Similar presentations:
Mixed Reality
1. Mixed Reality
KTmo1-7Dmitry Sukholovsky
2. Contents
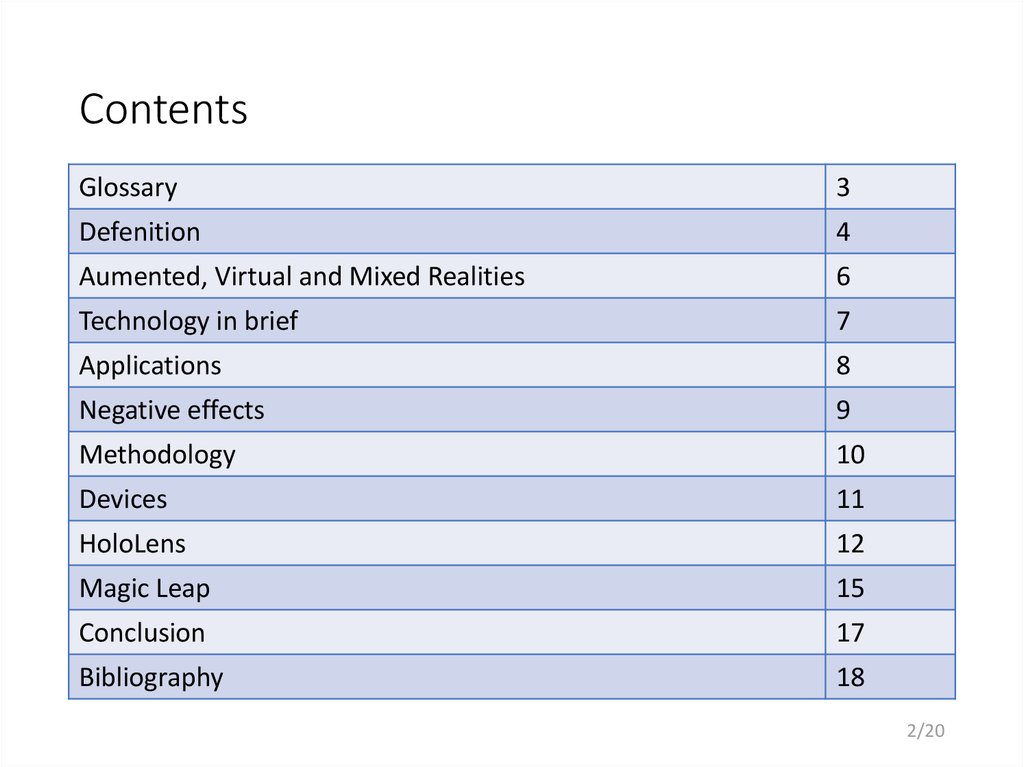
Glossary3
Defenition
4
Aumented, Virtual and Mixed Realities
6
Technology in brief
7
Applications
8
Negative effects
9
Methodology
10
Devices
11
HoloLens
12
Magic Leap
15
Conclusion
17
Bibliography
18
2/20
3. Glossary
• Virtual reality (VR) is an interactive computer-generated experiencetaking place within a simulated environment.
• Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience of a real-world
environment where the objects that reside in the real-world are
"augmented" by computer-generated perceptual information.
• Universal Windows Platform (UWP) is an open source API created by
Microsoft and first introduced in Windows 10. The purpose of this
platform is to help develop universal apps that run on Windows 10,
Windows 10 Mobile, Xbox One and HoloLens without the need to be
re-written for each.
• The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is
seen at any given moment.
