Similar presentations:
Basic Programming Simatic S7-300
1. Basic Programming Simatic S7-300
By:Andri Kuncoro
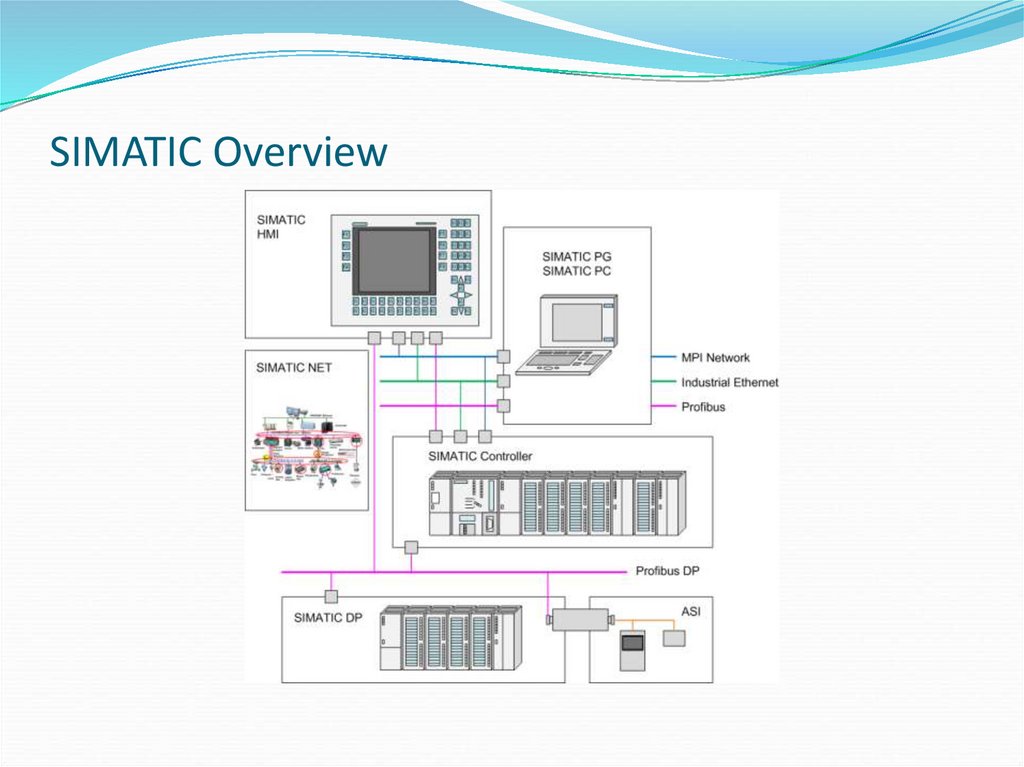
2. SIMATIC Overview
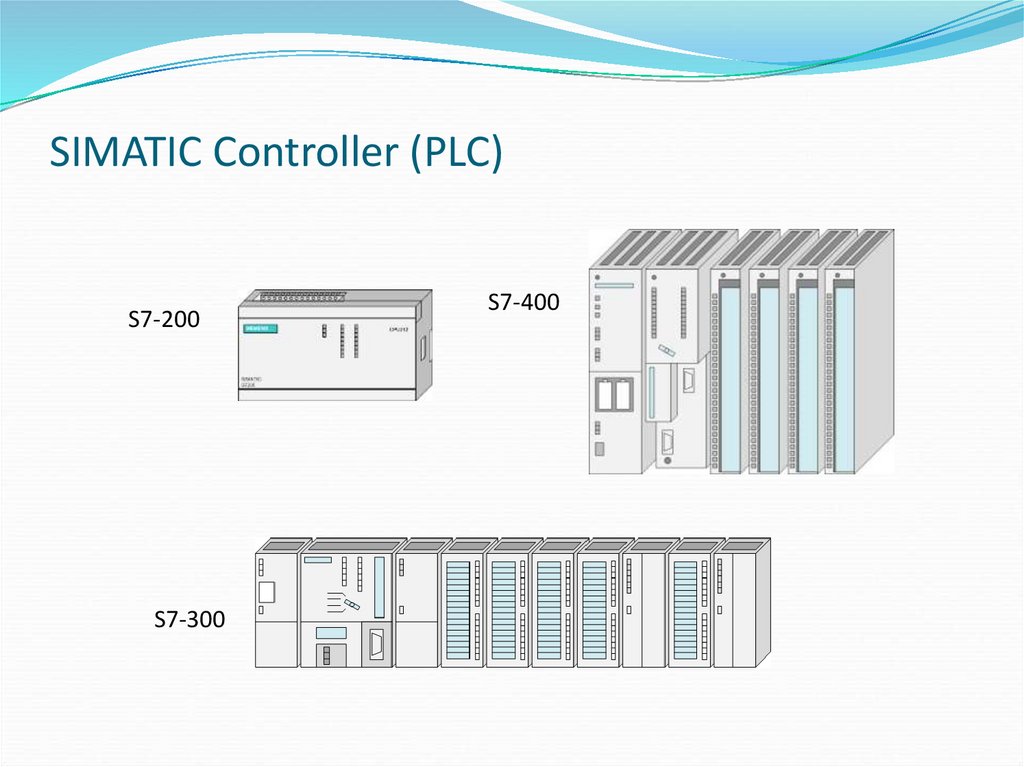
3. SIMATIC Controller (PLC)
S7-200S7-300
S7-400
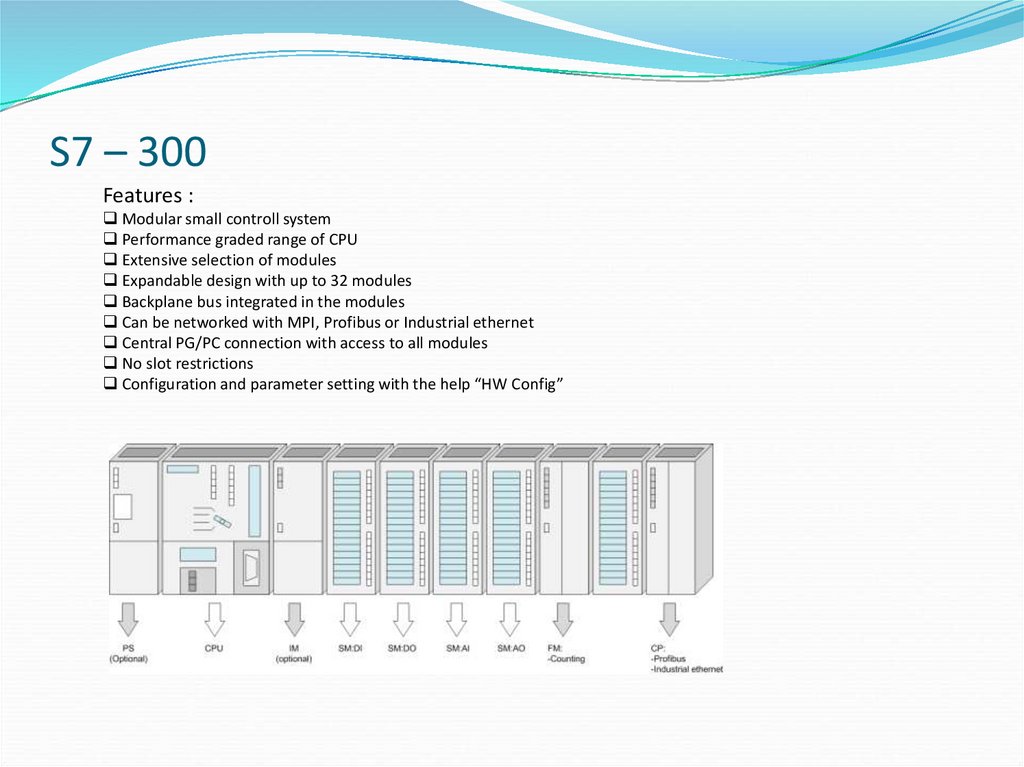
4. S7 – 300
Features :Modular small controll system
Performance graded range of CPU
Extensive selection of modules
Expandable design with up to 32 modules
Backplane bus integrated in the modules
Can be networked with MPI, Profibus or Industrial ethernet
Central PG/PC connection with access to all modules
No slot restrictions
