Similar presentations:
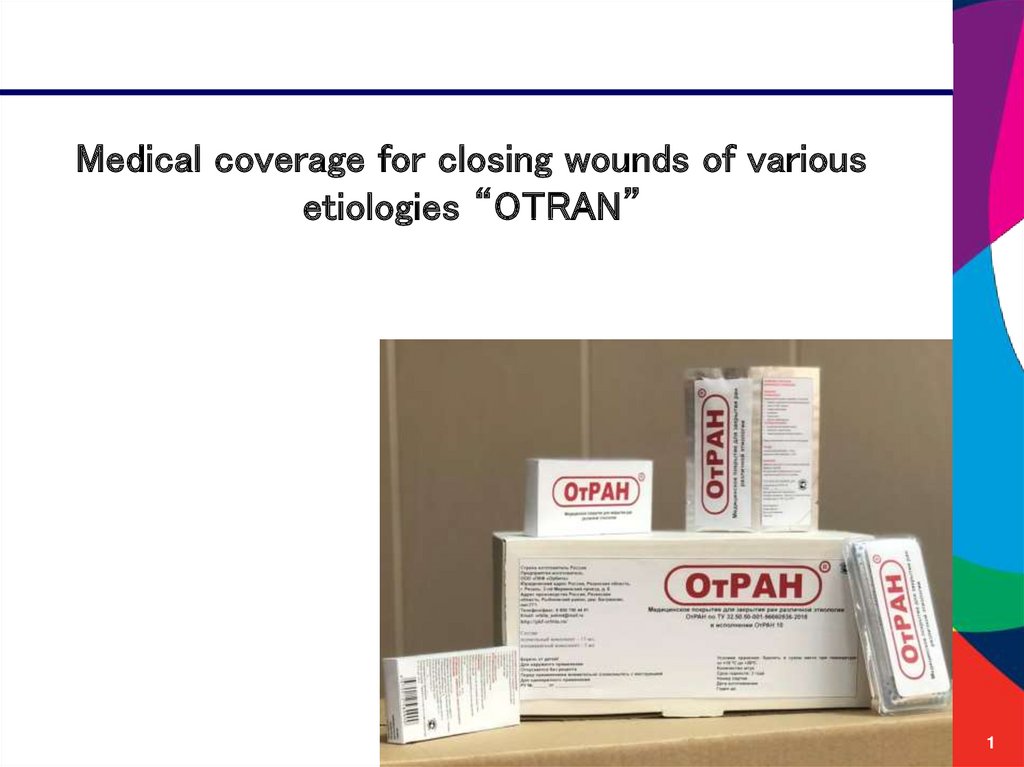
Medical coverage for closing wounds of various etiologies “OTRAN”
1. Medical coverage for closing wounds of various etiologies “OTRAN”
12. Текущее состояние
2) PatentsPatents were obtained for polyurethane
compositions for coating OTRAN, for the
1) Application
production technology of a number of
nanoparticles used for the Project’s
products.
The methodology of application has been
fully developed. Methodological
recommendations on application for medical
institutions and educational films have been
prepared.
At the moment, Medical coverage for the
closure of wounds of various etiologies.
OTRAN is at the stage of registration in the
Russian Federation.
4) Sales
The products have been
successfully tested in
medical institutions.
Идут переговоры с гос.
структурами РЖД, МЧС, ВС России и
другими ведомствами о закупках
«ОтРАН».
PKF ORBIT LLC
(Ryazan)
Contracts with 2
distributors of medical
products.
3) Production
Small-scale production was set up in the
amount of up to 50 thousand pieces. per month.
Worked out a plan to build mass production.
Selected technological equipment.
5) Development
Work is underway to further improve the coating and
packaging "OTRAN".
2
3. Продукция
descriptionMedical coverage for closing wounds of various etiologies
intelligence
The coverage of “OTRAN” is currently at the registration stage.
base
composition
The coating is a two-component polyurethane foam composition in packaging of
aluminized polyethylene.
The coating is obtained by mixing two components:
• polyol (with the addition of nanocrystalline boehmite);
• isocyanate,
The foam mass, when applied to the wound, forms a fine-porous elastic coating
with a thickness of 0.8-1 cm. The coverage area depends on the volume of the
mixed components.
OTRAN 5 – 50 см2
OTRAN 10 – 100 см2
OTRAN 20 – 200 см2
Special:
application
hospitals;
Army, Ministry of Emergency
Situations, spec. services;
fleet;
fire services;
sports organizations;
traumatic production.
Veterinary, breeding farms and
livestock breeding.
Household:
for the treatment of any domestic
injuries and burns;
self-treatment of wounds;
fishing;
tourism;
home and car first aid kit;
sport, active rest;
Pets.
3
4. Продукция
Purpose of the productFor treatment:
10 см
Product properties
The coating is sterile at the time of
application;
Fresh wounds of any origin;
It has an analgesic effect;
15 см
Patients with nonhealing wounds;
Accelerates the healing process by 1.5-2
times;
Trophic ulcers of any origin;
Waterproof, with good wound aeration;
Bedsores;
The product is available in several
dimensional modifications providing
closing surfaces:
• OTRAN 5 – 50 см2
• OTRAN 10 – 100 см2
• OTRAN 20 – 200 см2
Burns;
Prevention of tissue infection in
skeletal traction;
Closure of donor wounds;
Protection of the skin around the
fistula of the gastrointestinal tract;
Strengthening drains on the skin of
the body.
- For more information about the clinical results of treatment, see Appendix.
Perfectly protects against secondary
infection and trauma;
Through the coating is possible the
introduction of drugs;
Well absorbs exudate and firmly fixed to
healthy skin around the wound for 5-7
days, without requiring care;
Easy and painlessly removed from the
wound after use.
4
5.
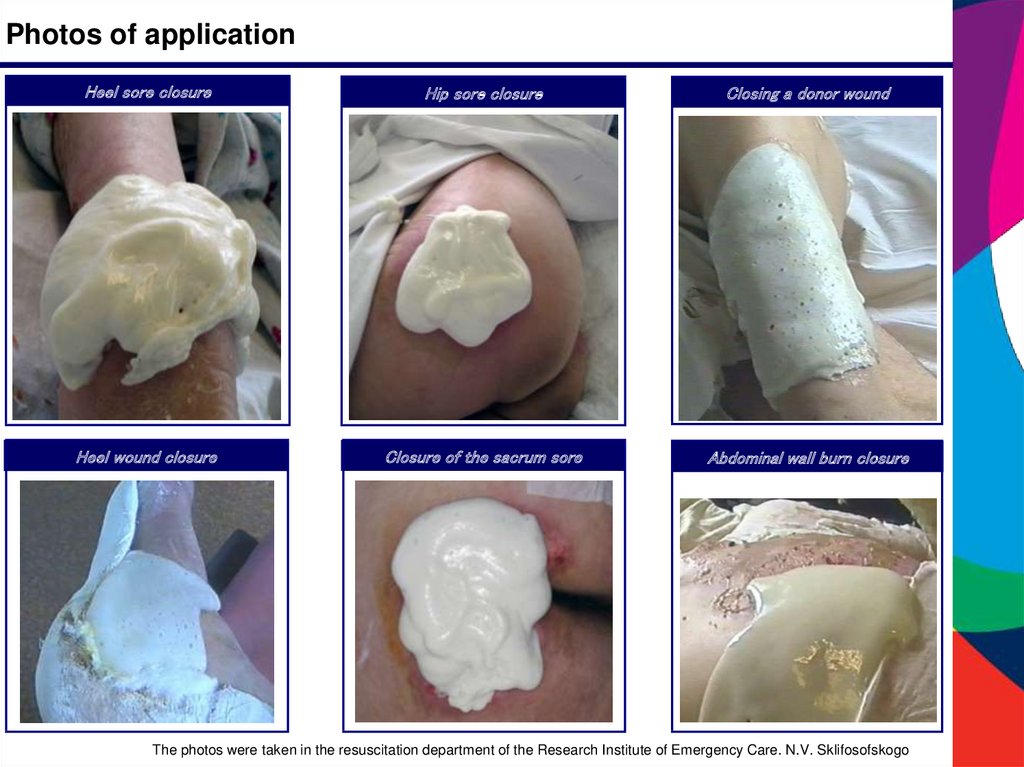
Photos of applicationHeel sore closure
Hip sore closure
Closing a donor wound
Heel wound closure
Closure of the sacrum sore
Abdominal wall burn closure
The photos were taken in the resuscitation department of the Research Institute of Emergency Care. N.V. Sklifosofskogo
6.
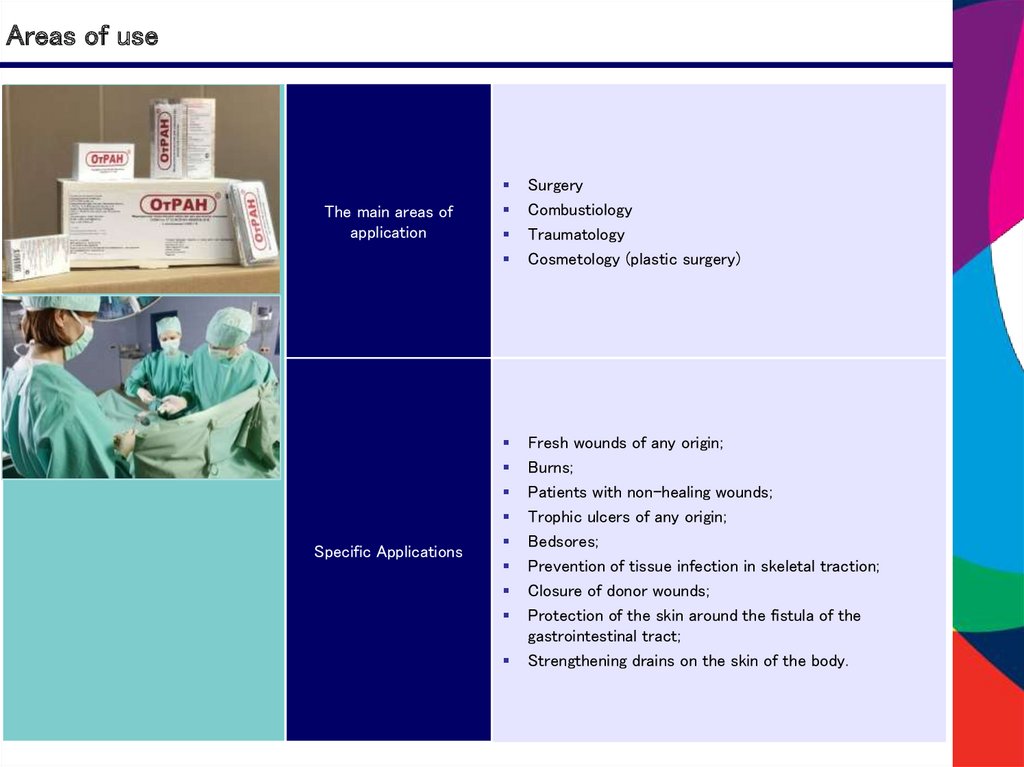
Areas of useThe main areas of
application
Specific Applications
Surgery
Combustiology
Traumatology
Cosmetology (plastic surgery)
Fresh wounds of any origin;
Burns;
Patients with non-healing wounds;
Trophic ulcers of any origin;
Bedsores;
Prevention of tissue infection in skeletal traction;
Closure of donor wounds;
Protection of the skin around the fistula of the
gastrointestinal tract;
Strengthening drains on the skin of the body.
