Similar presentations:
Pathology Of Hypertension
1.
Pathology Of Hypertension2. Hypertension - Introduction
Silent Killer – painless – complications
Leading risk factor – MI & Stroke
Number one reason for drug prescription
25% of population, <35% aware
Complications alert to diagnosis but
late…
3.
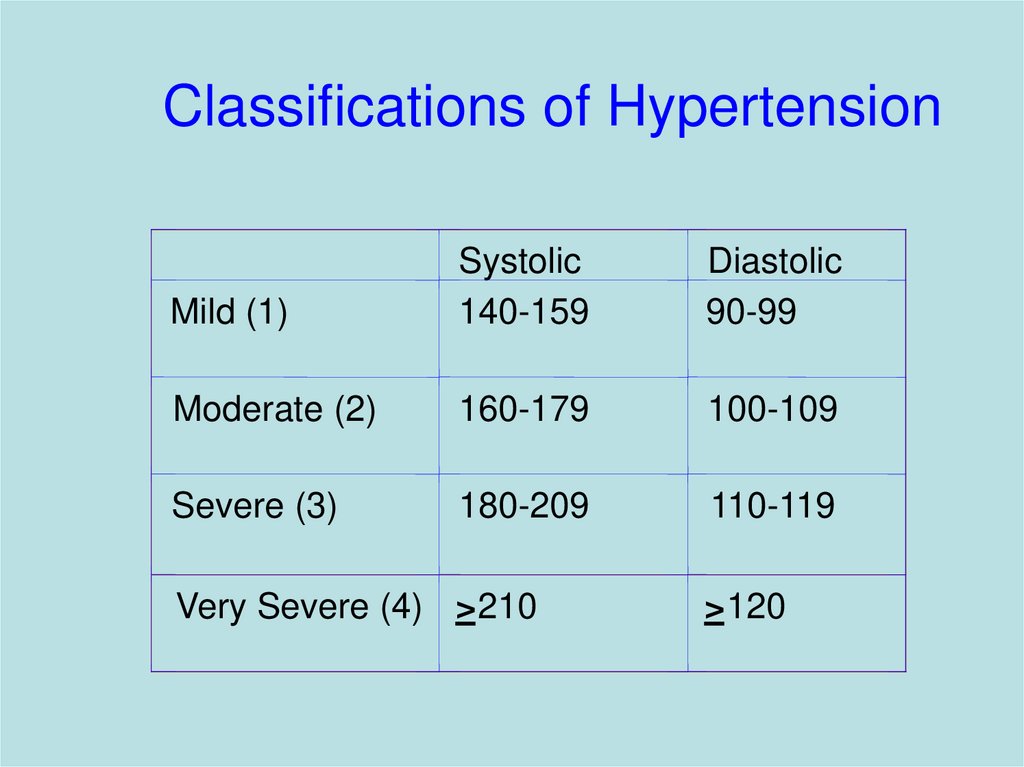
Classifications of HypertensionMild (1)
Systolic
140-159
Diastolic
90-99
Moderate (2)
160-179
100-109
Severe (3)
180-209
110-119
Very Severe (4) >210
>120
4.
Classifications of Hypertension1. Benign Hypertension
2. Malignant / Accelerated Hypertension
(Diastolic >120)
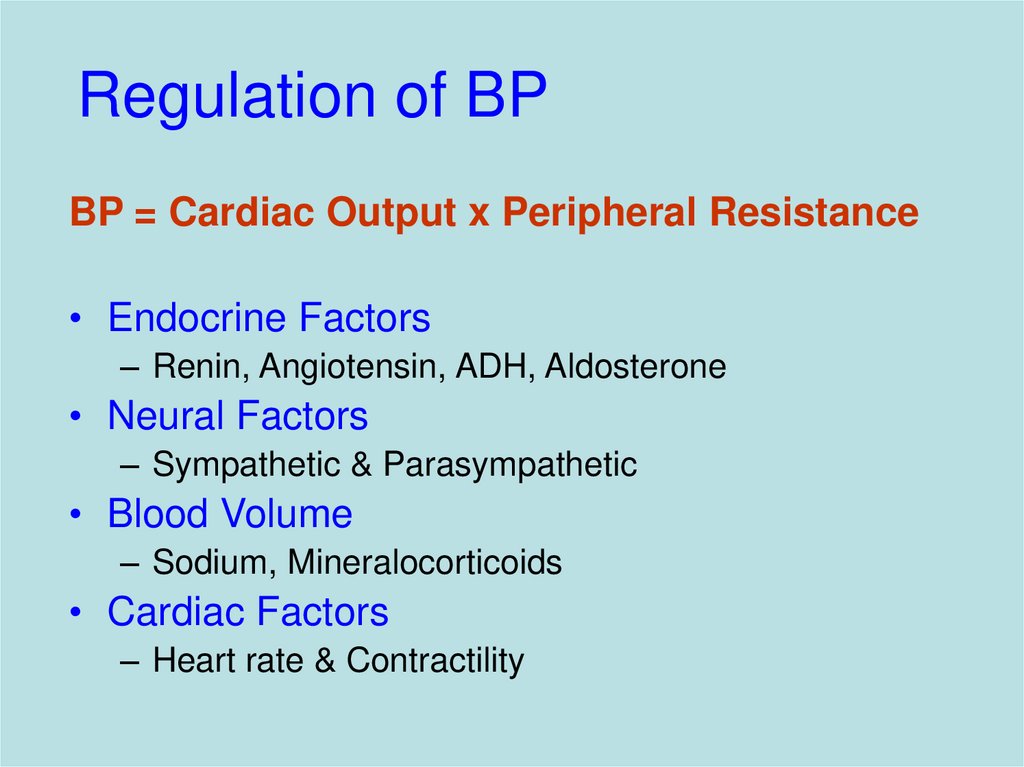
5. Regulation of BP
BP = Cardiac Output x Peripheral Resistance• Endocrine Factors
– Renin, Angiotensin, ADH, Aldosterone
• Neural Factors
– Sympathetic & Parasympathetic
• Blood Volume
– Sodium, Mineralocorticoids
• Cardiac Factors
– Heart rate & Contractility
6.
