Similar presentations:
Cellular Respiration
1. Cellular Respiration
2. Metabolic reactions
• Many reactions are involved in the metabolism of anorganism:
ANABOLIC-CATABOLIC reactions
• 6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight= C6H12O6 + 6O2
• C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
HYDROLYSIS:
• Cleavage (расщепление) of a complex molecule into its
subunits by adding water
ex: maltose + H2O = glucose + glucose
DEHYDRATION:
• Condensation reaction when from smaller molecules or
subunits, complex molecule formed and water is released
ex: glucose + glucose = maltose + H2O
3.
4.
EXOTHERMIC:• When from reaction among products heat is released
ex: glucose + O2 = H2O + CO2 + energy + heat*
*this reaction passes in our muscles
ENDOTHERMIC:
• When reaction needs heat energy and occurs by taking heat
energy from environment
ex: evaporation of water in order to body to keep normal body
temperature
REDOX reactions
OXYDATION:
When as a result of reaction some atom loses electron
ex: K=K++eREDUCTION:
When as a result of reaction atom accepts electron
ex: Cl2+2e-=2Cl-
5.
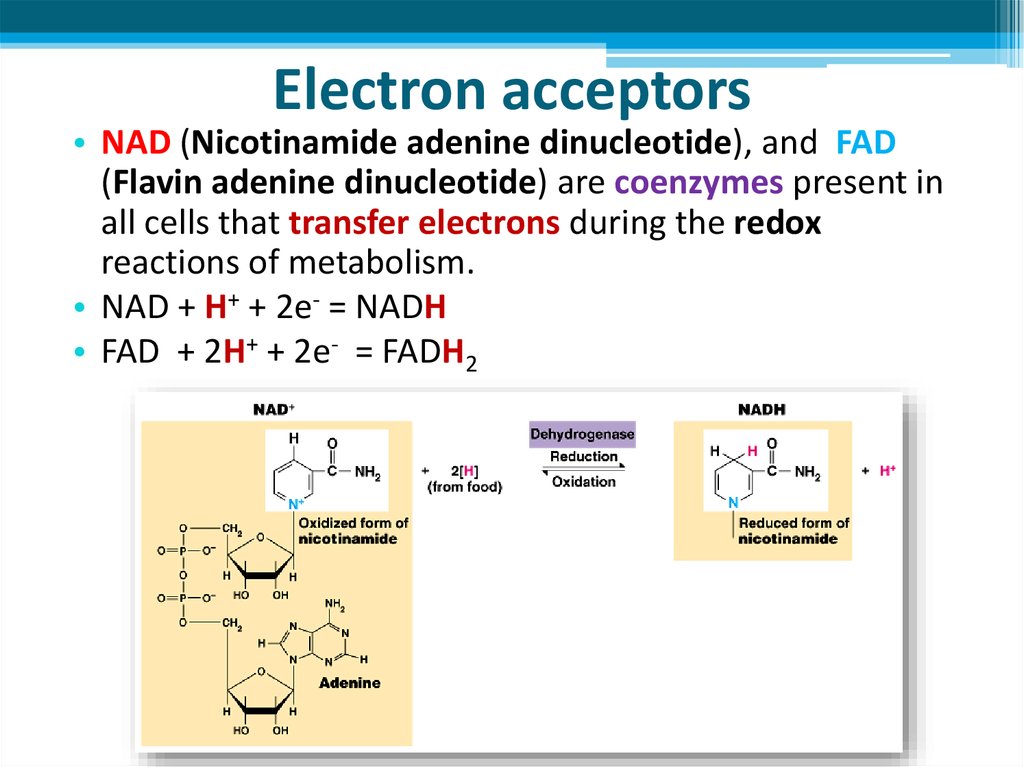
6. Electron acceptors
• NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and FAD(Flavin adenine dinucleotide) are coenzymes present in
all cells that transfer electrons during the redox
reactions of metabolism.
• NAD + H+ + 2e- = NADH
• FAD + 2H+ + 2e- = FADH2
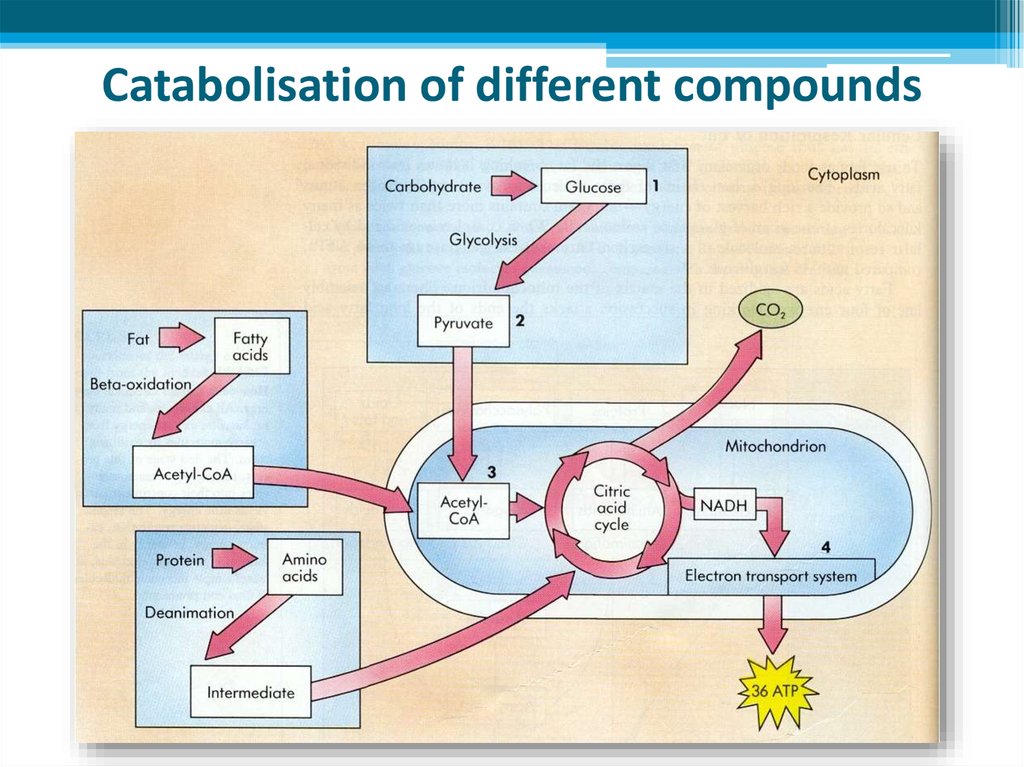
7. Cellular respiration
• Cellular respiration is a kind of catabolism in whichenergy of food molecules, especially glucose is released
as ATP and heat.
