Similar presentations:
ThinPrep® Pap Test Diagnostic Challenges and Differential
1. ThinPrep® Pap Test Diagnostic Challenges and Differential Diagnoses
Hologic Proprietary © 20122.
Hologic Proprietary © 20123. ThinPrep® Characteristics
• Wet Fixation– enhanced cytoplasmic and nuclear detail
– variability in nuclear staining
• Cell Size
– proportionately smaller
– single cells more prominent
– cells may round up in solution e.g.. adenocarcinoma
• Smear Pattern
– Cellular material not pulled out in mucous
– Mechanical artifacts eliminated
• Specimen Background
– Cellular debris may appear clumped
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
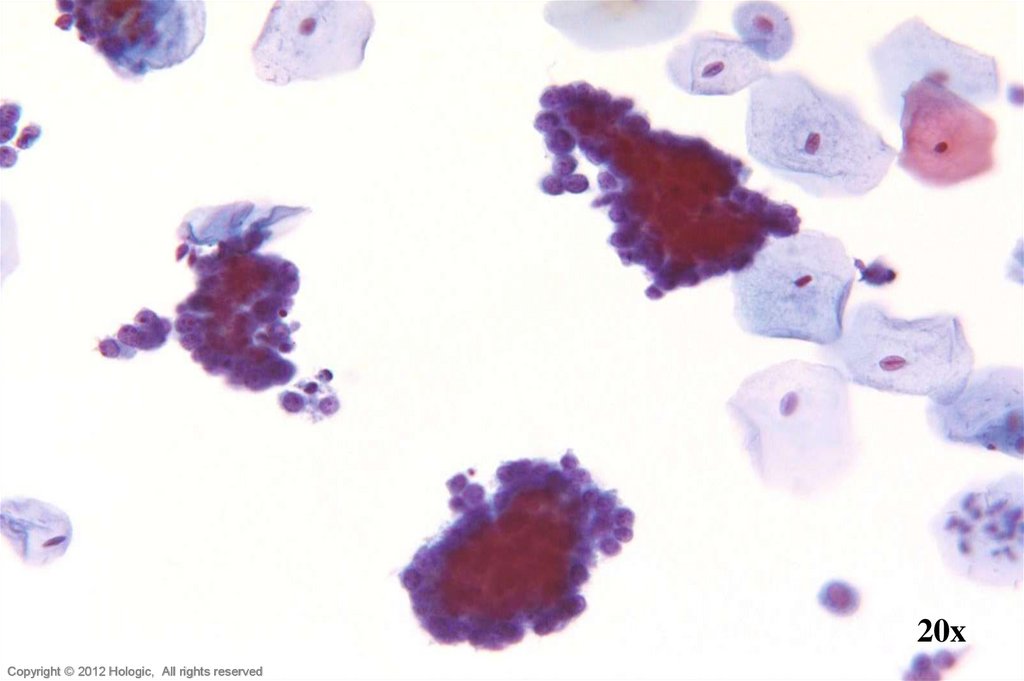
4. Differential Diagnoses
• Endocervical Adenocarcinoma vs. Poorly Differentiated SquamousCell Carcinoma (SCC)
• Endocervical Adenocarcinoma vs. Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
• Endometrial Adenocarcinoma vs. Small Cell Squamous Carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma-in-situ vs. Tubal Metaplasia
• HSIL vs. Single Endometrial Cells
• HSIL vs. Immature Squamous Metaplasia
• Poorly Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma vs. Repair
