Similar presentations:
Rheumatic endocarditis
1. Kazakh National Medical University named after S.J.Asfendiyarov
Departament of foreign languagesTheme:
Rheumatic endocarditis
Checked by:Bayanbaeva A.A.
Done by : Sabit B.M.
General medicine 14-008-2k
Almaty 2015-2016y
2. Rheumatism (Sokolsky-Bouillaud disease)
is the infectiously-allergic disease which ischaracterized by system disorganization of
connecting tissue with the dominant defeat of
the heart-vessels system.
An exciter is the β-haemolitic streptococcus of
group A. 1-3 % of peoples which had streptococci
quinsies will be ill by rheumatism. This mean that is
the inclination coupled with X-chromosome.
2
3. Clinico-morphologic forms of rheumatism
cardiovascular;polyarthritic;
nodular;
cerebral.
3
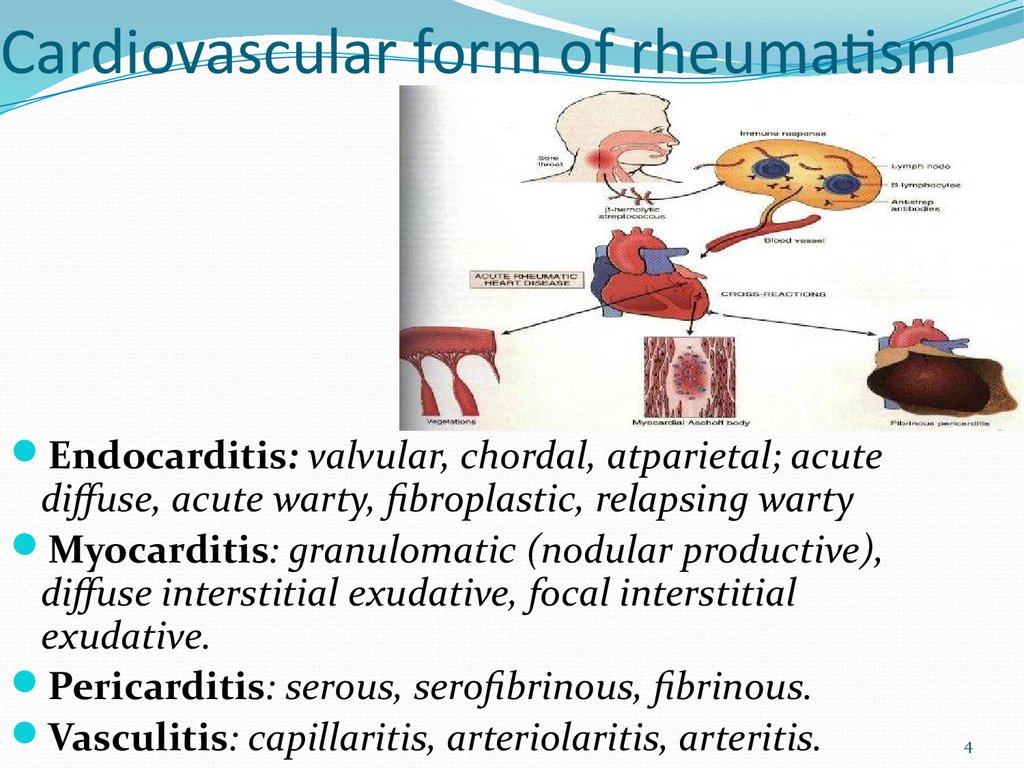
4. Cardiovascular form of rheumatism
Endocarditis: valvular, chordal, atparietal; acutediffuse, acute warty, fibroplastic, relapsing warty
Myocarditis: granulomatic (nodular productive),
diffuse interstitial exudative, focal interstitial
exudative.
Pericarditis: serous, serofibrinous, fibrinous.
Vasculitis: capillaritis, arteriolaritis, arteritis.
