Similar presentations:
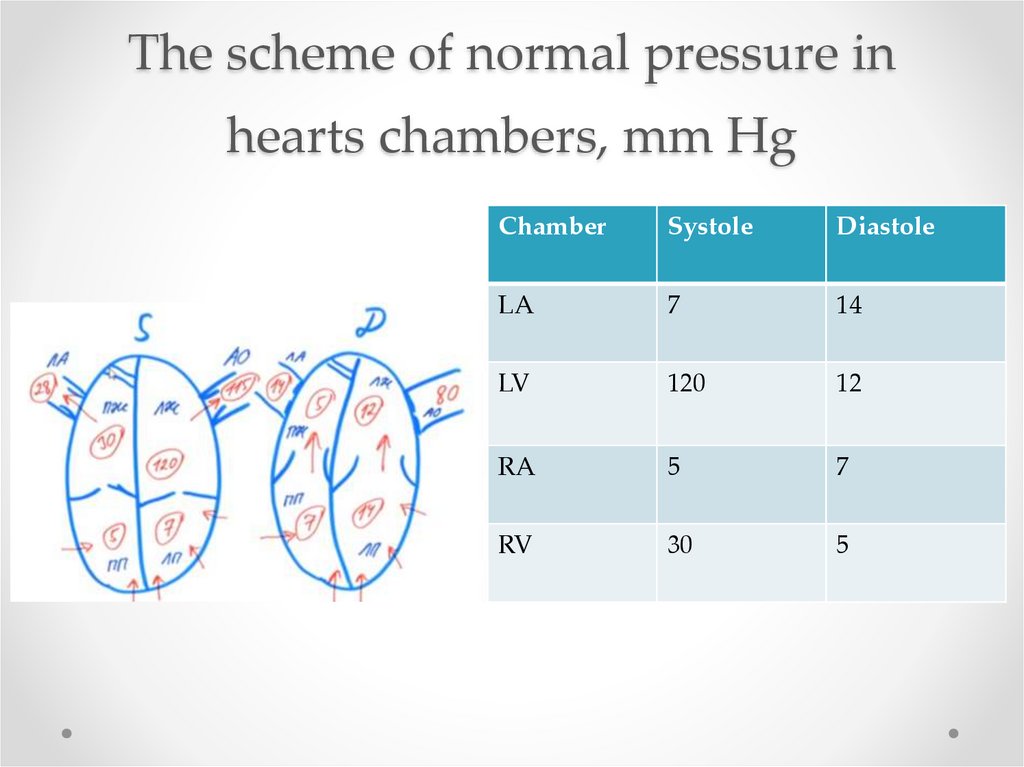
The scheme of normal pressure in hearts chambers, mm Hg
1.
Made by Abhishek Raj2nd year (PSMU)
Group # 37
Teacher – Doctor Olga Goryacheva
2.
3. The scheme of normal pressure in hearts chambers, mm Hg
ChamberSystole
Diastole
LA
7
14
LV
120
12
RA
5
7
RV
30
5
4. c
