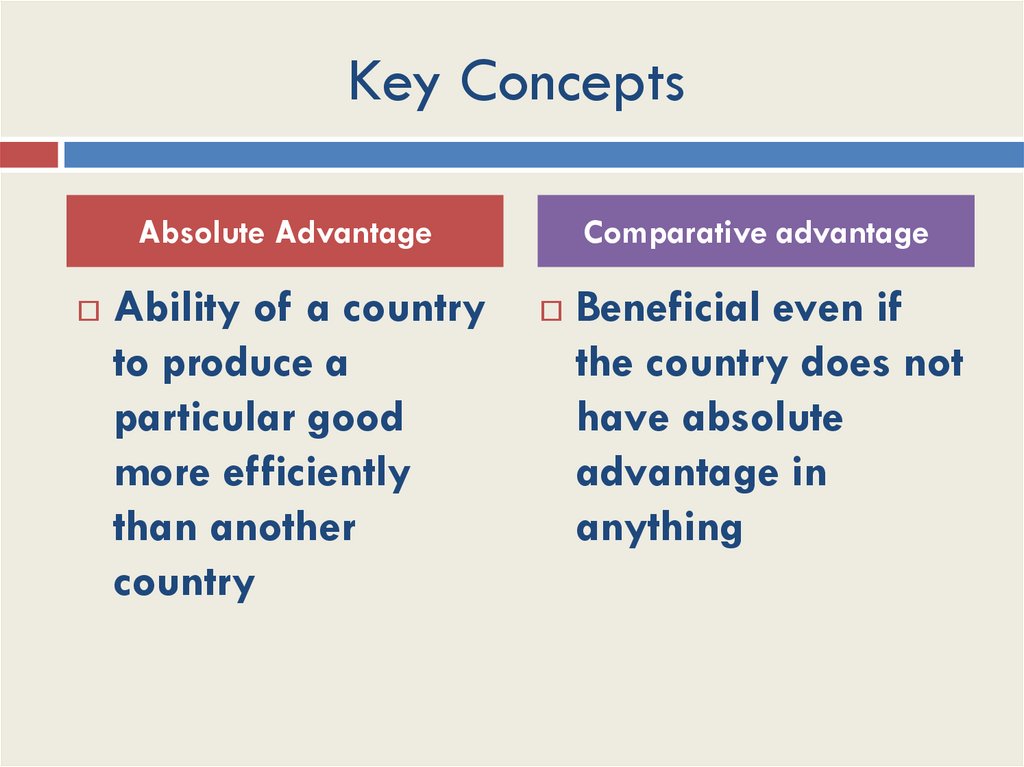
Key ConceptsAbsolute Advantage
Ability of a country
to produce a
particular good
more efficiently
than another
country
Comparative advantage
Beneficial even if
the country does not
have absolute
advantage in
anything
13.
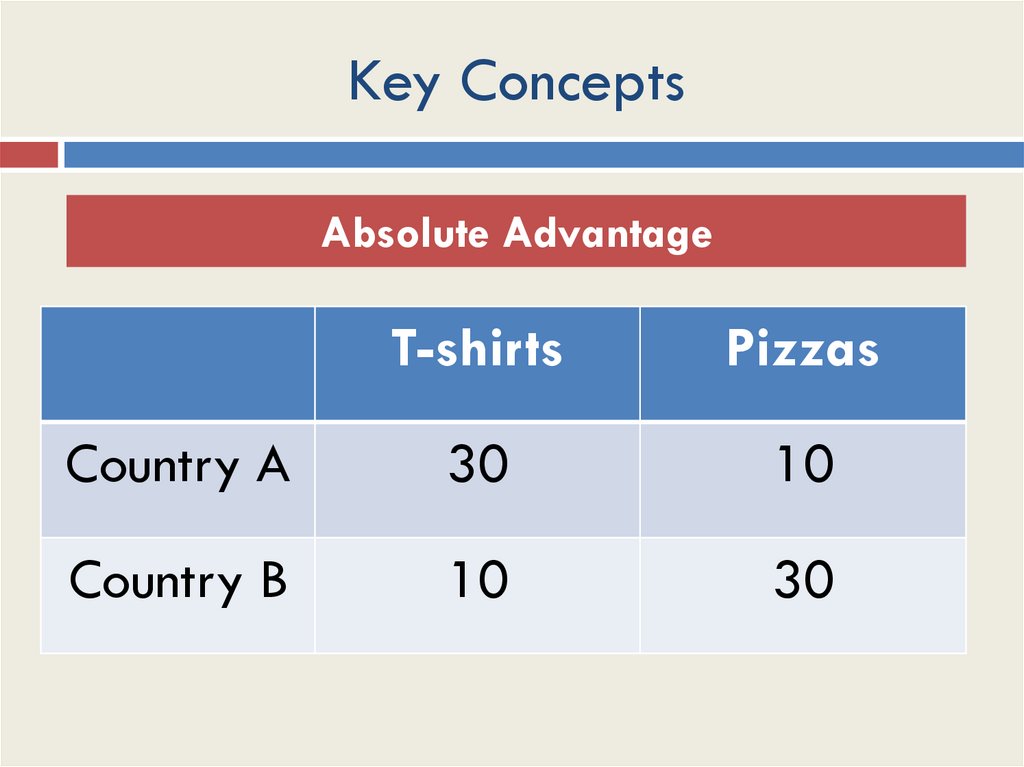
Key ConceptsAbsolute Advantage
T-shirts
Pizzas
Country A
30
10
Country B
10
30
14.
