Similar presentations:
Stages of the energy metabolism
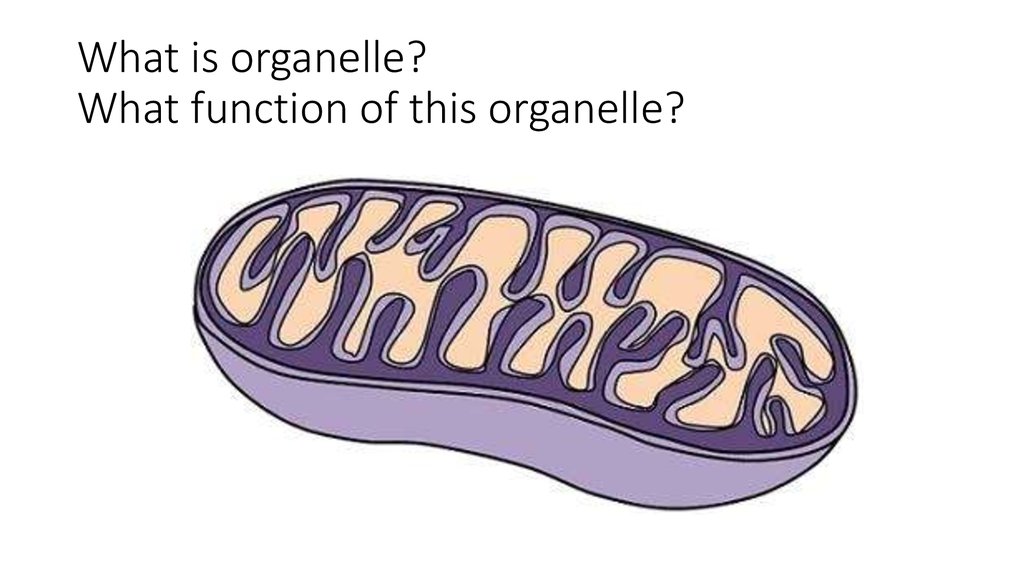
1. What is organelle? What function of this organelle?
2.
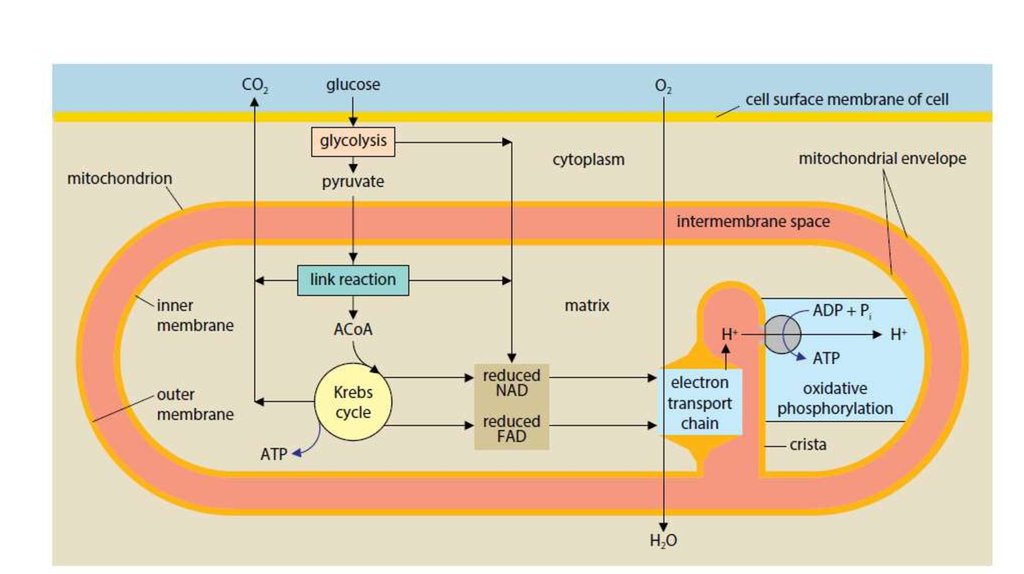
3. The stages of energy metabolism
4. Learning objective
•to describe the stages of energymetabolism
5. Success criteria
1.Knows the stages of an energetic exchange2.Describes the stages of an energetic
exchange
3.Explains each stage of an energetic
exchange
6. Terminology
Digestion and hydrolysis, catabolic reactions,anaerobic respiration, aerobic respiration,
ATP, ADP and Pi, substrate, glucose, pyruvate,
pyruvic acid, degradation, oxidation,
glycolysis, organic molecules, Krebs cycle,
ETC, protons, cytoplasm, nutrients, oxygen,
water, carbon dioxide, energy requiring,
energy producing.