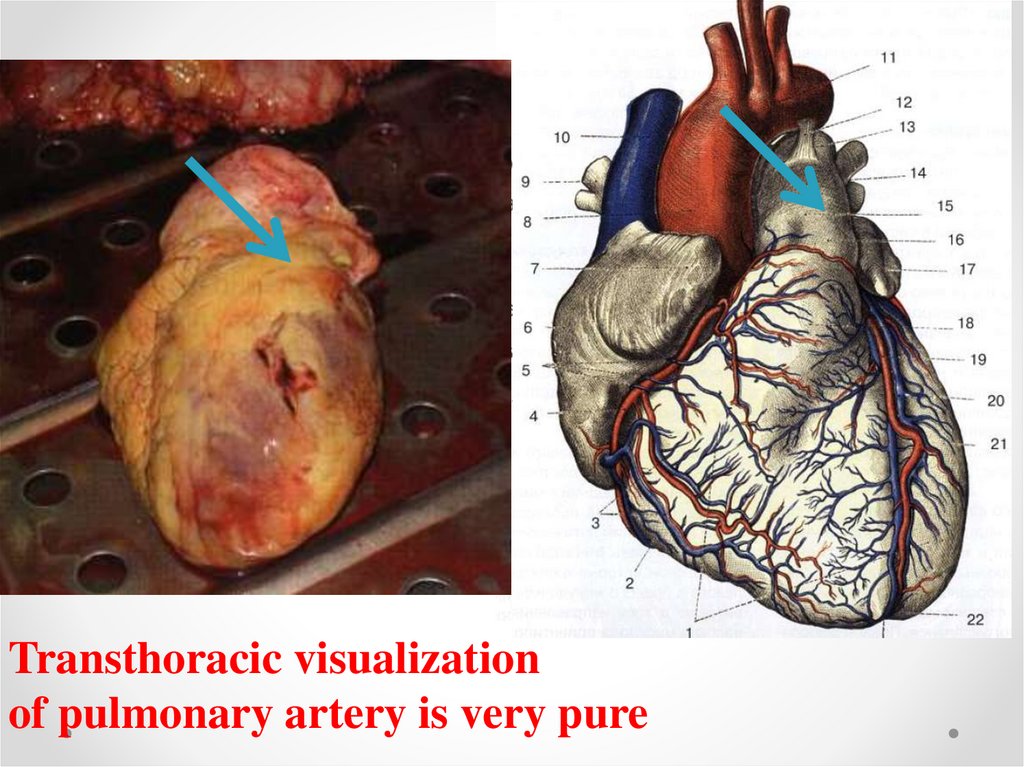
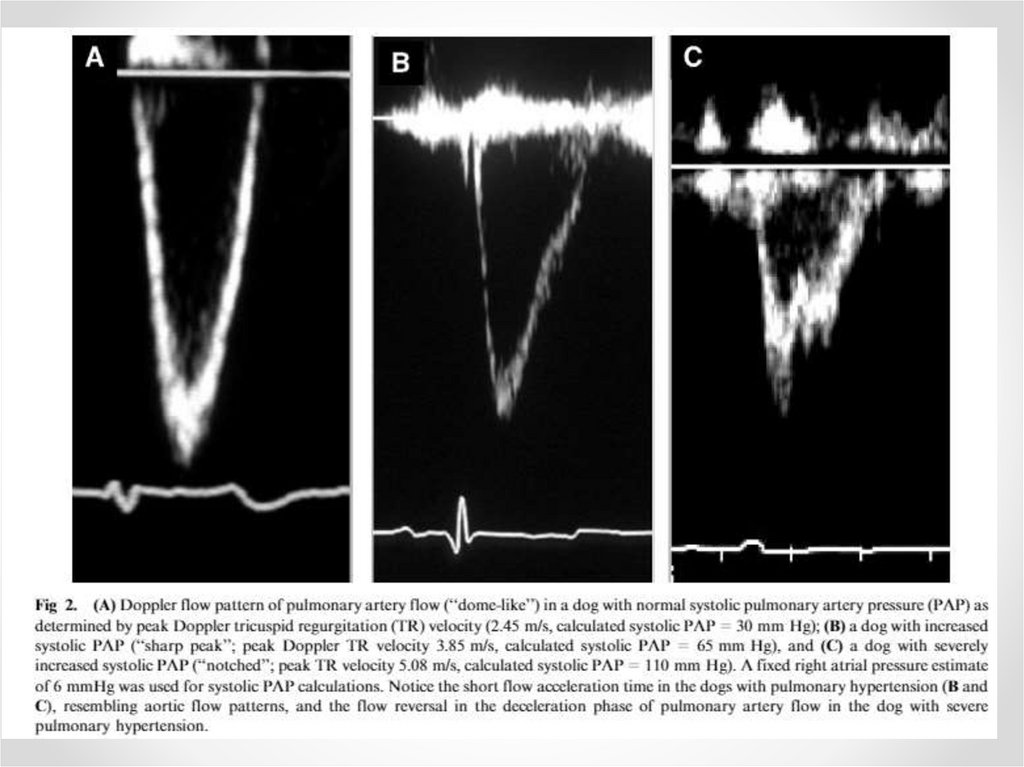
Transthoracic visualizationof pulmonary artery is very pure
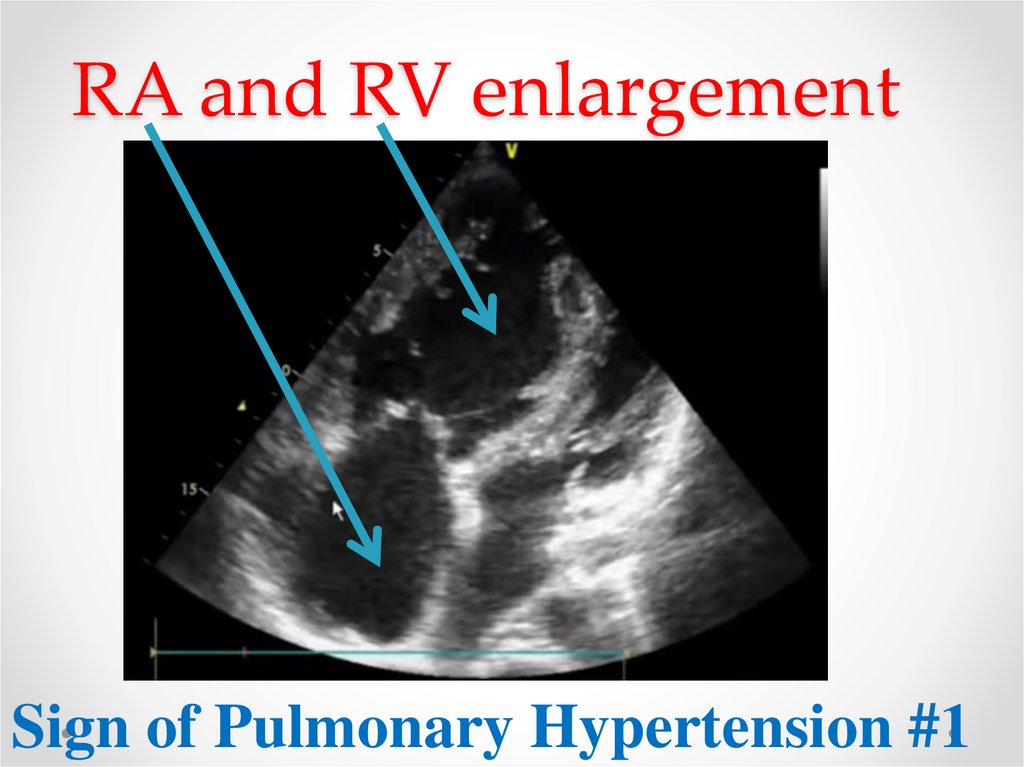
5. RA and RV enlargement
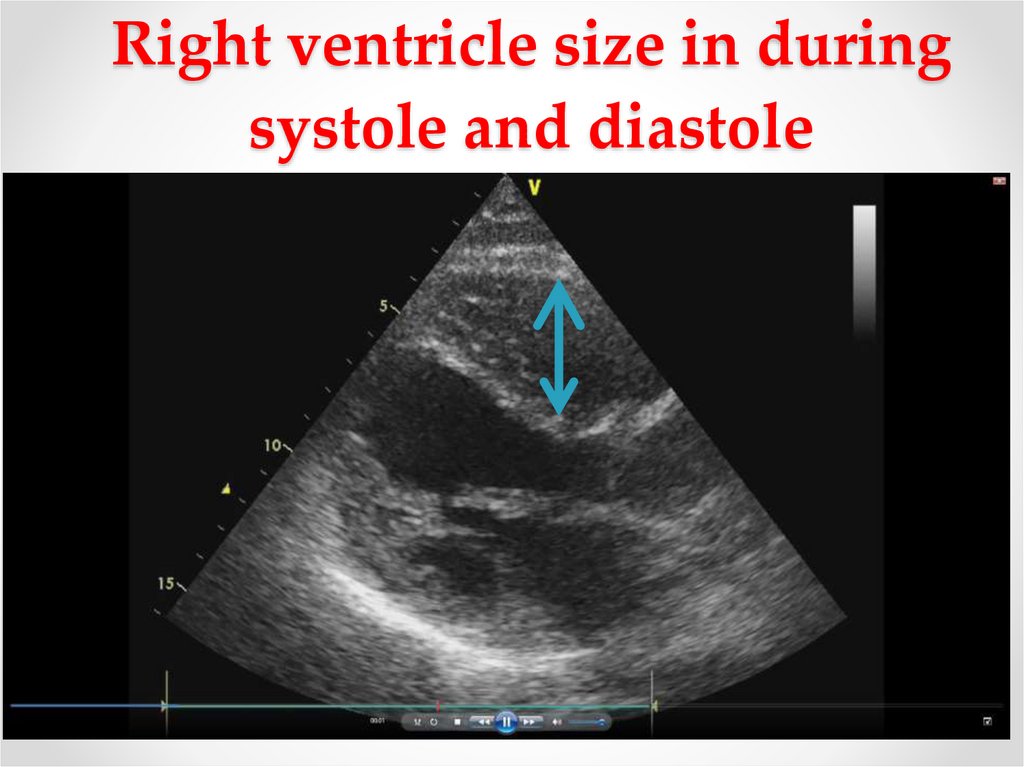
Sign of Pulmonary Hypertension #16. Right ventricle size in during systole and diastole
