Similar presentations:
Introduction of Mobile. Cloud Computing
1.
Introduction of MobileCloud Computing
Mobile Cloud
Computing
2.
What is a mobile cloudcomputing?
3. Motivation
Motivation– Mobile devices (e.g., smartphone, tablet pcs, etc) are increasingly
becoming an essential part of human life,
– Dream of “Information at your fingertips anywhere anytime”,
– Mobile devices still lack in resources compared to a conventional
information processing device such as PCs and laptops
Soultion
› Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC)
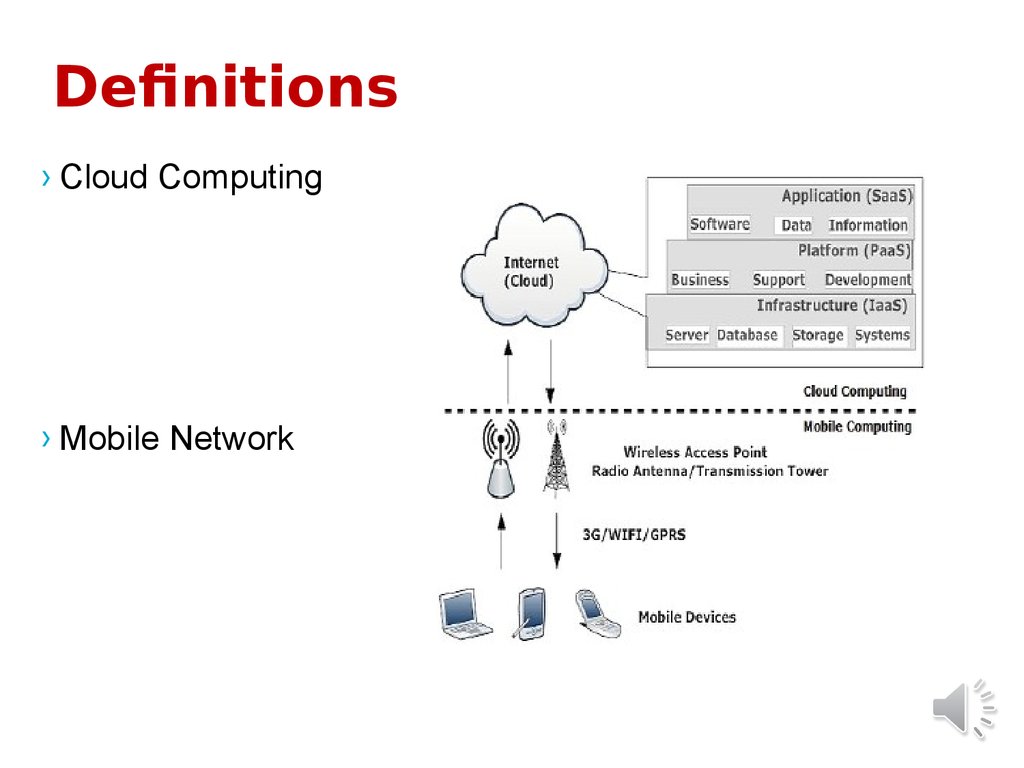
4. Definitions
› Cloud Computing› Mobile Network
5. Definitions
utilityCluster
Grid
Cloud
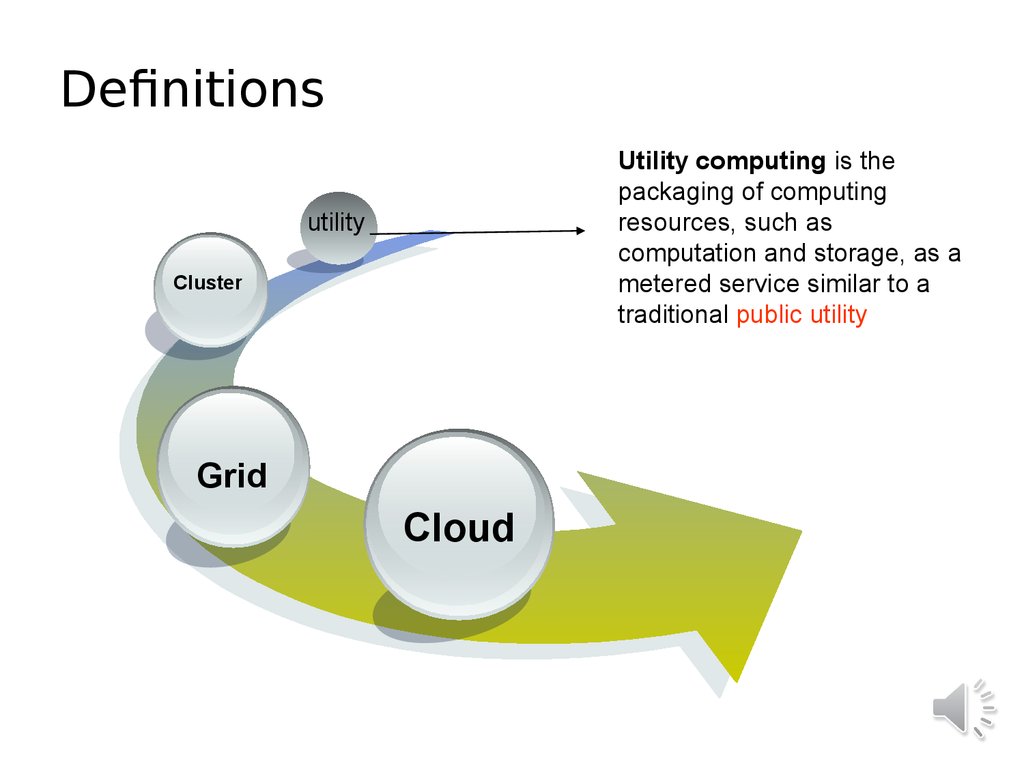
6. Definitions
Utility computing is thepackaging of computing
resources, such as
computation and storage, as a
metered service similar to a
traditional public utility
utility
Cluster
Grid
Cloud
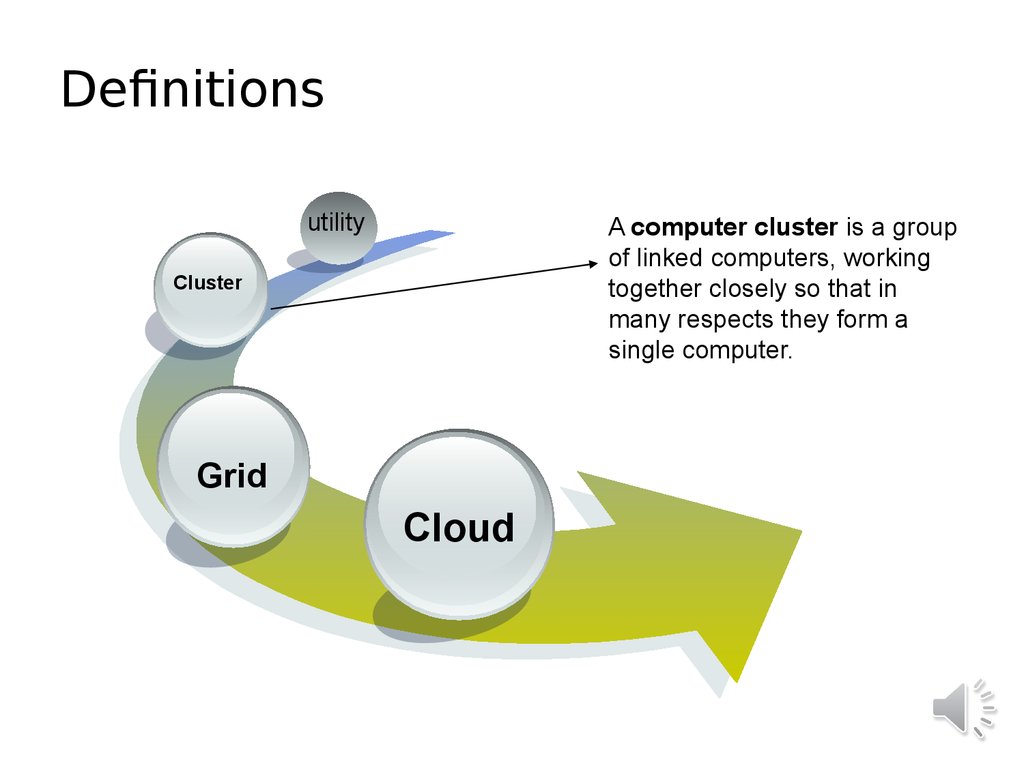
7. Definitions
utilityA computer cluster is a group
of linked computers, working
together closely so that in
many respects they form a
single computer.
