Similar presentations:
Introduction to Cloud Computing. Module 1. Cloud Computing
1.
Fundamental of CloudComputing & Enterprise
Course Code: CSIT243
Module 1
Introduction
Prepared by
Dr. Seema Rawat
Department of Information Technology and Engineering
Amity University Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Info@amity.uz
Prepared by
Dr. Seema Rawat
Department of Information Technology and Engineering
Amity University Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Info@amity.uz
2.
Module 1 Introduction to Cloud Computing1. Introduction to Cloud Computing
2. Basics of cloud computing
3. Architecture: Layers of Cloud Computing
4. Types of cloud computing
5. Cloud Computing Features
6. Cloud Delivery Models
7. Security issues Cloud Computing
8. Advantages and disadvantages pros and cons, benefits
9. Deployment challenges Cloud service development
10.Cloud Computing Challenges
2
3.
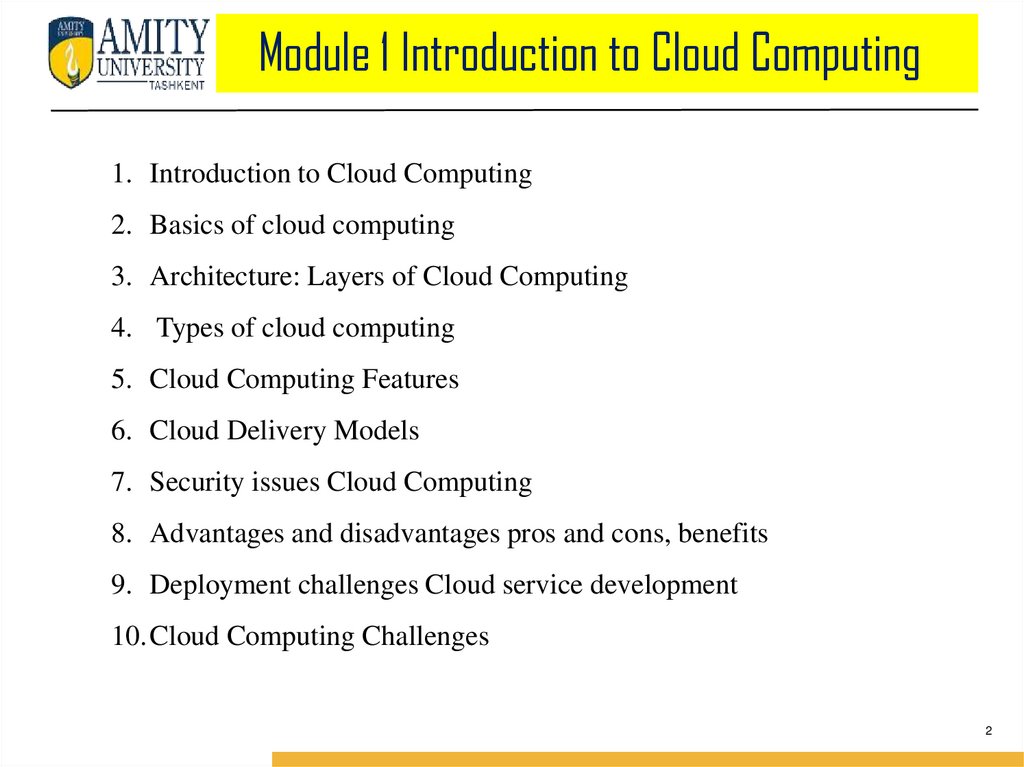
Cloud ComputingCloud Computing provides us a means by which we can access
the applications as utilities, over the Internet. It allows us to
create, configure, and customize applications online.
3
4.
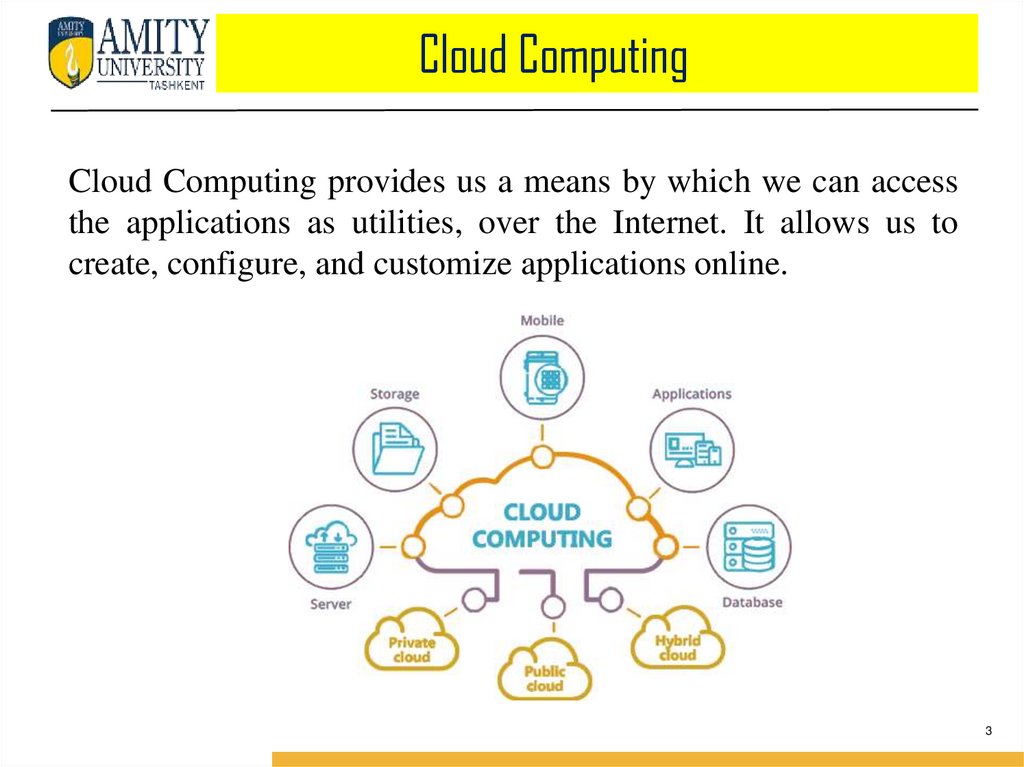
What is Cloud?1. The term Cloud refers to a Network or Internet. In other words, we can say that
Cloud is something, which is present at remote location.
2. Cloud can provide services over network, i.e., on public networks or on private
networks, i.e., WAN, LAN or VPN.
3. Applications such as e-mail, web conferencing, customer relationship
management (CRM),all run in cloud.
4
5.
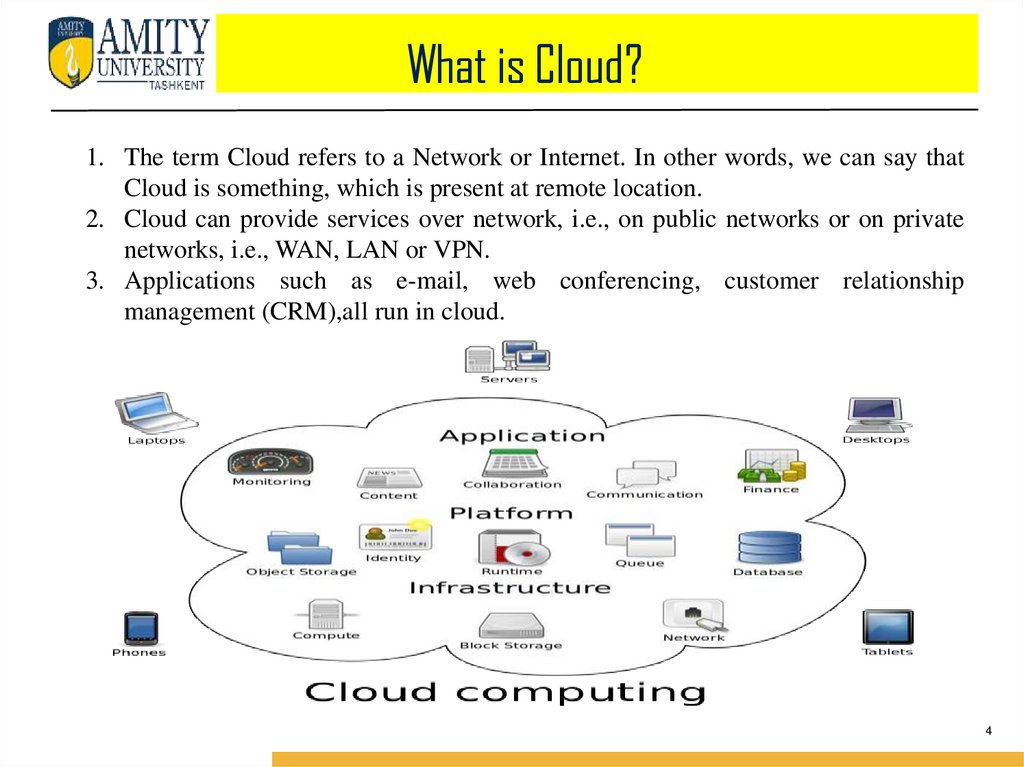
What is Cloud Computing?Cloud Computing refers to manipulating, configuring, and accessing the
applications online. It offers online data storage, infrastructure and application.
5
6.
