Similar presentations:
Mechanisms of passive transport
1.
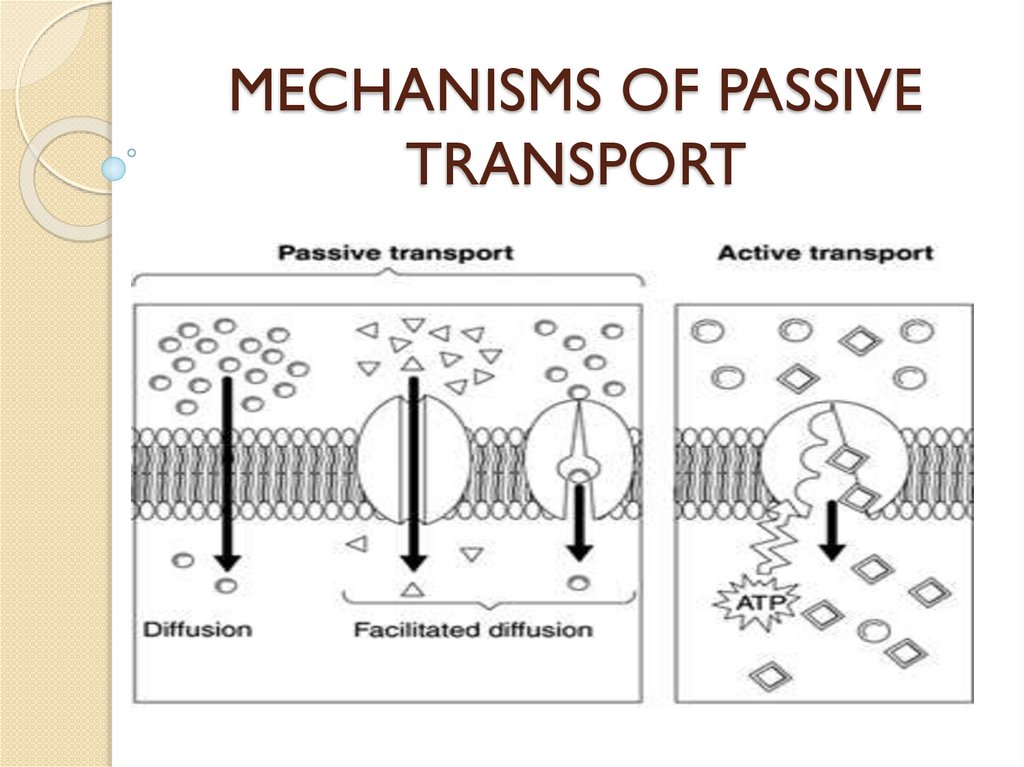
MECHANISMS OF PASSIVETRANSPORT
2.
Lesson objectivesTo explain the mechanism of passive
transport.
3.
How cell regulates thetransport of the molecules through
the membrane ?
4.