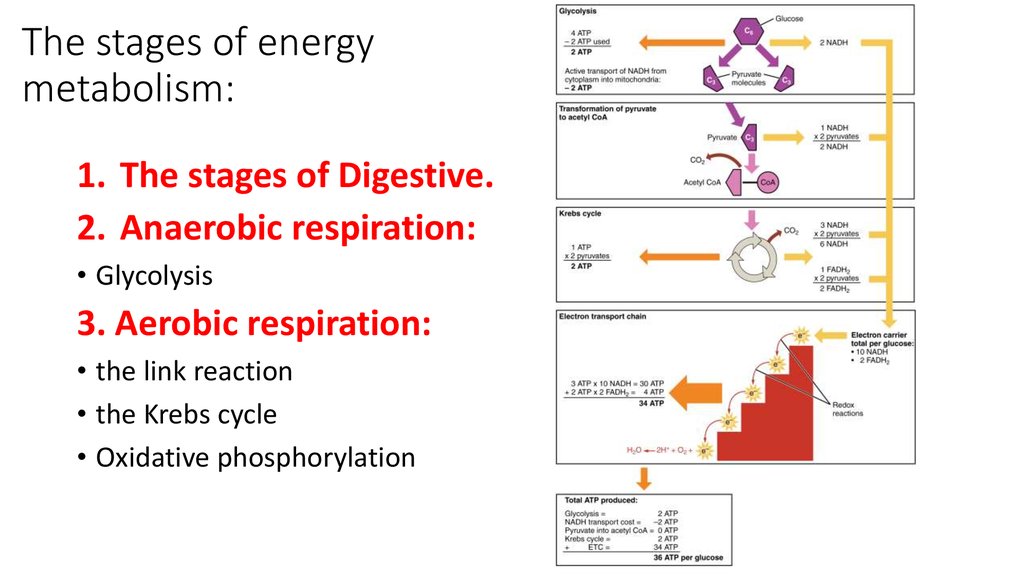
7. The stages of energy metabolism:
1. The stages of Digestive.2. Anaerobic respiration:
• Glycolysis
3. Aerobic respiration:
• the link reaction
• the Krebs cycle
• Oxidative phosphorylation
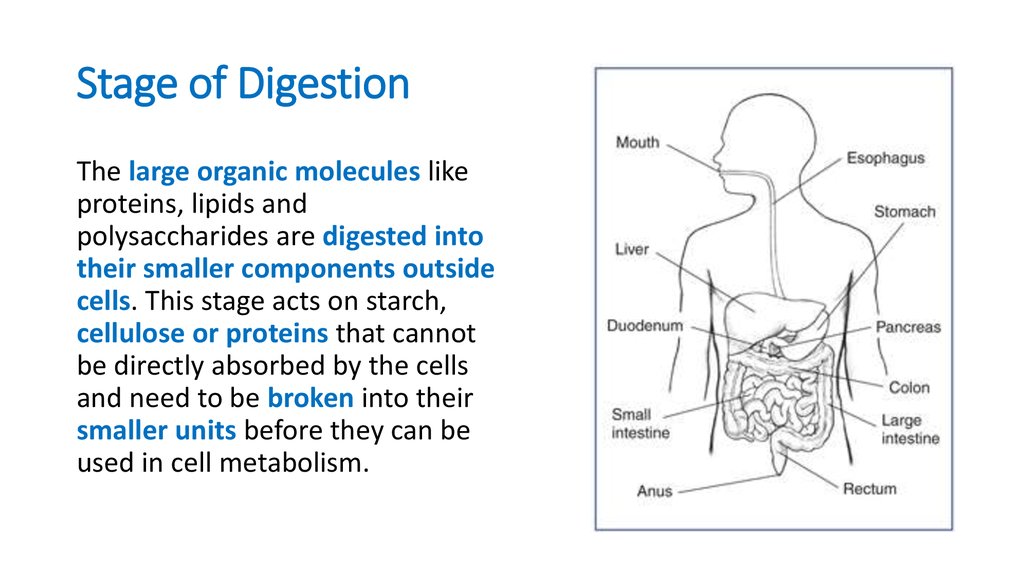
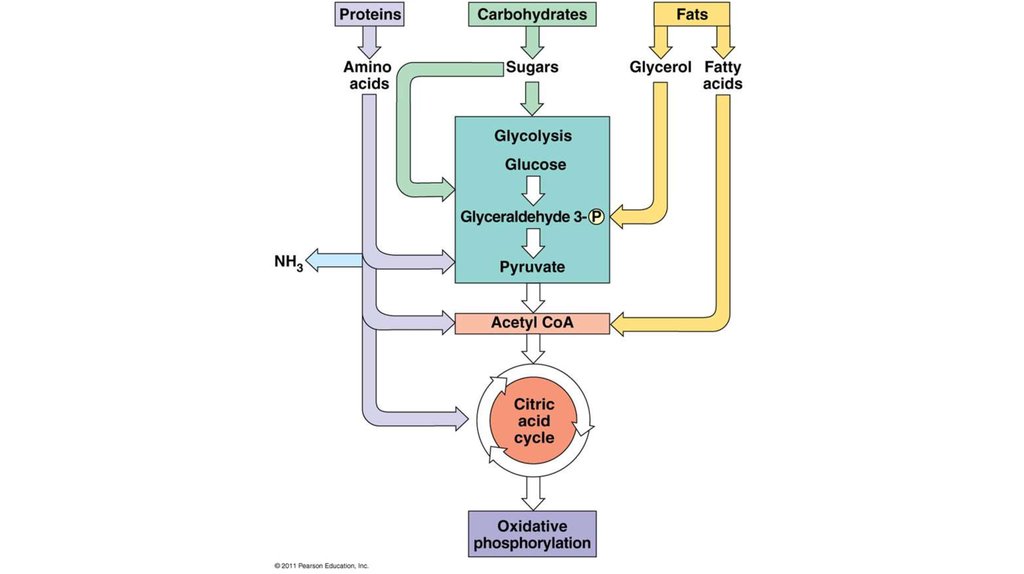
8. Stage of Digestion
The large organic molecules likeproteins, lipids and