4
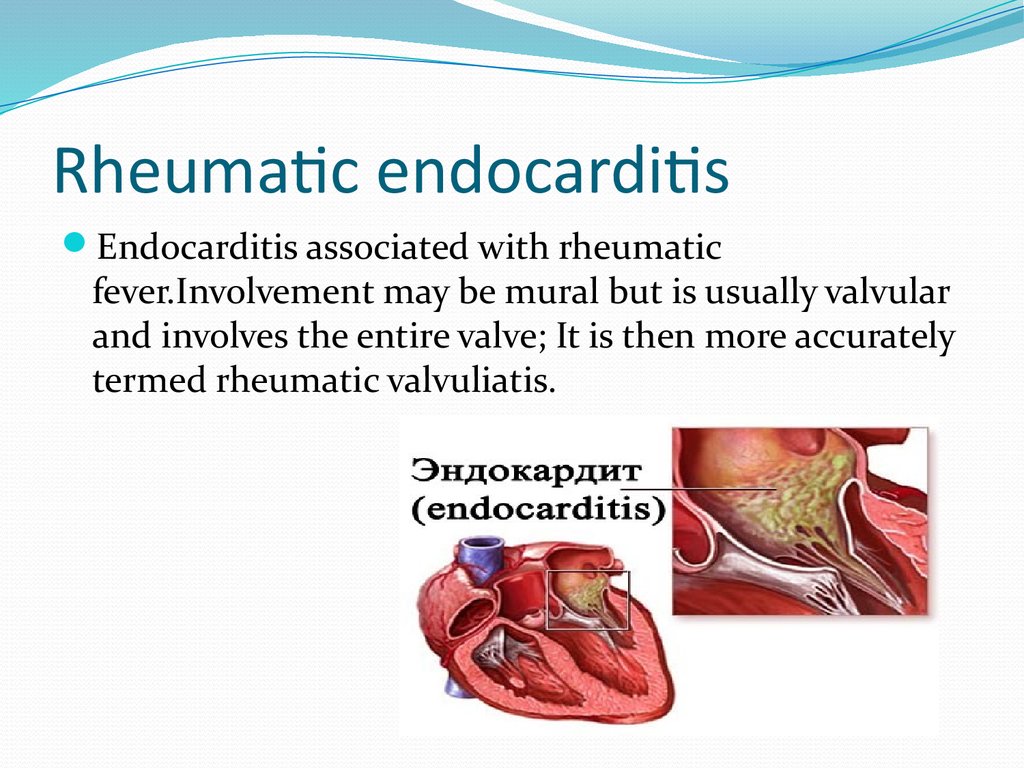
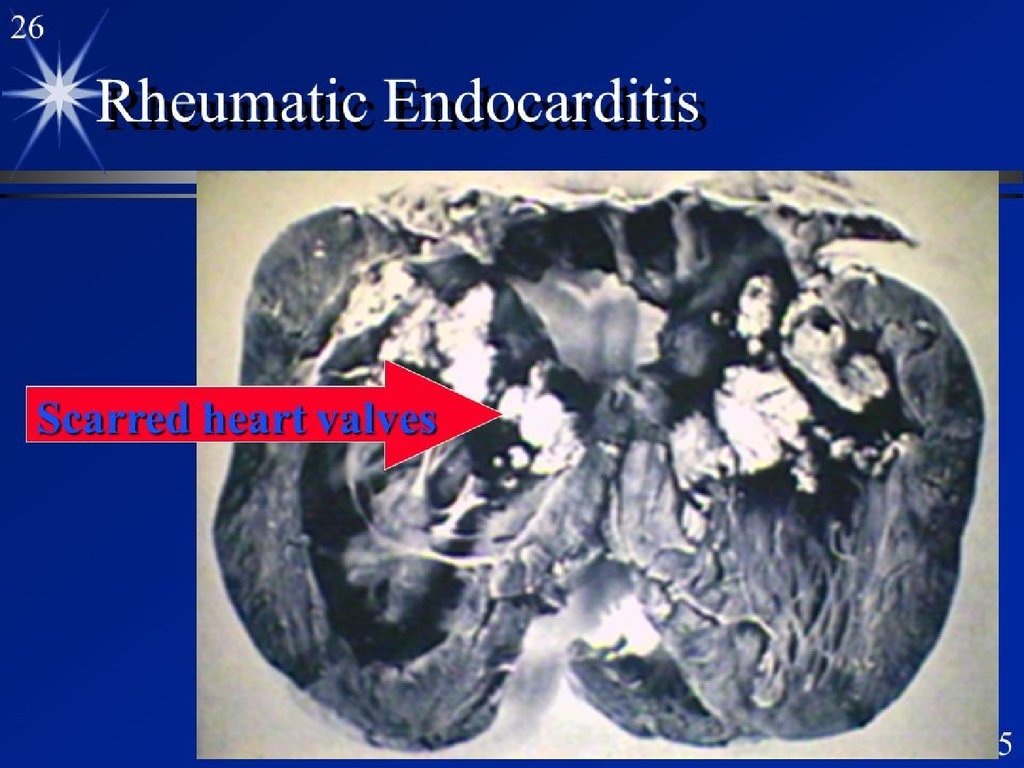
5. Rheumatic endocarditis
Endocarditis associated with rheumaticfever.Involvement may be mural but is usually valvular
and involves the entire valve; It is then more accurately
termed rheumatic valvuliatis.