Cluster
Grid
Cloud
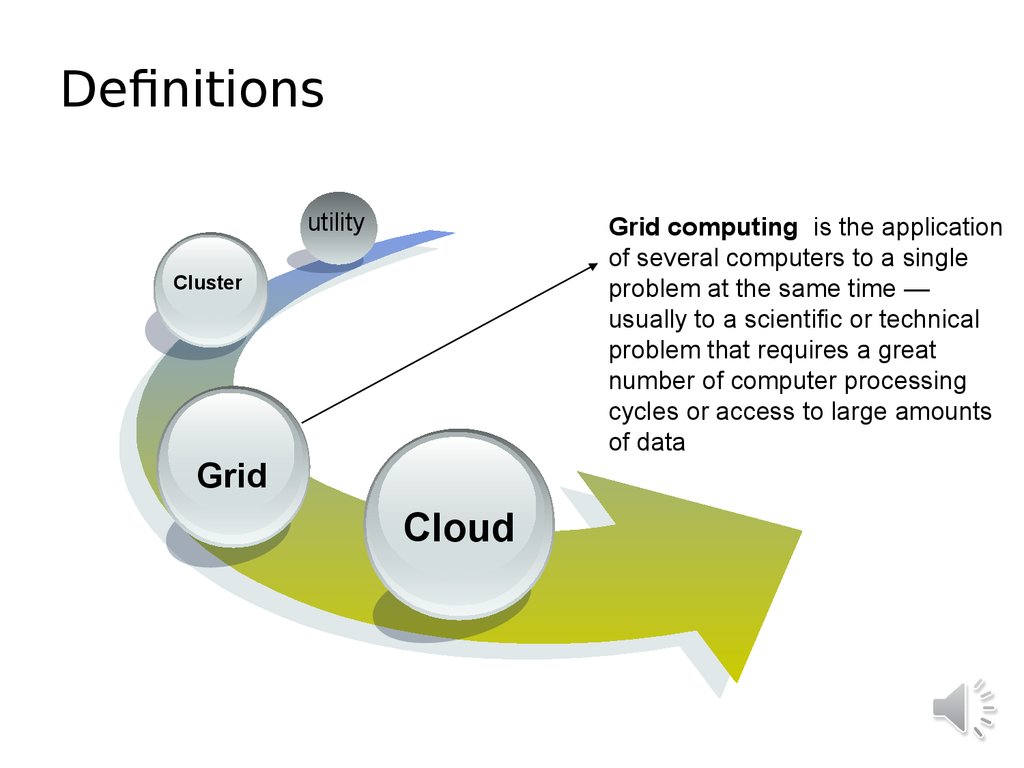
8. Definitions
utilityGrid computing is the application
of several computers to a single
problem at the same time —
usually to a scientific or technical
problem that requires a great
number of computer processing
cycles or access to large amounts
of data
Cluster
Grid
Cloud
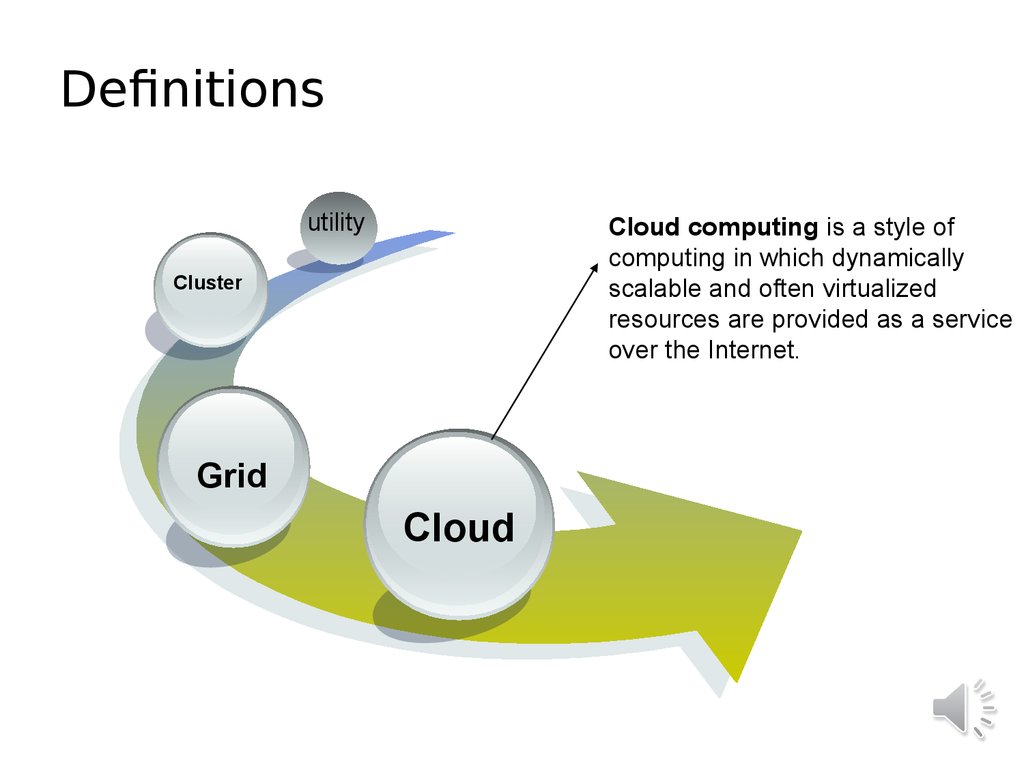
9. Definitions
utilityCloud computing is a style of
computing in which dynamically
scalable and often virtualized
resources are provided as a service
over the Internet.
Cluster
Grid
Cloud
10. What is Cloud Computing?
NIST Definition“A model for enabling convenient, ondemand network access to a
shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks,
servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly
provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service
provider interaction”
Cloud computing is a style of computing in which dynamically
scalable and often virtualized resources are provided as a serve
over the Internet.
11.