Configuration and parameter setting with the help “HW Config”
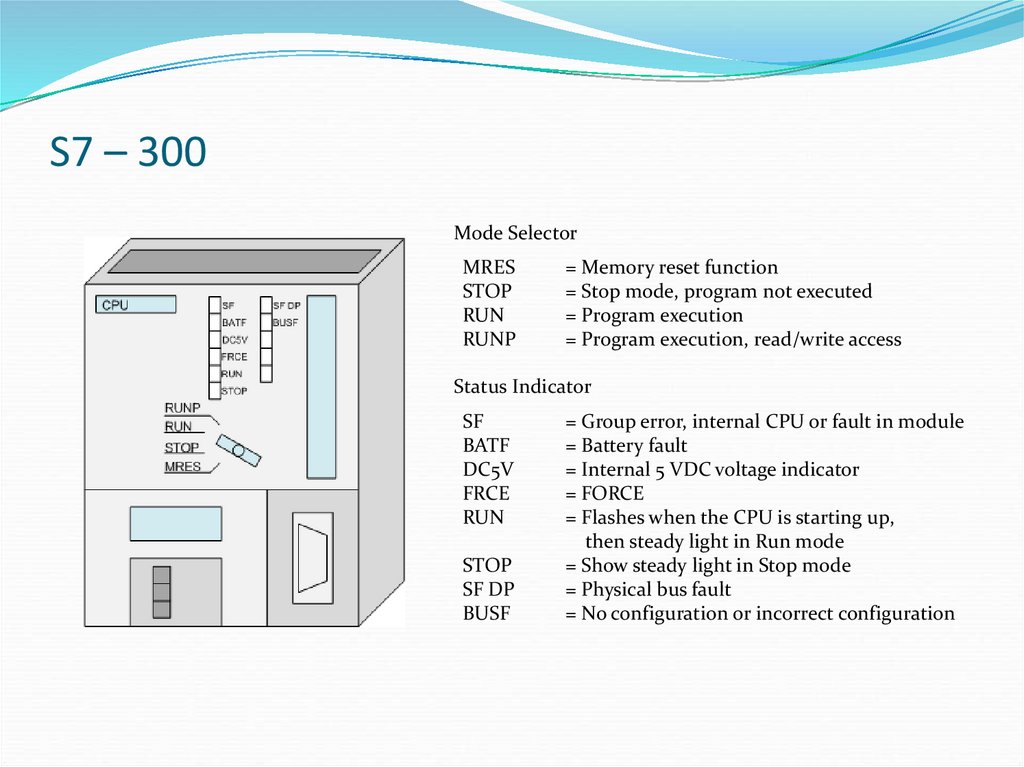
5. S7 – 300
Mode SelectorMRES
STOP
RUN
RUNP
= Memory reset function
= Stop mode, program not executed
= Program execution
= Program execution, read/write access
Status Indicator
SF
BATF
DC5V
FRCE
RUN
STOP
SF DP
BUSF
= Group error, internal CPU or fault in module
= Battery fault
= Internal 5 VDC voltage indicator
= FORCE
= Flashes when the CPU is starting up,
then steady light in Run mode
= Show steady light in Stop mode
= Physical bus fault
= No configuration or incorrect configuration
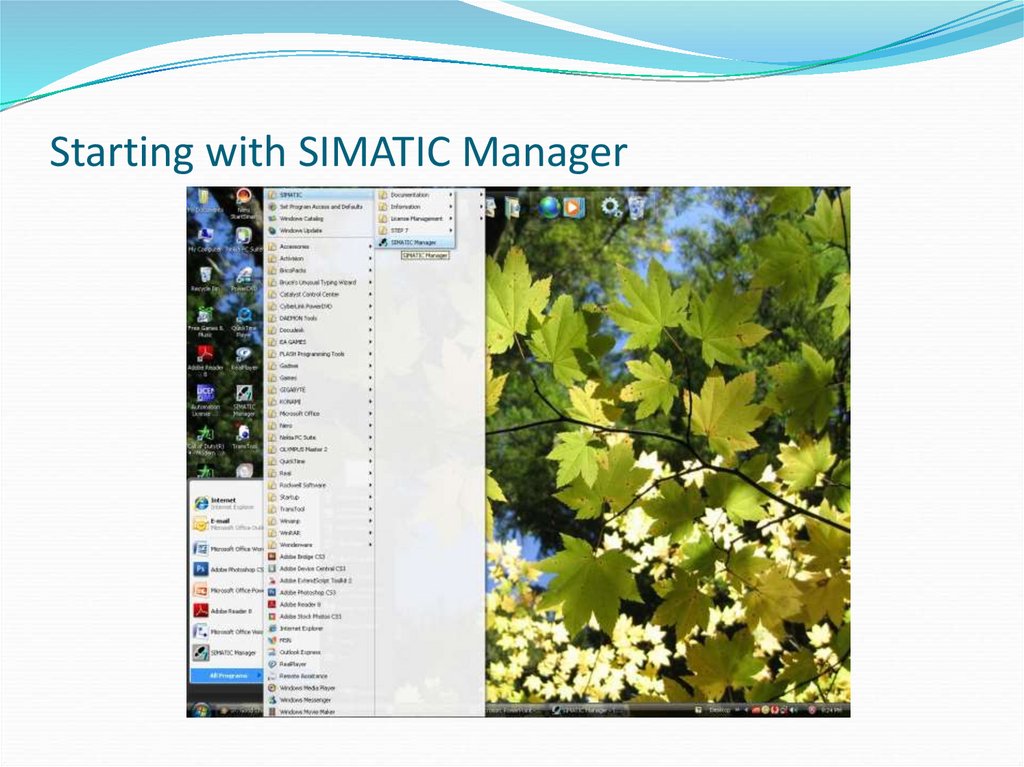
6. Starting with SIMATIC Manager
