Similar presentations:
Displays require ideas and knowledge electronics
1.
Displays require ideas and knowledgeelectronics
displays
materials
optics
2.
3.
… By sizeDisplay built into the contact lens
Aerial view of landscape display
4.
the observation distance D = 3500 * A, where A is the linear pixel size.5.
Liquid crystal display devicesliquid crystal display (LCD) is a thin, flat electronic
visual display that uses the light modulating properties
of liquid crystals (LCs).
Display – Conductor of Information Magistral
6.
Ways of passing light through liquid crystal displays7.
Transmissive mode8.
Reflective mode9.
Transflective mode10.
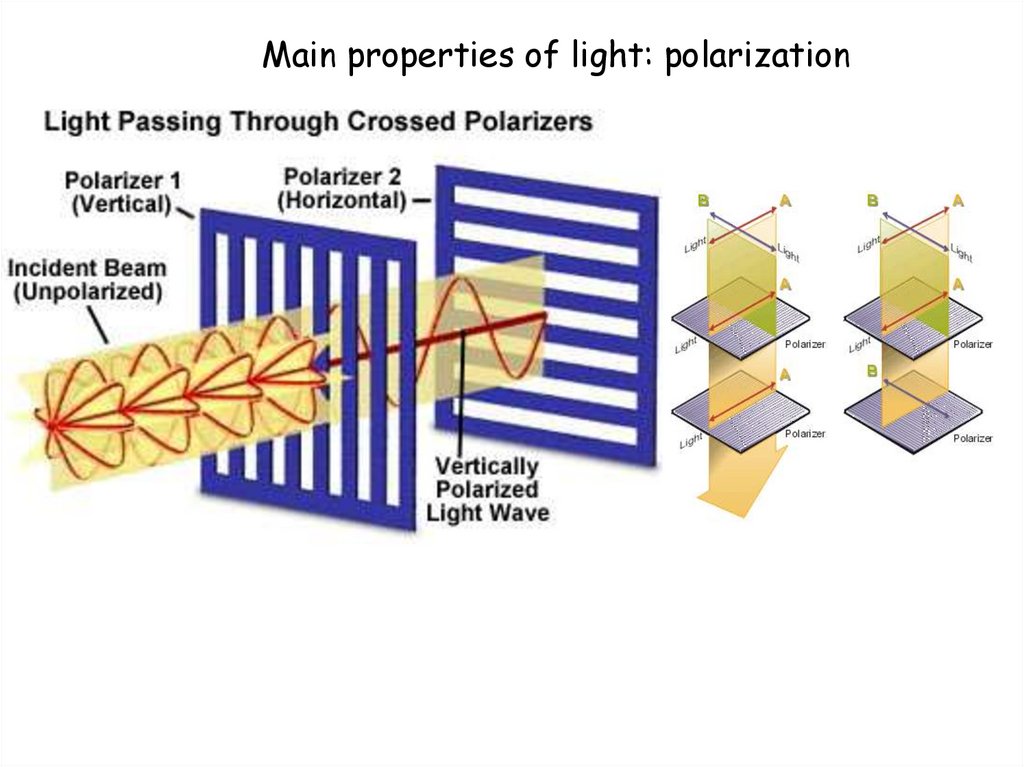
Main properties of light: polarization11.
Crystal property: birefringence12.
Liquid crystalsnm
nm
13.
Fredericks effect in an electric fieldE
F
F
14.