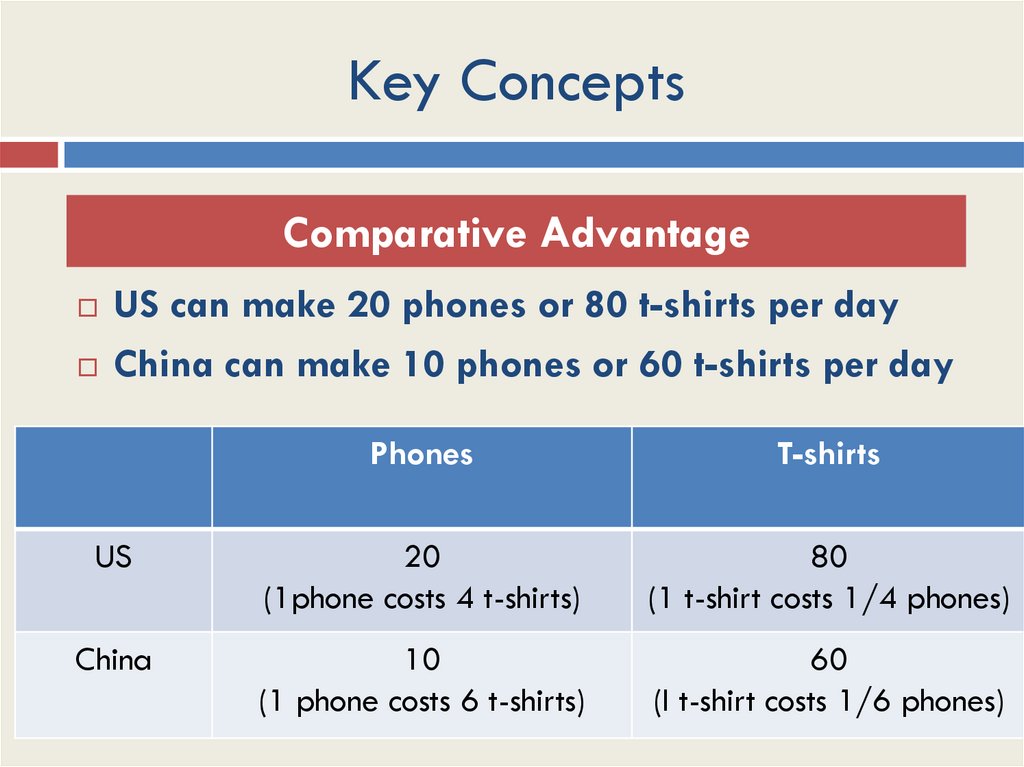
Key ConceptsComparative Advantage
US can make 20 phones or 80 t-shirts per day
China can make 10 phones or 60 t-shirts per day
Phones
T-shirts
US
20
(1phone costs 4 t-shirts)
80
(1 t-shirt costs 1/4 phones)
China
10
(1 phone costs 6 t-shirts)
60
(I t-shirt costs 1/6 phones)
15.
Week EightMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (20
min)
• Interactive
Activities
16.
Current Events17.