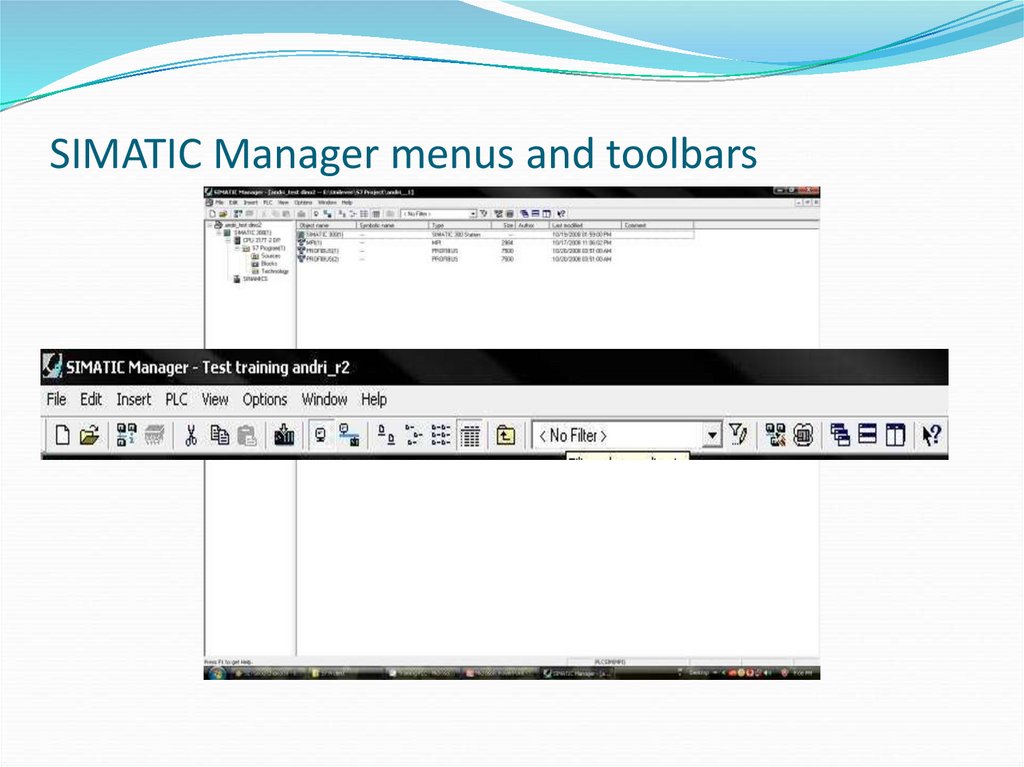
7. SIMATIC Manager menus and toolbars
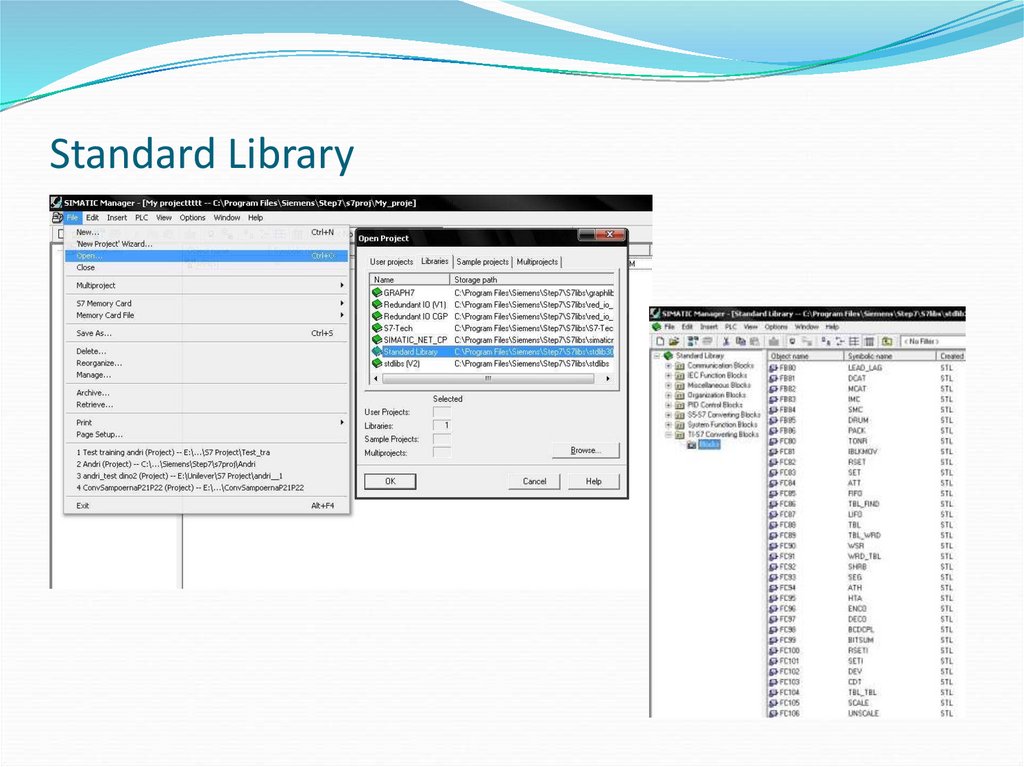
8. Standard Library
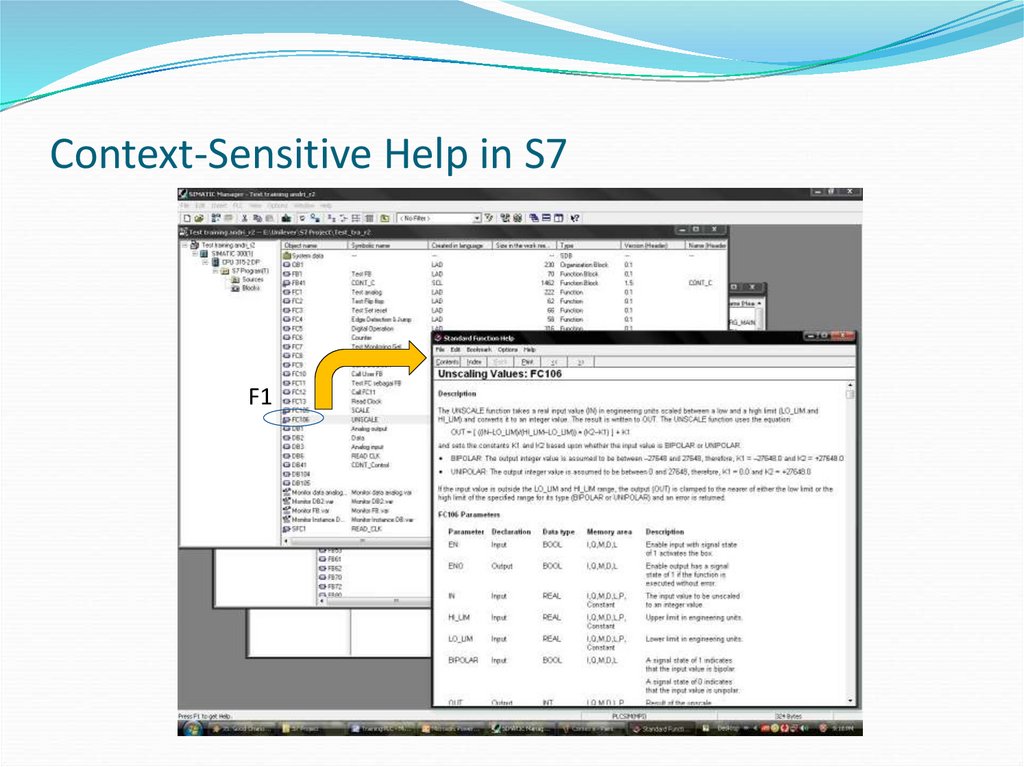
9. Context-Sensitive Help in S7
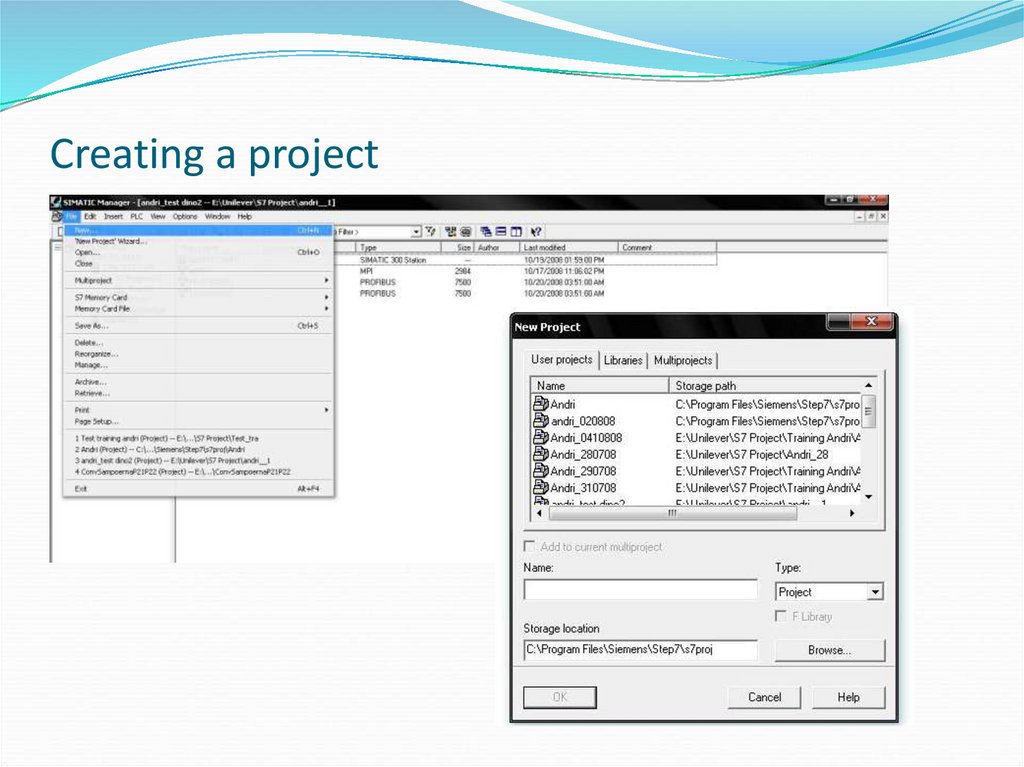
F110. Creating a project
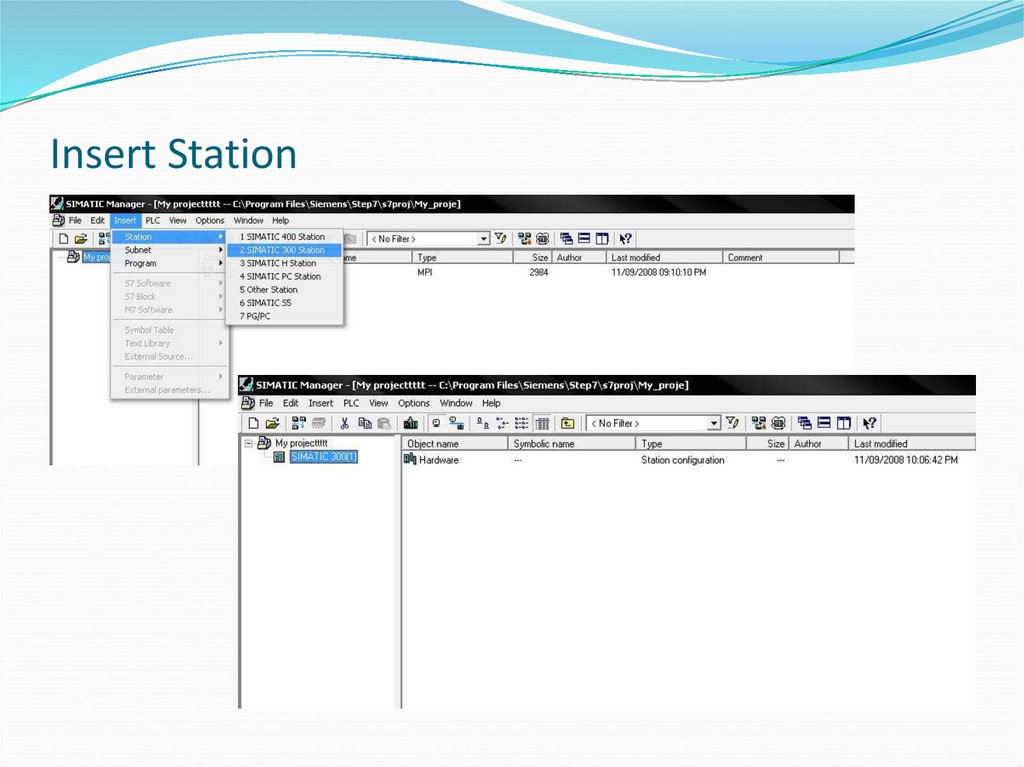
11. Insert Station
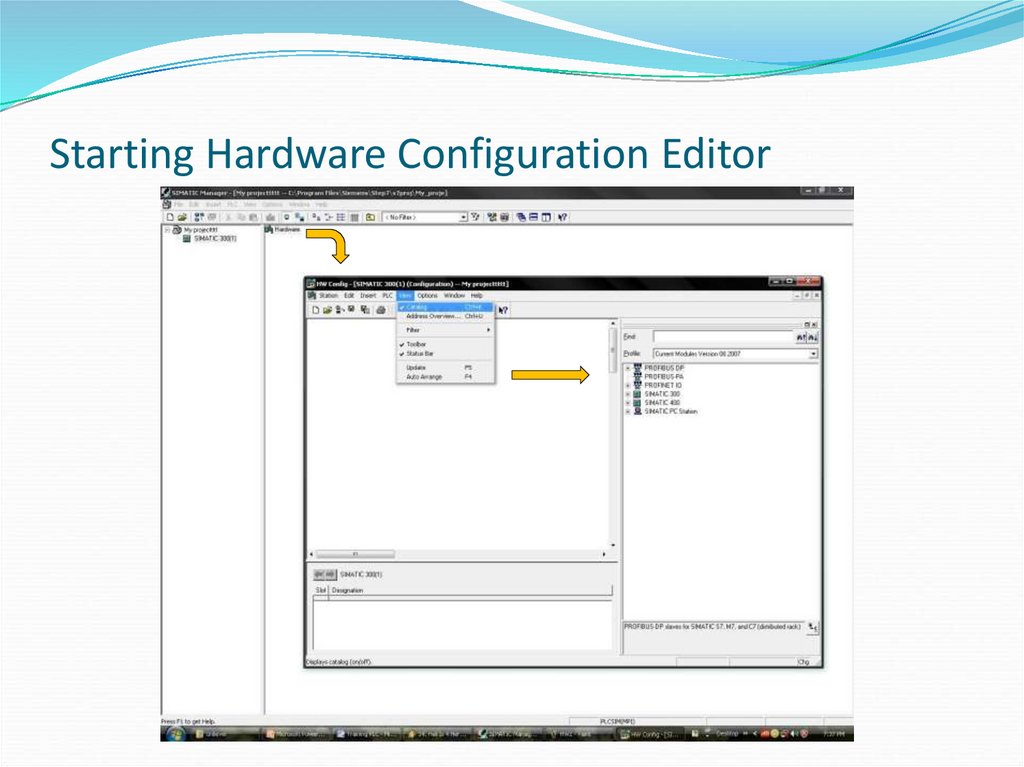
12. Starting Hardware Configuration Editor
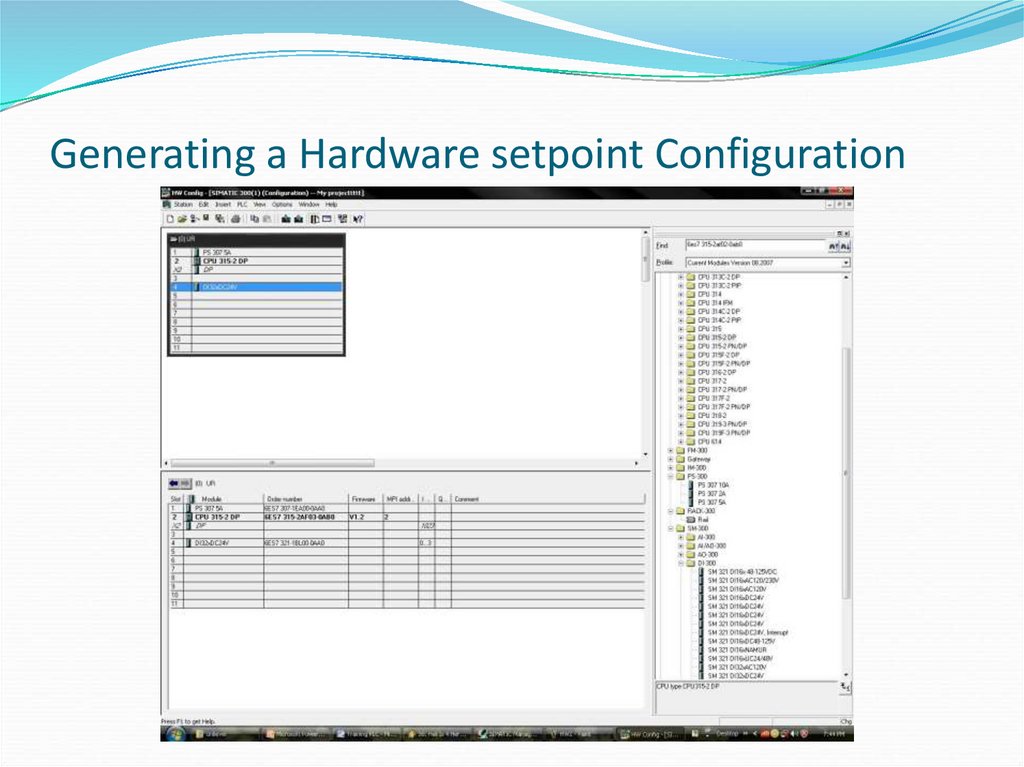
13. Generating a Hardware setpoint Configuration
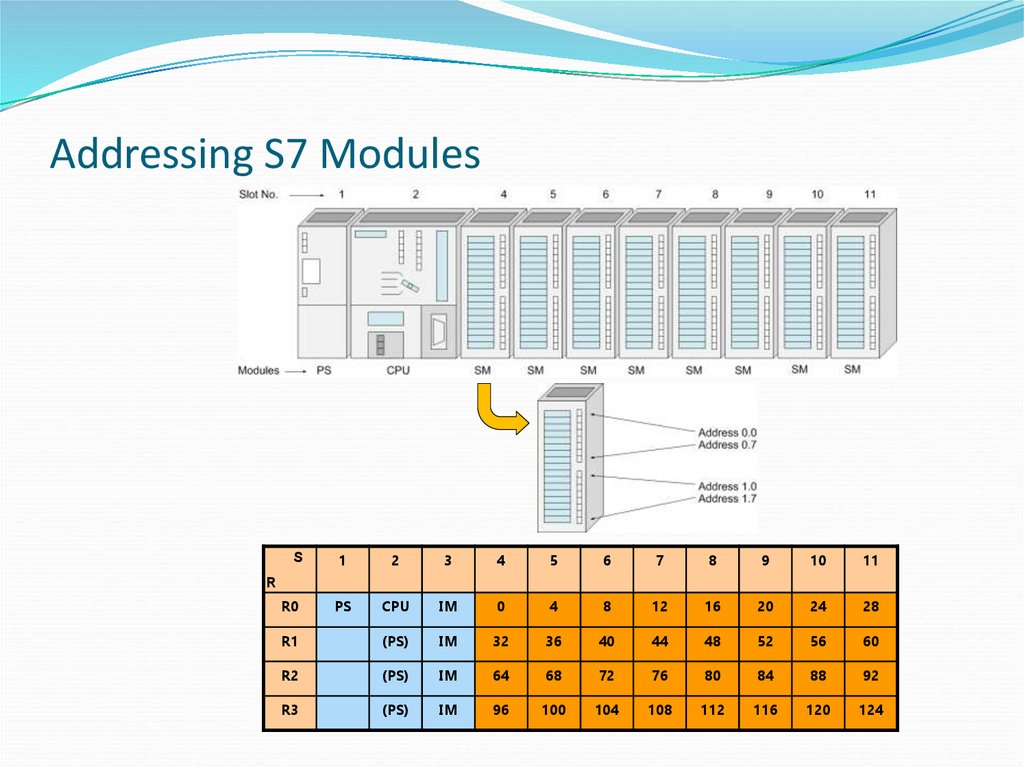
14. Addressing S7 Modules
S1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
R0
PS
CPU
IM