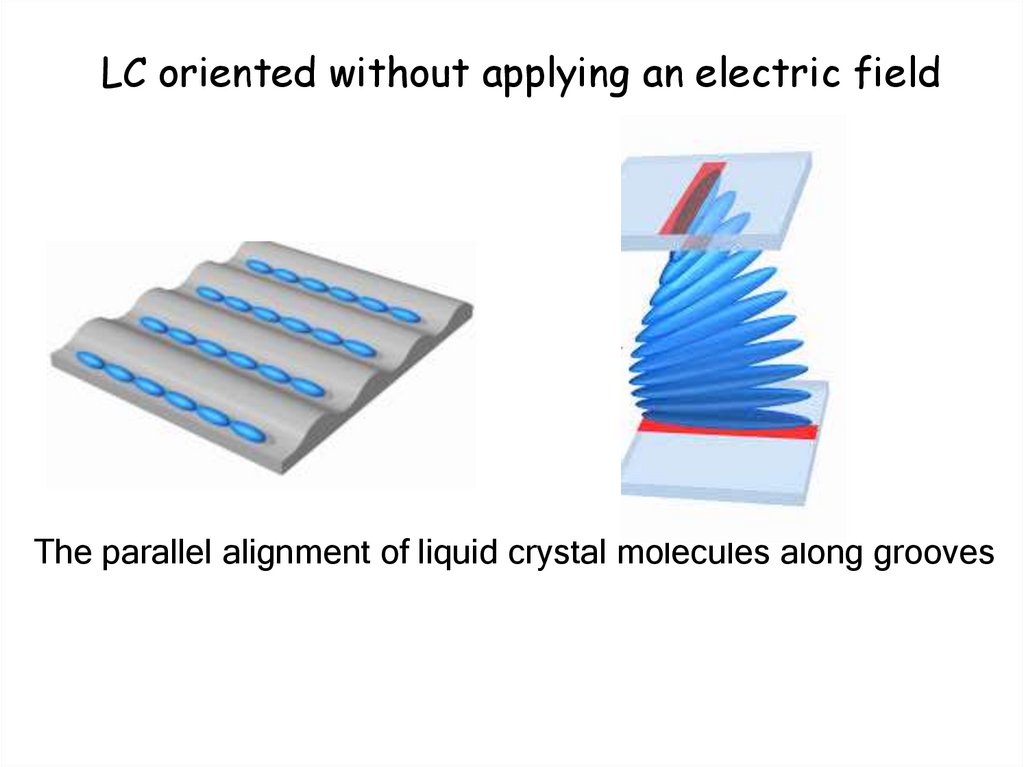
LC oriented without applying an electric fieldThe parallel alignment of liquid crystal molecules along grooves
15.
The basic structure of the liquid crystal cell16.
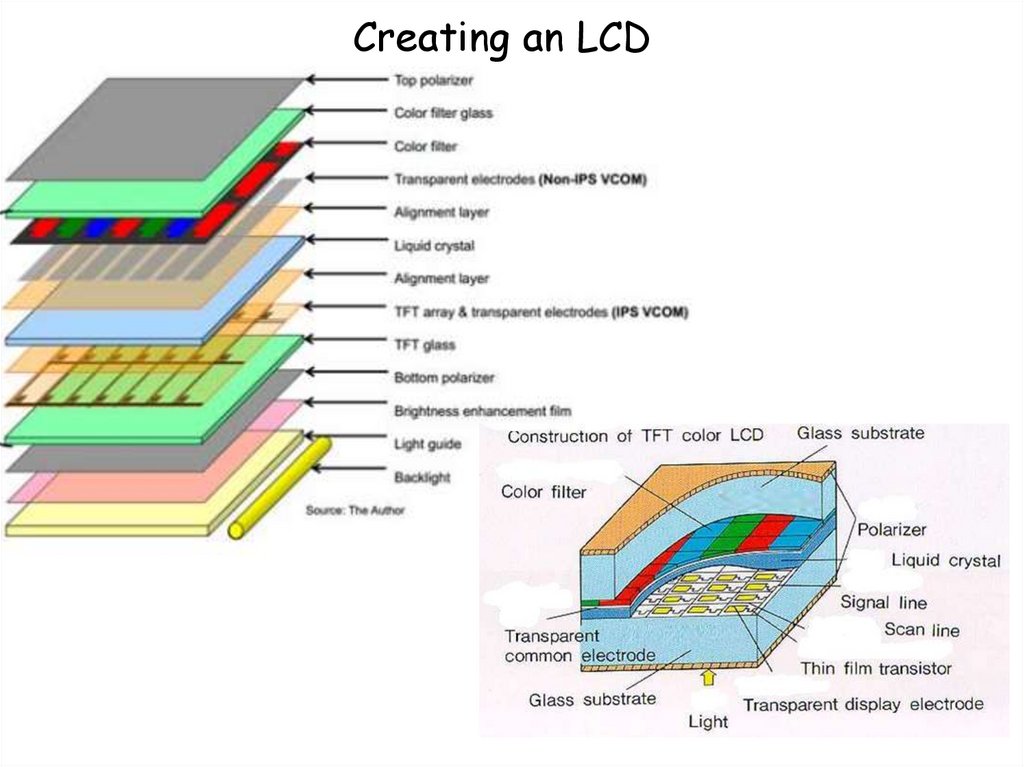
Creating an LCD17.
TFT LCD Configuration18.
TFT LCD technology process19.