TheoryHeckscher-Ohlin
Countries have different factor endowments
that determines their comparative advantage:
Land
Labour
Capital
Country will export goods that make use of its
abundant resources
18.
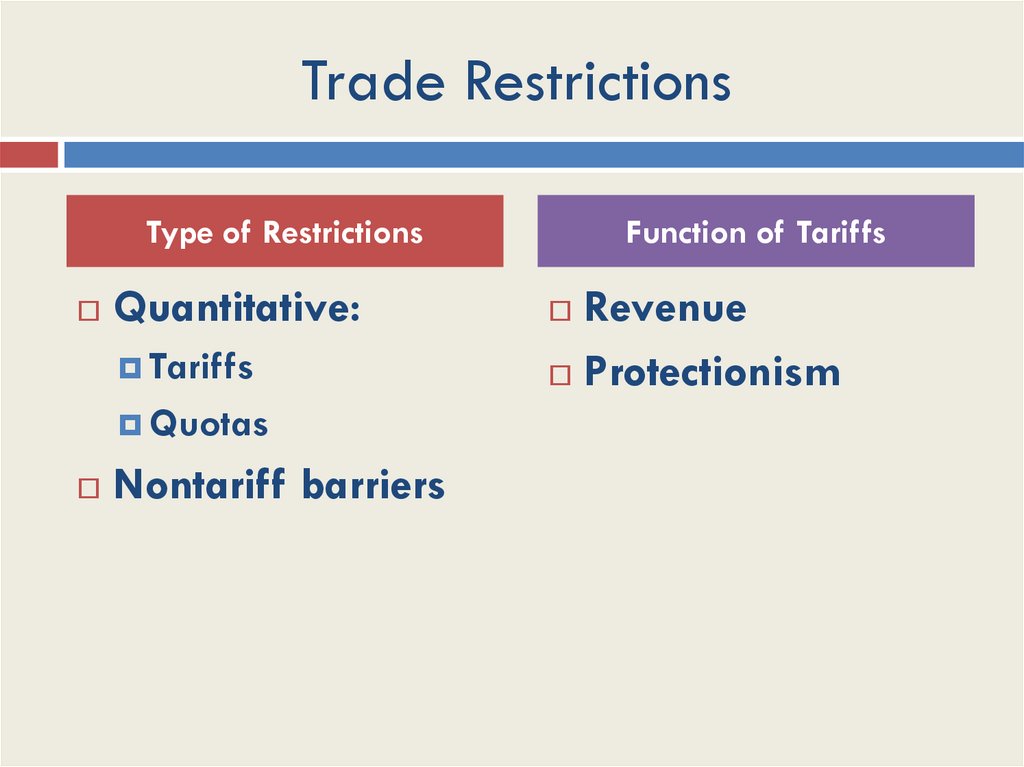
Trade RestrictionsType of Restrictions
Quantitative:
Tariffs
Quotas
Nontariff barriers
Function of Tariffs
Revenue
Protectionism
19.