• Oxygen in the air we breathe makes the production of
ATP more efficient, although some ATP is made without
oxygen.
• Metabolic processes that require oxygen are called
aerobic.
• Metabolic processes that do not require oxygen are
called anaerobic, which means “without air”.
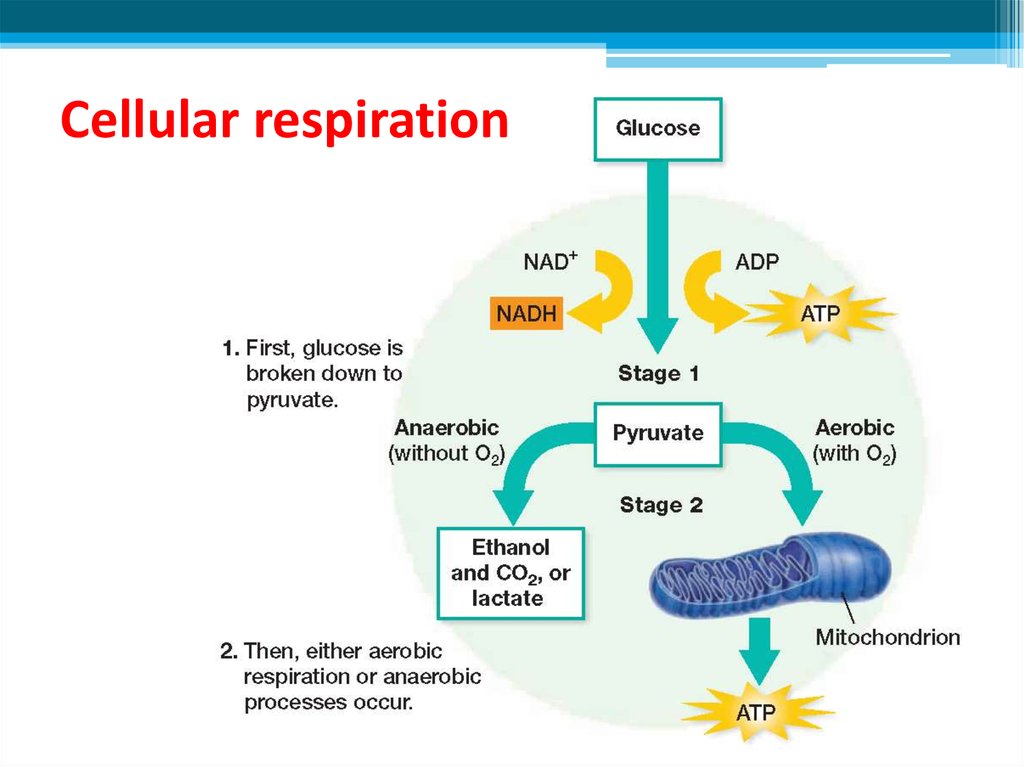
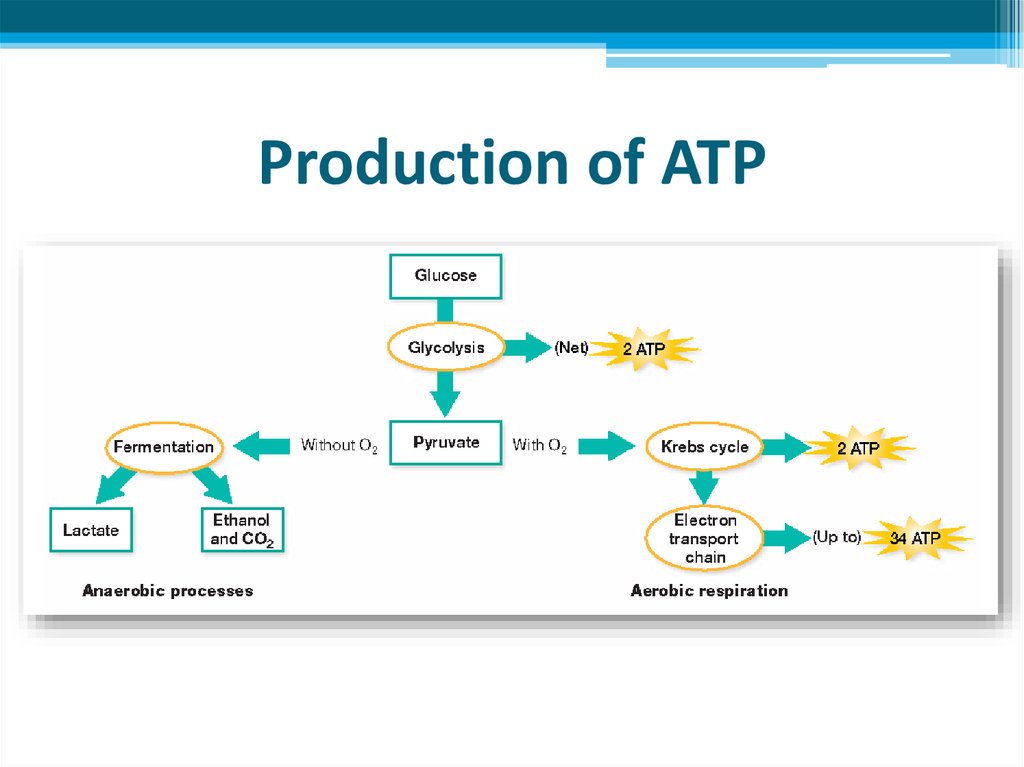
8. Stages of cellular respiration
• The breakdown of glucose during cellular respirationcan be summarized by the following equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
glucose oxygen gas carbon dioxide water
ATP
• Cellular respiration occurs in two stages:
Stage 1 Glucose is converted to pyruvate, producing
a small amount of ATP and NADH.
Stage 2 When oxygen is present, pyruvate and
NADH are used to make a large amount of ATP.
When oxygen is not present, pyruvate is converted
to either lactic acid or alcohol and carbon dioxide.
