Similar presentations:
Blood biochemistry
1. BLOOD BIOCHEMISTRY
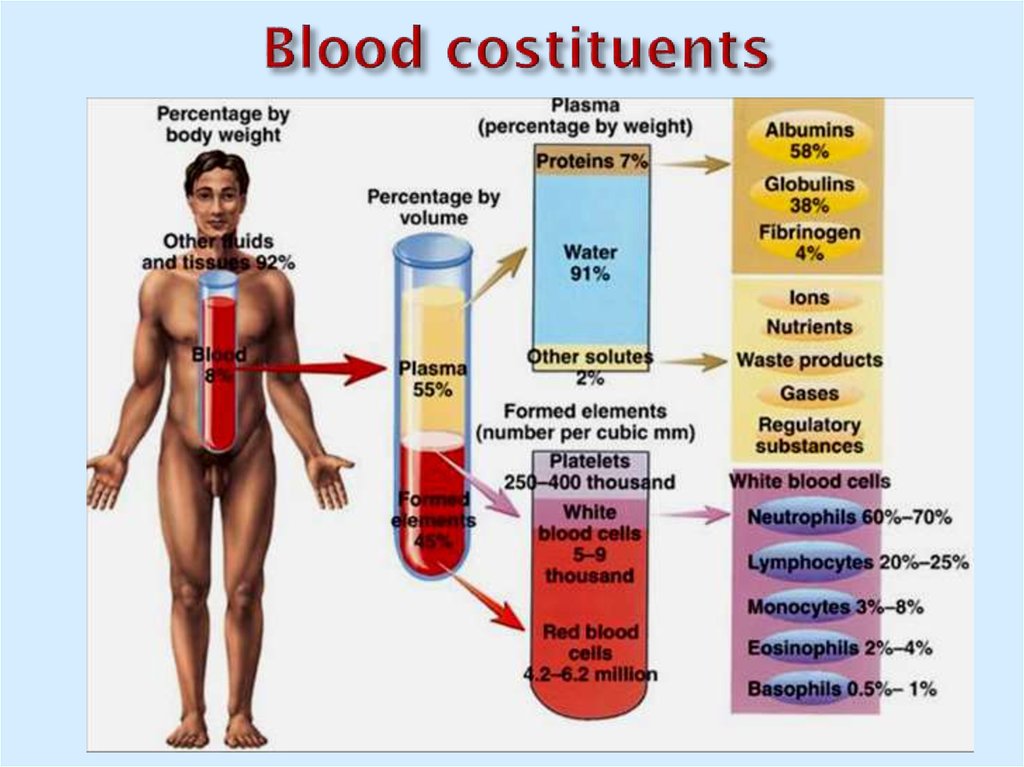
2. Blood costituents
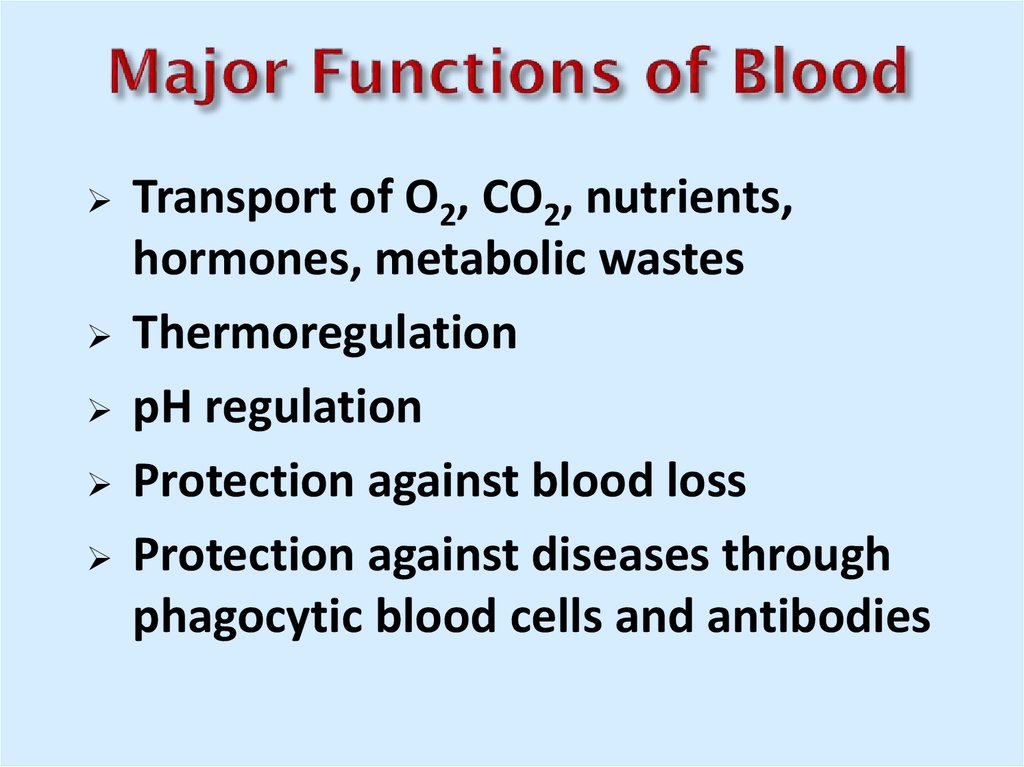
3. Major Functions of Blood
Transport of O2, CO2, nutrients,hormones, metabolic wastes
Thermoregulation
pH regulation
Protection against blood loss
Protection against diseases through
phagocytic blood cells and antibodies
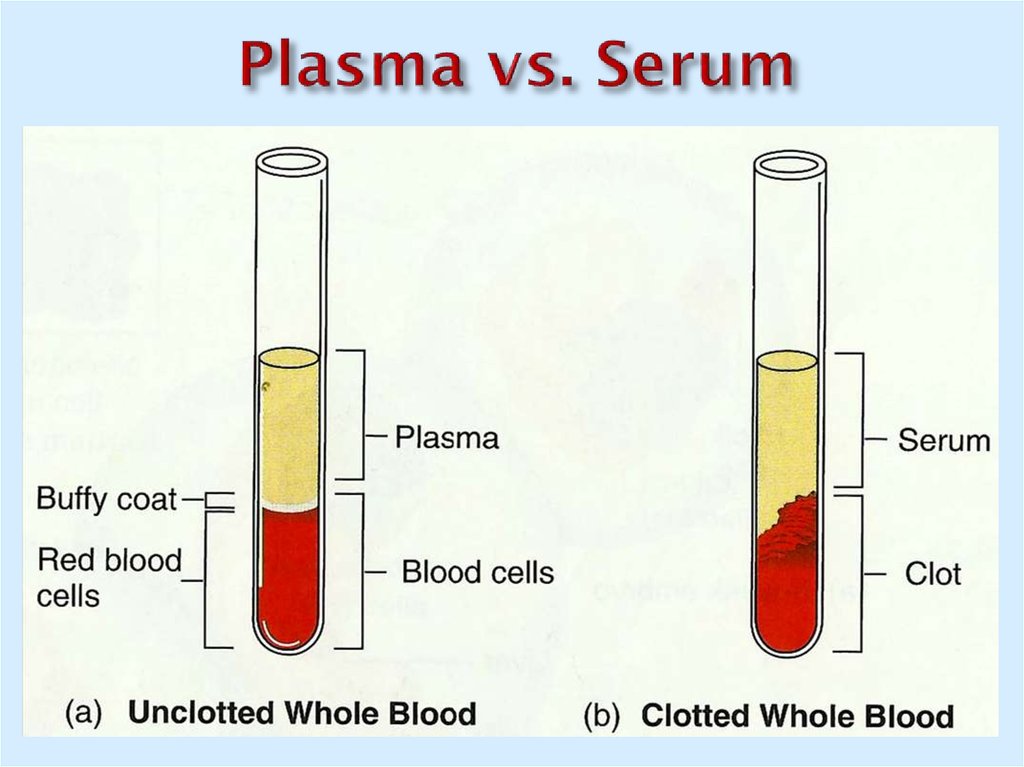
4. Plasma vs. Serum
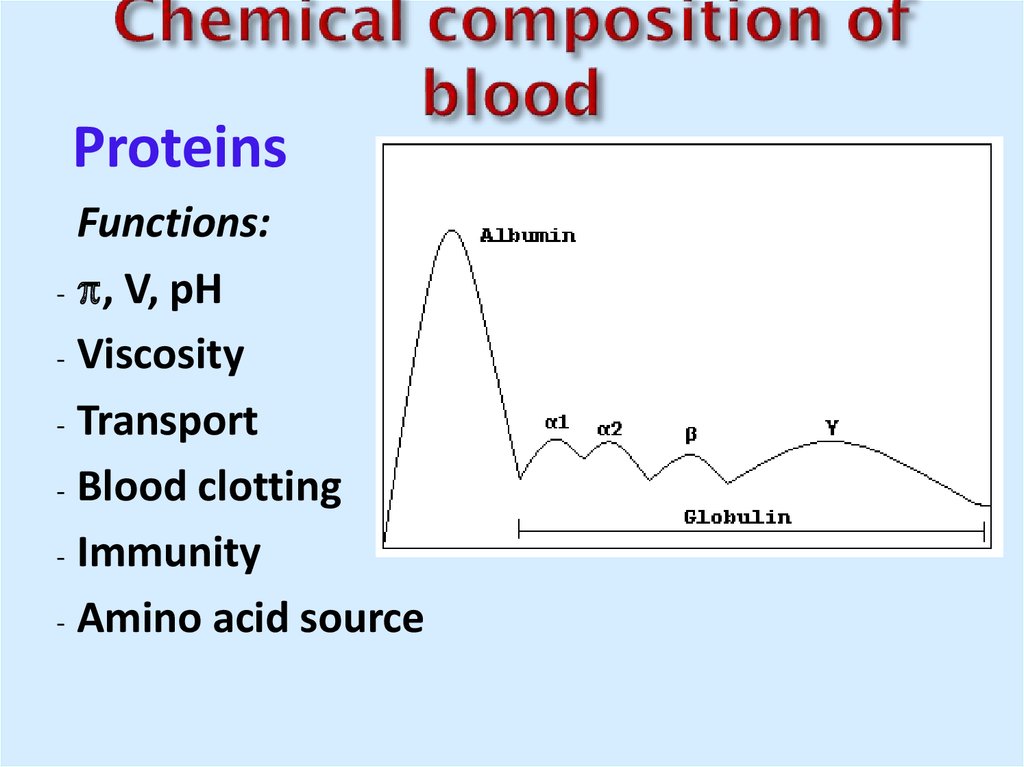
5. Chemical composition of blood
ProteinsFunctions:
- , V, pH