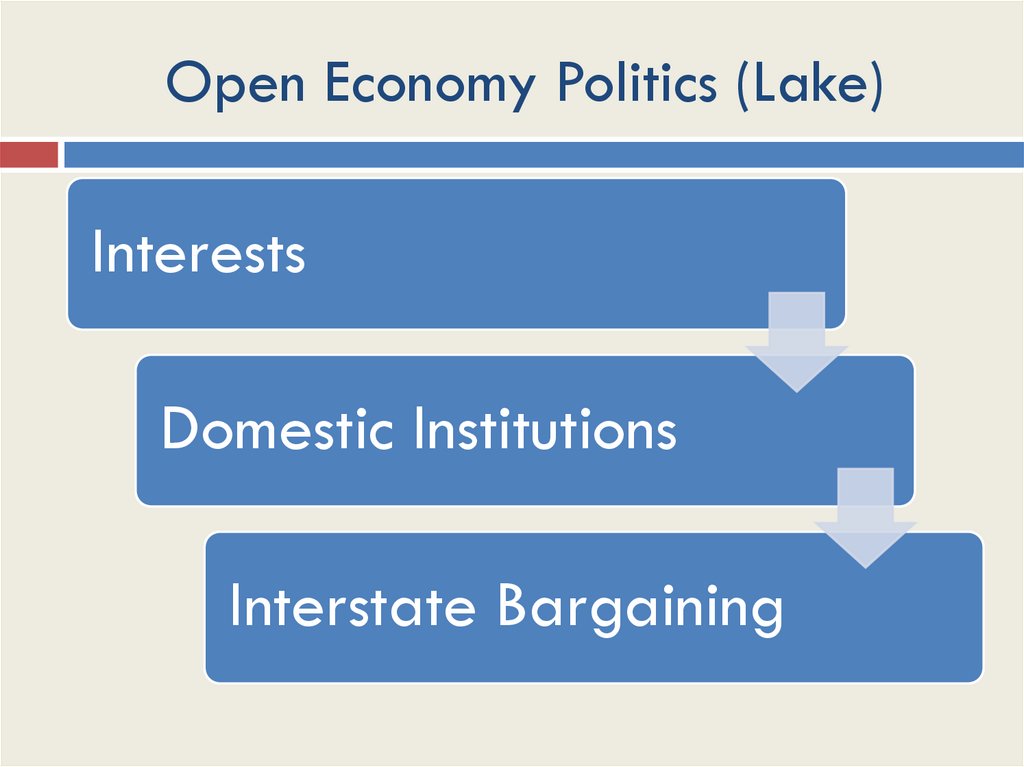
Open Economy Politics (Lake)Interests
Domestic Institutions
Interstate Bargaining
20.
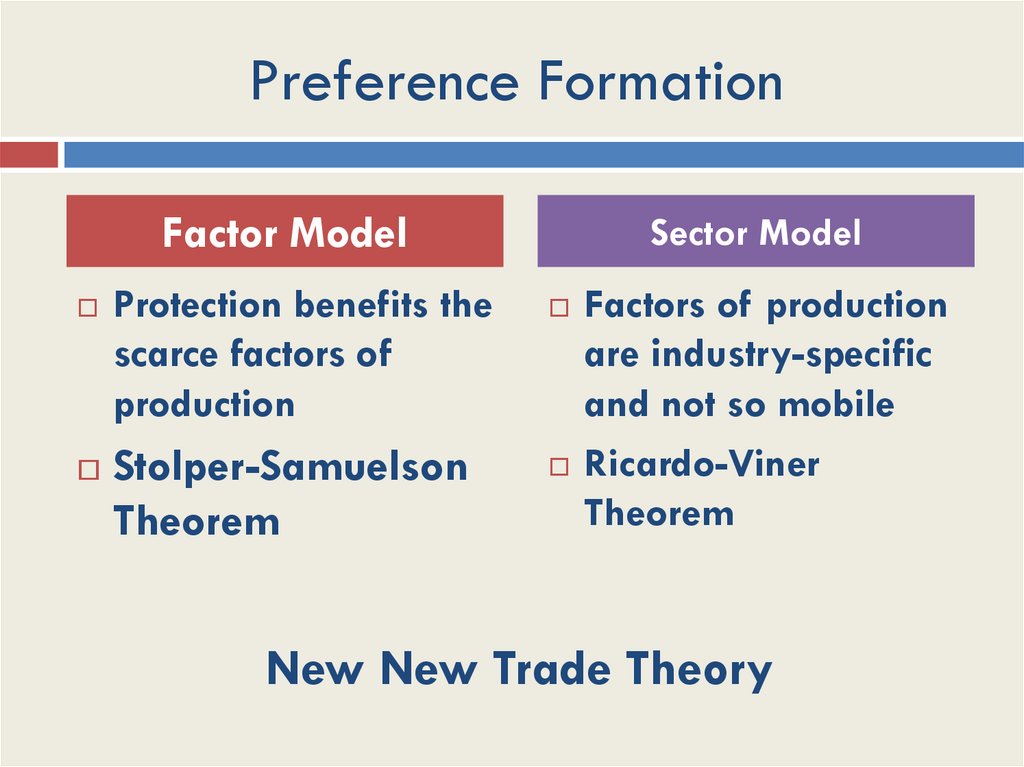
Preference FormationFactor Model
Protection benefits the
scarce factors of
production
Stolper-Samuelson
Theorem
Sector Model
Factors of production
are industry-specific
and not so mobile
Ricardo-Viner
Theorem
New New Trade Theory
21.