polysaccharides are digested into
their smaller components outside
cells. This stage acts on starch,
cellulose or proteins that cannot
be directly absorbed by the cells
and need to be broken into their
smaller units before they can be
used in cell metabolism.
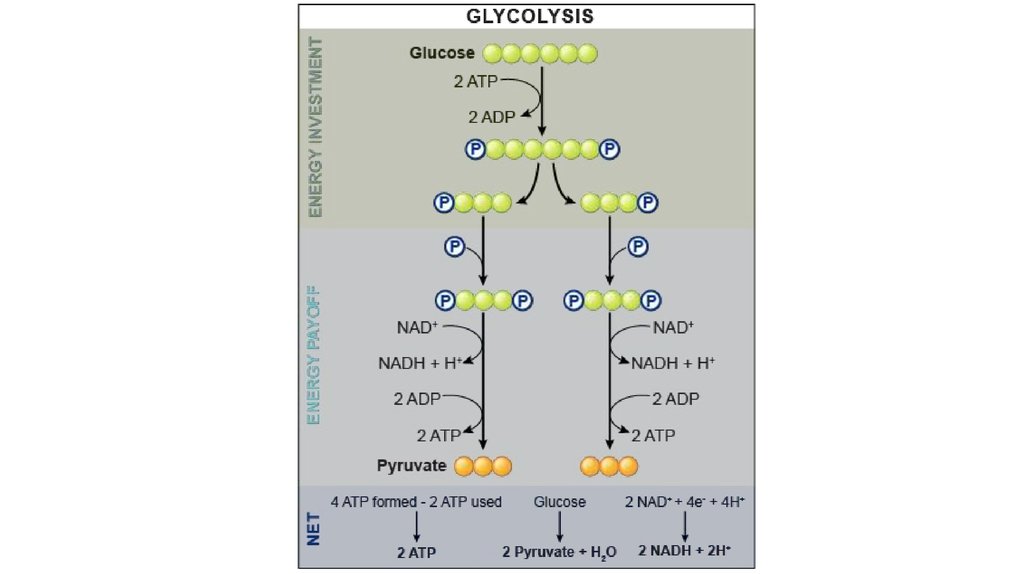
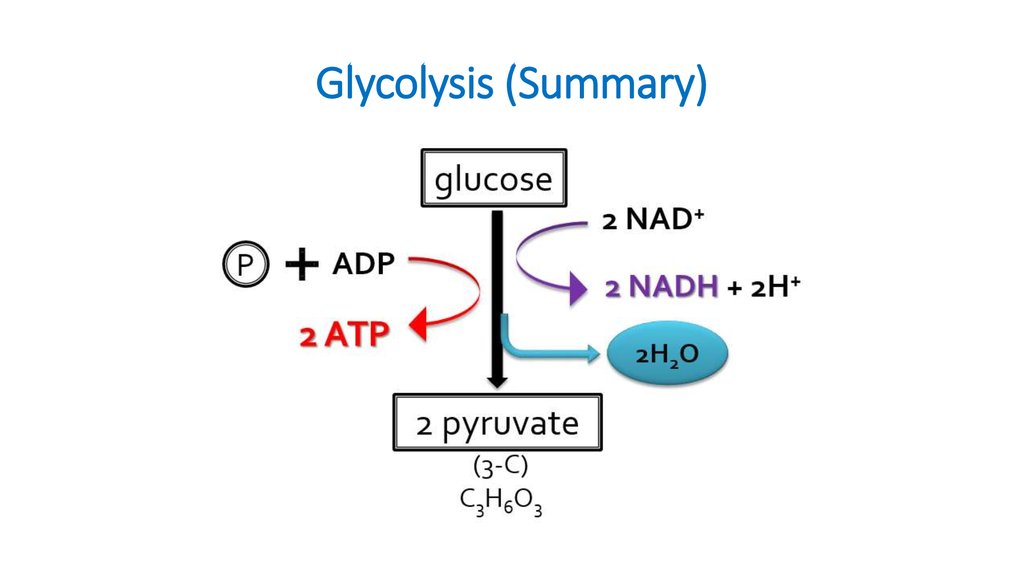
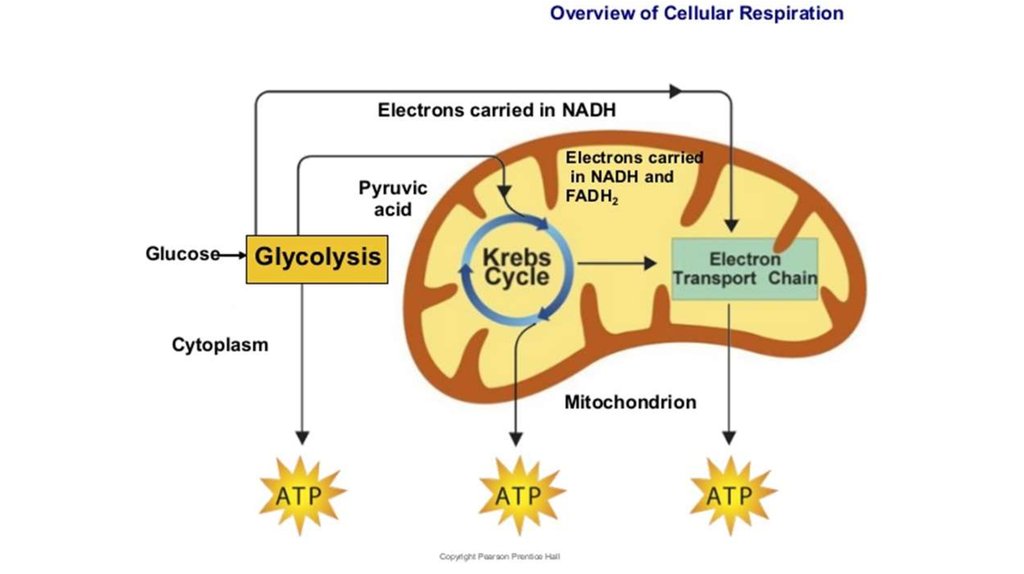