- Viscosity
- Transport
- Blood clotting
- Immunity
- Amino acid source
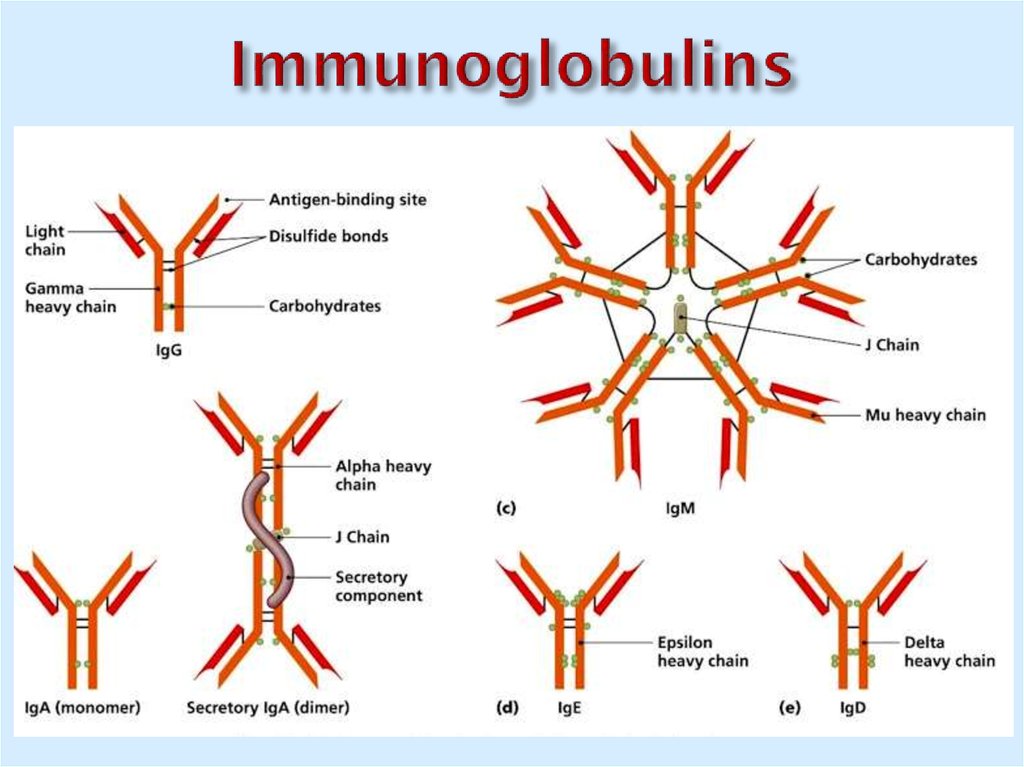
6. Immunoglobulins
7. Chemical composition of blood
C-reactive proteinInterferon
Antitrypsin
Enzymes: - excretory
- secretory
- indicator
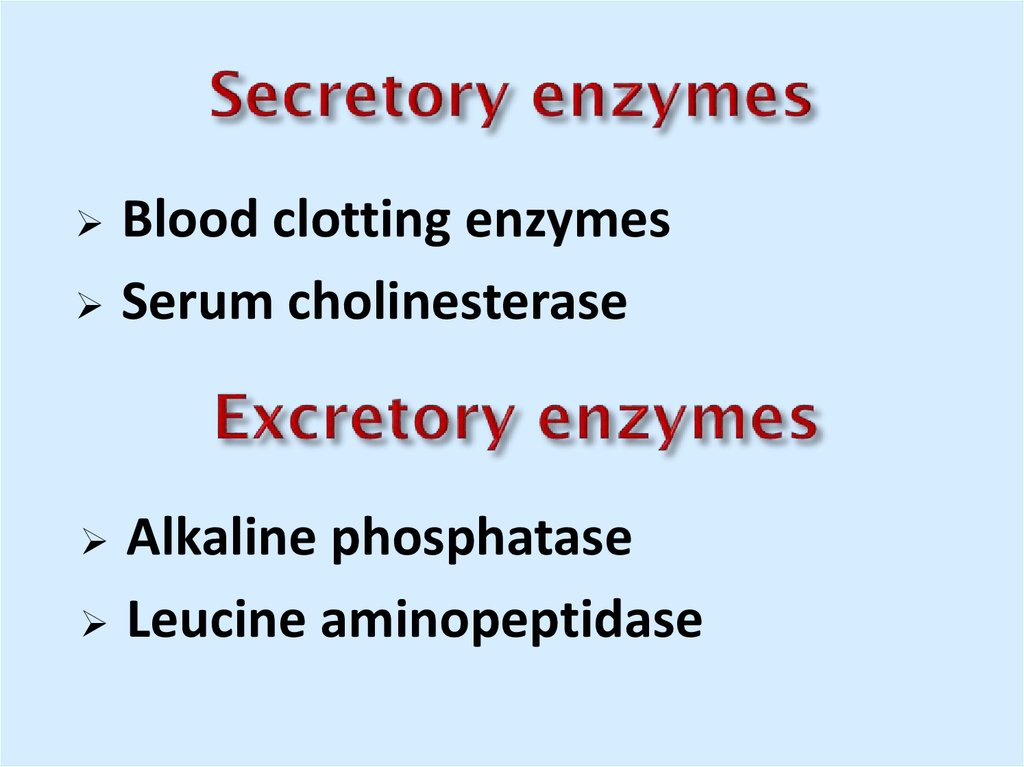
8. Secretory enzymes
Blood clotting enzymesSerum cholinesterase
Alkaline phosphatase
Leucine aminopeptidase
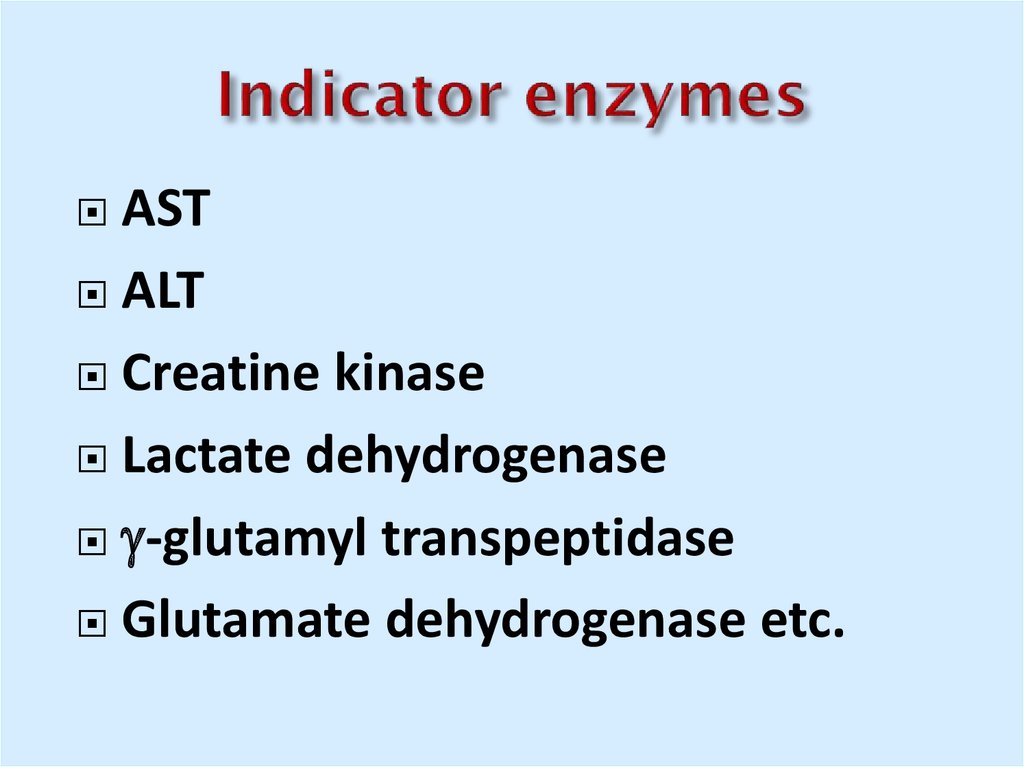
9. Indicator enzymes
ASTALT
Creatine kinase
Lactate dehydrogenase
-glutamyl transpeptidase
Glutamate dehydrogenase etc.
