Similar presentations:
Myocardial infarction, pathological anatomy, complications, causes of death. The relationship of atherosclerosis and IDH
1. Practical skills in pathological anatomy-2 MODULE: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Тopic №2. Myocardial infarction, pathological anatomy,
complications, causes of death. Therelationship of atherosclerosis and IDH. Essential
and symptomatic hypertension. Morphological
characteristics, outcomes, causes of death.
Prepared by:
d.m.s. Shabdarbayeva D.M.
2. The purpose
• Secure the knowledge of the mechanism offormation of atherosclerotic plaque and arterial
hypertensions
3. Learning objectives:
• The student should know:• etiology, pathogenesis and pathological anatomy of IDH. Periods and
complications of IDH. Etiology, pathogenesis, morphology and
morphogenesis of atherosclerosis, to differentiate clinical and
morphological forms of atherosclerosis and complications.
Determination of essential hypertension (EH). Be able to describe the
stages of HD, the morphology of benign and malignant hypertension.
To differentiate the various forms of HD based on clinical and
morphological signs.
• The student should be able to:
• diagnosed by macro- and micropreparations clinical and morphological
forms of IDH, to be able to allocate the main etiological factors and
pathogenesis of IDH. Diagnosing of macro- and micropreparations
stages of atherosclerosis and various forms of HD based on clinical and
morphological signs.
4.
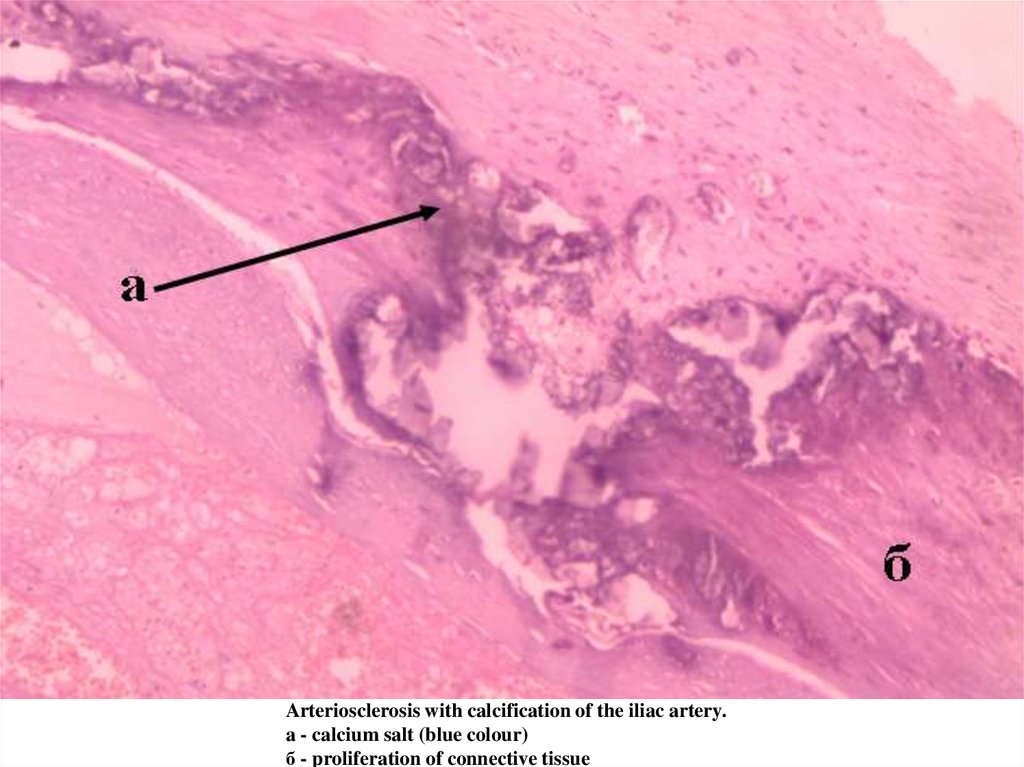
Arteriosclerosis with calcification of the iliac artery.a - calcium salt (blue colour)
б - proliferation of connective tissue
5.
Arteriosclerosis with calcification of the iliac artery and thrombosis.a - calcium salt (blue colour)
6.
7.
Ischemic infarction of kidney with area of demarcation inflammationa - necrosis; б - hemorrhage; в - accumulation of leucocytes
8.
9.
10.