стр. 6
7.
Prerequisites of creationТTraditional dressings (bandage, cotton wool and gauze) have significant drawbacks:
¡¡
trauma,
low hydroscopicity
decay in a wound, etc.
Modern dressings and coatings do not have these disadvantages, but not one of the coatings on the market is not
“ideal” or universal, because they either have a clear specialization in the type of wounds, or have some kind of
deficiency, for example, inconvenience in use (lack of adhesion to wound - the need to use additional fixing bandages
There are a number of requirements for the “perfect dressing” formulated by T. Turner in 1990. : *
To create and control the wound environment moisture optimum for healing;
Provide and control the optimal gas composition of the wound environment;
Maintain an optimal concentration of hydrogen ions (pH) in the wound;
To provide heat insulation of the wound from the external environment;
Be impervious to microorganisms on both sides;
Be non-toxic, do not contain substances or fragments that can interfere with healing;
Be atraumatic without causing pain or damage to the newly formed tissue or epithelium when changing the
dressing.
* - such requirements became the basis for the start of work to create a coating
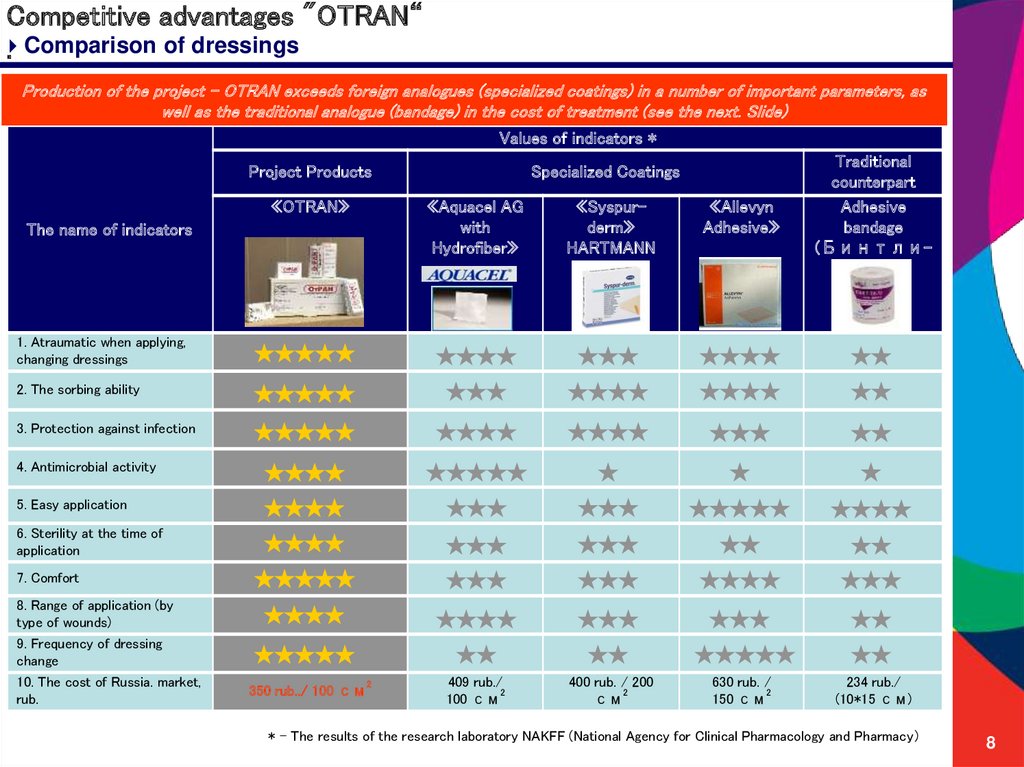
8. Competitive advantages "OTRAN“ .
Competitive advantages "OTRAN“Comparison
of dressings
.
Production of the project - OTRAN exceeds foreign analogues (specialized coatings) in a number of important parameters, as
well as the traditional analogue (bandage) in the cost of treatment (see the next. Slide)
Values of indicators *
«Aquacel AG
with
Hydrofiber»
«Syspurderm»
HARTMANN
«Allevyn
Adhesive»
Traditional
counterpart
Adhesive
bandage
(БинтлиМ)
409 rub./
2
100 см
400 rub. / 200
2
см
630 rub. /
2
150 см
234 rub./
(10*15 см)
Project Products
«OTRAN»
The name of indicators
Specialized Coatings
1. Atraumatic when applying,
changing dressings
2. The sorbing ability
3. Protection against infection
4. Antimicrobial activity
5. Easy application
6. Sterility at the time of
application
7. Comfort
8. Range of application (by
type of wounds)
9. Frequency of dressing
change
10. The cost of Russia. market,
rub.
350 rub../ 100 см
2
* - The results of the research laboratory NAKFF (National Agency for Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacy)
8
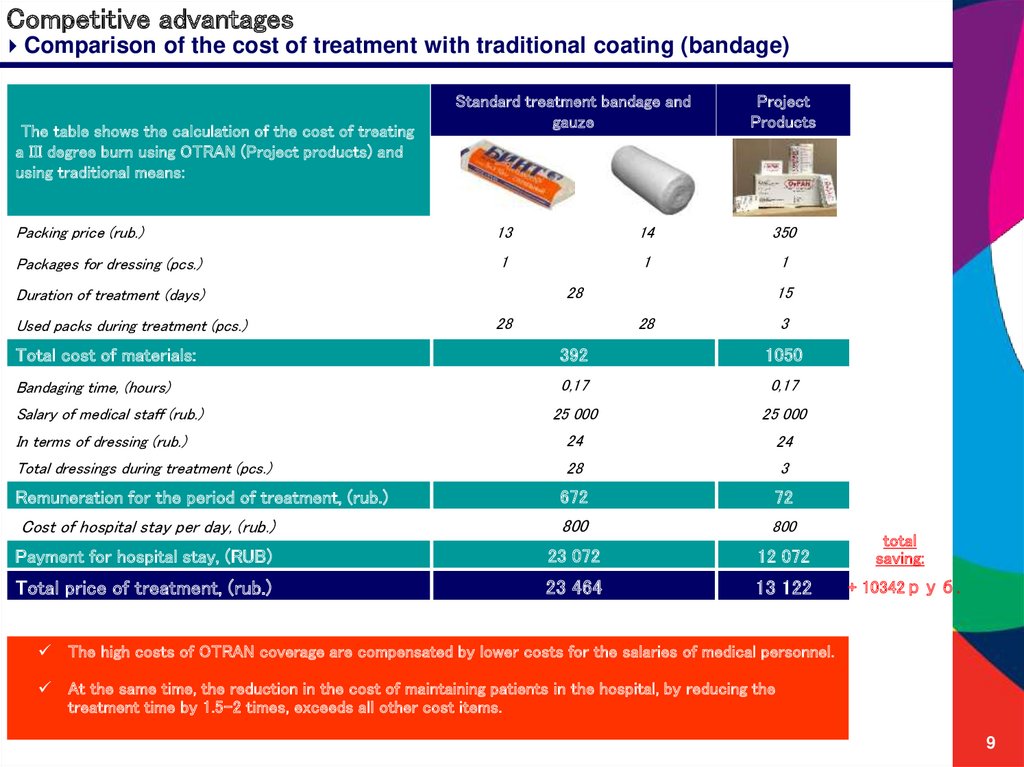
9. Competitive advantages
Comparison of the cost of treatment with traditional coating (bandage)The table shows the calculation of the cost of treating
a III degree burn using OTRAN (Project products) and
using traditional means:
Standard treatment bandage and
gauze
Project
Products
Packing price (rub.)
13
14
350
Packages for dressing (pcs.)
1
1
1
28
Duration of treatment (days)
Used packs during treatment (pcs.)
28
15
28
3
Total cost of materials:
392
1050
Bandaging time, (hours)
0,17
0,17
25 000
25 000
In terms of dressing (rub.)
24
24
Total dressings during treatment (pcs.)
28
3
Remuneration for the period of treatment, (rub.)
672
72
Cost of hospital stay per day, (rub.)
800
800
Payment for hospital stay, (RUB)
23 072
12 072
total
saving:
Total price of treatment, (rub.)
23 464
13 122
+ 10342руб.
Salary of medical staff (rub.)
The high costs of OTRAN coverage are compensated by lower costs for the salaries of medical personnel.
At the same time, the reduction in the cost of maintaining patients in the hospital, by reducing the
treatment time by 1.5–2 times, exceeds all other cost items.
9
10. Description of production technology
Blend productionThe site of preparation of the
polymer mixture (Sarov)
Mixing basic chemicals that form
the basis of the polyurethane foam
composition
Mix packing
Mix filling station
(Ryazan)
Filling is carried out in specially
designed bags of aluminized
polyethylene:
Packaging
Packaging area
(Ryazan)
Preparation of the product OTRAN
for transportation on
warehouse or delivery to the
consumer:
1) Fill 2 component mixture with
nanobaemic in the “reactor
package”.