7.
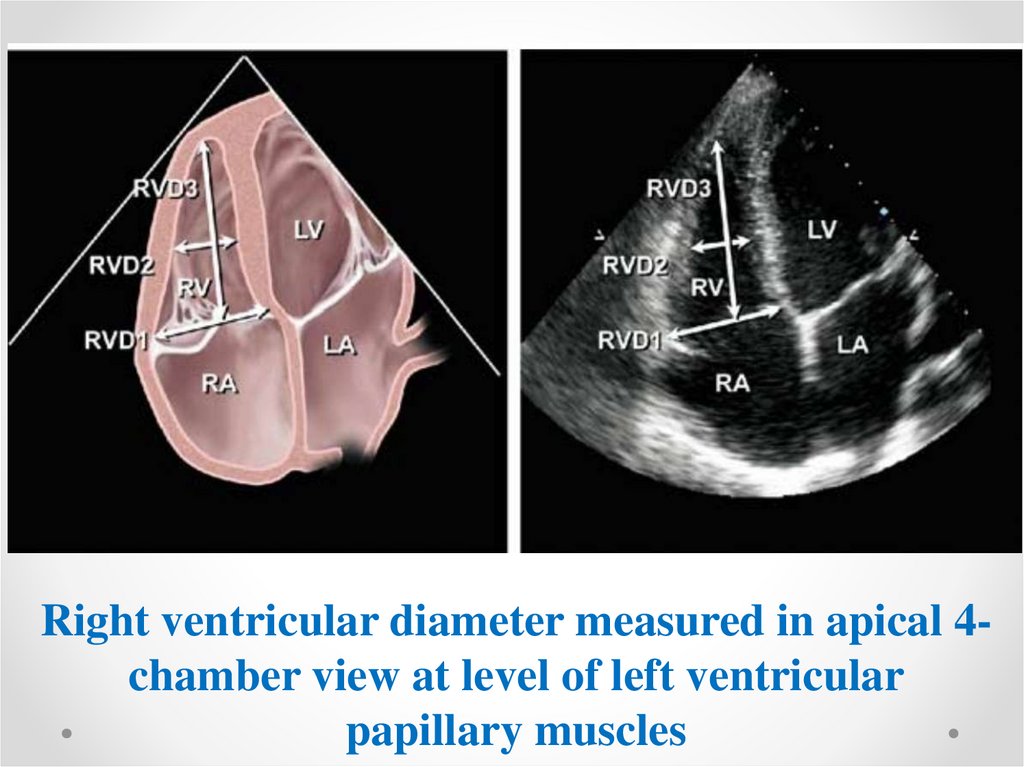
Right ventricular diameter measured in apical 4chamber view at level of left ventricularpapillary muscles
8.
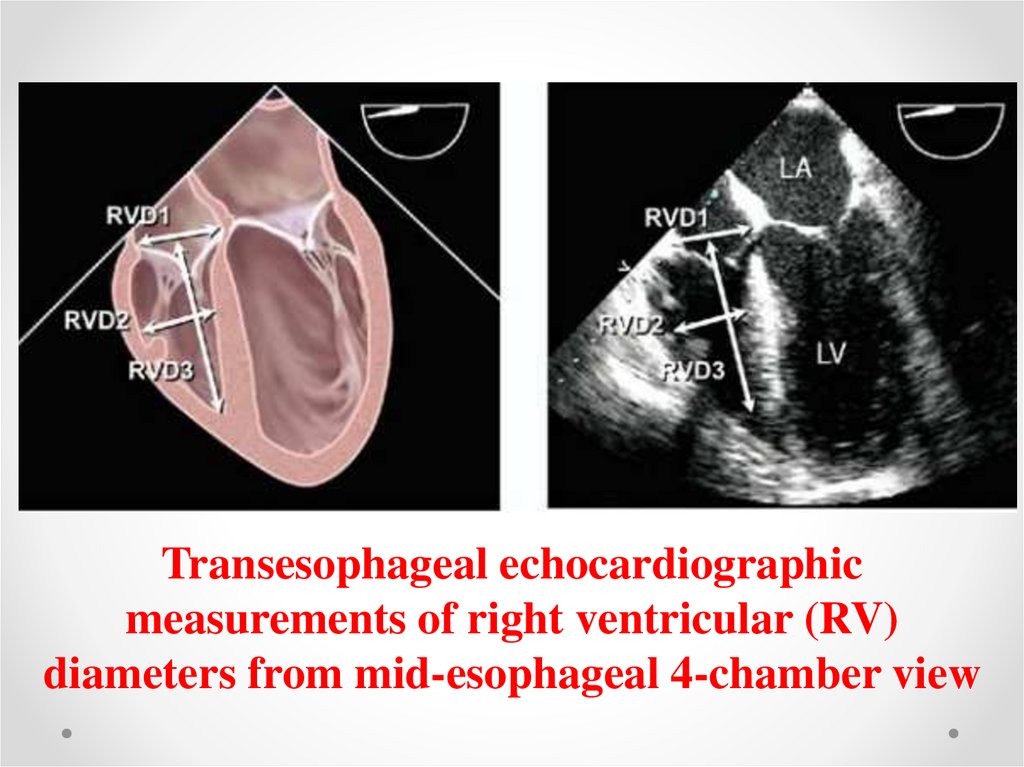
Transesophageal echocardiographicmeasurements of right ventricular (RV)
diameters from mid-esophageal 4-chamber view
9.