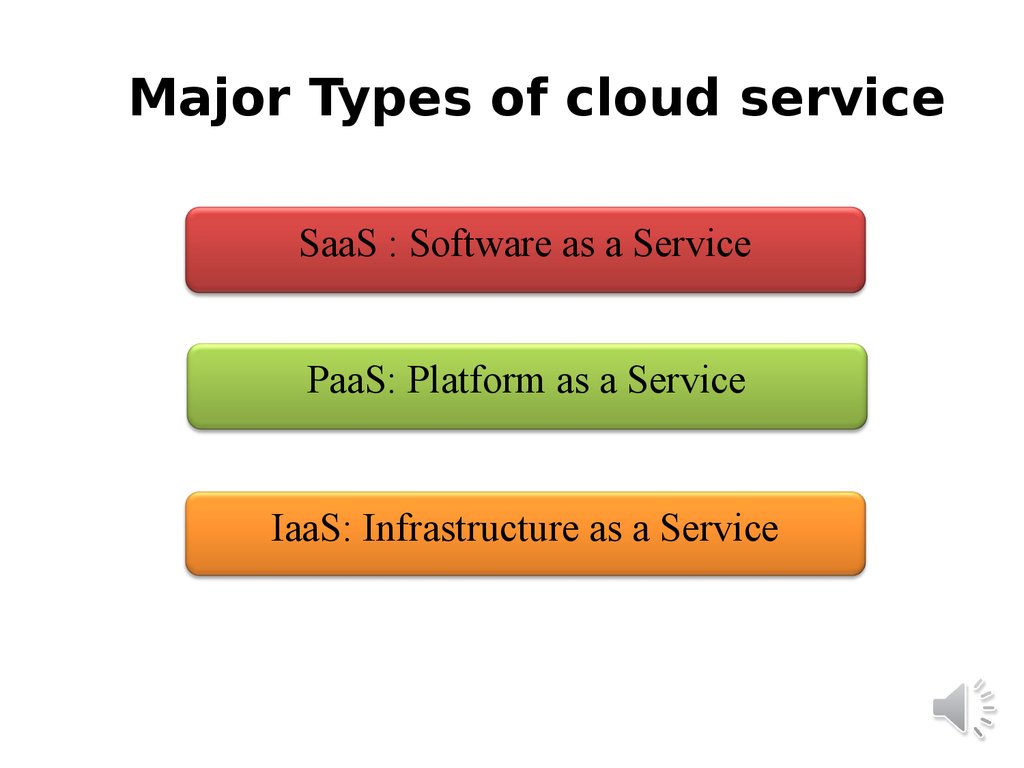
Major Types of cloud serviceSaaS : Software as a Service
PaaS: Platform as a Service
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
12.
13.
Service Delivery ModelExamples
Amazon
Microsoft
Salesforce
SaaS
PaaS
IaaS
Products and companies shown for illustrative purposes only and should not
be construed as an endorsement
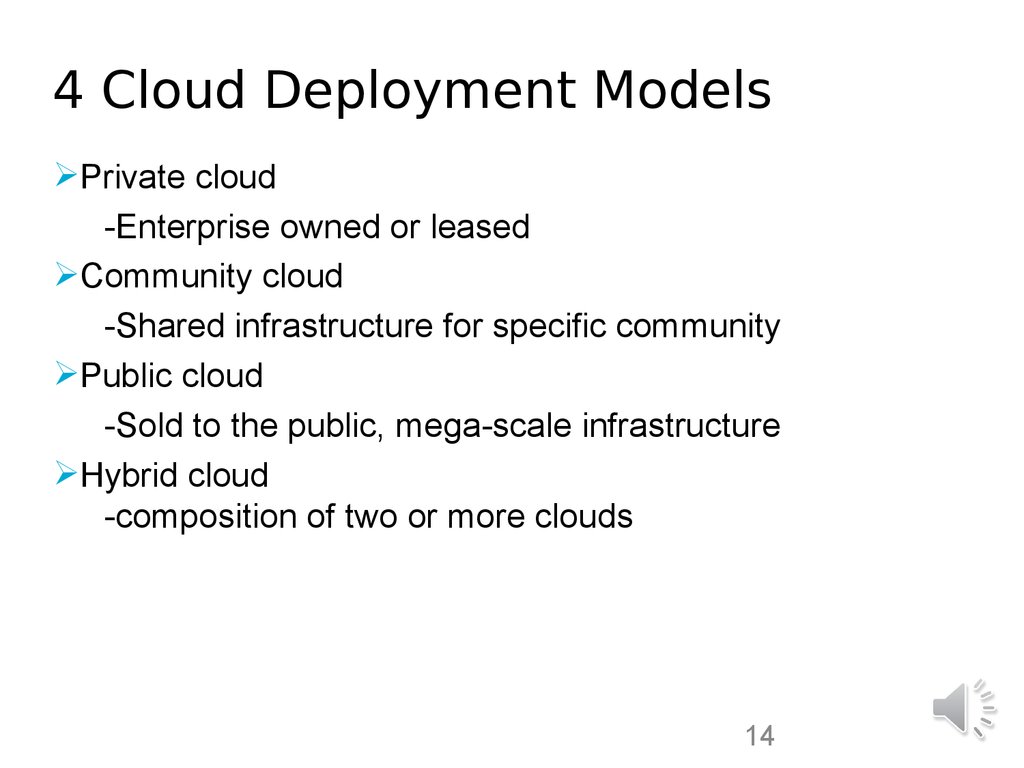
14. 4 Cloud Deployment Models
Private cloud-Enterprise owned or leased
Community cloud
-Shared infrastructure for specific community
Public cloud
-Sold to the public, mega-scale infrastructure
Hybrid cloud
-composition of two or more clouds
14
15.
Cloud Efficiencies andImprovements
Cost efficiencies
Time efficiencies
Power efficiencies
Improved process control
Improved security
“Unlimited” capacity
$
Burst capacity (overprovisioning)
Short-duration projects
Cancelled or failed missions
Network connectivity
• Standardized, updated base images
• Centrally auditable log servers
• Centralized authentication systems
• Improved forensics (w/ drive image)
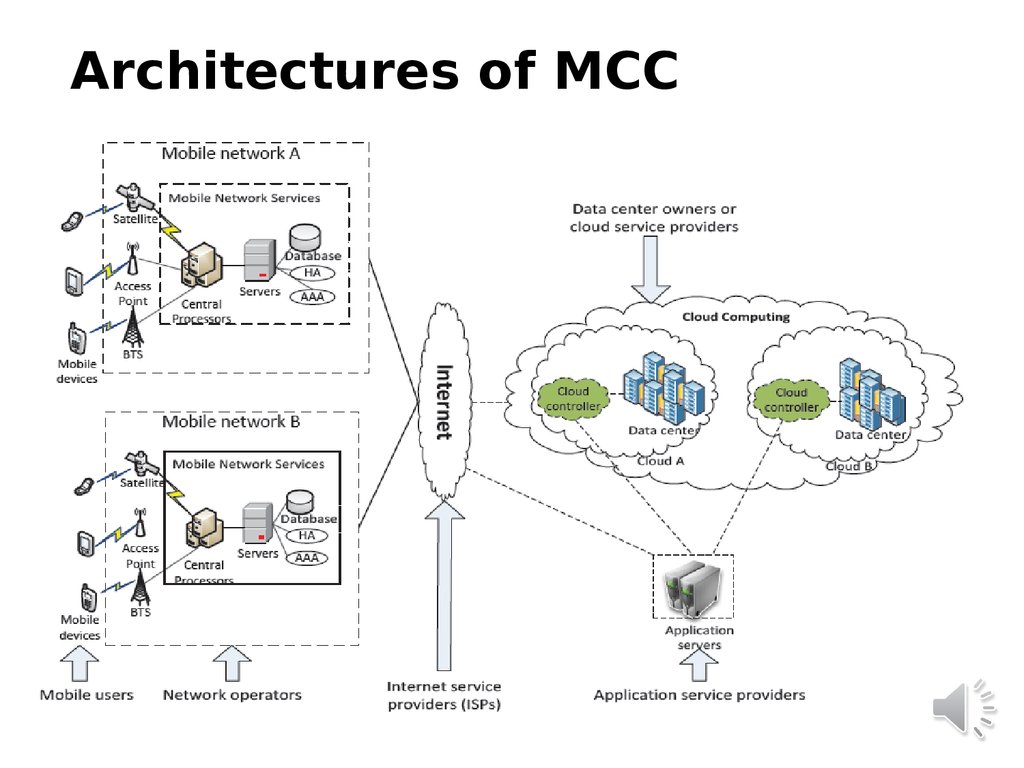
16. Where is the MCC?
Definition›
Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC) at
its simplest, refers to an infrastructure
where both the data storage and the
data processing happen outside of the
mobile
device.