9. Cellular respiration
10.
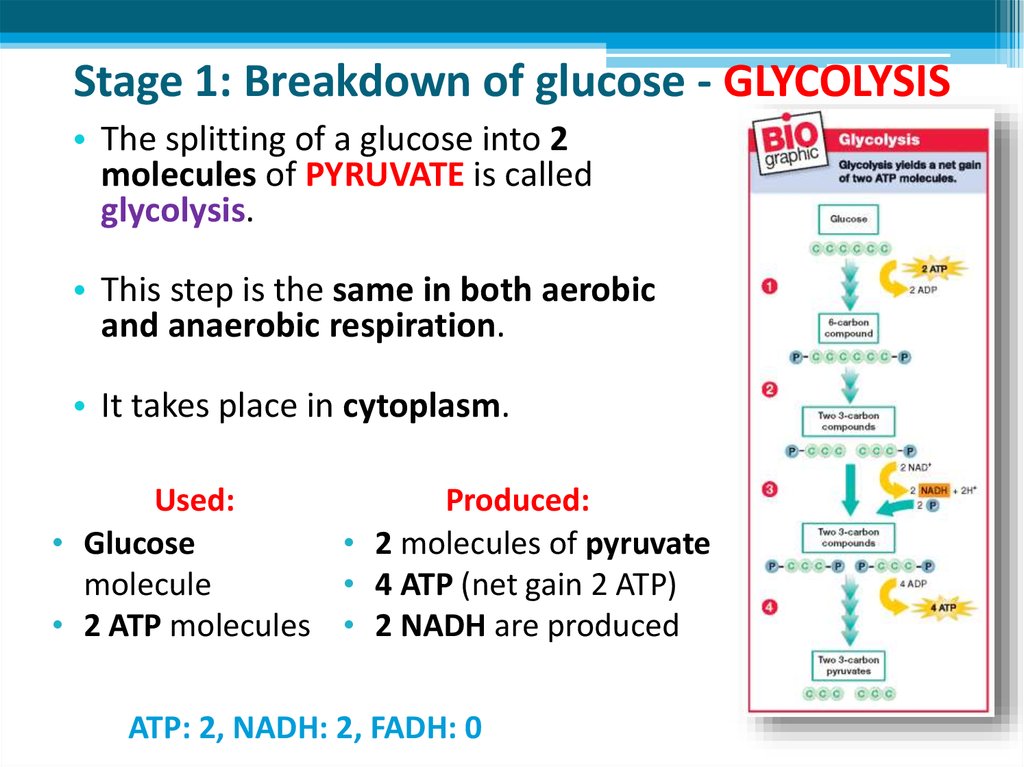
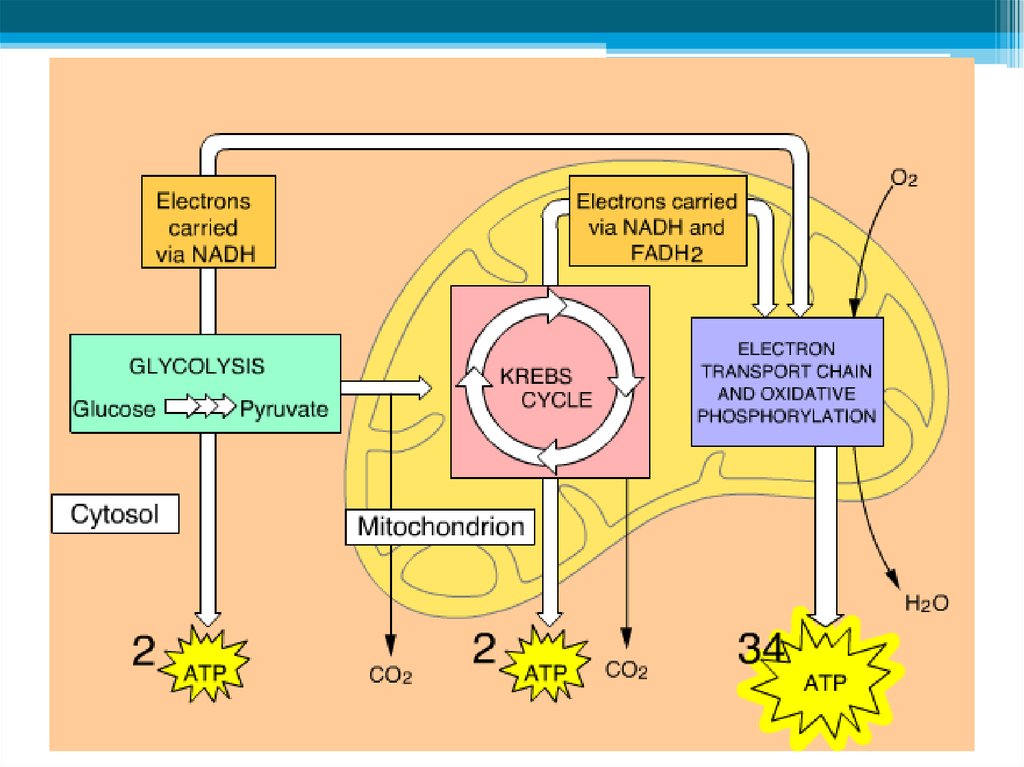
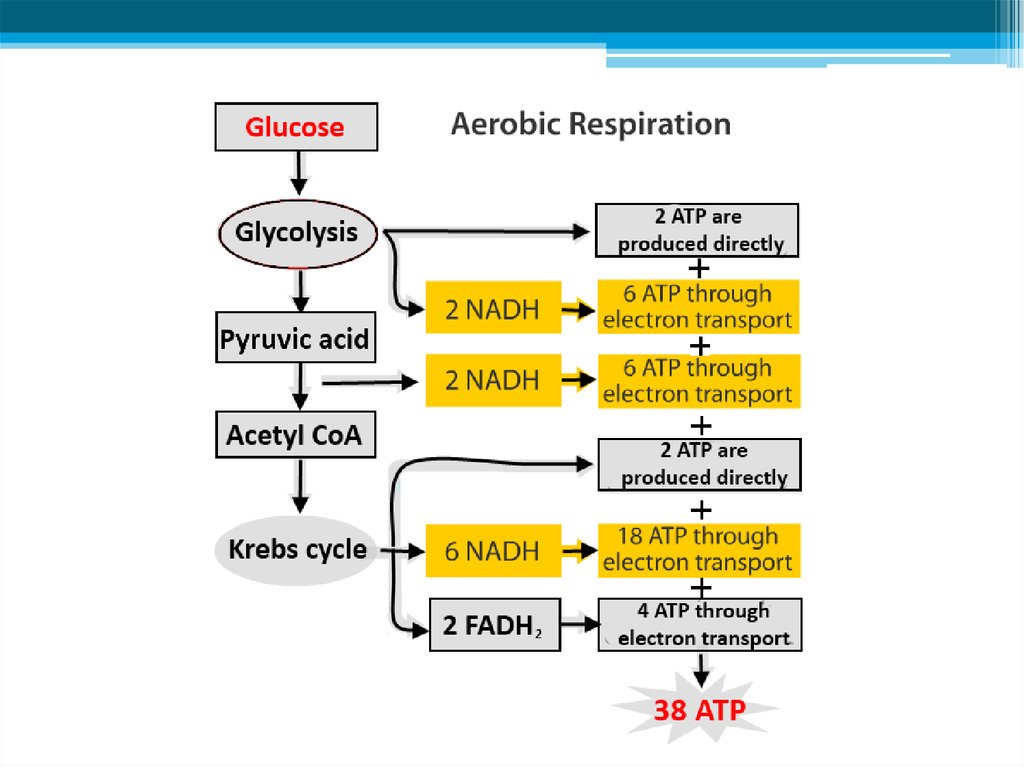
11. Stage 1: Breakdown of glucose - GLYCOLYSIS
• The splitting of a glucose into 2molecules of PYRUVATE is called
glycolysis.