9. Anaerobic respiration:
Glycolysis:• “sugar splitting”
• Believed to be ancient (early
prokaryotes - no O2 available)
• Occurs in cytosol
• Partially oxidizes glucose (6C) to 2
pyruvates (3C)
• Net gain: 2 ATP + 2NADH
• Also makes 2H2O
• No O2 required
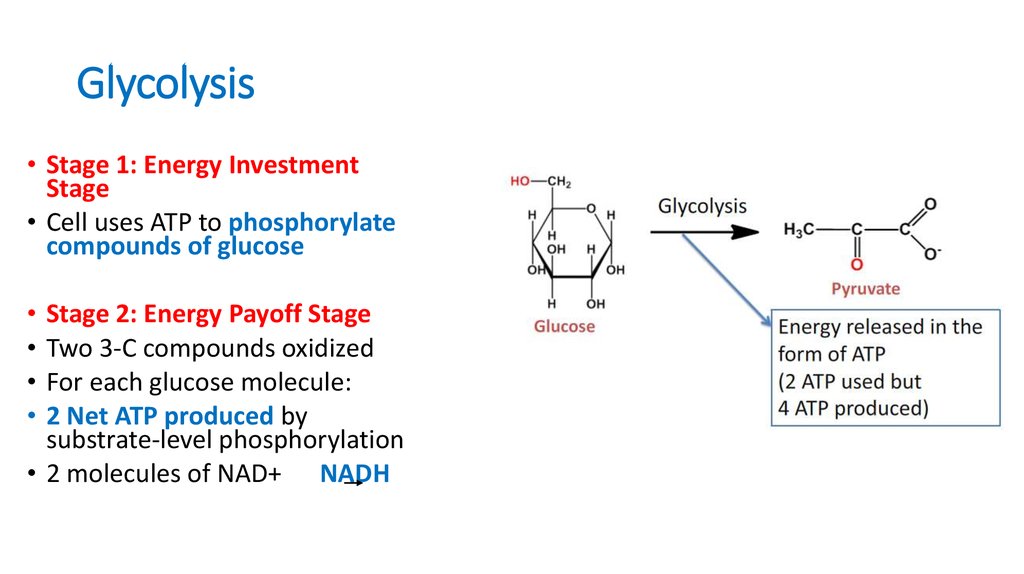
10. Glycolysis
• Stage 1: Energy InvestmentStage
• Cell uses ATP to phosphorylate