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
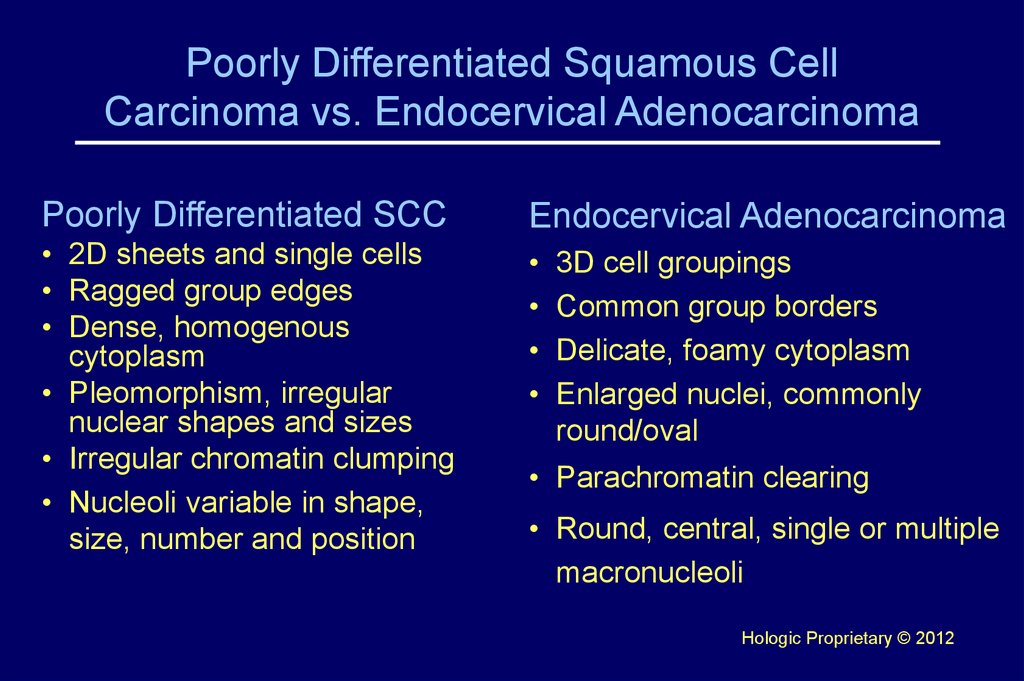
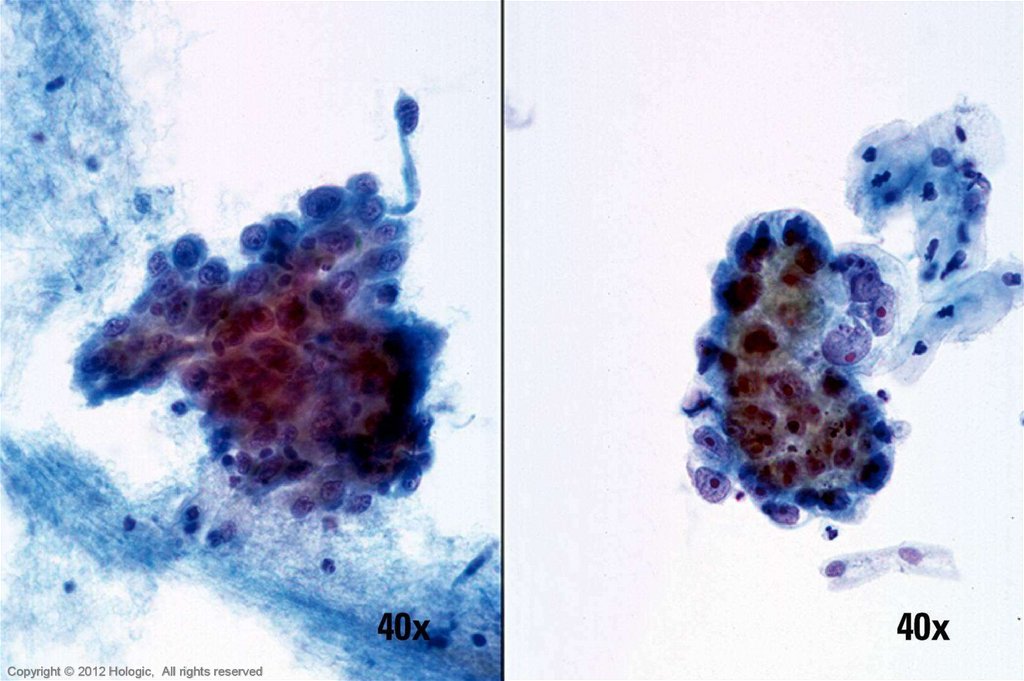
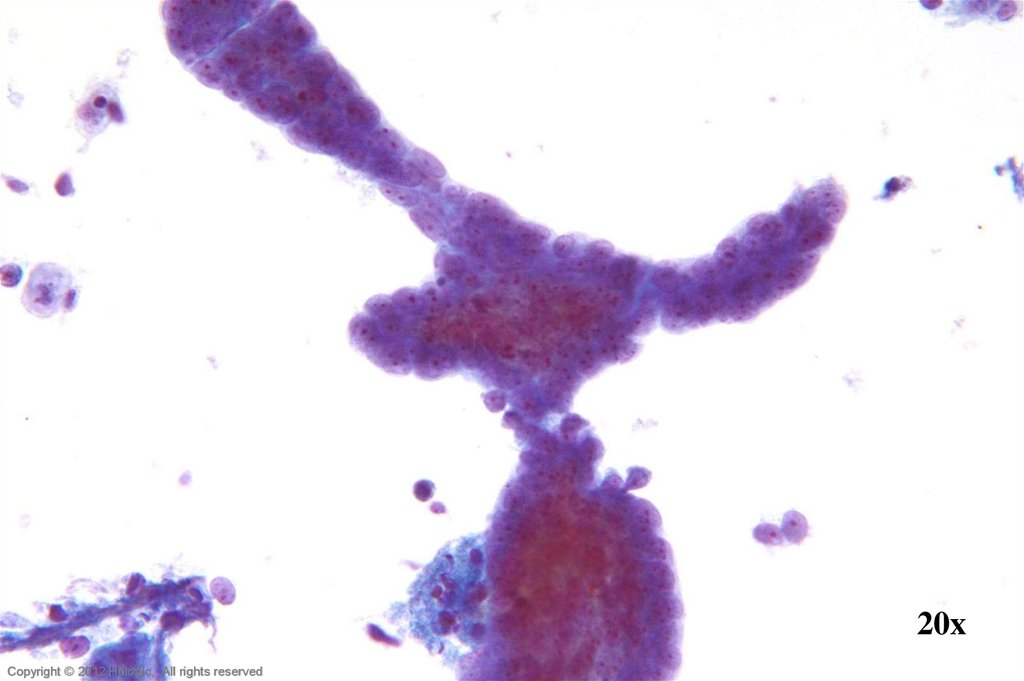
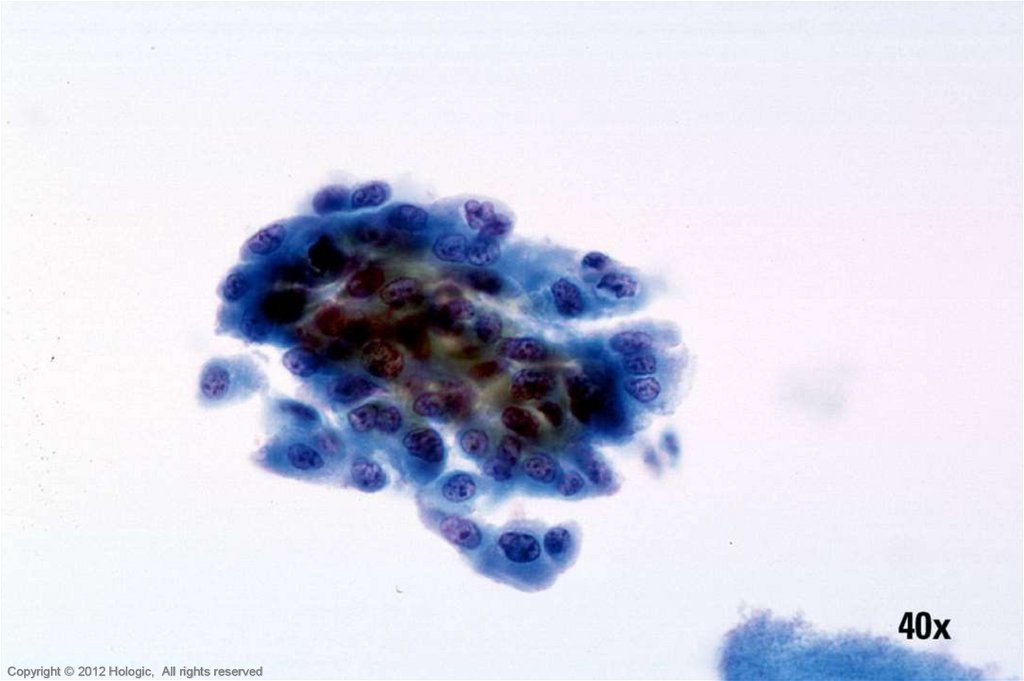
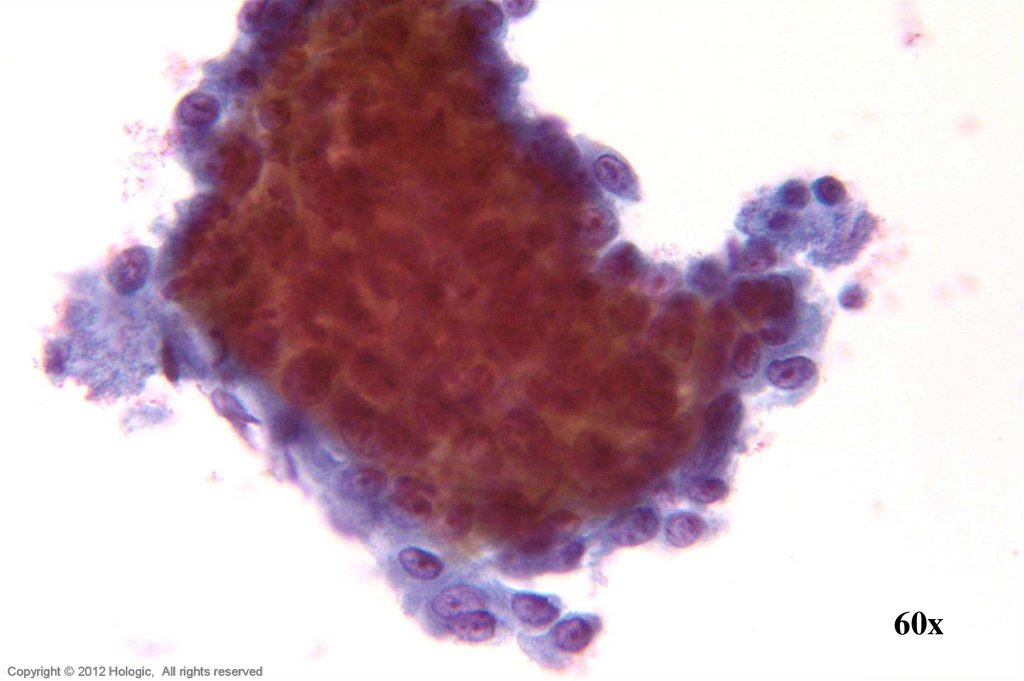
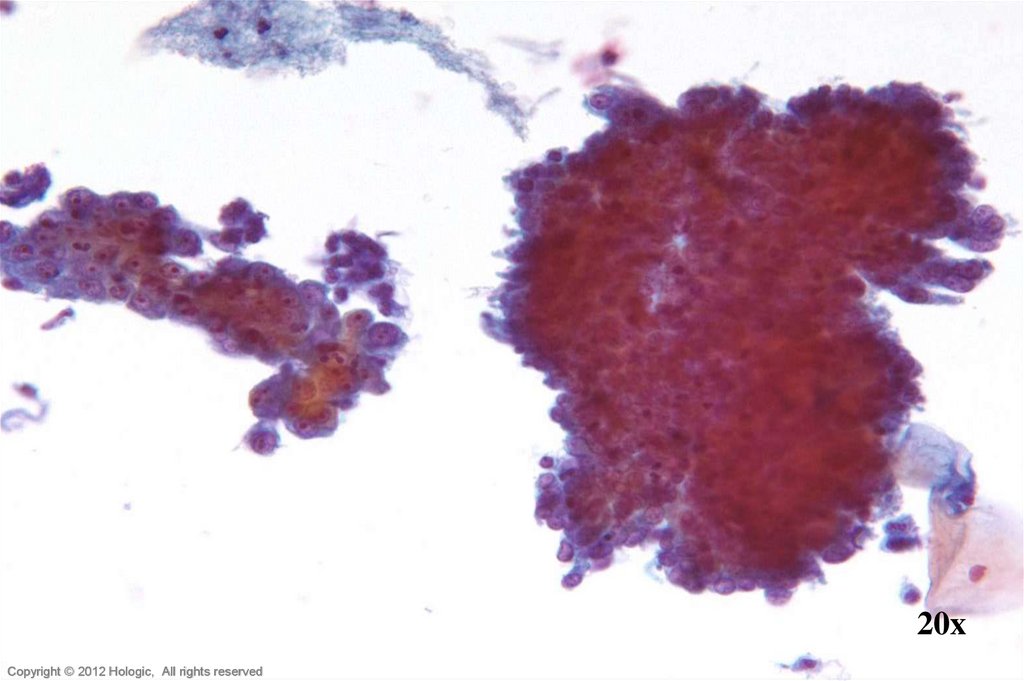
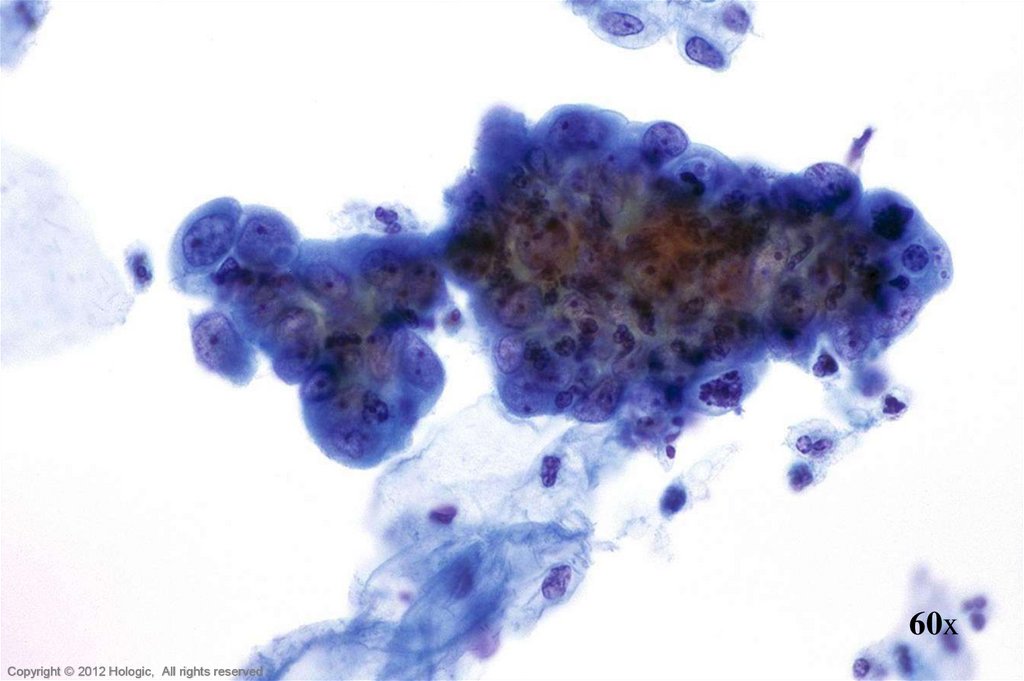
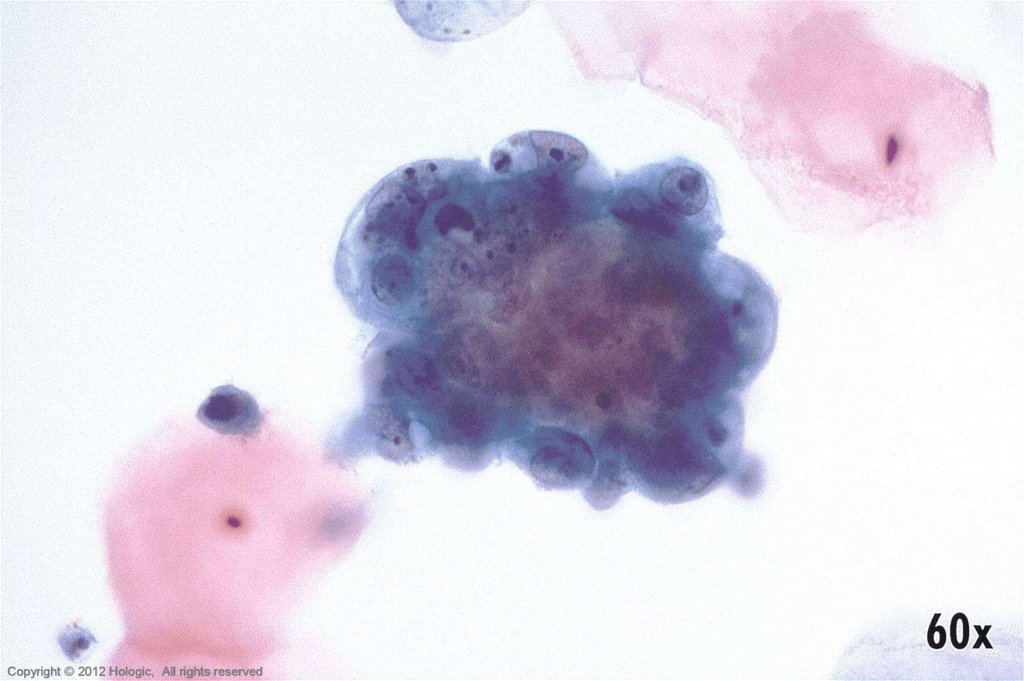
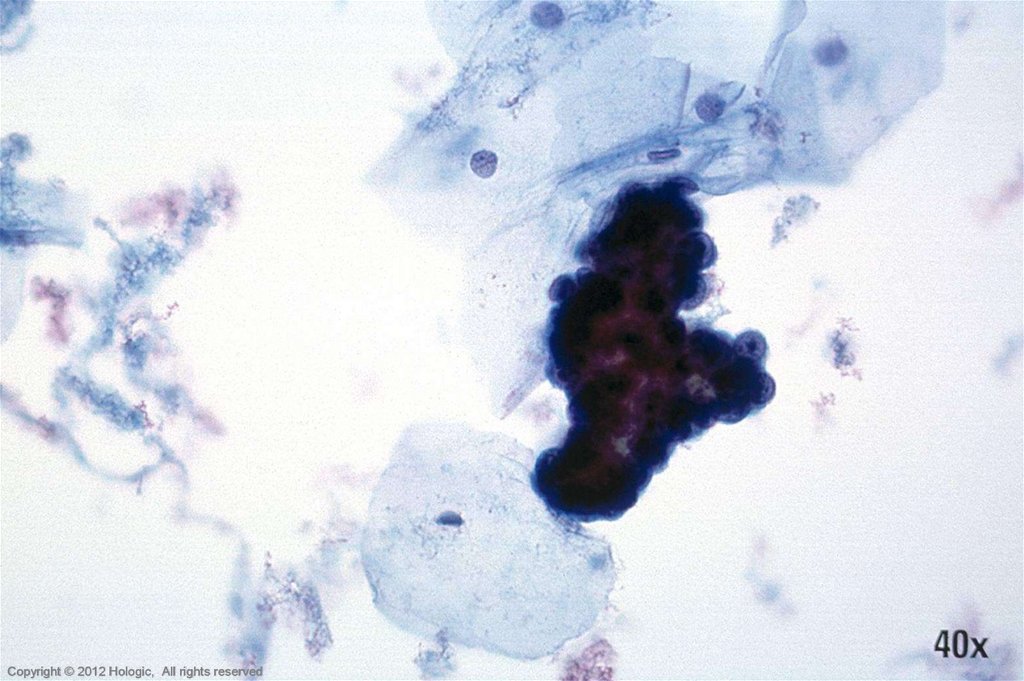
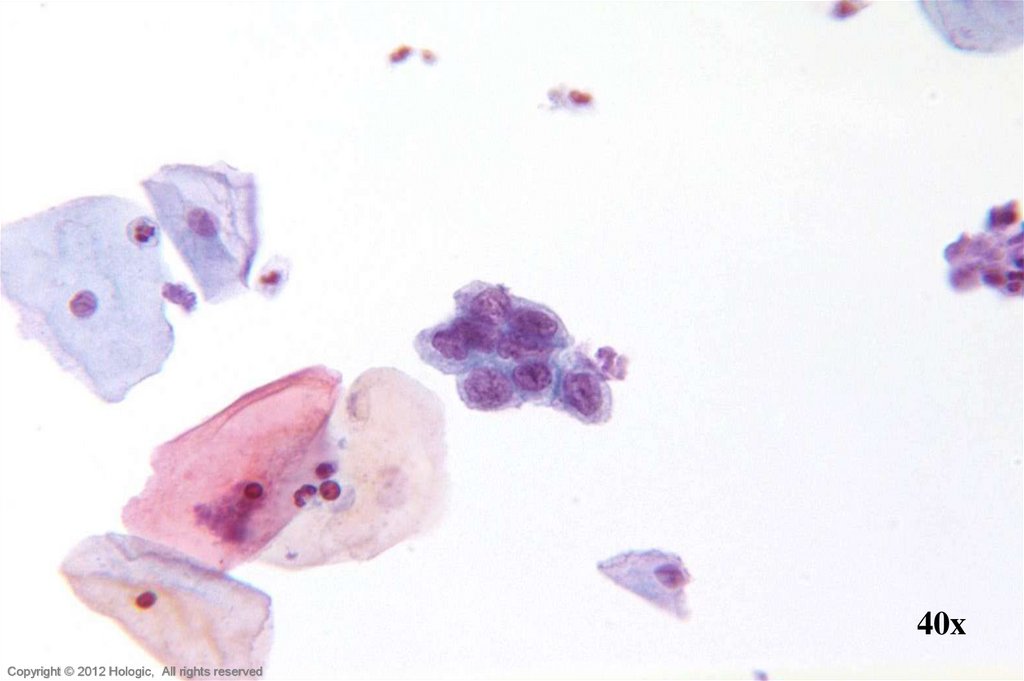
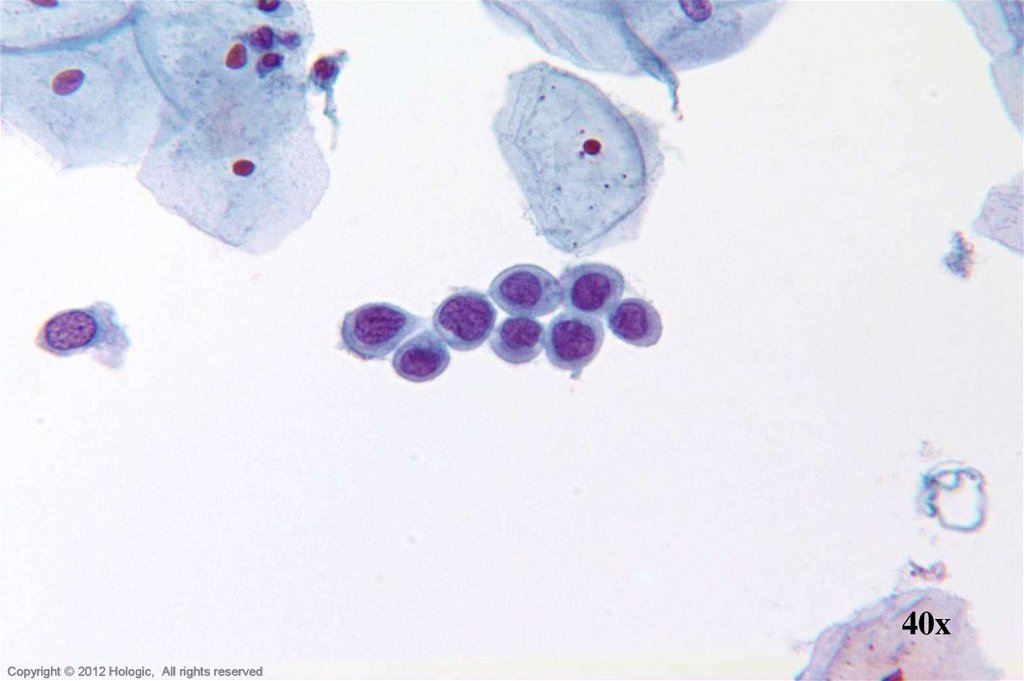
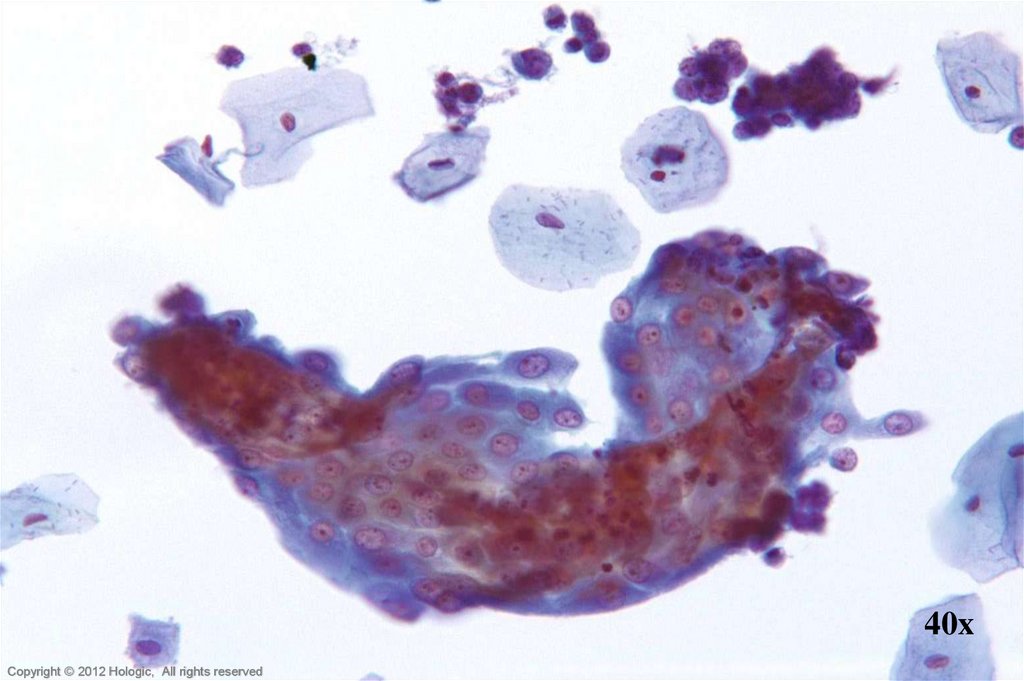
5. Poorly Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma vs. Endocervical Adenocarcinoma
Poorly Differentiated SCCEndocervical Adenocarcinoma
• 2D sheets and single cells
• Ragged group edges
• Dense, homogenous
cytoplasm
• Pleomorphism, irregular
nuclear shapes and sizes
• Irregular chromatin clumping
• Nucleoli variable in shape,
size, number and position
3D cell groupings
Common group borders
Delicate, foamy cytoplasm
Enlarged nuclei, commonly
round/oval
• Parachromatin clearing
• Round, central, single or multiple
macronucleoli
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
6.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
7.
20xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
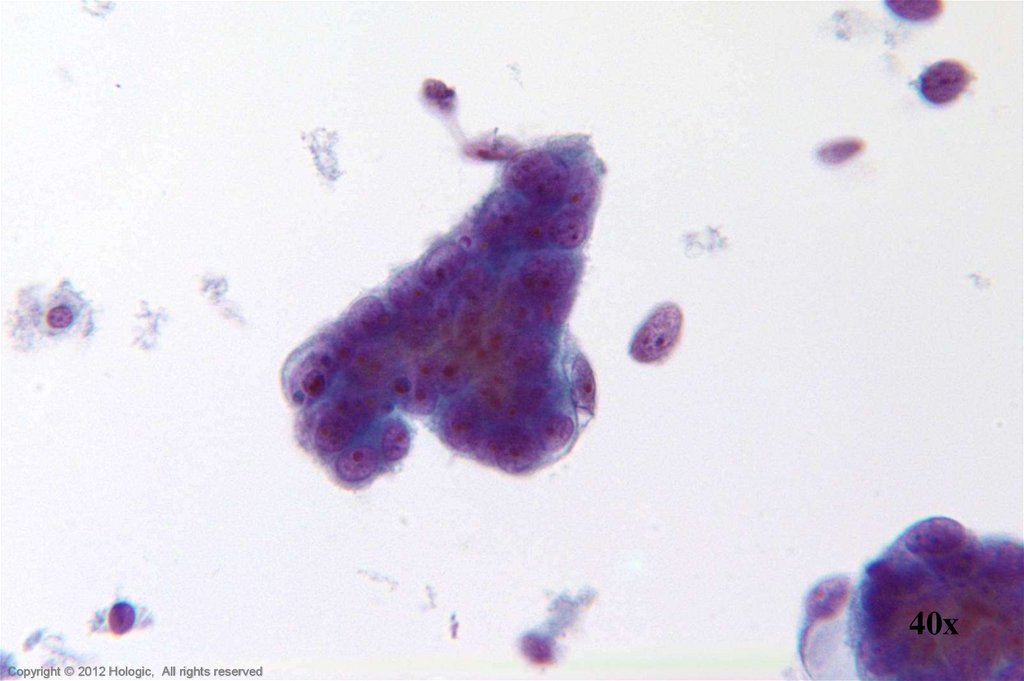
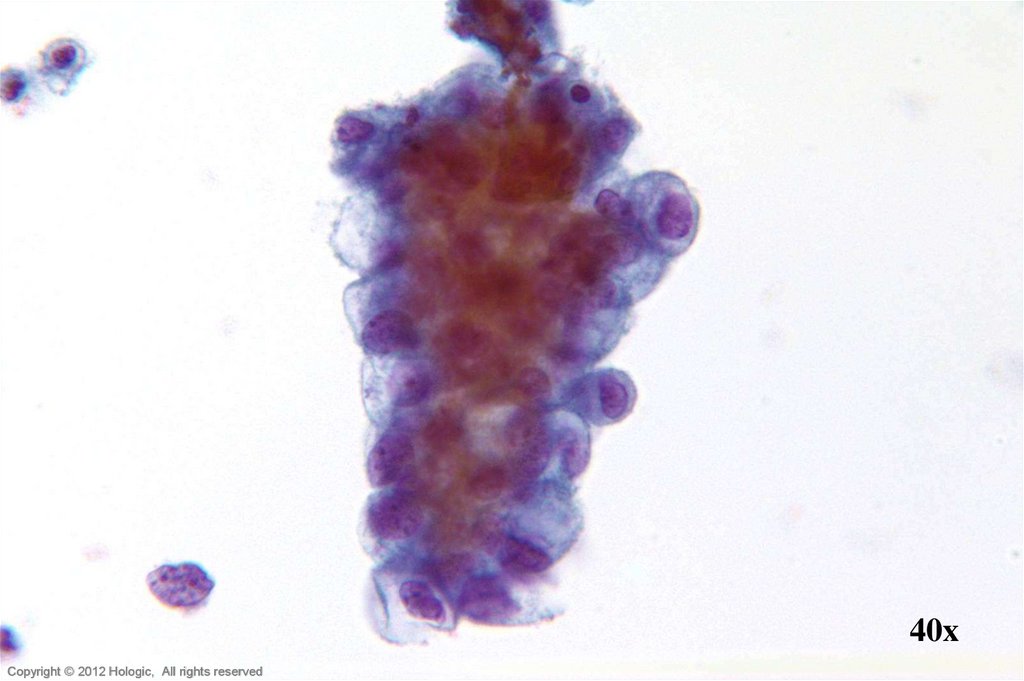
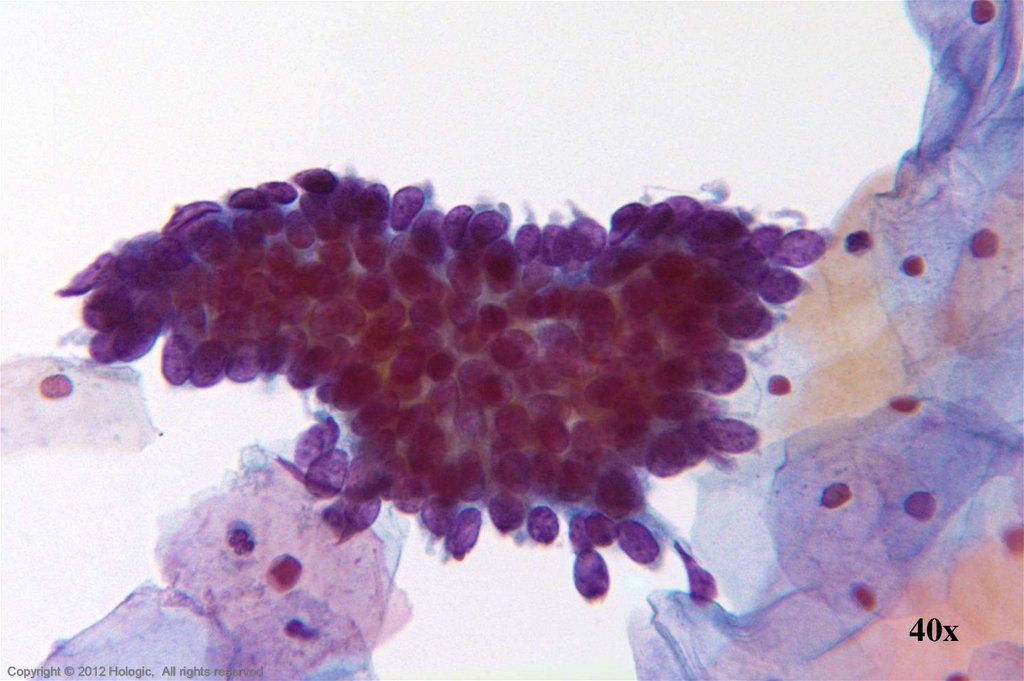
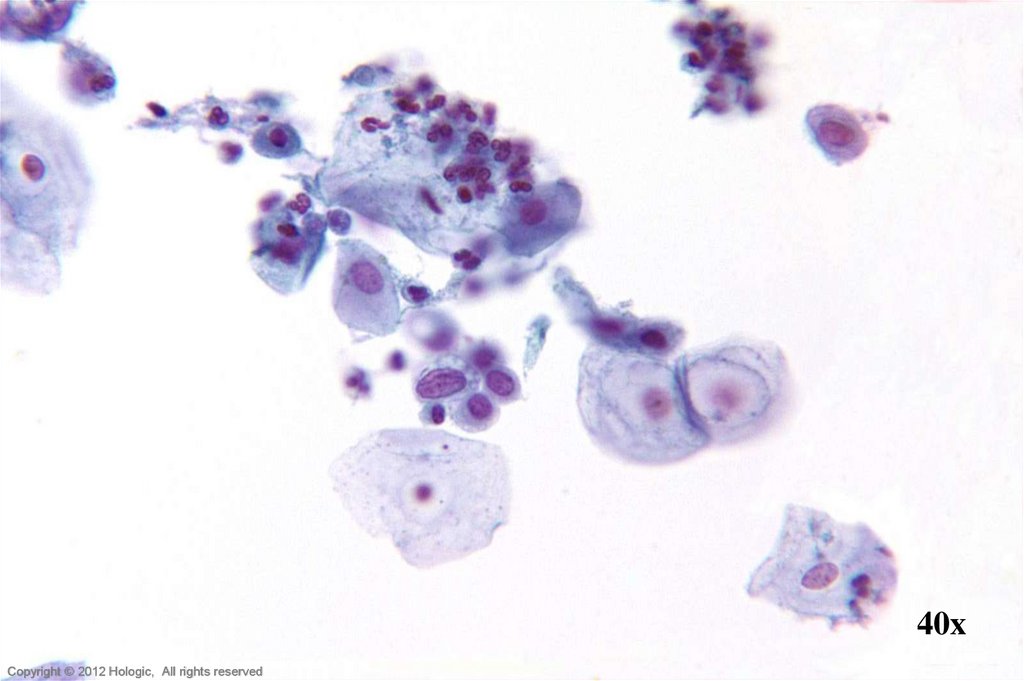
8.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
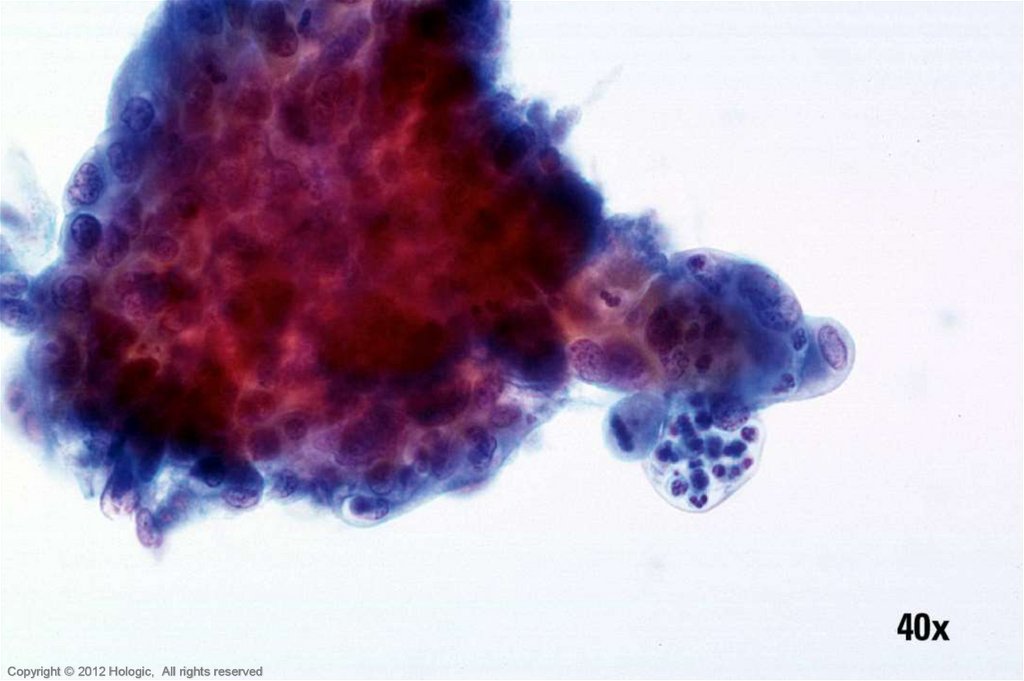
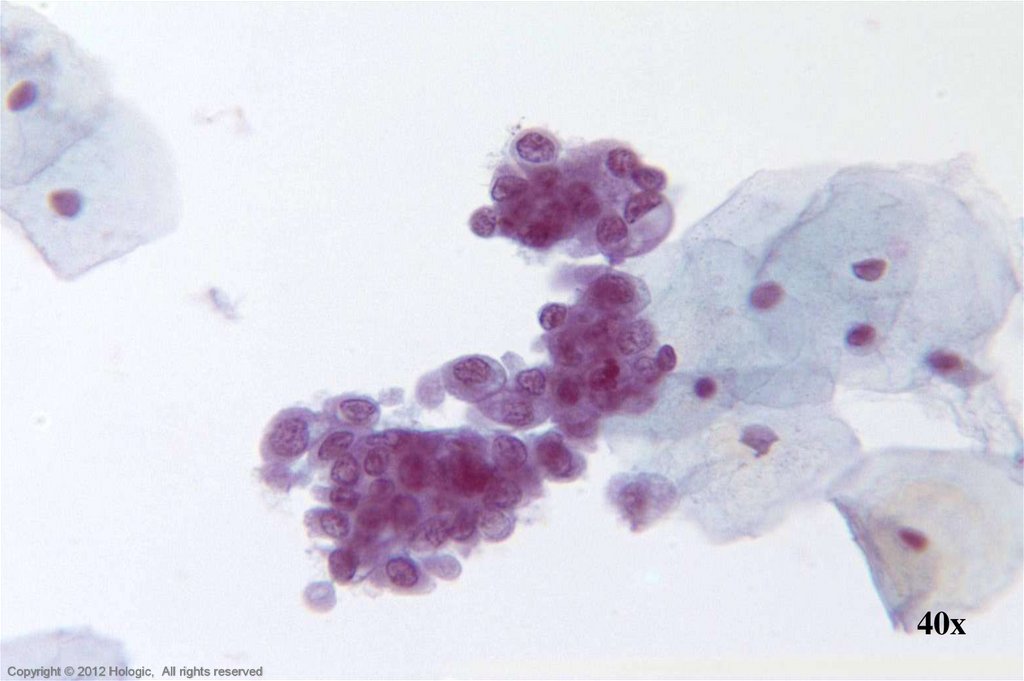
9.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
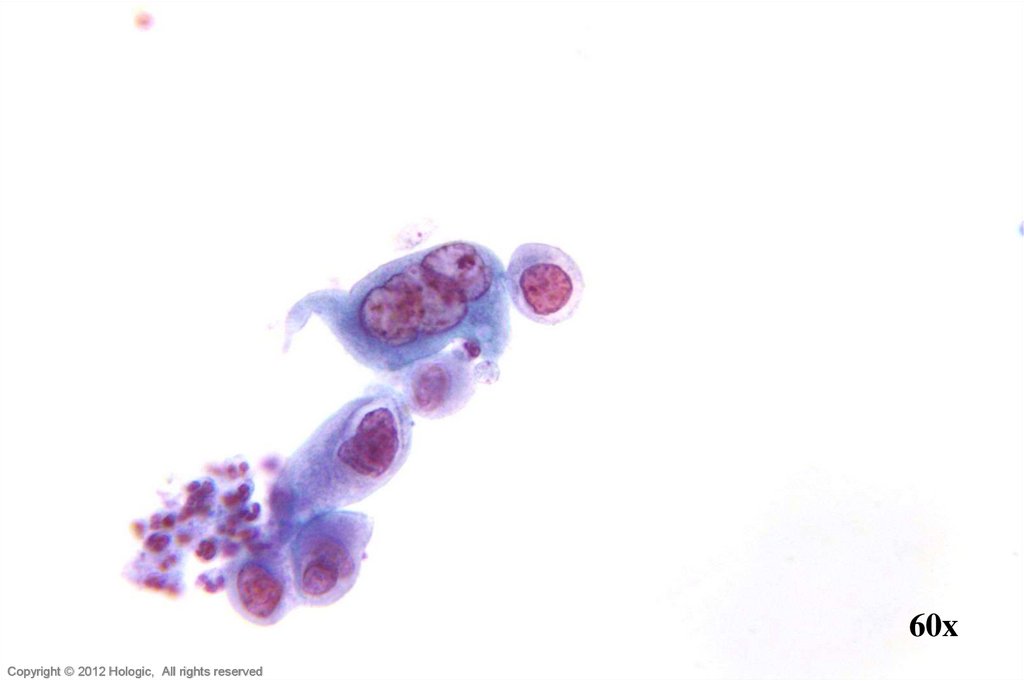
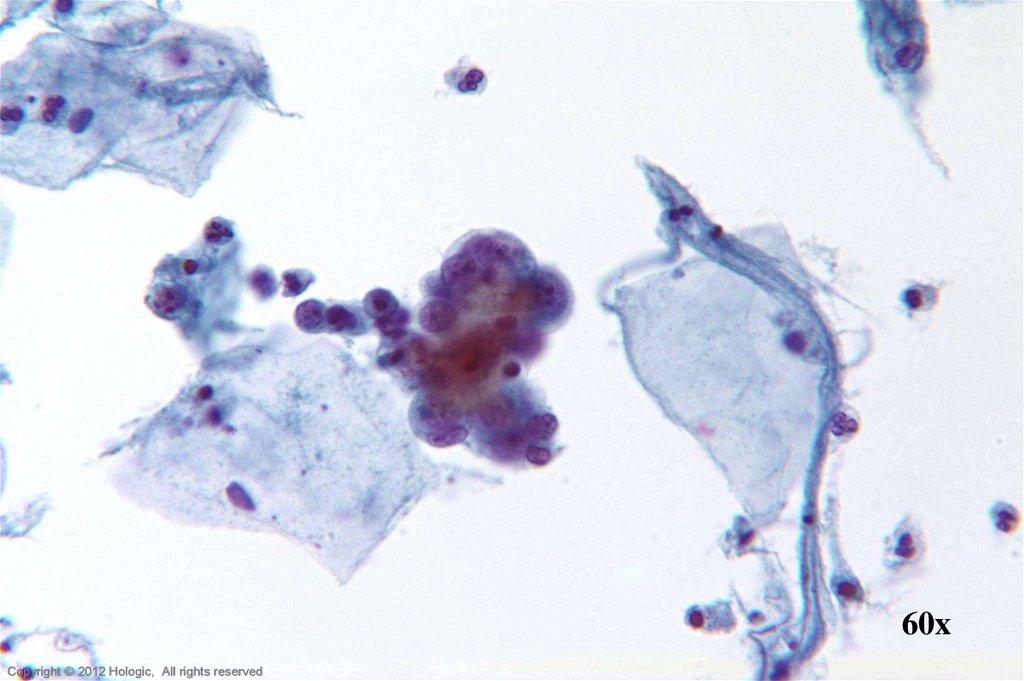
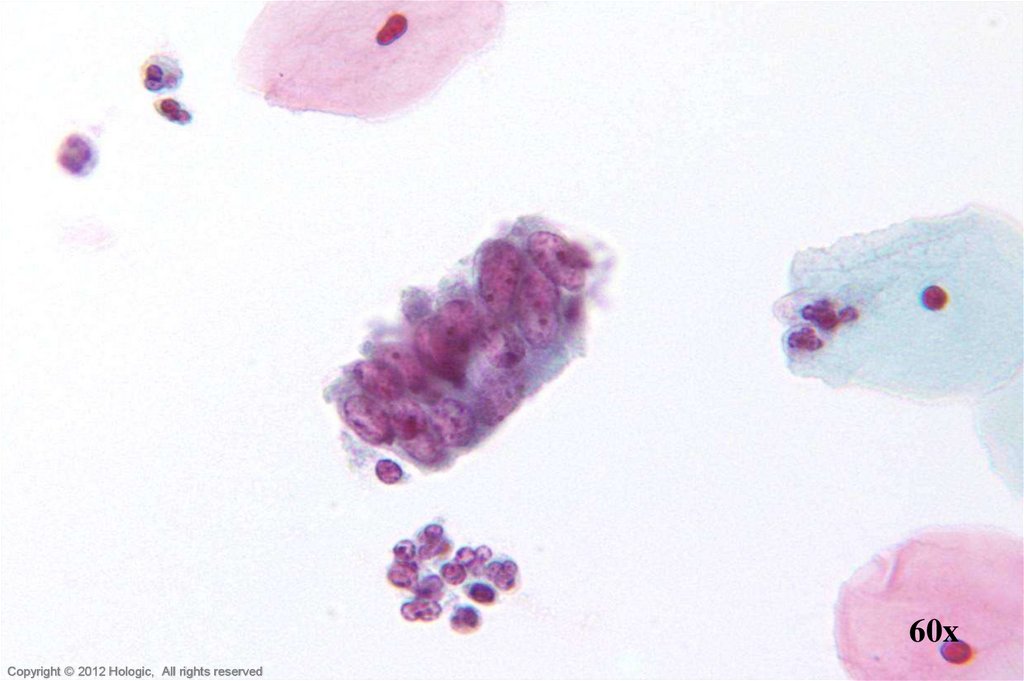
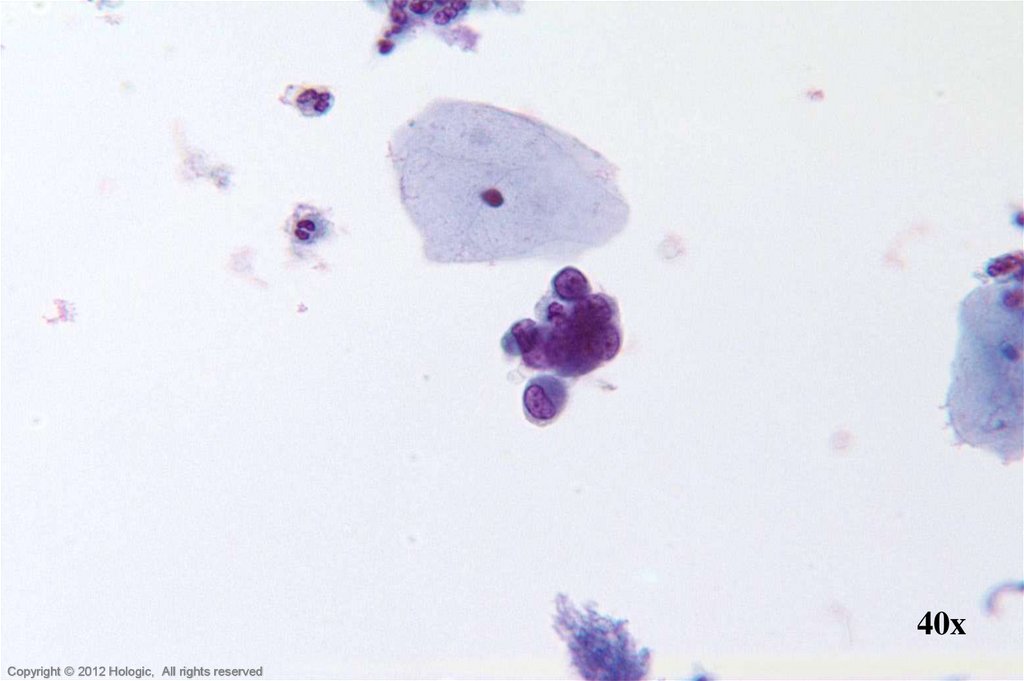
10.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
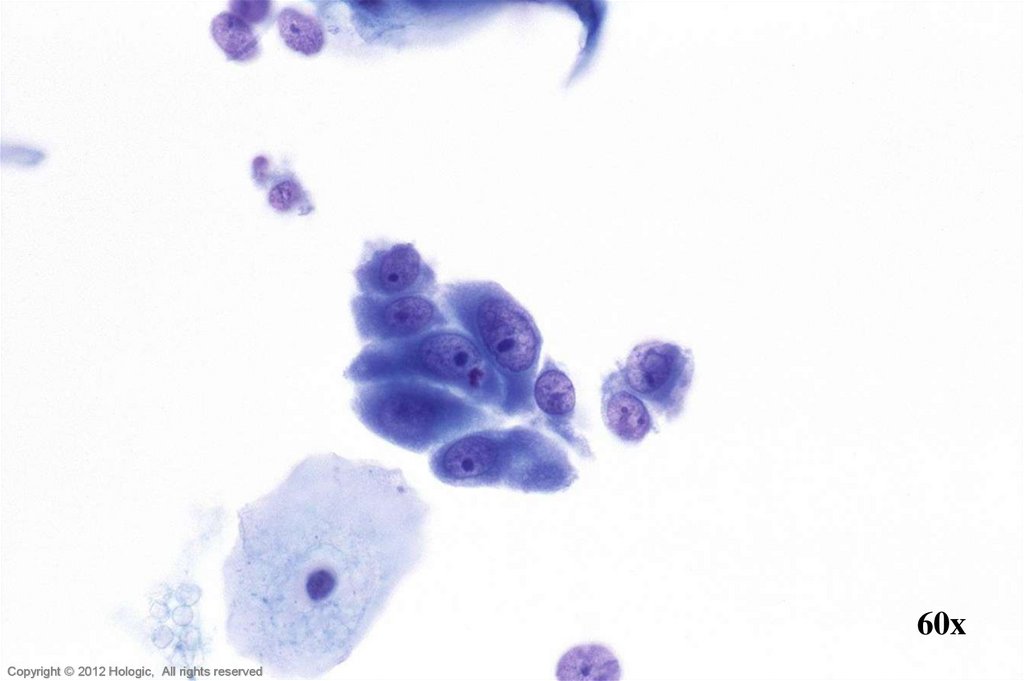
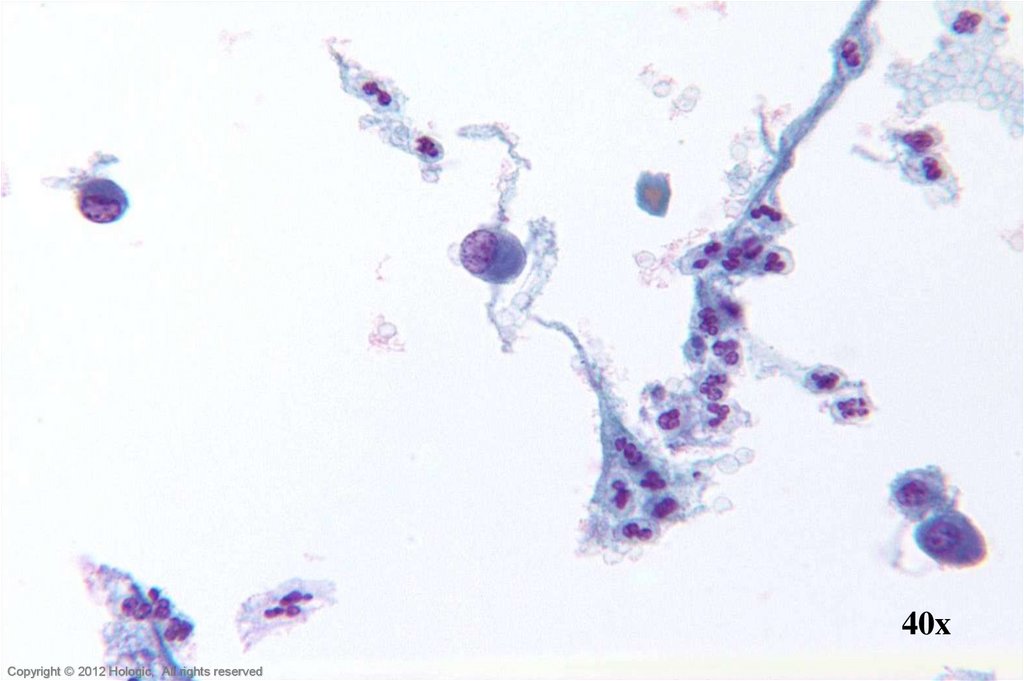
11.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
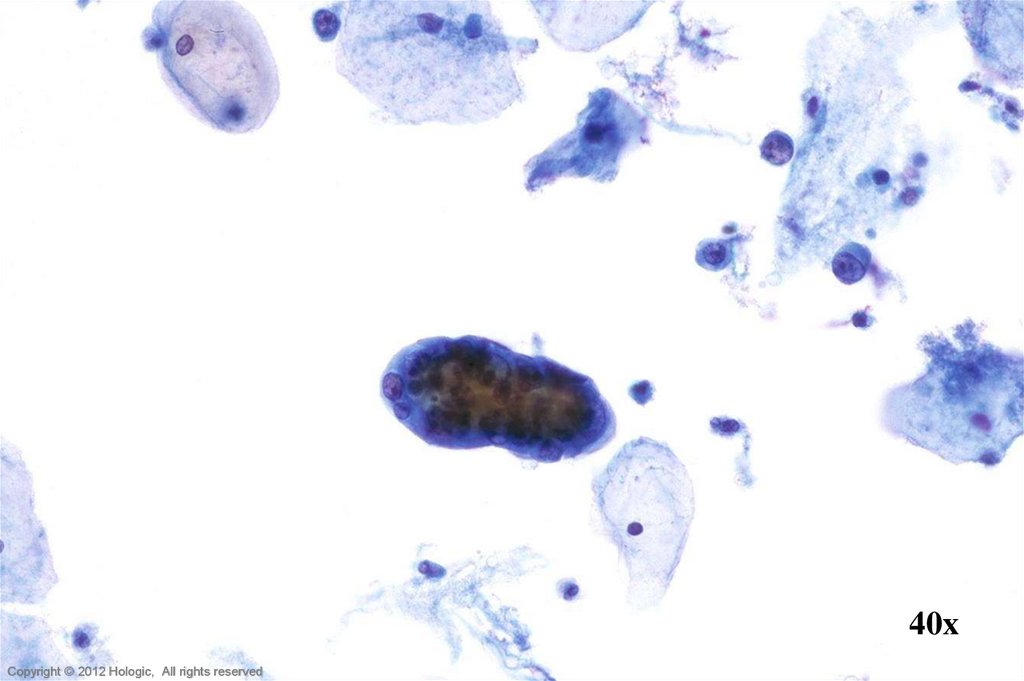
12.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
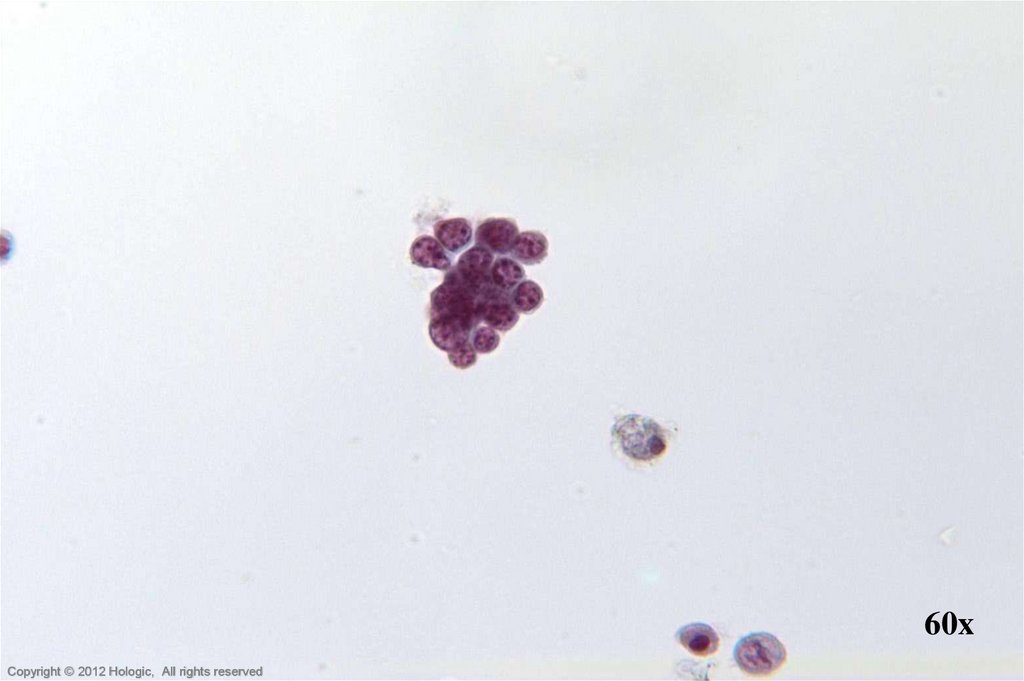