• This step is the same in both aerobic
and anaerobic respiration.
• It takes place in cytoplasm.
Used:
Produced:
• Glucose
• 2 molecules of pyruvate
molecule
• 4 ATP (net gain 2 ATP)
• 2 ATP molecules • 2 NADH are produced
ATP: 2, NADH: 2, FADH: 0
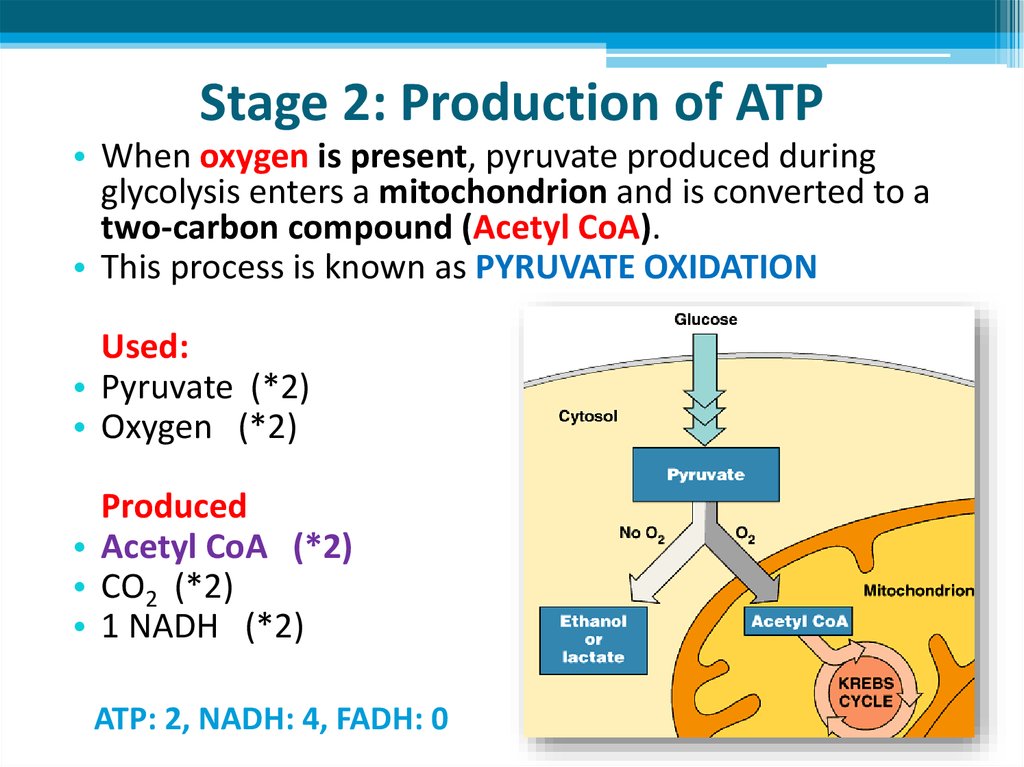
12. Stage 2: Production of ATP
• When oxygen is present, pyruvate produced duringglycolysis enters a mitochondrion and is converted to a
two-carbon compound (Acetyl CoA).
• This process is known as PYRUVATE OXIDATION
Used:
• Pyruvate (*2)
• Oxygen (*2)
Produced
• Acetyl CoA (*2)
• CO2 (*2)
• 1 NADH (*2)
ATP: 2, NADH: 4, FADH: 0
13.