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
R1
(PS)
IM
32
36
40
44
48
52
56
60
R2
(PS)
IM
64
68
72
76
80
84
88
92
R3
(PS)
IM
96
100
104
108
112
116
120
124
R
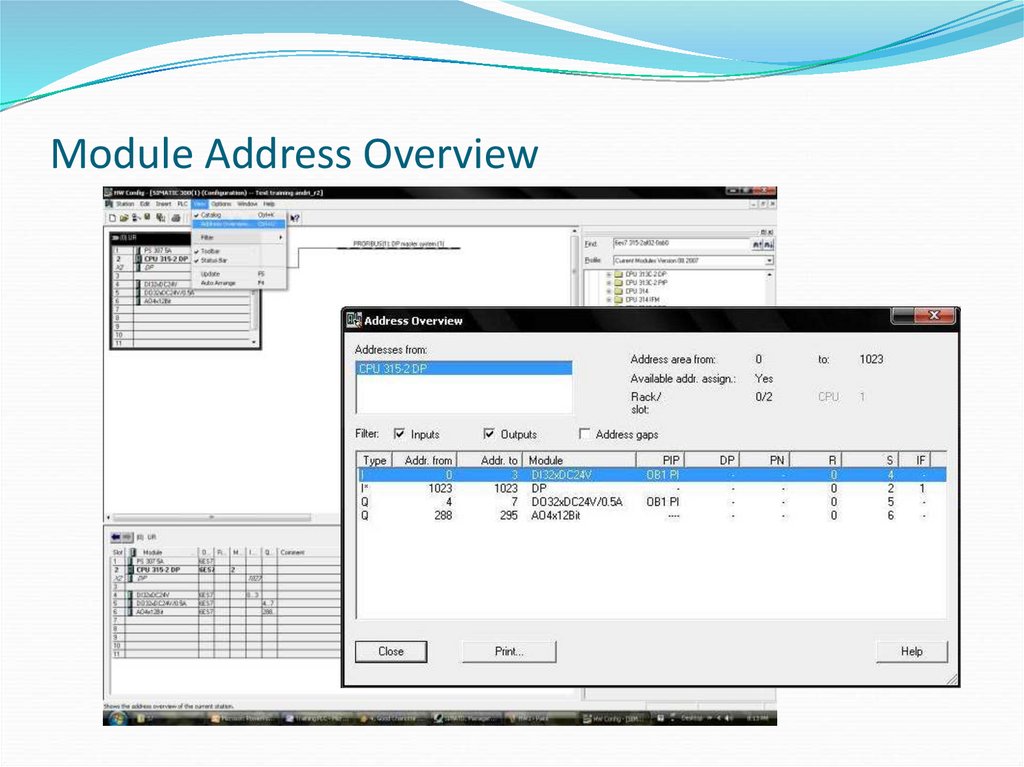
15. Module Address Overview
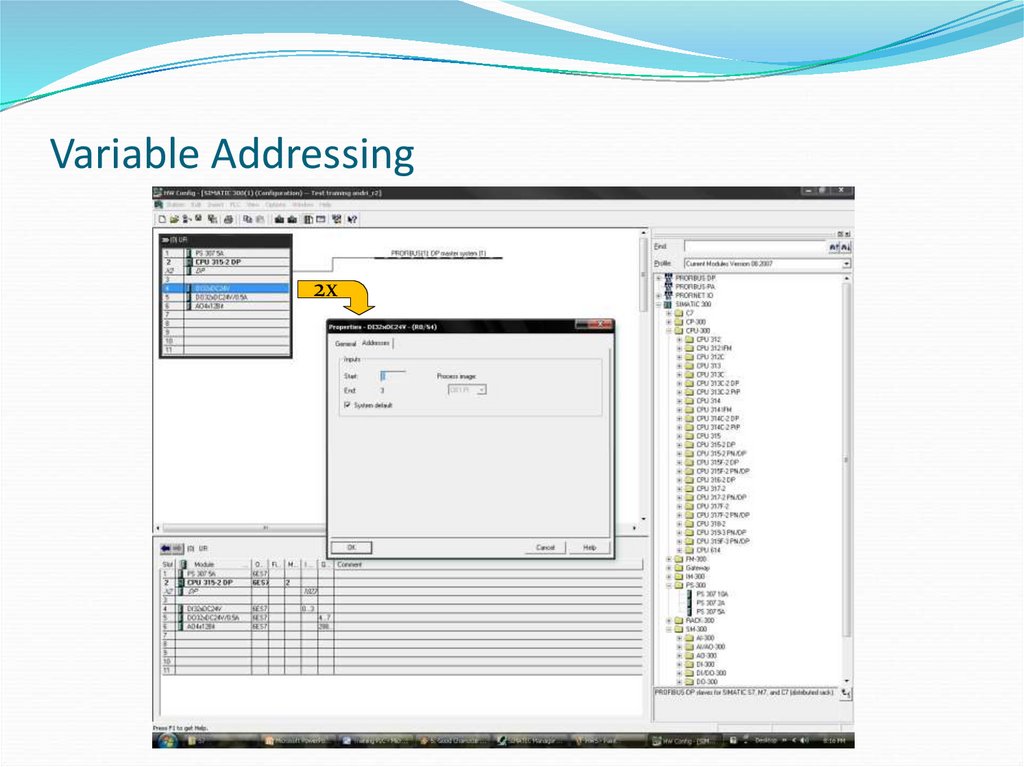
16. Variable Addressing
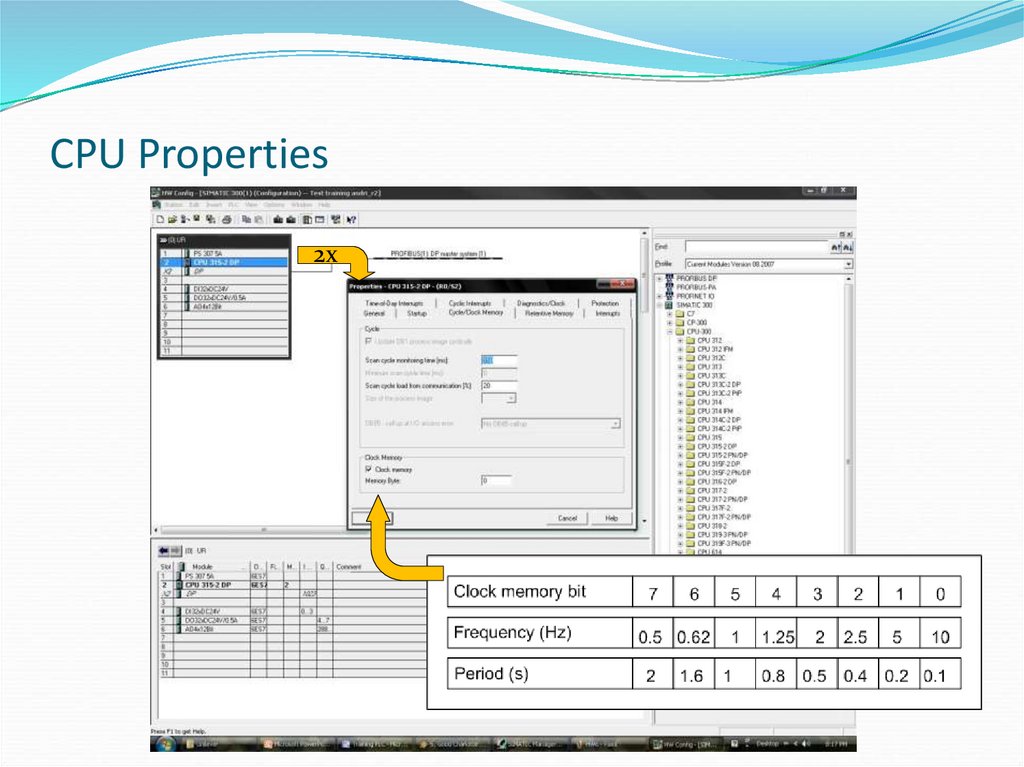
2x17. CPU Properties
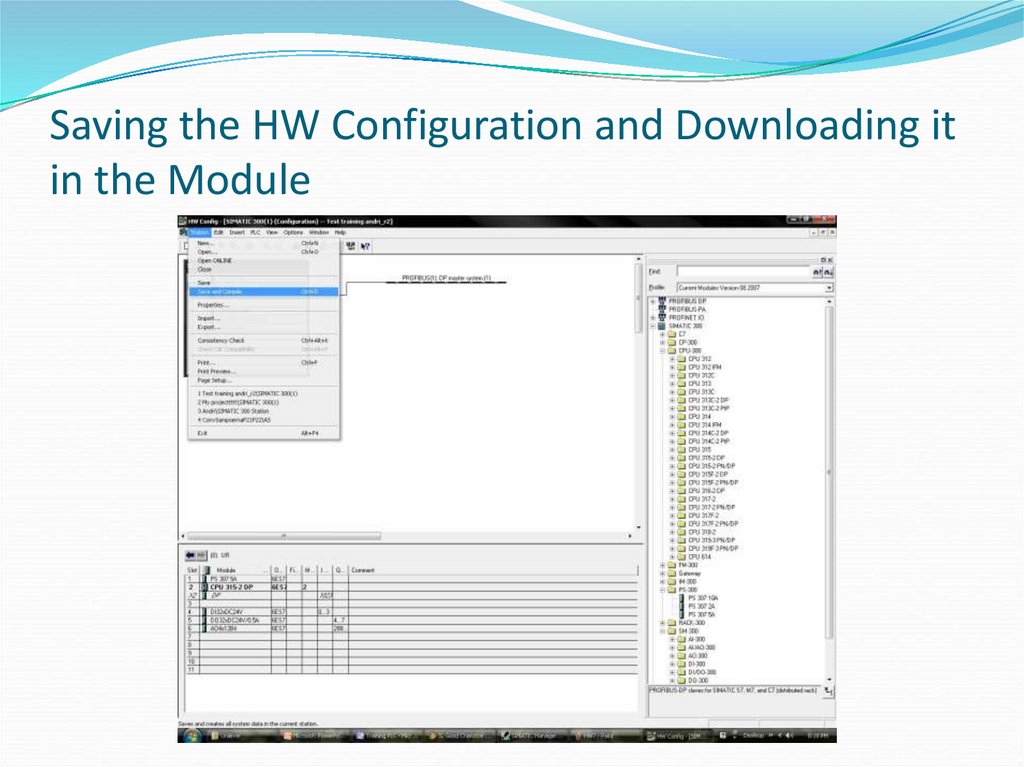
2x18. Saving the HW Configuration and Downloading it in the Module
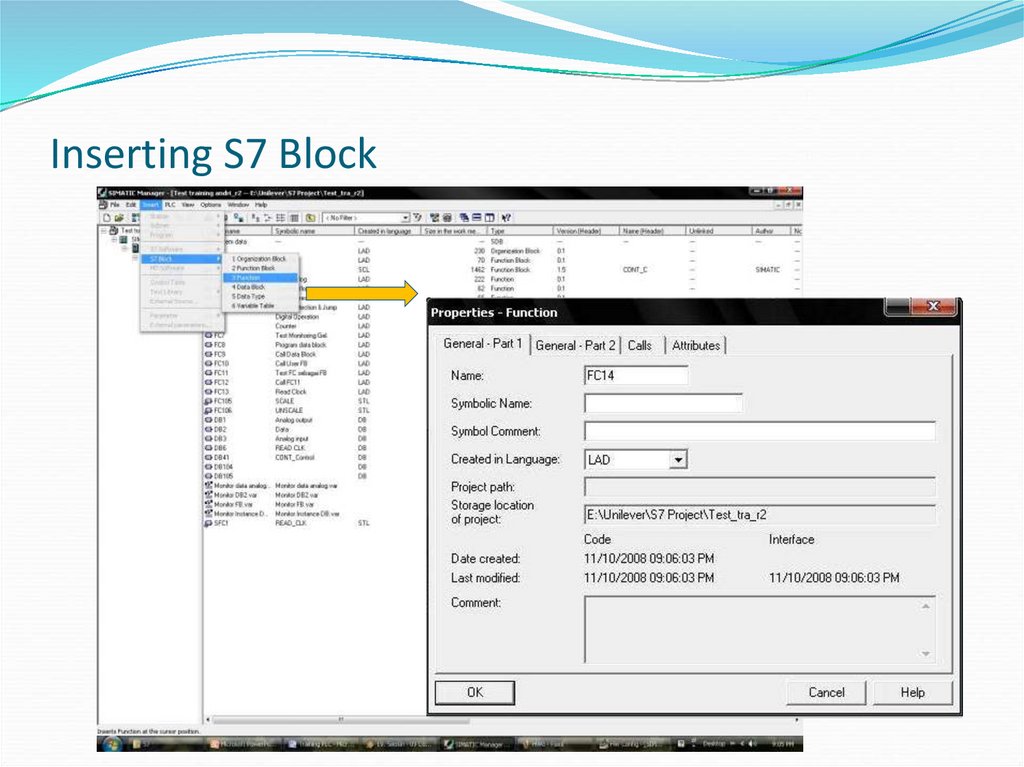
19. Inserting S7 Block
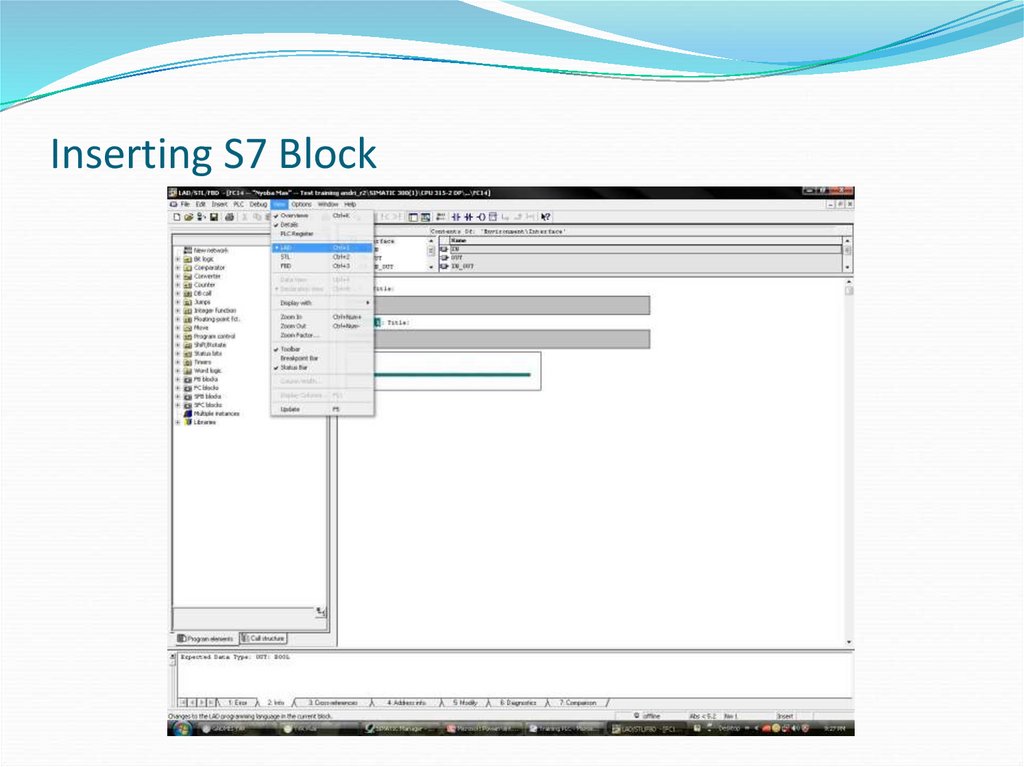
20. Inserting S7 Block
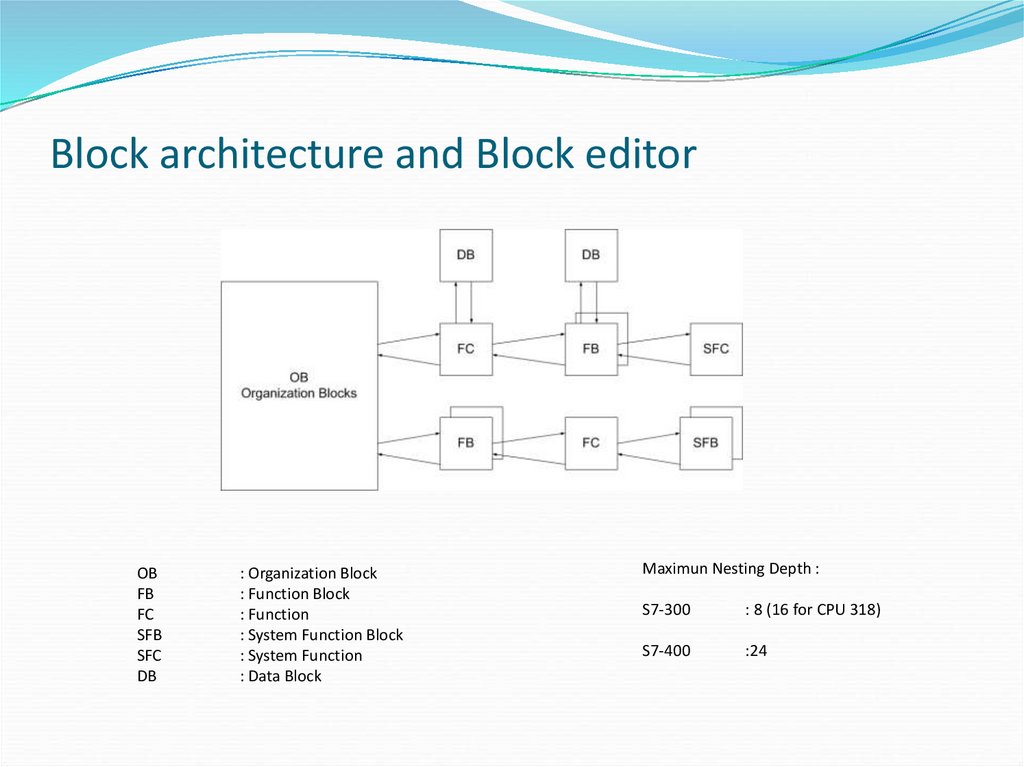