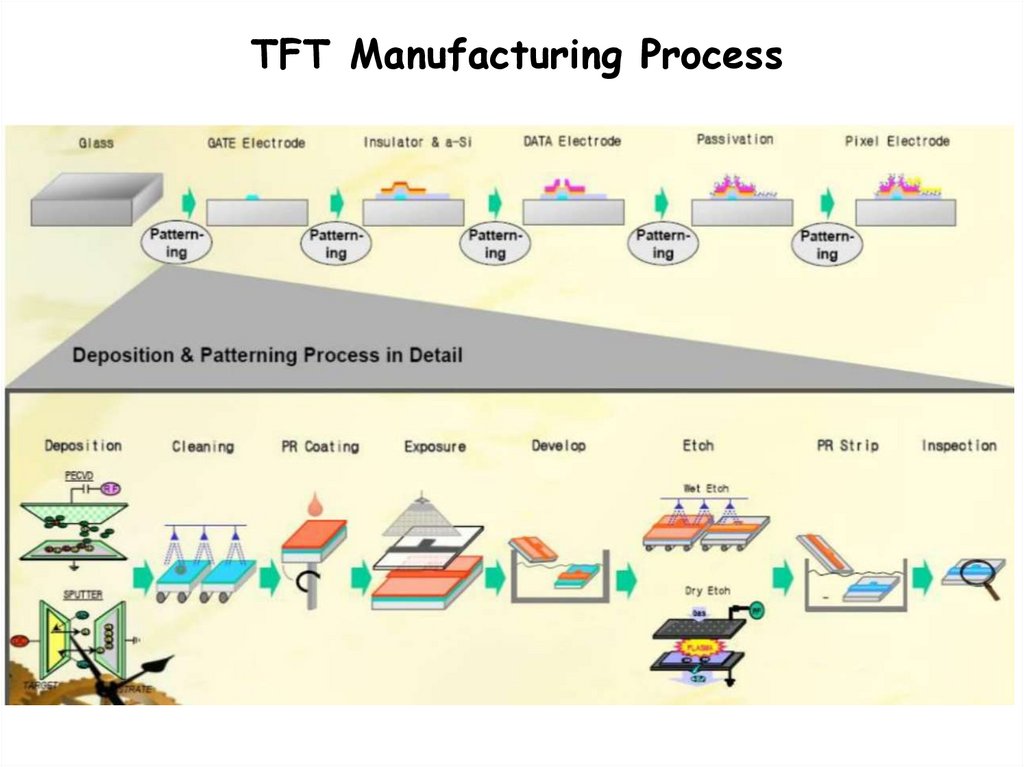
TFT Manufacturing Process20.
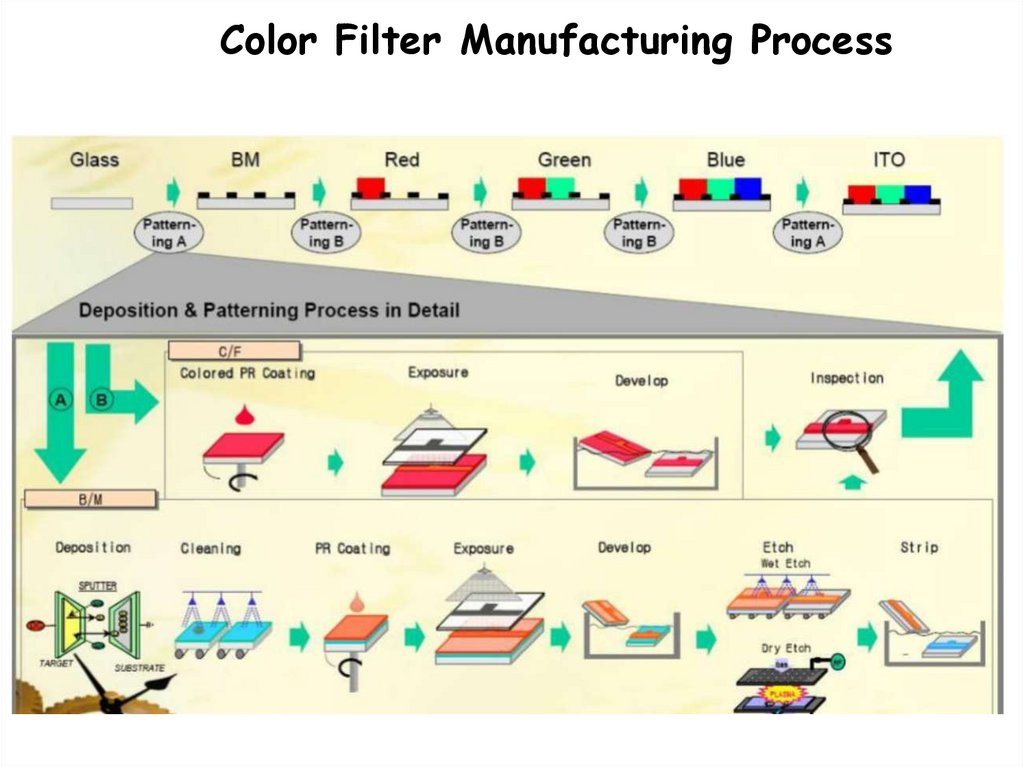
Color Filter Manufacturing Process21.