13.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
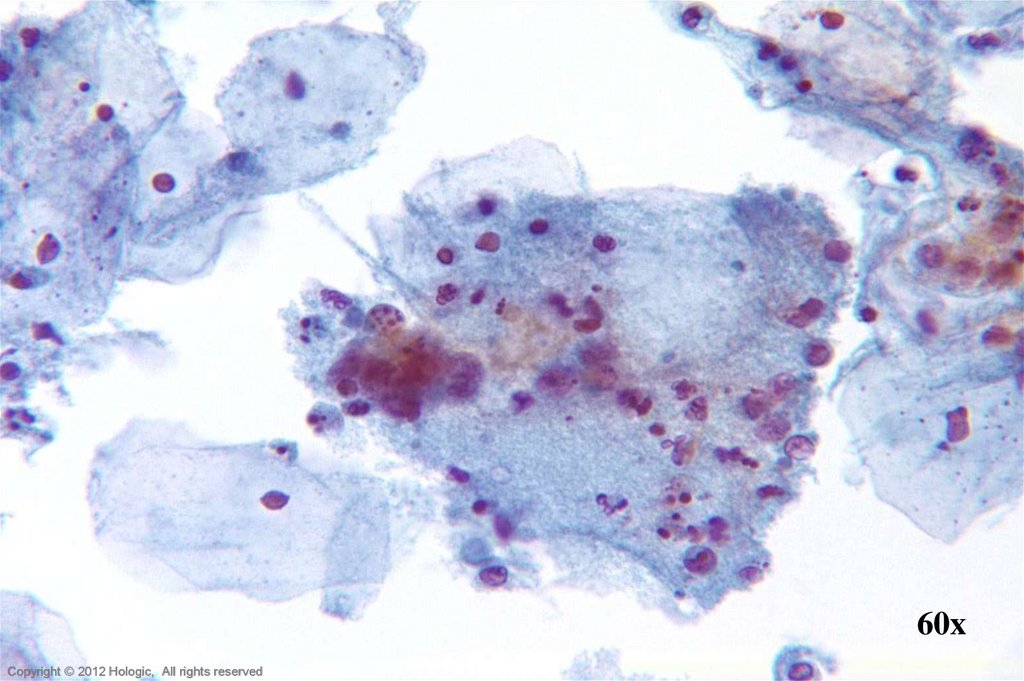
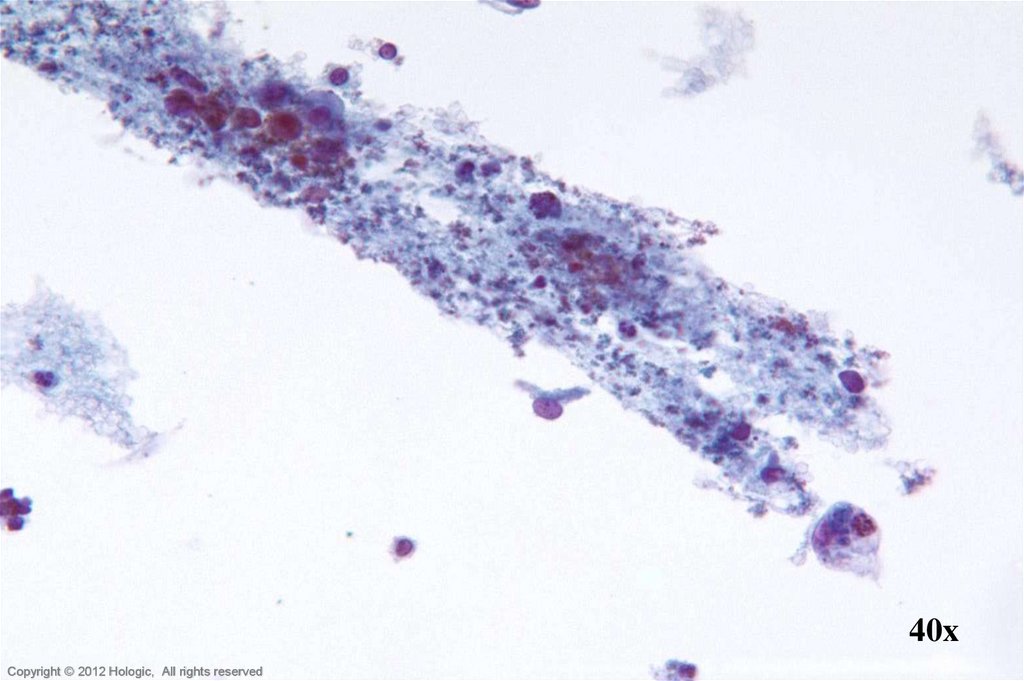
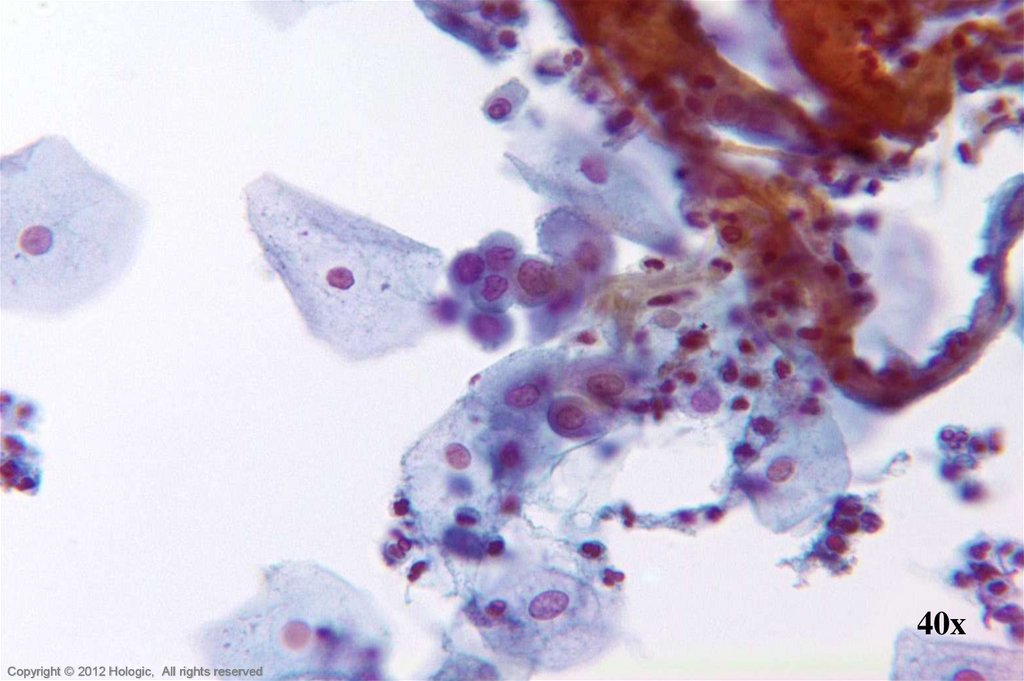
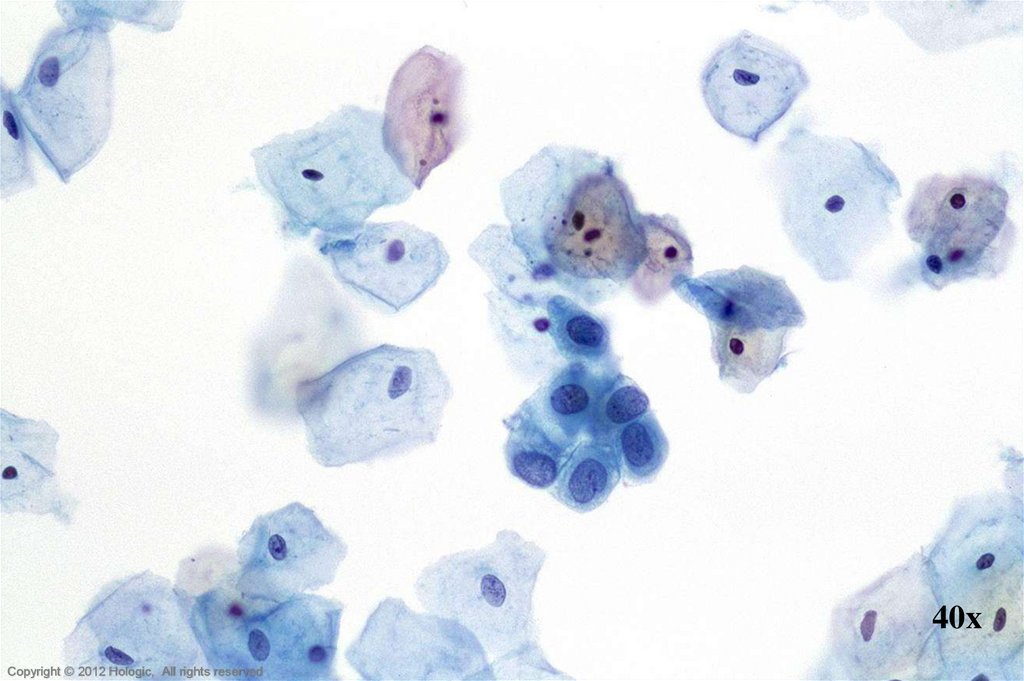
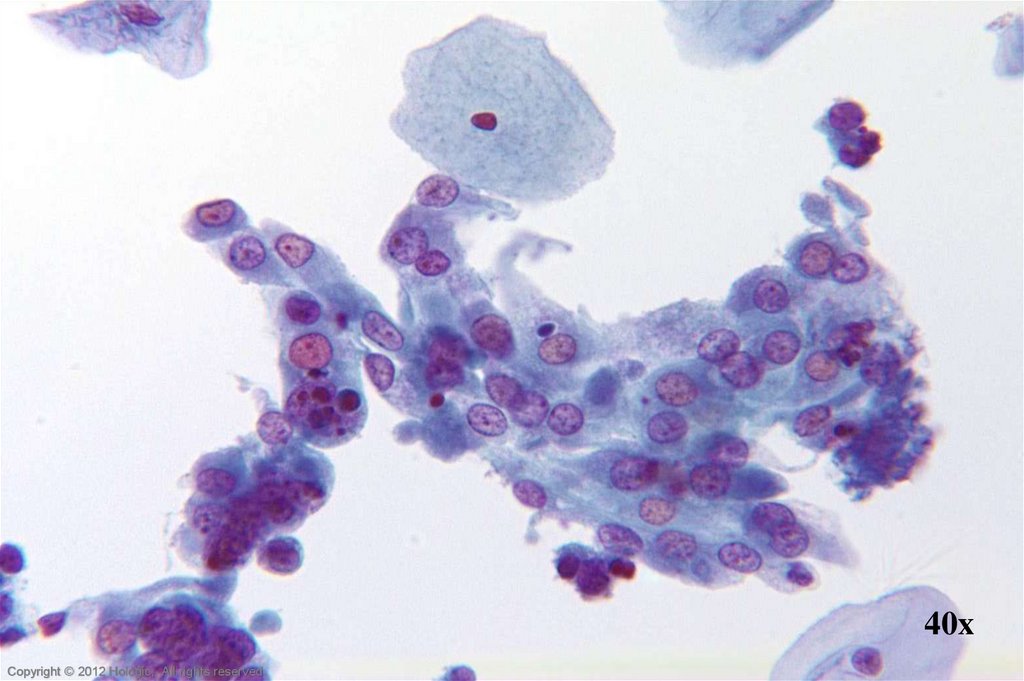
14. Endocervical Adenocarcinoma vs. Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
Endocervical AdenocarcinomaEndometrial Adenocarcinoma
• Abundant abnormal material
– directly scraped
• Well preserved material
• Cells and cell groupings generally
larger in size
• Abundant, foamy cytoplasm,
occasionally columnar shaped
• AIS precursor with endocervical
architecture may be seen
• Isolated abnormal groups
– cell shedding
• Variable preservation of cells
• Cells and cell groupings generally
smaller in size
• Scant, cyanophilic cytoplasm with
occasional conspicuous vacuoles
• Mature hormonal pattern, watery
transudate may be seen