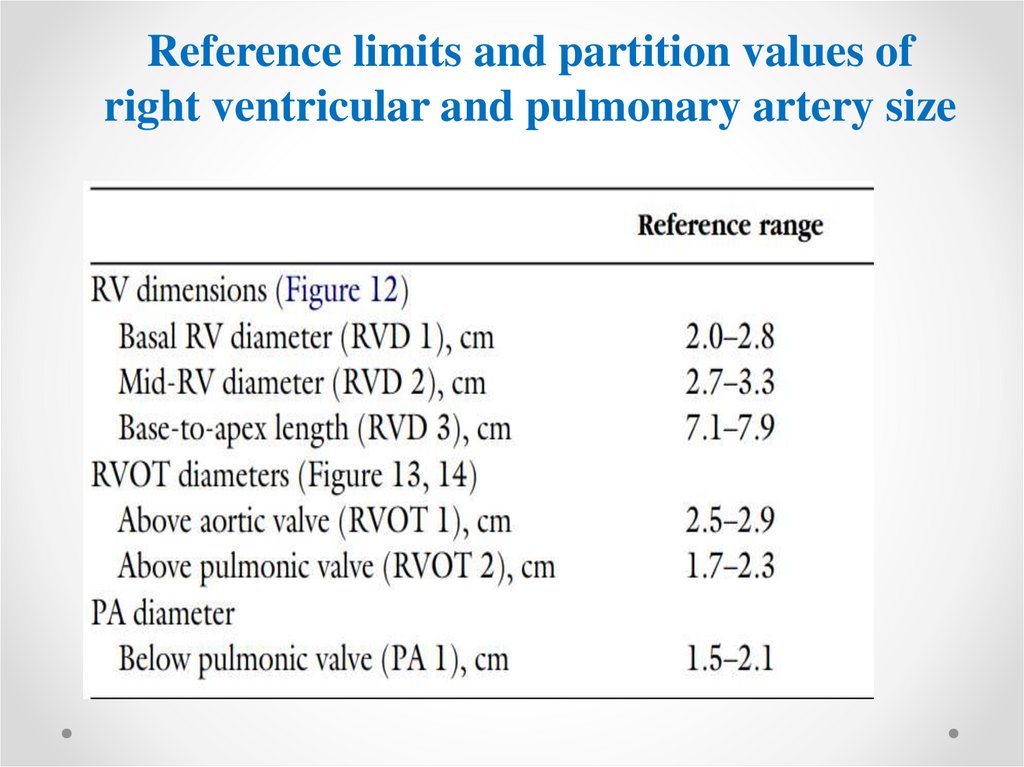
Reference limits and partition values ofright ventricular and pulmonary artery size
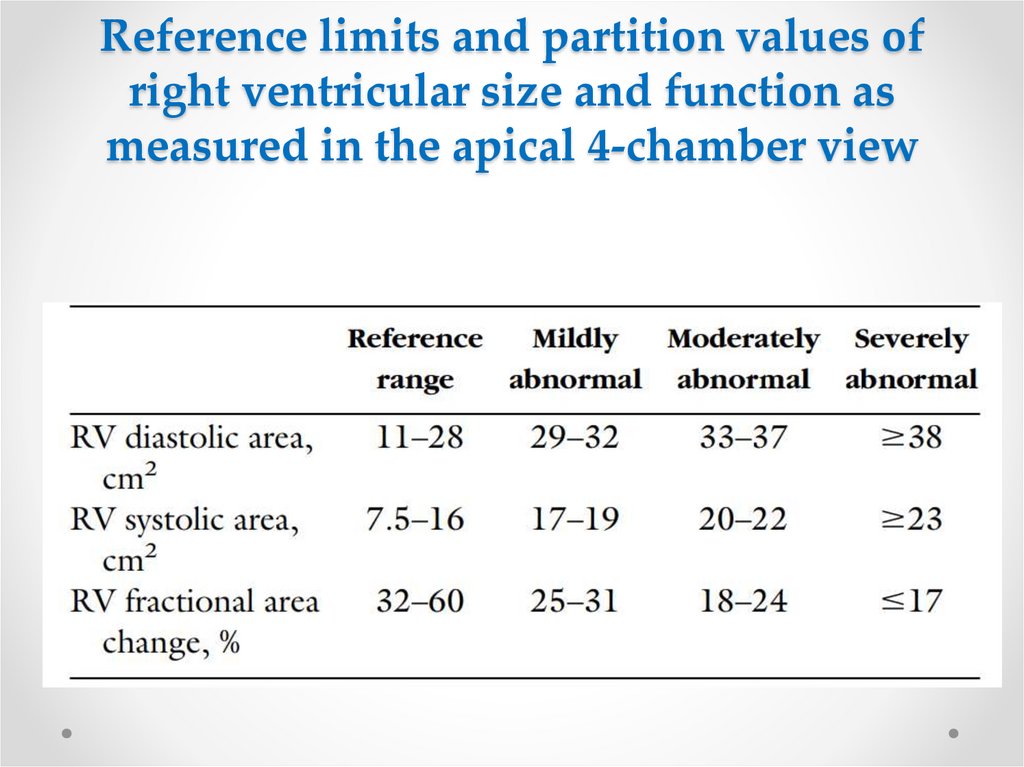
10. Reference limits and partition values of right ventricular size and function as measured in the apical 4-chamber view
11.