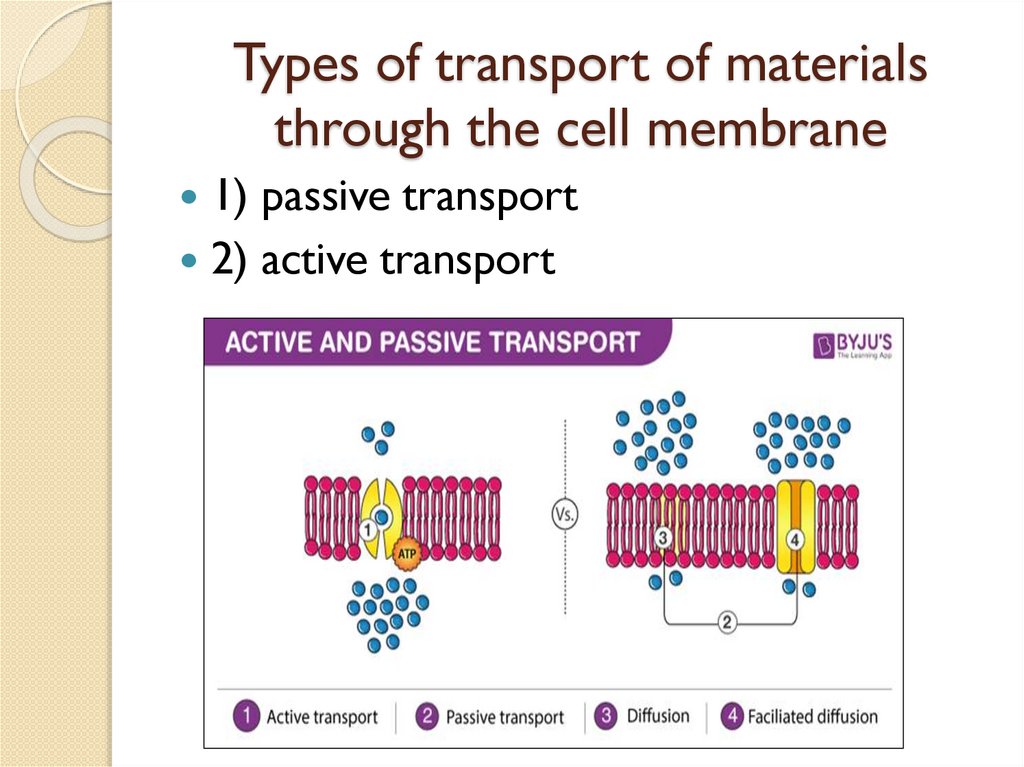
Types of transport of materialsthrough the cell membrane
1) passive transport
2) active transport
5.
PASSIVE TRANSPORTPassive transport is a movement materials across
cell membranes without need of energy input.
It moves by gradient of concentration: from area
of high concentration to the area of low
concentration till the concentration is equal in
both sides.
6.
Gradient of concentrationConcentration gradient is
difference in concentration of
substances between two
regions.
Ex: concentration gradient of
CO2 in alveoli and capillaries
that surround them is different:
CO2 is higher in capillaries than
in alveoli so it moves from
capillaries to alveoli.
7.
Types of passive transportThere are 3 types of passive transport:
1) simple diffusion
2) facilitated diffusion
3) osmosis
8.
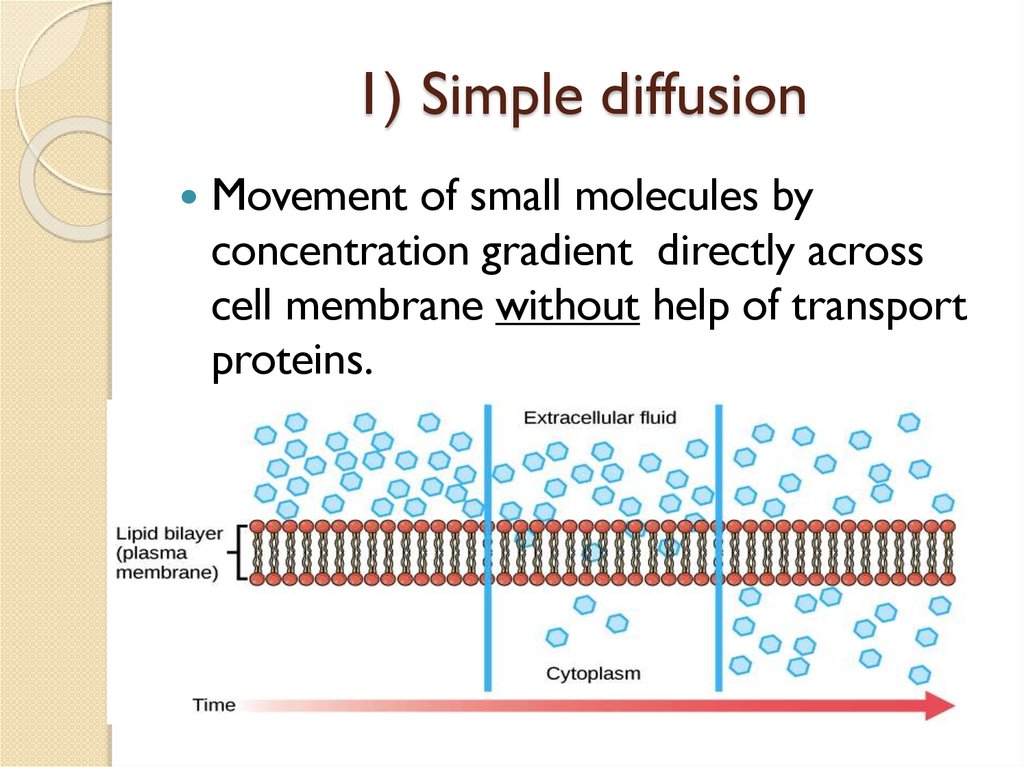
1) Simple diffusionMovement of small molecules by
concentration gradient directly across
cell membrane without help of transport
proteins.