3/20
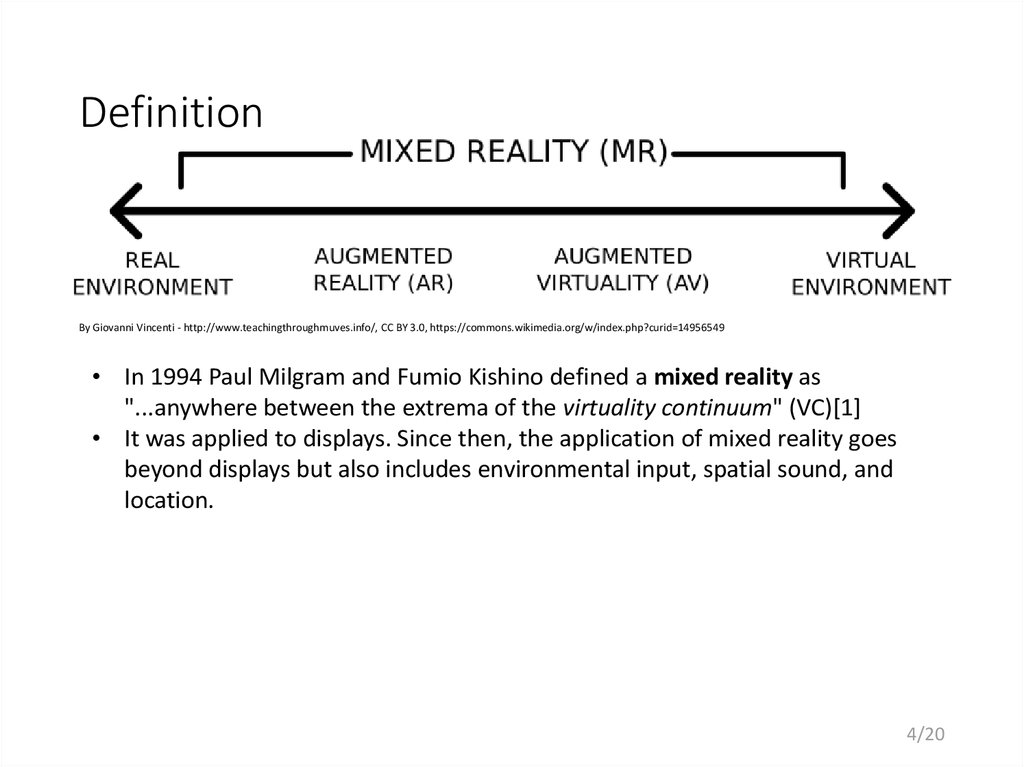
4. Definition
By Giovanni Vincenti - http://www.teachingthroughmuves.info/, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=14956549• In 1994 Paul Milgram and Fumio Kishino defined a mixed reality as
"...anywhere between the extrema of the virtuality continuum" (VC)[1]
• It was applied to displays. Since then, the application of mixed reality goes
beyond displays but also includes environmental input, spatial sound, and
location.
4/20
5.
Matteo Valoriani, Etna dev 2016 — Introduction to Mixed Reality with HoloLens5/20
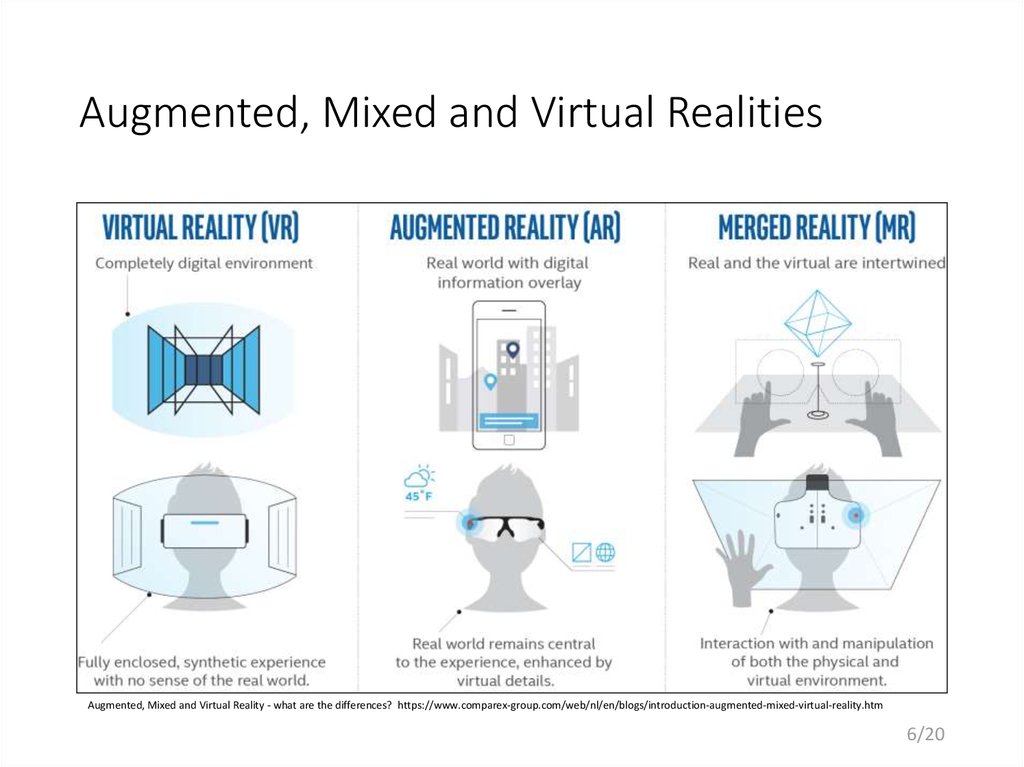
6. Augmented, Mixed and Virtual Realities
Augmented, Mixed and Virtual Reality - what are the differences? https://www.comparex-group.com/web/nl/en/blogs/introduction-augmented-mixed-virtual-reality.htm6/20
7. Technology in Brief
• In a nutshell, MR allows the viewer to see virtual objects that appearreal, accurately mapped into the real world.
• This particular subset of the “reality” technologies has the potential
to truly blur the boundaries between what we are, what everything
else is, and what we need to know about it all[2].