GFRRenin by JGA
Aldosterone
Angiotensin II
Sodium Retention
Blood Volume
Vasoconstriction
P. Resistance
Hypertension
7. Hypertension-Risk factors
• Genetics- family history• Diet-high intake of sodium
• Lifestyle-stressful
• Weight- obesity
• Alcohol-increased intake
• Oral contraceptives
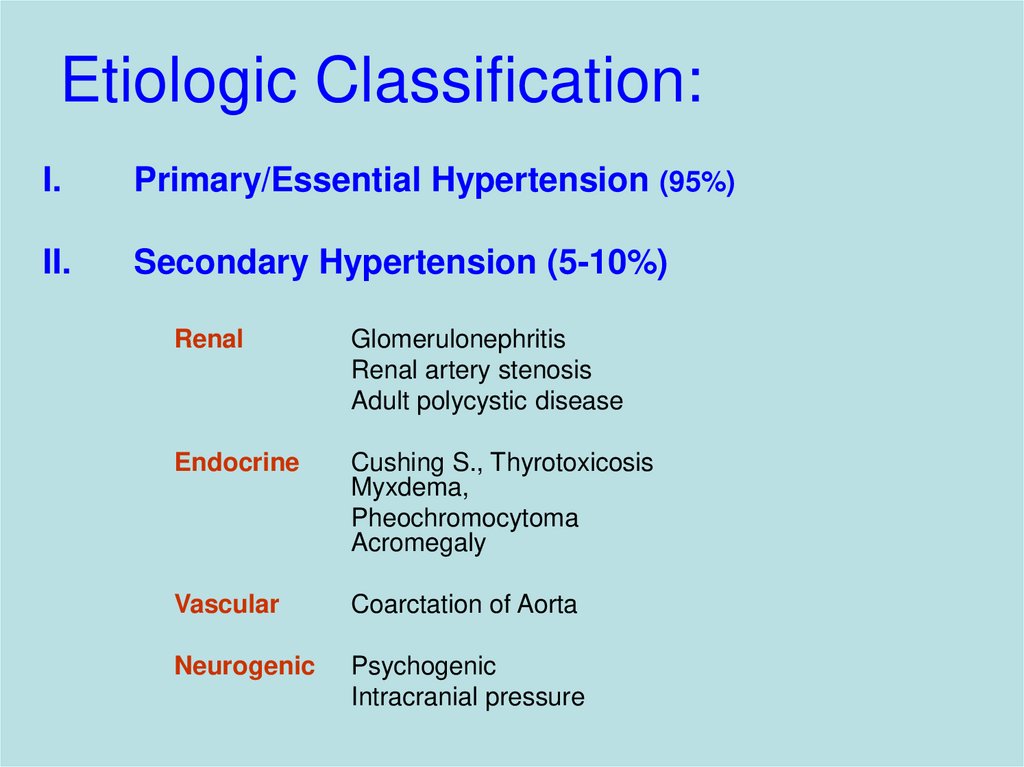
8. Etiologic Classification:
I.Primary/Essential Hypertension (95%)
II.