Mobile
cloud
applications move the computing
power and data storage away from
mobile phones and into the cloud,
bringing applications and mobile
computing to not just smartphone
users but a much broader range of
mobile subscribers”
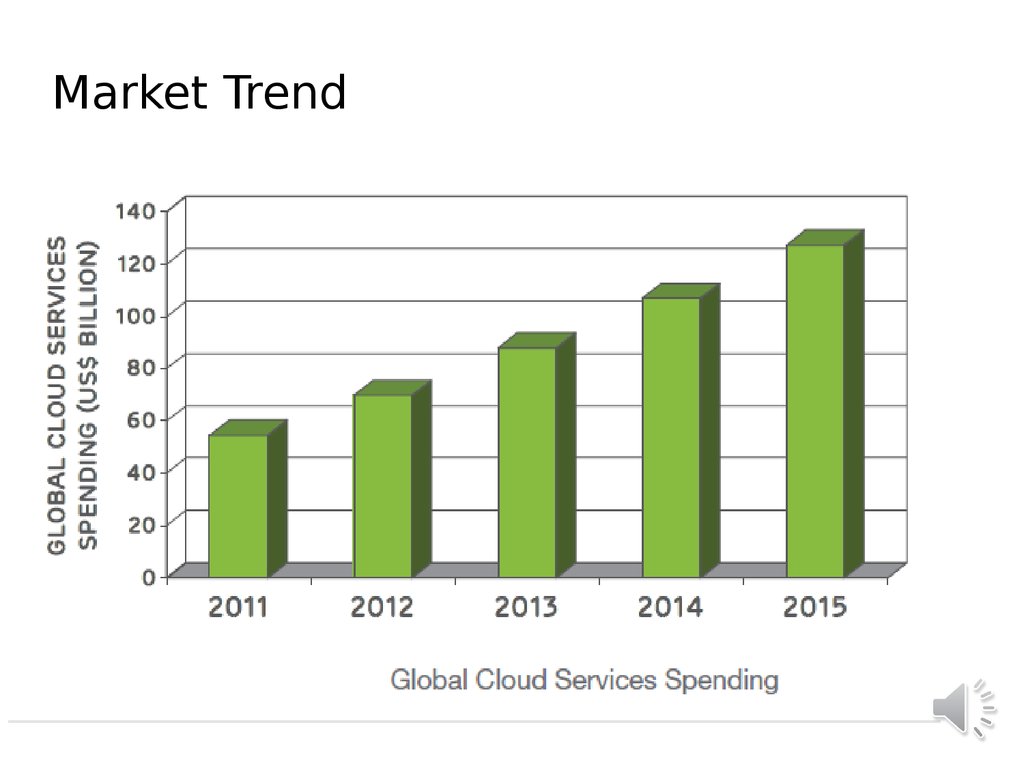
17. Market Trend
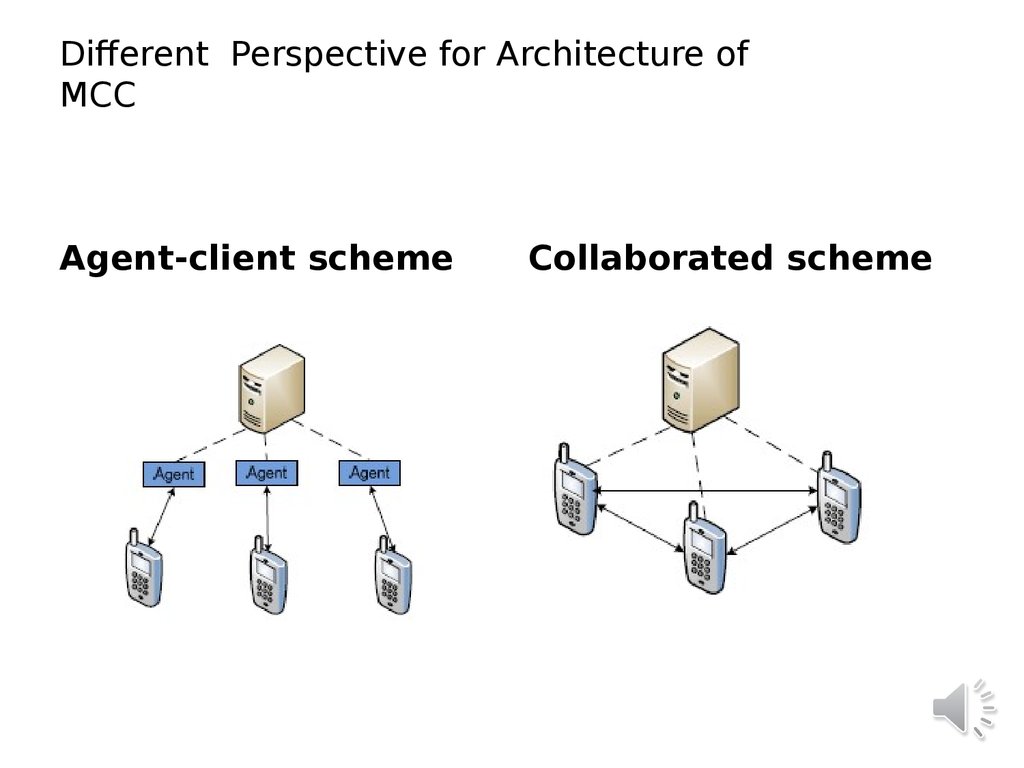
18. Different Perspective for Architecture of MCC
Agent-client schemeCollaborated scheme
19. Architectures of MCC
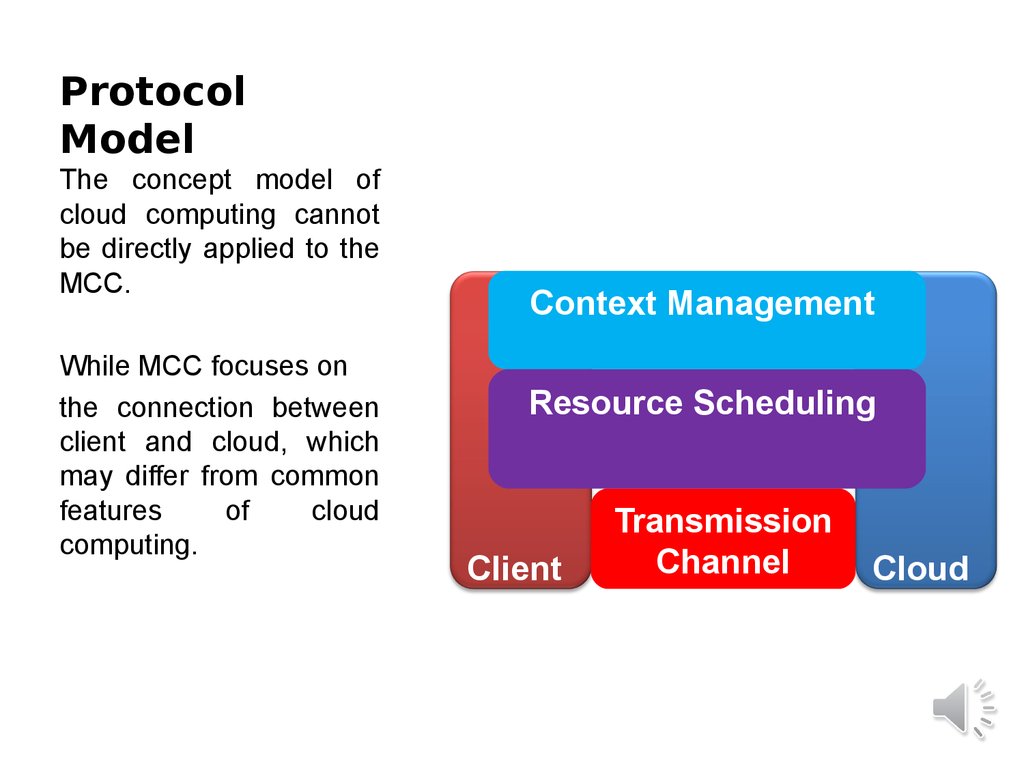
20. Protocol Model
The concept model ofcloud computing cannot
be directly applied to the
MCC.
