Similar presentations:
Decoupling mutational processes in human germline
1. Decoupling mutational processes in human germline
Vladimir SeplyarskiySunyaev lab
Department of Biomedical Informatics
Harvard Medical School
2. DNA and it’s function
DNA->RNA->ProteinDNA double stranded molecule
Each strand have direction
3. Transcription and replication
DNA->DNADNA->RNA
3`
5`
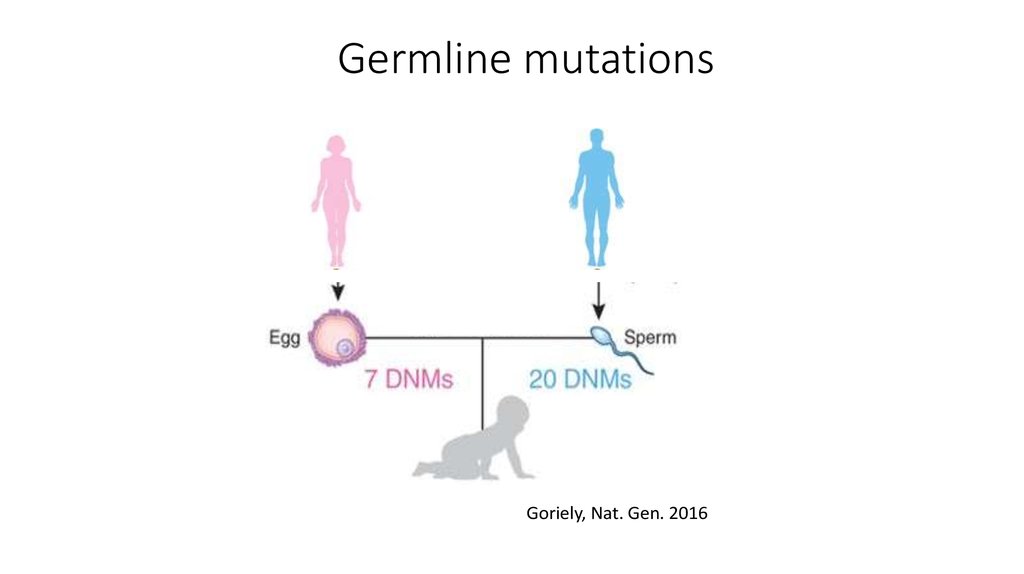
4. Germline mutations
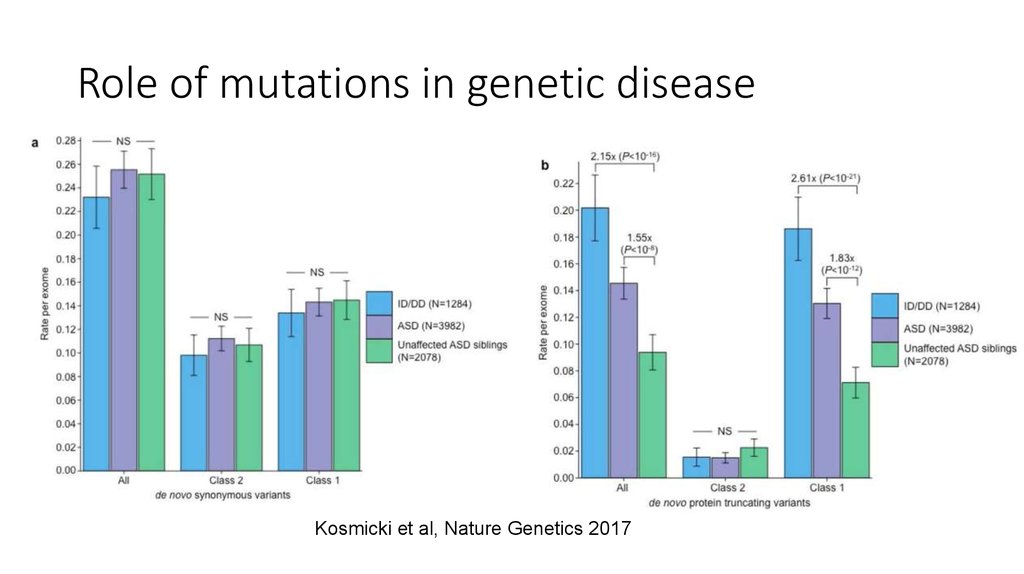
Goriely, Nat. Gen. 20165. Role of mutations in genetic disease
Kosmicki et al, Nature Genetics 20176. Germline mutations are induced by a mixture of mutational processes
Mutationalspectra
Mutational
processes
Observed mutations
7. Spatial variation in intensity of the mutational processes generates diverse mutational patterns
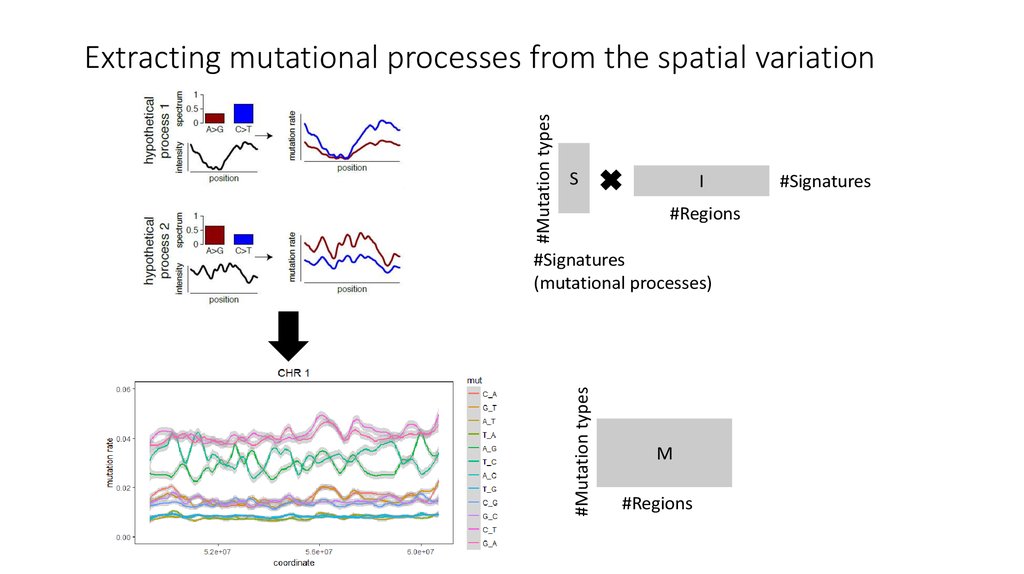
8. Extracting mutational processes from the spatial variation
#Mutation typesExtracting mutational processes from the spatial variation
S
I
#Regions
#Mutation types
#Signatures
(mutational processes)
M
#Regions
#Signatures