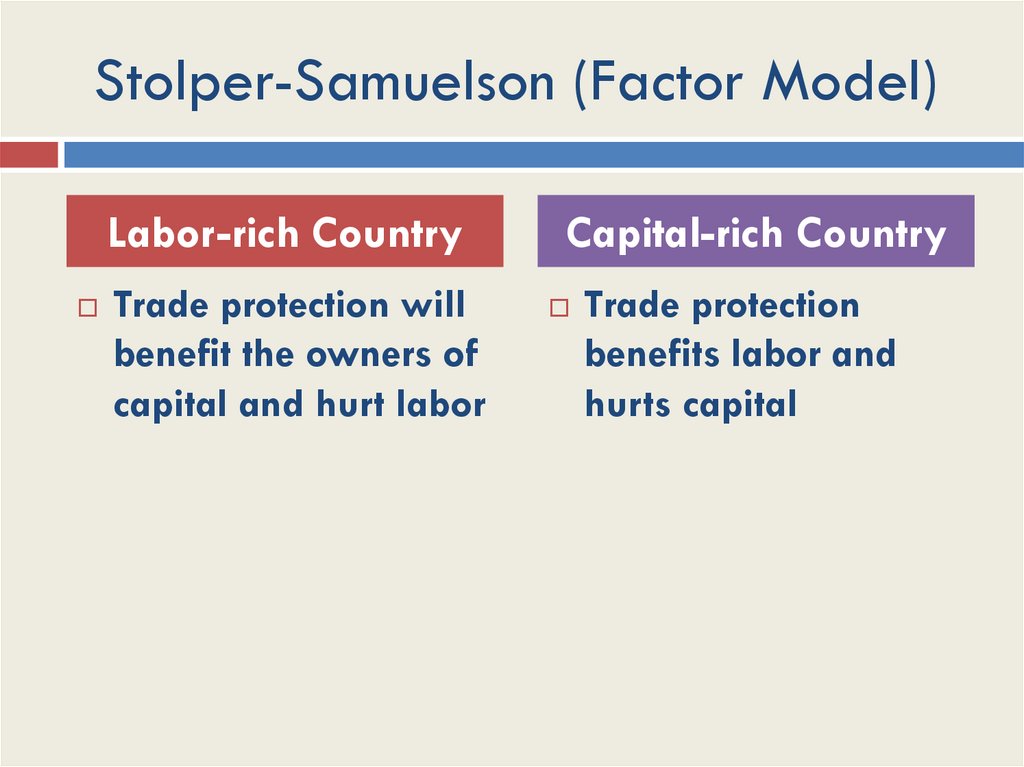
Stolper-Samuelson (Factor Model)Labor-rich Country
Trade protection will
benefit the owners of
capital and hurt labor
Capital-rich Country
Trade protection
benefits labor and
hurts capital
22.
Week EightMonday
Wednesday
Friday
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Lecture on
trade (40
min)
• Current
Events (10
min)
• Kahoot (10
min)
• Lecture (20
min)
• Interactive
Activities
23.
Current Events24.