9.
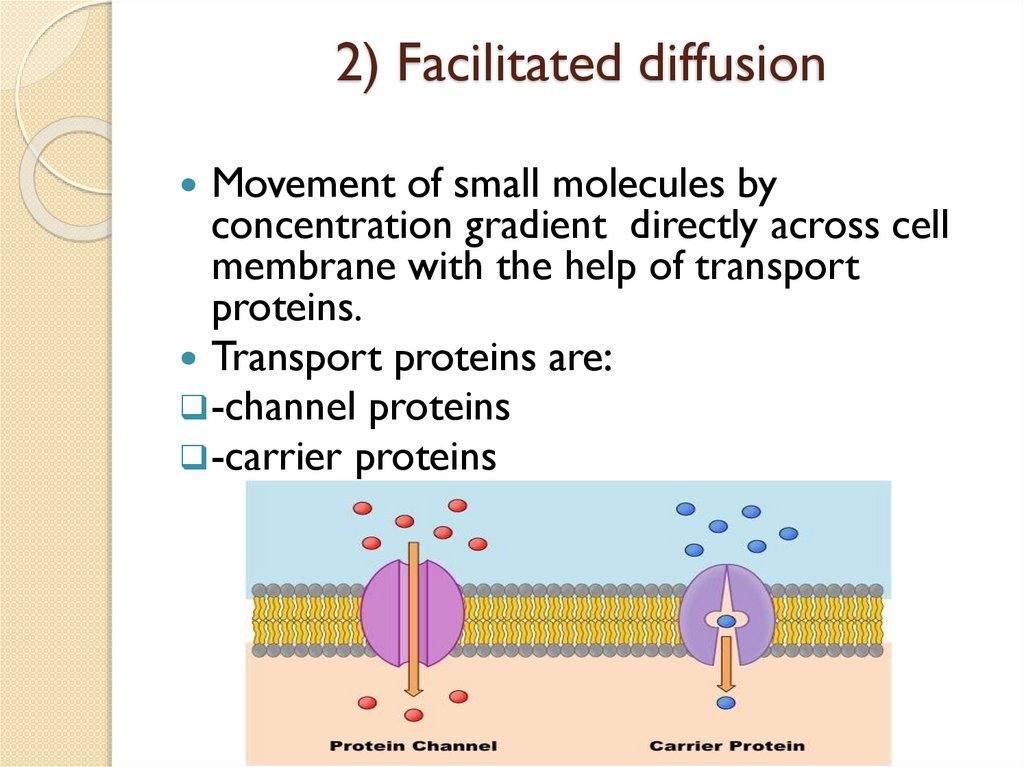
2) Facilitated diffusionMovement of small molecules by
concentration gradient directly across cell
membrane with the help of transport
proteins.
Transport proteins are:
-channel proteins
-carrier proteins
10.