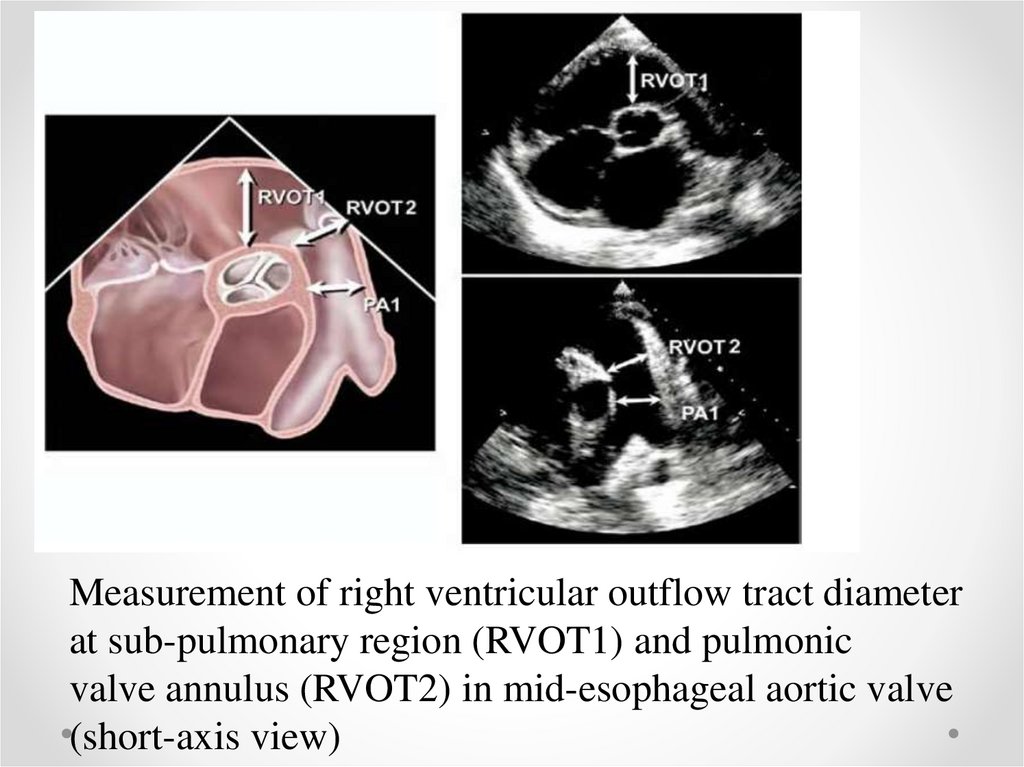
Measurement of right ventricular outflow tract diameterat sub-pulmonary region (RVOT1) and pulmonic
valve annulus (RVOT2) in mid-esophageal aortic valve
(short-axis view)
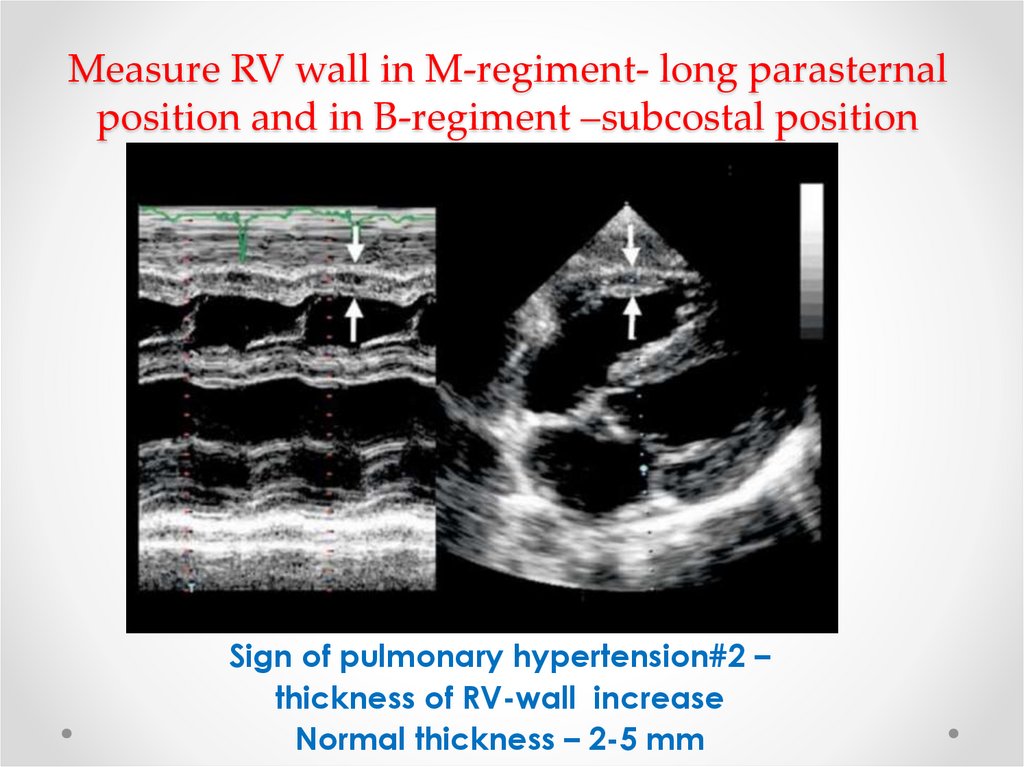
12. Measure RV wall in M-regiment- long parasternal position and in B-regiment –subcostal position
Sign of pulmonary hypertension#2 –thickness of RV-wall increase