Kahoot25.
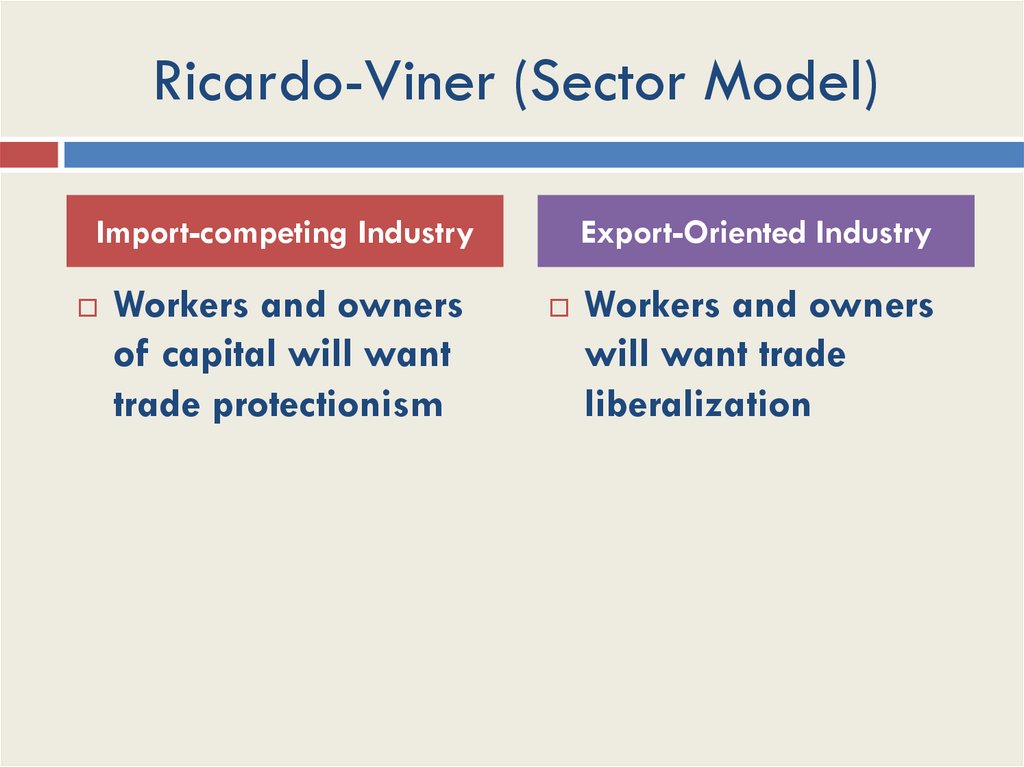
Ricardo-Viner (Sector Model)Import-competing Industry
Workers and owners
of capital will want
trade protectionism
Export-Oriented Industry
Workers and owners
will want trade
liberalization
26.
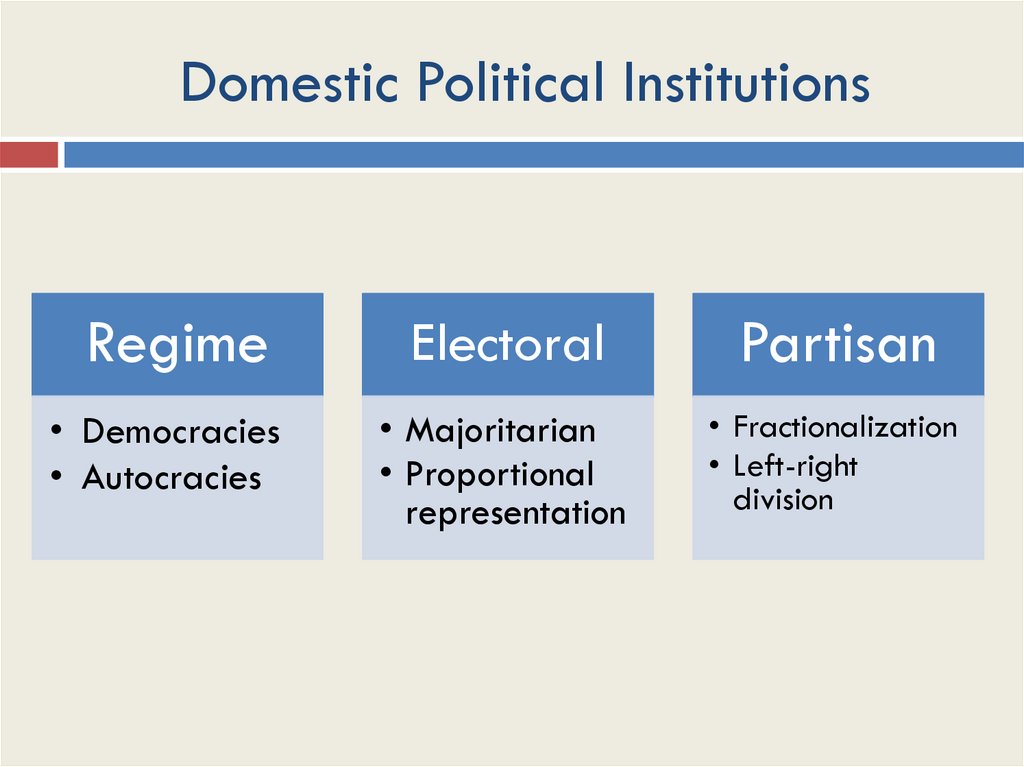
Domestic Political InstitutionsRegime
Electoral
Partisan
• Democracies
• Autocracies
• Majoritarian
• Proportional
representation
• Fractionalization
• Left-right
division
27.