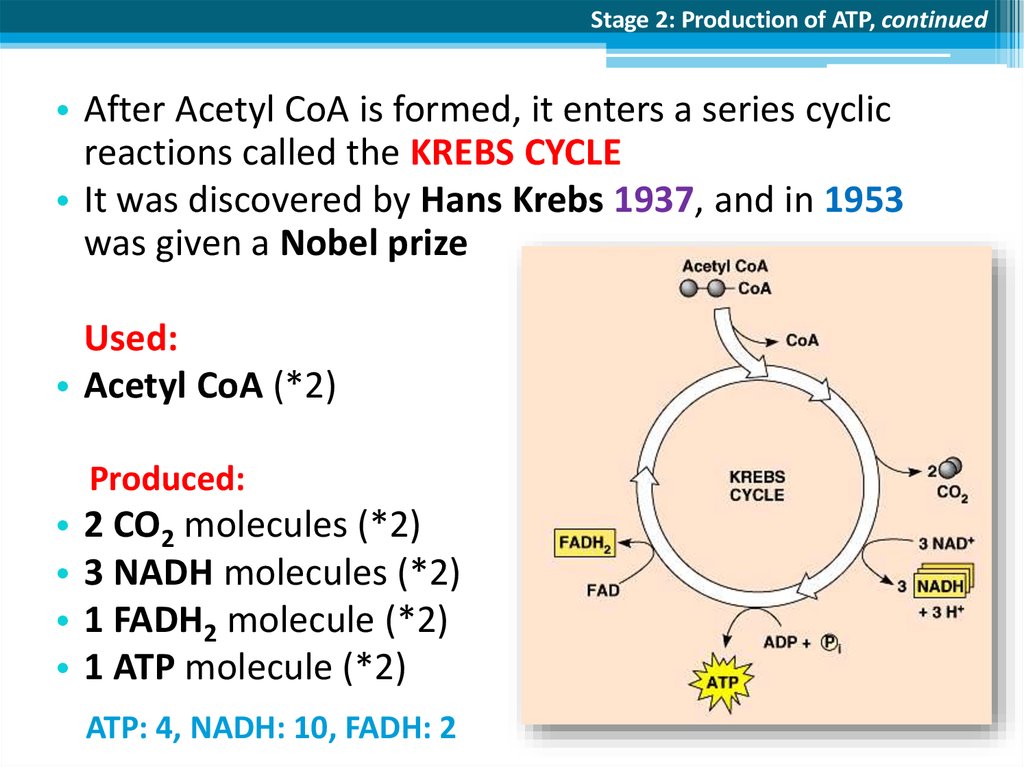
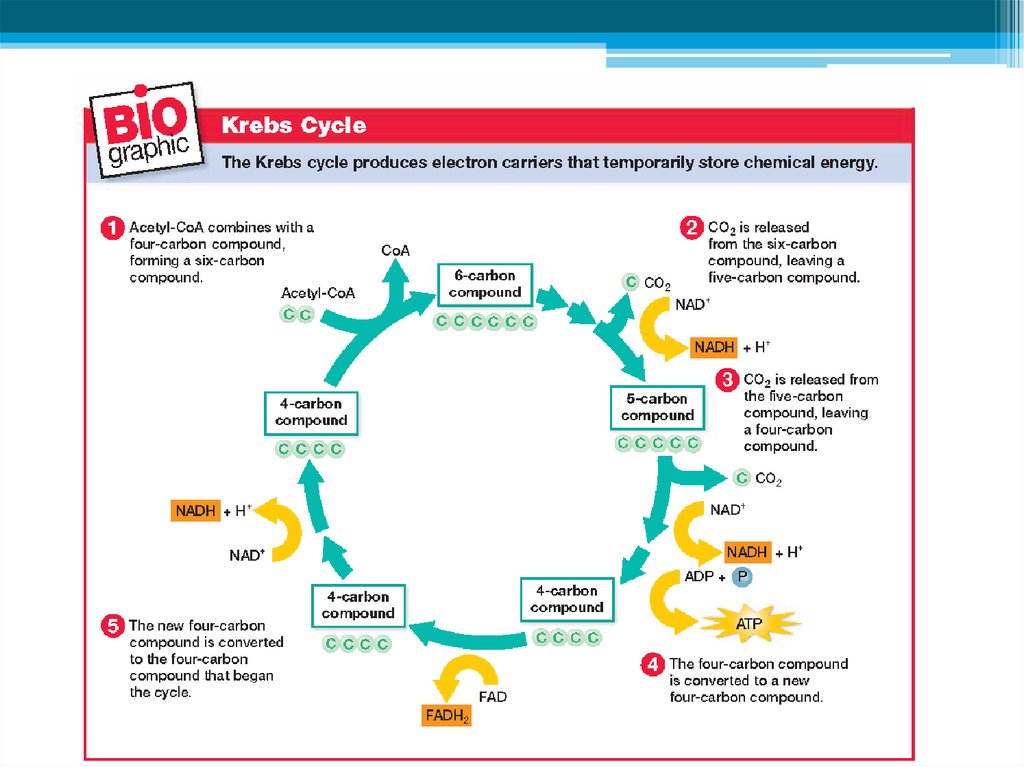
Stage 2: Production of ATP, continued• After Acetyl CoA is formed, it enters a series cyclic
reactions called the KREBS CYCLE
• It was discovered by Hans Krebs 1937, and in 1953
was given a Nobel prize
Used:
• Acetyl CoA (*2)
Produced:
2 CO2 molecules (*2)
3 NADH molecules (*2)
1 FADH2 molecule (*2)
1 ATP molecule (*2)
ATP: 4, NADH: 10, FADH: 2
14.
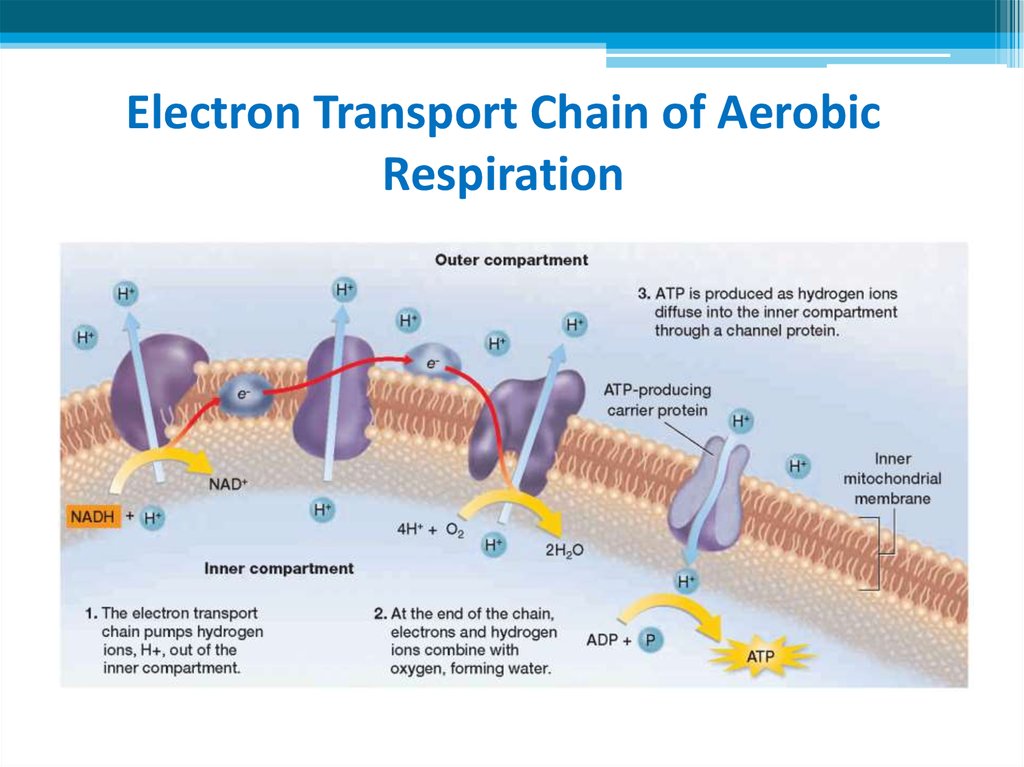
15. Electron transport chain
Stage 2: Production of ATP, continuedElectron transport chain
• In aerobic respiration, electrons donated by NADH and
FADH2 pass through an electron transport chain (ETC).