Production and addition of
nanosized particles on the
example of nano-boehmite
One of the main active substances
providing a given level of the final
characteristics of the product
10
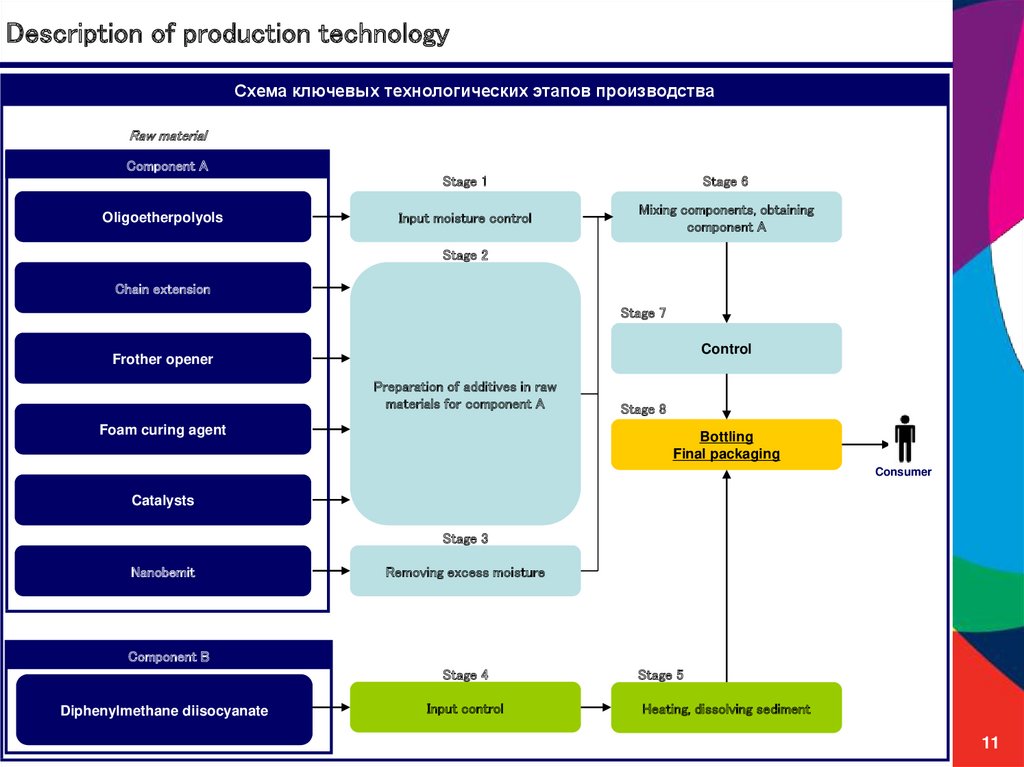
11. Description of production technology
Схема ключевых технологических этапов производстваRaw material
Component A
Oligoetherpolyols
Stage 1
Stage 6
Input moisture control
Mixing components, obtaining
component A
Stage 2
Chain extension
Stage 7
Control
Frother opener
Preparation of additives in raw
materials for component A
Foam curing agent
Stage 8
Bottling
Final packaging
Consumer
Catalysts
Stage 3
Nanobemit
Removing excess moisture
Component B
Stage 4
Diphenylmethane diisocyanate
Input control
Stage 5
Heating, dissolving sediment
11
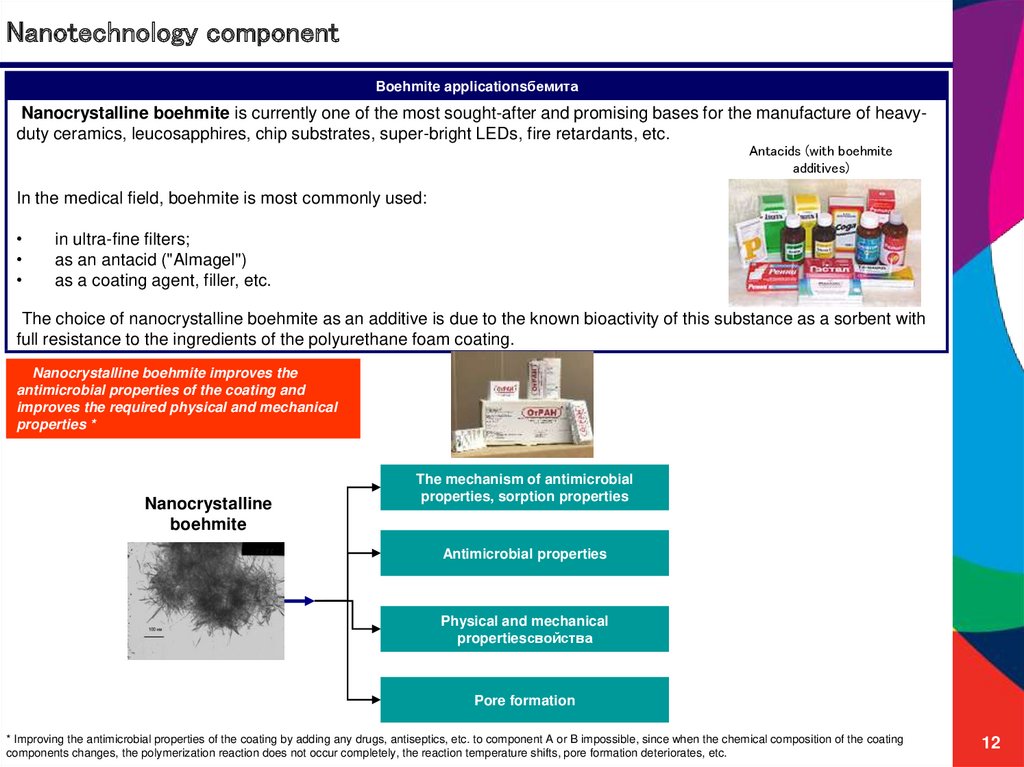
12. Nanotechnology component
Boehmite applicationsбемитаNanocrystalline boehmite is currently one of the most sought-after and promising bases for the manufacture of heavyduty ceramics, leucosapphires, chip substrates, super-bright LEDs, fire retardants, etc.
Antacids (with boehmite
additives)
In the medical field, boehmite is most commonly used:
in ultra-fine filters;
as an antacid ("Almagel")
as a coating agent, filler, etc.
The choice of nanocrystalline boehmite as an additive is due to the known bioactivity of this substance as a sorbent with
full resistance to the ingredients of the polyurethane foam coating.
Nanocrystalline boehmite improves the
antimicrobial properties of the coating and
improves the required physical and mechanical
properties *
Nanocrystalline
boehmite
The mechanism of antimicrobial
properties, sorption properties
Antimicrobial properties
Physical and mechanical
propertiesсвойства
Pore formation
* Improving the antimicrobial properties of the coating by adding any drugs, antiseptics, etc. to component A or B impossible, since when the chemical composition of the coating
components changes, the polymerization reaction does not occur completely, the reaction temperature shifts, pore formation deteriorates, etc.
12
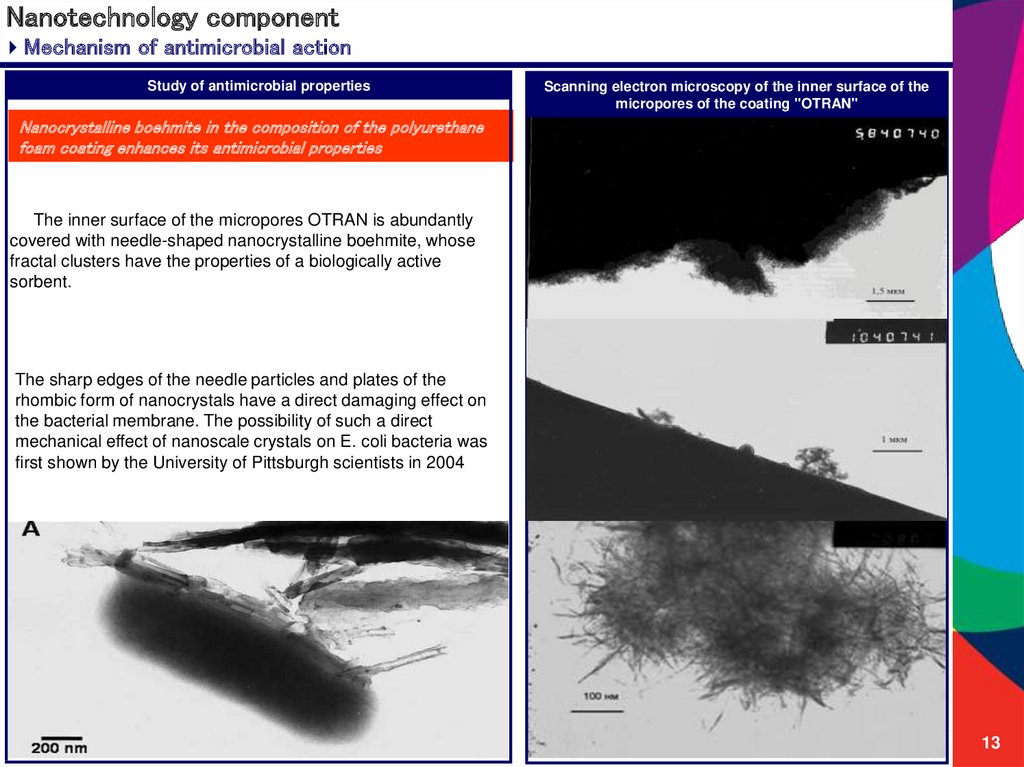
13. Nanotechnology component
Mechanism of antimicrobial actionStudy of antimicrobial properties
Scanning electron microscopy of the inner surface of the
micropores of the coating "OTRAN"
Nanocrystalline boehmite in the composition of the polyurethane
foam coating enhances its antimicrobial properties
The inner surface of the micropores OTRAN is abundantly
covered with needle-shaped nanocrystalline boehmite, whose
fractal clusters have the properties of a biologically active
sorbent.