10.
Hypoproteinemia - kidneys andliver lesions, protein deficiency
Hyperproteinemia - severe
diarrhea, vomiting, burns
Disproteinemia – change in protein
ratio
11. Chemical composition of blood
Non-protein nitrogen compoundsNitrogen-free organic compounds
Electrolytes
Micronutrients
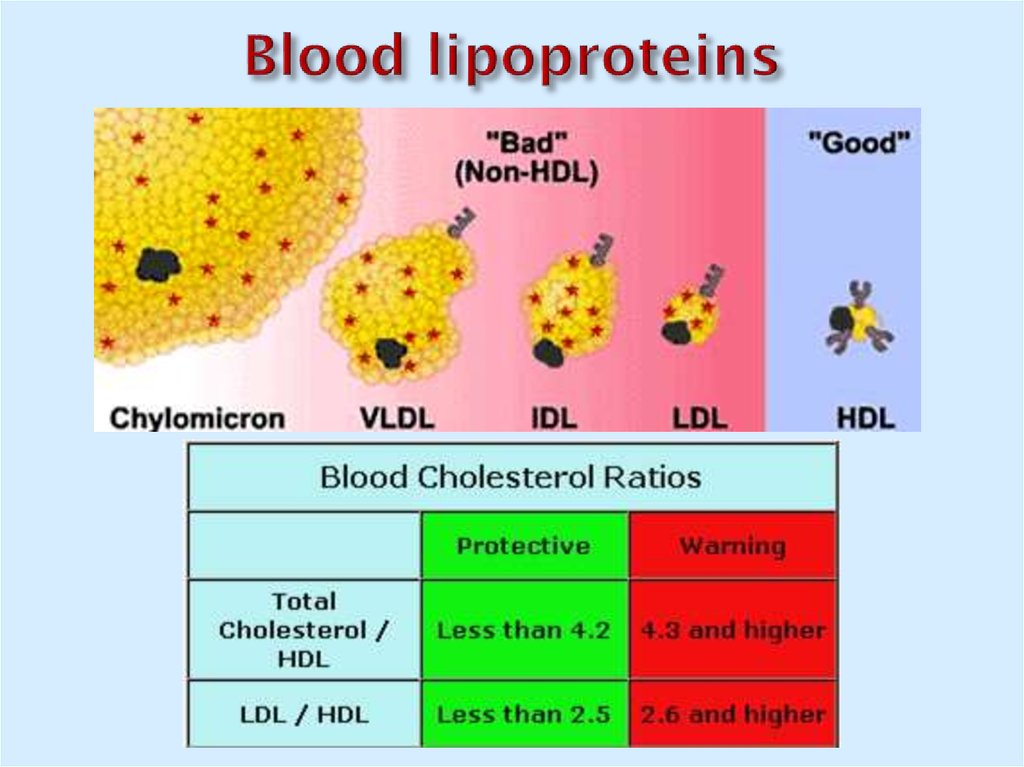
12. Blood lipoproteins
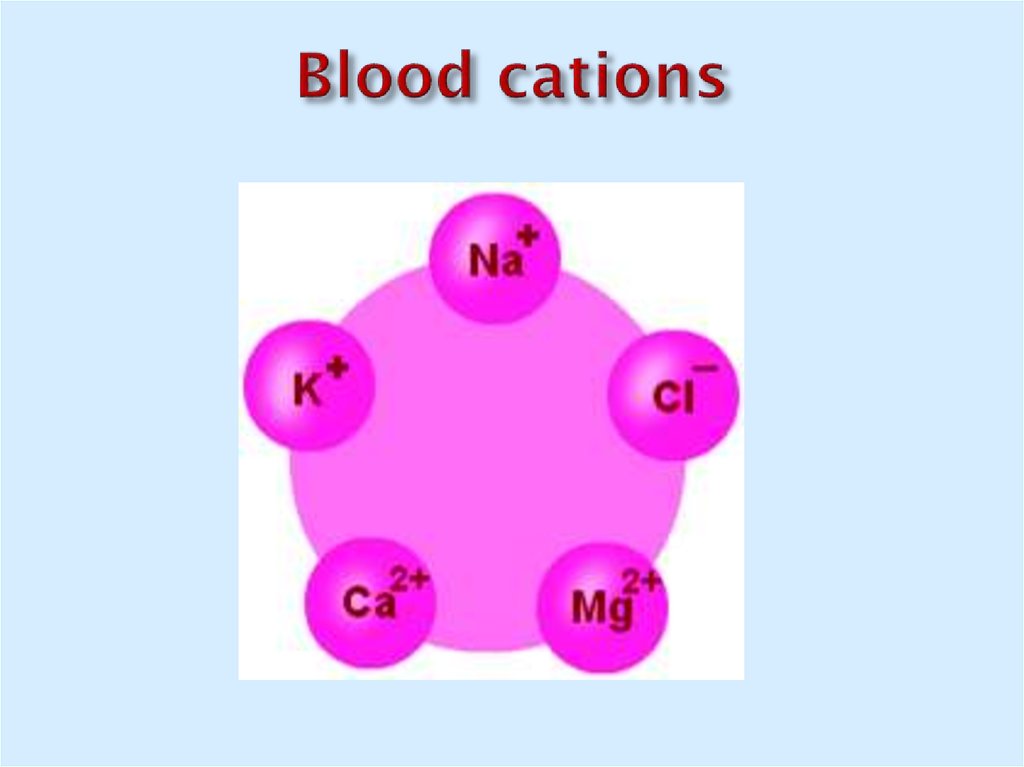
13. Blood cations
14. Blood anions
ChlorideBicarbonate
Phosphates
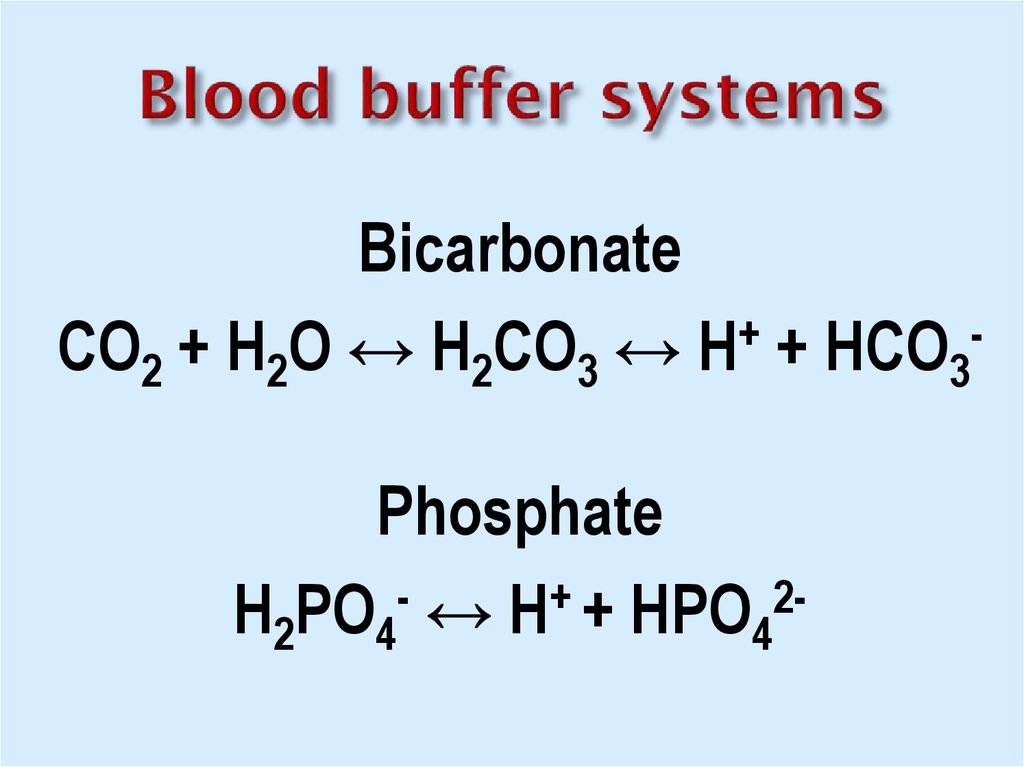