• In eukaryotic cells, the electron transport chain is located in
the inner membranes of mitochondria.
• It is the highly organized system of enzymes and coenzymes
• In here from each NADH molecule 3 ATPs are formed
3*10 NADH = 30 ATPs
• And from each FADH2 molecule 2 ATPs are formed
2*2 FADH2 = 4 ATPs
• The net gain of ATP produced in ETC is equal to 34 ATP
• As a result of whole aerobic respiration, net 38 ATPs are
produced
16.
Electron Transport Chain of AerobicRespiration
17.
18.
19. Catabolisation of different compounds
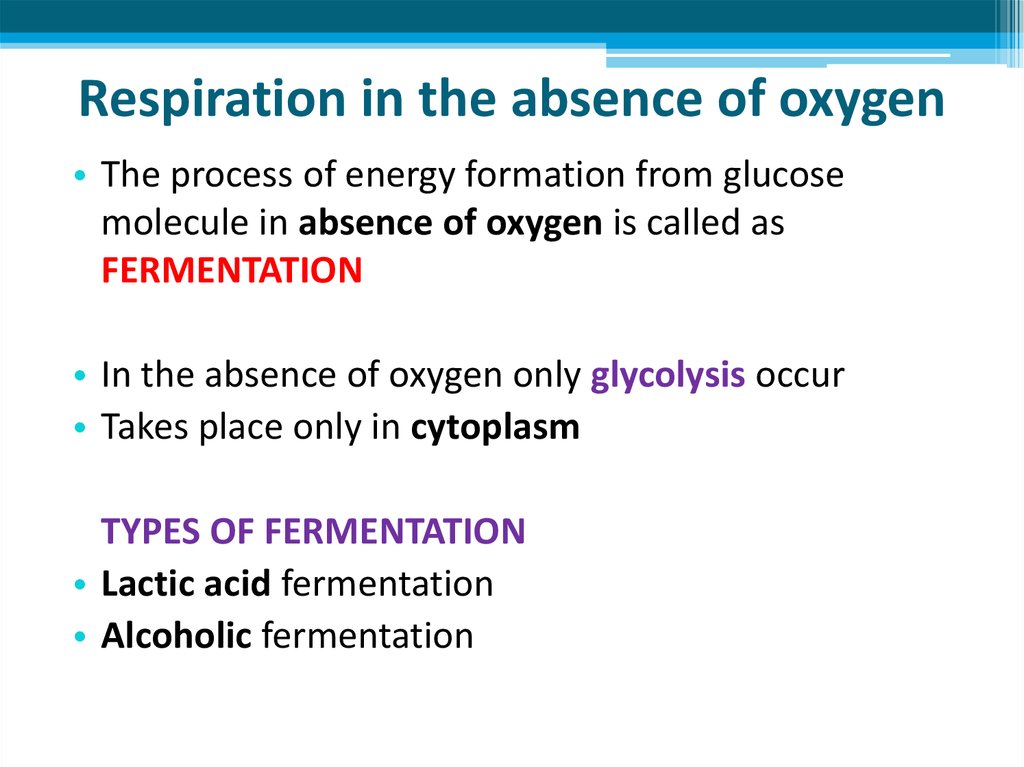
20. Respiration in the absence of oxygen
• The process of energy formation from glucosemolecule in absence of oxygen is called as
FERMENTATION
• In the absence of oxygen only glycolysis occur
• Takes place only in cytoplasm
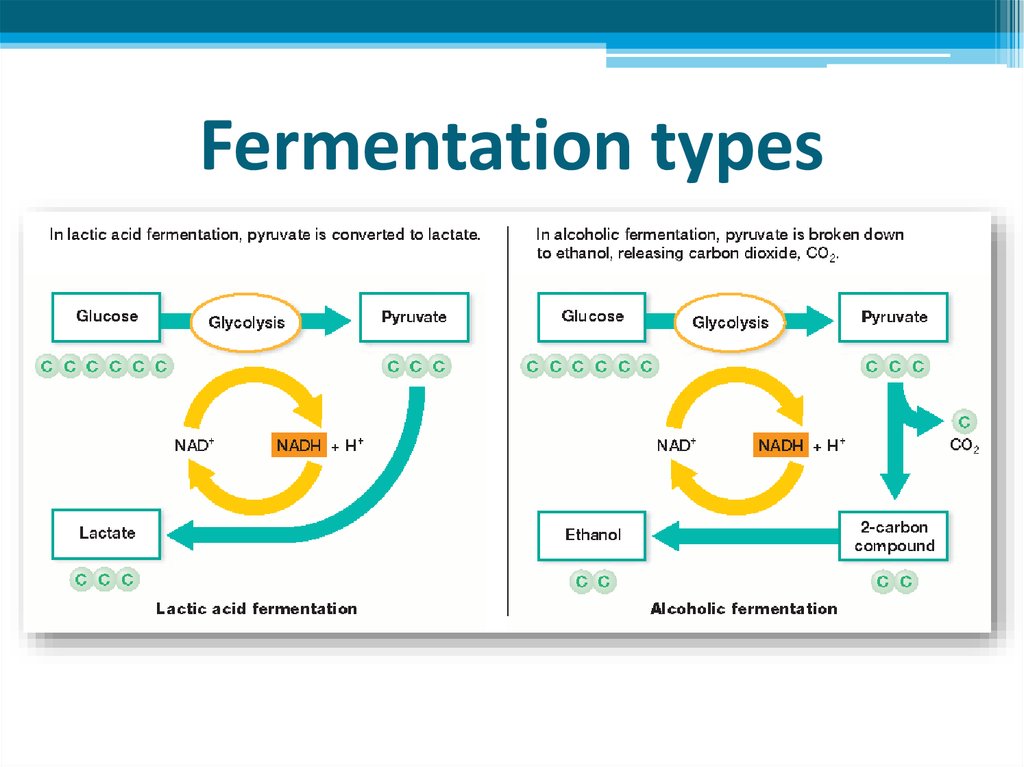