6. Endocarditis
67.
8. Symptoms
Symptoms include:Fever,chills;
Weakness,low energy;
Sweatiness,especially at night;
Shortness of breath;
Cough;
Loss of appetite,body weight;
9.
Chest pain;Abdominal pain;
Nausea and vomiting;
Painful red patches on the fingres
10. Diagnostics
Examination of suspected infective endocarditisincludes a detailed examination of the patient,and
especially careful
cardiac auscultation;
various blood tests;
ECG;
Echocardiography.
11.
Pathological changes:early stage: serous endocarditis , valve swelling,translucent
Microscopically: valve become loose due to serous
exudate , accompanied by macrophages entering and
fibrinoid necrosis of collagen fiber.
Concomitant involvement of the endocardium and the leftsided valves by inflammatory foci typically results the
small (diameter 1- to 2-mm) vegetations .
12.
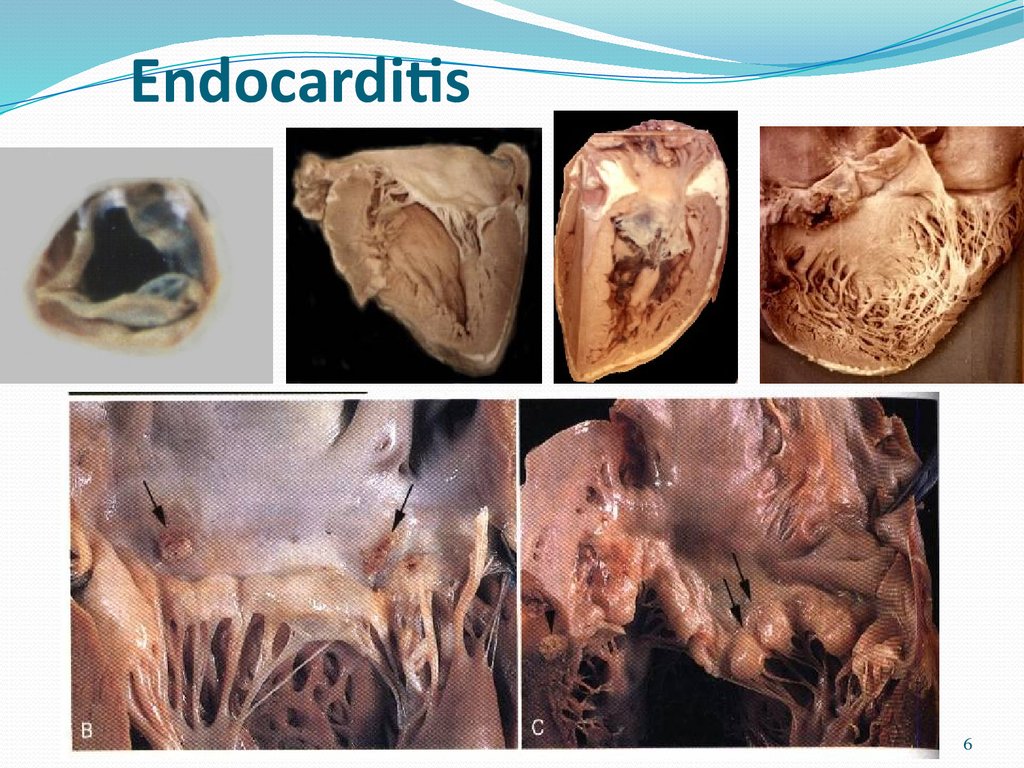
Acute rheumatic endocarditis: small (diameter 1- to 2-mm) vegetations along the mitral valvemargin, insufficient to cause valvular deformation.
13.