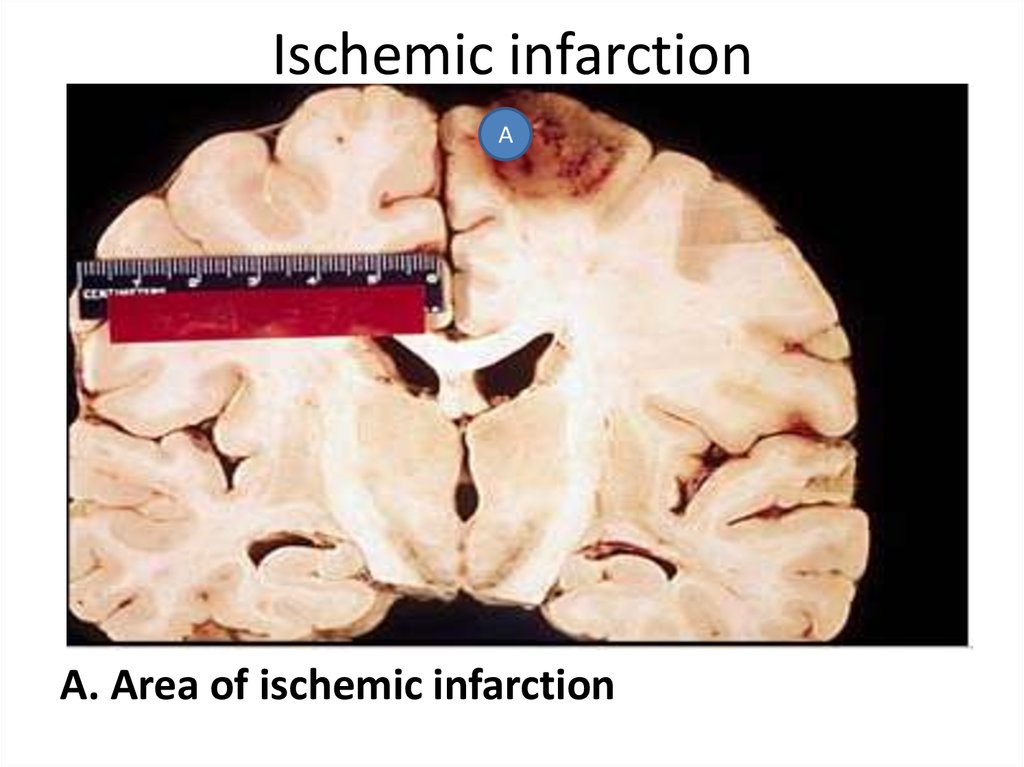
11. Ischemic infarction
АА. Area of ischemic infarction
12. Cerebral infarction
ГА
Б
В
А. BRIDGE
Б. AREA OF INFARCTION
В. THROMBOSIS OF BASILAR ARTERY
Г. CEREBELLUM
13. Cerebral infarction in the middle cerebral artery
АА. AREA of FRESH INFARCTION
14. Organization of the infarction
АА. Area of organization of the infarction
15. Hemorrhagic cerebral infarction
АБ
Г
А. Hemorragic infarction
Б. GIPPOKAMP
В. BLACK SUBSTANCE
Г. Tootsy
В
В
Г
Б
16. Fibrinoid necrosis during malignant hypertension
АБ
• А. glomerular loops
• Б. fibrinoid necrosis
17.
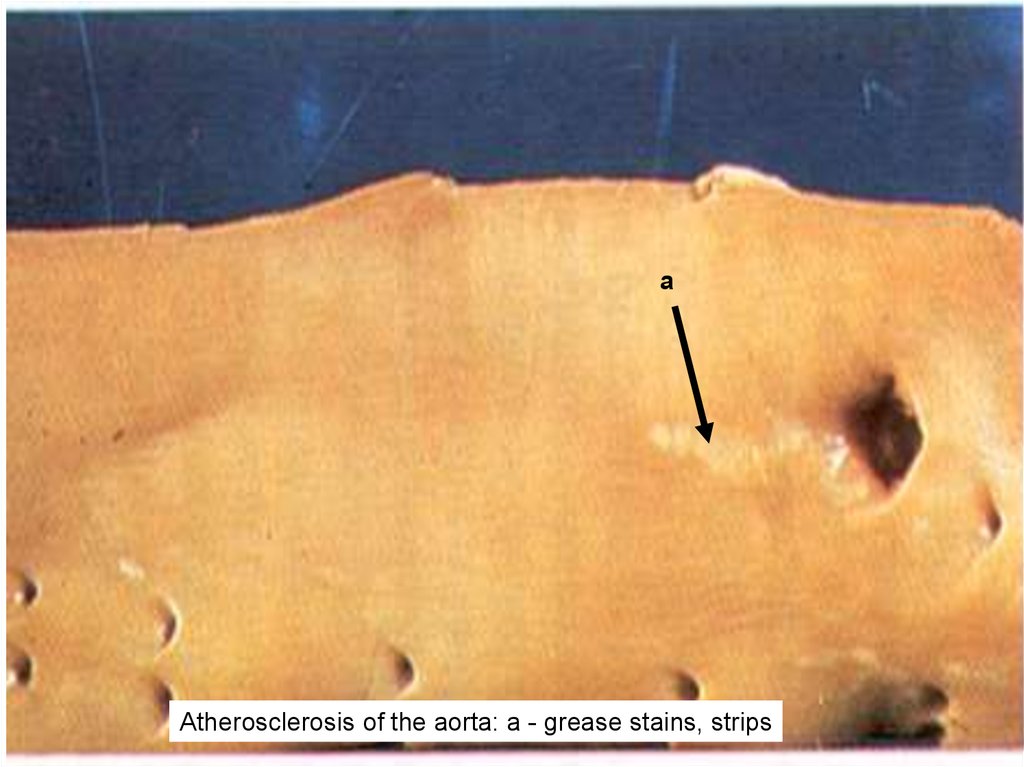
аAtherosclerosis of the aorta: a - grease stains, strips
18.
аб
Atherosclerosis of the aorta: a - grease stains,
б - starting fibrous plaques
19.
аAtherosclerosis of the aorta: a - fibrous plaques with ulceration
20.
аб
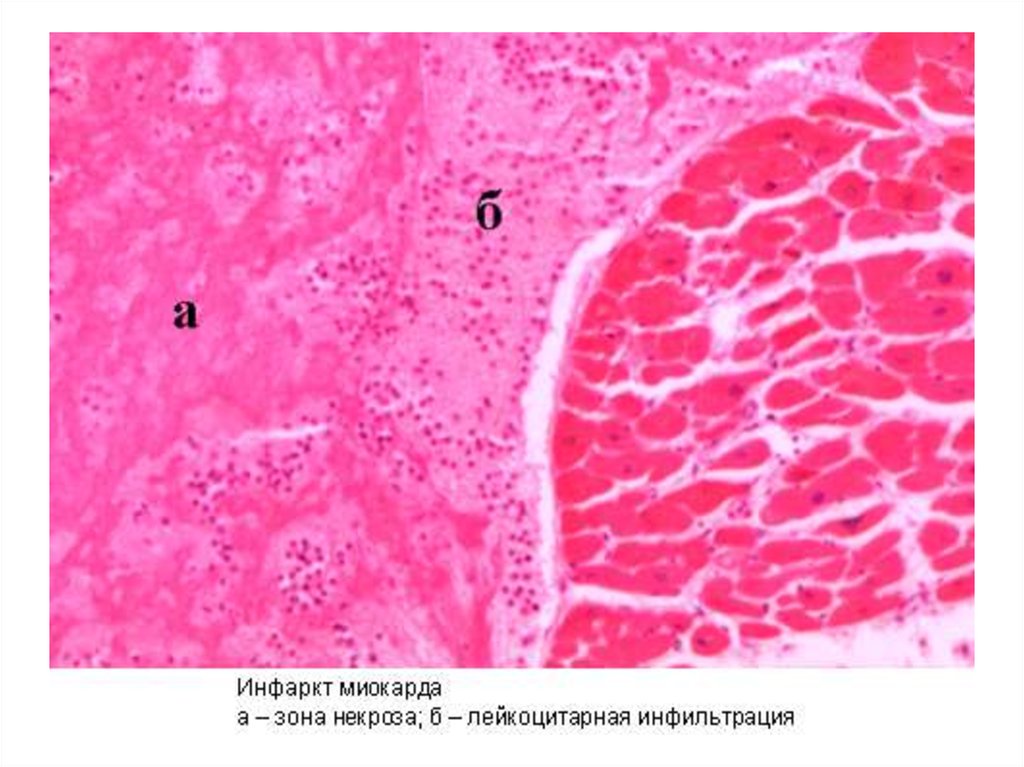
Myocardial infarction: a - necrotic zone
б - zone of cardiosclerosis
21.