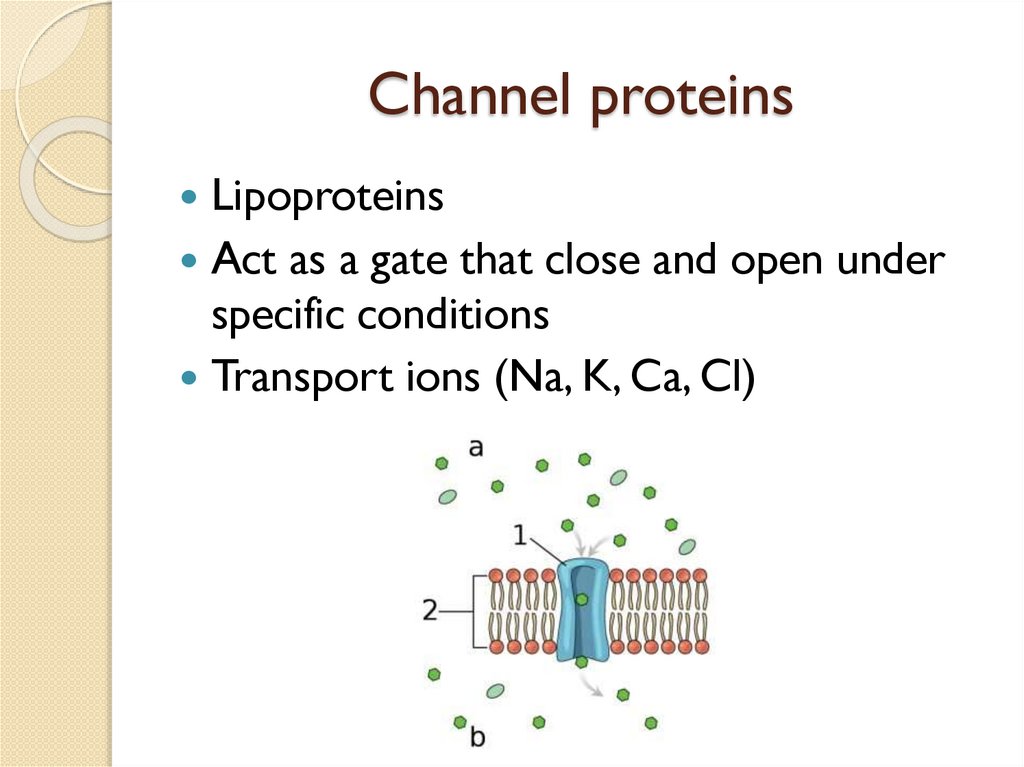
Channel proteinsLipoproteins
Act as a gate that close and open under
specific conditions
Transport ions (Na, K, Ca, Cl)
11.
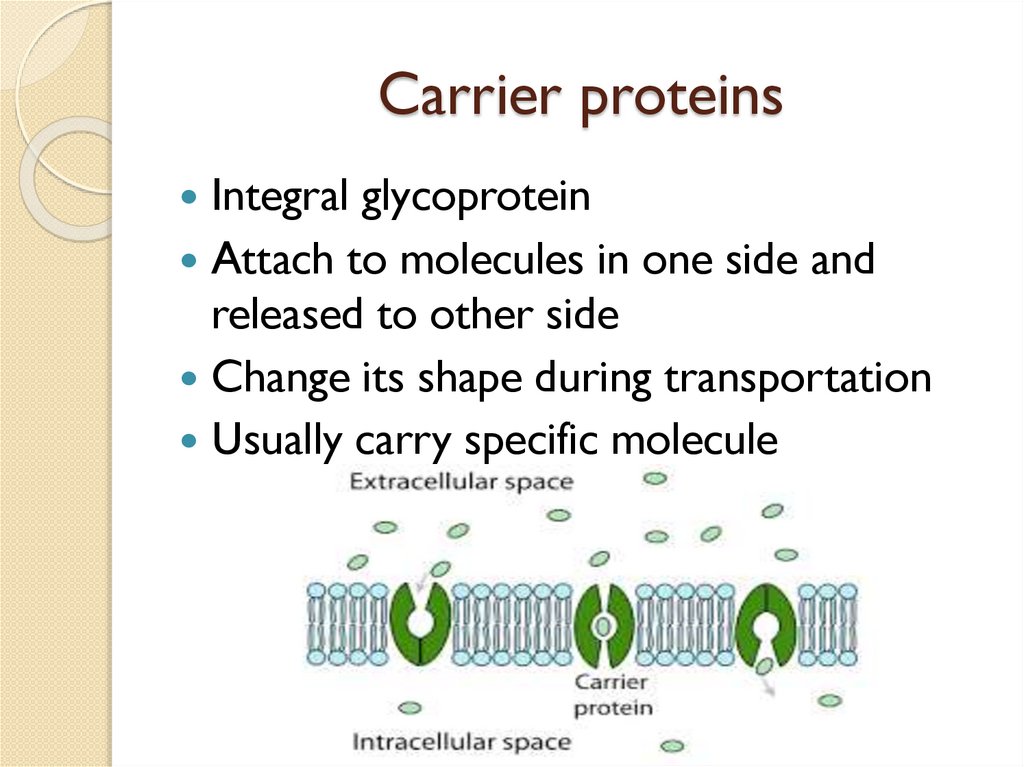
Carrier proteinsIntegral glycoprotein
Attach to molecules in one side and
released to other side
Change its shape during transportation
Usually carry specific molecule
12.