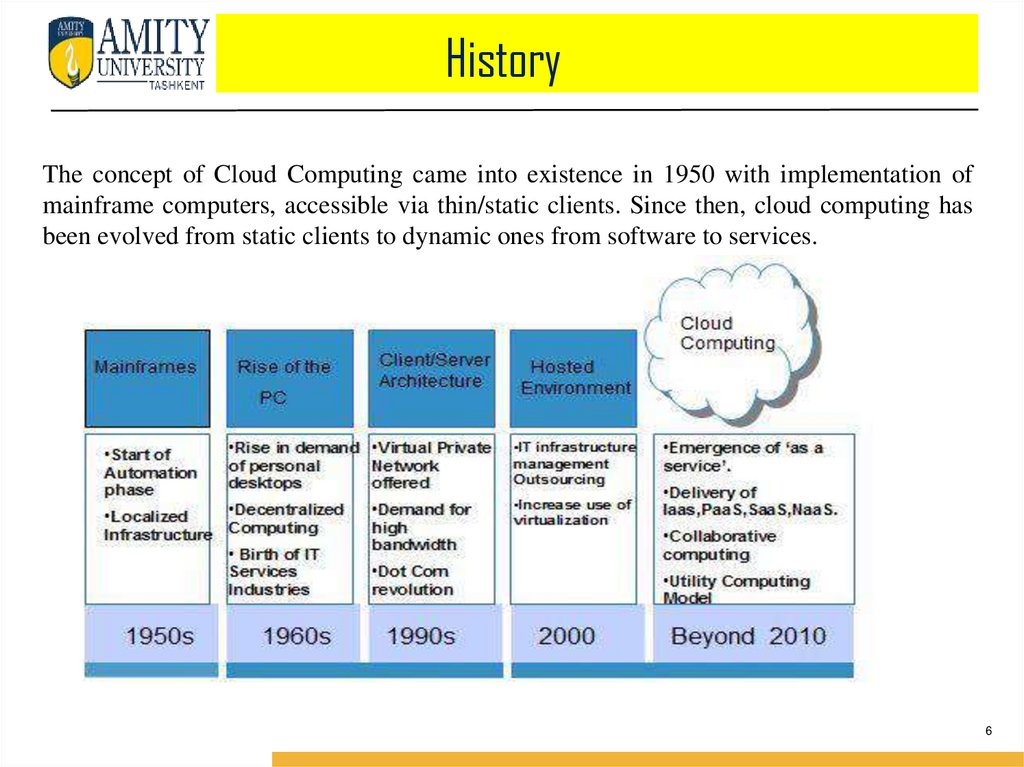
HistoryThe concept of Cloud Computing came into existence in 1950 with implementation of
mainframe computers, accessible via thin/static clients. Since then, cloud computing has
been evolved from static clients to dynamic ones from software to services.
6
7.
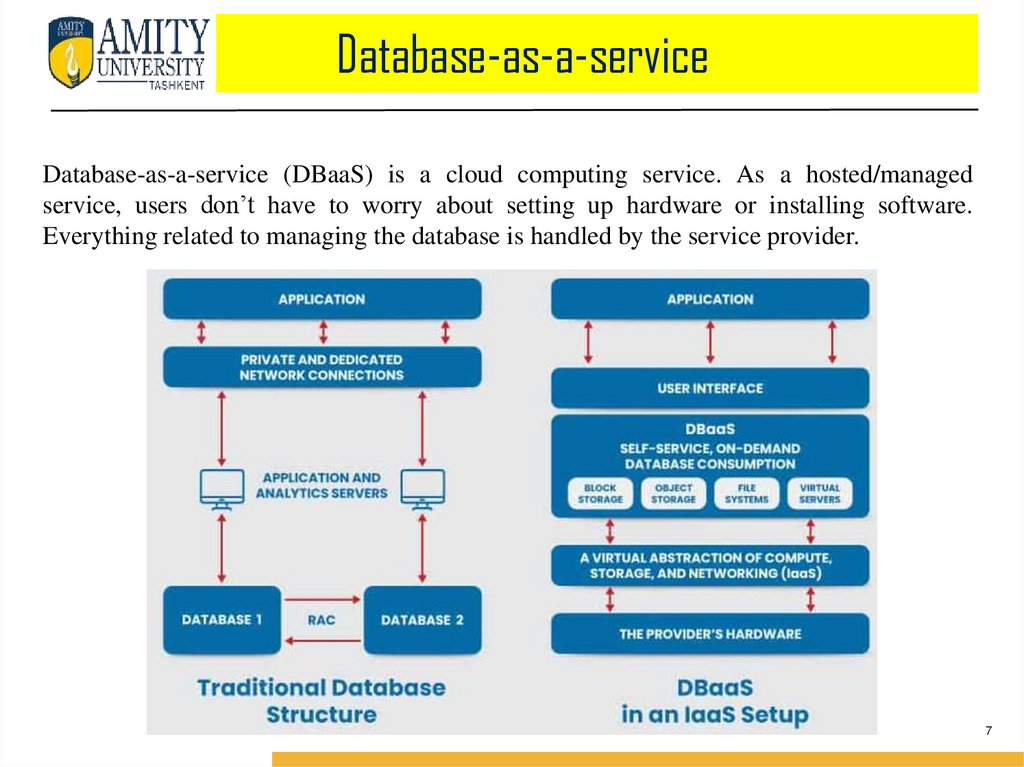
Database-as-a-serviceDatabase-as-a-service (DBaaS) is a cloud computing service. As a hosted/managed
service, users don’t have to worry about setting up hardware or installing software.
Everything related to managing the database is handled by the service provider.
7
8.
Database-as-a-serviceDBaaS (also known as managed database service) is a cloud computing service
that lets users access and use a cloud database system without purchasing and
setting up their own hardware, installing their own database software, or managing
the database themselves.
The cloud provider takes care of everything from periodic upgrades to backups to
ensuring that the database system remains available and secure 24/7.
The market for DBaaS and cloud databases is among the fastest-growing Softwareas-a-Service (SaaS) markets, expected to grow to US $320 billion by 2025.
Major cloud providers offer a wide array of DBaaS options, including relational
database management systems (RDBMs), as well as non-relational or NoSQL
databases, such as document and column stores.
8
9.
Database-as-a-serviceMost DBaaS offerings include integrated management tools that simplify the
process of configuring, monitoring, and maintaining your databases. These
include logging, key management, and activity tracking utilities.
Database management systems available in IBM’s managed database portfolio
include IBM Db2, Cloudant, MongoDB, Elasticsearch, etcd, PostgreSQL, Redis,
and RabbitMQ
9
10.
Benefits of DBaaSDBaaS offers your organization significant financial, operational, and strategic
benefits:
Cost Savings: Laying down infrastructure for database management is expensive;
scaling it as needed is costly and often wasteful.
Scalability—up and down: You can quickly and easily provision additional storage
and computing capacity at run time if you need it, and you can scale down your
database cluster during non-peak usage times to save cost.
Simpler, Less Costly Management: To manage and maintain a database onpremises, you’d need an in-house administrative team. With DBaaS, the cloud
provider manages everything (although you can choose to manage certain aspects
yourself if you wish).
Rapid Development and Faster Time-to-Market: With an on-premises database
system, development teams typically need to request access through IT, a process
that can take days or weeks.
10
11.
Benefits of DBaaSData and Application Security: Cloud database providers typically offer enterprise
grade security, including features like default encryption of data at rest and in-transit
and integrated identity and access management controls. Some also meet specific
regulatory compliance standards.
Reduced Risk: DBaaS offerings from major cloud providers typically include a
service-level agreement (SLA) guaranteeing a certain amount of uptime. In the
unlikely event that your provider doesn’t meet the requirements stipulated in the
SLA, you’ll be compensated for any excess downtime you experience.
Software Quality: The major cloud providers offer a wide variety of highly
configurable DBaaS options—each preselected for quality, so you won’t have to
worry about the wading through hundreds of different databases.
11
12.
Governance / Management as a ServiceGovernance as a Service is an integrated governance platform. An easy and flexible
solution for Compliance, Portfolio, Risk, Demand, Resource, Contract, Supplier
Workflow and Document Management. NHS Change and Regulatory Governance.
Features:
Portfolio Management
Compliance Management
Demand Management
Contract Management
Supplier Management
Resource Management
Governance Workflow Management
Asset Management
Business Process Management
Document Management
12
13.
Benefits of GaaS /MaaSBenefits of GaaS / MaaS are as follows:
Regulation Monitoring and Reporting
Change Governance and Reporting
Resource Balancing
Demand Management
Change Control
Risk Analysis
Remediation Tracking
Automated, repeatable and audited runbooks. Learn and continuously improve.
Track benefits to strategies and track across projects, resources, costs
Reduce cost of change, increase transparency regulation and policy control.
13
14.
GaaS /MaaS14
15.
Storage as a ServiceStorage as a service (SaaS) is a cloud business model in which a company leases or
rents its storage infrastructure to another company or individuals to store data.
Small companies and individuals often find this to be a convenient methodology
for managing backups, and providing cost savings in personnel, hardware and
physical space.
As an alternative to storing magnetic tapes in a traditional manner, IT
administrators are meeting their storage and backup needs by service level
agreements (SLAs) with an SaaS provider, usually on a cost-per-gigabyte-stored and
cost-per-data-transferred basis.
The storage provider provides the client with the software required to access their
stored data.
Storage as a service is prevalent among small to mid-sized businesses, as no initial
budget is required to set up hard drives, servers and IT staff. Storage as a service is
fast becoming the method of choice to all small and medium scale businesses.
15
16.
Benefits of SaaSTop 10 advantage of Storage as a Services:
Cost– factually speaking, backing up data isn’t always cheap, especially when take
the cost of equipment into account. Additionally, there is the cost of the time it takes
to manually complete routine backups. Storage as a service reduces much of the cost
associated with traditional backup methods, providing ample storage space in the
cloud for a low monthly fee.
Invisibility – Storage as a service is invisible, as no physical presence of it is seen
in its deployment and so it doesn’t take up valuable office space.
Security – In this service type, data is encrypted both during transmission and
while at rest, ensuring no unauthorized user access to files.
Automation – Storage as a service makes the tedious process of backing up easy to
accomplish through automation. Users can simply select what and when they want to
backup, and the service does all the rest.
Accessibility – By going for storage as a service, users can access data from smart
phones, netbooks to desktops and so on.
16
17.