Primary-contracted kidney22. Atherosclerosis of coronary artery
ВА
Б
A. Lumen by obturated thrombus
Б. atherosclerotic plaque
B. AREA of plaque rupture
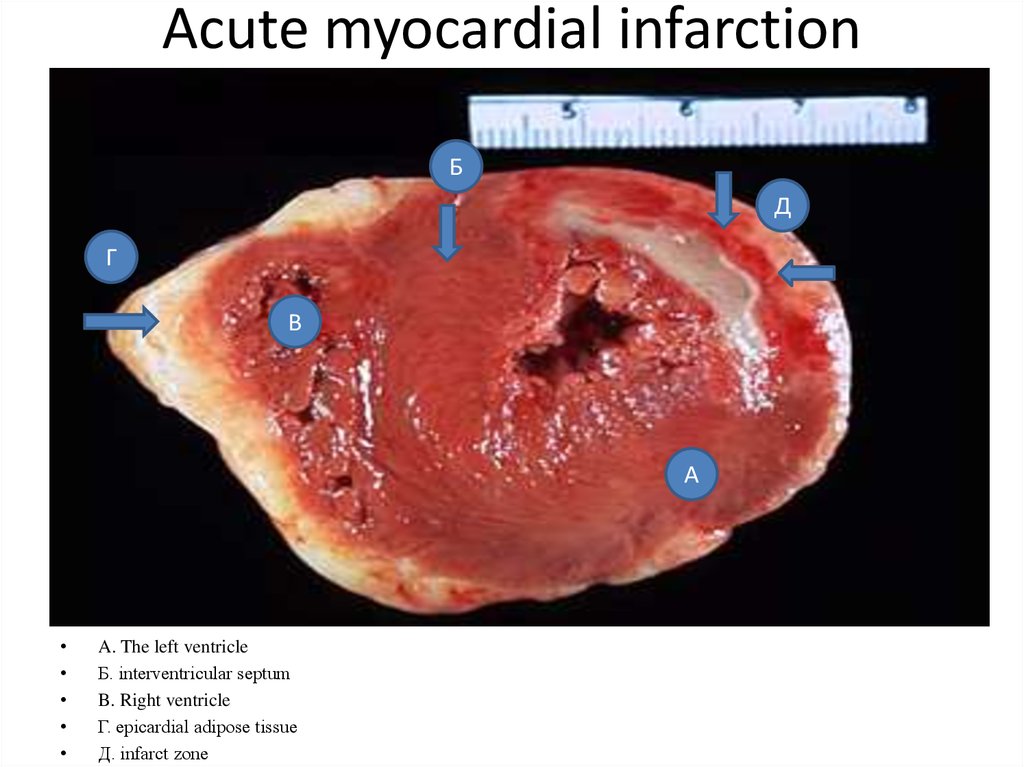
23. Acute myocardial infarction
БД
Г
В
А
A. The left ventricle
Б. interventricular septum
B. Right ventricle
Г. epicardial adipose tissue
Д. infarct zone
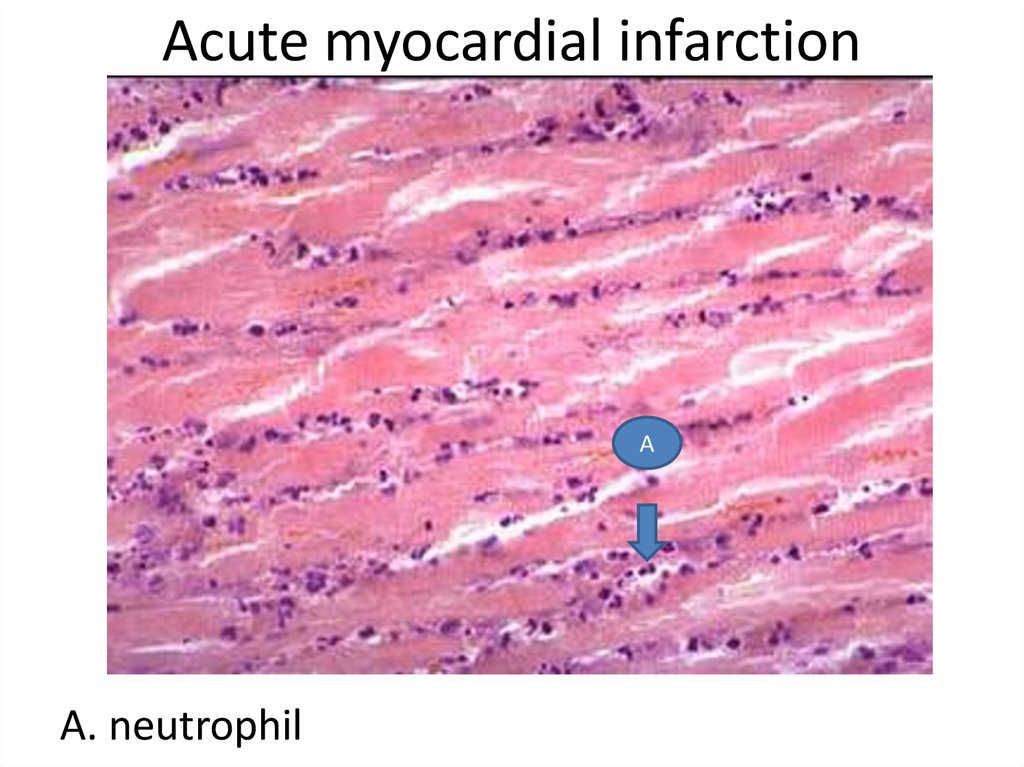
24. Acute myocardial infarction
АА. neutrophil
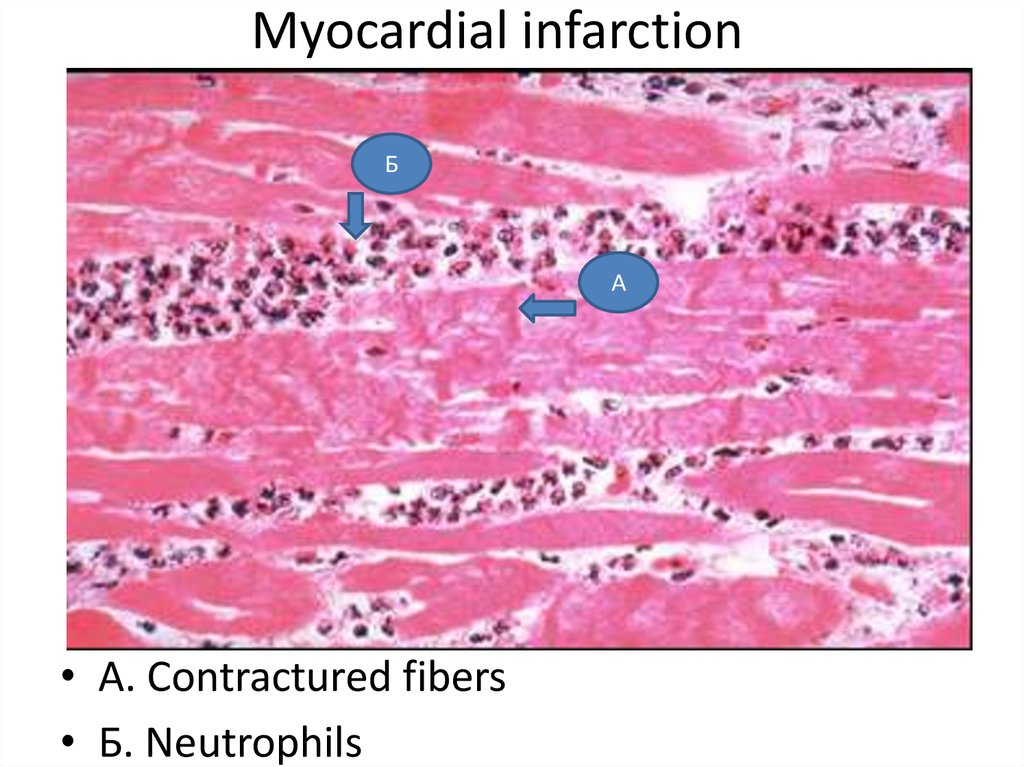
25. Myocardial infarction
БА
• A. Contractured fibers
• Б. Neutrophils