3)OsmosisOsmosis is a process by
which the molecules of a
solvent (water) pass from
a solution of low
concentration to a
solution of high
concentration through a
semi-permeable
membrane.
Water, like other
substances, moves from an
area of high concentration
to one of low
concentration.
13.
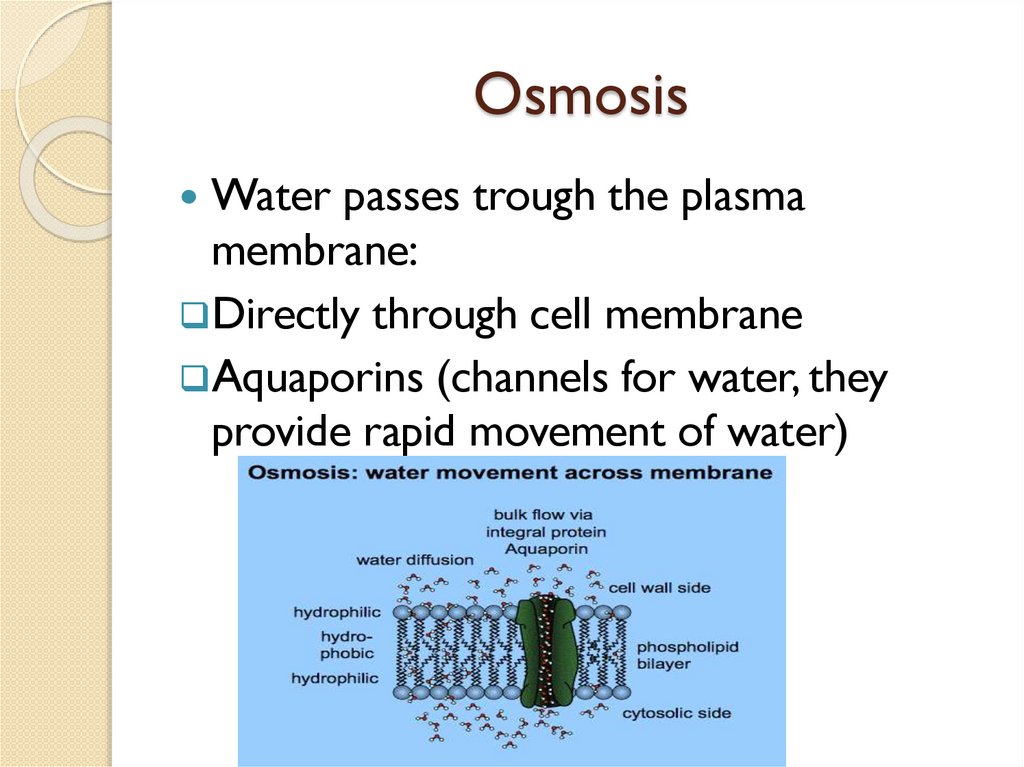
OsmosisWater passes trough the plasma
membrane:
Directly through cell membrane
Aquaporins (channels for water, they
provide rapid movement of water)
14.
Let’s do the activity on p. 6315.
HomeworkRead p.62-63
Answer to literacy questions on p 63
Do research time on p63.
New words








 biology
biology