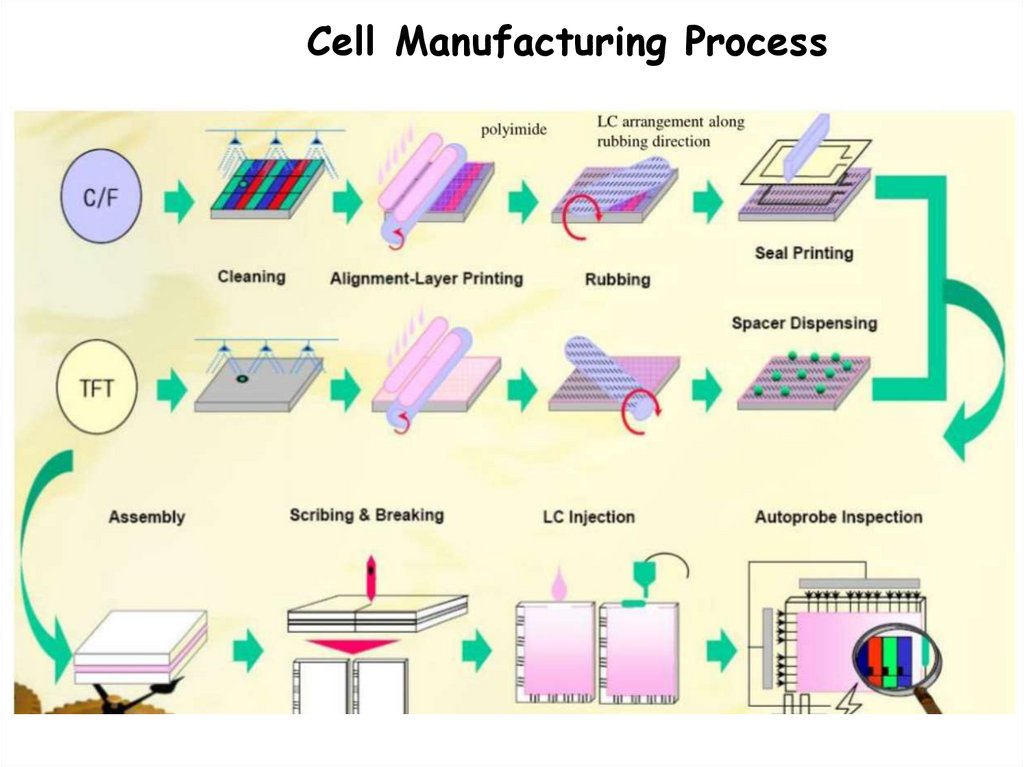
Cell Manufacturing Process22.
Targets applied in TFT-LCD manufacturing23.
Technology of Fabrication24.
Organic Light Emitting Diodes(OLEDs)
25.
LCD VS EMISSIVE DISPLAYSLCD
Emissive Displays
26.
OLED Device Operation27.
OLED Diagram28.
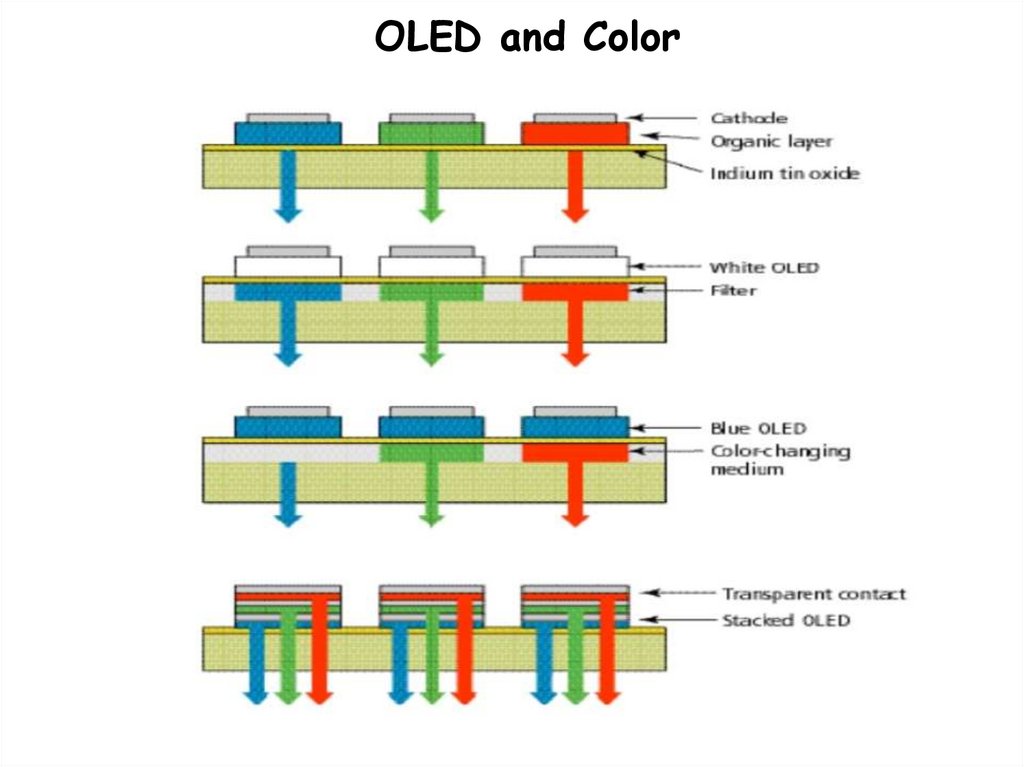
OLED and Color29.