26. Postinfarction rupture of the wall of left ventricular
АА. Zone of infarction
Б. Zone of rupture
Б
27. Myocardial rupture
АБ
В
Г
A canal of rupture
Б. Zone of transmural myocardium
B. zone of coagulation infarction
Г. Field of unchanged myocardium
28. Left ventricular aneurysm, thrombosis
БА
• A. aneurysm and thrombosis
• Б. subendocardial scars
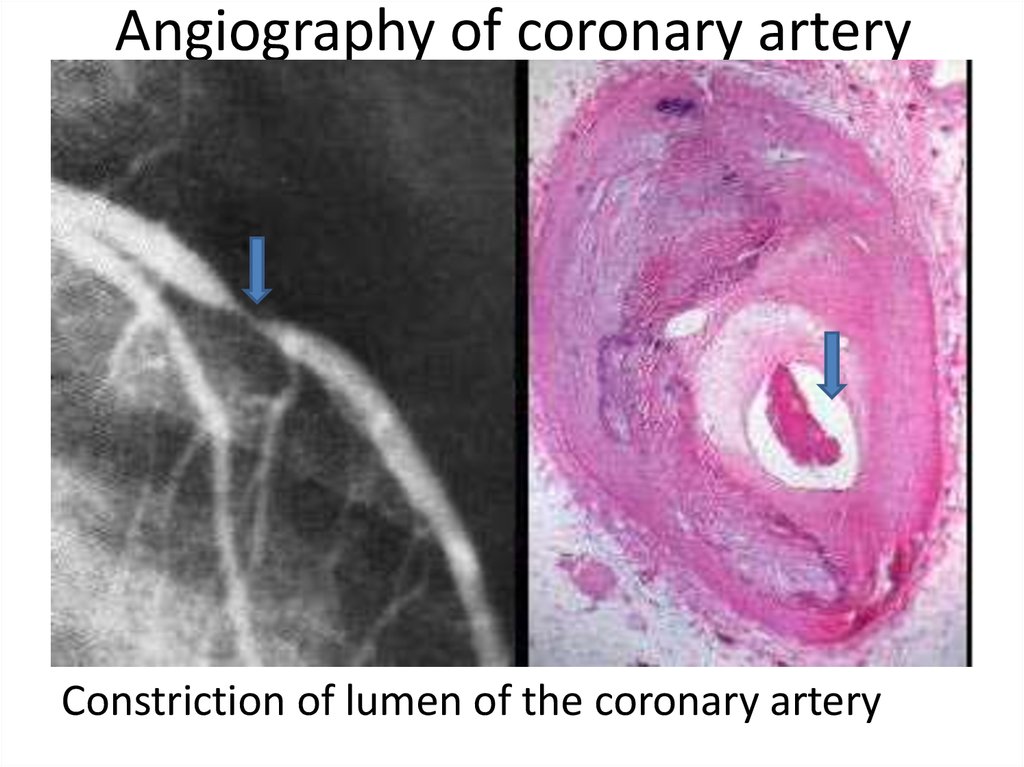
29. Angiography of coronary artery
• А. constriction of a coronary artery30. Angiography of coronary artery
Constriction of lumen of the coronary artery31. Atherosclerosis and thrombosis of coronary artery