Benefits of SaaSSyncing – Syncing ensures your files are automatically updated across all of
your devices. This way, the latest version of a file a user saved on their desktop is
available on your smart phone.
Sharing – Online storage services allow the users to easily share data with just
a few clicks
Collaboration – Cloud storage services are also ideal for collaboration
purposes. They allow multiple people to edit and collaborate on a single file or
document. Thus, with this feature users need not worry about tracking the latest
version or who has made what changes.
Data Protection – By storing data on cloud storage services, data is well
protected by all kind of catastrophes such as floods, earthquakes and human
errors.
Disaster Recovery – as said earlier, data stored in cloud is not only protected
from catastrophes by having the same copy at several places, but can also favor
disaster recovery to ensure business continuity.
17
18.
Storage as a Service18
19.
Testing as a Service (TaaS)TESTING AS A SERVICE (TaaS) is an outsourcing model, in which testing
activities are outsourced to a third party that specializes in simulating real-world
testing environments and finding bugs in the software product.
TaaS is used when
1.A company lacks the skills or resources to carry out testing internally
2.Don't want the in-house developers to influence the results of the testing
process (which they could if done internally)
3.Save on Cost
4.Increase the speed of test execution and reduce software development time.
Types of TaaS are as follows:
1.Functional Testing as a Service: TaaS Functional Testing may include UI/GUI
Testing, regression, integration and automated User Acceptance Testing (UAT) but
not necessary to be part of functional testing
19
20.
Testing as a Service (TaaS)2.Performance Testing as a Service: Multiple users are accessing the application at
the same time. TaaS mimic as a real-world users environment by creating virtual
users and performing the load and stress test
3.Security Testing as a Service: TaaS scans the applications and websites for any
vulnerability
Benefits of TaaS are as follows:
1.Flexible Test Execution and Test Assets
2.Some users claim 40-60% savings in the cloud testing vs. the traditional testing
model
3.Achieve a fast return of investments by eliminating the investment made after
hardware procurement, management, and maintenance, software licensing, etc.
4.Deliver product in quicker time through rapid procurement, project set-up, and
execution
5.Ensure data integrity and anytime anywhere accessibility
6.Reduce operational costs, maintenance costs, and investments
7.Pay as you use
20
21.
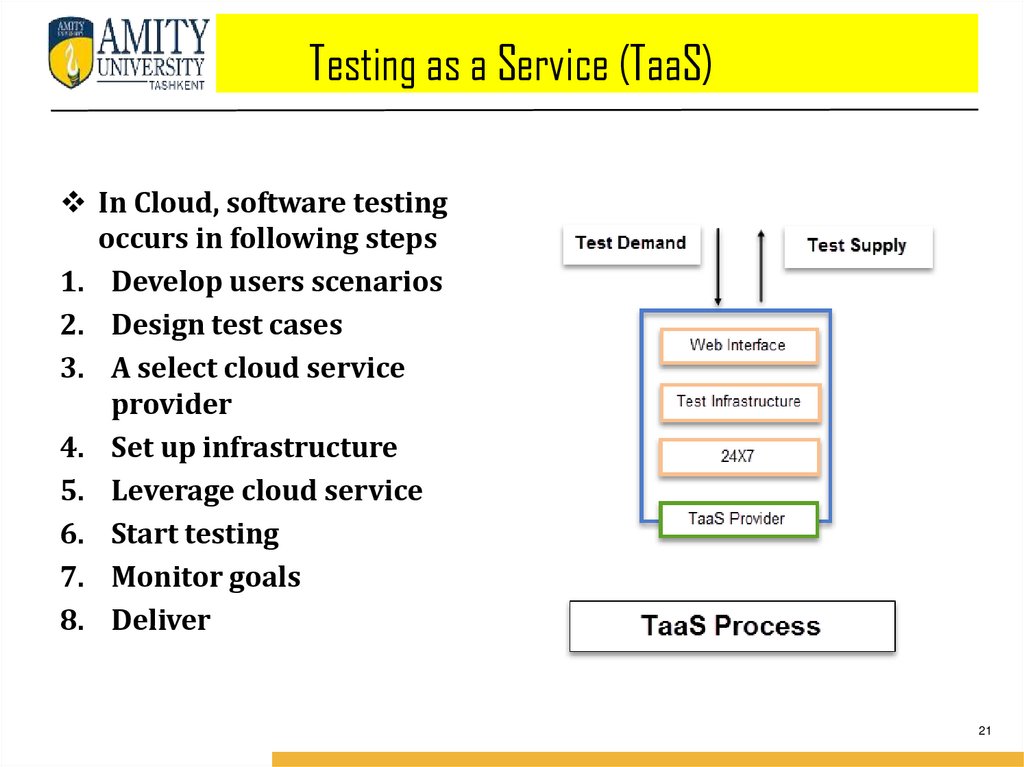
Testing as a Service (TaaS)In Cloud, software testing
occurs in following steps
1. Develop users scenarios
2. Design test cases
3. A select cloud service
provider
4. Set up infrastructure
5. Leverage cloud service
6. Start testing
7. Monitor goals
8. Deliver
21
22.
Benefits of Cloud Computing22
23.
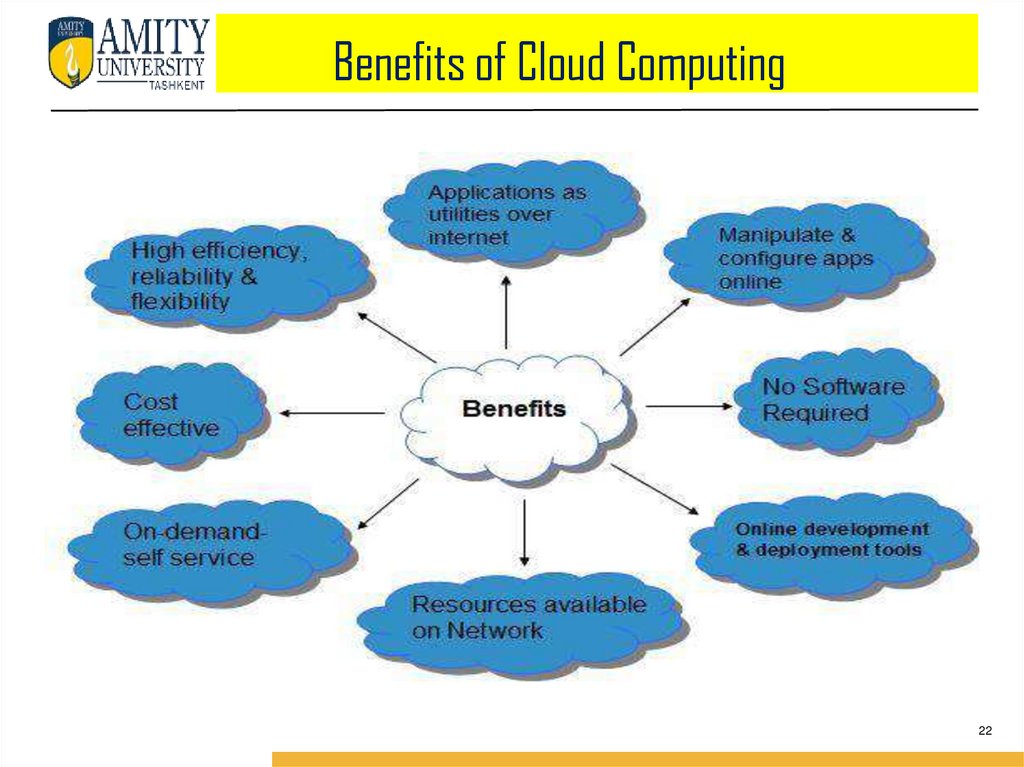
BenefitsCloud Computing has numerous advantages. Some of them are listed below:
1. One can access applications as utilities, over the Internet.
2. Manipulate and configure the application online at any time.
3. It does not require to install a specific piece of software to access or
manipulate cloud application.
4. Cloud Computing offers online development and deployment tools,
programming runtime environment through Platform as a Service model.
5. Cloud resources are available over the network in a manner that provides
platform independent access to any type of clients.
6. Cloud Computing offers on-demand self-service. The resources can be used
without interaction with cloud service provider.
7. Cloud Computing is highly cost effective because it operates at higher
efficiencies with greater utilization. It just requires an Internet connection.
8. Cloud Computing offers load balancing that makes it more reliable
23
24.
Risks of Cloud Computing1.
SECURITY & PRIVACY
It is the biggest concern about cloud computing. Since data
management and infrastructure management in cloud is provided
by third-party, it is always a risk to handover the sensitive
information to such providers.
Although the cloud computing vendors ensure more secure
password protected accounts, any sign of security breach would
result in loss of clients and businesses.
2.
LOCK-IN
It is very difficult for the customers to switch from one Cloud
Service Provider (CSP) to another. It results in dependency on a
particular CSP for service.
24
25.
Risks of Cloud Computing3.
ISOLATION FAILURE
This risk involves the failure of isolation mechanism that separates
storage, memory, routing between the different tenants.
4.
MANAGEMENT INTERFACE COMPROMISE
In case of public cloud provider, the customer management
interfaces are accessible through the Internet.
5.
INSECURE OR INCOMPLETE DATA DELETION
It is possible that the data requested for deletion may not get
deleted. It happens either because extra copies of data are stored but
are not available or disk destroyed also stores data from other tenants.
25
26.