TYPES OF FERMENTATION
• Lactic acid fermentation
• Alcoholic fermentation
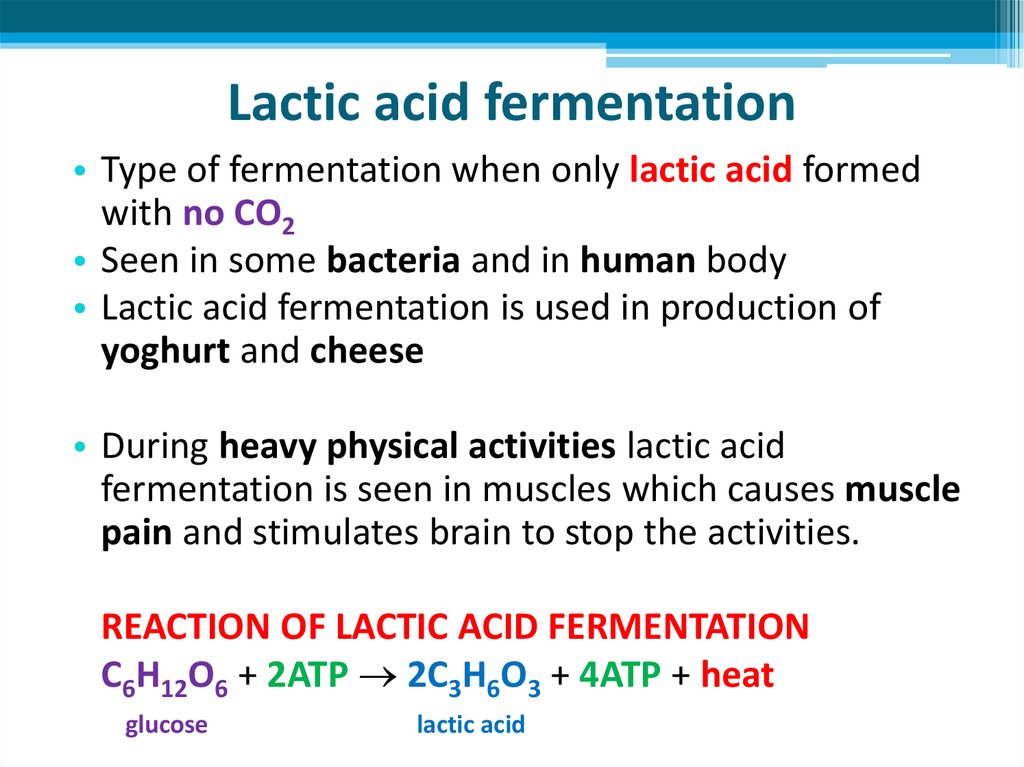
21. Lactic acid fermentation
• Type of fermentation when only lactic acid formedwith no CO2
• Seen in some bacteria and in human body
• Lactic acid fermentation is used in production of
yoghurt and cheese
• During heavy physical activities lactic acid
fermentation is seen in muscles which causes muscle
pain and stimulates brain to stop the activities.
REACTION OF LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION
C6H12O6 + 2ATP 2C3H6O3 + 4ATP + heat
glucose
lactic acid
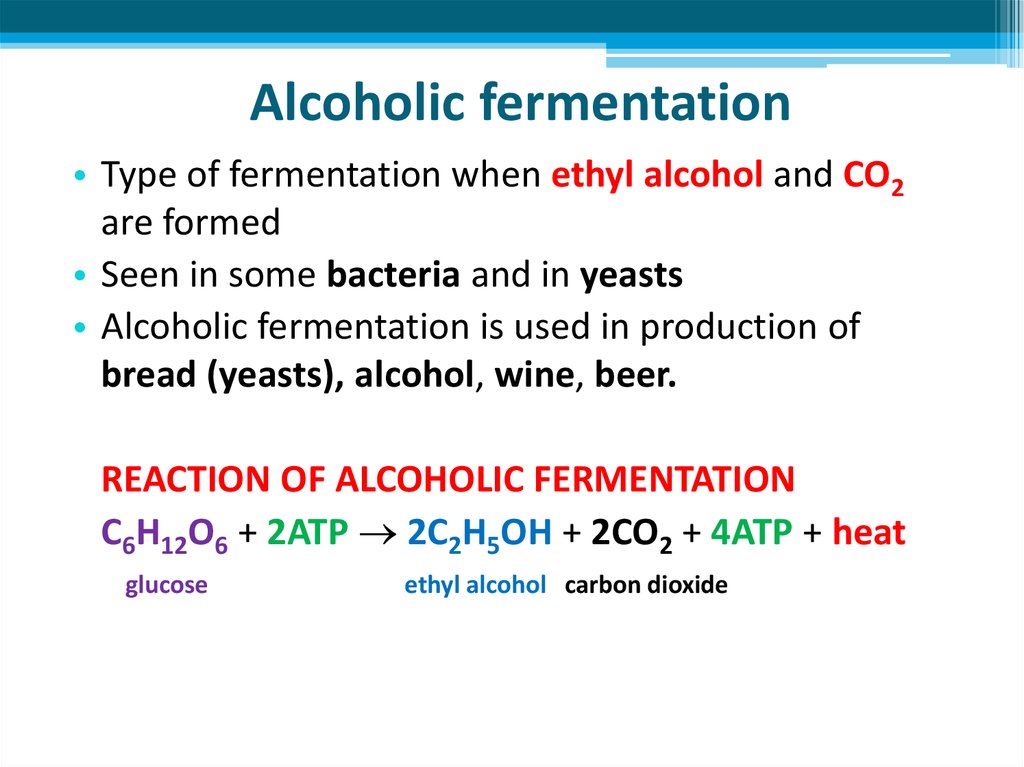
22. Alcoholic fermentation
• Type of fermentation when ethyl alcohol and CO2are formed
• Seen in some bacteria and in yeasts
• Alcoholic fermentation is used in production of
bread (yeasts), alcohol, wine, beer.