Types 0f OLED30.
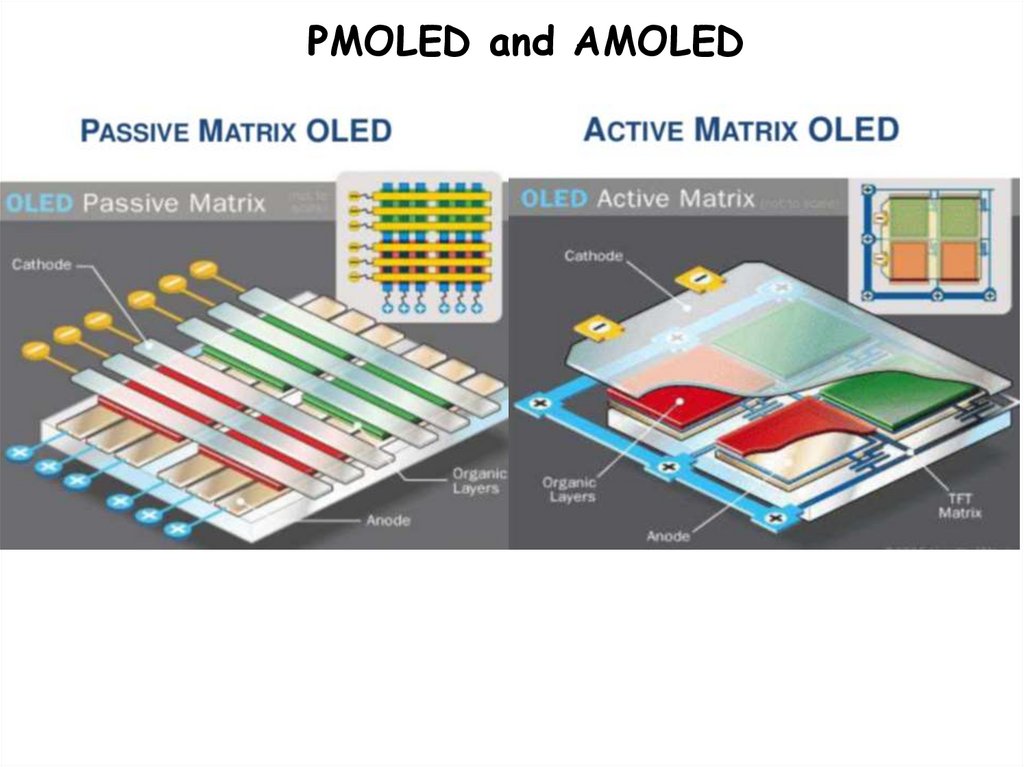
PMOLED and AMOLED31.
Transparent and Top Emitting OLED32.
Flexible and White OLED33.