The sharp edges of the needle particles and plates of the
rhombic form of nanocrystals have a direct damaging effect on
the bacterial membrane. The possibility of such a direct
mechanical effect of nanoscale crystals on E. coli bacteria was
first shown by the University of Pittsburgh scientists in 2004
13
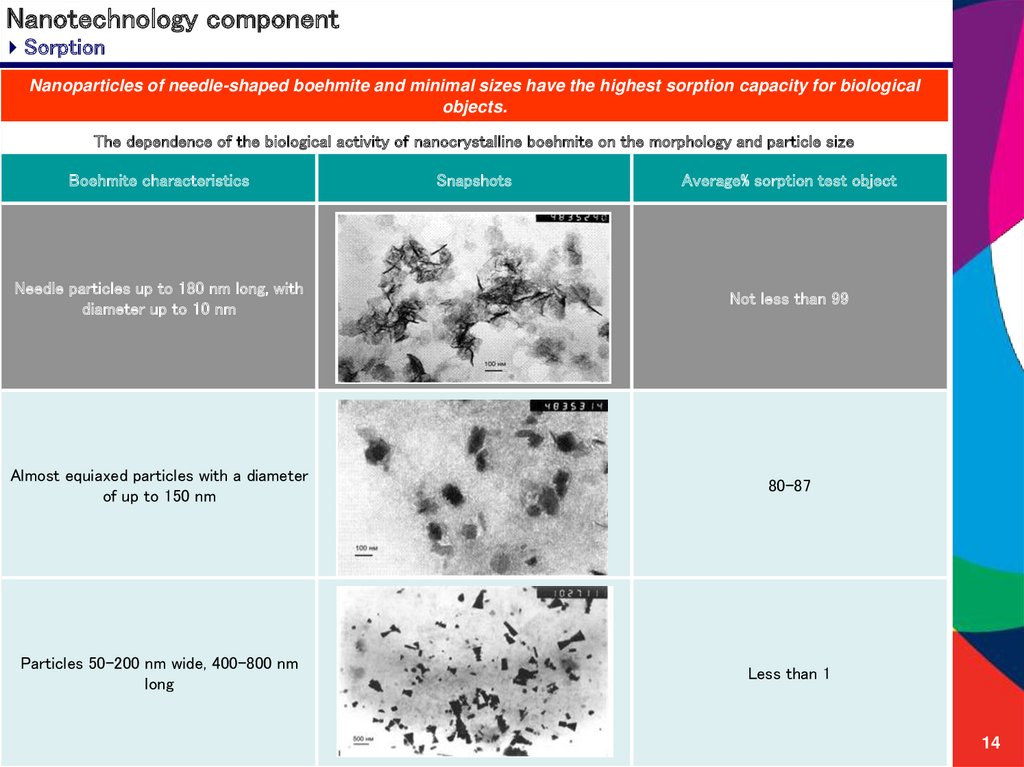
14. Nanotechnology component
SorptionNanoparticles of needle-shaped boehmite and minimal sizes have the highest sorption capacity for biological
objects.
The dependence of the biological activity of nanocrystalline boehmite on the morphology and particle size
Boehmite characteristics
Snapshots
Average% sorption test object
Needle particles up to 180 nm long, with
diameter up to 10 nm
Not less than 99
Almost equiaxed particles with a diameter
of up to 150 nm
80-87
Particles 50-200 nm wide, 400-800 nm
long
Less than 1
14
15. Nanotechnology component
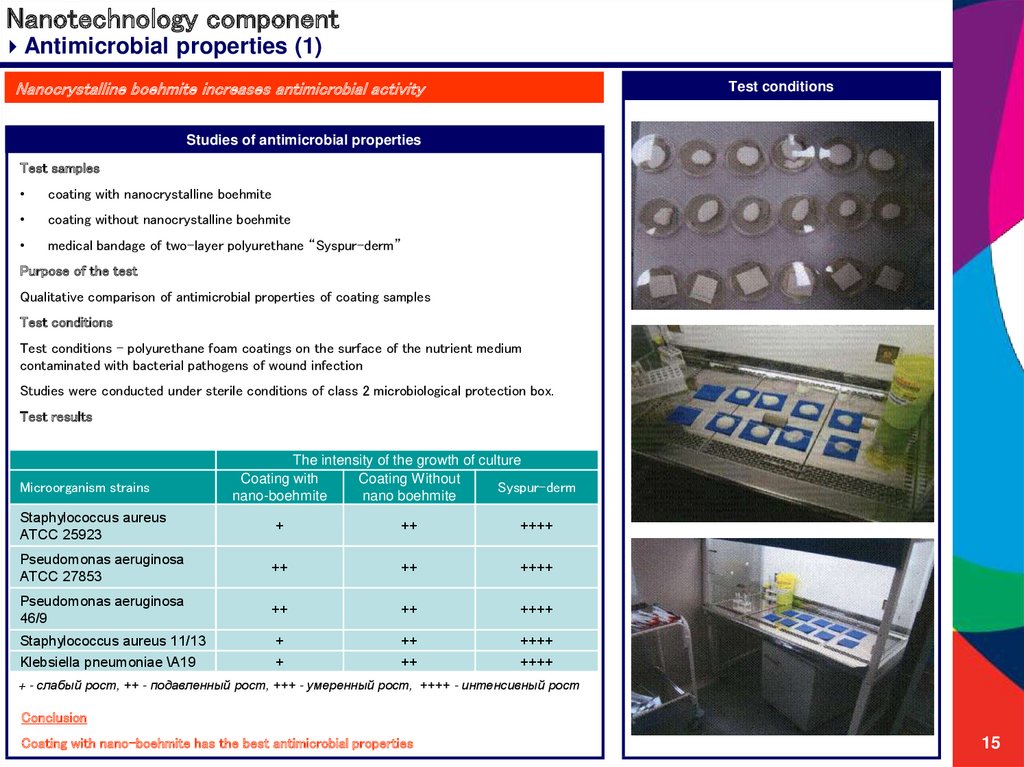
Antimicrobial properties (1)Nanocrystalline boehmite increases antimicrobial activity
Test conditions
Studies of antimicrobial properties
Test samples
coating with nanocrystalline boehmite
coating without nanocrystalline boehmite
medical bandage of two-layer polyurethane “Syspur-derm”
Purpose of the test
Qualitative comparison of antimicrobial properties of coating samples
Test conditions
Test conditions - polyurethane foam coatings on the surface of the nutrient medium
contaminated with bacterial pathogens of wound infection
Studies were conducted under sterile conditions of class 2 microbiological protection box.
Test results
Microorganism strains
The intensity of the growth of culture
Coating with
Coating Without
Syspur-derm
nano-boehmite
nano boehmite
Staphylococcus aureus
ATCC 25923
+
++
++++
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
ATCC 27853
++
++
++++
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
46/9
++
++
++++
Staphylococcus aureus 11/13
Klebsiella pneumoniae \A19
+
+
++
++
++++
++++
+ - слабый рост, ++ - подавленный рост, +++ - умеренный рост, ++++ - интенсивный рост
Conclusion
Coating with nano-boehmite has the best antimicrobial properties
15
16. Nanotechnology component
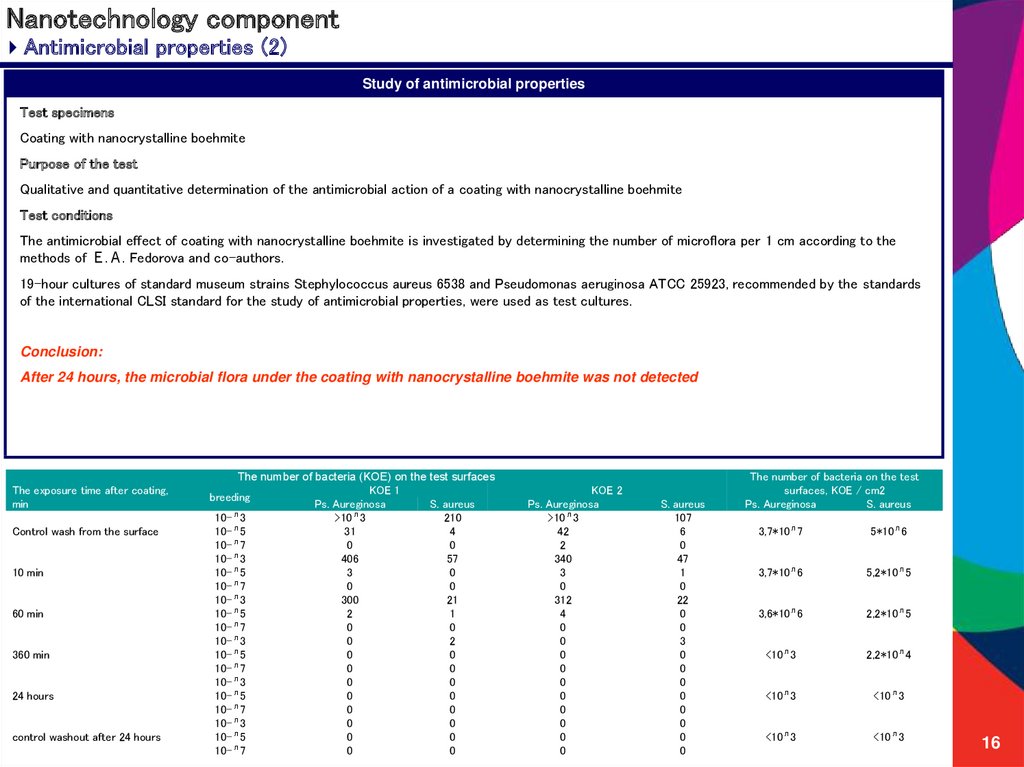
Antimicrobial properties (2)Study of antimicrobial properties
Test specimens
Coating with nanocrystalline boehmite
Purpose of the test
Qualitative and quantitative determination of the antimicrobial action of a coating with nanocrystalline boehmite
Test conditions
The antimicrobial effect of coating with nanocrystalline boehmite is investigated by determining the number of microflora per 1 cm according to the
methods of Е.А. Fedorova and co-authors.
19-hour cultures of standard museum strains Stephylococcus aureus 6538 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 25923, recommended by the standards
of the international CLSI standard for the study of antimicrobial properties, were used as test cultures.
Conclusion:
After 24 hours, the microbial flora under the coating with nanocrystalline boehmite was not detected
The exposure time after coating,
min
Control wash from the surface
10 min
60 min
360 min
24 hours
control washout after 24 hours
The number of bacteria (KOE) on the test surfaces
KOE 1
breeding
Ps. Aureginosa
S. aureus
10-л3
>10л3
210
10-л5
31
4
10-л7
0
0
10-л3
406
57
10-л5
3
0
10-л7
0
0
10-л3
300
21
10-л5
2
1
10-л7
0
0
10-л3
0
2
10-л5
0
0
10-л7
0
0
10-л3
0
0
10-л5
0
0
10-л7
0
0
10-л3
0
0
10-л5
0
0
10-л7
0
0
KOE 2
Ps. Aureginosa
>10л3
42
2
340
3
0
312
4
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
S. aureus
107
6
0
47
1
0
22
0
0
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
The number of bacteria on the test
surfaces, KOE / cm2
Ps. Aureginosa
S. aureus
3,7*10л7
5*10л6
3,7*10л6
5,2*10л5
3,6*10л6
2,2*10л5
<10л3
2,2*10л4
<10л3
<10л3
<10л3
<10л3
16
17. Nanotechnology component
Physical and mechanical propertiesFrom the conducted research it follows that
nanocrystalline boehmite improves the demanded
physical and mechanical properties.