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
15.
20xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
16.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
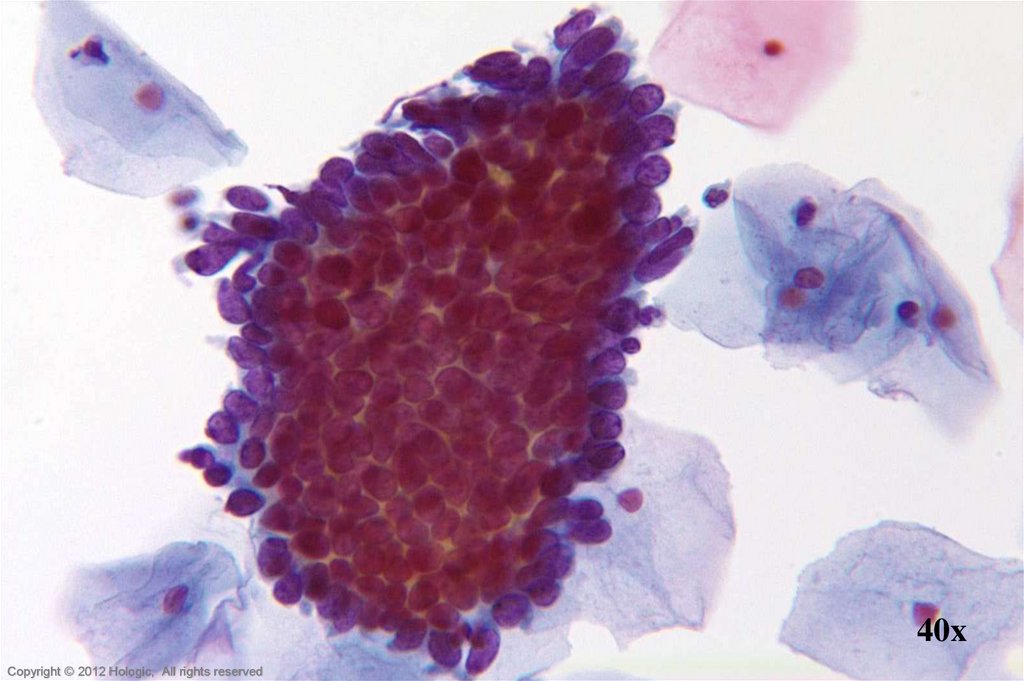
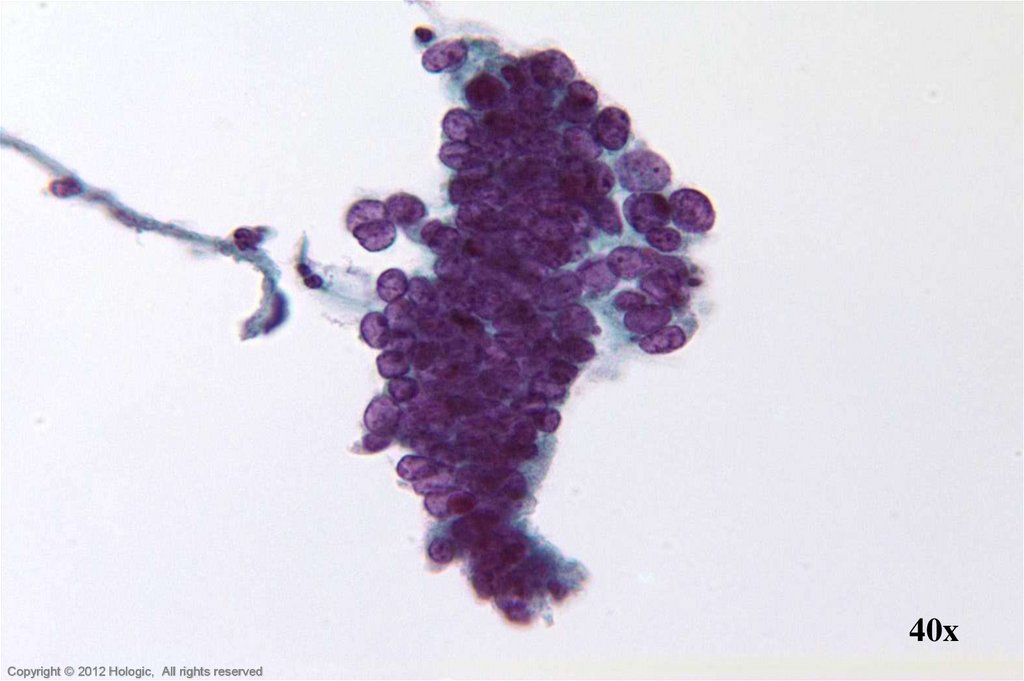
17.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
18.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
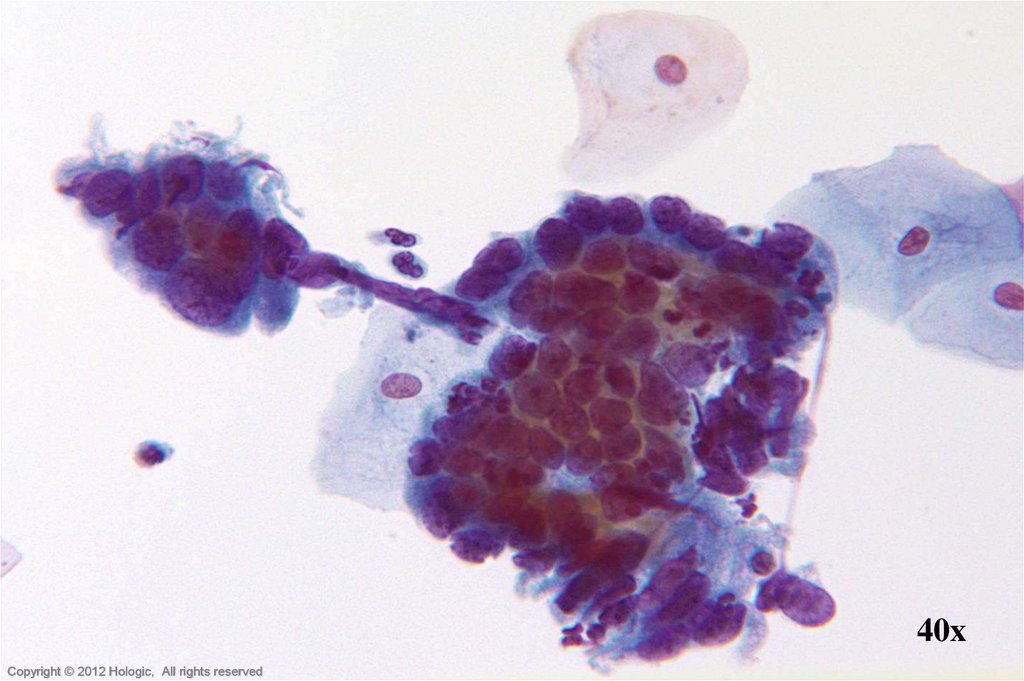
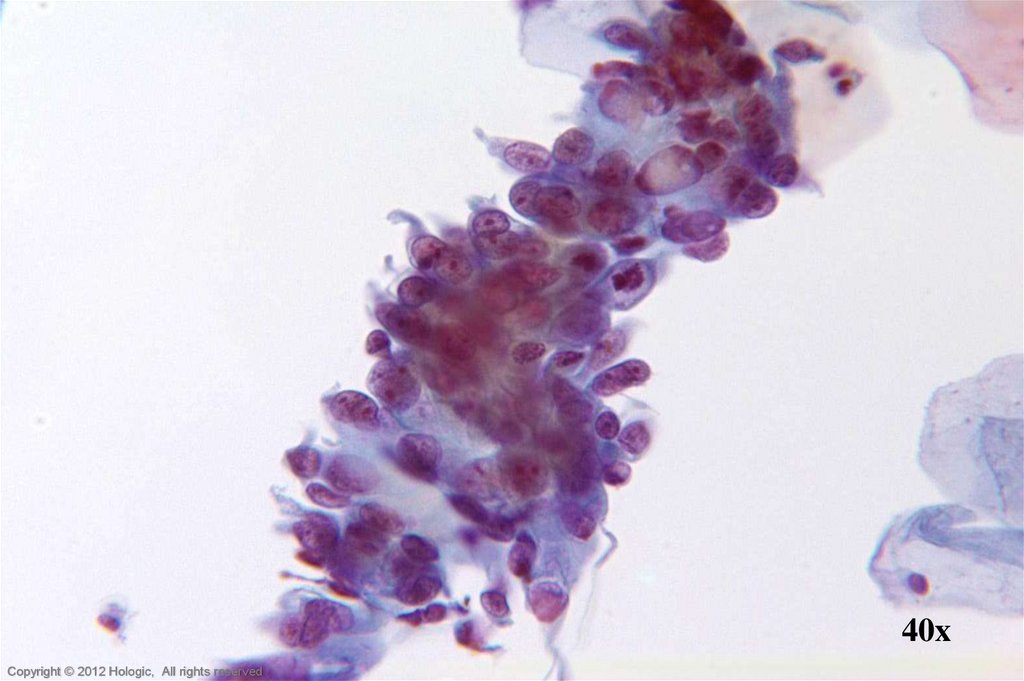
19.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
20.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
21.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
22.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
23.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
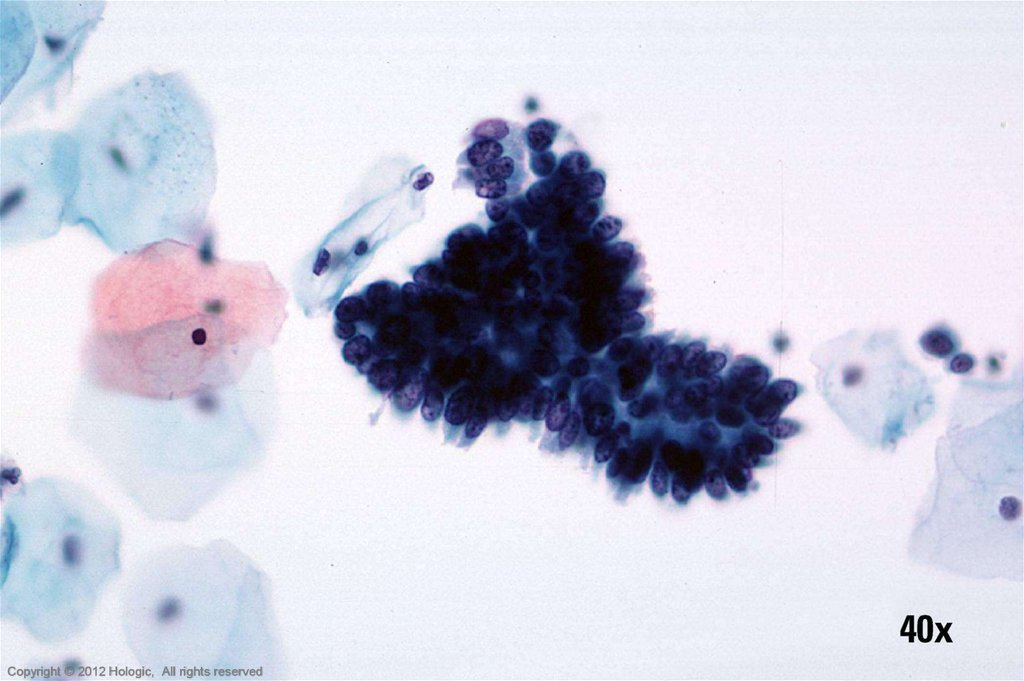
24.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
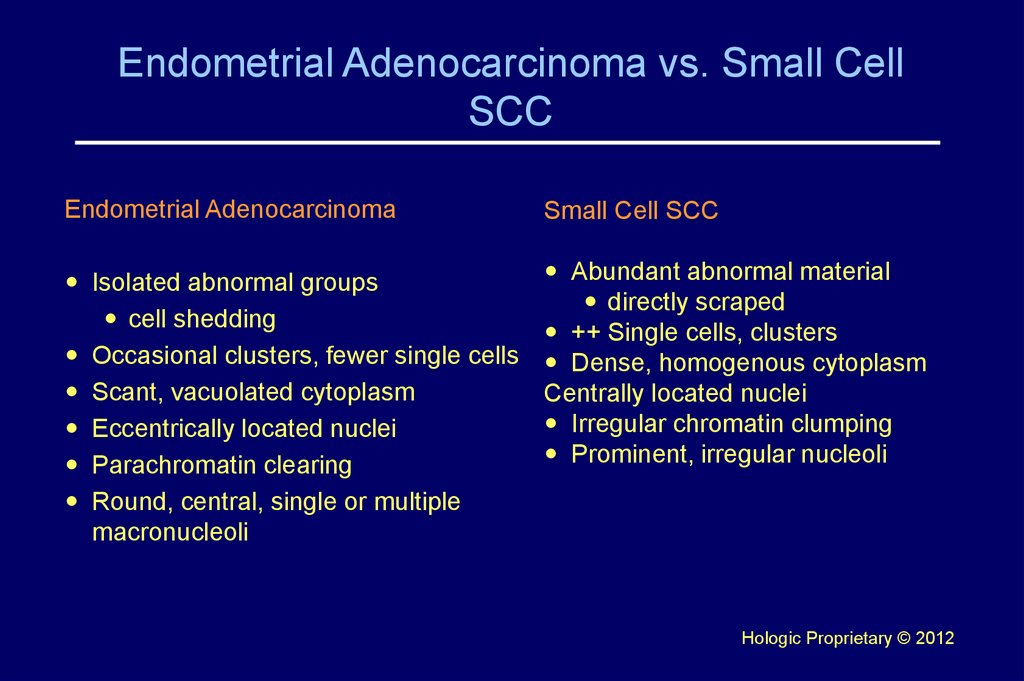
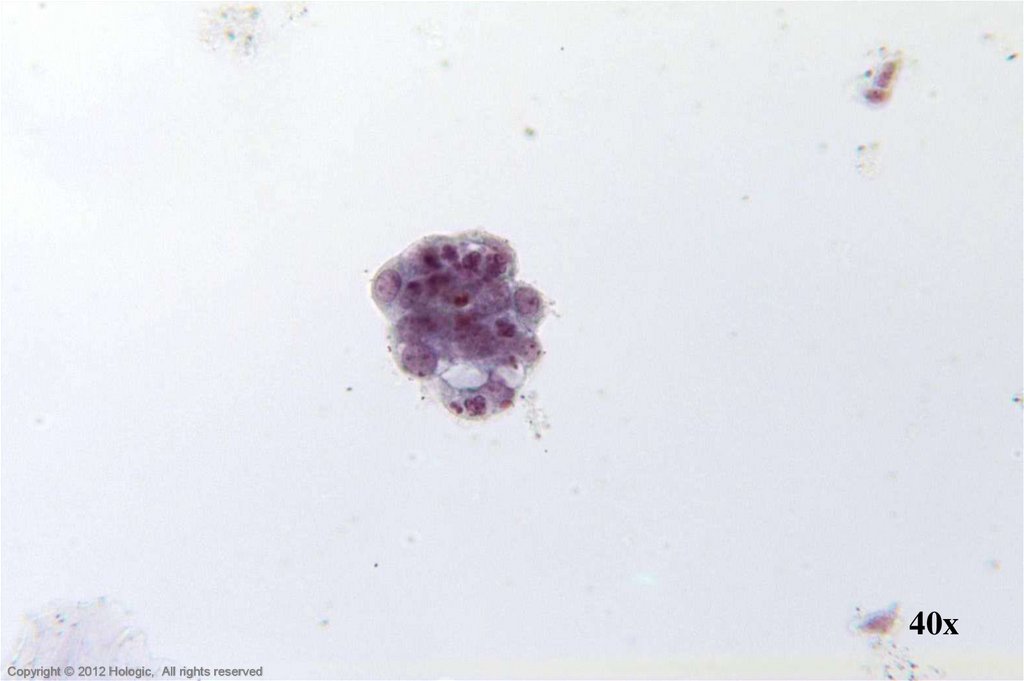
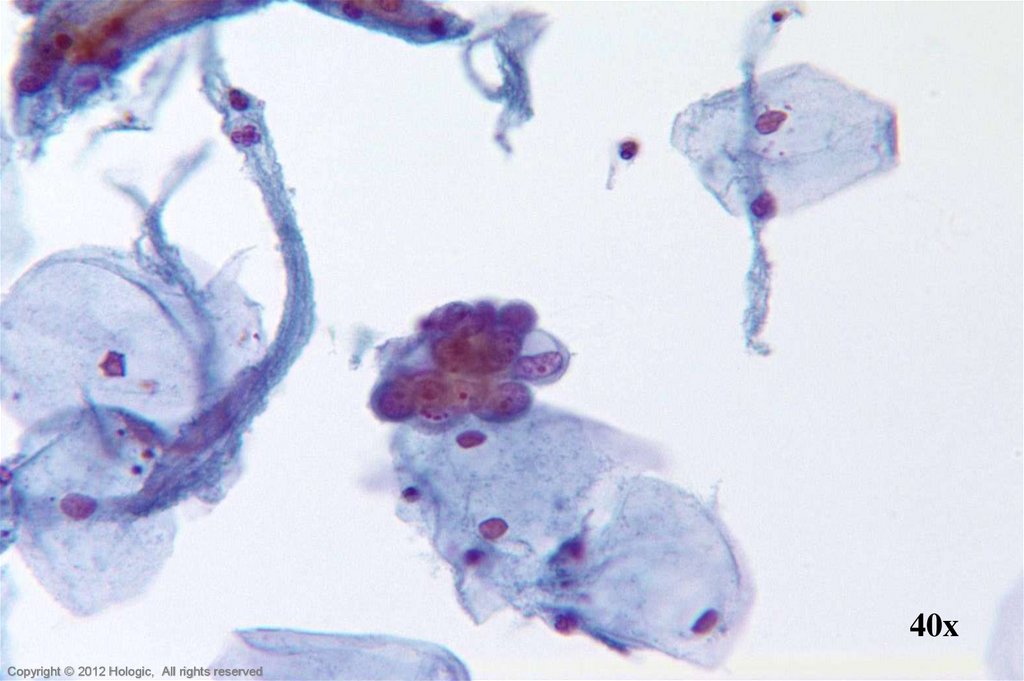