7/20
8. Applications
• Education• Engineering
• Entertainment
• Healthcare
• Military
• Business
8/20
9. Negative effects
IEEE Committee has created the following sections [3] within mixedreality to help address some problems:
1. Social Interactions
2. Mental Health
3. Education and Training
4. The Arts 5. Privacy Access and Control
9/20
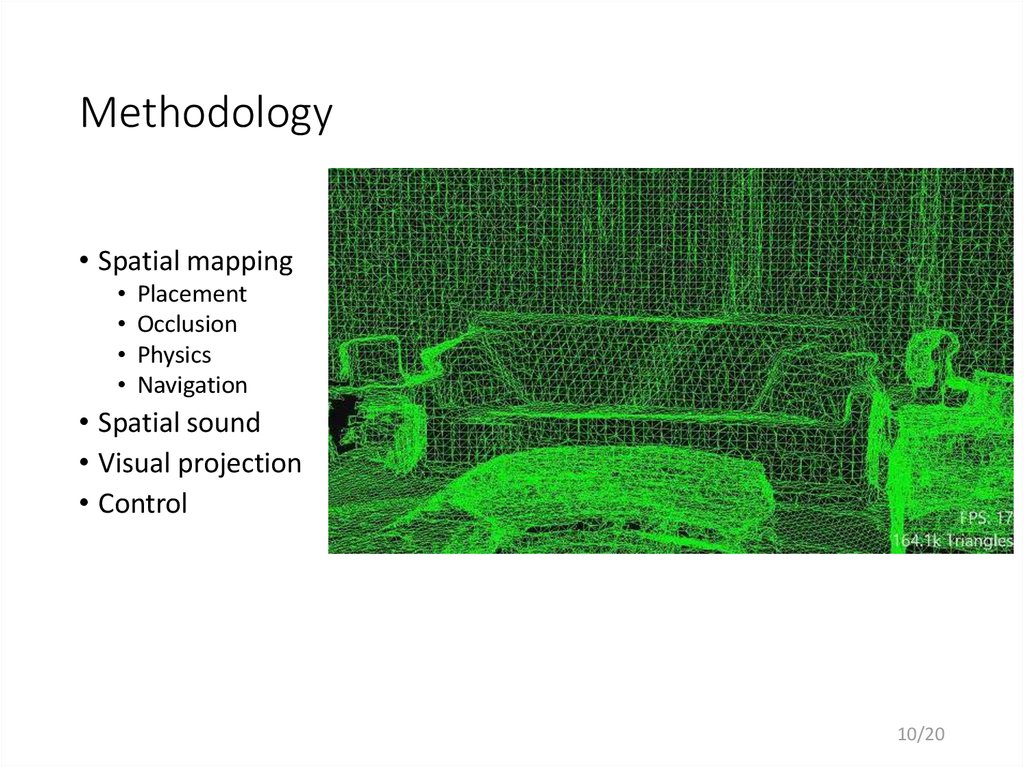
10. Methodology
• Spatial mappingPlacement
Occlusion
Physics
Navigation
• Spatial sound
• Visual projection
• Control
10/20
11. Devices
Microsoft HoloLensName
Magic Leap One
March 30, 2016
Release date
August 8th, 2018
$3000 Developer
edition,
$5000 Consumer
edition
Price
$2,295,
$2,790 Professional
Development Edition"
horizontal 30°
vertical 17.5°
FoV
horizontal 40°
vertical 30°
2-3 hours of active use
average 5.5 hours
Battery Life
Up to 3 h
11/20
12. Microsoft HoloLens
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens• Runs on Windows 10
• Supports almost all UWP apps
• Only 3 UWP apps can run simultaneously
• Only 1 3D app
• Low FPS when >20 holograms
12/20
13. Holograms
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/mixed-reality/hologramHolograms
HoloLens lets you create holograms, objects made of light and sound
that appear in the world around you, just as if they were real objects.
13/20
14. Control
GazeGestures
Voice
14/20
15. Magic Leap One
• Lightwear (glasses)• Lightpack (computing core)
• Control (controller)
15/20
16.
Runs on Lumin OS
Better performance
Controller support
Less apps
https://twitter.com/helloBrent/status/1017115200984633344
16/20
17. Summary
• Not many devices• Useful mostly for developers
• Problems
Limited FOV
Price
Battery life
Multitasking
• Not many apps
17/20
18. Bibliography
1.P. Milgram and A. F. Kishino 1994 - "Taxonomy of Mixed Reality
Visual Displays“ - IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems.
pp. 1321–1329.
2. Designing for Mixed Reality - Kharis O'Connell - O'Reilly Media, Inc.
2016
3. Mixed Reality in Information and Communications Technology
Committee - Ethically Aligned Design, Version 2 - The IEEE Global
Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems – P217239
18/20















 english
english