Normal thickness – 2-5 mm
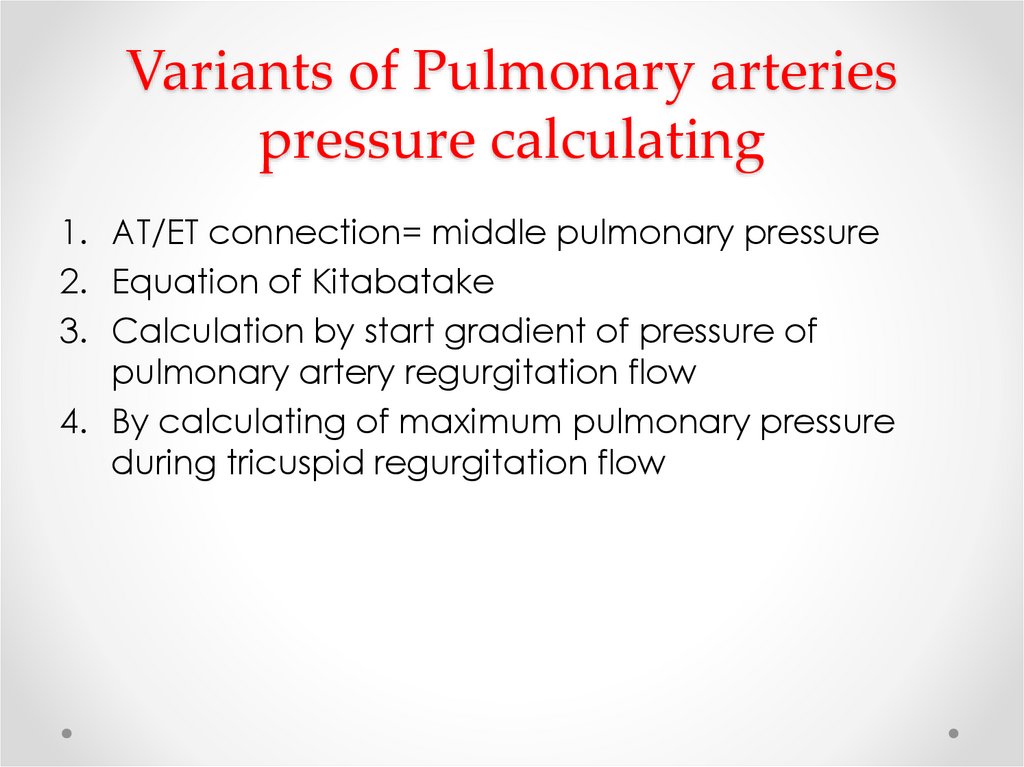
13. Variants of Pulmonary arteries pressure calculating
1. AT/ET connection= middle pulmonary pressure2. Equation of Kitabatake
3. Calculation by start gradient of pressure of
pulmonary artery regurgitation flow
4. By calculating of maximum pulmonary pressure
during tricuspid regurgitation flow