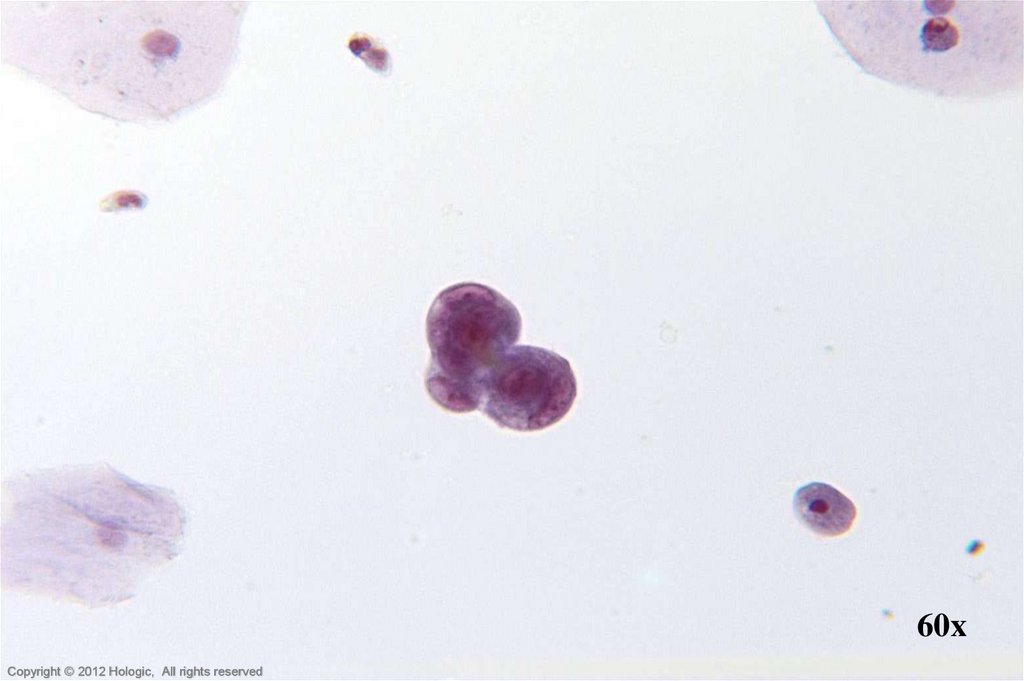
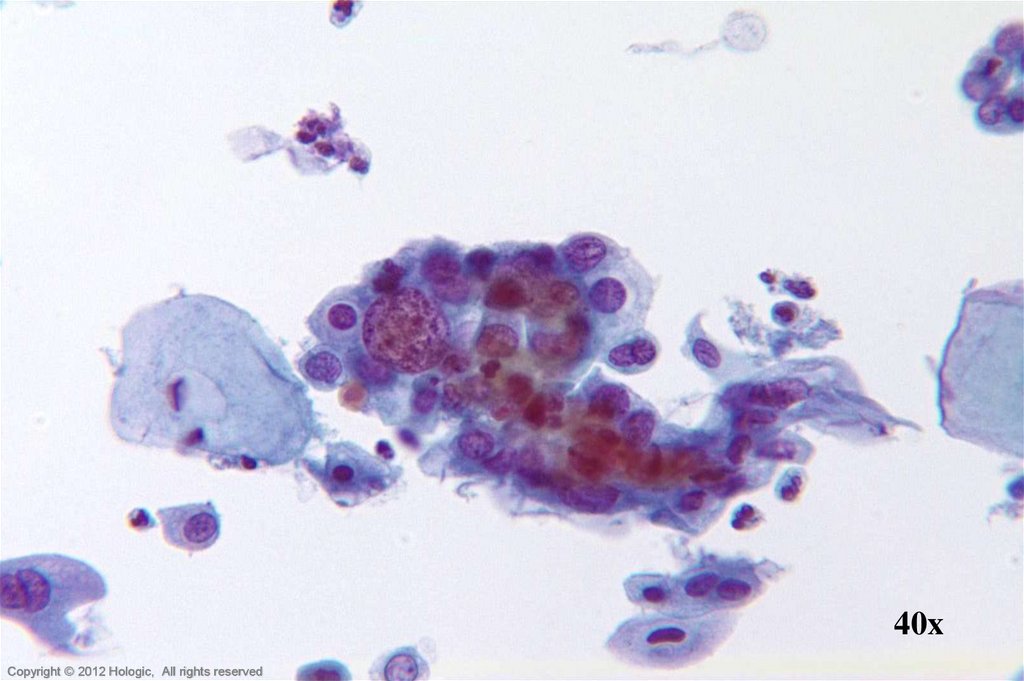
25. Endometrial Adenocarcinoma vs. Small Cell SCC
Endometrial AdenocarcinomaSmall Cell SCC
Isolated abnormal groups
cell shedding
Occasional clusters, fewer single cells
Scant, vacuolated cytoplasm
Eccentrically located nuclei
Parachromatin clearing
Round, central, single or multiple
macronucleoli
Abundant abnormal material
directly scraped
++ Single cells, clusters
Dense, homogenous cytoplasm
Centrally located nuclei
Irregular chromatin clumping
Prominent, irregular nucleoli
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
26.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
27.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
28.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
29.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
30.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
31.
20xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
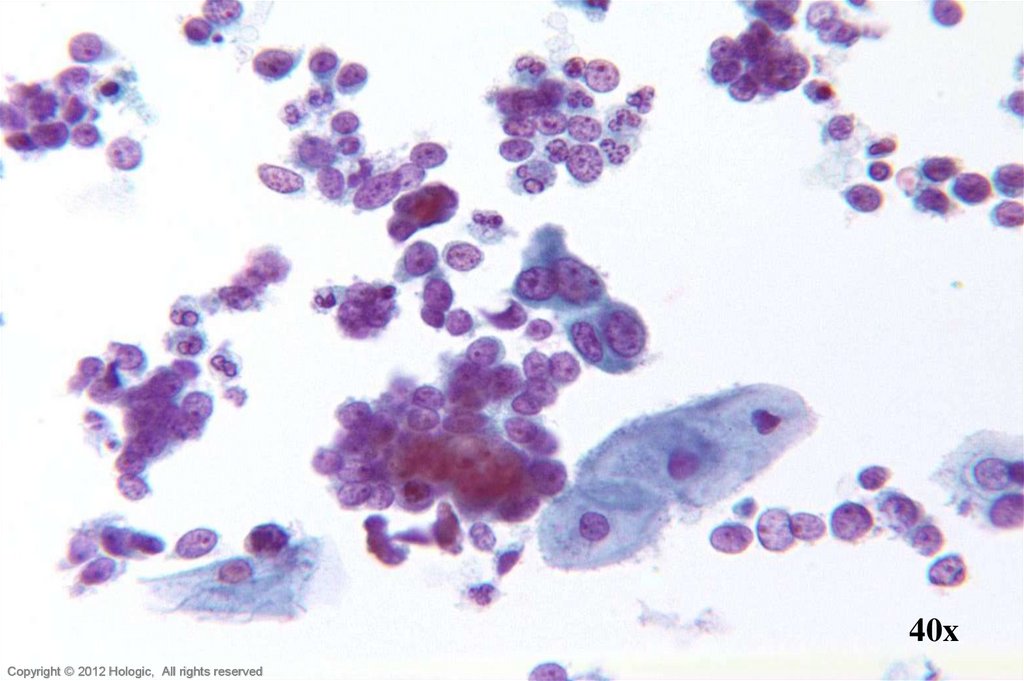
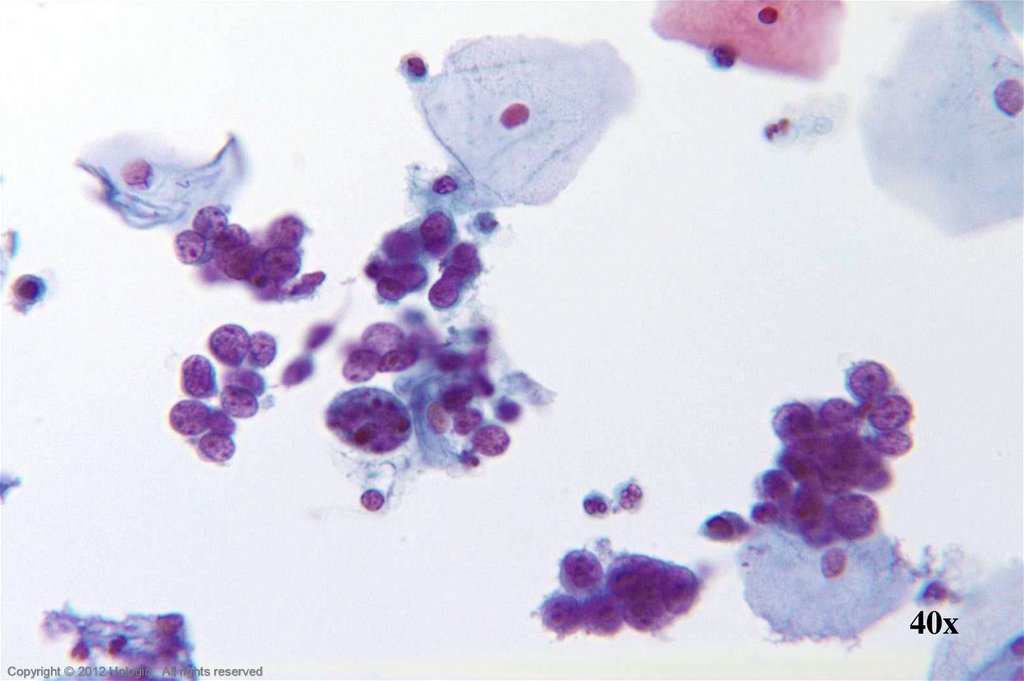
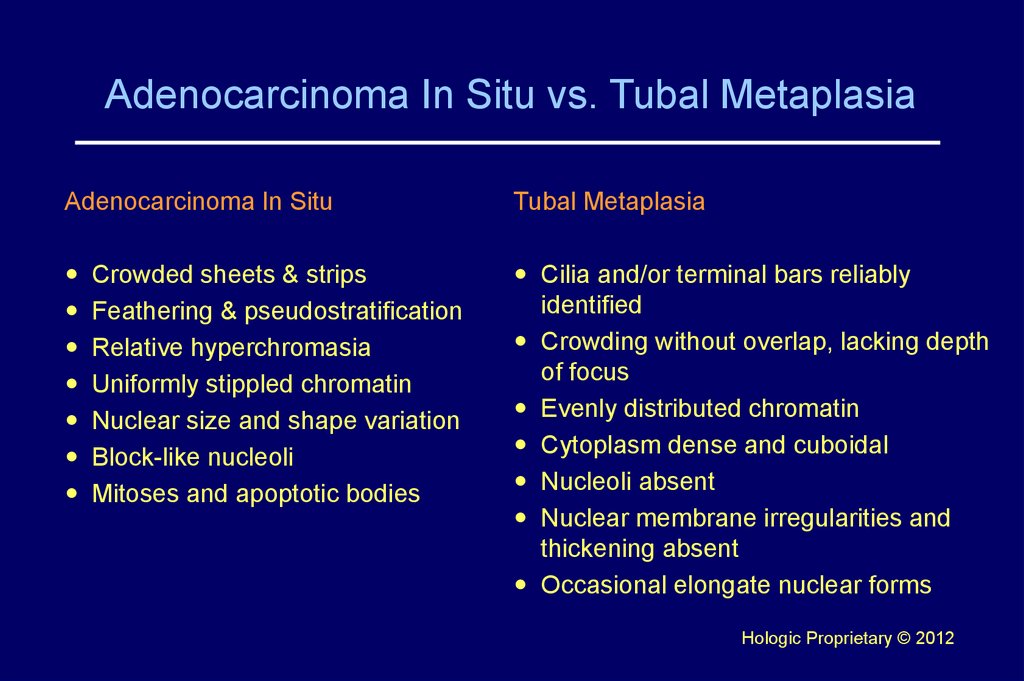
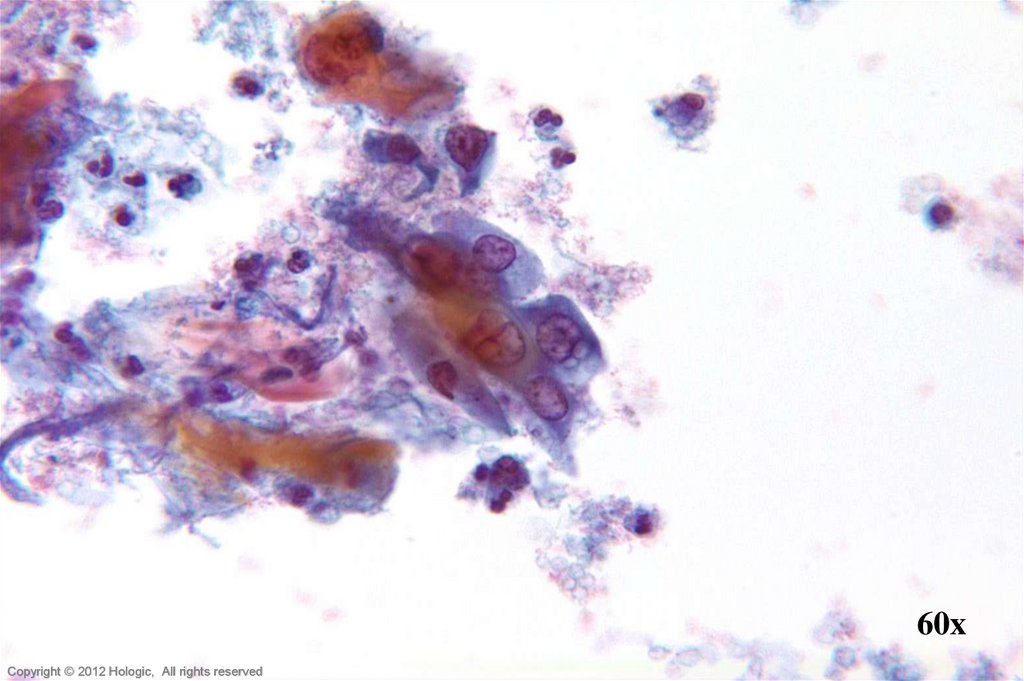
32. Adenocarcinoma In Situ vs. Tubal Metaplasia
Adenocarcinoma In SituTubal Metaplasia
Cilia and/or terminal bars reliably
identified
Crowding without overlap, lacking depth
of focus
Evenly distributed chromatin
Cytoplasm dense and cuboidal
Nucleoli absent
Nuclear membrane irregularities and
thickening absent
Occasional elongate nuclear forms
Crowded sheets & strips
Feathering & pseudostratification
Relative hyperchromasia
Uniformly stippled chromatin
Nuclear size and shape variation
Block-like nucleoli
Mitoses and apoptotic bodies
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
33.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
34.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
35.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
36.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
37.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
38.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
39.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
40.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
41.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
42.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
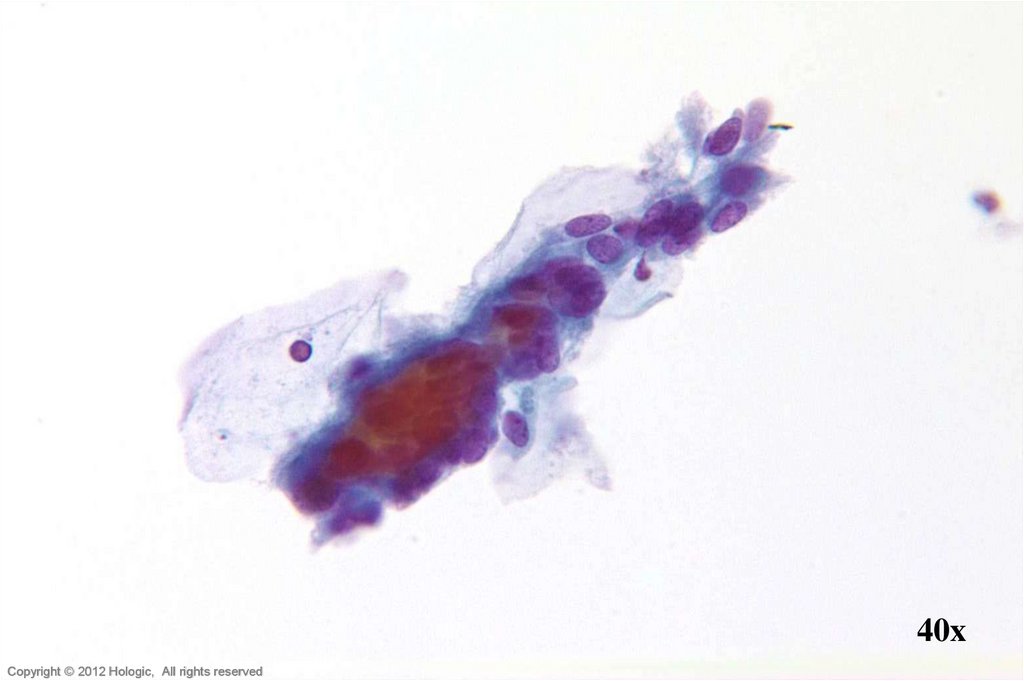
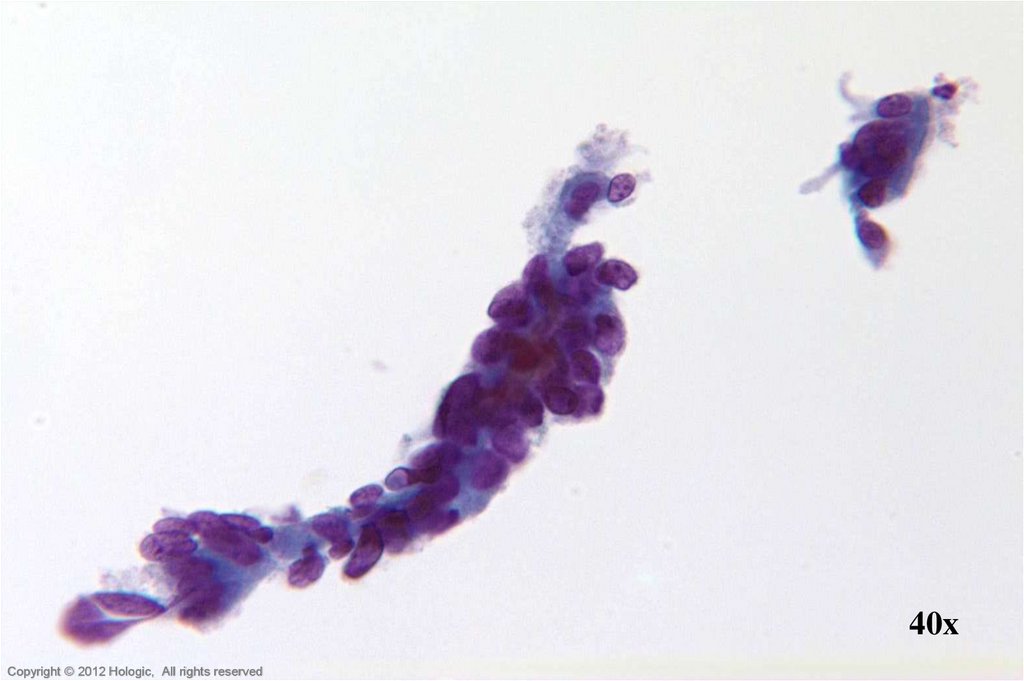
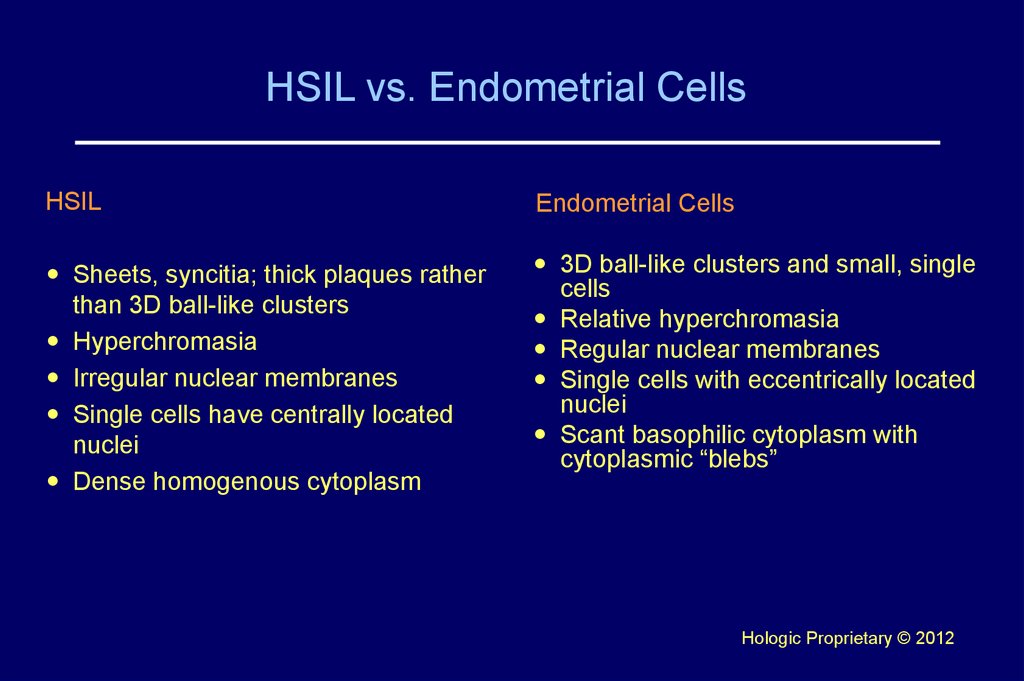
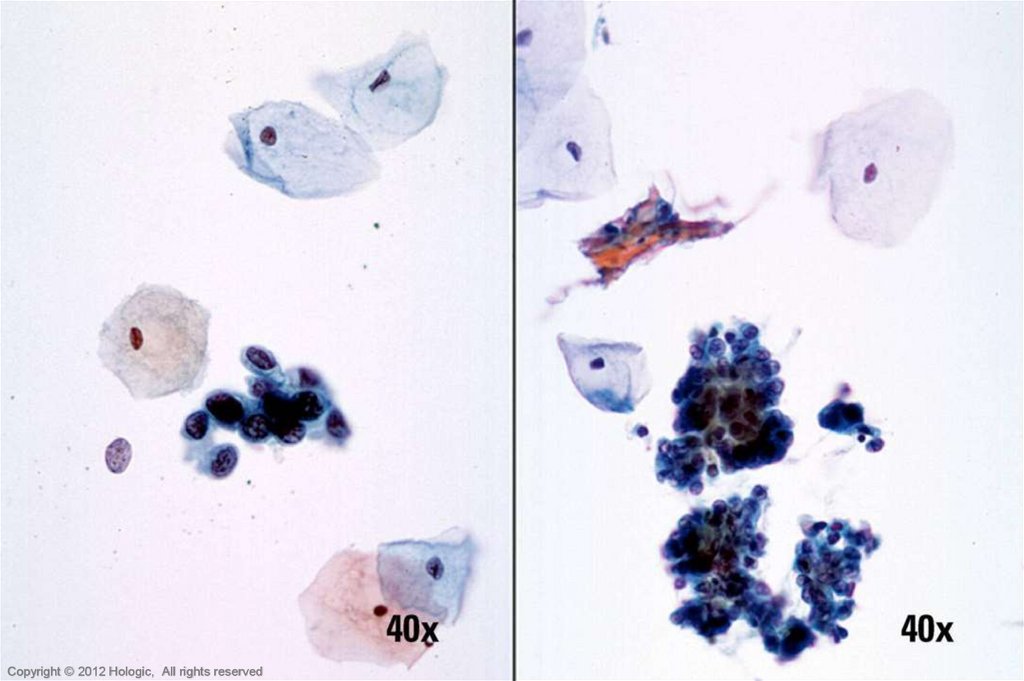
43. HSIL vs. Endometrial Cells
HSILEndometrial Cells
Sheets, syncitia; thick plaques rather
than 3D ball-like clusters
Hyperchromasia
Irregular nuclear membranes
Single cells have centrally located
nuclei
Dense homogenous cytoplasm
3D ball-like clusters and small, single
cells
Relative hyperchromasia
Regular nuclear membranes
Single cells with eccentrically located
nuclei
Scant basophilic cytoplasm with
cytoplasmic “blebs”
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
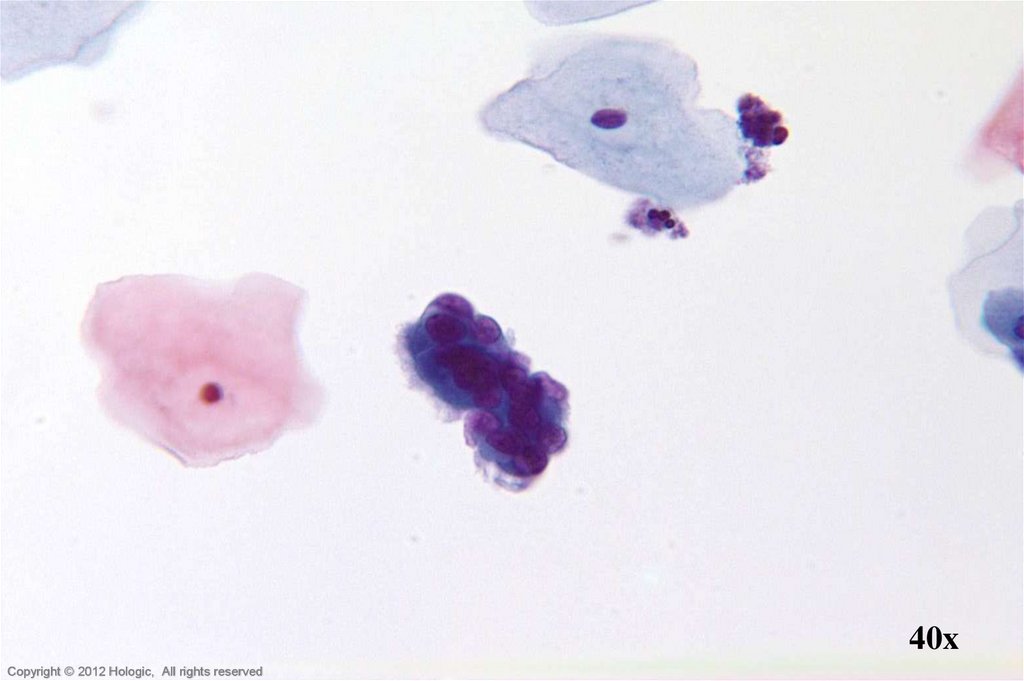
44.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
45.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
46.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
47.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
48.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
49.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
50.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
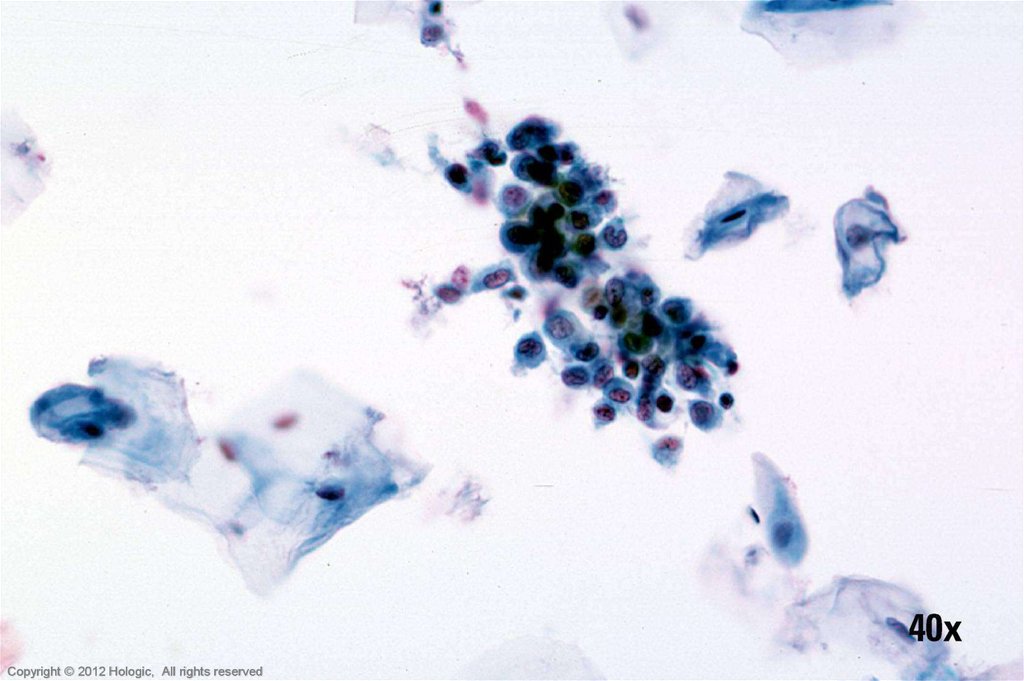
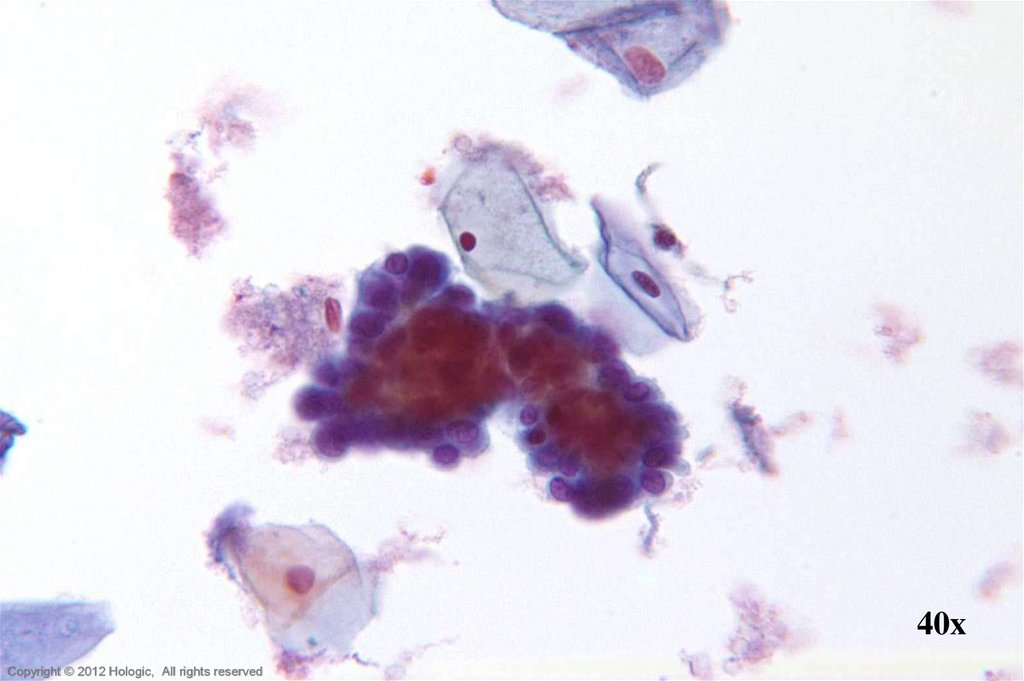