АА. The thrombus in the lumen of the coronary artery
32. Thrombosis of coronary artery
ВБ
Г
Д
A. Intima
Б. Thrombosis
B. Recanalization
Г. Middle membrane
Д. Аdventitia
А
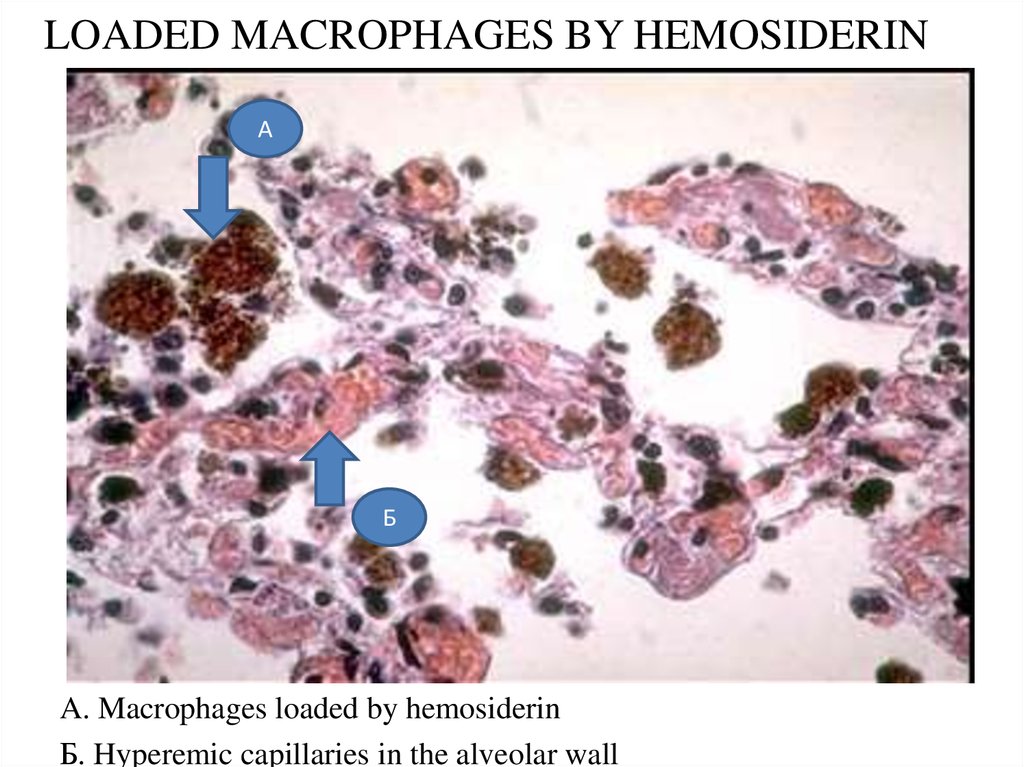
33. LOADED MACROPHAGES BY HEMOSIDERIN
АБ
A. Macrophages loaded by hemosiderin
Б. Hyperemic capillaries in the alveolar wall
34. Kidneys. Arterio- and atherosclerosis
АА
• А. CORTICAL SCARS
35. The kidneys, atherosclerosis.
The kidneys, atherosclerosis.Г
В
А
Б
A. Hyalinized VESSELS