15. Blood buffer systems
Bicarbonate+
СО2 + Н2О ↔ Н2СО3 ↔ Н + НСО3
Phosphate
+
2Н2РО4 ↔ Н + НРО4
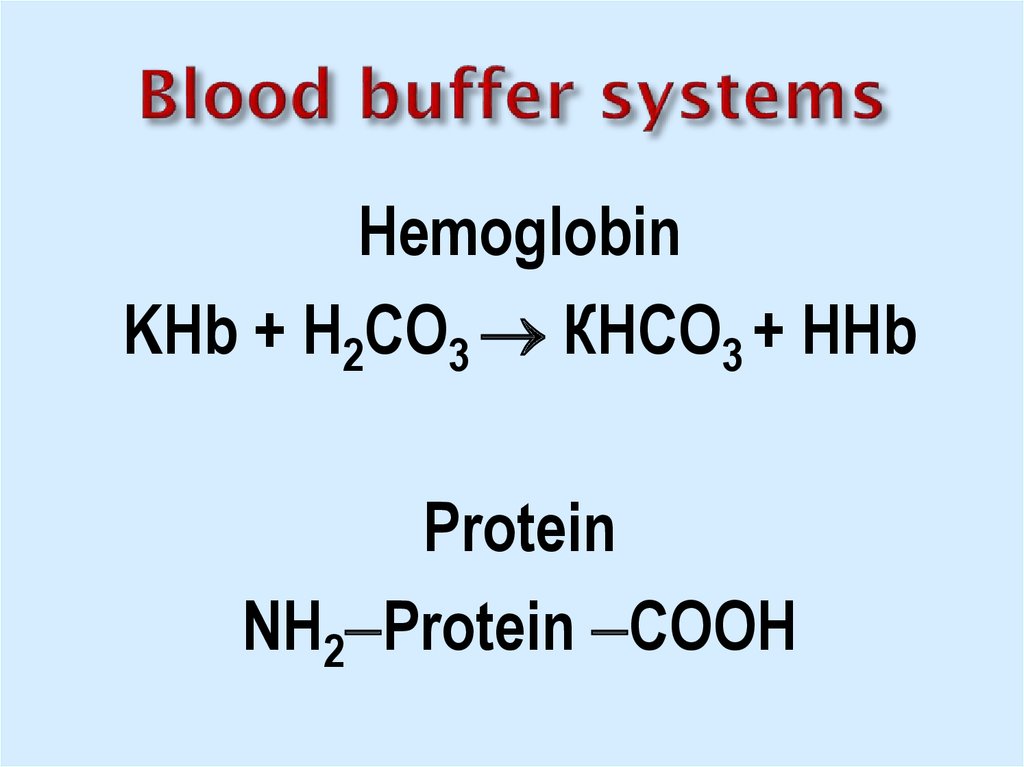
16. Blood buffer systems
HemoglobinKHb + Н2СО3 КНСО3 + ННb
Protein
NH2 Protein COOH
17. Eritrocyte metabolism
No nucleus, ribosome, mitochondriaAnaerobic glycolysis
Pentose phosphate pathway
2,3-biphosphoglicerate regulates Hb
affinity to oxygen
Protection of Hb from oxidation:
Methemoglobin reductase
NADPH, glutatione
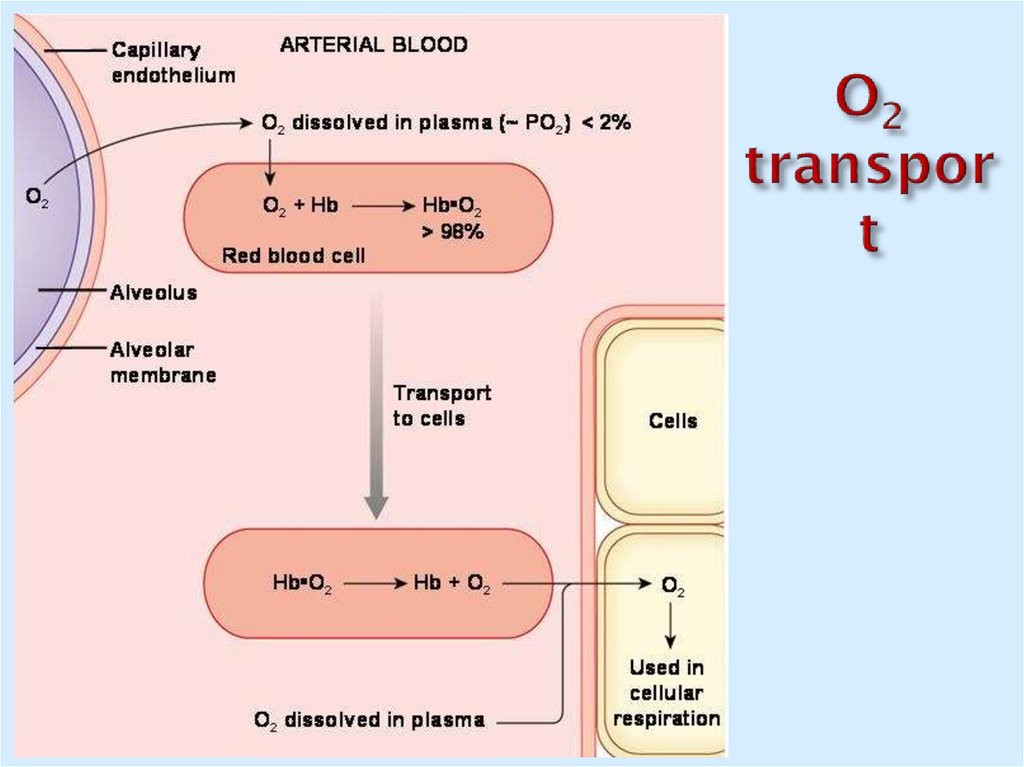