21. Block architecture and Block editor
OBFB
FC
SFB
SFC
DB
: Organization Block
: Function Block
: Function
: System Function Block
: System Function
: Data Block
Maximun Nesting Depth :
S7-300
: 8 (16 for CPU 318)
S7-400
:24
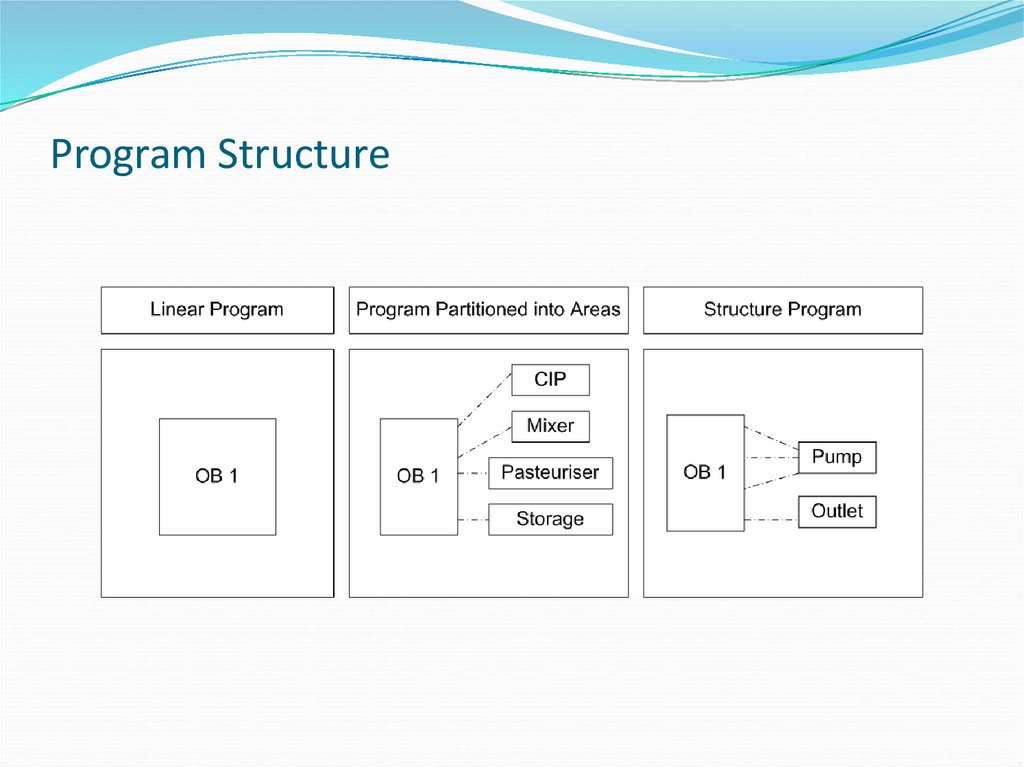
22. Program Structure
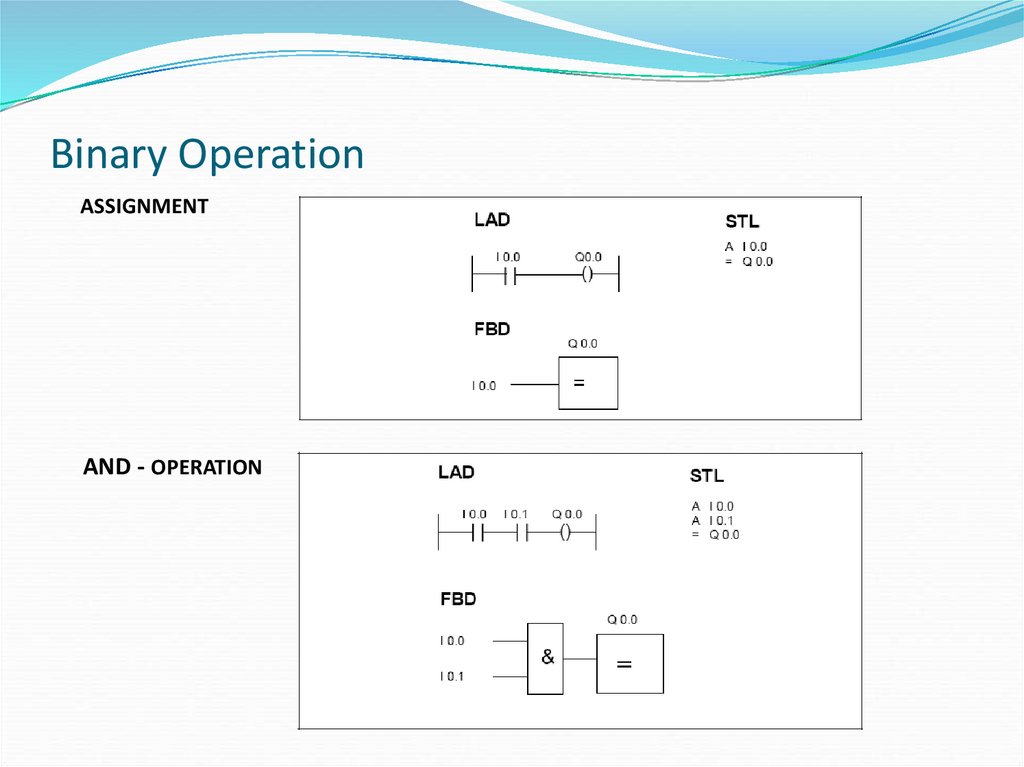
23. Binary Operation
ASSIGNMENTAND - OPERATION
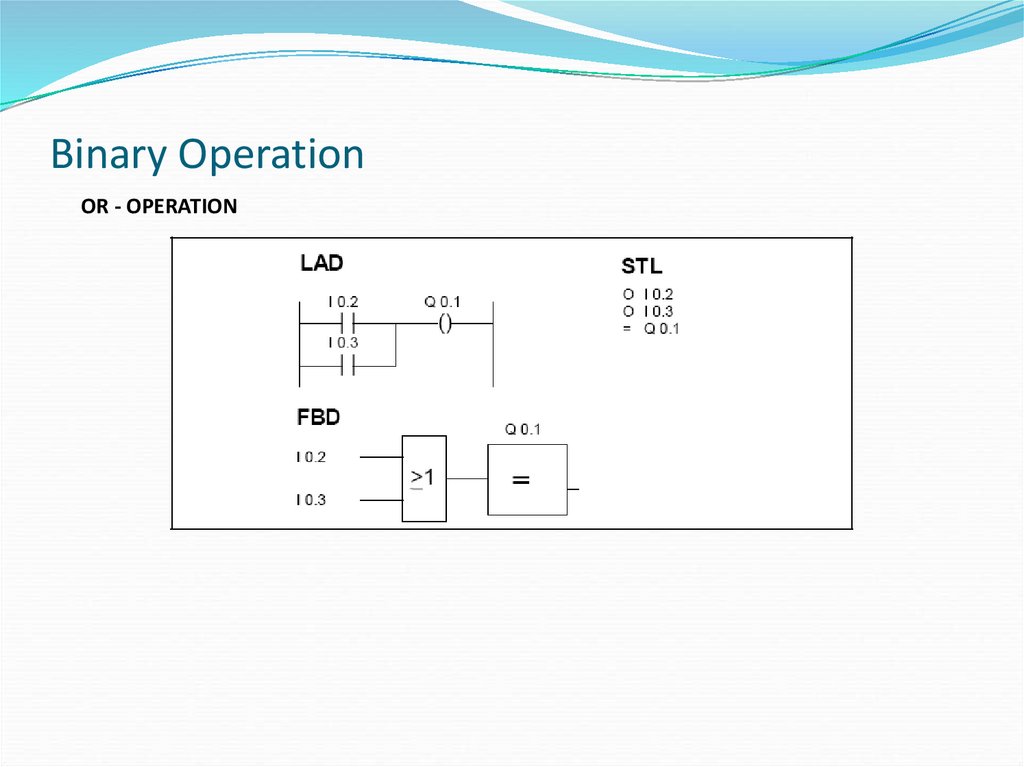
24. Binary Operation
OR - OPERATION25. Binary Operation
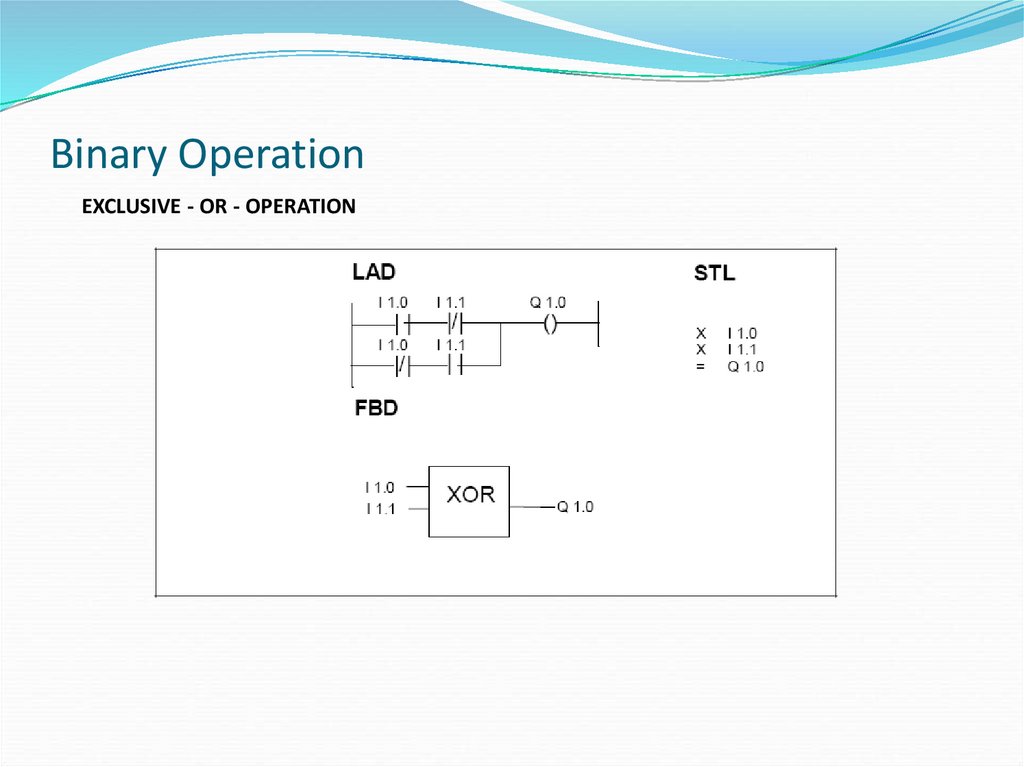
EXCLUSIVE - OR - OPERATION26. Binary Operation
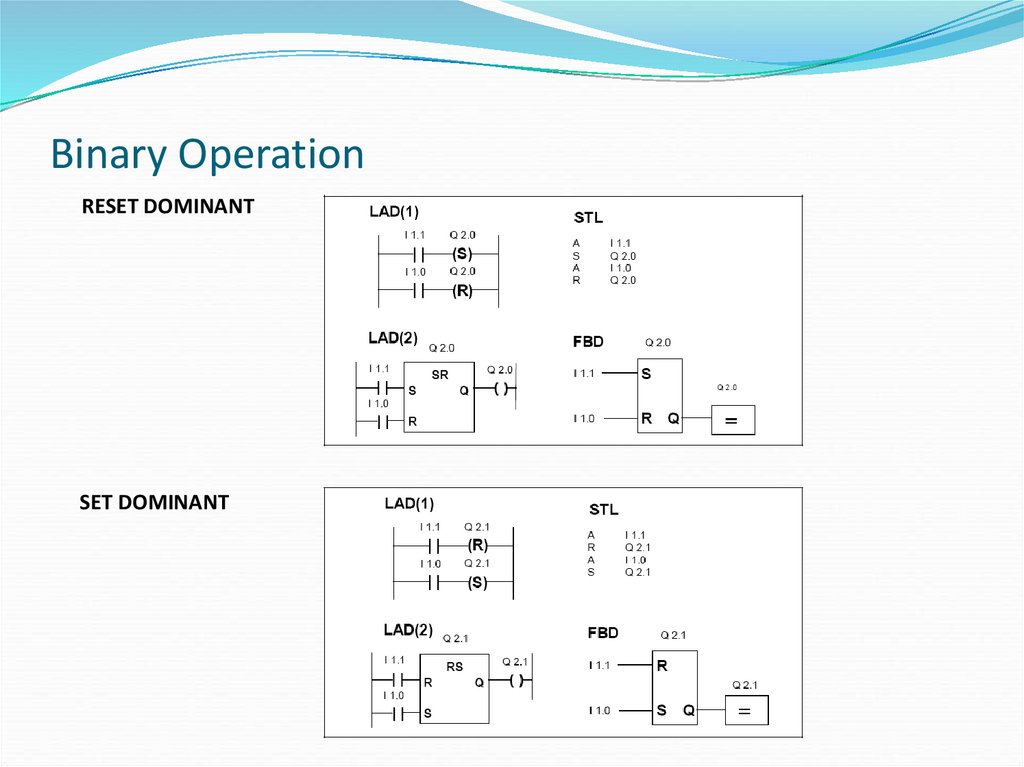
RESET DOMINANTSET DOMINANT
27. Binary Operation