Secondary Hypertension (5-10%)
Renal
Glomerulonephritis
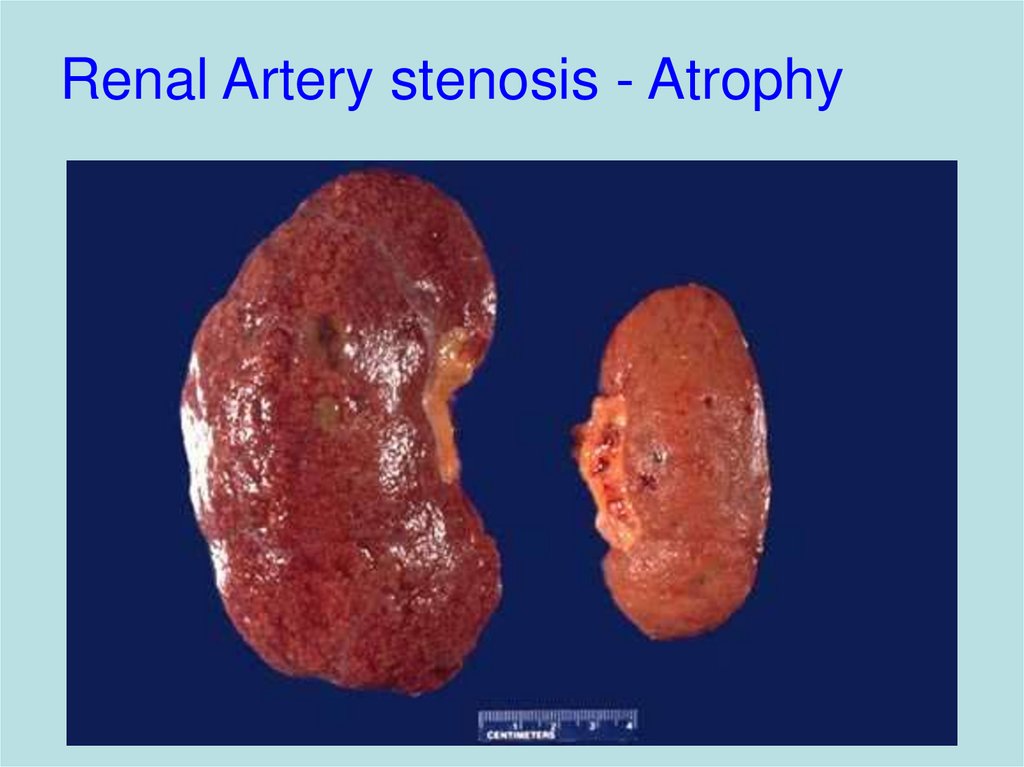
Renal artery stenosis
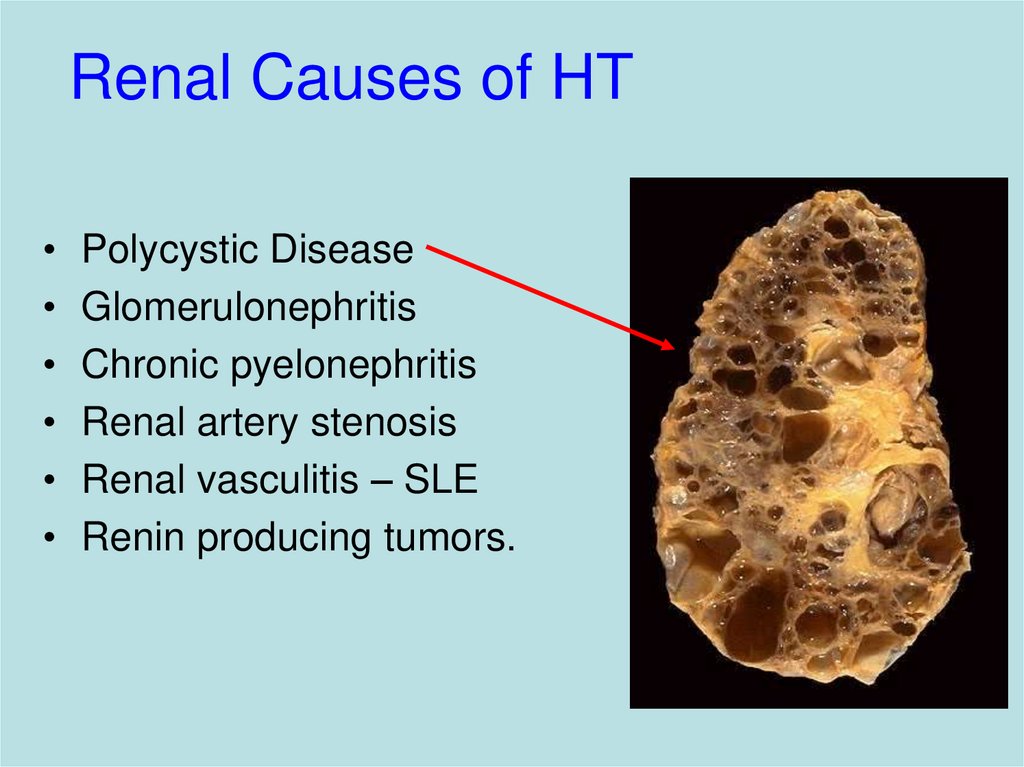
Adult polycystic disease
Endocrine
Cushing S., Thyrotoxicosis
Myxdema,
Pheochromocytoma
Acromegaly
Vascular
Coarctation of Aorta
Neurogenic
Psychogenic
Intracranial pressure
9. Renal Causes of HT
Polycystic Disease
Glomerulonephritis
Chronic pyelonephritis
Renal artery stenosis
Renal vasculitis – SLE
Renin producing tumors.