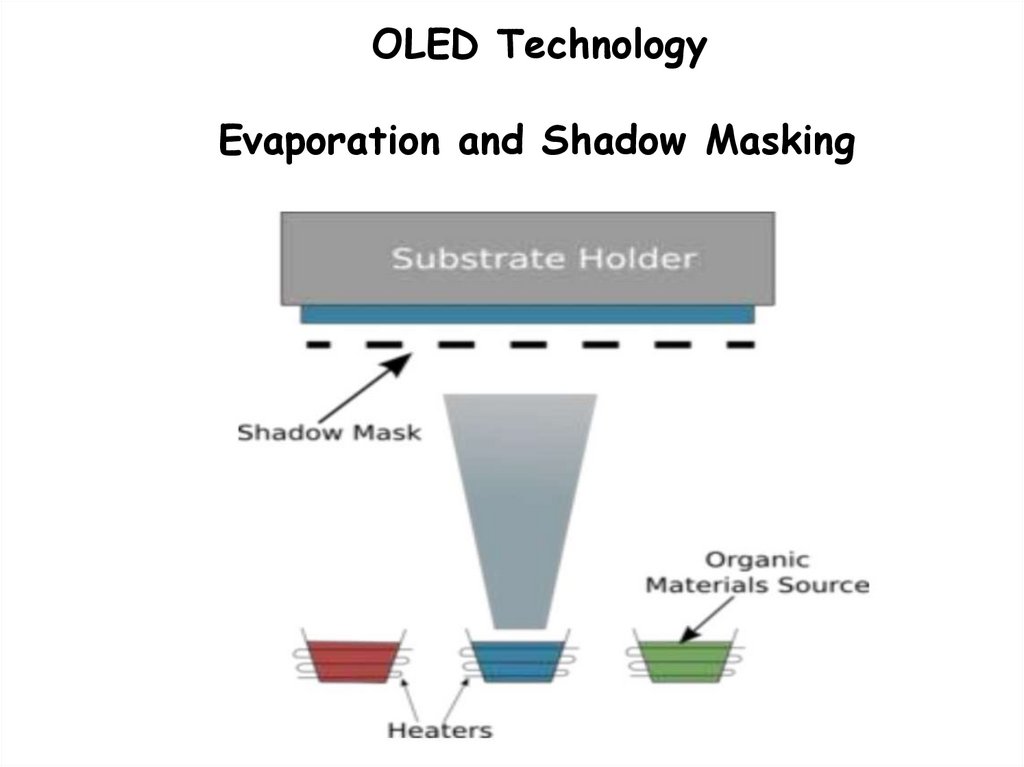
OLED TechnologyEvaporation and Shadow Masking
34.
OLED TechnologyInkjet Printing and organic vapor phase deposition
35.
OLED Application36.
MicroLEDDisplays
37.
What is a MicroLED38.
What is a MicroLED Display?• Also known as micro-LED,
mLED or µLED.
• MicroLED displays comprise
several microscopic LEDs,
which self-illuminate per
display pixel - just like an OLED
(Organic Light Emitting Diode)
panel would, only MicroLED
uses inorganic material.
• MicroLED features miniature
length less than 100 µm. Via
mass transfer technology µm–
level trio-color RGB MicroLEDs
are moved onto substrate ,
creating MicroLED display in
various size.
39.
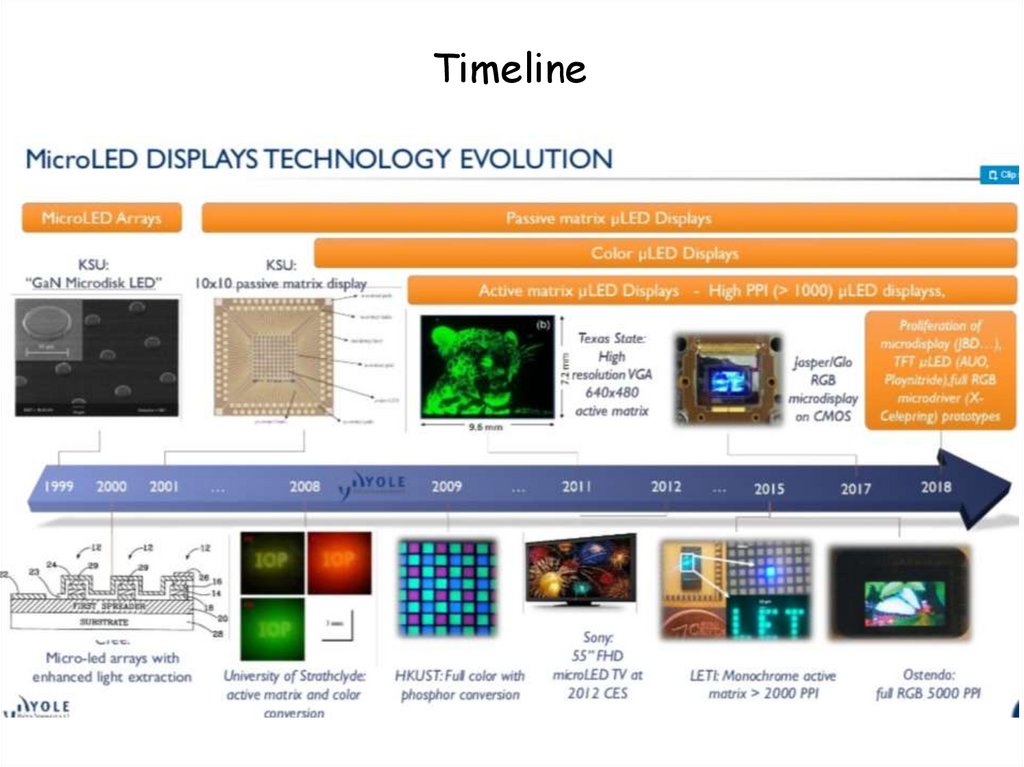
Timeline40.