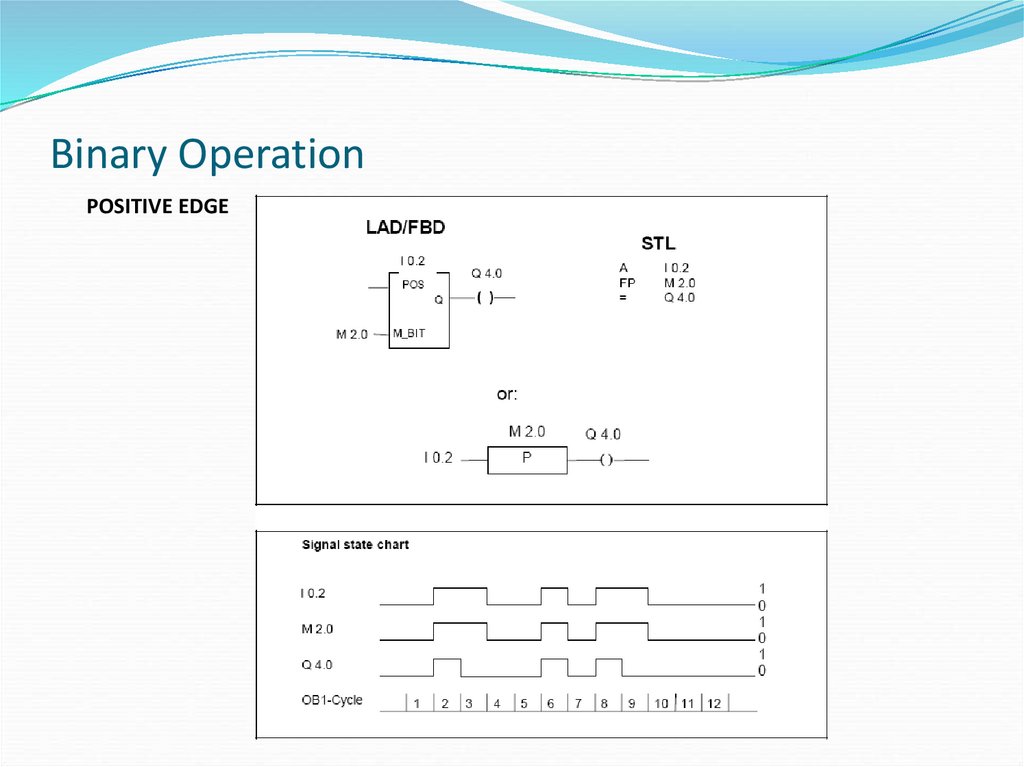
POSITIVE EDGE28. Binary Operation
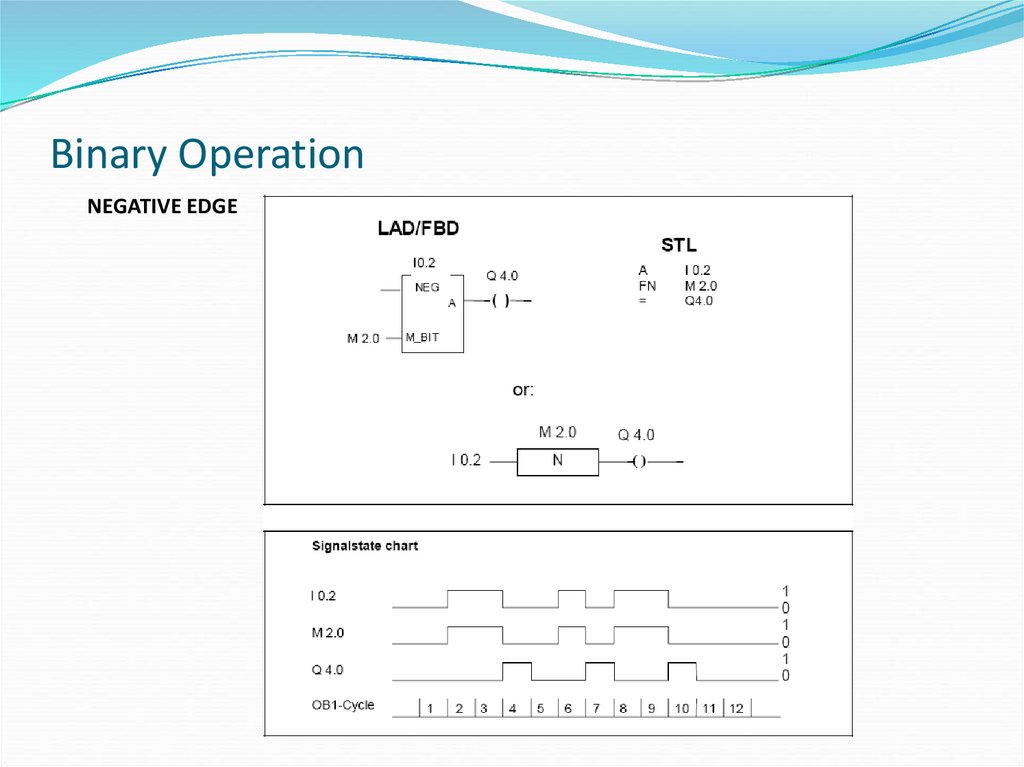
NEGATIVE EDGE29. Binary Operation
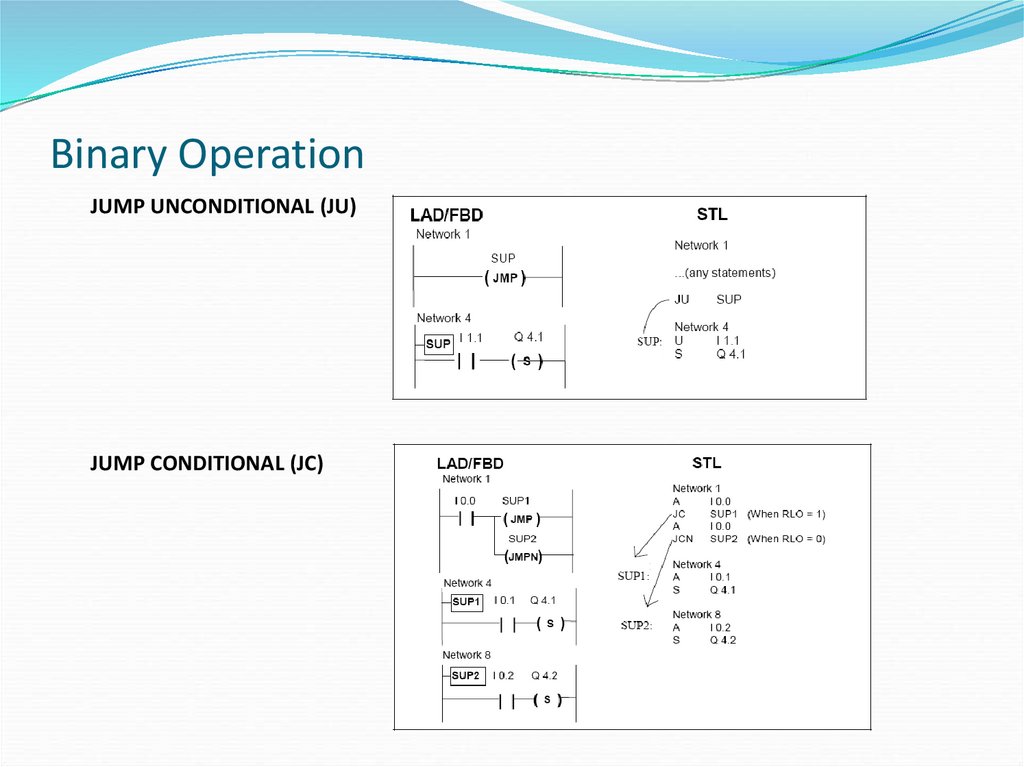
JUMP UNCONDITIONAL (JU)JUMP CONDITIONAL (JC)
30. Digital Operation
BITBYTE
For a unit of 8 binary characters, the term BYTE is used. A byte has the size of 8 bits.
WORD
A word also has the size of 2 bytes or 16 bits.
DOUBLE-WORD
A double-word corresponds to the word length of 32 binary characters.
A double-word also has the size of 2 words, 4 bytes, or 32 bits.
31. Digital Operation
Beberapa operand di S7 :1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Operand input(I)