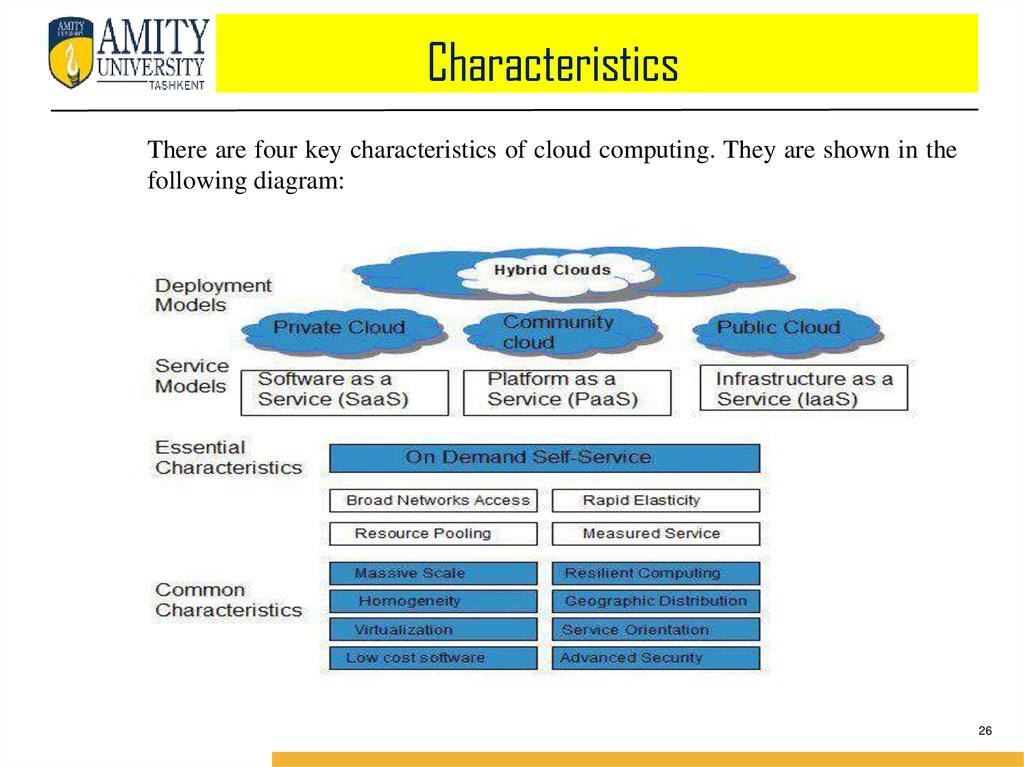
CharacteristicsThere are four key characteristics of cloud computing. They are shown in the
following diagram:
26
27.
CharacteristicsON DEMAND SELF-SERVICE
Cloud Computing allows the users to use web services and resources on
demand. One can logon to a website at any time and use them.
BROAD NETWORK ACCESS
Since Cloud Computing is completely web based, it can be accessed from
anywhere and at any time.
RESOURCE POOLING
Cloud Computing allows multiple tenants to share a pool of resources. One
can share single physical instance of hardware, database and basic
infrastructure.
RAPID ELASTICITY
It is very easy to scale up or down the resources at any time. Resources
used by the customers or currently assigned to customers are automatically
monitored and resources. It make it possible
MEASURED SERVICE
Service Models & Deployment Models
27
28.
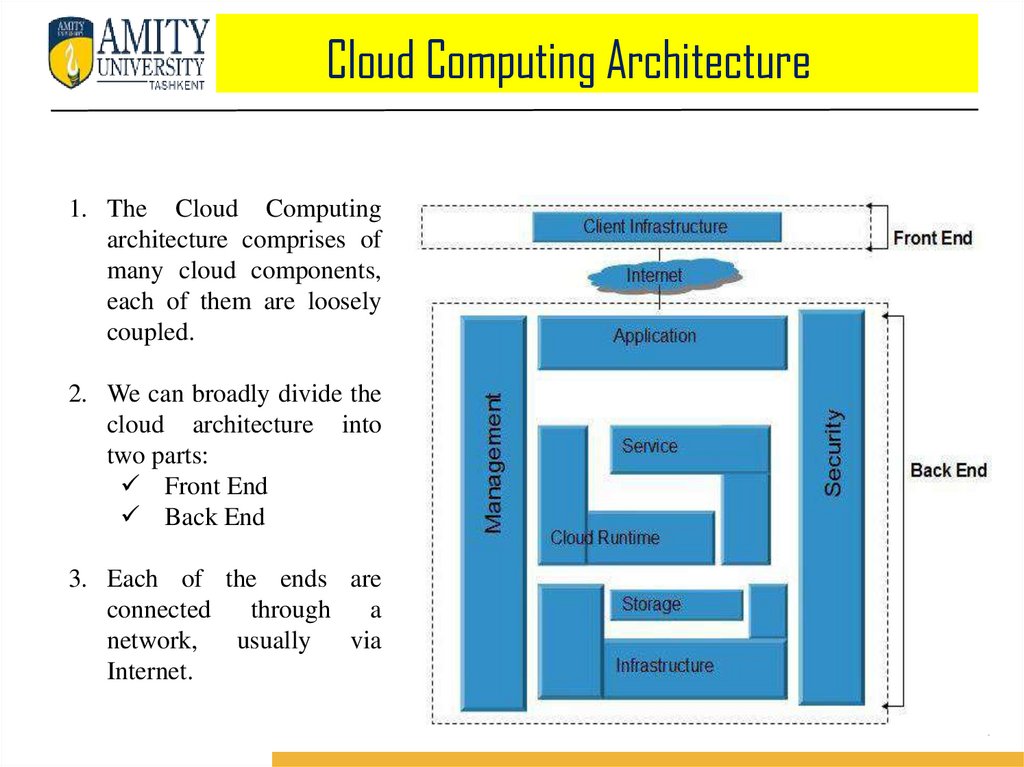
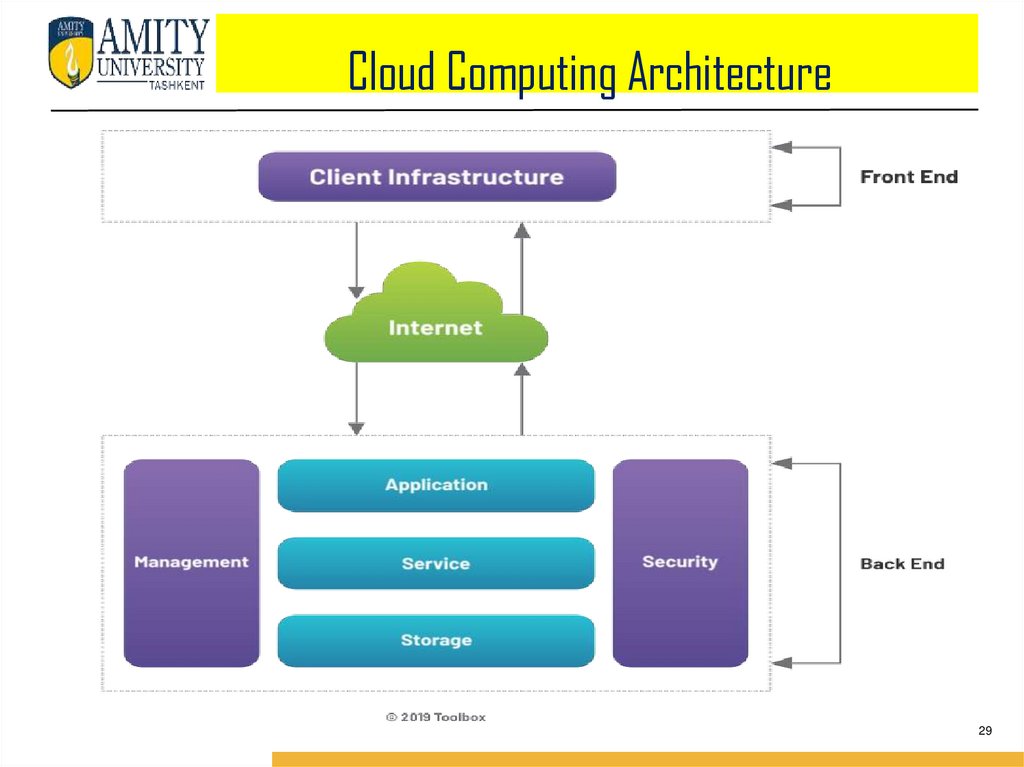
Cloud Computing Architecture1. The Cloud Computing
architecture comprises of
many cloud components,
each of them are loosely
coupled.
2. We can broadly divide the
cloud architecture into
two parts:
Front End
Back End
3. Each of the ends are
connected
through
a
network,
usually
via
Internet.
28
29.
Cloud Computing Architecture29
30.
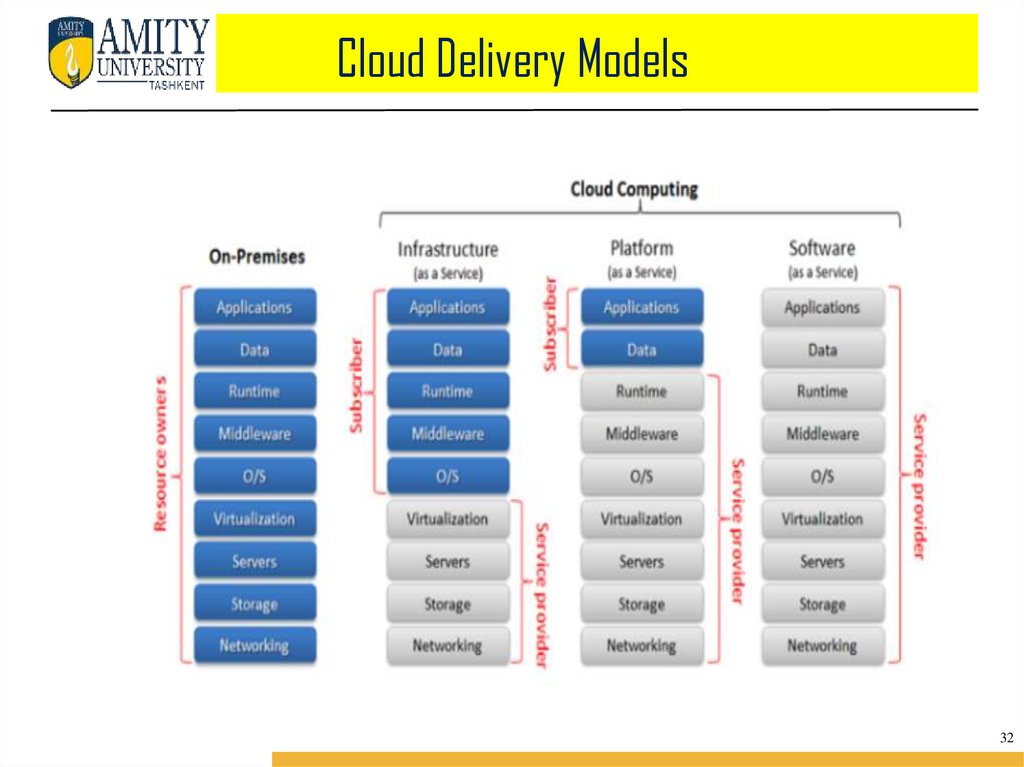
Cloud Computing Architecture1. FRONT END : Front End refers to the client part of cloud computing system. It
consists of interfaces and applications that are required to access the cloud
computing platforms, e.g., Web Browser.