10. Renal Artery stenosis - Atrophy
11. Etiology
I- Secondary HT:(Known abnormal control)
II- Essential HT
(Multifactorial etiology)
– Increased peripheral resistance
(sympathetic tone)
– Stress , hormonal, neural
– Genetic, familial, life style
12. Postulated mechanisms of Essential Hypertension
1.Defect in sodium excretion2.Defect in cell membrane function:
-Na/Ca transport
-Increased vasoconstrictive response
3.Increased sympathetic response
13. Malignant Hypertension
• Rapidly progressive often leads to endorgan damage.
• May complicate any type of HTN
– Widespread arterial necrosis and thrombosis
– Rapid development of renal failure
– Hypertensive encephalopathy
– Left ventricular failure
14. Morphology:
• Large Blood Vessels (Macroangiopathy)– Atherosclerosis. HT is a major risk factor in AS.
• Small Blood Vessels (Microangiopathy)
– Arteriolosclerosis
Organ damage:
• Heart
– LVH, Hypertensive cardiomyopathy
• Kidney
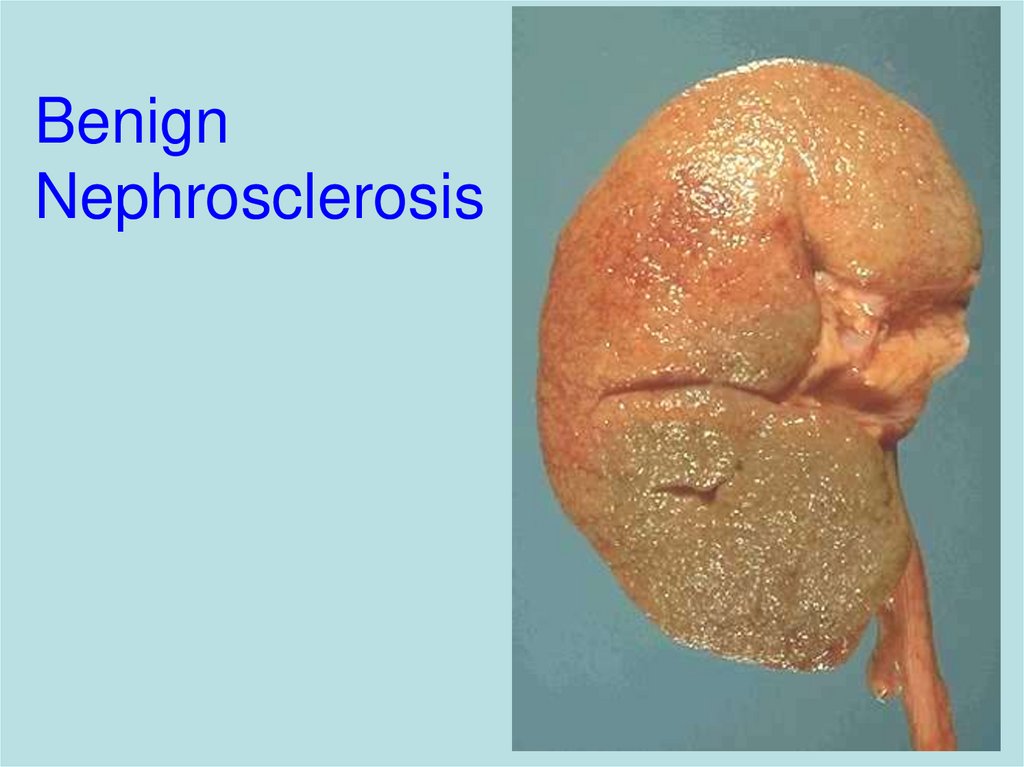
– Benign nephrosclerosis
• Eyes
– Hypertensive retinopathy
• Brain
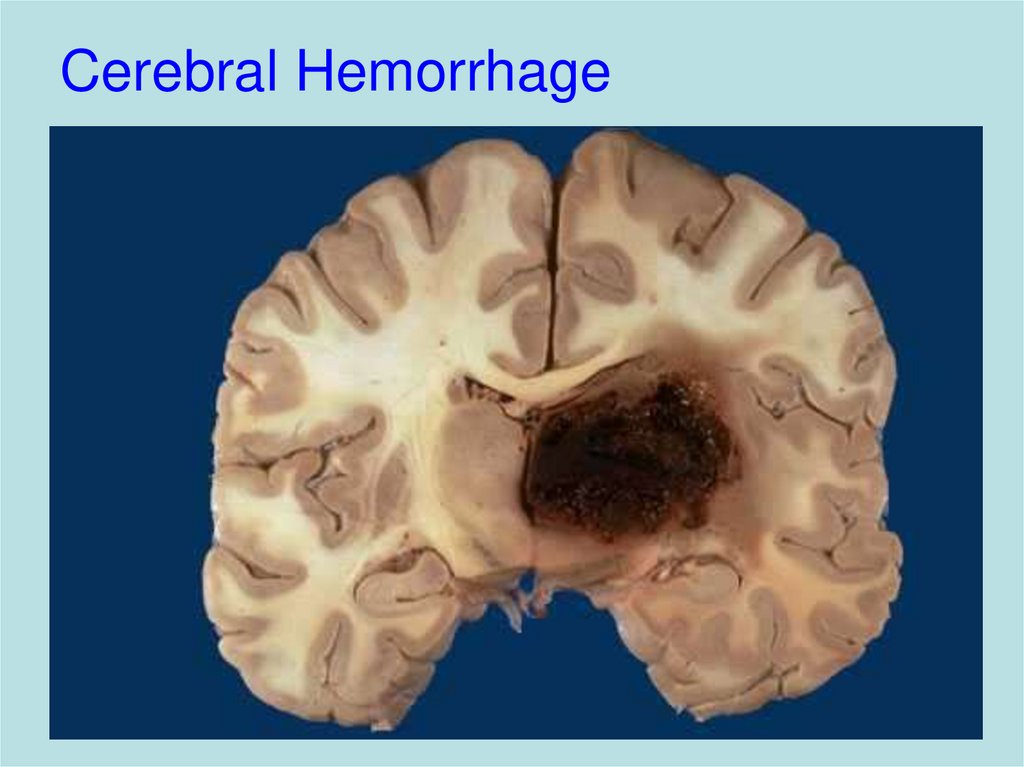
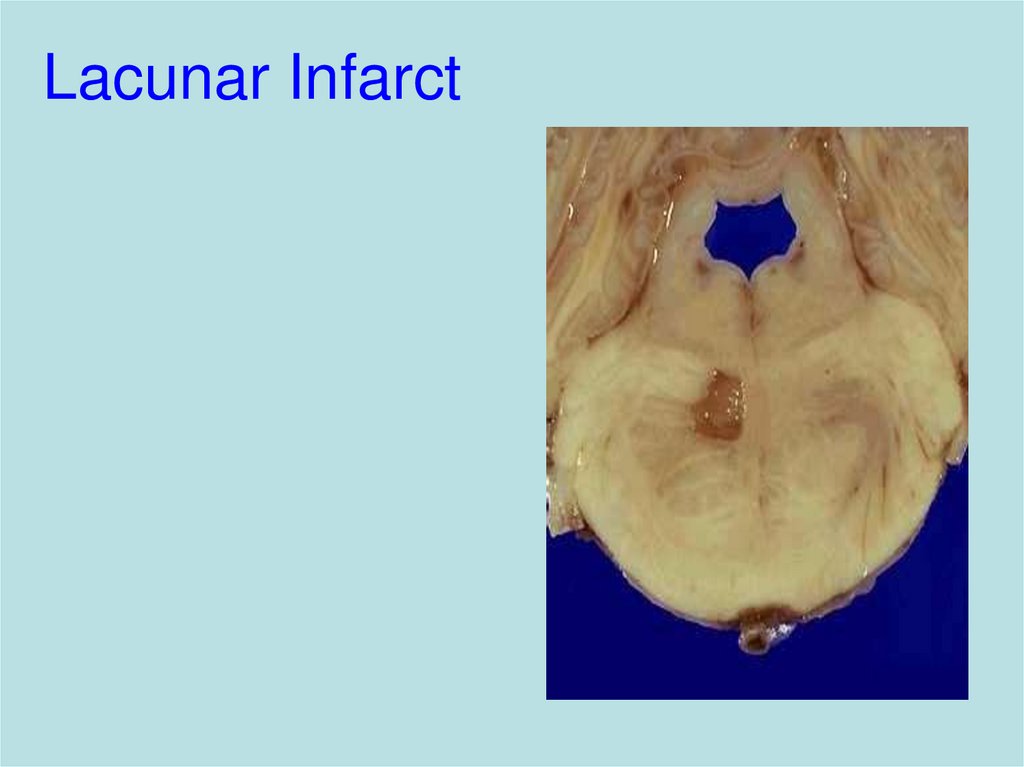
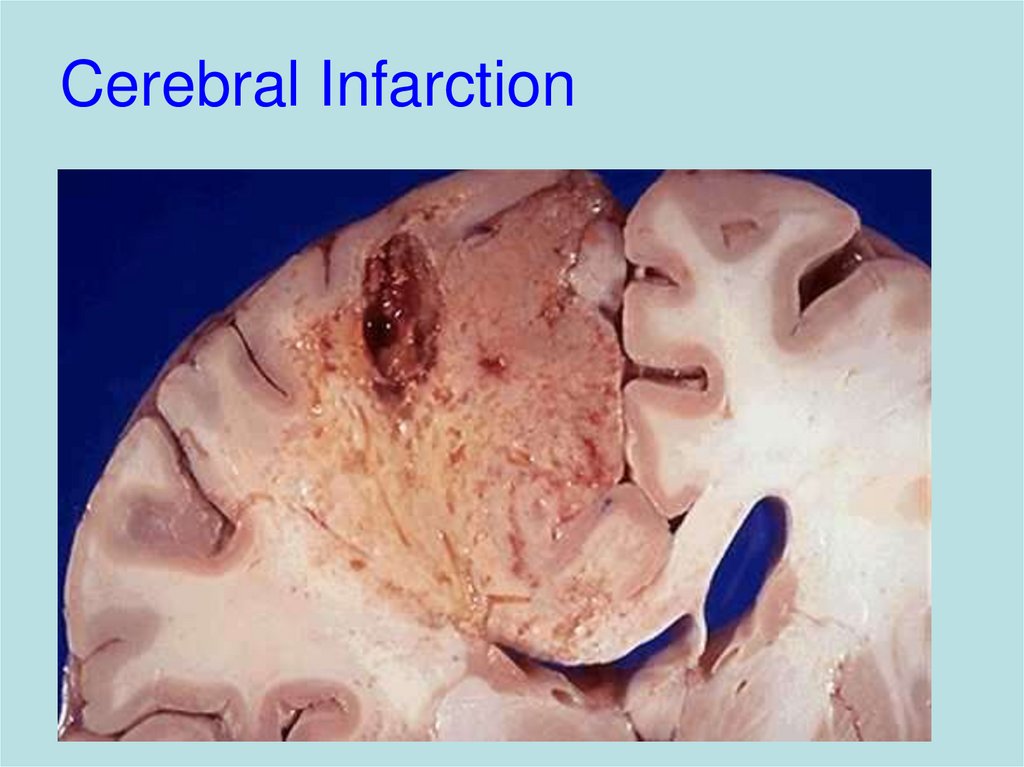
– Haemorrhage, infarction
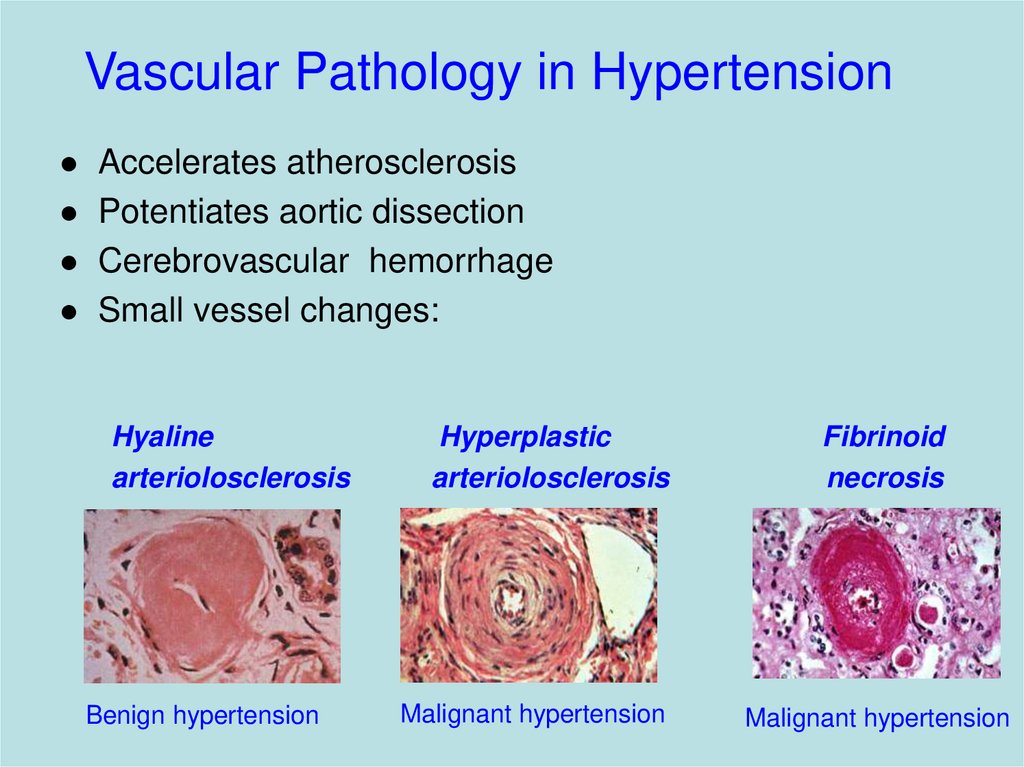
15. Vascular Pathology in Hypertension
Accelerates atherosclerosisPotentiates aortic dissection
Cerebrovascular hemorrhage
Small vessel changes:
Hyaline