The study of physical and mechanical properties
Purpose: conducting physical and mechanical testing of
coatings with nanocrystalline boehmite
Samples: 5 samples of coating, approximately 250 * 250 * 60
mm in size (three coatings without boehmite and two coatings
with boehmite)
Test methods: work was carried out to determine the following
physicomechanical indicators — compressive stress at 40%
strain, relative elongation and breaking stress under tension,
tear strength, apparent density, relative residual strain.
Used equipment: machine for compressing and stretching
materials, die-cutting press, cutting machine / band saw, scales
(0.001 and 0.0001), caliper, micrometer, thickness gauge.
Sample to determine the strength of tear
Name of the indicator
tensile strength
tensile stress
Dimension
N/m
Sample coverage
No boehmite
Boehmite
98 (50 mm / min)
102 (50 mm / min)
133 (500 mm / min)
186 (500 mm / min)
kPa
64
63
elongation at break
%
115
88
compression stress
kPa
3,1
4,7
%
1,9
2,8
kg / m3
59,5
65,5
relative residual strain in compression
apparent density
17
18. Nanotechnology component
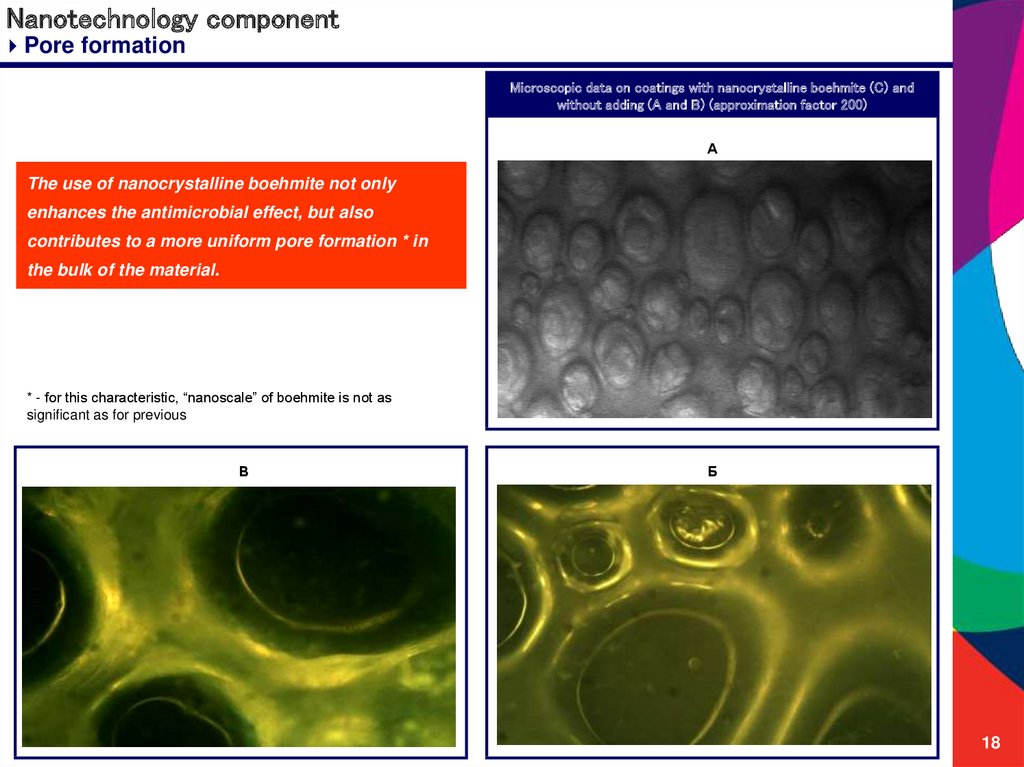
Pore formationMicroscopic data on coatings with nanocrystalline boehmite (C) and
without adding (A and B) (approximation factor 200)
А
The use of nanocrystalline boehmite not only
enhances the antimicrobial effect, but also
contributes to a more uniform pore formation * in
the bulk of the material.
* - for this characteristic, “nanoscale” of boehmite is not as
significant as for previous
В
Б
18
19. Classification of dressings
Traditionaldressings
Adhesive plasters:
Standard packaging - 2 adhesive plasters 5 cm2 each;
Fixing bandages (bandages):
Standard packaging - bandage 7 m long, 10 cm wide
Wet wound dressings:
Hydrocolloid dressings;
Hydrofiber dressings;
Hydrogels;
Alginate dressings;
Absorbent dressings;
Современ
Transparent bandages.
ные
перевязо Antimicrobial wound dressings:
чные
Antimicrobial dressings with silver;
средства
Antimicrobial dressings without silver;
Other:
Cultured tissue;
Biologically interacting dressings:
Collagen dressings;
Dressings containing hyaluronic acid.
19
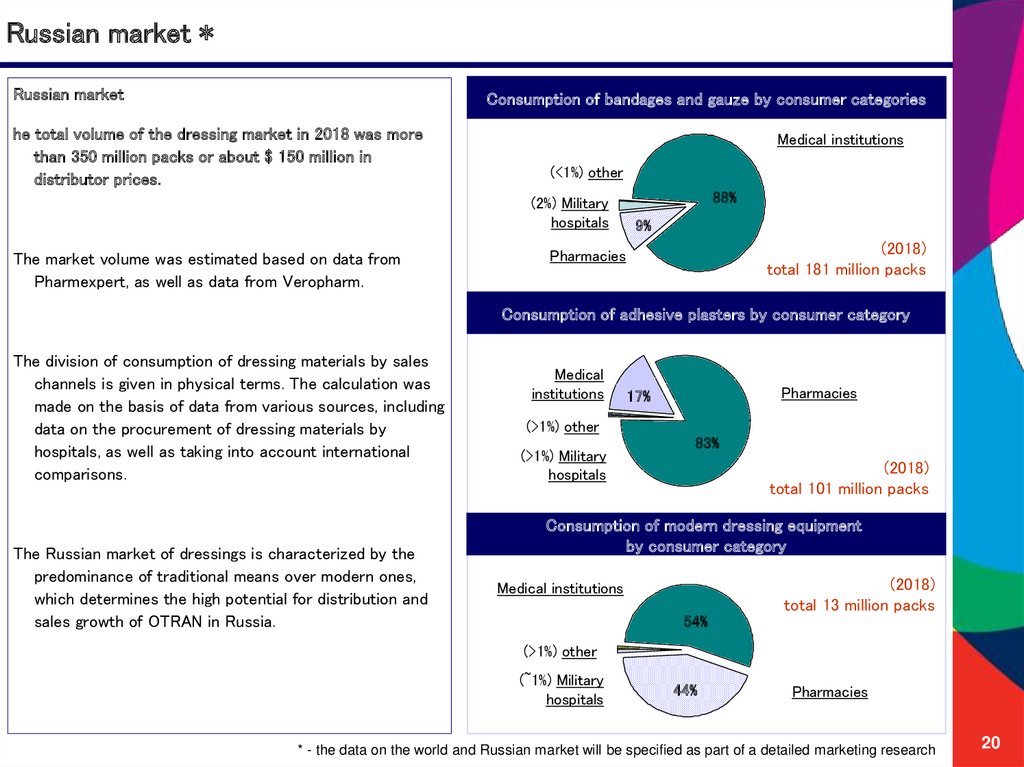
20. Russian market *
Russian marketConsumption of bandages and gauze by consumer categories
he total volume of the dressing market in 2018 was more
than 350 million packs or about $ 150 million in
distributor prices.
Medical institutions
(<1%) other
(2%) Military
hospitals
The market volume was estimated based on data from
Pharmexpert, as well as data from Veropharm.
88%
9%
(2018)
total 181 million packs
Pharmacies
Consumption of adhesive plasters by consumer category
The division of consumption of dressing materials by sales
channels is given in physical terms. The calculation was
made on the basis of data from various sources, including
data on the procurement of dressing materials by
hospitals, as well as taking into account international
comparisons.
The Russian market of dressings is characterized by the
predominance of traditional means over modern ones,
which determines the high potential for distribution and
sales growth of OTRAN in Russia.
Medical
institutions
Pharmacies
17%
(>1%) other
(>1%) Military
hospitals
83%
(2018)
total 101 million packs
Consumption of modern dressing equipment
by consumer category
(2018)
total 13 million packs
Medical institutions
54%
(>1%) other
(~1%) Military
hospitals
44%
Pharmacies
* - the data on the world and Russian market will be specified as part of a detailed marketing research
20
21. Certification
2122. Patents
2223.
Test and Experiment ResultsTesting of the first generation of polyurethane foam
coating "SAREL", 2002 was carried out in 3 leading research
institutions of the country:
Institute of Surgery them. A.V. Vishnevsky
Institute of Emergency Medical Care. N.V. Sklifosovsky
Moscow Medical Academy. THEM. Sechenov.
When studying the scope of application of the
coating, it was found that “OTRAN”:
optimizes the course of the wound process in
patients with:
trophic ulcers
long-term non-healing, burn, gunshot wounds
and also actively affects the wound process in
patients with diabetes mellitus complicated by
diabetic foot syndrome
The main proven properties of the product:
Excellent water and bio-insulation properties;
Excellent sorption properties;
No adhesion to wet surfaces with good adhesion to dry
surfaces;
Non-toxicity, self-sterilization when mixing components;
Absolute repetition of the relief of the wound surface;
Improved capillary blood flow in the affected area.