2. BACK END : Back End refers to the cloud itself. It consists of all the resources
required to provide cloud computing services. It comprises of huge data storage,
virtual machines, security mechanism, services, deployment models, servers, etc.
Important Points
It is the responsibility of the back end to provide built-in security mechanism,
traffic control and protocols.
The server employs certain protocols, known as middleware, helps the
connected devices to communicate with each other.
30
31.
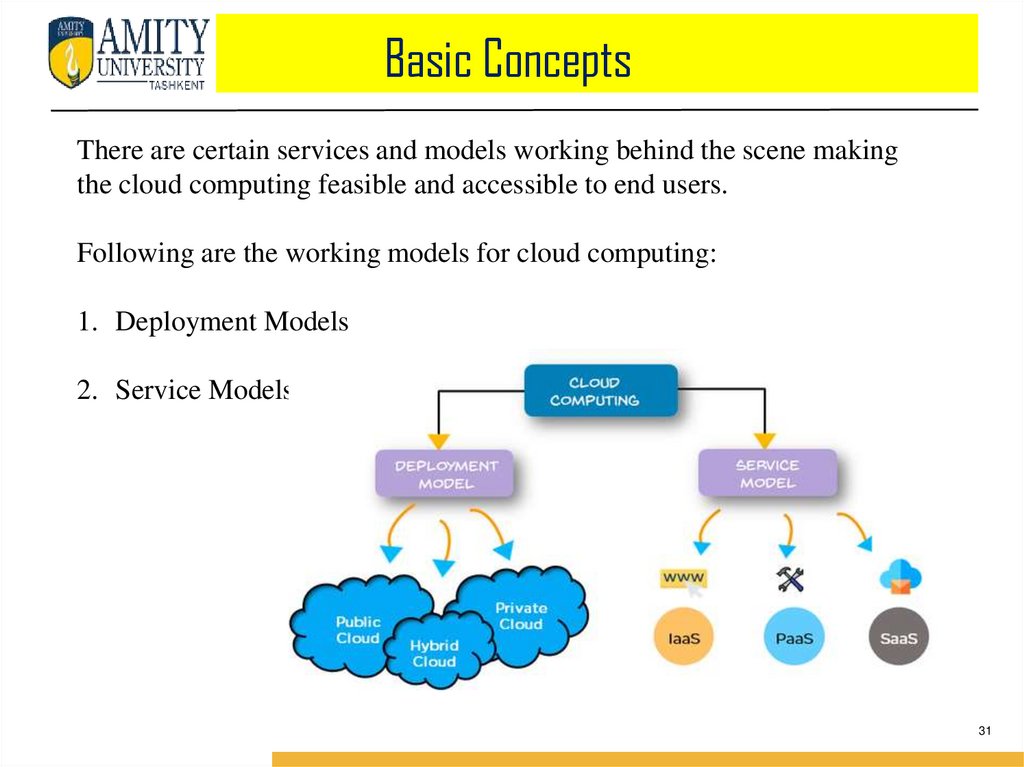
Basic ConceptsThere are certain services and models working behind the scene making
the cloud computing feasible and accessible to end users.
Following are the working models for cloud computing:
1. Deployment Models
2. Service Models
31
32.
DEPLOYMENT MODELS1.
2.
Deployment models define the type of access to the cloud, i.e., how
the cloud is located?
Cloud can have any of the four types of access: Public ,Private,
Hybrid and Community.
32
33.
Deployment Models1. PUBLIC CLOUD :The Public Cloud allows systems and services to be easily
accessible to the general public. Public cloud may be less secure because of its
openness, e.g., e-mail.
2. PRIVATE CLOUD :The Private Cloud allows systems and services to be
accessible within an organization. It offers increased security because of its
private nature.
3. COMMUNITY CLOUD : The Community Cloud allows systems and services
to be accessible by group of organizations.
4. HYBRID CLOUD :The Hybrid Cloud is mixture of public and private cloud.
However, the critical activities are performed using private cloud while the
non-critical activities are performed using public cloud.
33
34.
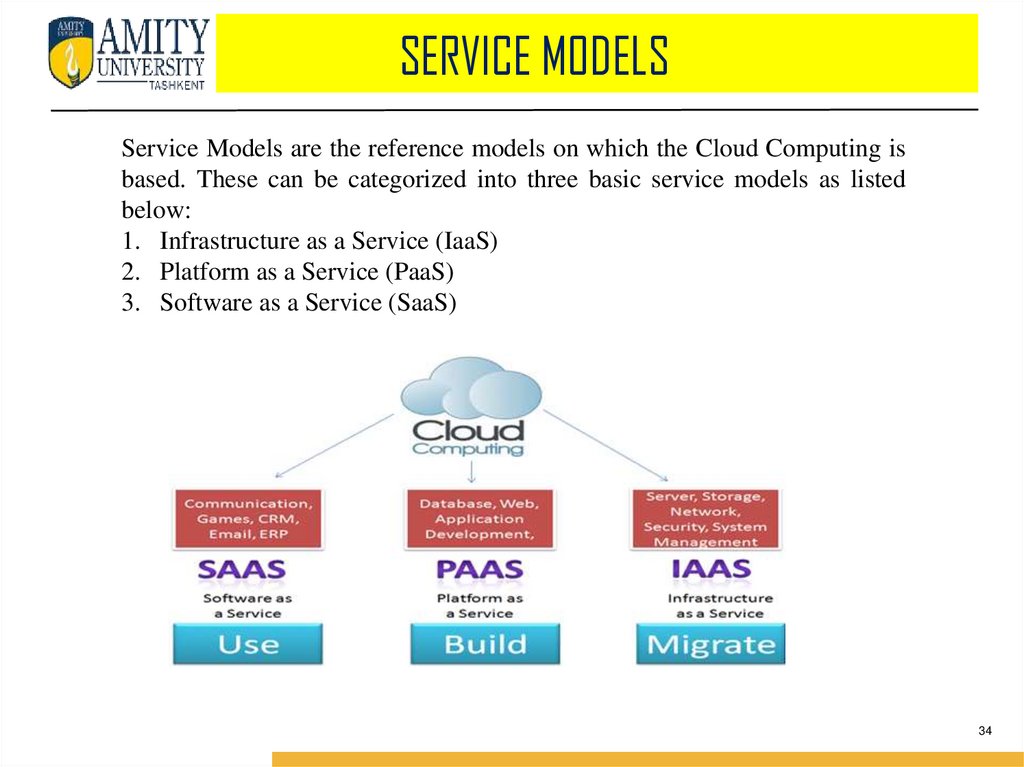
SERVICE MODELSService Models are the reference models on which the Cloud Computing is
based. These can be categorized into three basic service models as listed
below:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
34
35.
SERVICE MODELS1. There are many other service models
all of which can take the form like
XaaS, i.e., Anything as a Service.
2. This can be Network as a Service,
Business as a Service, Identity as a
Service, Database as a Service or
Strategy as a Service.
3. The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
is the most basic level of service.
4. Each of the service models make use
of the underlying service model, i.e.,
each inherits the security and
management mechanism from the
underlying model, as shown diagram
35
36.
SERVICE MODELS1. INFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICE (IAAS) : IaaS provides access to
fundamental resources such as physical machines, virtual machines,
virtual storage, etc.
2. PLATFORM AS A SERVICE (PAAS) : PaaS provides the runtime
environment for applications, development & deployment tools, etc.
3. SOFTWARE AS A SERVICE (SAAS) : SaaS model allows to use
software applications as a service to end users.
36
37.
CLOUD DELIVERY MODELS1. There are three elementary cloud service delivery
models which are denoted as SPI MODEL.
2. The term SPI is an acronym that stands for Software,
Platform and Infrastructure.
a)
b)
c)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service model (IaaS)
22
38.
Cloud Delivery Models1.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
a) In the Software as a Service (SaaS) model, the client can access the provider’s
infrastructure through an interface. Most commonly used interfaces are web
browsers.
b) In this model a single instance on the service provider’s end supports multiple
access instants on the client’s side.
c) SaaS is closely related to the application service provider (ASP) and on
demand computing software delivery models. The hosted application
management model of SaaS is similar to ASP, where the provider hosts the
customer’s software and delivers it to approved end users over the internet.
d) Organizations can integrate SaaS applications with other software using
application programming interfaces (APIs). For example, a business can write
its own software tools and use the SaaS provider's APIs to integrate those tools
with the SaaS offering.
23
39.
Cloud Delivery ModelsAdvantages : SaaS removes the need for organizations to install and run applications on their
own computers or in their own data centers. This eliminates the expense of hardware
acquisition, provisioning and maintenance, as well as software licensing, installation and
support. Other benefits of the SaaS model include:
a) Flexible payments: Rather than purchasing software to install, or
additional hardware to support it, customers subscribe to a SaaS offering.