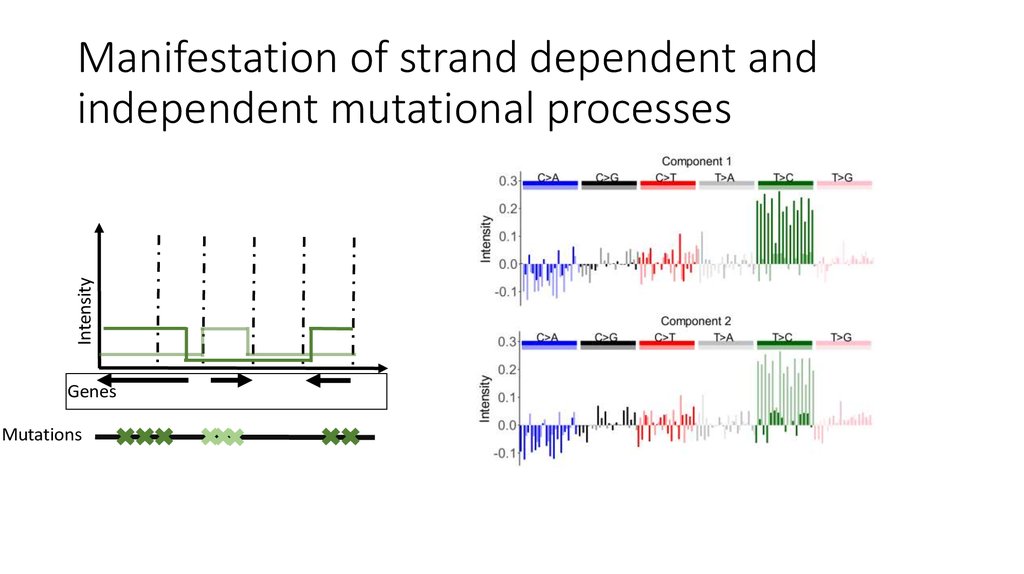
9. Manifestation of strand dependent and independent mutational processes
10. Mutational asymmetry in genes
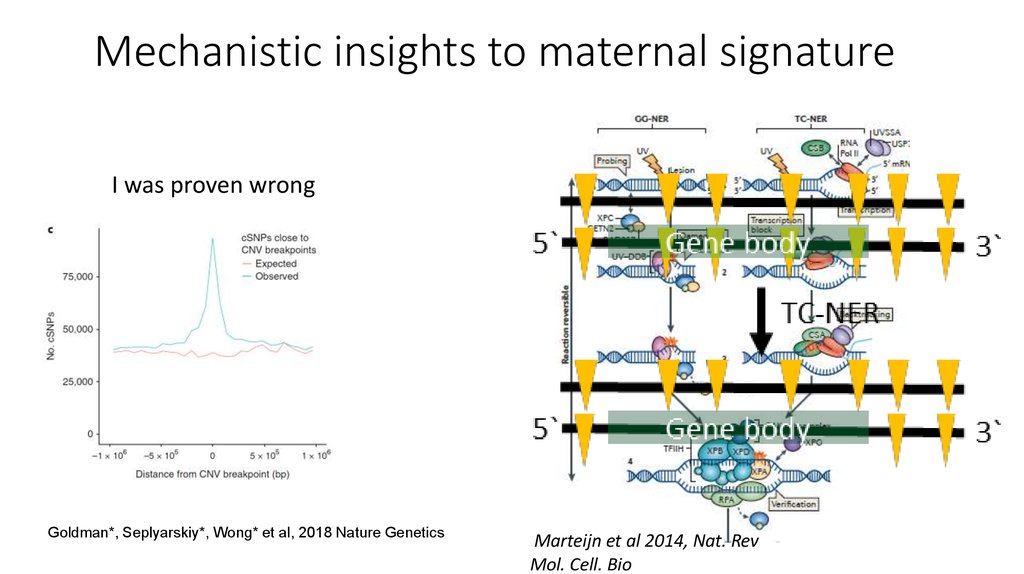
Marteijn et al 2014, Nat. RevMol. Cell. Bio
Hu et al, 2017 PNAS
11. Manifestation of strand dependent and independent mutational processes
IntensityManifestation of strand dependent and
independent mutational processes
Genes
Mutations
12. What do we find?
13. Replication Program
Arneodo lab, Plos Comp 201214. What do we find
15. Process 7/8 have local bursts
maternal regionsde novo clusters
FHIT
16. Process 7/8 – maternal signature
Goldman*, Seplyarskiy*, Wong* et al, 2018 Nature GeneticsJónsson et al, 2017 Nature
17. We are able to predict genomic regions susceptible to maternal clusters
18. Process 7/8– maternal signature
Goldman*, Seplyarskiy*, Wong* et al, 2018 Nature Genetics19. Process 7/8 asymmetric in respect to transcription
20. Process 7/8 asymmetric in respect to transcription
21. Mechanistic insights to maternal signature
I was proven wrongGoldman*, Seplyarskiy*, Wong* et al, 2018 Nature Genetics
Marteijn et al 2014, Nat. Rev
Mol. Cell. Bio
22. C>G mutations created by secondary mechanism (wrong already)
C>G mutations created by secondarymechanism (wrong already)
Clustered mutation contain few C>G substitutions,
But started with different mutation type
23. Third of maternal age effect localized in the regions with high level of the process 7/8
24. Signatures 4 and 5 (maternal signatures) summary
Insights about maternal signature• Maternal signature sensitive to the direction of transcription and replication (no
evidence for DNA breaks)
• Characteristic scale of the signature about 20Mb, but highest intensity achieved on
non-transcribed strand of long genes
• We find evidence for transcription associated mutagenesis
Signatures
5 (maternal
signatures)
summary
• Maternal
signature is4byand
product
of the activity of
error-prone polymerase
25.
AcknowledgementsSignature extraction
Colaborators:
J. Goldmann, P.Kharchenko,
C. Gilissen, W. Wong
Ruslan Soldatov
TOPMed population working
group
Supervision
Shamil Sunyaev



















 biology
biology