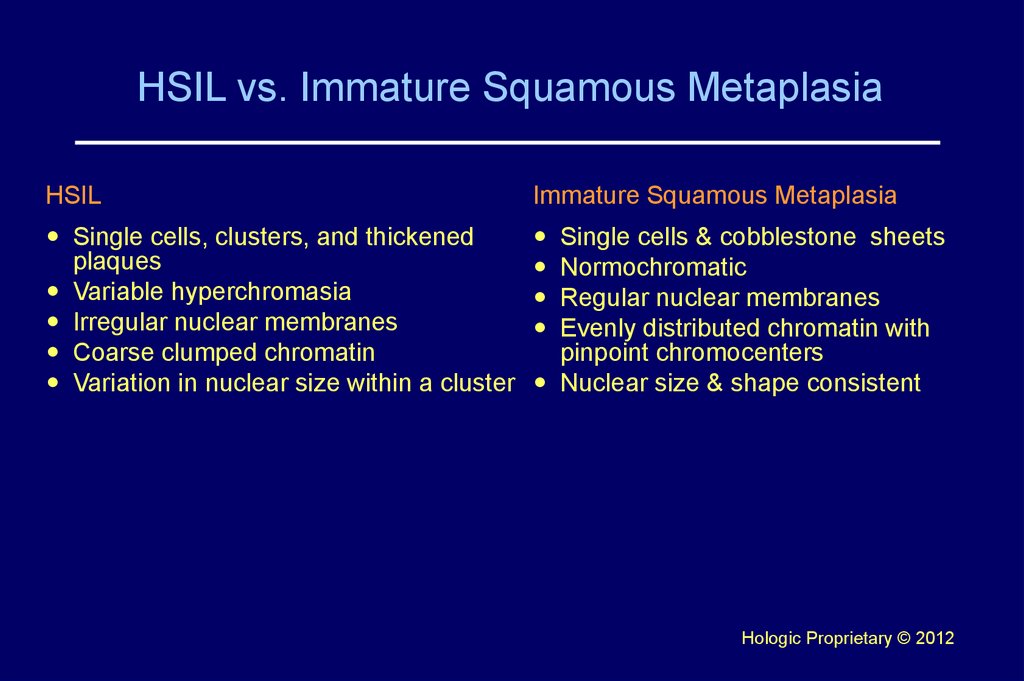
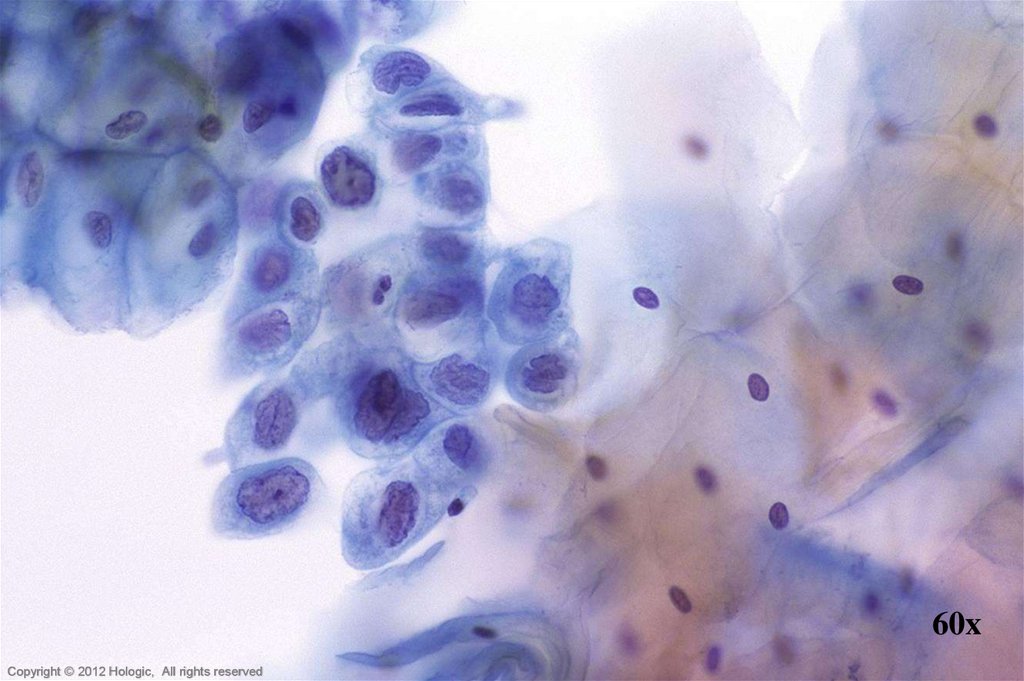
51. HSIL vs. Immature Squamous Metaplasia
HSILImmature Squamous Metaplasia
Single cells, clusters, and thickened
plaques
Variable hyperchromasia
Irregular nuclear membranes
Coarse clumped chromatin
Variation in nuclear size within a cluster
Single cells & cobblestone sheets
Normochromatic
Regular nuclear membranes
Evenly distributed chromatin with
pinpoint chromocenters
Nuclear size & shape consistent
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
52.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
53.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
54.
40x40x
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
55.
40x40x
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
56.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
57.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
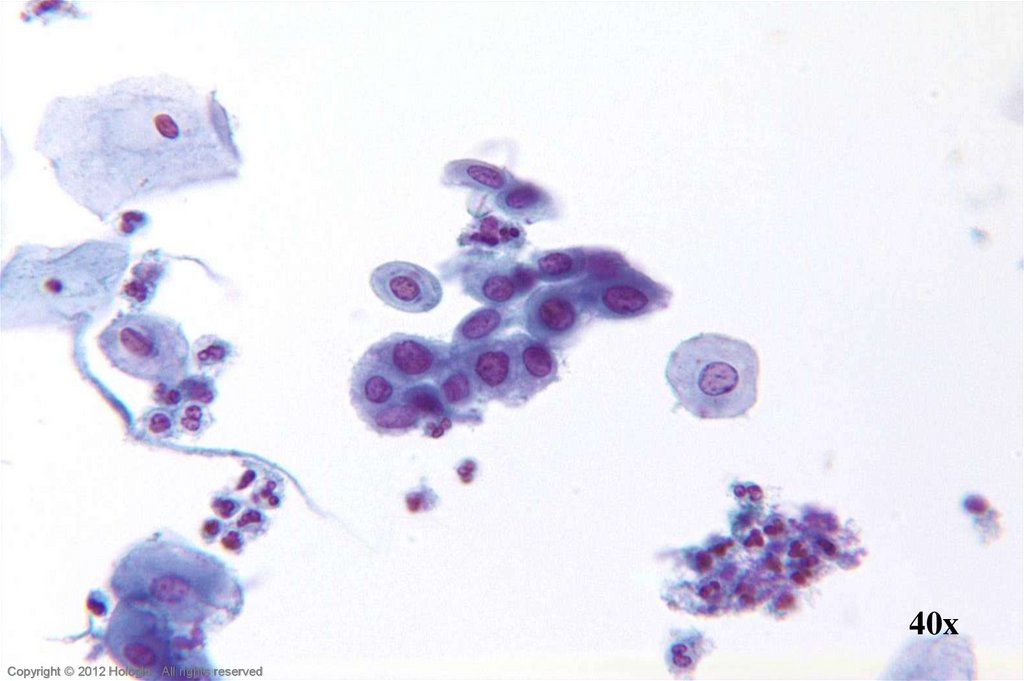
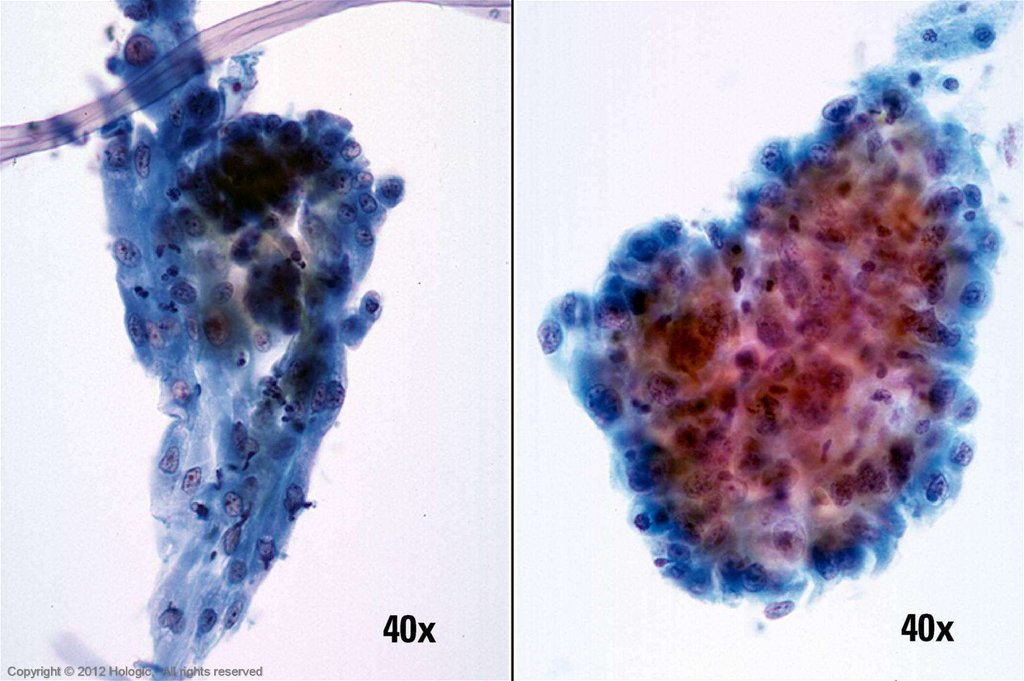
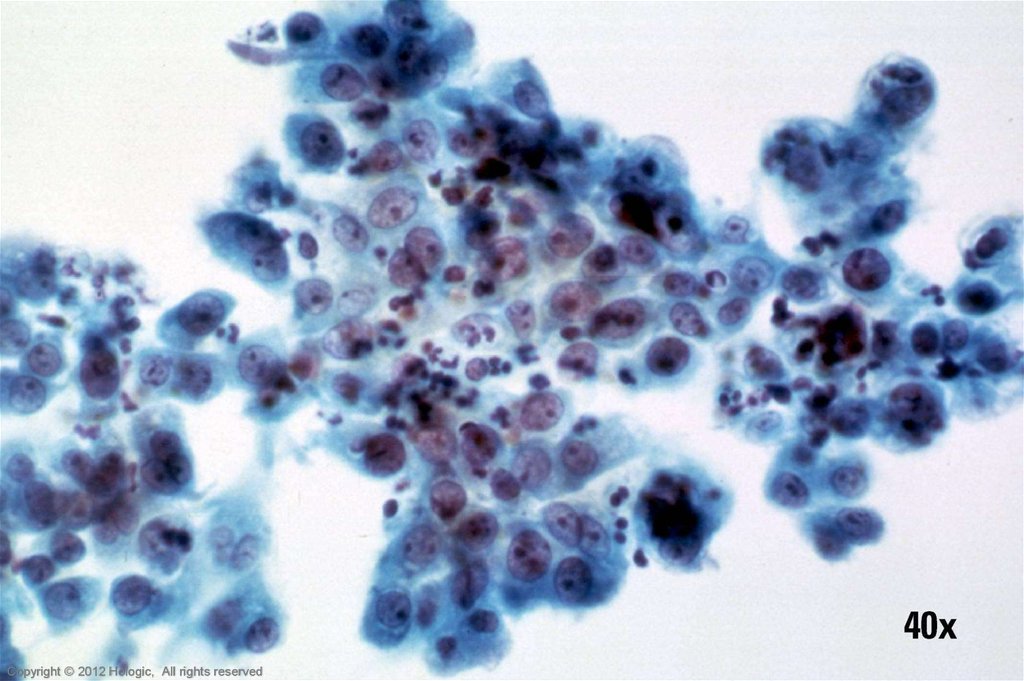
58. Repair vs. Poorly Differentiated SCC
Repair (typical)Poorly Differentiated SCC
Poorly cohesive sheets and single cells
Cohesive sheets
Irregular nuclear shapes & sizes
Significant nuclear size variation but
Thickened nuclear membranes
typically round/oval in shape
Irregular chromatin clumping
Nucleoli variable in shape, size, number
Thin, well defined nuclear membranes
and position
More open chromatin pattern with minimal
Some nuclei display nucleoli, some nuclei
variability
do not
Centrally located macronucleoli with
smooth, round contours
Virtually all nuclei display nucleoli
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
59.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
60.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
61.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
62.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
63.
40xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
64.
60xHologic Proprietary © 2012
Copyright © 2012 Hologic, All rights reserved
65. Trademark Statement
CytoLyt, Hologic, PreservCyt, ThinPrep, andUroCyte are registered trademarks of
Hologic, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the
United States. CytoLyt, Hologic, PreservCyt,
ThinPrep, UroCyte and associated logos are
trademarks of Hologic, Inc. and/or its
subsidiaries in other countries.
All other trademarks are the property of their
respective owners.
Hologic Proprietary © 2012
66. Any Questions?
Part No. 86798-001 Rev. 001Hologic Proprietary © 2012







 medicine
medicine