Generally, they pay for this service on a monthly basis using a pay-as-you-go
model.
b) Scalable usage: Cloud services like SaaS offer high vertical scalability,
which gives customers the option to access more, or fewer, services or
features on-demand.
c) Automatic updates: Rather than purchasing new software, customers can
rely on a SaaS provider to automatically perform updates and patch
management. This further reduces the burden on in-house IT staff.
d) Accessibility and persistence: Since SaaS applications are delivered over
the Internet, users can access them from any Internet-enabled device and
location.
24
40.
Cloud Delivery ModelsDisadvantages :
a)
SaaS also poses some potential disadvantages. Businesses must rely
on outside vendors to provide the software, keep that software up and
running, track and report accurate billing and facilitate a secure
environment for the business' data.
b) Issues can arise when providers experience service disruptions,
impose unwanted changes to service offerings, or experience a
security breach, all of which can have a profound effect on the
customers' ability to use SaaS offerings.
c)
To proactively mitigate these issues, customers should understand
their SaaS provider's service-level agreement, and make sure it is
enforced.
25
41.
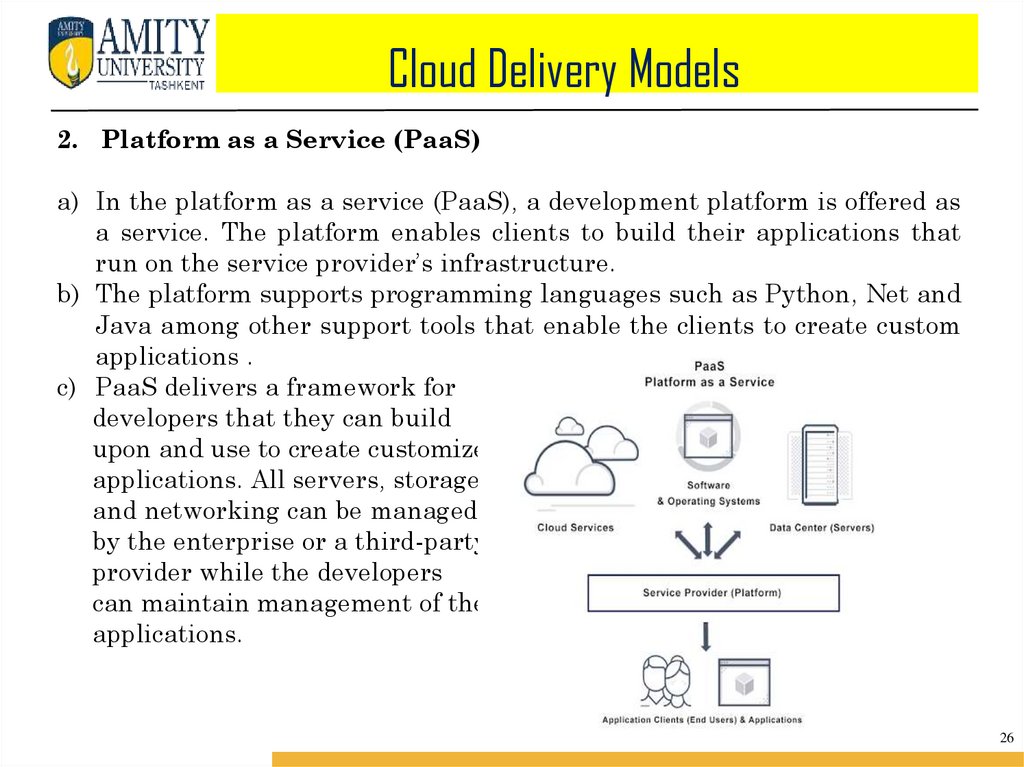
Cloud Delivery Models2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
a) In the platform as a service (PaaS), a development platform is offered as
a service. The platform enables clients to build their applications that
run on the service provider’s infrastructure.
b) The platform supports programming languages such as Python, Net and
Java among other support tools that enable the clients to create custom
applications .
c) PaaS delivers a framework for
developers that they can build
upon and use to create customized
applications. All servers, storage,
and networking can be managed
by the enterprise or a third-party
provider while the developers
can maintain management of the
applications.
26
42.
Cloud Delivery ModelsAdvantages :
No matter the size of your company, using PaaS offers numerous
advantages, including:
a)
b)
c)
d)
a)
b)
c)
Simple, cost-effective development and deployment of apps
Scalable
Highly available
Developers can customize apps without the headache of
maintaining the software
Significant reduction in the amount of coding needed
Automation of business policy
Easy migration to the hybrid model
27
43.
Cloud Delivery ModelsDisadvantages:
a) Data security : Organizations can run their own apps and services using
PaaS solutions, but the data residing in third-party, vendor-controlled cloud
servers poses security risks and concerns.
b) Integrations: The complexity of connecting the data stored within an
onsite data center or off-premise cloud is increased, which may affect which
apps and services can be adopted with the PaaS offering.
c) Vendor lock-in: Business and technical requirements that drive decisions
for a specific PaaS solution may not apply in the future. If the vendor has
not provisioned convenient migration policies, switching to alternative PaaS
options may not be possible without affecting the business.
d) Runtime issues: In addition to limitations associated with specific apps
and services, PaaS solutions may not be optimized for the language and
frameworks of your choice.
e) Examples of PaaS : Popular examples of PaaS include AWS Elastic Beanstalk,
Windows Azure, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, and OpenShift.
28
44.
Cloud Delivery Models3. Infrastructure as a Service Model (IaaS)
a)
For the Infrastructure as a service model (IaaS), the service provider
provides basic computing abilities to the clients.
b) The client gains control of the storage, networks, and other computing
capabilities by renting the services from the provider.
c) Though the customer has control over the storage system and operating
system, they do not control the overall cloud infrastructure.
d) IaaS clients are responsible for managing aspects such as applications,
runtime, OSes, middleware, and data.
e) However, providers of the IaaS manage the servers, hard drives,
networking, virtualization, and storage.
f) Some providers even offer more services beyond the virtualization layer,
such as databases or message queuing.
29
45.
Cloud Delivery ModelsAdvantages: IaaS offers many advantages, including:
a) The most flexible cloud computing model
b) Easy to automate deployment of storage, networking, servers, and
processing power
c) Hardware purchases can be based on consumption
d) Clients retain complete control of their infrastructure
e) Resources can be purchased as-needed
f) Highly scalable
30
46.
CLOUD DELIVERY MODELSIaaS Limitations and Concerns
a) Security : While the customer is in control of the apps, data, middleware, and the
OS platform, security threats can still be sourced from the host or other virtual
machines (VMs).
b) Internal resources and training : Additional resources and training may be
required for the workforce to learn how to effectively manage the infrastructure.
Customers will be responsible for data security, backup, and business continuity.
c) Multi-tenant security: Since the hardware resources are dynamically allocated
across users as made available, the vendor is required to ensure that other customers
cannot access data deposited to storage assets by previous customers.
d) Examples of IaaS : Popular examples of IaaS include DigitalOcean, Linode,
Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metacloud, Microsoft Azure, and
Google Compute Engine (GCE).
31
47.
Cloud Delivery Models32
48.
security issues cloud computingSecurity issues experienced with software-as-a-service (SaaS)
Lack of visibility into what data is within cloud applications
Theft of data from a cloud application by malicious actor
Incomplete control over who can access sensitive data
Inability to monitor data in transit to and from cloud applications
Cloud applications being provisioned outside of IT visibility (e.g., shadow
IT)
Lack of staff with the skills to manage security for cloud applications
Inability to prevent malicious insider theft or misuse of data
Advanced threats and attacks against the cloud application provider
Inability to assess the security of the cloud application provider’s
operations
Inability to maintain regulatory compliance
33
49.
security issues cloud computingSecurity issues experienced with infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)
Cloud workloads and accounts being created outside of IT visibility (e.g.,
shadow IT)
Incomplete control over who can access sensitive data
Theft of data hosted in cloud infrastructure by malicious actor
Lack of staff with the skills to secure cloud infrastructure
Lack of visibility into what data is in the cloud
Inability to prevent malicious insider theft or misuse of data
Lack of consistent security controls over multi-cloud and on-premises
environments
Advanced threats and attacks against cloud infrastructure
Inability to monitor cloud workload systems and applications for
vulnerabilities
Lateral spread of an attack from one cloud workload to another
34
50.
security issues cloud computingSecurity issues experienced with platform-as-a-service (PaaS)
Lack of interoperability: Diverse computational resources may lead to
security breaches if objects’ access to the resources cannot be handled in a
standard way. This may cause a set of resources to halt or a setting that is
proven to be secure for a specific resource to be a breach for another.
Vulnerable hosts: Multi-tenancy has been studied since the earliest
multi-user operating systems. Today, the concept covers a wider
perspective where the user objects are spread over interconnected multiuser hosts.
Vulnerable objects: The security of an object can be breached in one of
the following three ways in PaaS clouds. First, service provider may access
any user object that reside on its hosts. Second, users may mutually attack
each other’s objects that are the tenants of the same host. Finally, a third
party may directly attack a user object.
35
51.