Test results
! The use of the product of the project allows to
reduce the time of treatment of patients by 2-3
times
! There are no direct contraindications to the use of
the coating, with the exception of rare cases of
abundant suppuration, anaerobic and sinus
infection
23
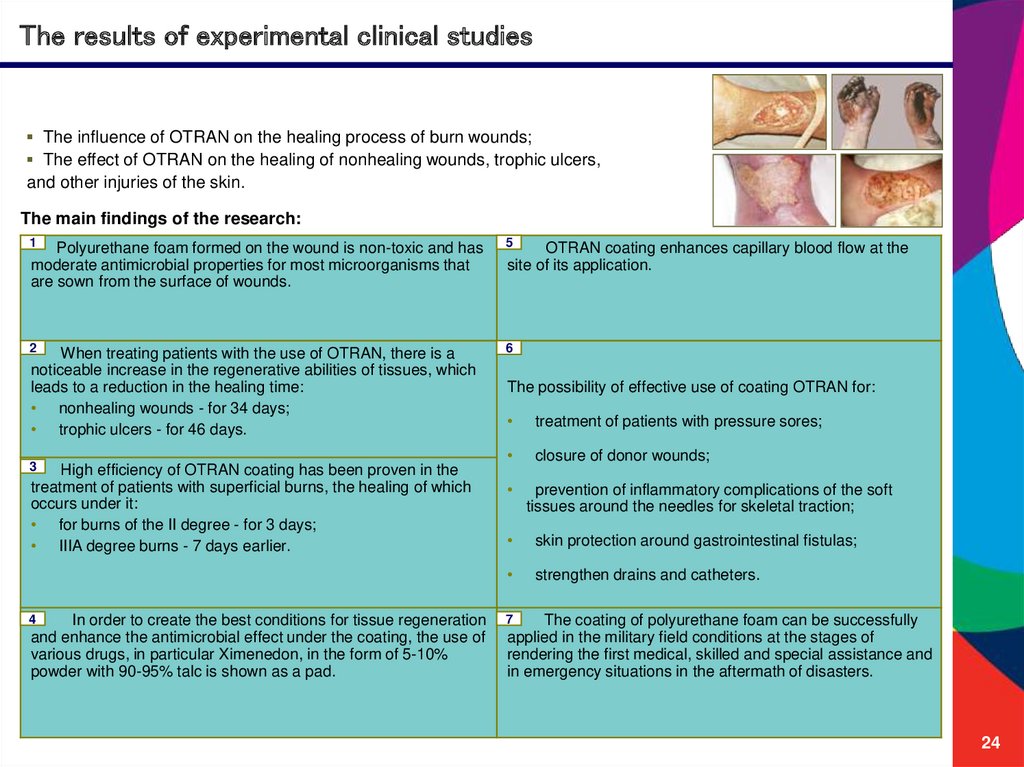
24.
The results of experimental clinical studiesThe influence of OTRAN on the healing process of burn wounds;
The effect of OTRAN on the healing of nonhealing wounds, trophic ulcers,
and other injuries of the skin.
The main findings of the research:
1
Polyurethane foam formed on the wound is non-toxic and has
moderate antimicrobial properties for most microorganisms that
are sown from the surface of wounds.
5
2
6
When treating patients with the use of OTRAN, there is a
noticeable increase in the regenerative abilities of tissues, which
leads to a reduction in the healing time:
• nonhealing wounds - for 34 days;
• trophic ulcers - for 46 days.
3
High efficiency of OTRAN coating has been proven in the
treatment of patients with superficial burns, the healing of which
occurs under it:
• for burns of the II degree - for 3 days;
• IIIA degree burns - 7 days earlier.
4С
In order to create the best conditions for tissue regeneration
and enhance the antimicrobial effect under the coating, the use of
various drugs, in particular Ximenedon, in the form of 5-10%
powder with 90-95% talc is shown as a pad.
OTRAN coating enhances capillary blood flow at the
site of its application.
The possibility of effective use of coating OTRAN for:
treatment of patients with pressure sores;
closure of donor wounds;
prevention of inflammatory complications of the soft
tissues around the needles for skeletal traction;
skin protection around gastrointestinal fistulas;
strengthen drains and catheters.
7П
The coating of polyurethane foam can be successfully
applied in the military field conditions at the stages of
rendering the first medical, skilled and special assistance and
in emergency situations in the aftermath of disasters.
24
25.
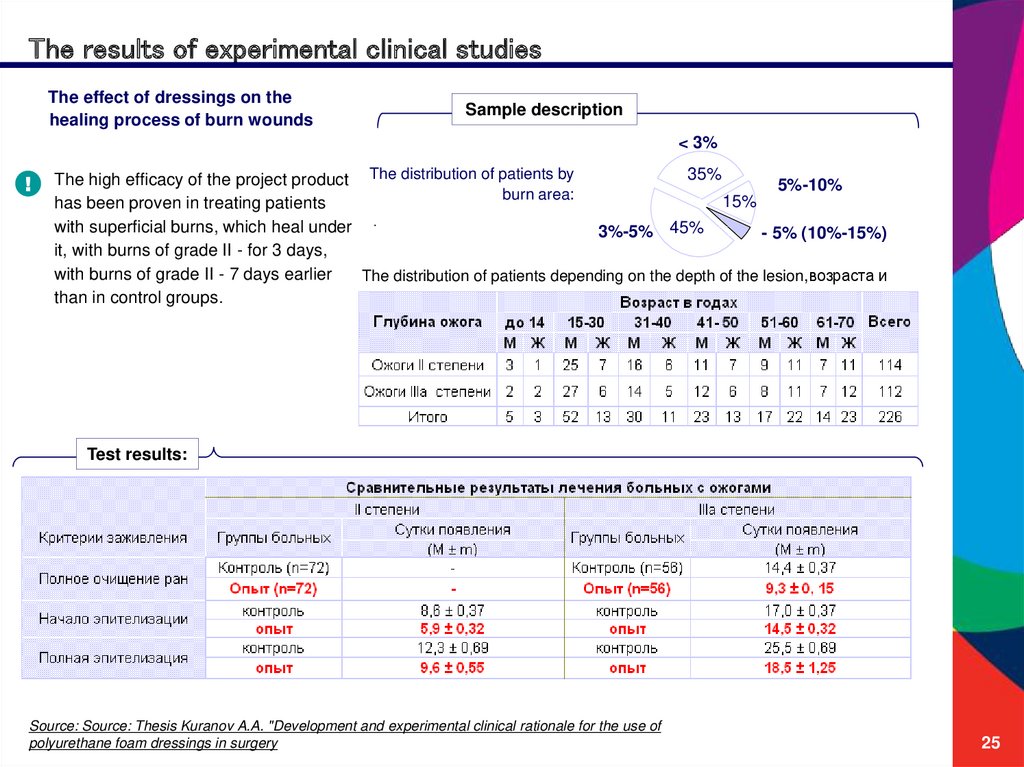
The results of experimental clinical studiesThe effect of dressings on the
healing process of burn wounds
Sample description
< 3%
35%
The high efficacy of the project product The distribution of patients by
5%-10%
burn area:
15%
has been proven in treating patients
with superficial burns, which heal under
3%-5% 45%
- 5% (10%-15%)
it, with burns of grade II - for 3 days,
with burns of grade II - 7 days earlier
The distribution of patients depending on the depth of the lesion,возраста и
пола:
than in control groups.
¡¡
Test results:
Source: Source: Thesis Kuranov A.A. "Development and experimental clinical rationale for the use of
polyurethane foam dressings in surgery
25
26.
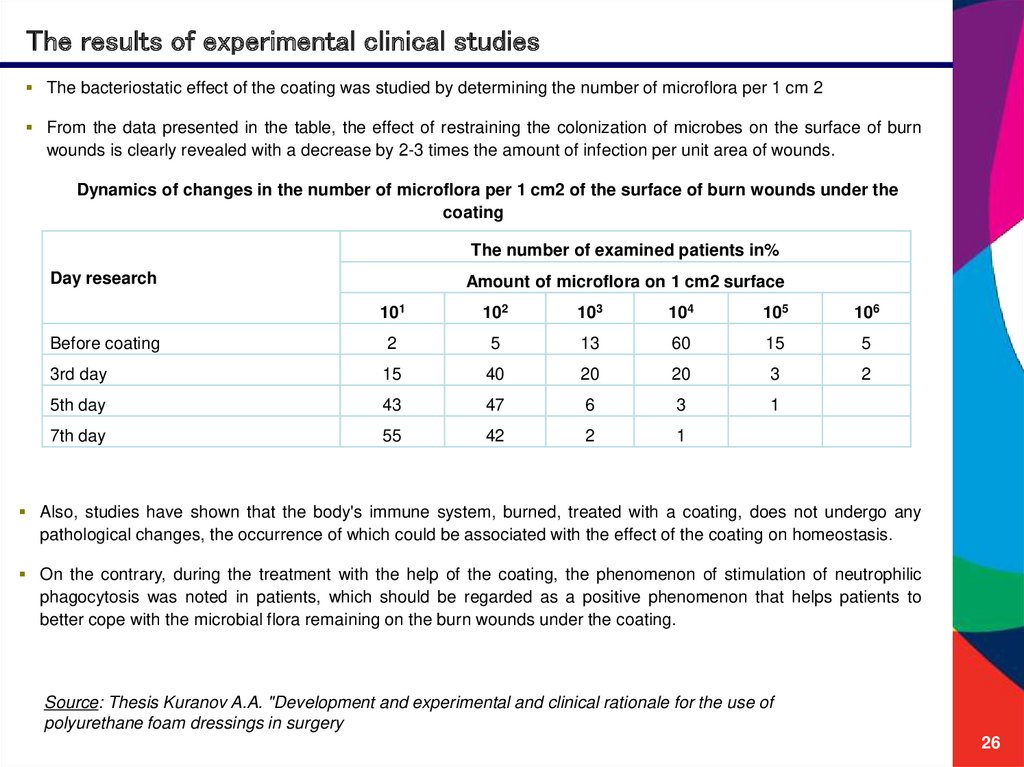
The results of experimental clinical studiesThe bacteriostatic effect of the coating was studied by determining the number of microflora per 1 cm 2
From the data presented in the table, the effect of restraining the colonization of microbes on the surface of burn
wounds is clearly revealed with a decrease by 2-3 times the amount of infection per unit area of wounds.
Dynamics of changes in the number of microflora per 1 cm2 of the surface of burn wounds under the
coating
The number of examined patients in%
Day research
Amount of microflora on 1 cm2 surface
101
102
103
104
105
106
Before coating
2
5
13
60
15
5
3rd day
15
40
20
20
3
2
5th day
43
47
6
3
1
7th day
55
42
2
1
Also, studies have shown that the body's immune system, burned, treated with a coating, does not undergo any
pathological changes, the occurrence of which could be associated with the effect of the coating on homeostasis.
On the contrary, during the treatment with the help of the coating, the phenomenon of stimulation of neutrophilic
phagocytosis was noted in patients, which should be regarded as a positive phenomenon that helps patients to
better cope with the microbial flora remaining on the burn wounds under the coating.
Source: Thesis Kuranov A.A. "Development and experimental and clinical rationale for the use of
polyurethane foam dressings in surgery
26
27.