arteriolosclerosis
Benign hypertension
Hyperplastic
arteriolosclerosis
Malignant hypertension
Fibrinoid
necrosis
Malignant hypertension
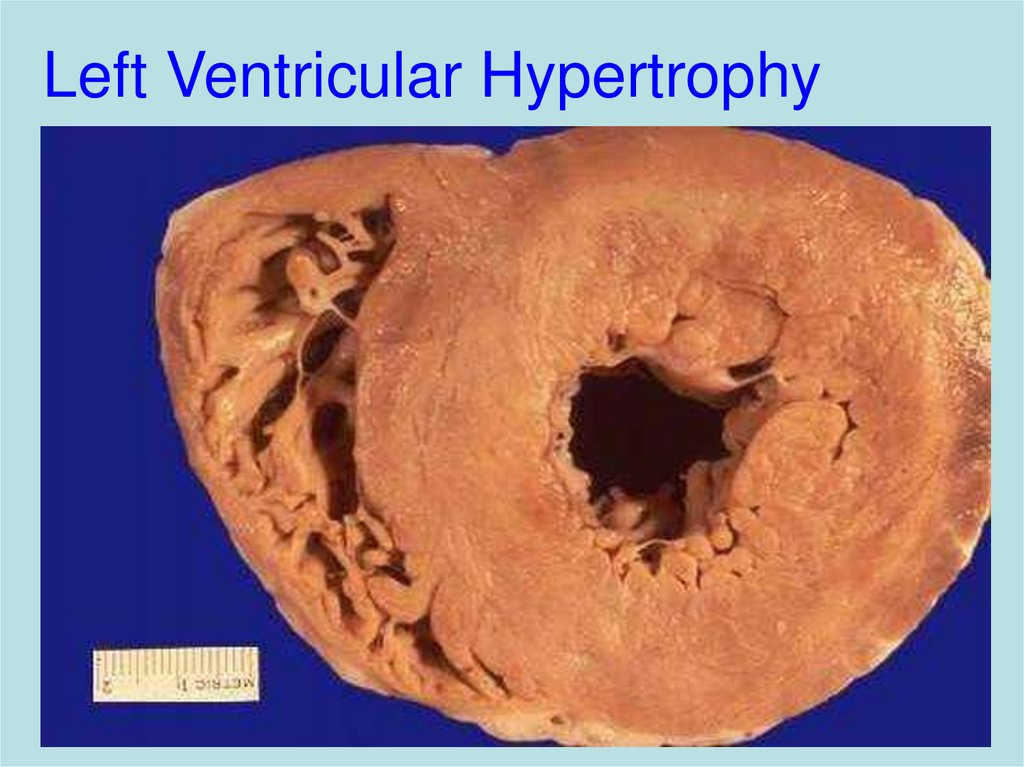
16. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
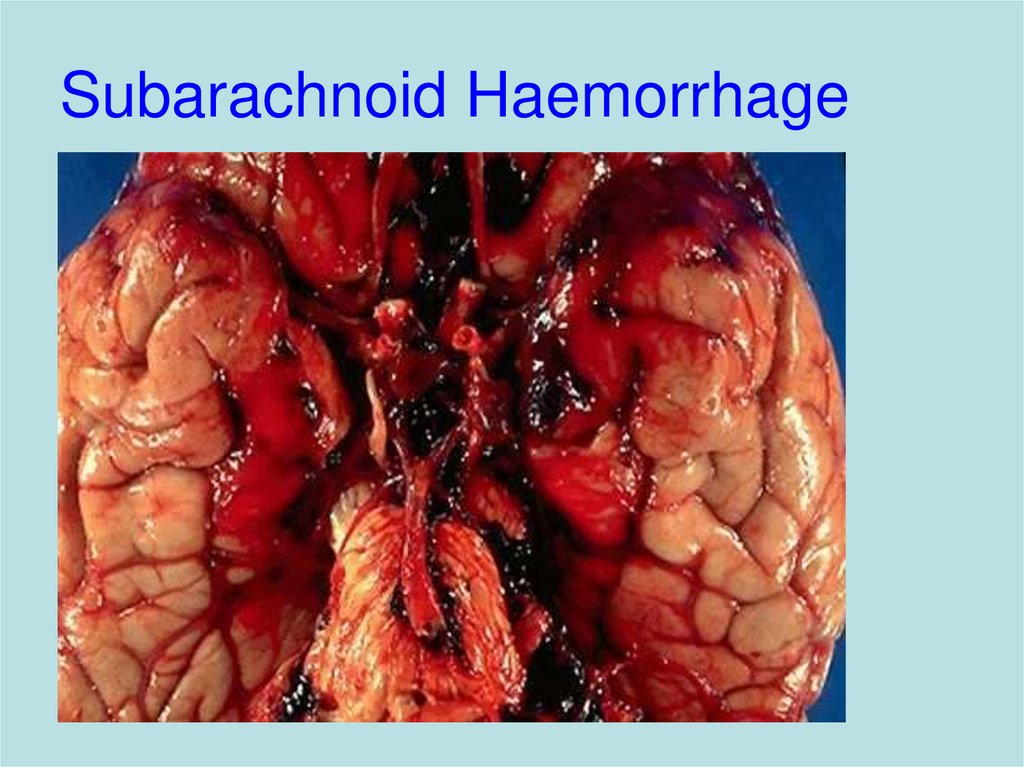
17. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
18. Cerebral Hemorrhage
19. Lacunar Infarct
20. Benign Nephrosclerosis
21. Cerebral Infarction
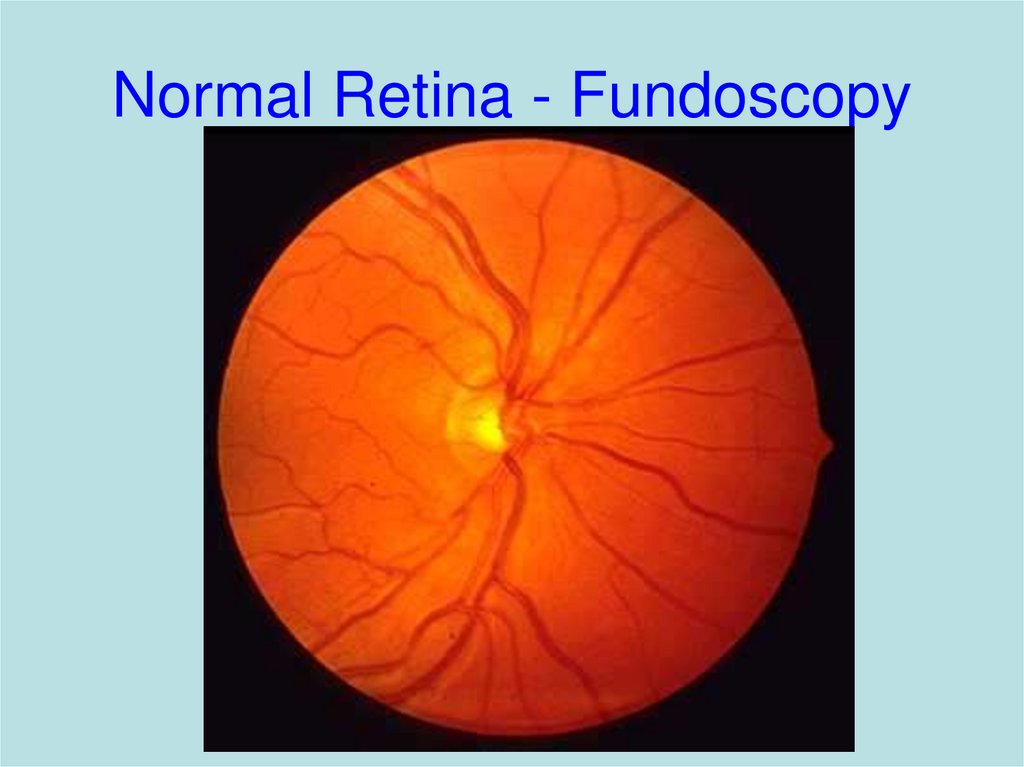