Б. FIBROSIS OF INTIMA
B. SCLEROSIS of glomeruli
Г. Tubular atrophy
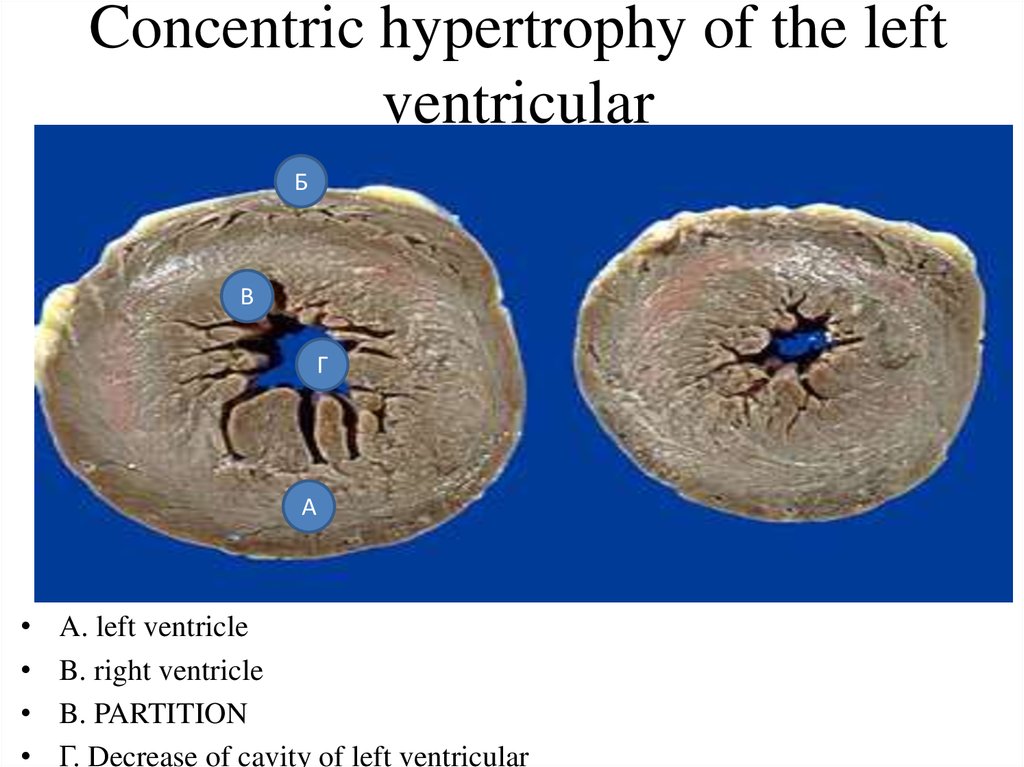
36. Concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricular
БВ
Г
А
A. left ventricle
B. right ventricle
B. PARTITION
Г. Decrease of cavity of left ventricular
37. Еxcision of aortic
АВ
Б
• A. adventitia
• Б. aortic intima
• B. hematoma dissecting tunica
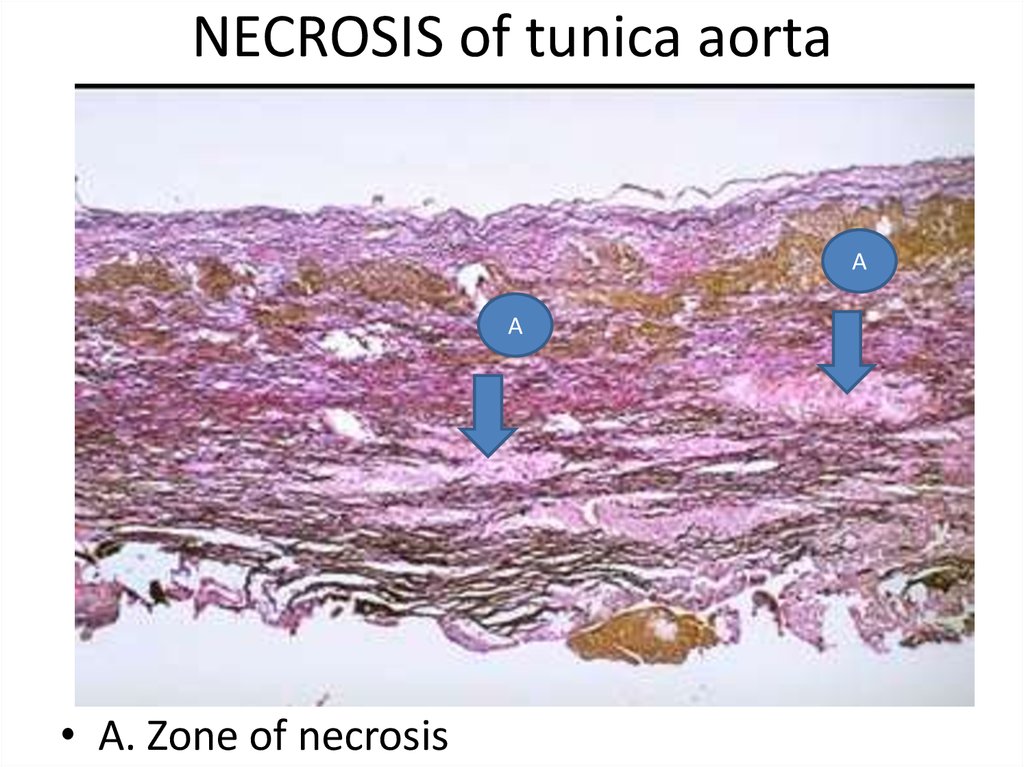
38. NECROSIS of tunica aorta
АА
• А. Zone of necrosis
39. Atherosclerotic aneurysm of the abdominal aorta
АБ
В
A. mushroom ANEURYSM
Б. iliac artery