compounds of glucose
Stage 2: Energy Payoff Stage
Two 3-C compounds oxidized
For each glucose molecule:
2 Net ATP produced by
substrate-level phosphorylation
• 2 molecules of NAD+ NADH
11.
12. Each group fills its posters on the energy stages of metabolism.
• Success criteria:• Correctly write the stages of energy metabolism.
• Describe each stage
• Show the start and end products of each stage
• Draw charts of each phase of energy metabolism
13. Glycolysis (Summary)
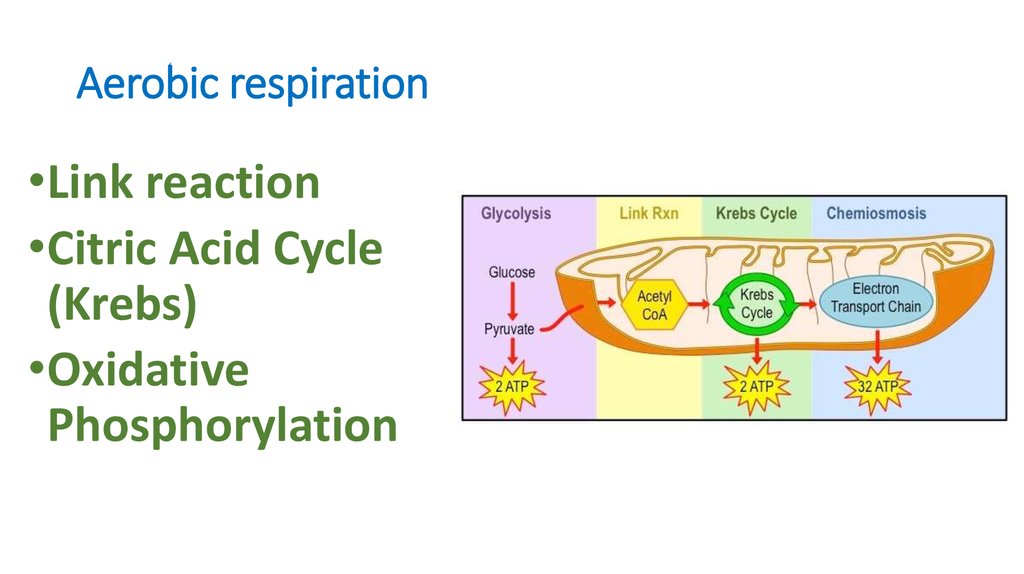
14. Aerobic respiration
•Link reaction•Citric Acid Cycle
(Krebs)
•Oxidative
Phosphorylation
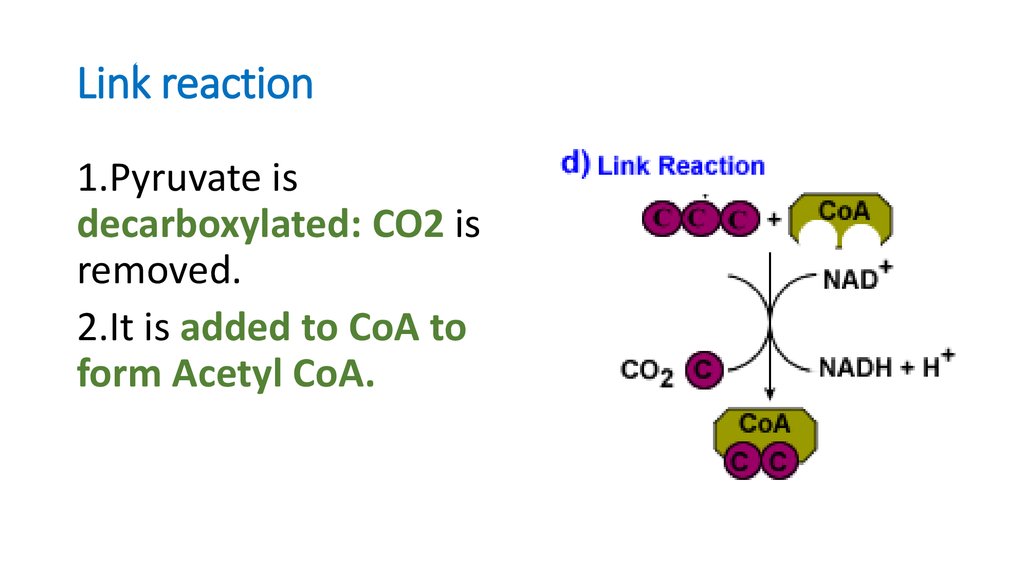
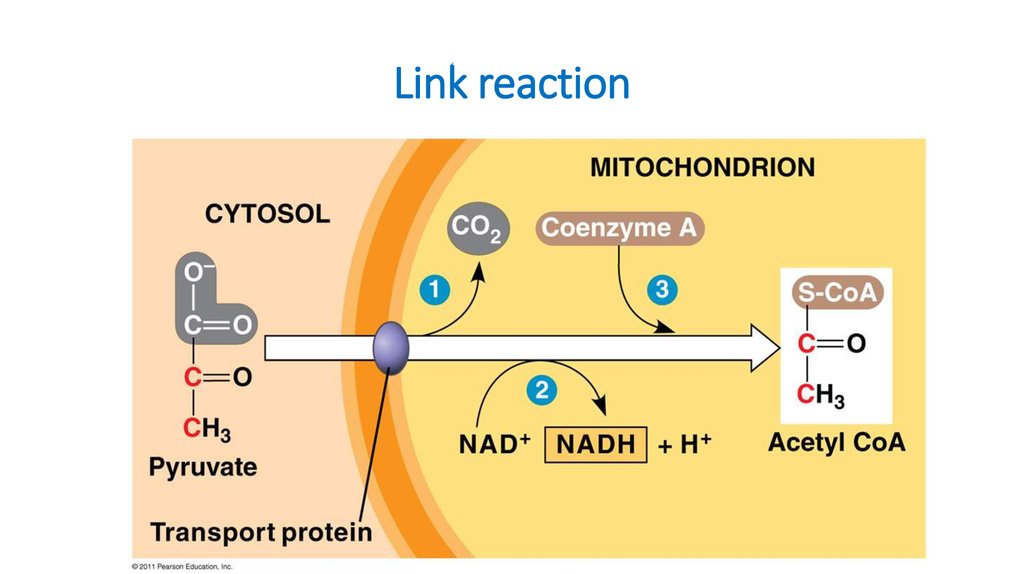
15. Link reaction
1.Pyruvate isdecarboxylated: CO2 is
removed.