18. O2 transport
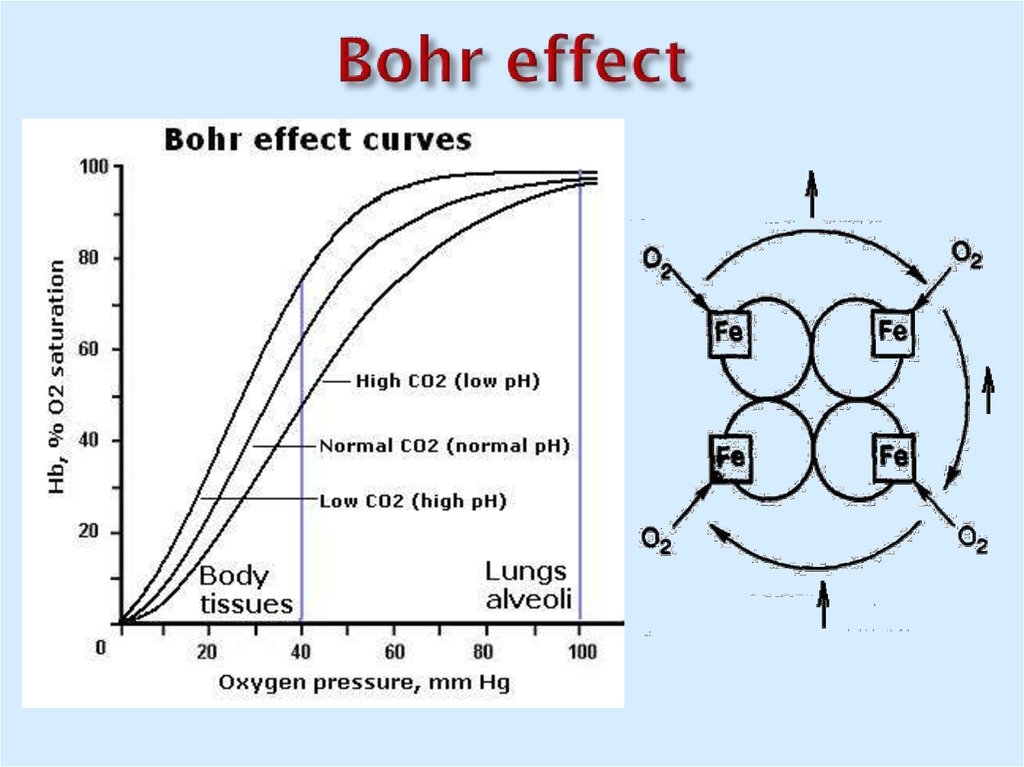
19. Bohr effect
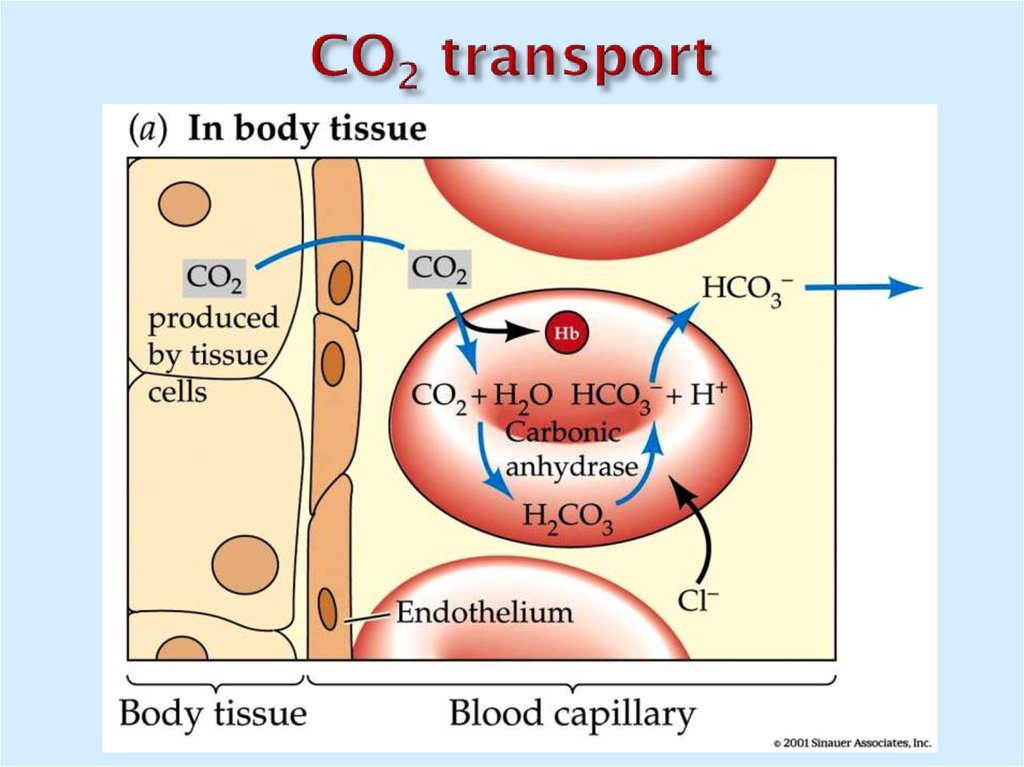
20. CO2 transport
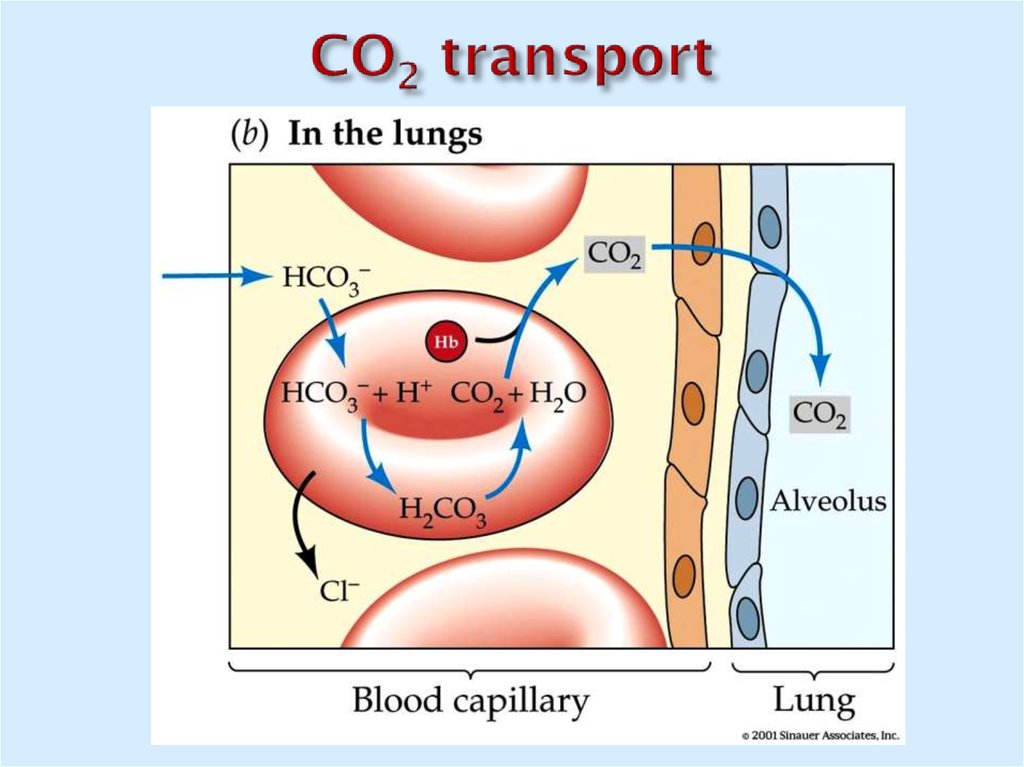
21. CO2 transport
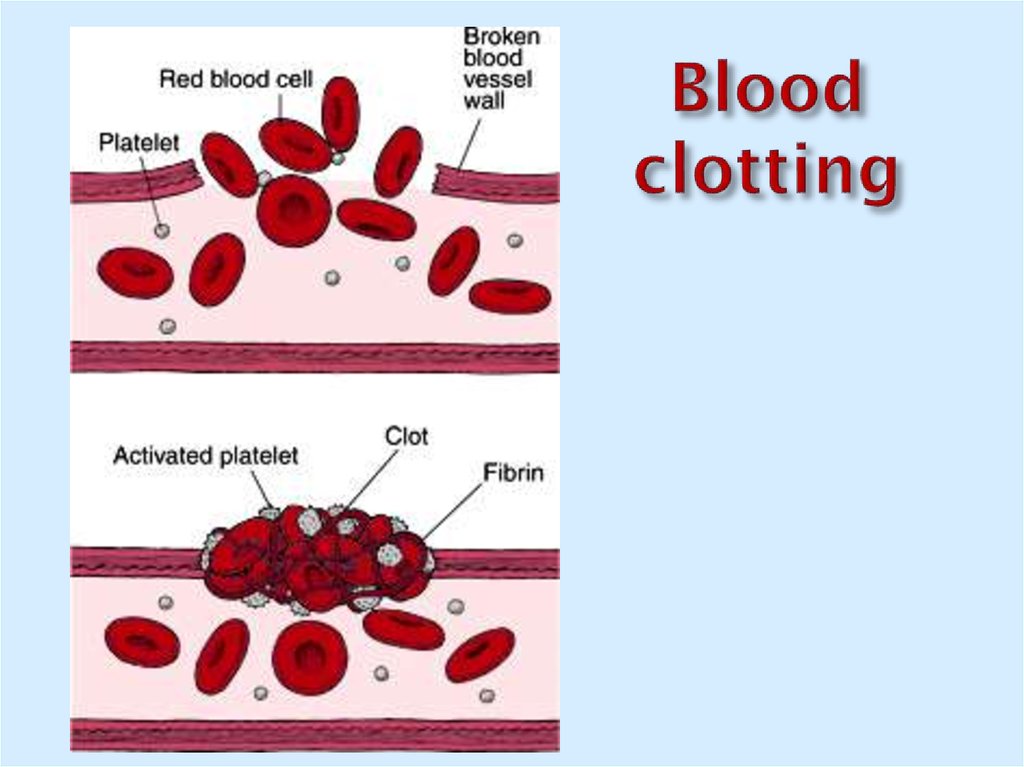
22. Blood clotting
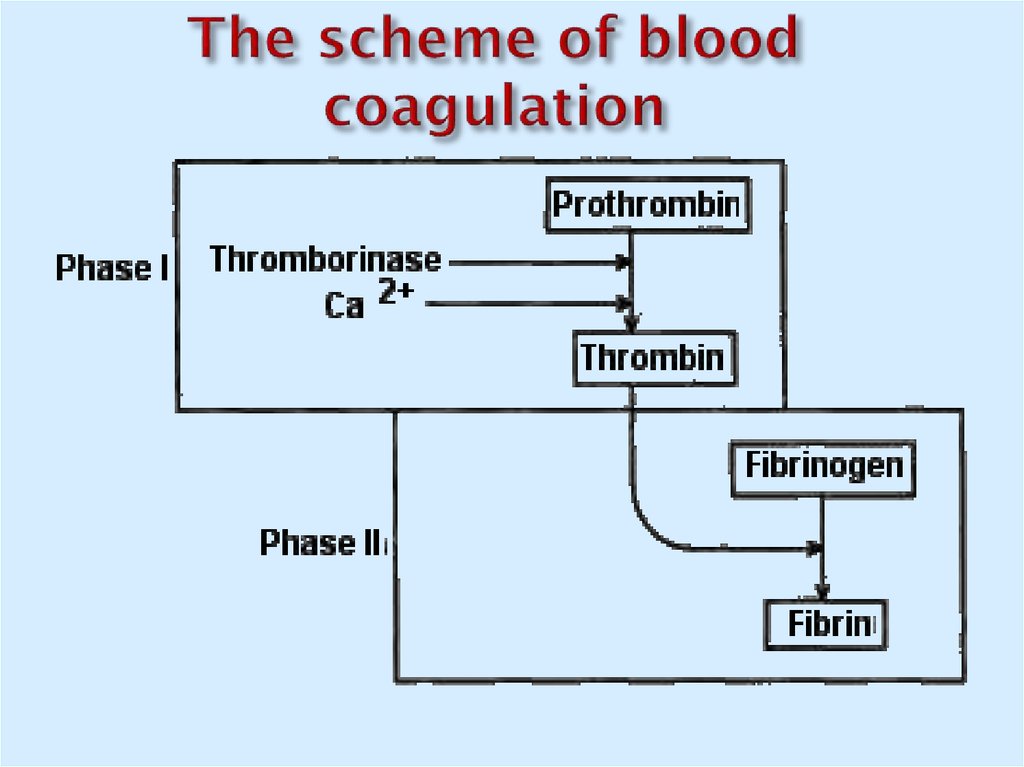
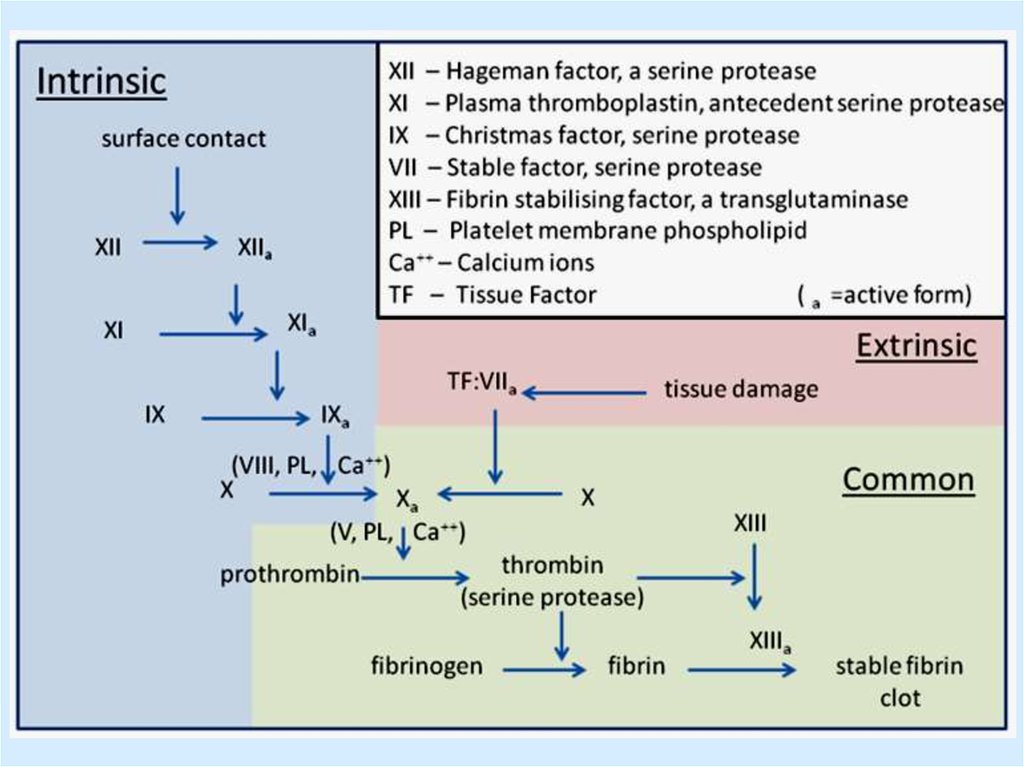
23. The scheme of blood coagulation
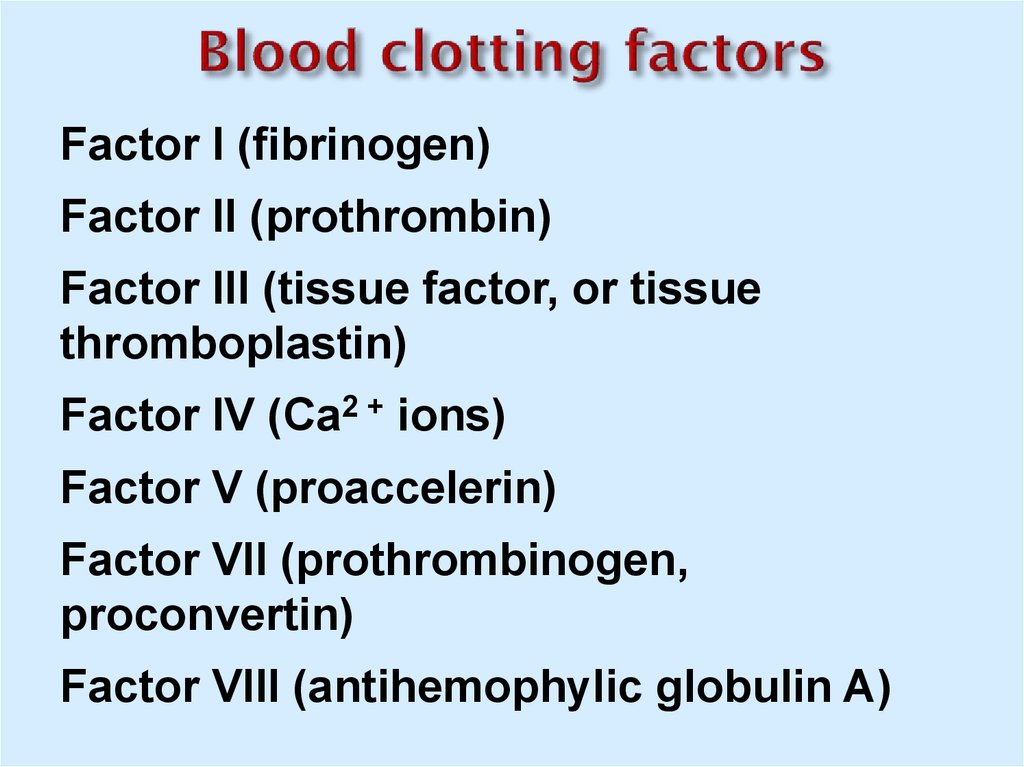
24. Blood clotting factors
Factor I (fibrinogen)Factor II (prothrombin)
Factor III (tissue factor, or tissue
thromboplastin)
Factor IV (Ca2 + ions)
Factor V (proaccelerin)
Factor VII (prothrombinogen,
proconvertin)
Factor VIII (antihemophylic globulin A)
25. Blood clotting factors
Factor IX (antihemophylic globulin B,Christmas factor)
Factor X (Stuart - Power factor)
Factor XI (Rosenthal factor,
plasma thromboplastin)
Factor XII (Hageman factor)
Factor XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor,
transglutaminase)
Factors of platelets.