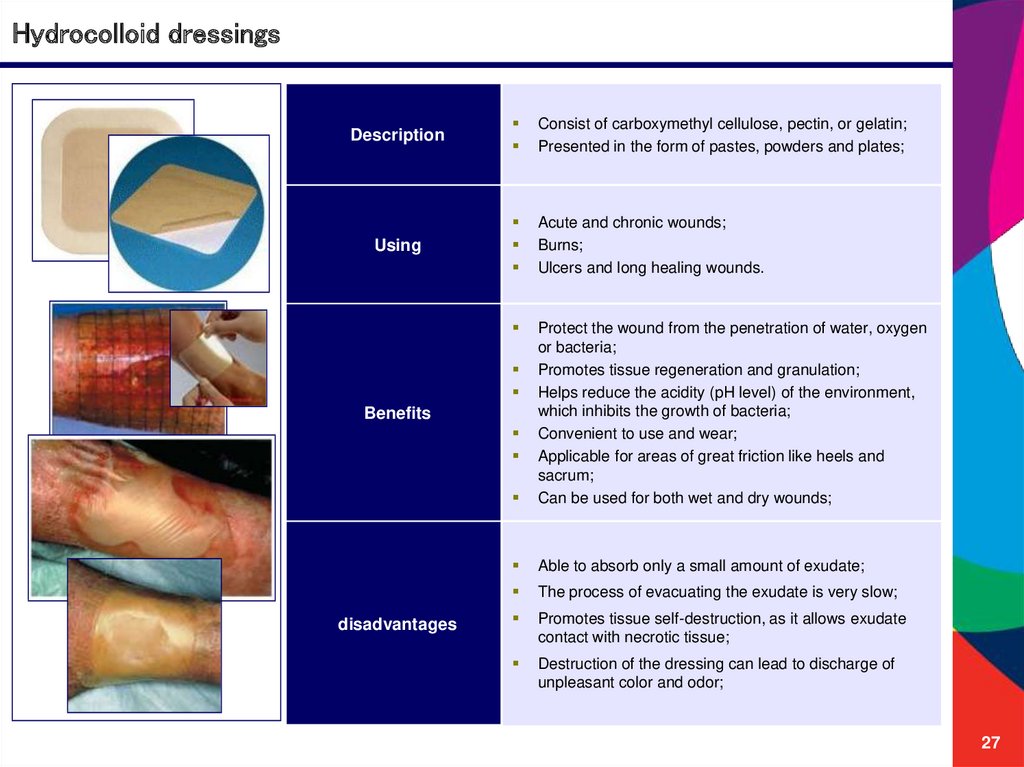
Hydrocolloid dressingsDescription
Consist of carboxymethyl cellulose, pectin, or gelatin;
Presented in the form of pastes, powders and plates;
Using
Acute and chronic wounds;
Burns;
Ulcers and long healing wounds.
Protect the wound from the penetration of water, oxygen
or bacteria;
Promotes tissue regeneration and granulation;
Helps reduce the acidity (pH level) of the environment,
which inhibits the growth of bacteria;
Convenient to use and wear;
Applicable for areas of great friction like heels and
sacrum;
Can be used for both wet and dry wounds;
Able to absorb only a small amount of exudate;
The process of evacuating the exudate is very slow;
Promotes tissue self-destruction, as it allows exudate
contact with necrotic tissue;
Destruction of the dressing can lead to discharge of
unpleasant color and odor;
Benefits
disadvantages
27
28.
Hydrofibre HandwrapsDescription
Using
Intended for wounds with medium and abundant
exudate content:
Wounds;
Burns;
Trophic ulcers;
Longing wounds;
Bedsores etc.
Protect the wound from the penetration of water, oxygen
or bacteria;
Promotes tissue regeneration and granulation;
Helps reduce the acidity (pH level) of the environment,
which inhibits the growth of bacteria;
Convenient to use and wear;
Applicable for areas of great friction like heels and
sacrum;
Can be used for both wet and dry wounds;
The process of evacuating the exudate is very slow;
Destruction of the dressing can lead to discharge of
unpleasant color and odor;
Benefits
disadvantages
Hydrocolloid fibers consist;
The fiber composition is carboxymethyl cellulose, pectin,
or gelatin;
May contain antimicrobial agents;
28
29.
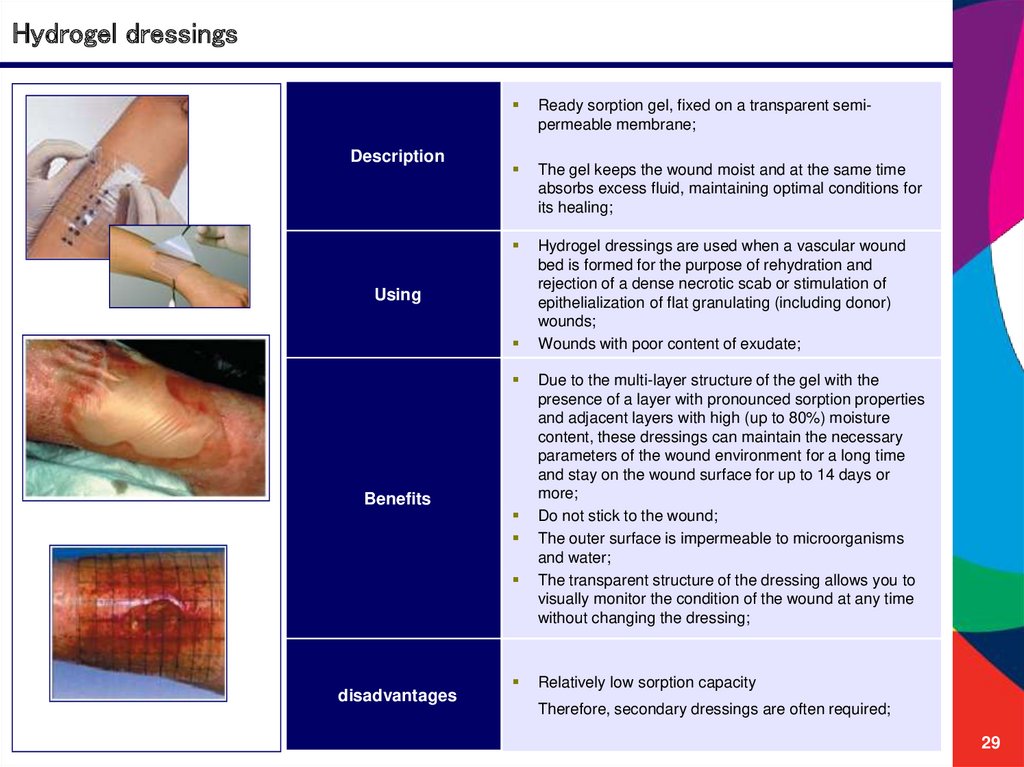
Hydrogel dressingsDescription
Ready sorption gel, fixed on a transparent semipermeable membrane;
The gel keeps the wound moist and at the same time
absorbs excess fluid, maintaining optimal conditions for
its healing;
Hydrogel dressings are used when a vascular wound
bed is formed for the purpose of rehydration and
rejection of a dense necrotic scab or stimulation of
epithelialization of flat granulating (including donor)
wounds;
Wounds with poor content of exudate;
Using
Benefits
disadvantages
Due to the multi-layer structure of the gel with the
presence of a layer with pronounced sorption properties
and adjacent layers with high (up to 80%) moisture
content, these dressings can maintain the necessary
parameters of the wound environment for a long time
and stay on the wound surface for up to 14 days or
more;
Do not stick to the wound;
The outer surface is impermeable to microorganisms
and water;
The transparent structure of the dressing allows you to
visually monitor the condition of the wound at any time
without changing the dressing;
Relatively low sorption capacity
Therefore, secondary dressings are often required;
29
30.
Alginate dressingsThey consist of brown seaweed extracts and are formed
into nonwoven fabric in the form of sheets and ropes;
Able to absorb a large amount of drainage from a wound
by forming a gel that keeps the wound moist, speeding
healing;
Using
Wounds with abundant drainage content;
Benefits
Very high absorption rate;
Promotes the evacuation of exudate from the wound;
Promote tissue regeneration;
Limited scope - only wounds with abundant exudate
content;
Used as a primary dressing and should be covered with
a gauze pad or a compress to extract excreta;
Fixatives are needed to secure the dressing on the
wound;
Description
disadvantages
30
31.
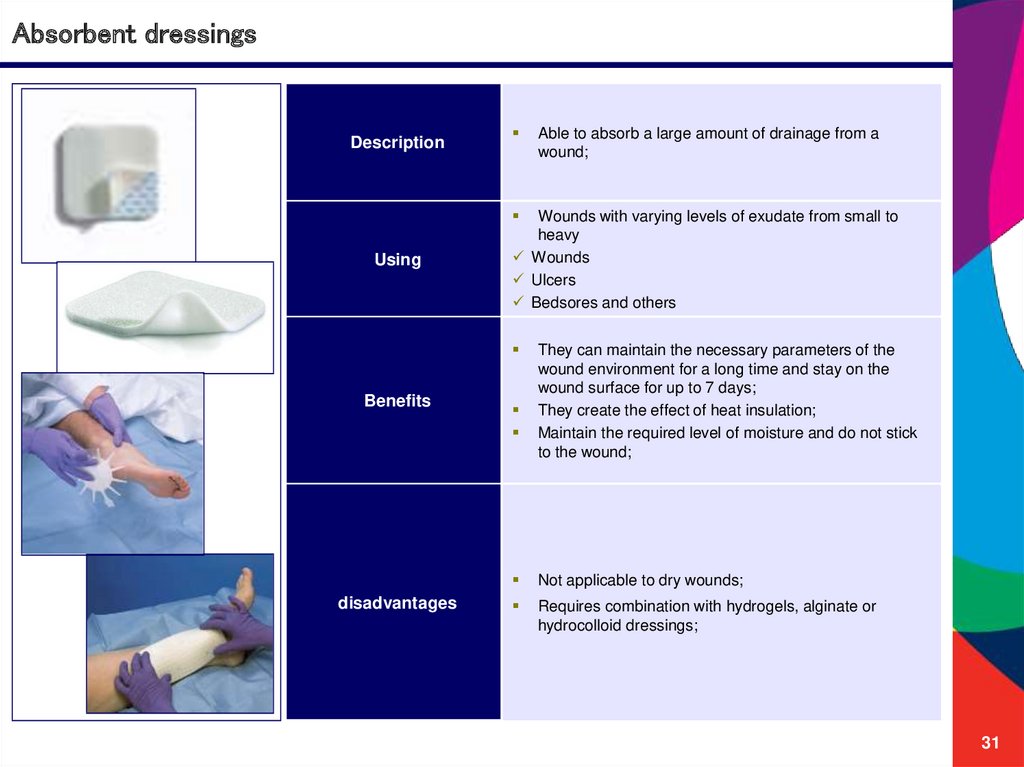
Absorbent dressingsDescription
Able to absorb a large amount of drainage from a
wound;
Using
Wounds with varying levels of exudate from small to
heavy
Wounds
Ulcers
Bedsores and others
Benefits
disadvantages
They can maintain the necessary parameters of the
wound environment for a long time and stay on the
wound surface for up to 7 days;
They create the effect of heat insulation;
Maintain the required level of moisture and do not stick
to the wound;
Not applicable to dry wounds;
Requires combination with hydrogels, alginate or
hydrocolloid dressings;
31
32.