While MCC focuses on
the connection between
client and cloud, which
may differ from common
features
of
cloud
computing.
Context Management
Resource Scheduling
Client
Transmission
Channel
Cloud
21. Resource Scheduling
› Resource scheduling components address the schedule ofresource, such as computing resource and storage
resource.
resource
› Assign the appropriate pricing mechanism to maximize
the revenue of mobile cloud computing systems and
provide incentives for mobile users,
› Considering different cases, e.g., resource may be
stable but applications may transmit to other places.
22. Context Management
› Context Enabled features of mobile device allow us toascertain additional
information from the computing device itself without the need for explicit user input.
› Two major classes of contexts:
– Social Context,
– Spatial context
23. Two major approaches
› Application partition and offloading technology play an important role for theimplementation of elastic applications.
› Application partition decompose complex workload to atomic ones, thus can be
processed concurrently.
› Offloading application can free burden of mobile devices.
24. Advantageous of MCC
Extending battery lifetimeImproving
capacity
power
data
storage
and
processing
Improving reliability
25. How MCC Can Extend Battery Lifetime?
Challenges:› Battery is one of the main
concerns for mobile devices,
› Traditional approaches need to
changes the structure of mobile
devices.
› The additional cost for the end
mobile users is not appealing in
wireless networks.
MCC’s solution:
› Computation
technique:
offloading
– Immigrate the large computations
and complex processing from
resource-limited devices (i.e.,
mobile devices) to resourceful
machines (i.e., servers in clouds).
› This avoids taking a long
application execution time on
mobile devices which results in
large amount of power
consumption.
26. How MCC Can Improve Storage Capacity?
Challenges› Users need more and more
capacity for saving the
essential information on
mobile devices,
› Need to change the device,
› More capacity, more weight
MCC’s solution
› MCC is developed to enable
mobile users to store/access
the large data on the cloud
through wireless networks,
› Examples
of
existing
services:
– Amazon
Simple
Storage
Service (Amazon S3),
– Image Exchange,
– Flickr, ShoZu.
27. How MCC Can Improve Reliability?
Challenges› Users need reliable backup
for their information,
› Lack of data security
model for both service
providers and users in
existing mobile users,
MCC’s solution
› Storing
data
or
running
applications on clouds is an
effective way to improve the
reliability since the data and
application are stored and backed
up on a number of computers.
28. Other advantageous of MCC
› Dynamic provisioning,› Scalability,
› Multi-tenancy,
› Ease of integration.
29. Applications of MCC
› Mobile commerce,› Mobile healthcare,
› Mobile learning,
› Mobile Gaming.
30. Mobile Commerce
› Mobile commerce (m-commerce) is a business model forcommerce using mobile devices.
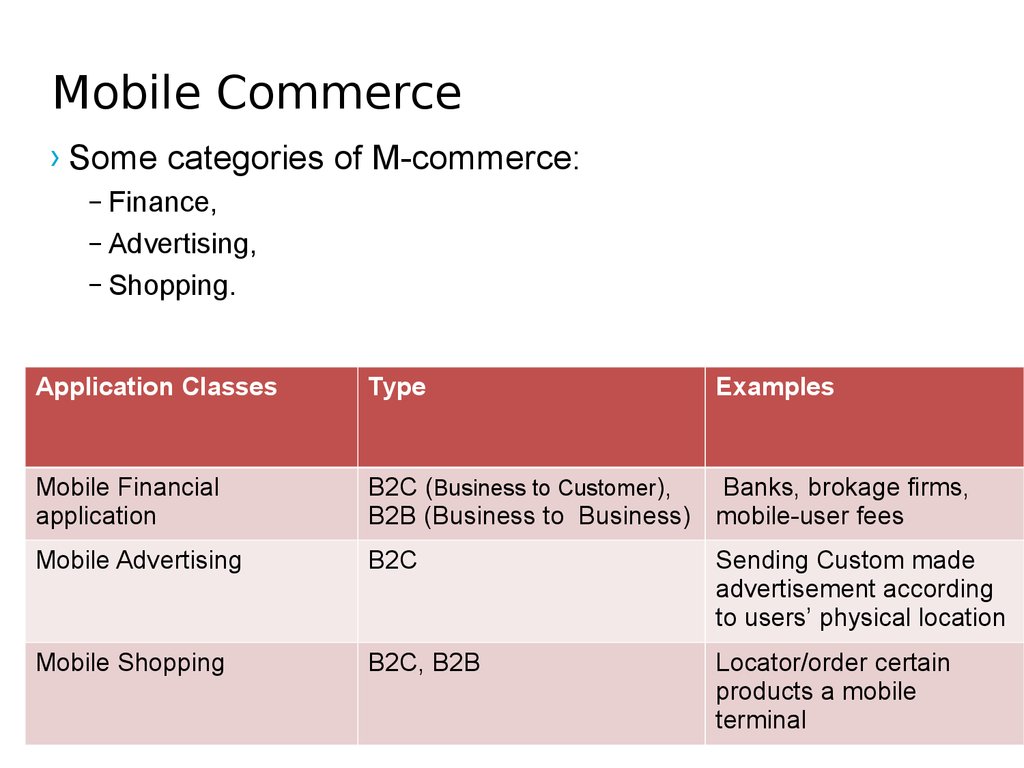
31. Mobile Commerce
› Some categories of M-commerce:– Finance,
– Advertising,
– Shopping.
Application Classes
Type
Examples
Mobile Financial
application
B2C (Business to Customer),
Banks, brokage firms,
B2B (Business to Business) mobile-user fees
Mobile Advertising
B2C
Sending Custom made
advertisement according
to users’ physical location
Mobile Shopping
B2C, B2B
Locator/order certain
products a mobile
terminal
32. Mobile Learning (M-LEARNING) = (E-LEARNING) + Mobility
Traditional m-learning applicationshave limitations in terms of
1- High cost of devices and network,
2- Low network transmission rate,
3- Limited educational resources
Cloud-based m-learning applications
are introduced to solve these limitations.
For example, utilizing a cloud with the
large storage capacity and powerful
processing ability, the applications
provide learners with much richer
services in terms of data (information)
size, faster processing speed, and
longer battery life.