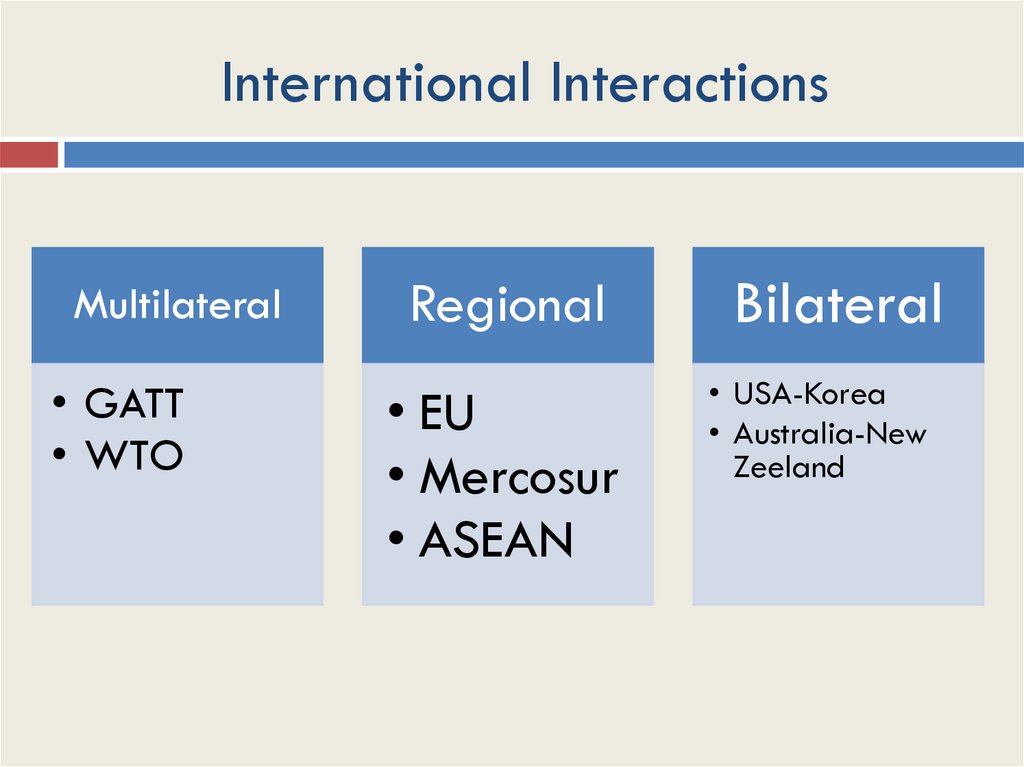
International InteractionsMultilateral
• GATT
• WTO
Regional
Bilateral
• EU
• Mercosur
• ASEAN
• USA-Korea
• Australia-New
Zeeland
28.
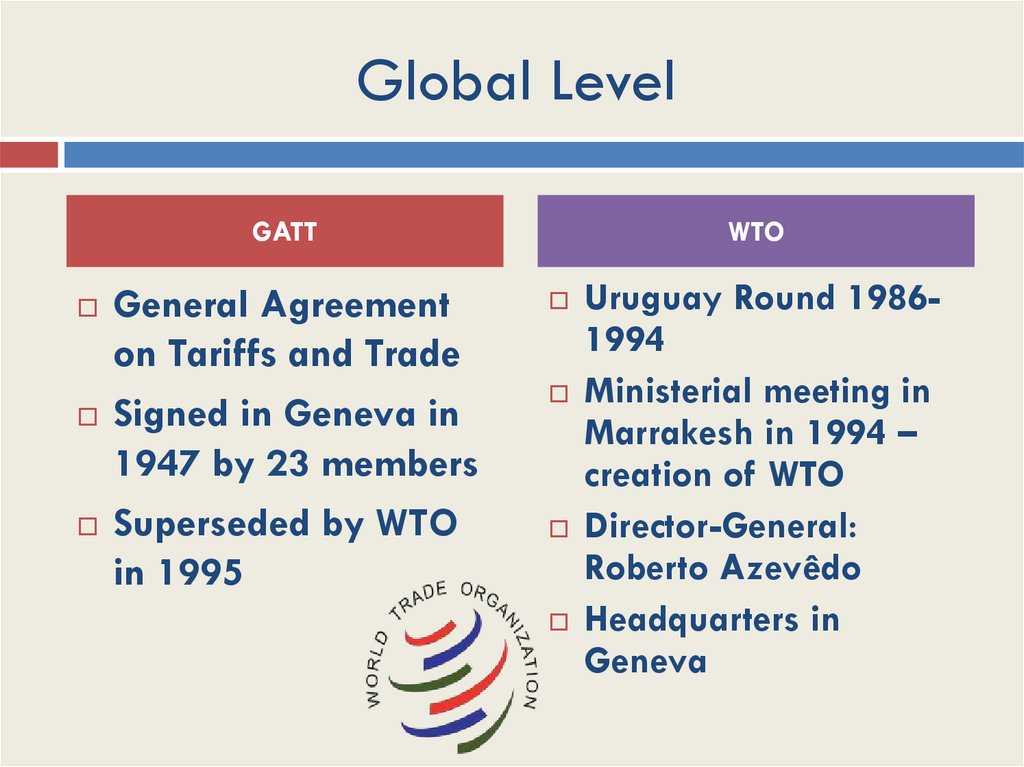
Global LevelGATT
General Agreement
on Tariffs and Trade
Signed in Geneva in
1947 by 23 members
Superseded by WTO
in 1995
WTO
Uruguay Round 19861994