2.It is added to CoA to
form Acetyl CoA.
16. Link reaction
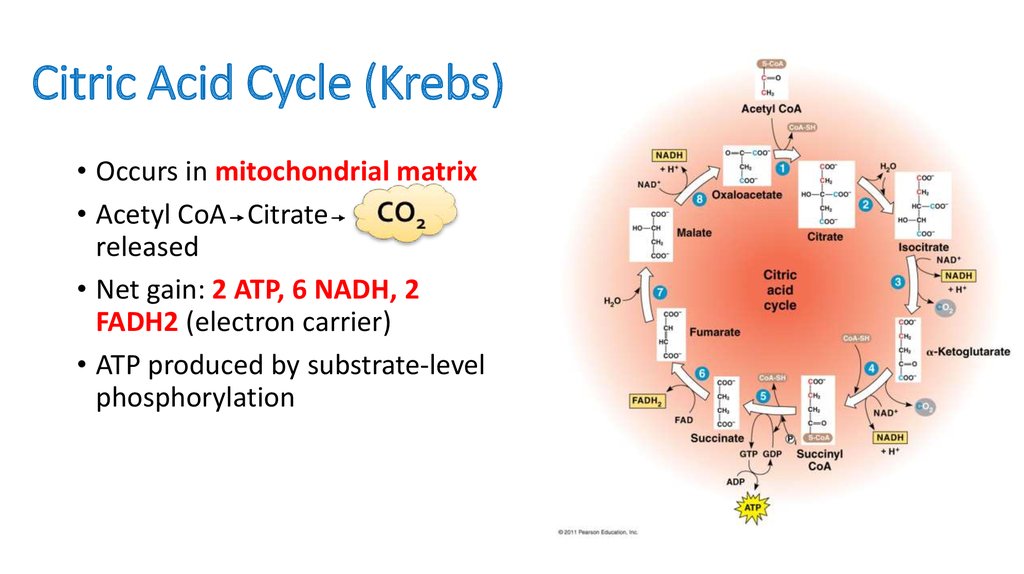
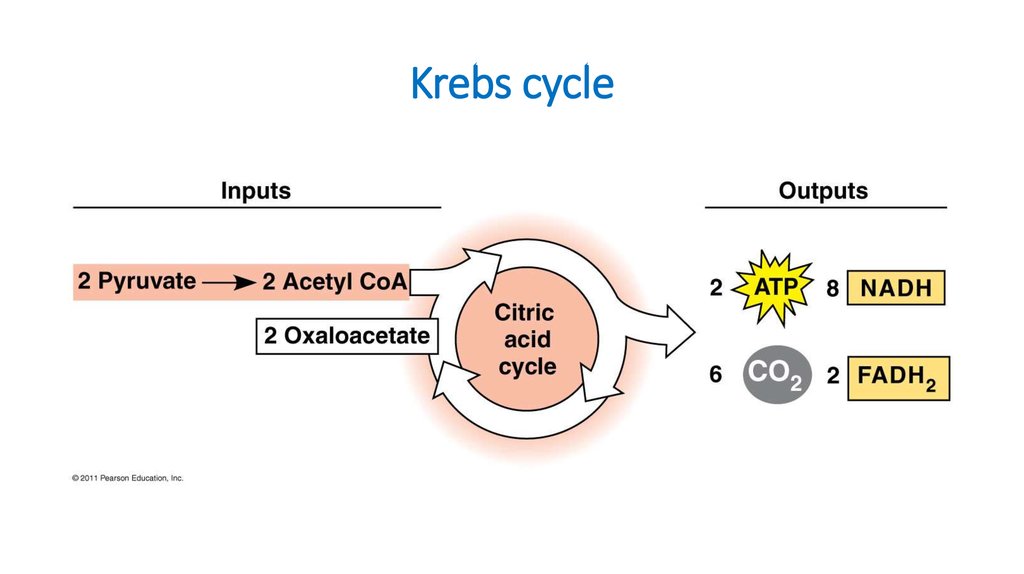
17. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs)
• Occurs in mitochondrial matrix• Acetyl CoA Citrate
released
• Net gain: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2
FADH2 (electron carrier)
• ATP produced by substrate-level
phosphorylation
18. Krebs cycle
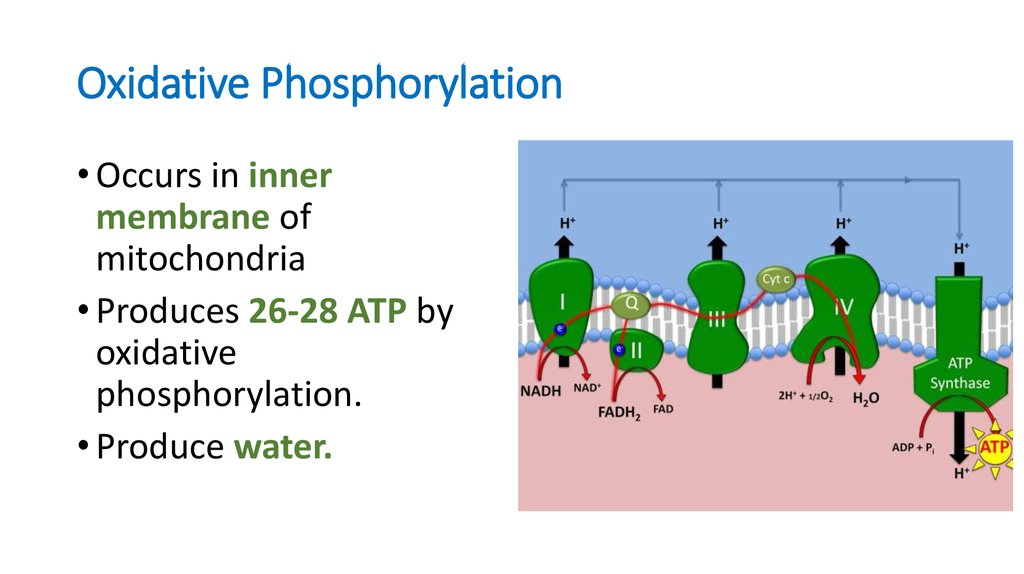