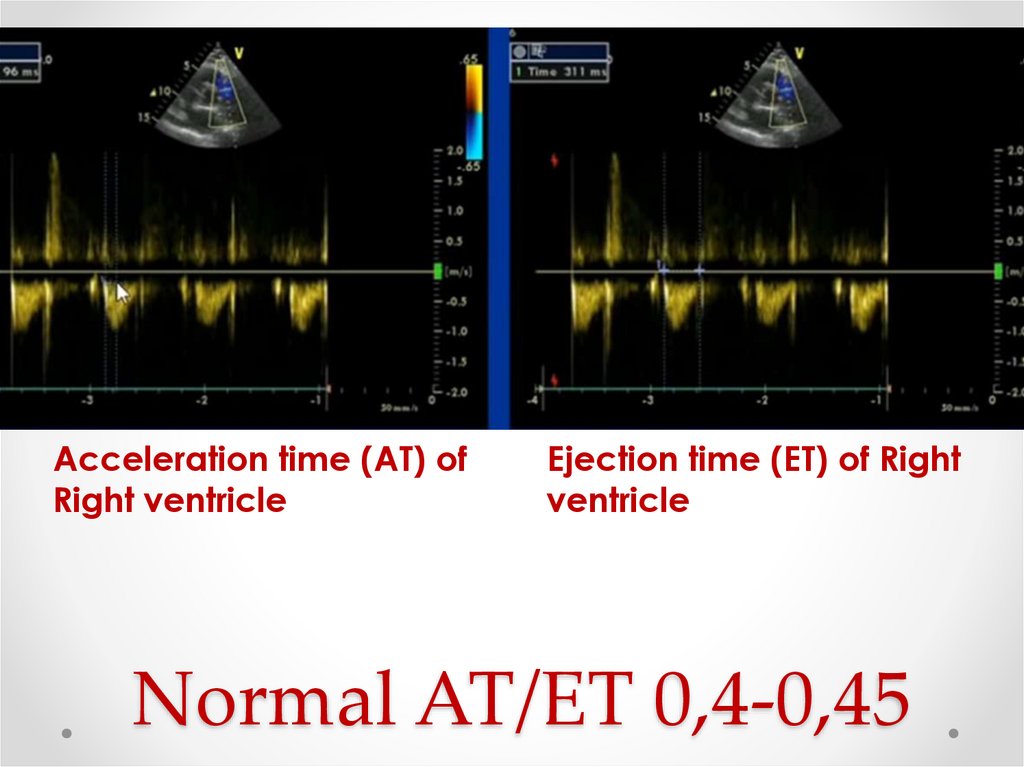
14. Normal AT/ET 0,4-0,45
Acceleration time (AT) ofRight ventricle
Ejection time (ET) of Right
ventricle
Normal AT/ET 0,4-0,45
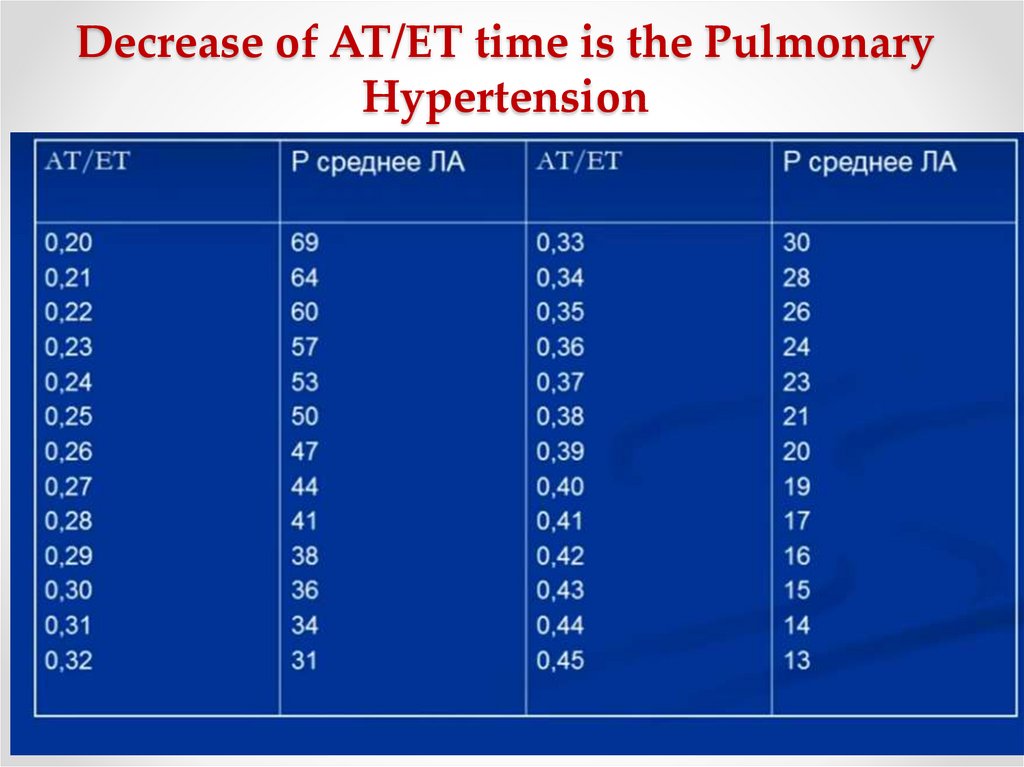
15. Decrease of AT/ET time is the Pulmonary Hypertension
16.
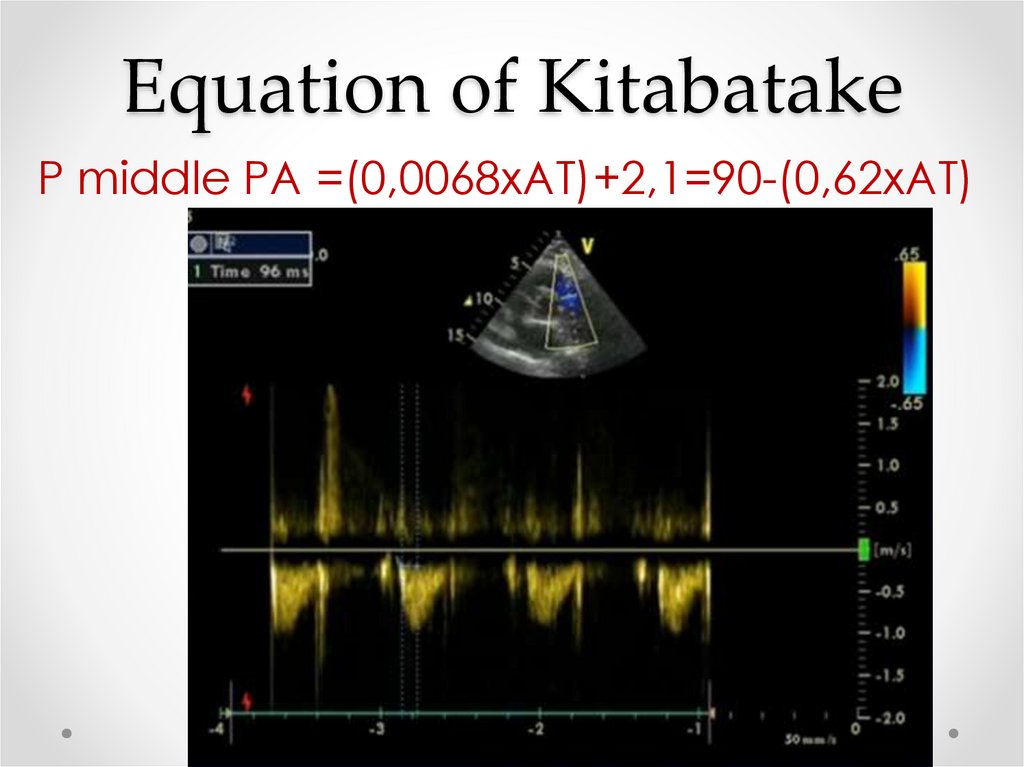
17. Equation of Kitabatake
P middle PA =(0,0068хАТ)+2,1=90-(0,62хАТ)18.