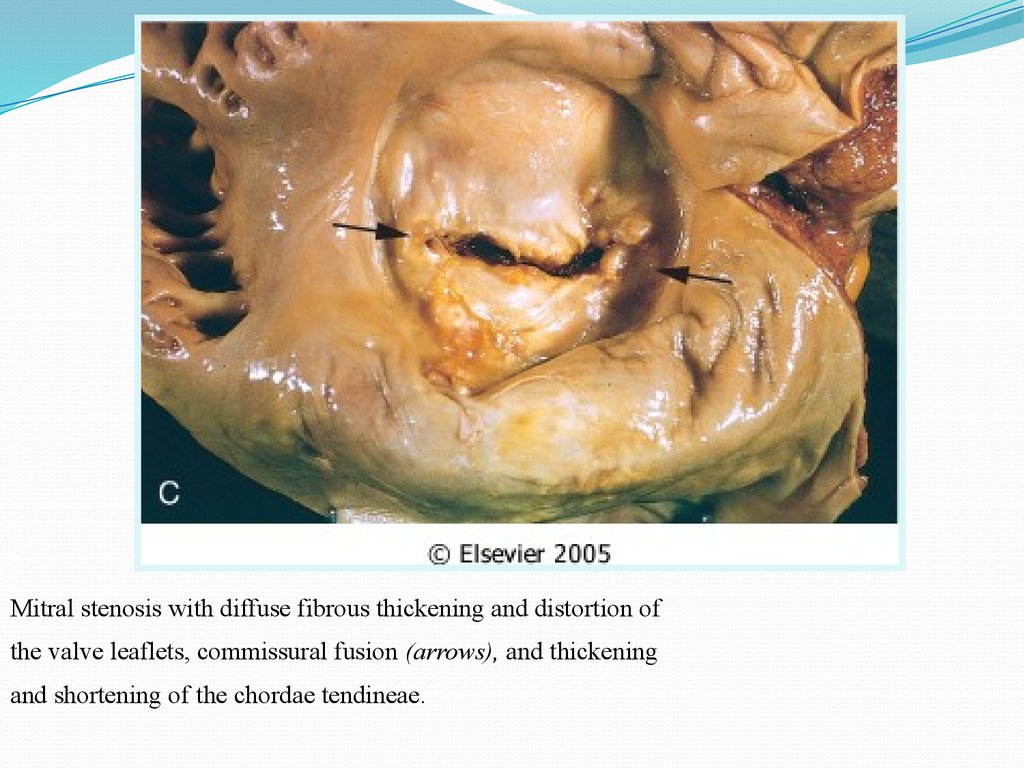
Mitral stenosis with diffuse fibrous thickening and distortion ofthe valve leaflets, commissural fusion (arrows), and thickening
and shortening of the chordae tendineae.
14.
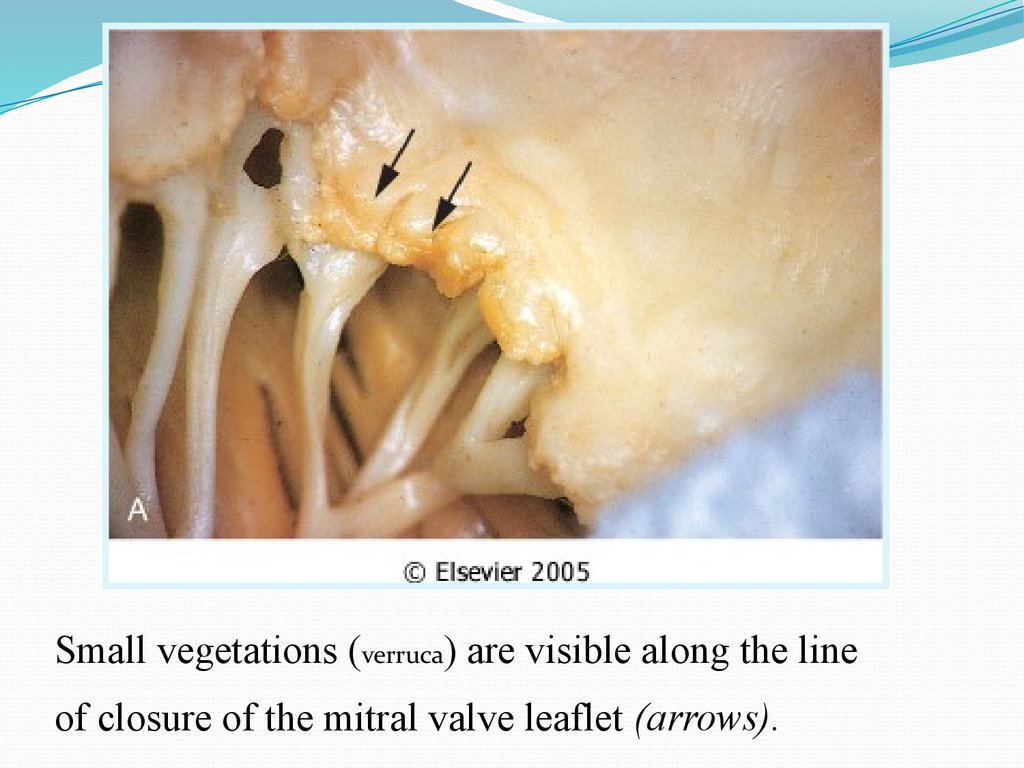
Small vegetations (verruca) are visible along the lineof closure of the mitral valve leaflet (arrows).