19. Oxidative Phosphorylation
• Occurs in innermembrane of
mitochondria
• Produces 26-28 ATP by
oxidative
phosphorylation.
• Produce water.
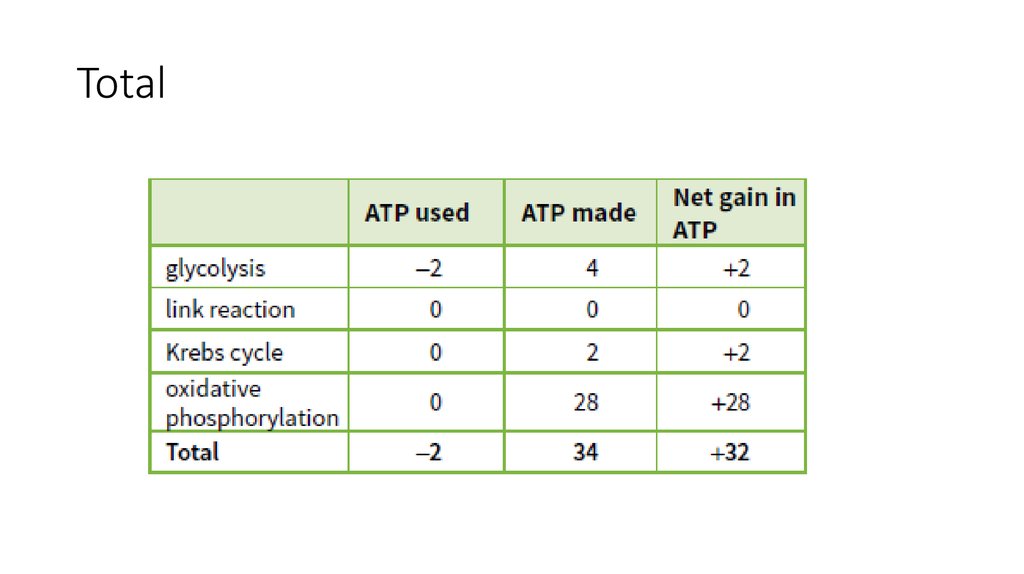
20. Total
21.
22.
23. Success criteria
1.Knows the stages of an energetic exchange2.Describes the stages of an energetic
exchange
3.Explains each stage of an energetic
exchange
24. Reflection:
•I learned, learned•it remains unclear
•above what is necessary to work








 biology
biology