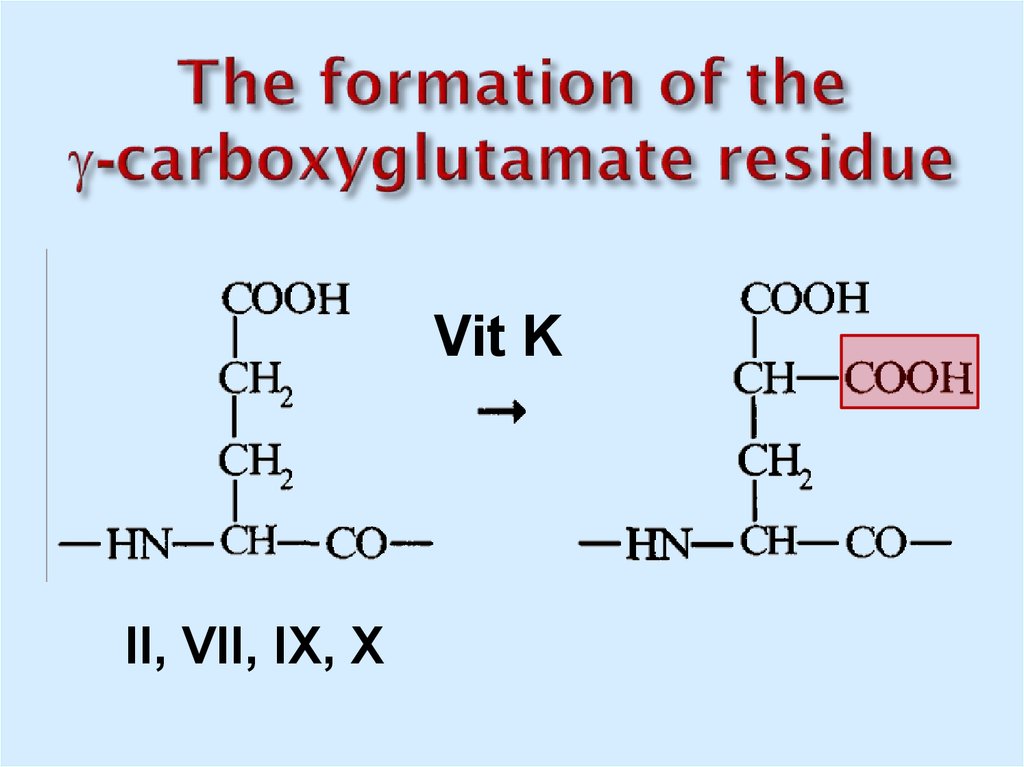
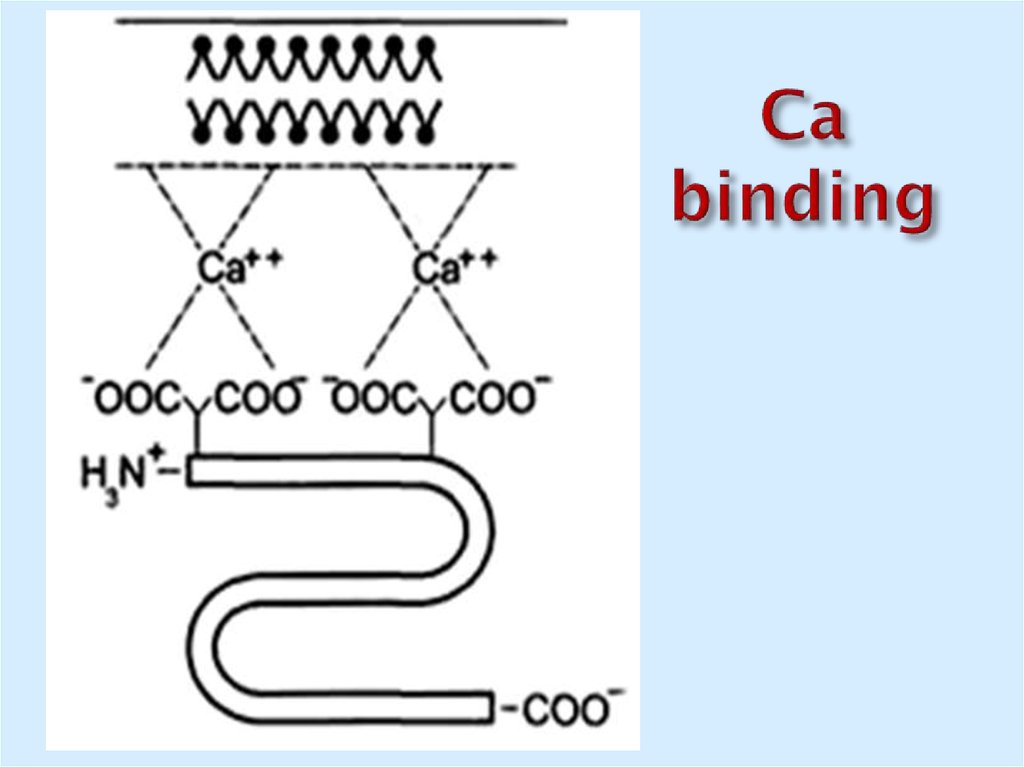
26. The formation of the -carboxyglutamate residue
Vit KII, VII, IX, X
27. Ca binding
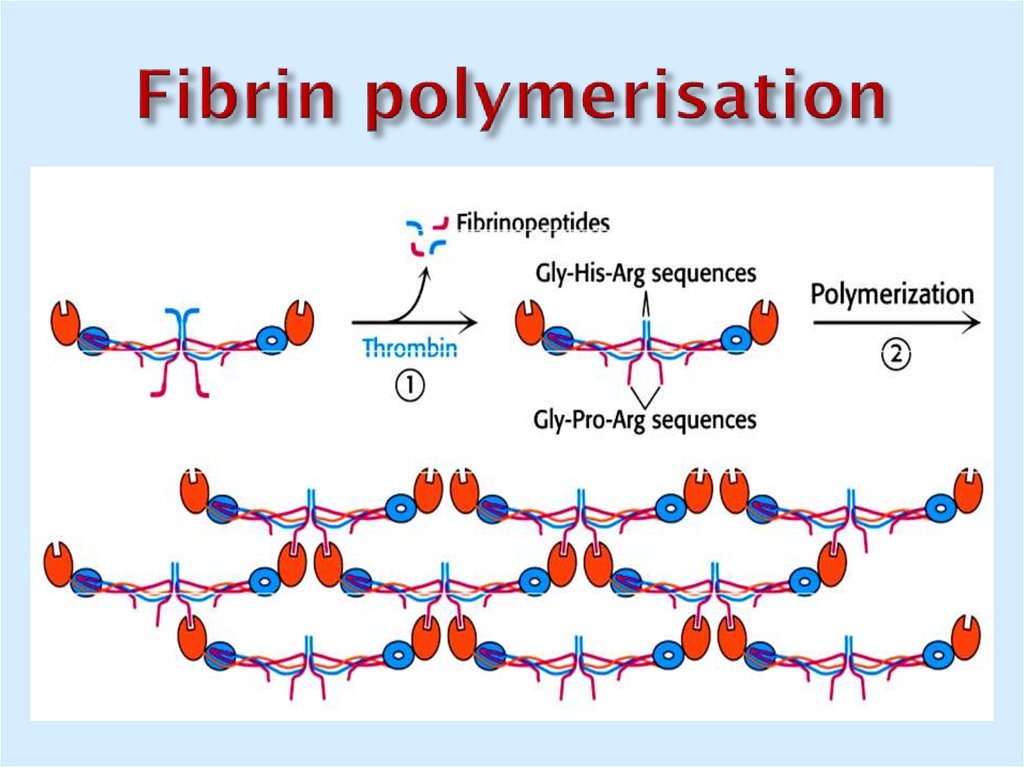
28. Fibrin polymerisation
29.