В. Large thrombus in the lumen
40. Hyperplastic arteriosclerosis
А• A. constricted lumen
• B. hyperplasia of smooth muscle cells
Б
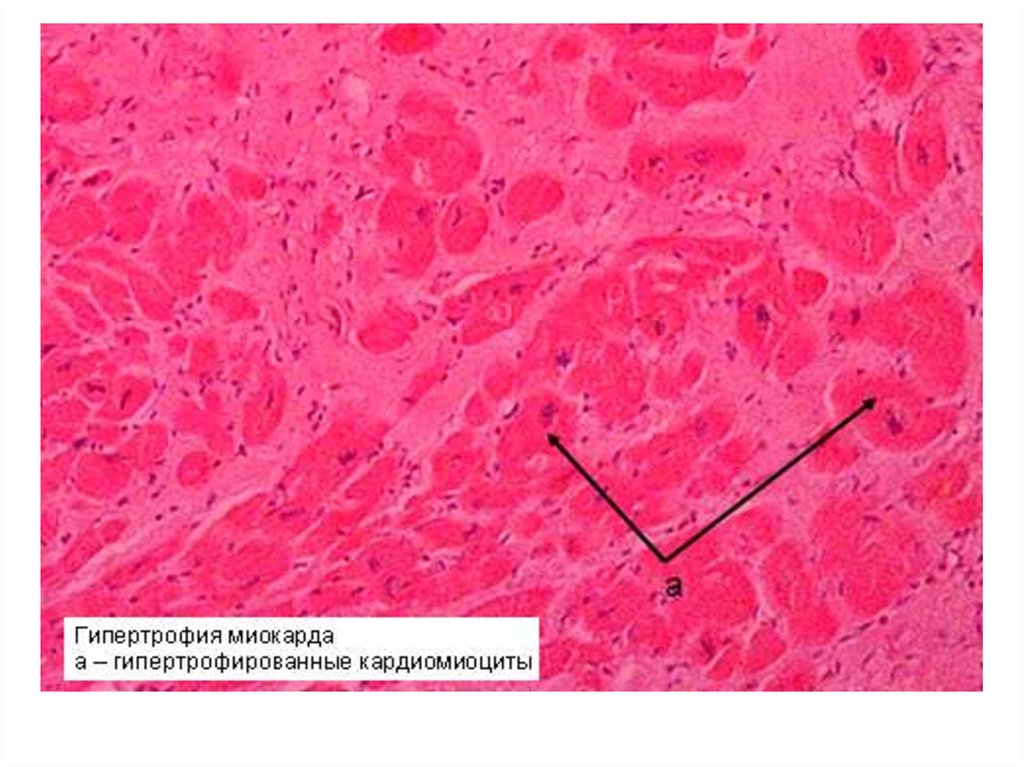
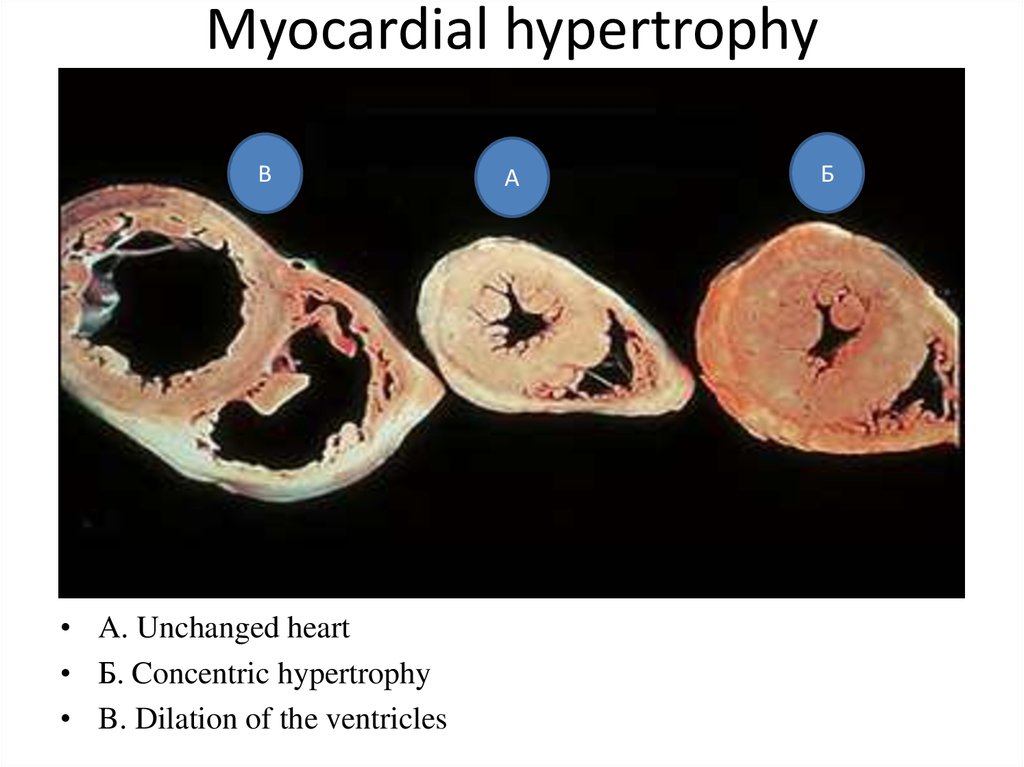
41. Myocardial hypertrophy
Myocardial hypertrophyВ
• A. Unchanged heart
• Б. Concentric hypertrophy
• B. Dilation of the ventricles
А
Б
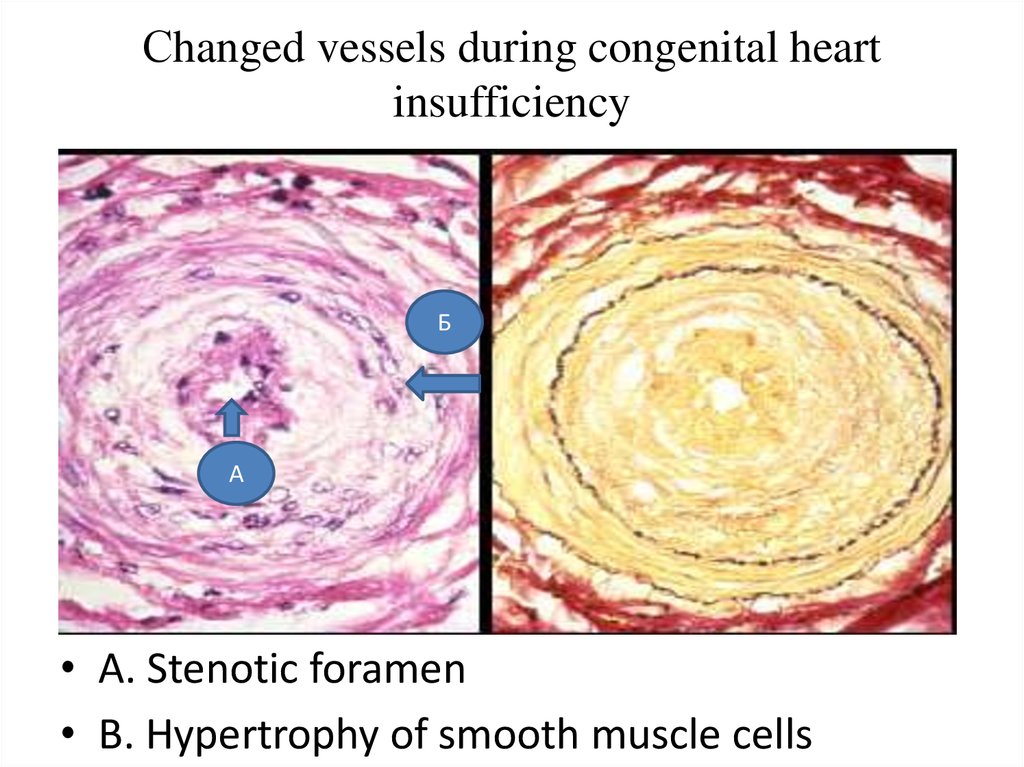
42. Сhanged vessels during congenital heart insufficiency
БА
• A. Stenotic foramen
• B. Hypertrophy of smooth muscle cells
43. Thrombosis of coronary artery
БА