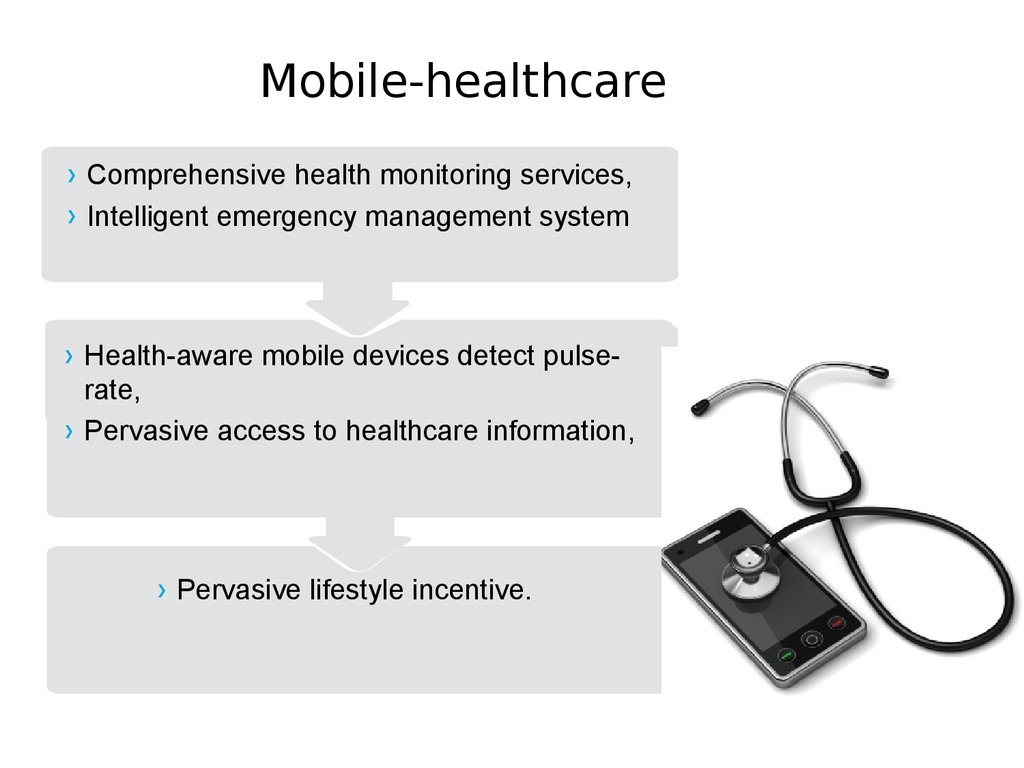
33. Mobile-healthcare
› Comprehensive health monitoring services,› Intelligent emergency management system
› Health-aware mobile devices detect pulserate,
› Pervasive access to healthcare information,
› Pervasive lifestyle incentive.
34. Mobile Gaming
› Mobile game (m-game) is a potential market generating revenues forservice providers.
› M-game can completely offload game engine requiring large computing
resource (e.g., graphic rendering) to the server in the cloud, and
gamers only interact with the screen interface on their devices.
35. Other applications on MCC
› Keyword based searching› Voice based searching
› Tag- Based searching
36.
› ISSUES ANDAPPROACHES OF MCC
Due to the integration
of two different fields,
i.e., cloud computing
and mobile networks,
MCC has to face many
technical challenges.
37. Issues in Mobile Communication Side
Network latency and limitedbandwidth
Availability
Heterogeneity
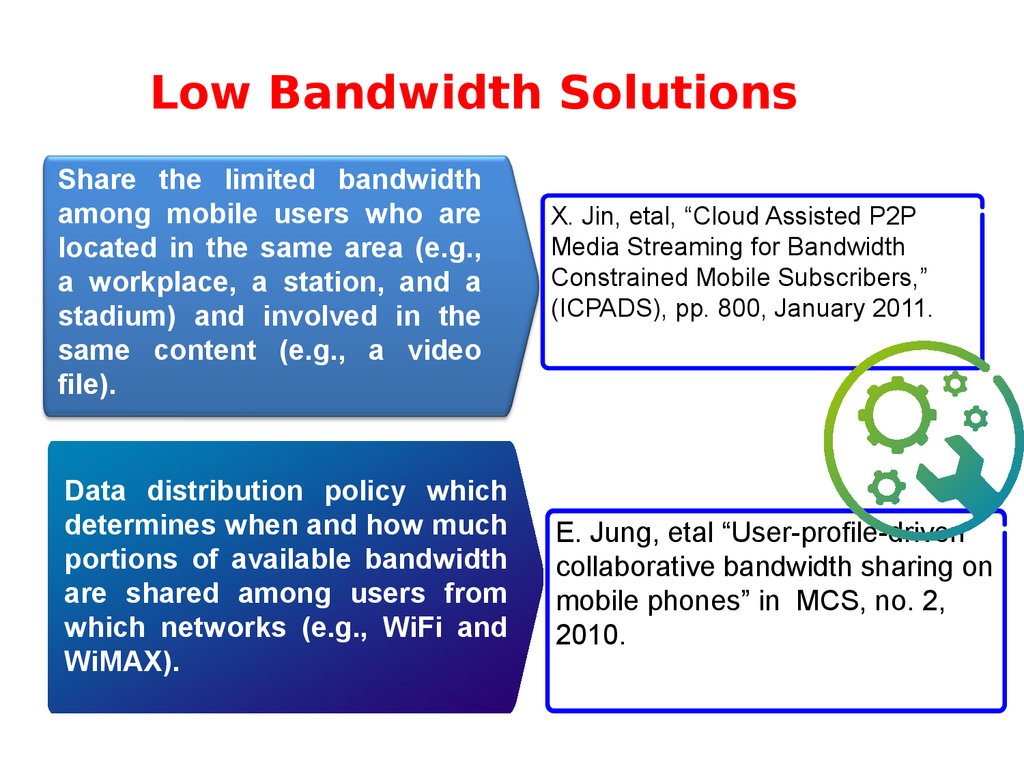
38. Low Bandwidth Solutions
Share the limited bandwidthamong mobile users who are
located in the same area (e.g.,
a workplace, a station, and a
stadium) and involved in the
same
content (e.g., a video
Availability
file).
Data distribution policy which
determines when and how much
portions of available bandwidth
are shared among users from
which networks (e.g., WiFi and
WiMAX).
X. Jin, etal, “Cloud Assisted P2P
Media Streaming for Bandwidth
Constrained Mobile Subscribers,”
(ICPADS), pp. 800, January 2011.
E. Jung, etal “User-profile-driven
collaborative bandwidth sharing on
mobile phones” in MCS, no. 2,
2010.
39. Availability Solutions
• Finding stable neighbour• WiFi multi-hop networking system
› G. Huerta “A virtual cloud computing provider for mobile
devices,” in MCS, 2010.
› L. Zhang,, “WiFace: a secure geosocial networking
system using WiFi-based multi-hop MANET,” in MSC,
2010.
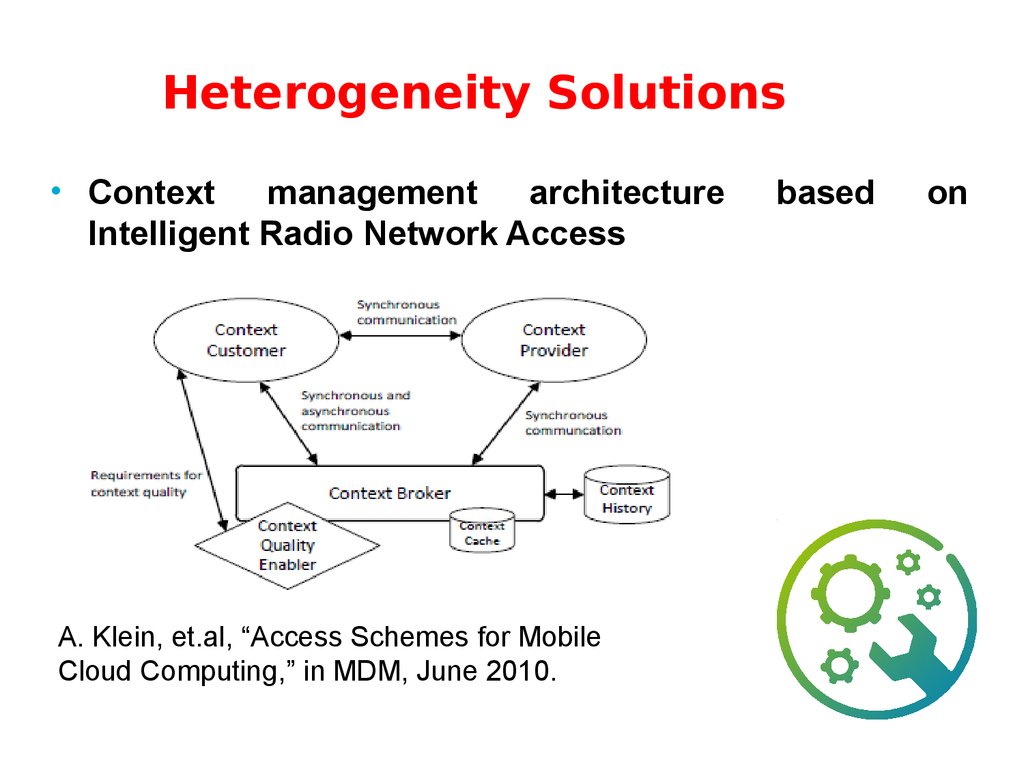
40. Heterogeneity Solutions
• Contextmanagement
architecture
Intelligent Radio Network Access
A. Klein, et.al, “Access Schemes for Mobile
Cloud Computing,” in MDM, June 2010.