22. Normal Retina - Fundoscopy
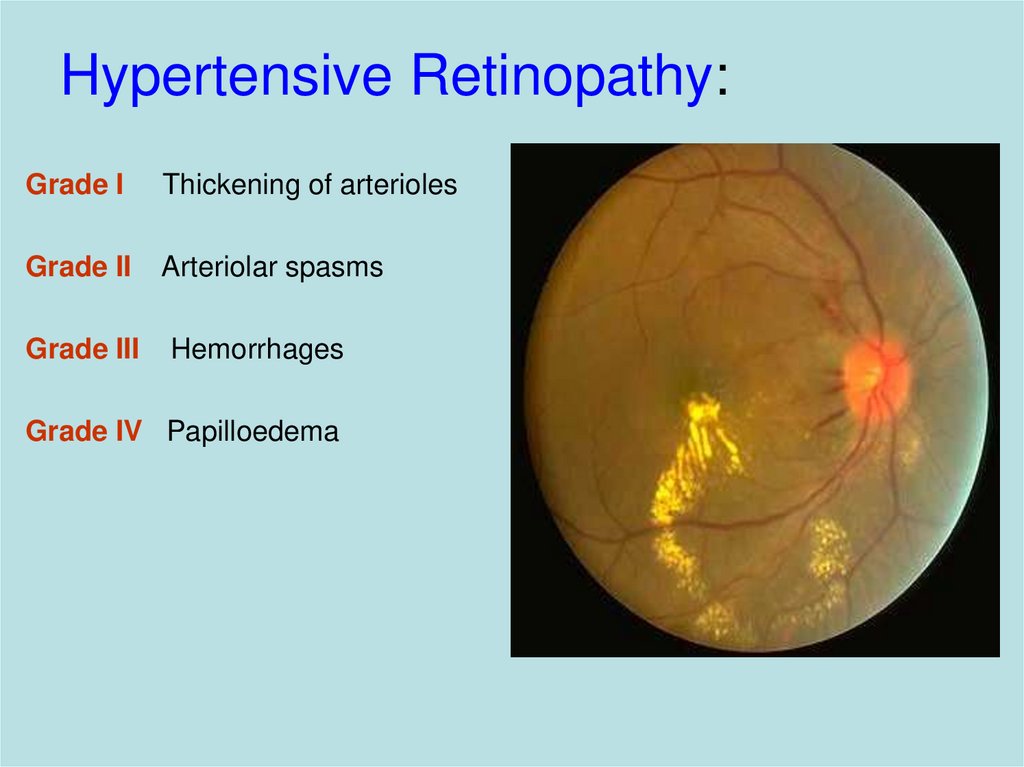
23. Hypertensive Retinopathy:
Grade IThickening of arterioles
Grade II
Arteriolar spasms
Grade III
Hemorrhages
Grade IV Papilloedema
24. Factors Indicating Adverse Prognosis in Hypertension
Black raceYounger age
Male sex
Persistent diastolic
pressure > 115 mm Hg
Smoking
Diabetes mellitus
Hypercholesterolemia
Obesity
Excess alcohol intake
Organ damage:
cardiac
eyes
renal
CNS






 medicine
medicine