Transparent bandagesDescription
Wounds with low exudate content;
Wounds that are not subject to repeated mechanical
stress;
Ulcers of the first stage;
Most effective for superficial wounds;
Prevent the entry of contaminants into the wound;
Pass oxygen and water vapor;
Transparency, which allows you to control the processes
in the wound without removing the dressing;
Requires combination with primary dressings;
Not suitable for wounds in areas of body subject to great
friction;
Using
Benefits
disadvantages
They consist of a flexible, transparent film of various
types of polymer, which is a sticky, waterproof
membrane that prevents the penetration of pollutants,
allowing oxygen and water vapor to enter the wound;
Used as a secondary dressing;
32
33.
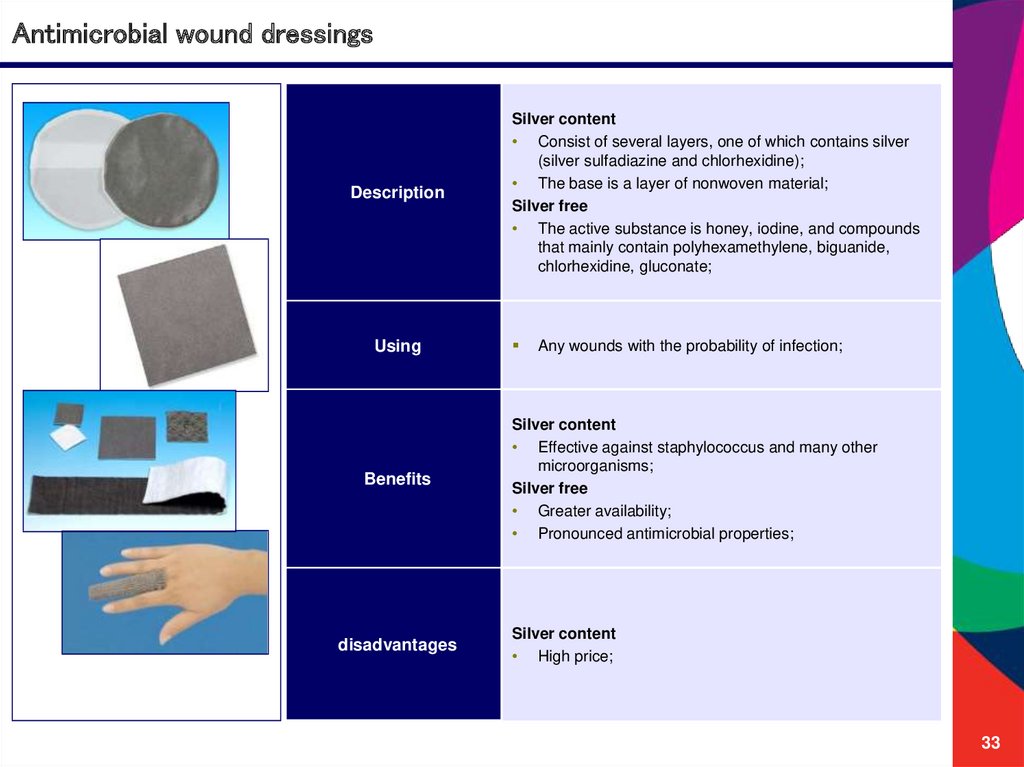
Antimicrobial wound dressingsDescription
Using
Benefits
disadvantages
Silver content
• Consist of several layers, one of which contains silver
(silver sulfadiazine and chlorhexidine);
• The base is a layer of nonwoven material;
Silver free
• The active substance is honey, iodine, and compounds
that mainly contain polyhexamethylene, biguanide,
chlorhexidine, gluconate;
Any wounds with the probability of infection;
Silver content
• Effective against staphylococcus and many other
microorganisms;
Silver free
• Greater availability;
• Pronounced antimicrobial properties;
Silver content
• High price;
33
34.
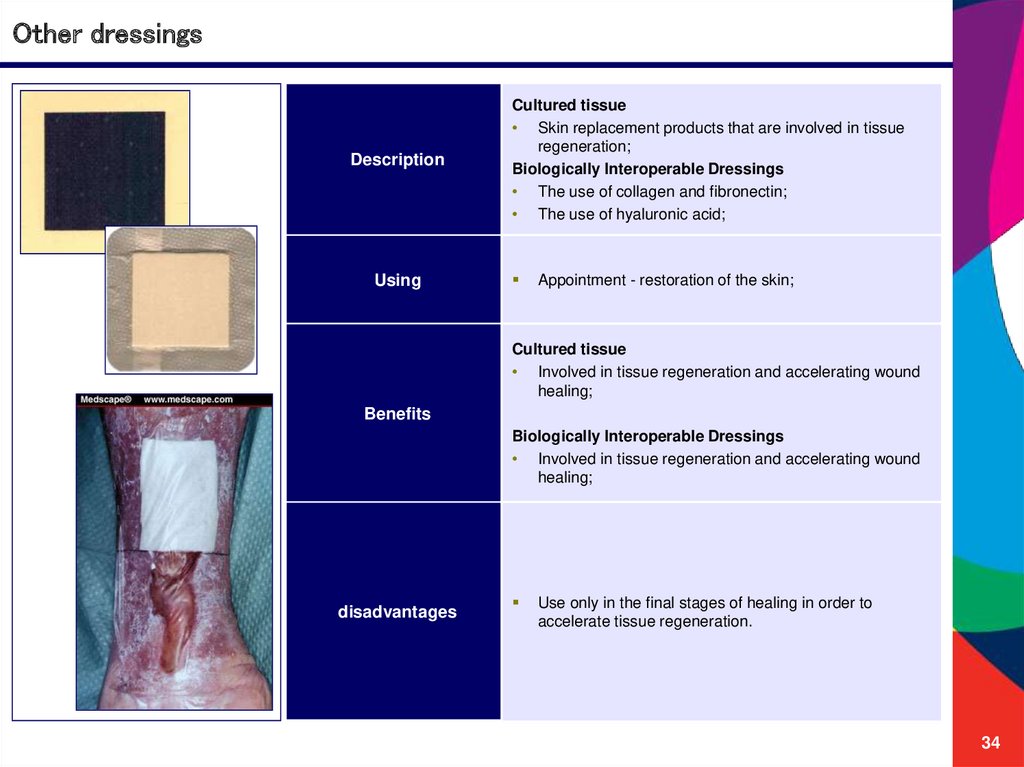
Other dressingsDescription
Using
Cultured tissue
• Skin replacement products that are involved in tissue
regeneration;
Biologically Interoperable Dressings
• The use of collagen and fibronectin;
• The use of hyaluronic acid;
Appointment - restoration of the skin;
Cultured tissue
• Involved in tissue regeneration and accelerating wound
healing;
Benefits
Biologically Interoperable Dressings
• Involved in tissue regeneration and accelerating wound
healing;
disadvantages
Use only in the final stages of healing in order to
accelerate tissue regeneration.
34
35.
Main competitive productsLyofoam dressing
Biatain foam dressing
Intended for treatment:
Intended for treatment:
• Fresh wounds of any origin;
Burns;
• Burns;
Postoperative wounds;
• Patients with nonhealing wounds;
Bedsores;
• Bedsores
Benefits
Benefits
Well absorbs exudate;
Well absorbs exudate;
Well evacuates exudate from the wound;
Well evacuates exudate from the wound;
disadvantages
disadvantages
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
The wound lasts no more than 4 days;
35
36.
Main competitive productsHydrocolloid dressing
Cutinova
Hydrocolloid dressing
Granuflex
Intended for treatment:
Intended for treatment:
Fresh wounds of any origin with level; low to medium wound
exudate;
Granulating wounds;
Ulcers;
Bedsores;
Diabetic foot;
Superficial burns;
Benefits
Well absorbs exudate
Burns;
Ulcers;
Benefits
Impervious to exudate and HIV;
It provokes the rehydration of necrotic tissue;
disadvantages
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
Protects against moisture penetration
disadvantages
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape.
Not suitable for wounds with copious exudate
36
37.
Main competitive productsHydrofiber dressing
Allevyn
Intended for treatment:
Ran with any level of exudate from small to abundant;
Burns;
Bedsores;
Ulcers and diabetic foot;
Benefits
Well absorbs exudate;
Protects against moisture penetration;
Maintains optimum moisture;
disadvantages
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
Does not prevent from repeated mechanical damage;
Hydrogel dressing
Hydrosorb
Intended for treatment:
Ran with low exudate content;
Dry wounds;
Burns;
Benefits
It provokes the death of necrotic tissue;
Maintains optimum moisture;
Able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
disadvantages
Does not prevent from repeated mechanical damage;
Not suitable for wounds with medium and abundant exudate
content;
37
38.
Main competitive productsAbsorbent dressing
Mepitel
Absorbent dressing
Mesorb
Intended for treatment:
Intended for treatment:
Wounds with any exudate content;
Run with any exudate content;
II degree burns;
Burns;
Skin lesions;
Benefits
Benefits
Absorbs and holds any amount of wound exudate;
Protects against moisture penetration;
disadvantages
Maintains optimum moisture;
Does not prevent from repeated mechanical damage;
disadvantages
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
Not able to occupy wounds of arbitrary shape;
Does not prevent from repeated mechanical damage;
38
39.
Main competitive products"Liquid Bandage"
BioCure Inc., (USA)
Foaming bandage
Designed to treat
Comfortable two-component silicone foaming bandage;
Ran;
Designed for the treatment of wounds in the form of
granulating cavities;
Burns;
Ulcers and pressure sores;
Benefits:
Accurately performs the wound cavity;
Simplifies deep wound management;
Protects sensitive postoperative structures;
Maintains a moist wound environment;
The product is under development.
Prevents premature closure of the edges of the skin wound;
Does not stick to the wound surface.
Product inferior to OTRANU by characteristics
39












 medicine
medicine