based
on
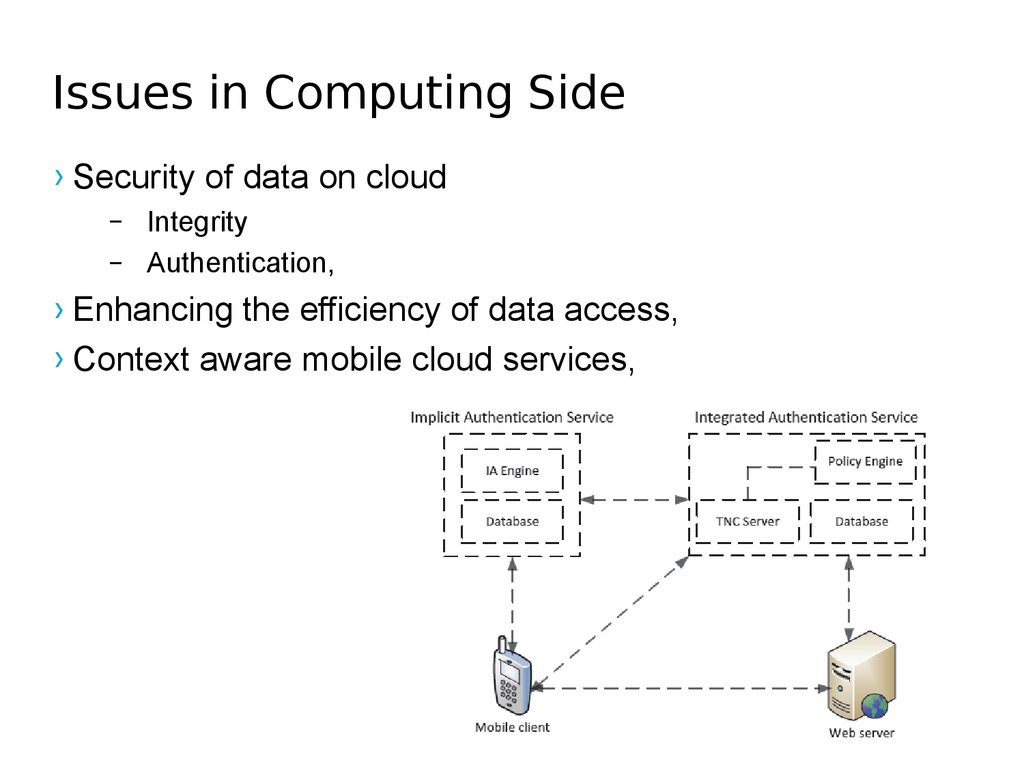
41. Issues in Computing Side
Computing offloadSecurity
Availability
Enhancing the efficiency of data
access
Context aware mobile cloud
services
42. Issue and Solutions in Computing Offload
› Offloading in the statistic environment is notalways the efficient way to save energy
– For small calculation and depending on the transmission
technology;
– Tradeoff between communication and computation cost.
G. Chen, et.al, “Studying energy trade offs in offloading computation/compilation in Javaenabled mobile devices,” IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, …2004.
43. Issue and Solutions in Computing Offload
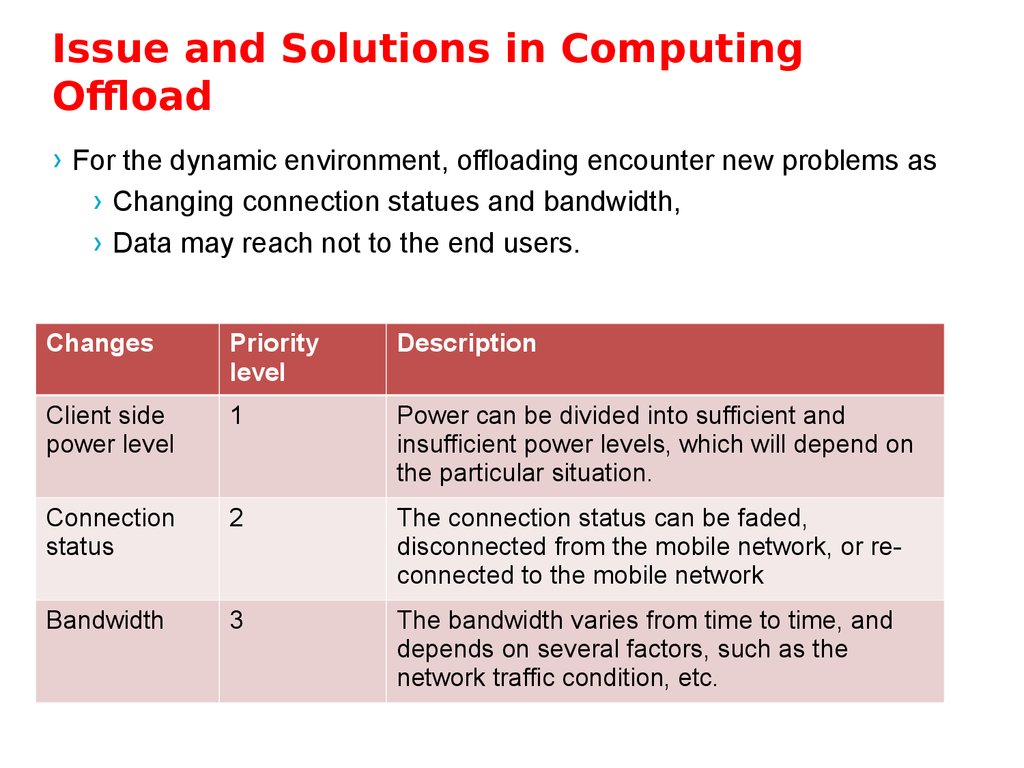
› For the dynamic environment, offloading encounter new problems as› Changing connection statues and bandwidth,
› Data may reach not to the end users.
Changes
Priority
level
Description
Client side
power level
1
Power can be divided into sufficient and
insufficient power levels, which will depend on
the particular situation.
Connection
status
2
The connection status can be faded,
disconnected from the mobile network, or reconnected to the mobile network
Bandwidth
3
The bandwidth varies from time to time, and
depends on several factors, such as the
network traffic condition, etc.
