Similar presentations:
Measure blood pressure in pulmonary artery echocardiography
1.
Made by – Abhishek Rajnd
2 year (PSMU)
Group number – 37
2. Ecocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producingan electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording – a
graph of voltage versus time – of the electrical activity
of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These
electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a
consequence of cardiac
muscle depolarization followed
by repolarization during each cardiac cycle
(heartbeat).
Echocardiography need…
3.
Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur innumerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac
rhythm disturbances inadequate coronary artery
blood flow and electrolyte disturbances (such
as hypoalemia and hyperalemia).
Echocardiography need…
4.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple test that canbe used to check your heart's rhythm and electrical
activity. Sensors attached to the skin are used to detect
the electrical signals produced by your heart each time
it beats.
Echocardiography need…
5. There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which
There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, whichrepresents the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which
represents the depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave,
which represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
Echocardiography need…
6. Electrodes and leads
Electrodes are the actual conductive pads attached tothe body surface. Any pair of electrodes can measure
the electrical potential difference between the two
corresponding locations of attachment. Such a pair
forms a lead. However, "leads" can also be formed
between a physical electrode and a virtual
electrode, known as the Wilson's central terminal,
whose potential is defined as the average potential
measured by three limb electrodes that are attached to
the right arm, the left arm, and the left foot,
respectively.
7.
Proper placement of the limbelectrodes
8. Placement of the precordial electrodes
Echocardiography need…9. BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood pressure is the pressure of circulating bloodon the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure
is due to work done by the heart by pumping
blood through the circulatory system. Used
without further specification, "blood pressure"
usually refers to the pressure in large arteries of the
systemic circulation.
Pulmonary pressure can not be taken as BP!!!!!
10. Measuring blood pressure
Measuring blood pressure with asphygmomanometer
a cuff that can be inflated with air,
a pressure meter (manometer)
for measuring air pressure in the cuff, and
a stethoscope for listening to the sound
the blood makes as it flows through the brachial
artery (the major artery found in your upper arm).
Pulmonary pressure can not be taken as BP!!!!!
11.
Pulmonary pressure can not be taken as BP!!!!!12. Blood pressure numbers mean ?
Blood pressure is measured using two numbers.The first number, called systolic blood pressure,
measures the pressure in your blood vessels when your
heart beats.
The second number, called diastolic blood pressure,
measures the pressure in your blood vessels when your
heart rests between beats.
If the measurement reads 120 systolic and 80 diastolic,
you would say, “120 over 80,” or write, “120/80 mmHg.”
13. Blood pressure chart of adult
Pulmonary pressure can not be taken as BP!!!!!Blood pressure chart of adult
14. The scheme of normal pressure in hearts chambers, mm Hg
ChamberSystole
Diastole
LA
7
14
LV
120
12
RA
5
7
RV
30
5
15. HYPERTENSION
Hypertension also known as high bloodpressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in
which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently
elevated. High blood pressure typically does not cause
symptoms. Long-term high blood pressure, however,
is a major risk factor for coronary artery
disease, stroke, heart failure, atrial
fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision
loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia
16. RA and RV enlargement
Sign of Pulmonary Hypertension #117. Measure RV wall in M-regiment- long parasternal position and in B-regiment –subcostal position
Sign of pulmonary hypertension #2 –thickness of RV-wall increase
18.
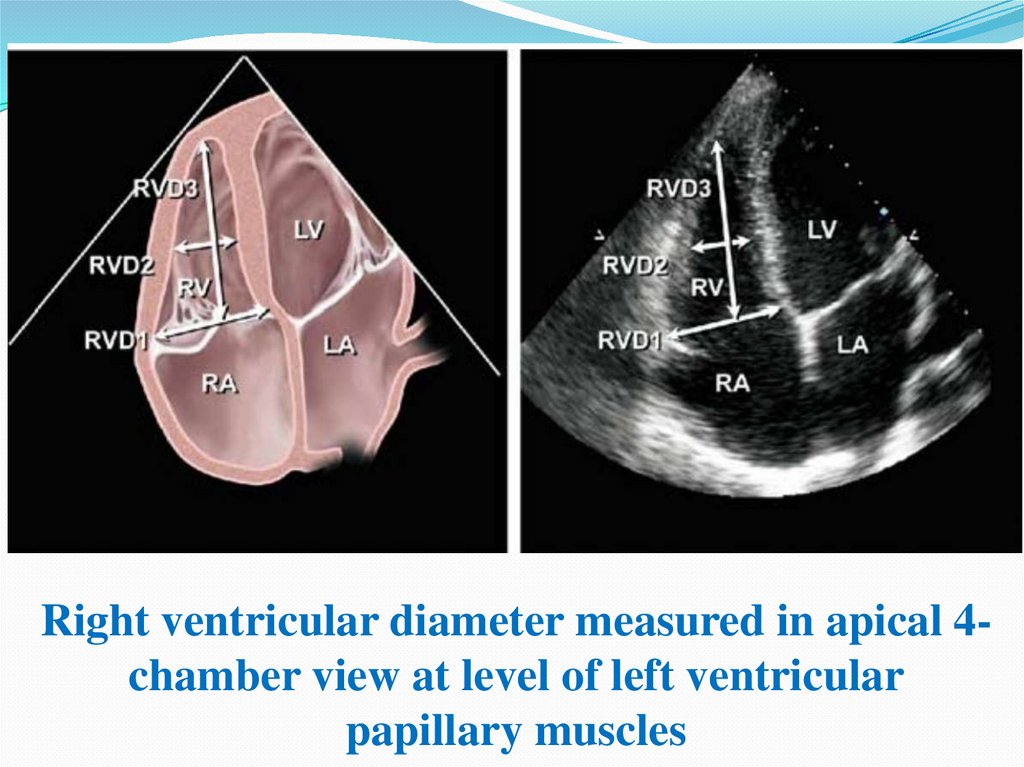
Right ventricular diameter measured in apical 4chamber view at level of left ventricularpapillary muscles

















 medicine
medicine