Production methods for micro-LEDs41.
Major manufacturing technology bricks42.
MicroLED and addressing structure43.
MicroLed Display Manufacturing ChallengesLight
extraction and
beam shaping
Color
Conversion
Massively Parallel
and High Accuracy
Pick and Place
Technology
LED Technology
(epitaxy, chips)
Source: MicroLED Displays 2017 report Yole Développement
Backplane
Hybridization
Defect
Management
and Testing
MicroLED
Displays
Supply Chain
44.
TFT-LCD vs OLED vs MicroLED45.
Applications of MicroLED• Smart Watches and
Wearables
• Virtual reality
• Augmented/Mixed
Reality
• Automotive HeadUp Display
• Large Video
Displays
• 8K UHD TVs
• Smartphones
• Laptop/Tablets
46.
Conclusion47.
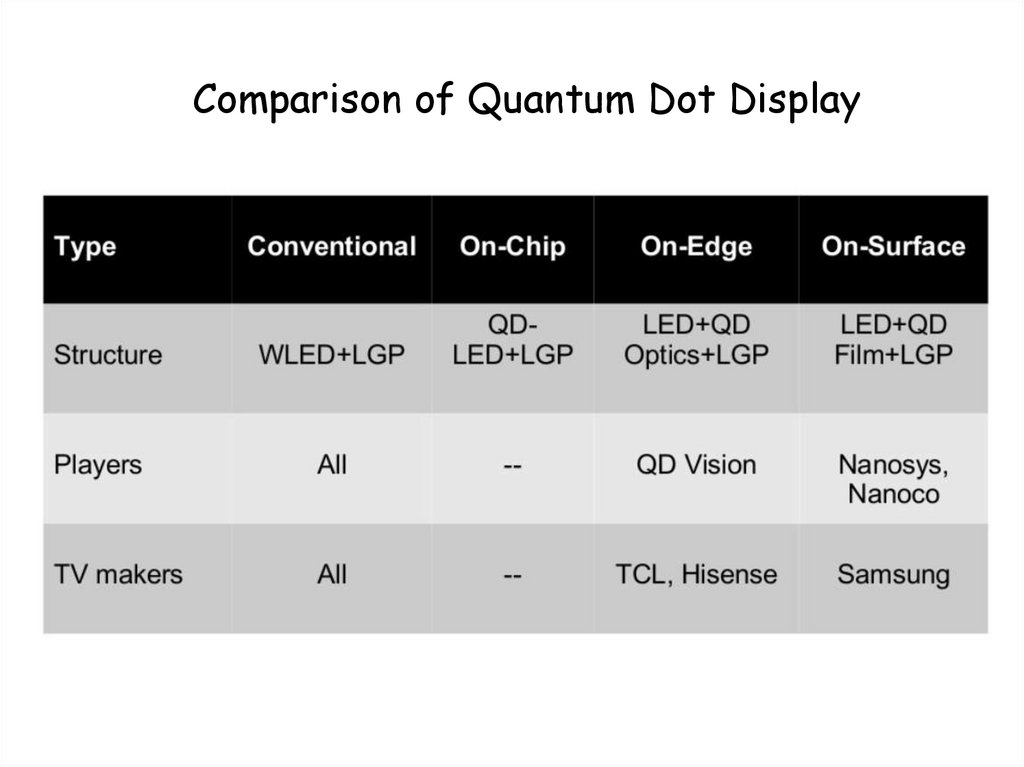
Quantum Dot Display48.
Quantum Dot Size and Color49.
White LED vs Quantum Dot50.
High Color GAMUT51.