Bit
Byte
Word
Double Word
Operand Output(Q)
Bit
Byte
Word
Double Word
Operand Flag(M)
Bit
Byte
Word
Double Word
Operand Timer(T)
T0
Operand Counter(C)
C0
I 0.0 - …
IB 0 - …
IW 0 - …
ID 0 - …
6. Operand Peripheral(PI)
Input Byte
Input Word
Output Byte
Output Word
PIB 0 - …
PIW 0 - …
PQB 0 - …
PQW 0 - …
Q 0.0 - …
QB 0 - …
QW 0 - …
QD 0 - …
7.Operand Data(D)
Bit
Byte
Word
Double Word
DBX 0.0 - …
DBB 0 - …
DBW 0 - …
DBD 0 - …
M 0.0 - …
MB 0 - …
MW 0 - …
MD 0 - …
32. Digital Operation
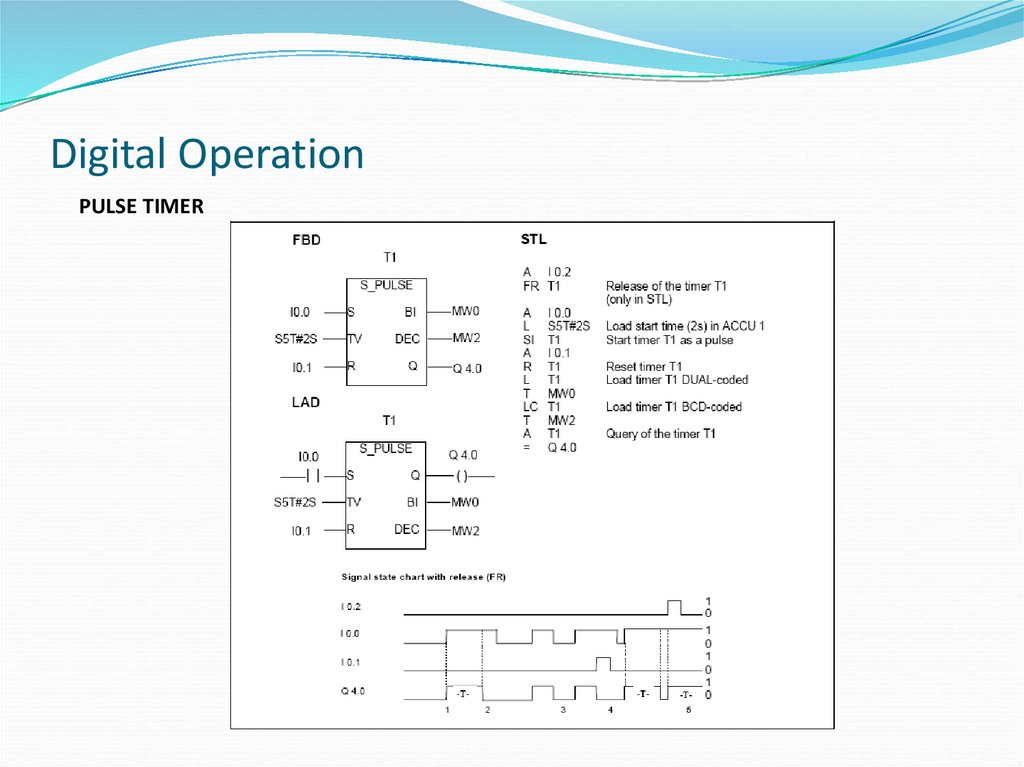
PULSE TIMER33. Digital Operation
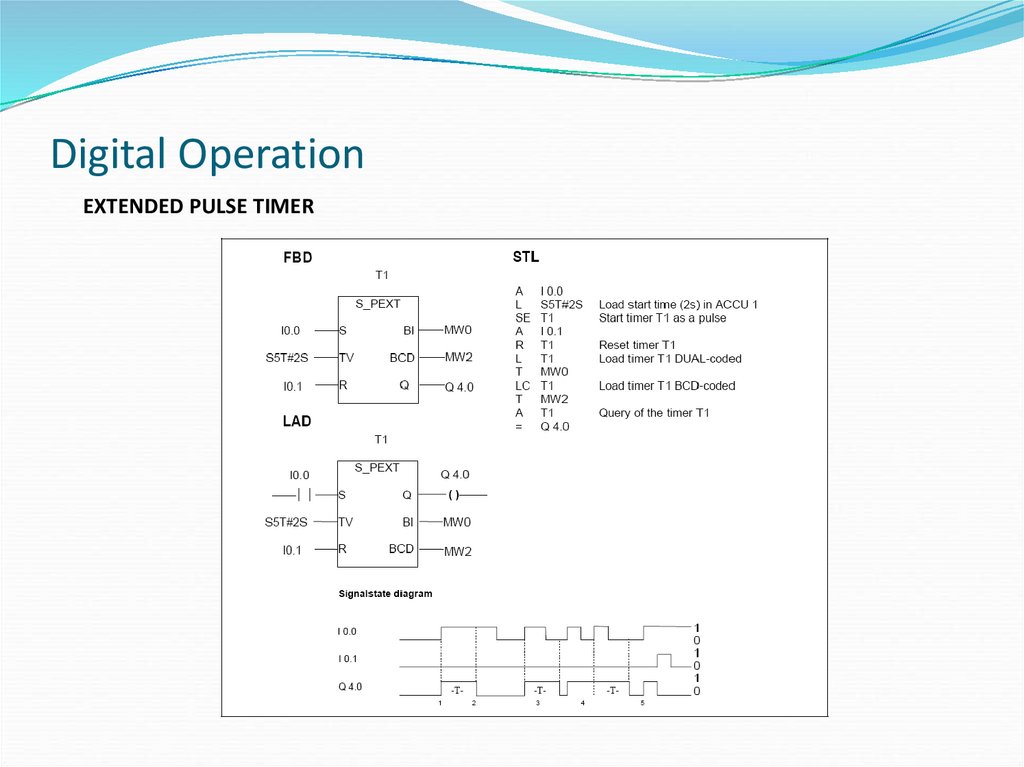
EXTENDED PULSE TIMER34. Digital Operation