44. Issues in Computing Side
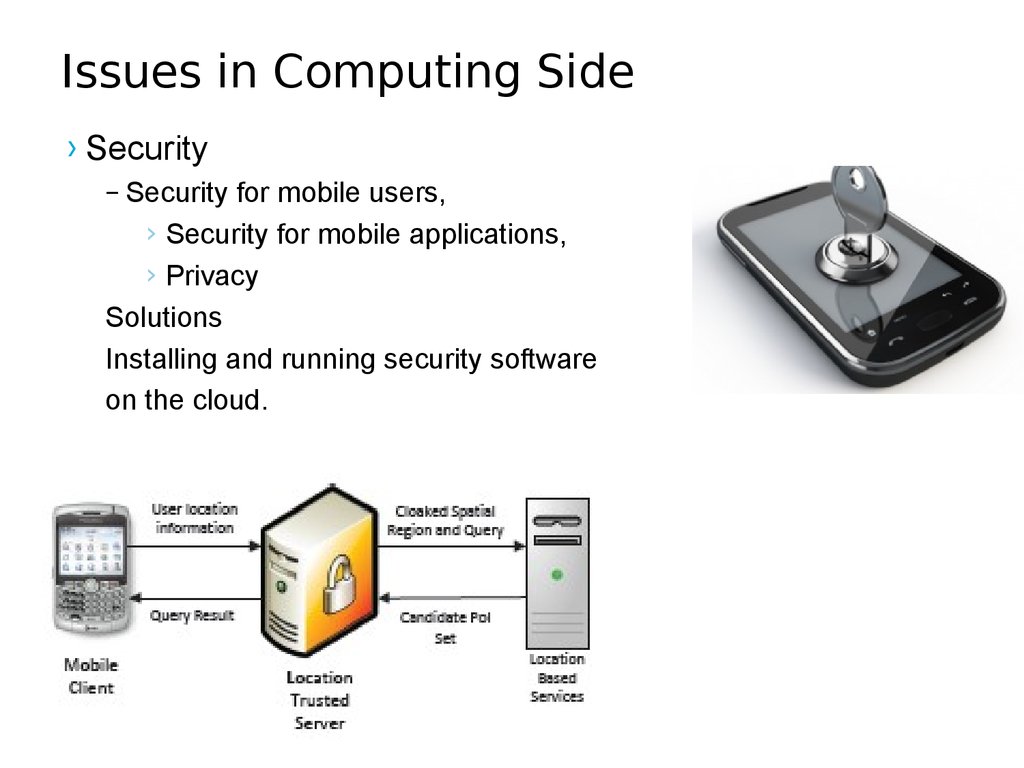
› Security– Security for mobile users,
› Security for mobile applications,
› Privacy
– Security of data on cloud
› Integrity
› Authentication,
45. Issues in Computing Side
› Security– Security for mobile users,
› Security for mobile applications,
› Privacy
Solutions
Installing and running security software
on the cloud.
46. Issues in Computing Side
› Security of data on cloud– Integrity
– Authentication,
› Enhancing the efficiency of data access,
› Context aware mobile cloud services,
47.
Open Issues48.
› How to combine the two technologyseamlessly?
– The main aim of MCC is to provide PC_like services to mobile
devices,
– How can the services from PC’s platforms be transplanted to
mobile devices?
49. Low bandwidth
› Mobility of users› Increasing the demand of mobile users,
– More Bandwidth is required to offer MCC.
› Solutions
– 4G networks (based on LTE)
– Femto cells
– Cognitive radios
50. Low bandwidth: 4G Solutions
› Increases bandwidth for subscribers up to 100 Mbit/s (for “LTEAdvanced” standard) and 128 Mbit/s (for “Wireless MANAdvanced” standard);
› Wider mobile coverage area,
› Quicker and reliable handoff,
› Varied services,
› Quality of service guarantee in LTE and Wi-Fi;
› Coexistence with other networks (HSPA+, GSM, WiMax)
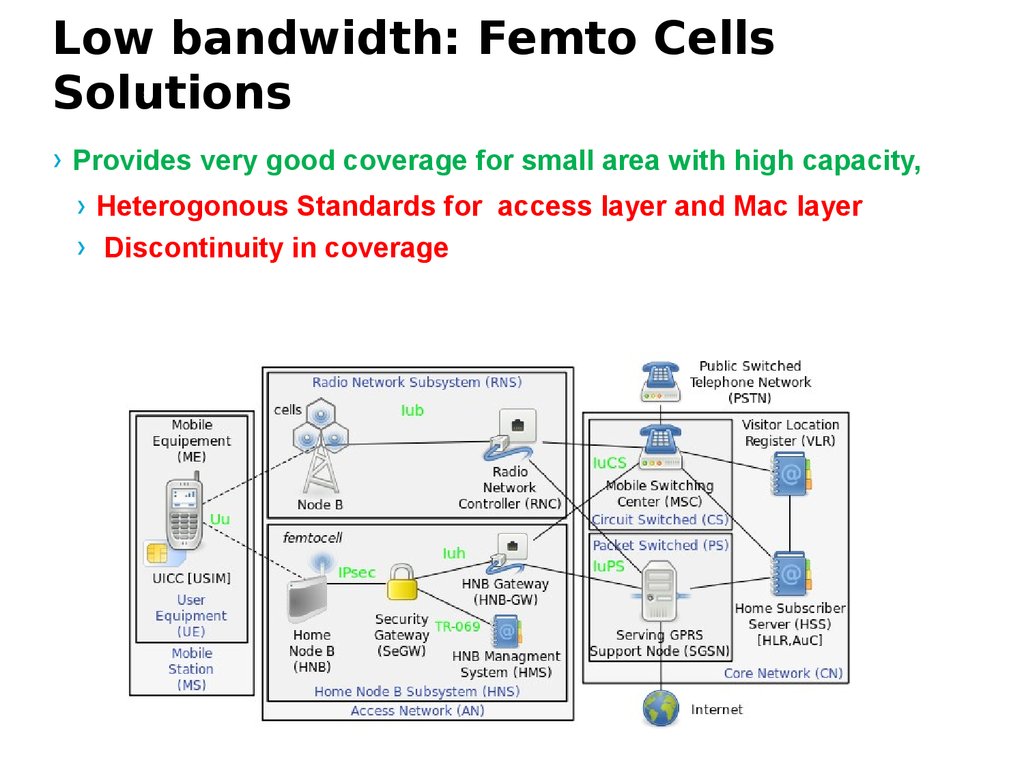
51. Low bandwidth: Femto Cells Solutions
› Provides very good coverage for small area with high capacity,› Heterogonous Standards for access layer and Mac layer
› Discontinuity in coverage
52. Low Bandwidth: Cognitive Radios Solutions
› Cognitive radio can be expected as a solution to achievemore spectrum utilization in mobile communication
environnent and increase the bandwidth efficiency.
– Cost
– Complexity
– Heterogeneity
– No- Interface
– None standard protocols
53. Handover (HO) in MCC
› Due to mobility of users, MCC encounters HO of usersduring the services
– Internetworking HO
– Intranetworking HO
› Latency
› Disconnection
› No protocol for HO between networks in MCC
54. Pricing Mechanism
› Using services in MCC involves with– Mobile service provider (MSP)
– Cloud service provider (CSP).
› MSPs and CSPs have different services management, customers
management, methods of payment and prices.
55. Service Convergence
› The development and competition of cloudservice providers can lead to the fact that in the
near future these services will be differentiated
according to the types, cost, availability and
quality.
› A single cloud is not enough to meet mobile
user’s demands.
› The new scheme is needed in which the mobile
users can utilize multiple cloud in a unified
fashion
› The mobile sky computing, will enable
providers
to
support
a
cross-cloud
communication and enable users to implement
mobile services and applications.
56. References
[1] Hoang T. Dinh, etal, “A survey of Mobile Cloud Computing: architecture,applications, and approaches”, Wireless communications and Mobile Computing
– Wiley, 2012.
[2] M. Satyanarayanan, “Mobile computing: the next decade,” in MCS, June
2010.
[3] Le Guan, etal. “A survey of research on mobile cloud computing”, IEEE/ACIS,
2010.
[4] H. Qui, etal. “Research on mobile cloud computing: review, trend and
perspective”, IEEE 2012.
[5] M. H. Tang, et.al “A dynamic mechanism for handling mobile computing
environmental changes,” in InfoScale, no. 7, pp. 1-9, May 2006.























 internet
internet software
software