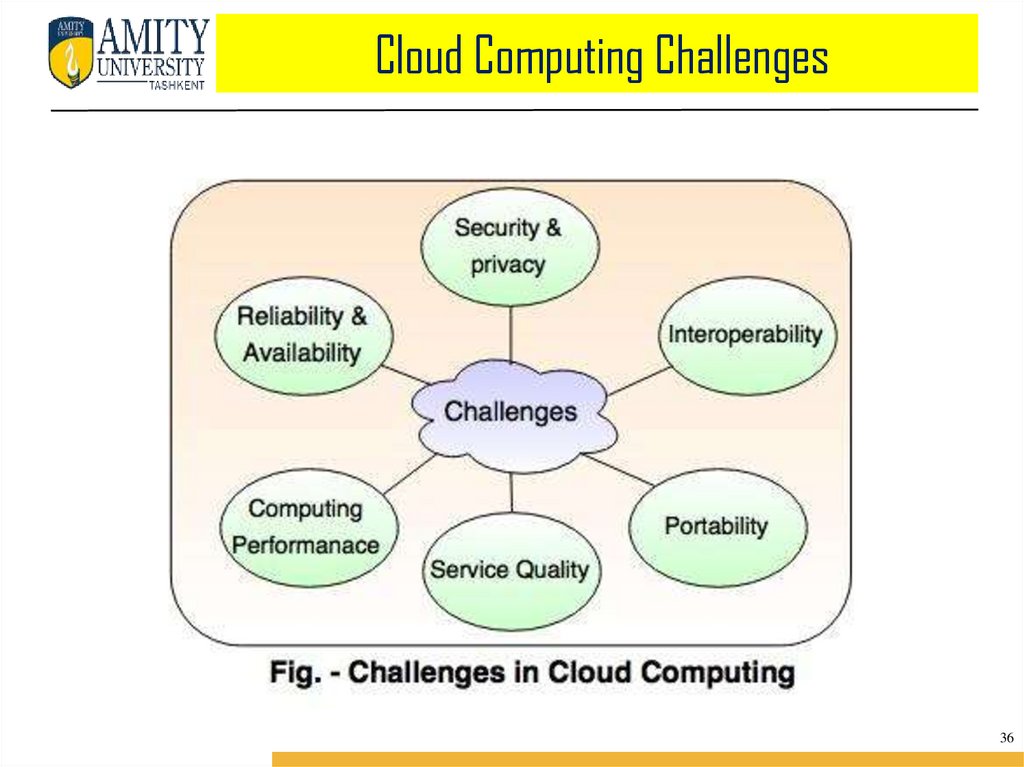
Cloud Computing Challenges36
52.
Cloud Computing Risks & ChallengesSecurity issues : To ensure your organization’s privacy and security is
intact, verify the SaaS provider has secure user identity management,
authentication, and access control mechanisms in place.
Cost management and containment : For the most part cloud
computing can save businesses money. In the cloud, an organization can
easily ramp up its processing capabilities without making large
investments in new hardware. Businesses can instead access extra
processing through pay-as-you-go models from public cloud providers.
Lack of resources/expertise: Organizations are increasingly placing
more workloads in the cloud while cloud technologies continue to rapidly
advance. Due to these factors, organizations are having a tough time
keeping up with the tools.
36
53.
Cloud Computing Risks & ChallengesGovernance/Control: To ensure your organization’s privacy and security
is intact, verify the SaaS provider has secure user identity management,
authentication, and access control mechanisms in place.
Compliance : That is an issue for anyone using backup services or cloud
storage. Every time a company moves data from the internal storage to a
cloud, it is faced with being compliant with industry regulations and laws.
Managing multiple clouds : The state of multi-cloud has grown
exponentially in recent years. Companies are shifting or combining public
and private clouds and as mentioned earlier, tech giants like Alibaba and
Amazon are leading the way.
Performance : The next prominent challenges of moving to cloud
computing expand on this partnership. Nevertheless, this partnership
often provides businesses with innovative technologies they wouldn’t
otherwise be able to access.
37
54.
Cloud service developmenta)
Cloud application development services aim to provide assistance with
developing, migrating or otherwise working on applications in order to
ensure that they run capably on cloud platforms.
b) It can include services related to consulting, development, migration,
integration or testing. Cloud application development service vendors may
help determine a choice of cloud platform, for example, private, public or
hybrid, or help a client figure out how to move functionality from outdated
legacy systems to the cloud.
c)
Cloud application development services are often presented along with
certain benefits, such as reducing risk for IT implementation or decreasing
time-to-market for applications. Businesses continue to use a variety of
cloud application development services in order to "get online" with cloud
applications that support their core operations.
39
55.
Deployment challenges1. Privacy and Security : Cloud architecture do not automatically grant security
compliance for the end-user data or apps on them, so apps written for cloud have to
be secure in their own terms. Some of the responsibility for this does fall to cloud
vendors. Cloud computing introduces another level of risks because essential services
are often outsourced to a third party, making it harder to maintain data integrity and
privacy.
2. Client incomprehension : There are also too many misunderstandings about how
public and private cloud work together, misunderstandings about how easy it is to
move from one kind of infrastructure to another. A good way to combat this is to
prevent customers with real-world examples of what is possible and why so that they
can base their understanding on the actual working.
56.
Cloud Computing Risks & ChallengesBuilding a private cloud : Creating an internal or private cloud will
cause a significant benefit: having all the data in-house. But IT managers
and departments will need to face building and gluing it all together by
themselves, which can cause one of the challenges of moving to cloud
computing extremely difficult.
Segmented usage and adoption : Instead, ad-hoc strategies sprouted,
fueled by several components. One of them was the speed of cloud
adoption. Another one was the staggered expiration of data center
contracts/equipment, which led to intermittent cloud migration. Finally,
there also were individual development teams using the public cloud for
specific applications or projects.
Migration : This is a process of moving an application to a cloud. An
although moving a new application is a straightforward process, when it
comes to moving an existing application to a cloud environment, many
cloud challenges arise.
38
57.
Deployment challenges3. Data Security : One of the major concerns associated with cloud computing is its
dependency on the cloud service provider. For uninterrupted and fast cloud service
you need to choose a vendor with proper infrastructure and technical expertise.
4. Address growing integration complexities : Many applications have complex
integration needs to connect to applications on the cloud network, as well as to other
on-premises applications. These include integrating existing cloud services with
existing enterprise applications and data structures.
5. Reliability and availability : Cloud service providers still lack the round-the-clock
service, this result in frequent outages. It is important to monitor the service being
provided using internal or third-party tools. It is vital to have plans to supervise usage,
performance and business dependency of these cloud services.
40
58.
Deployment challenges6. Performance and Bandwidth Cost : Businesses can save money on
hardware but they have to spend more for the bandwidth. This could be a
low cost for small applications but can be significantly high for the dataintensive applications.
7. Selecting the right cloud set-up : There are three types of cloud
environments available – private, public and hybrid. The secret of successful
cloud implementation lies in choosing the most appropriate cloud set-up.
Big companies feel safer with their vast data in private cloud environment,
small enterprises often benefit economically by hosting their services in
public cloud.
8. Dependency on Service Providers : One of the major issues with cloud
computing is its dependency on the service provider. The companies
providing cloud services charge businesses for utilizing cloud computing
services based on usage. Customers typically subscribe to cloud services to
avail their services.
41
59.
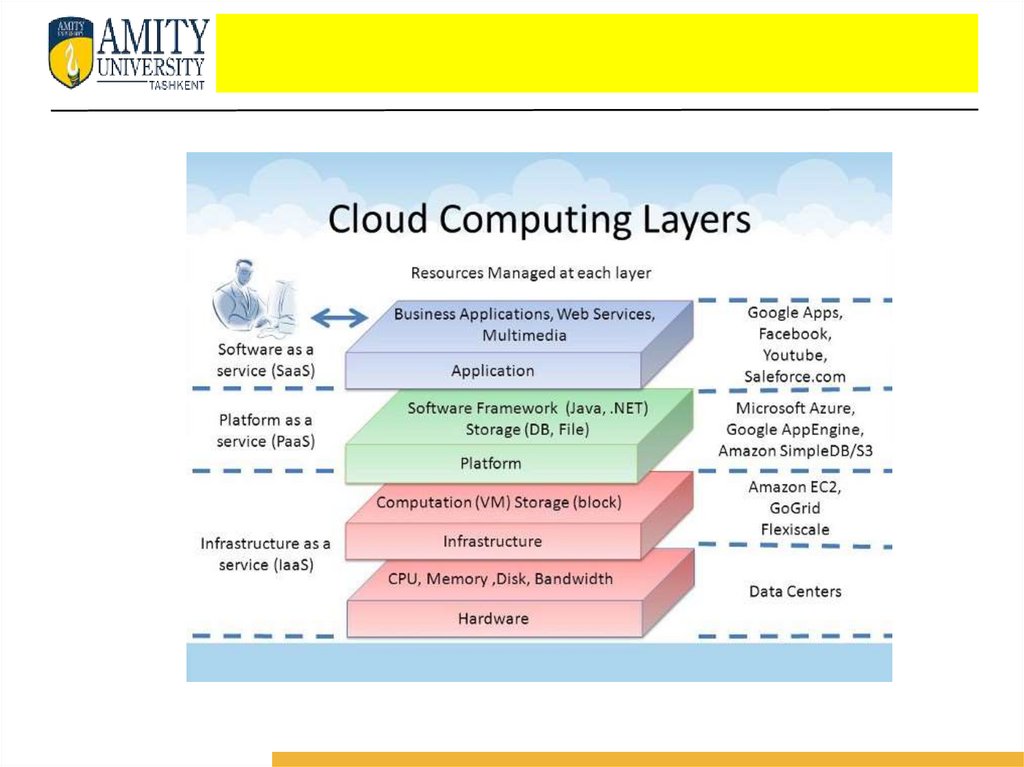
Layers of Cloud Computing• To gain a better understanding of the aforementioned terms, it is
important to understand the underlying components and layers which
make up the cloud.
• The architecture of Cloud Computing is mainly divided into gour
different layers as:
a) Hardware
b) Infrastructure
c) Platform
d) Software or Application
60.
61.
Types of Cloud ComputingThere are many different types of cloud computing used by companies
around the world. The most commonly used types of cloud computing
covers its types based on deployment and cloud services.
•These types are as follows are as follows.
1.Public Cloud
2.Private Cloud
3.Hybrid Cloud
4.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
5.Platform as a Service (PaaS)
6.Softwarere as a Service (SaaS)
62.