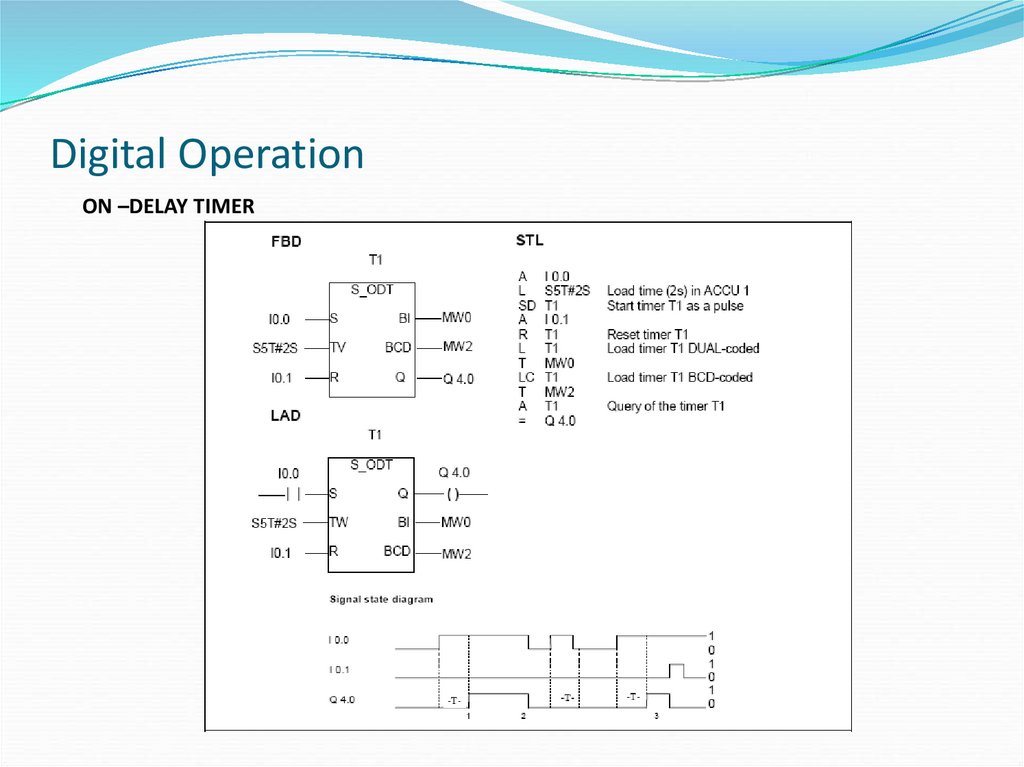
ON –DELAY TIMER35. Digital Operation
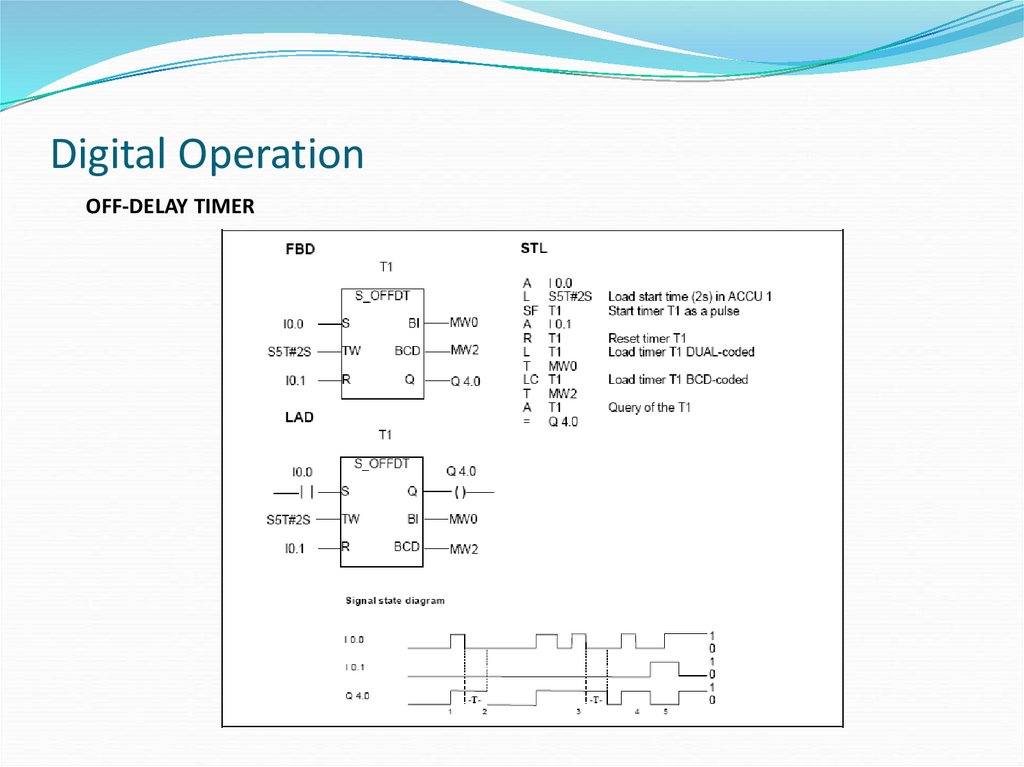
OFF-DELAY TIMER36. Digital Operation
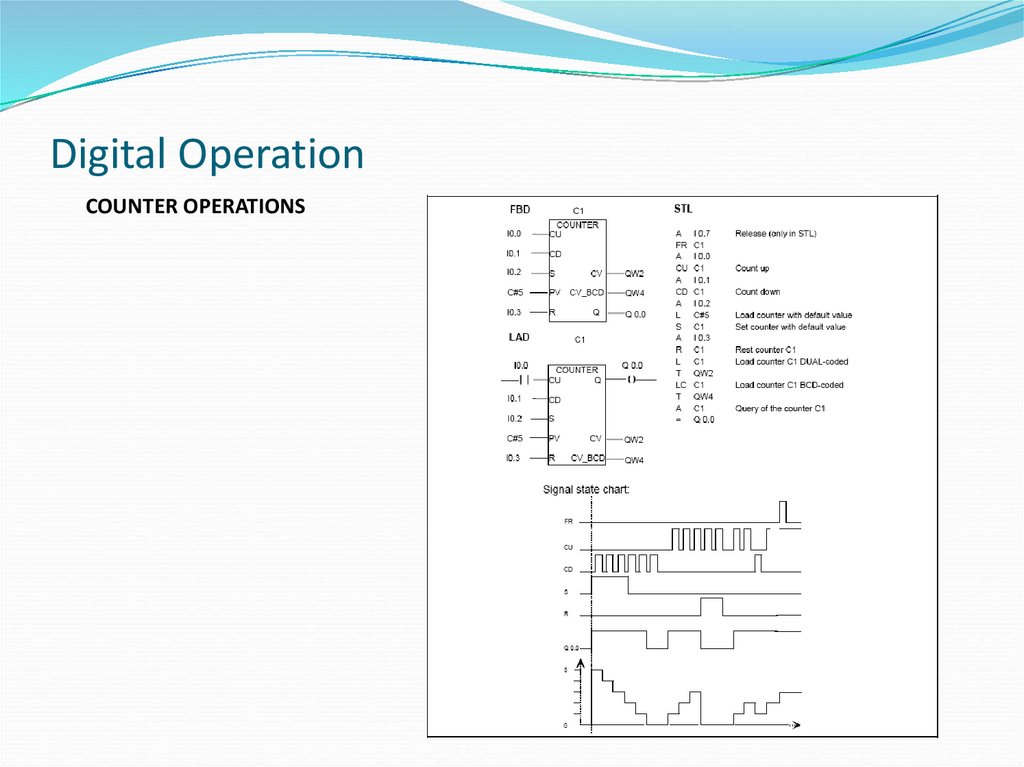
COUNTER OPERATIONS37. Digital Operation
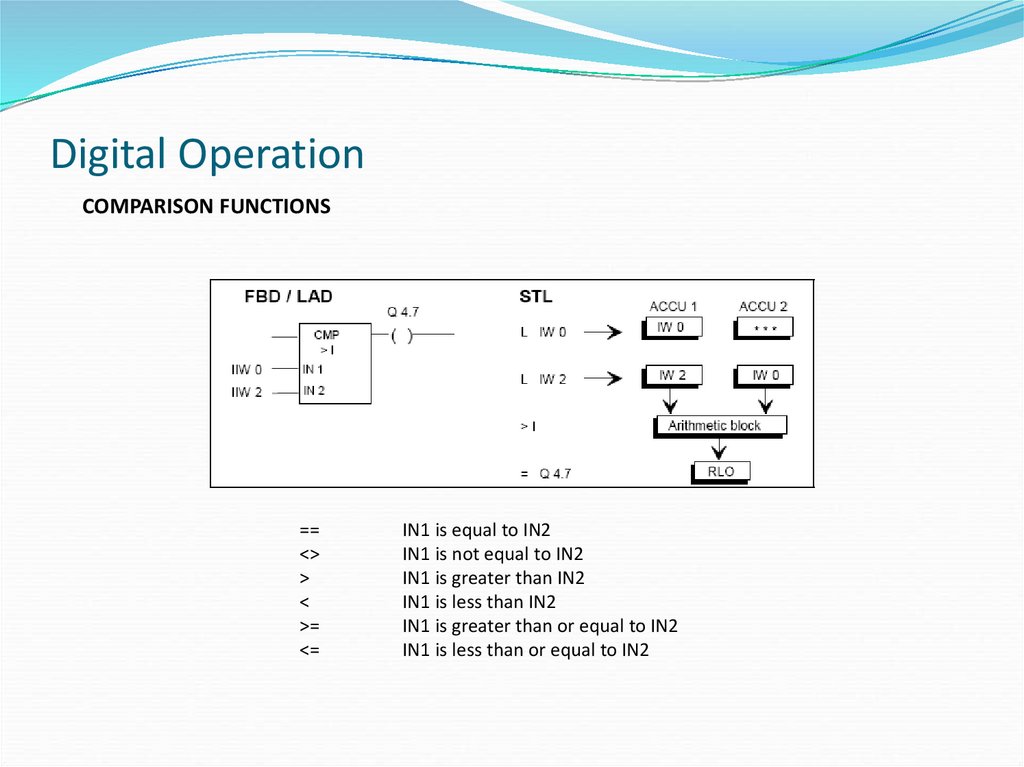
COMPARISON FUNCTIONS==
<>
>
<
>=
<=
IN1 is equal to IN2
IN1 is not equal to IN2
IN1 is greater than IN2
IN1 is less than IN2
IN1 is greater than or equal to IN2
IN1 is less than or equal to IN2
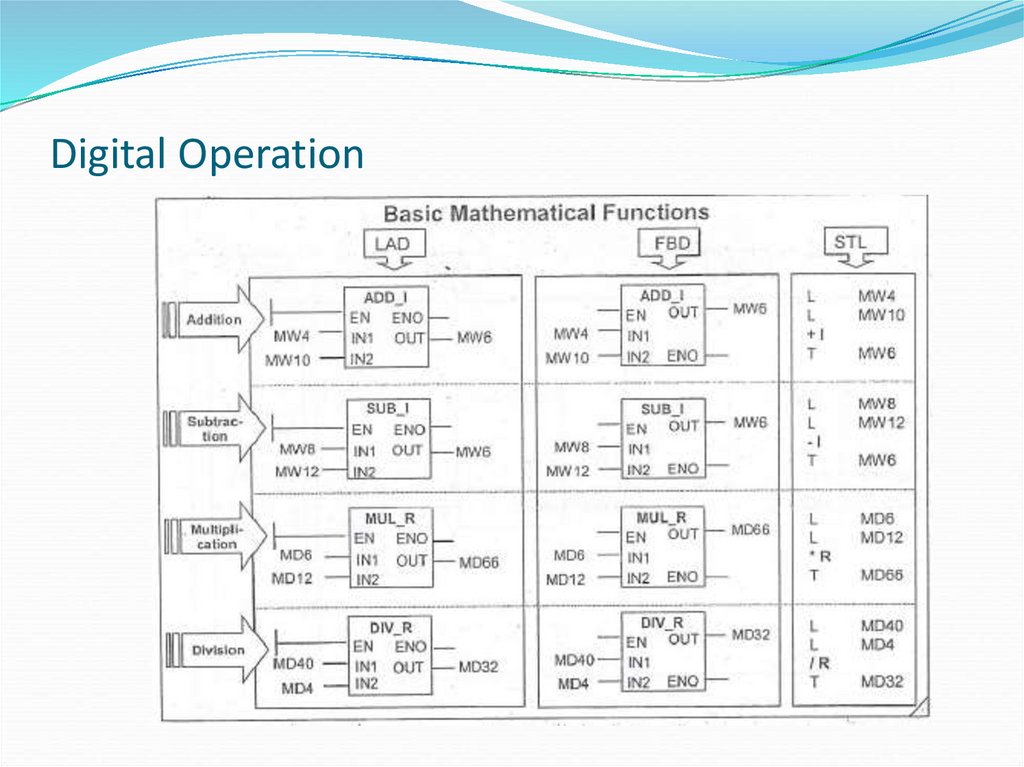
38. Digital Operation
39. Data Block
???40. Scale & Unscaled
Scale & Unscaled???






 electronics
electronics