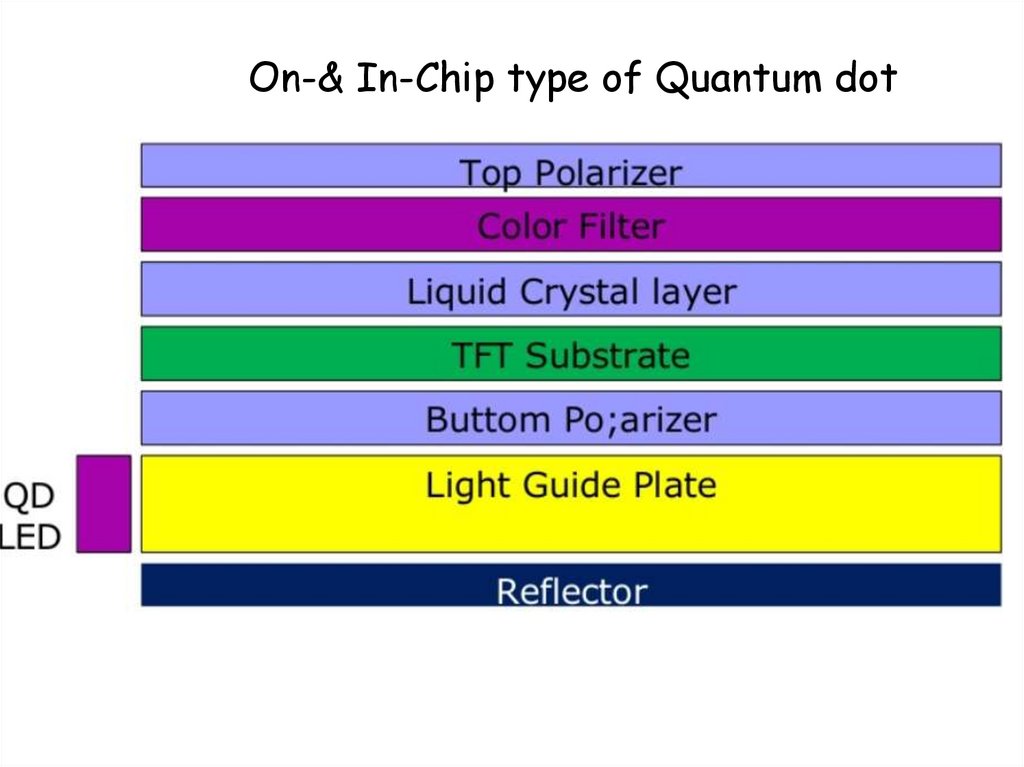
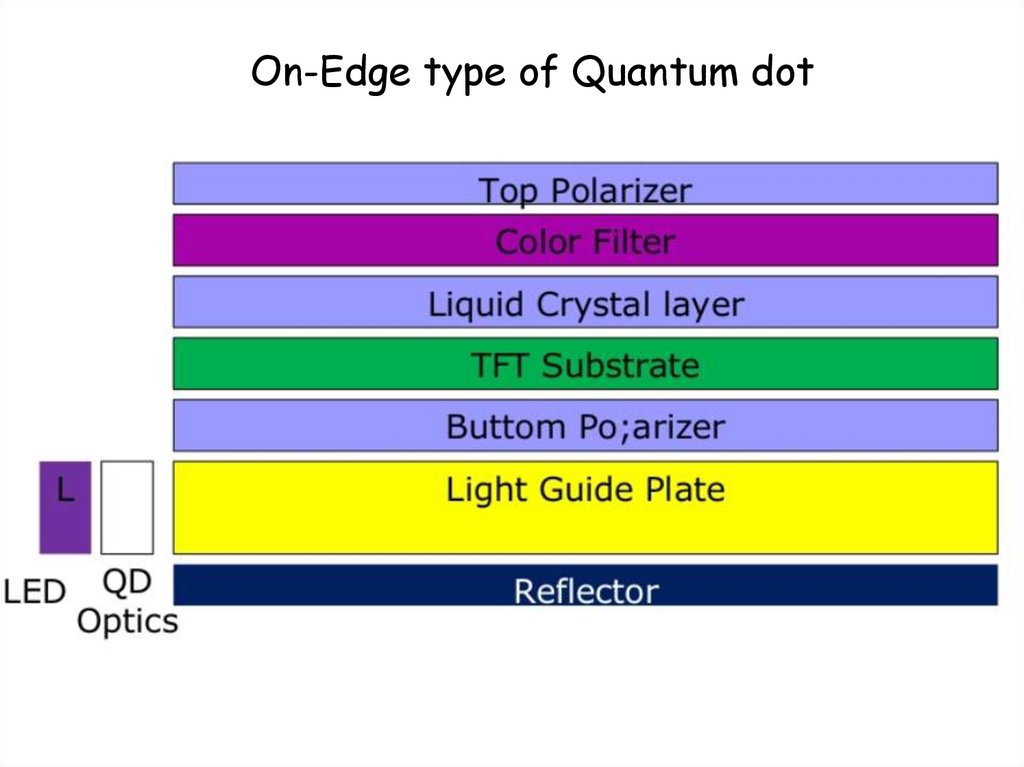
On-& In-Chip type of Quantum dot52.
MicroLED + Quantum dotsThe process flow of the full-color emission of quantum-dot-based micro LED display.













































 electronics
electronics