Ministerial meeting in
Marrakesh in 1994 –
creation of WTO
Director-General:
Roberto Azevêdo
Headquarters in
Geneva
29.
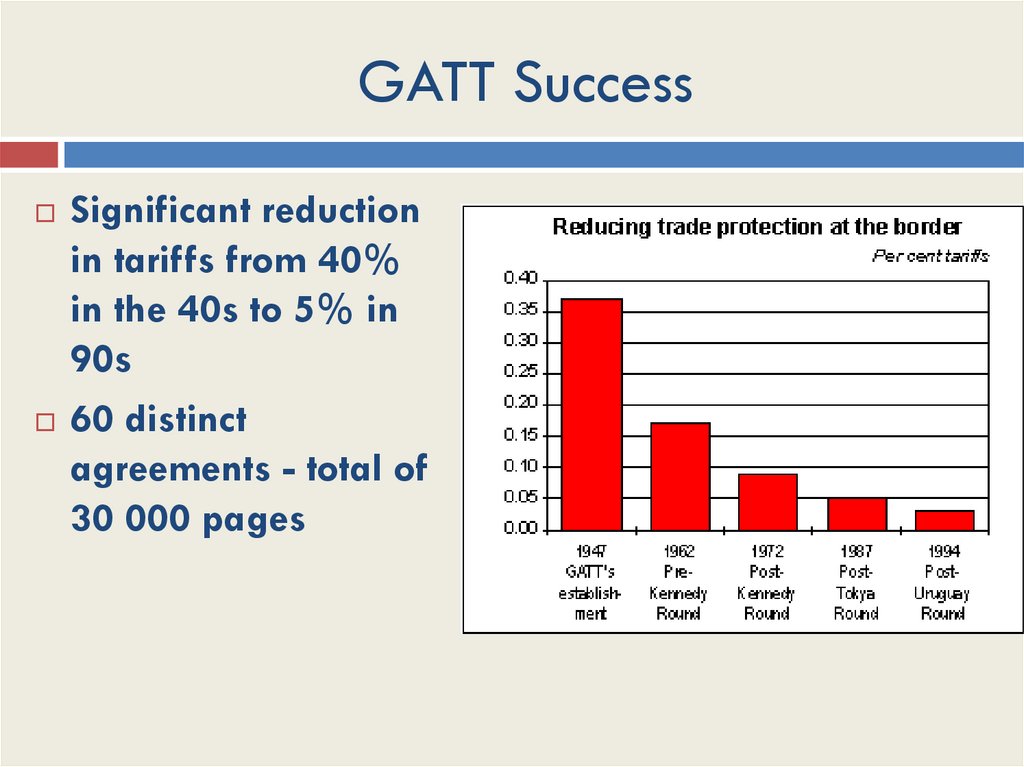
GATT SuccessSignificant reduction
in tariffs from 40%
in the 40s to 5% in
90s
60 distinct
agreements - total of
30 000 pages
30.
Q&ADr Maja
Savevska
Thank you for your attention











 economics
economics