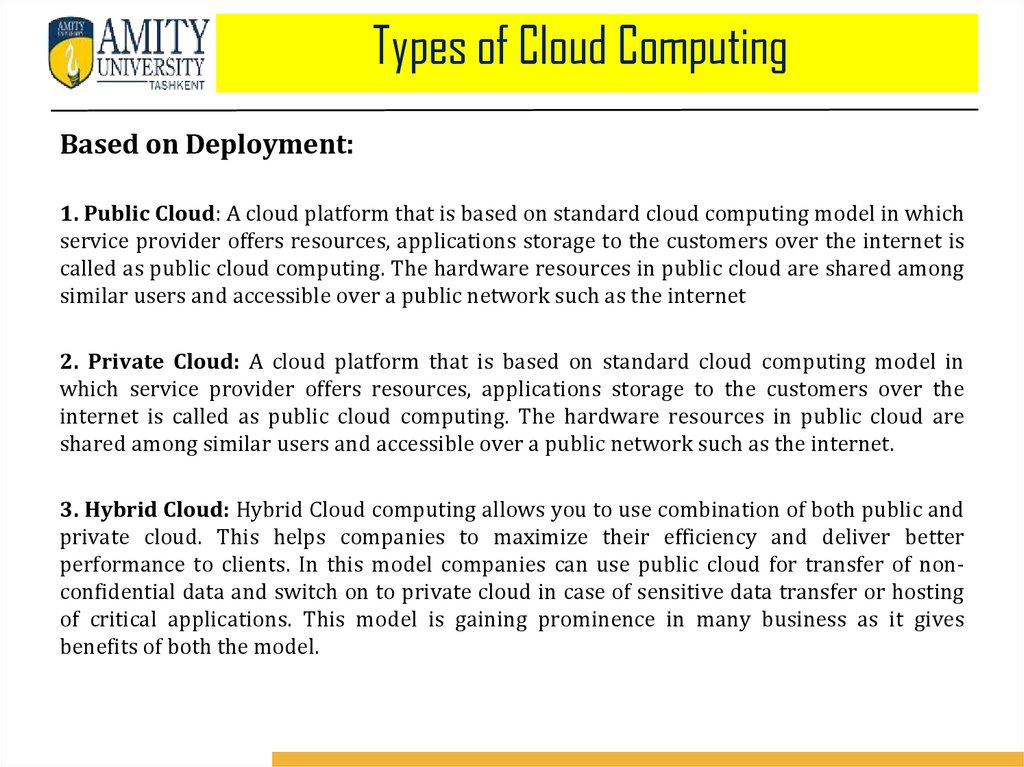
Types of Cloud ComputingBased on Deployment:
1. Public Cloud: A cloud platform that is based on standard cloud computing model in which
service provider offers resources, applications storage to the customers over the internet is
called as public cloud computing. The hardware resources in public cloud are shared among
similar users and accessible over a public network such as the internet
2. Private Cloud: A cloud platform that is based on standard cloud computing model in
which service provider offers resources, applications storage to the customers over the
internet is called as public cloud computing. The hardware resources in public cloud are
shared among similar users and accessible over a public network such as the internet.
3. Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid Cloud computing allows you to use combination of both public and
private cloud. This helps companies to maximize their efficiency and deliver better
performance to clients. In this model companies can use public cloud for transfer of nonconfidential data and switch on to private cloud in case of sensitive data transfer or hosting
of critical applications. This model is gaining prominence in many business as it gives
benefits of both the model.
63.
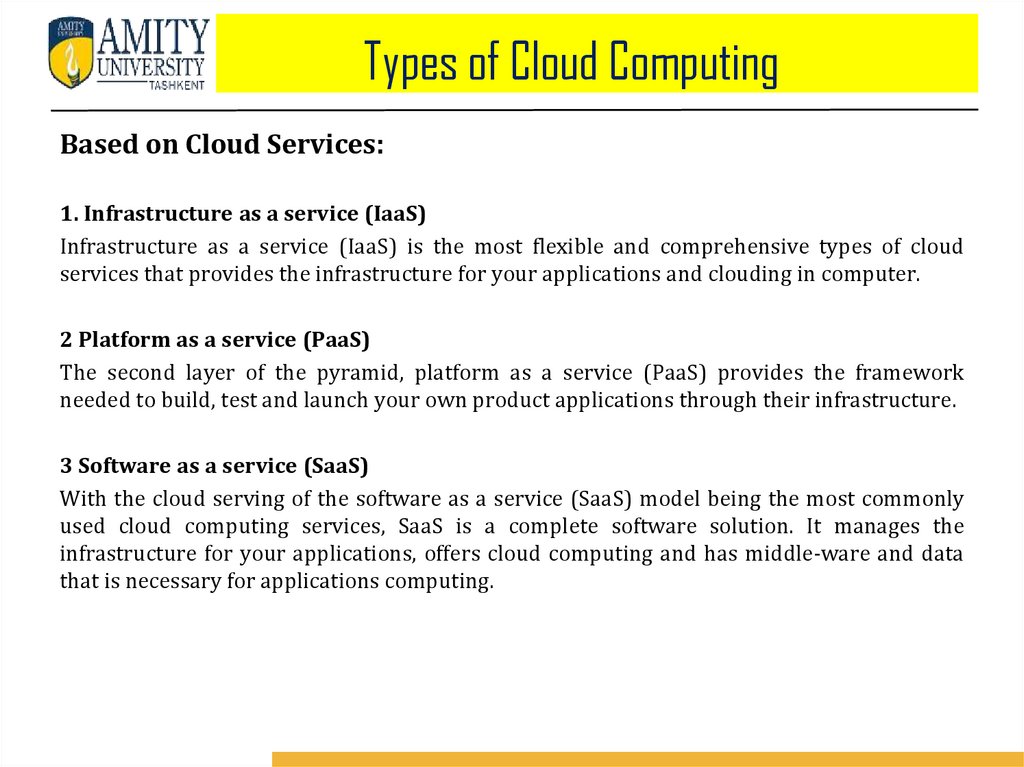
Types of Cloud ComputingBased on Cloud Services:
1. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is the most flexible and comprehensive types of cloud
services that provides the infrastructure for your applications and clouding in computer.
2 Platform as a service (PaaS)
The second layer of the pyramid, platform as a service (PaaS) provides the framework
needed to build, test and launch your own product applications through their infrastructure.
3 Software as a service (SaaS)
With the cloud serving of the software as a service (SaaS) model being the most commonly
used cloud computing services, SaaS is a complete software solution. It manages the
infrastructure for your applications, offers cloud computing and has middle-ware and data
that is necessary for applications computing.
64.
Types of Cloud Computing.
65.
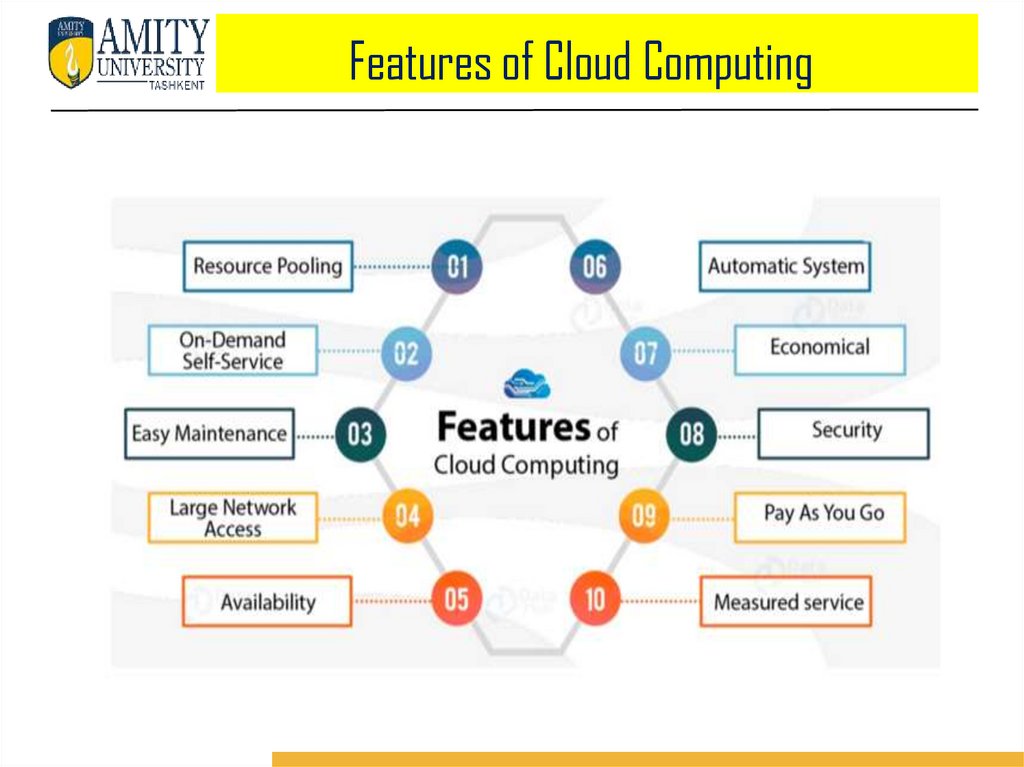
Features of Cloud Computing1. Some of the features that make cloud computing more suitable for the
industries as well as an individual. For example, we can pool any kind of
resources like CPU, GPU etc at any time.
2. Cloud Computing is an on-demand service which is very easy to maintain and
can be accessed from anywhere which are highly available.
3. Cloud computing is an automatic system which works automatically at the
backend for this we don’t need to worry about.
4. Cloud computing is very secure and cheap because of their pay as you go policy
for this we have to pay for only those resources which are being used. These
features make cloud computing more reliable easy to use and cheap service.





























 internet
internet