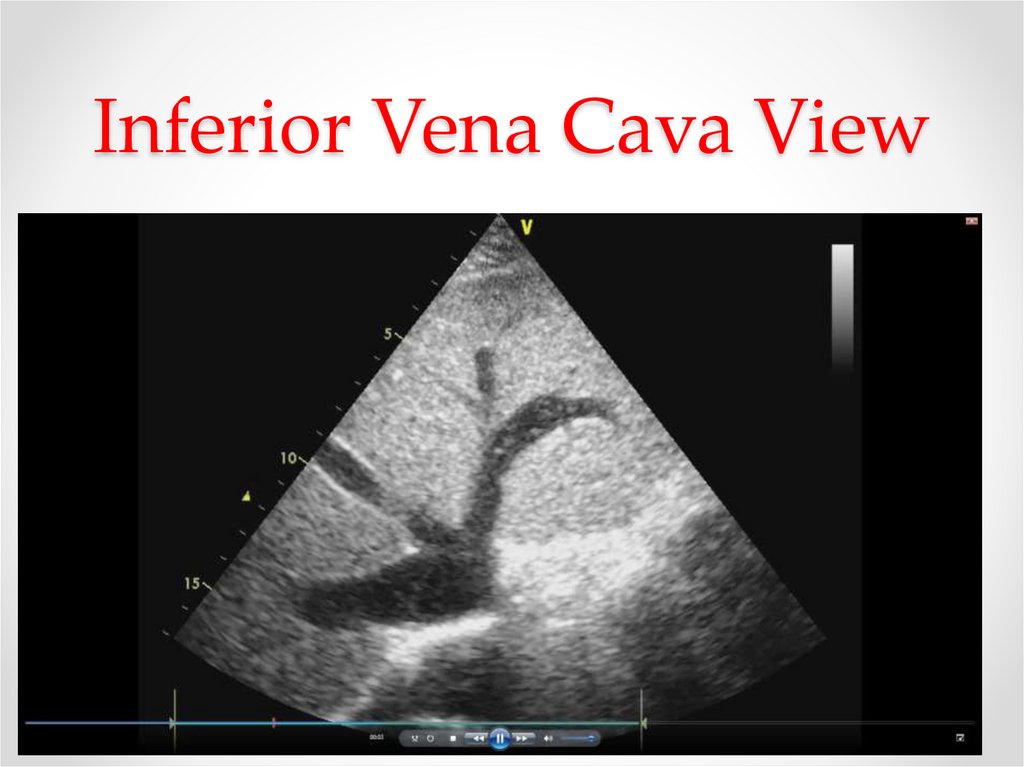
• The diameter of the Inferior vena cava (IVC) and thepercent decrease in the diameter during inspiration correlate
with RA and PA pressure.
• The normal IVC diameter is less than 1.7 cm. There is a
50% decrease in the diameter when the RA pressure is
normal (0-5 mm Hg).
• A dilated IVC (1.7 cm) with normal inspiratory collapse
(>50%) is suggestive of a mildly elevated RA pressure (6-10
mm Hg).
• When the inspiratory collapse is less than 50%, the RA
pressure is usually between 10 and 15 mm Hg.
• Finally, a dilated IVC without any collapse suggests a
markedly increased RA pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg.
19. Inferior Vena Cava View
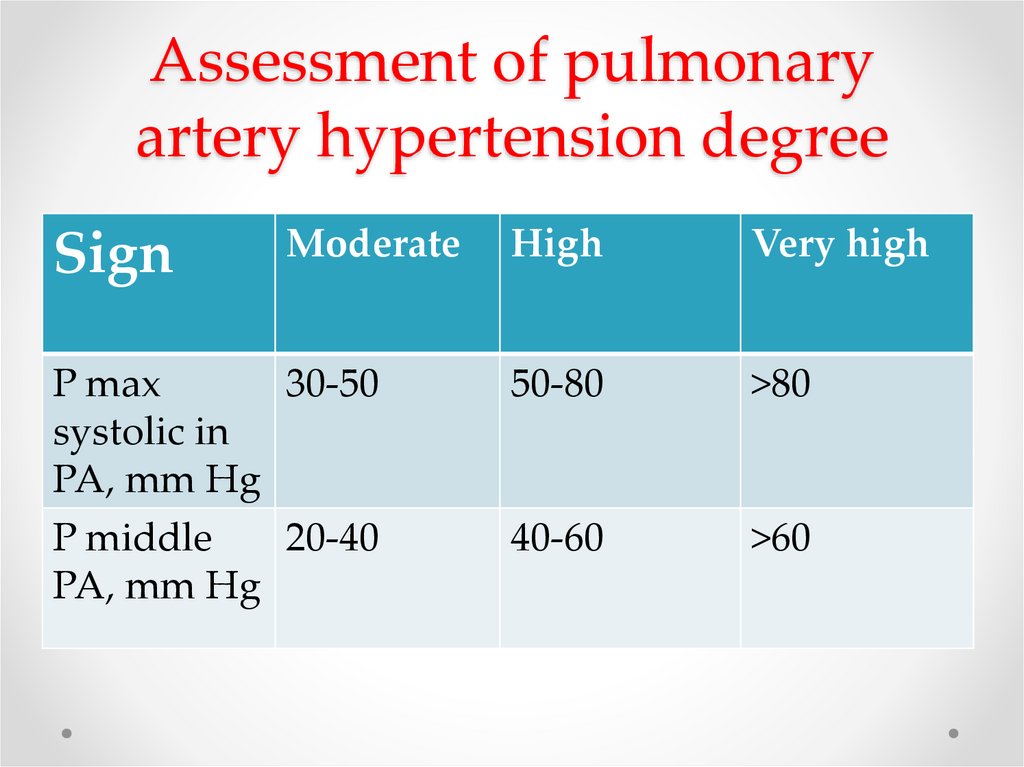
20. Assessment of pulmonary artery hypertension degree
SignModerate
P max
30-50
systolic in
PA, mm Hg
P middle
20-40
PA, mm Hg
High
Very high
50-80
>80
40-60
>60



 medicine
medicine