В
А. tunica
Б. intima
В. lumen
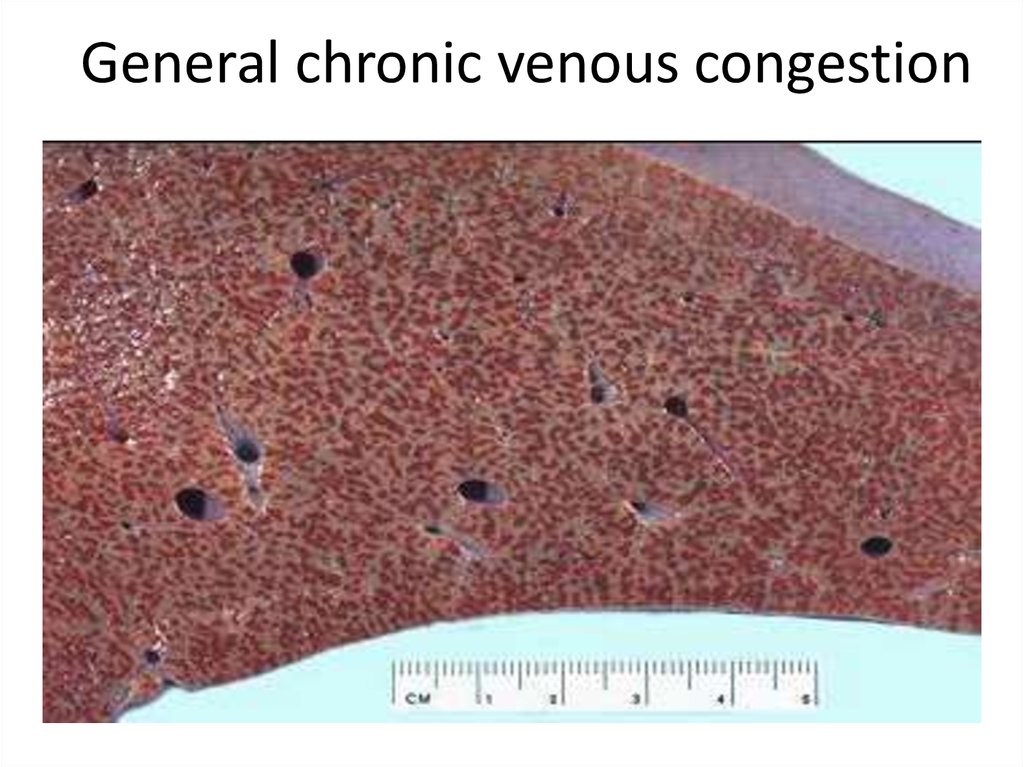
44. General chronic venous congestion
45. General chronic venous congestion
БА
• A. Triad
• Б. Congestion
46. Lung during chronic venous congestion
47. Edema of the lung
АБ
A. hyperemic intra alveolar septa
Б. intra alveolar transudate
48. Chronic venous congestion
АБ
• A. alveolar septa
• Б. macrophages with hemosiderin
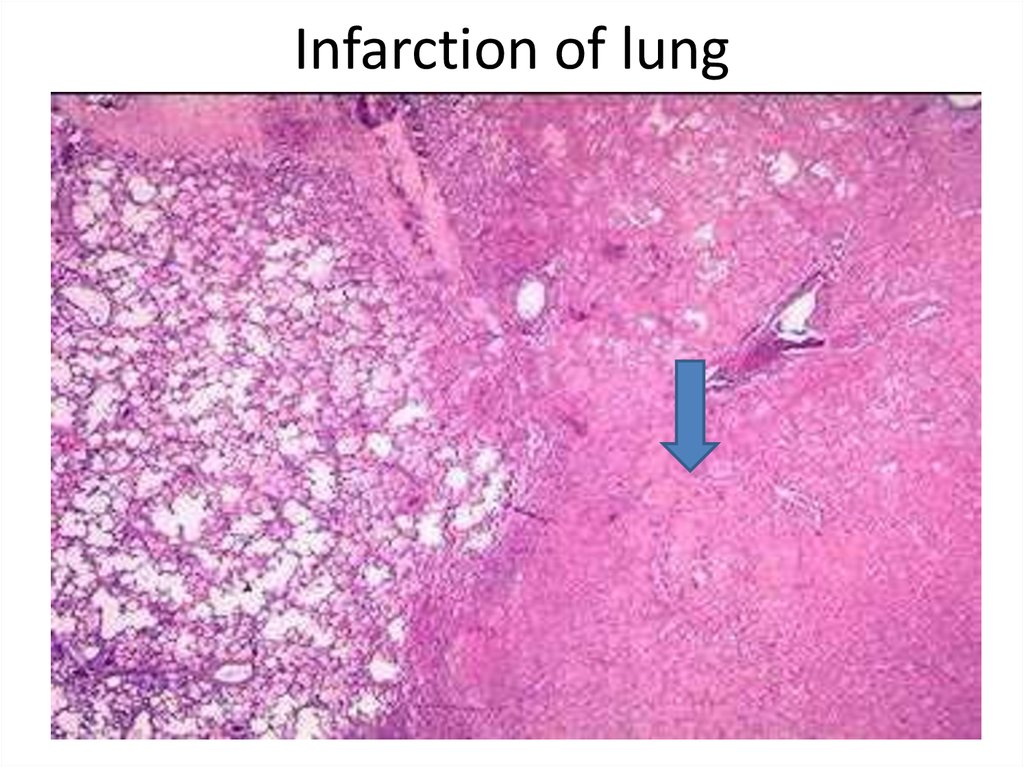
49. Infarction of lung
А• А. Infarction
• Б. Pleura
Б


































 medicine
medicine