REACTION OF ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION
C6H12O6 + 2ATP 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 4ATP + heat
glucose
ethyl alcohol carbon dioxide
23. Fermentation types
24. Production of ATP
25. Cellular respiration vs. Fermentation
26.
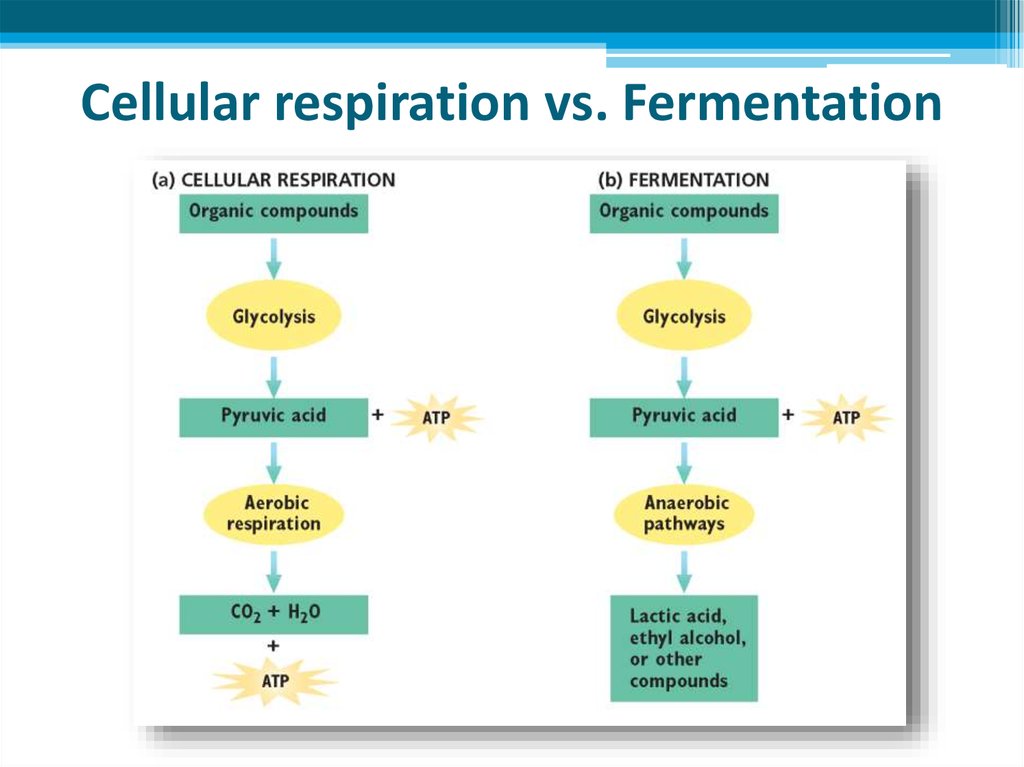
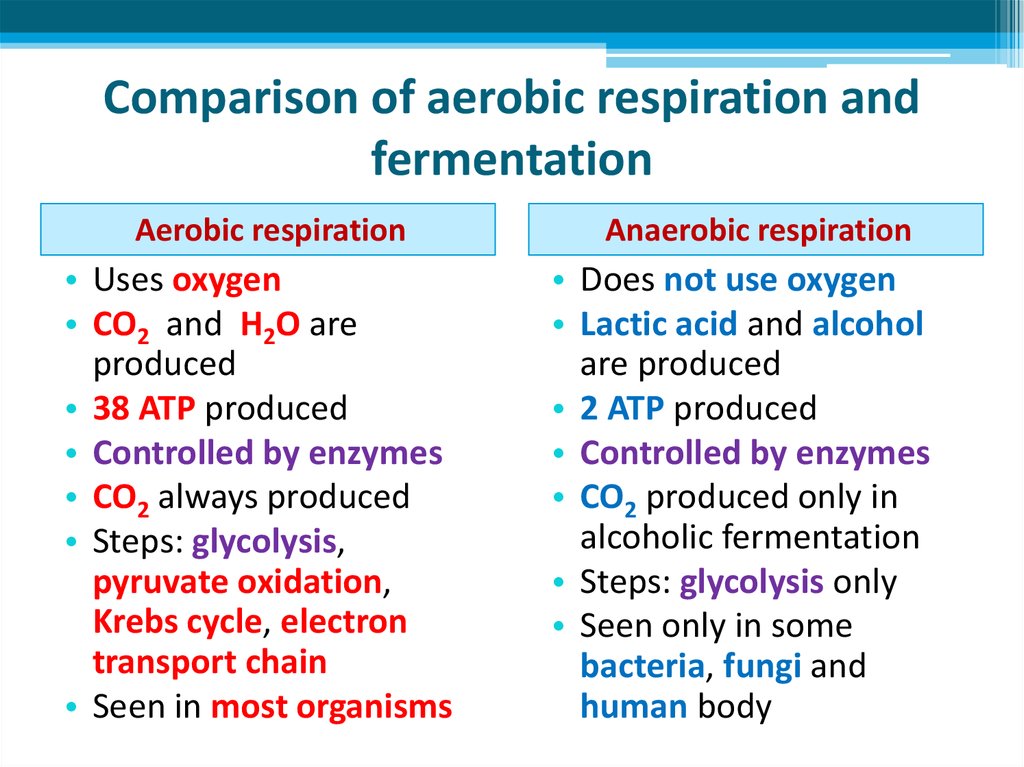
27. Comparison of aerobic respiration and fermentation
Aerobic respiration• Uses oxygen
• CO2 and H2O are
produced
• 38 ATP produced
• Controlled by enzymes
• CO2 always produced
• Steps: glycolysis,
pyruvate oxidation,
Krebs cycle, electron
transport chain
• Seen in most organisms
Anaerobic respiration
• Does not use oxygen
• Lactic acid and alcohol
are produced
• 2 ATP produced
• Controlled by enzymes
• CO2 produced only in
alcoholic fermentation
• Steps: glycolysis only
• Seen only in some
bacteria, fungi and
human body







 biology
biology