15.
16.
17.
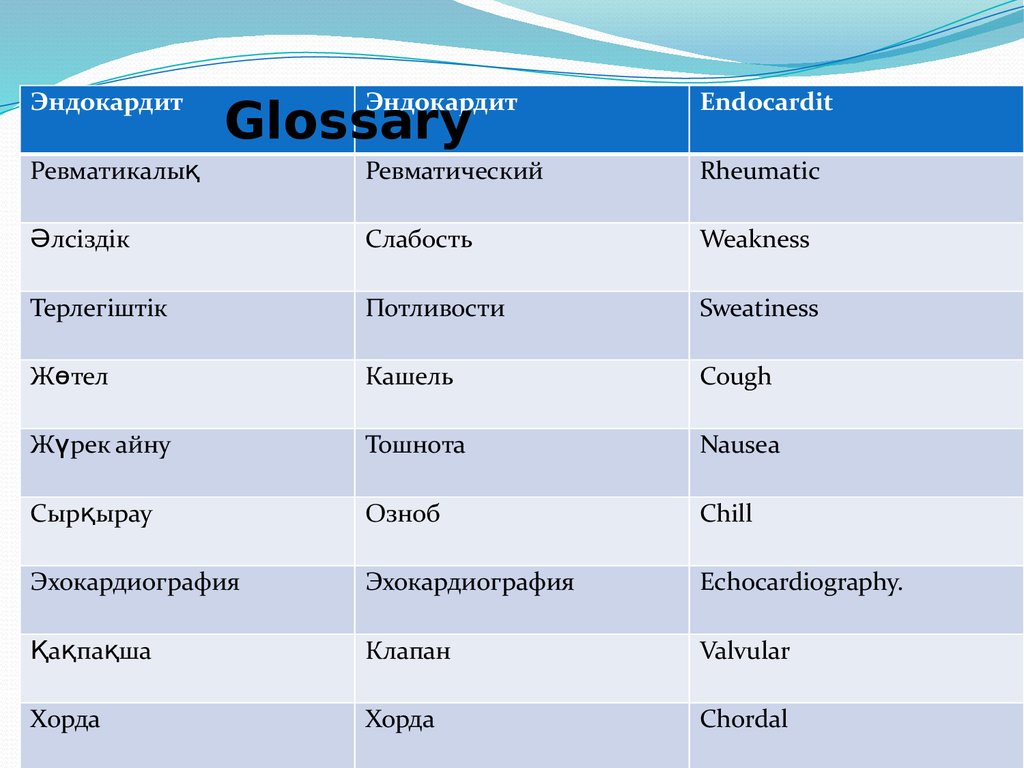
ЭндокардитЭндокардит
Endocardit
Ревматикалық
Ревматический
Rheumatic
Әлсіздік
Слабость
Weakness
Потливости
Sweatiness
Кашель
Cough
Жүрек айну
Тошнота
Nausea
Сырқырау
Озноб
Chill
Эхокардиография
Эхокардиография
Echocardiography.
Қақ
пақша
Клапан
Valvular
Хорда
Chordal
Glossary
Терлегіштік
Жөтел
Хорда
18. Spent literature
1)“Essential english for medicalstudents”
A.M.Maslova,Z.I.Winestein,L.S.Plebey
skaya
2)www.google.com
3)www.medicine.com
19.
Thank youfor attention










 medicine
medicine