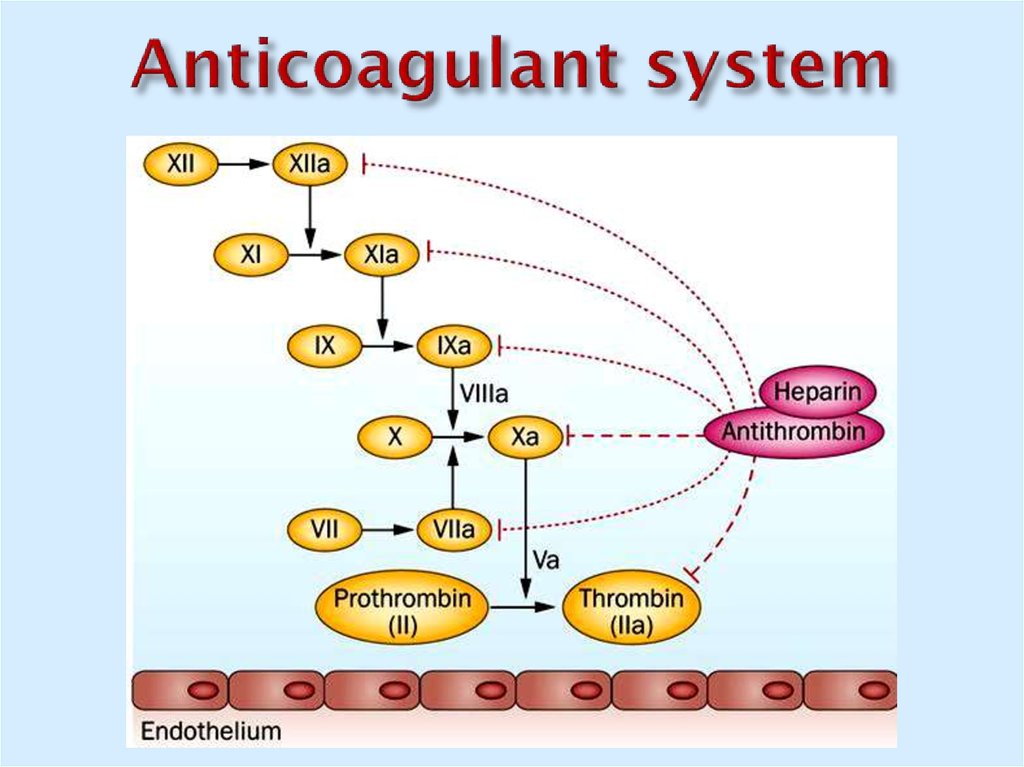
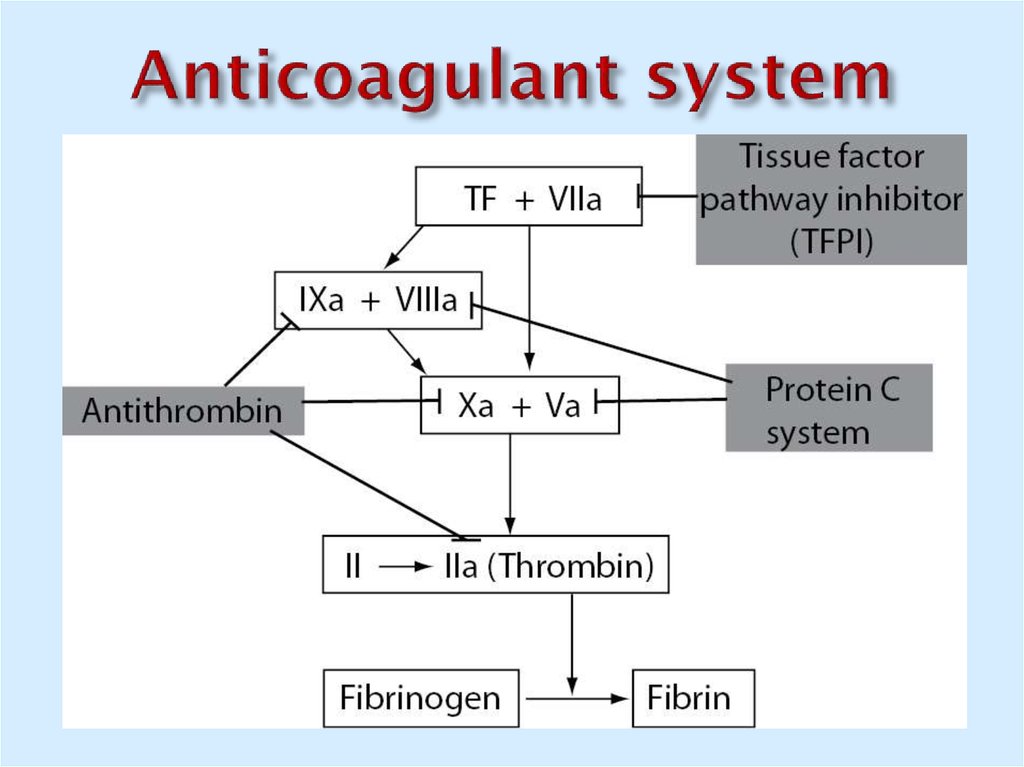
30. Anticoagulant system
31. Anticoagulant system
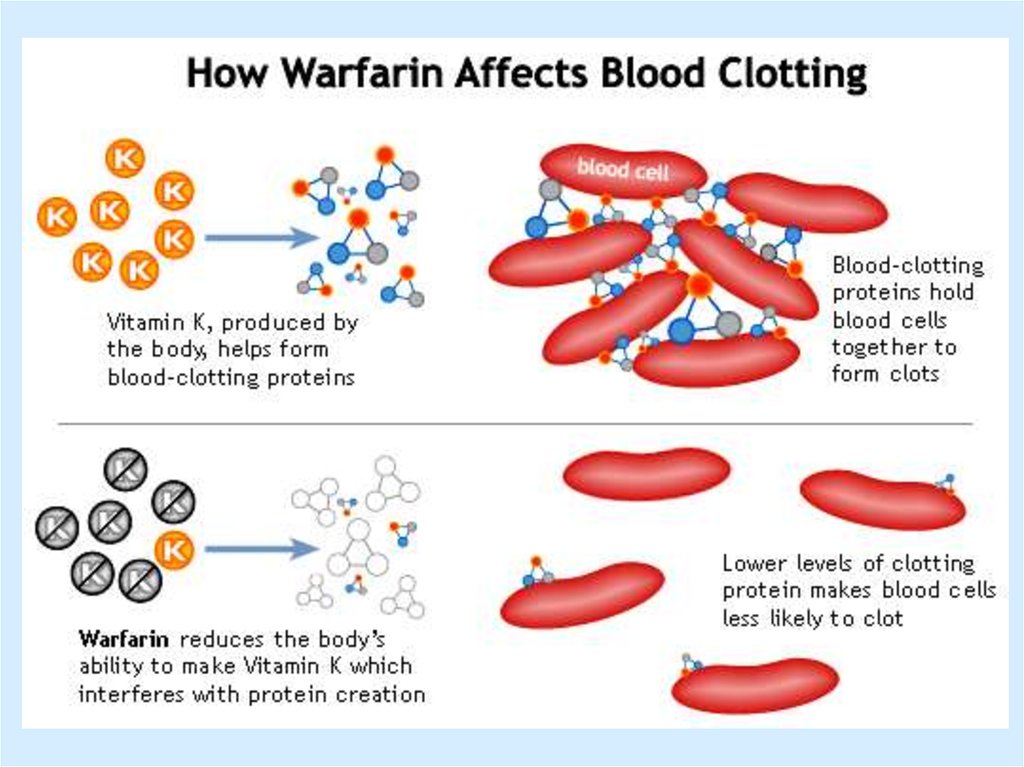
32.
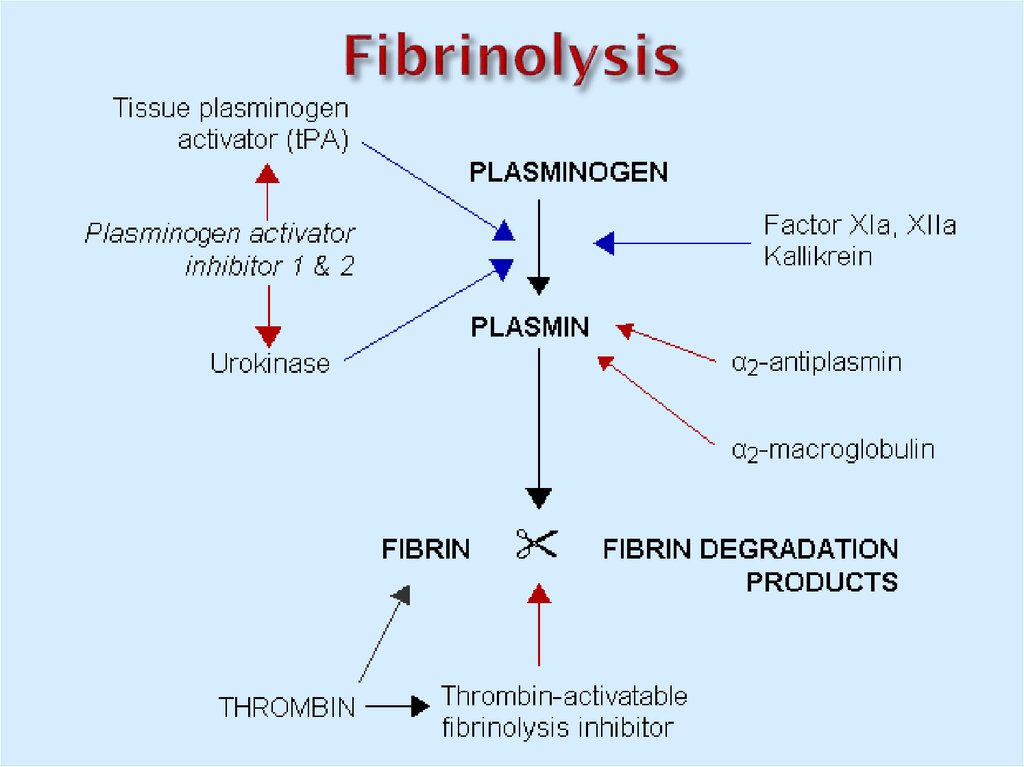
33. Fibrinolysis
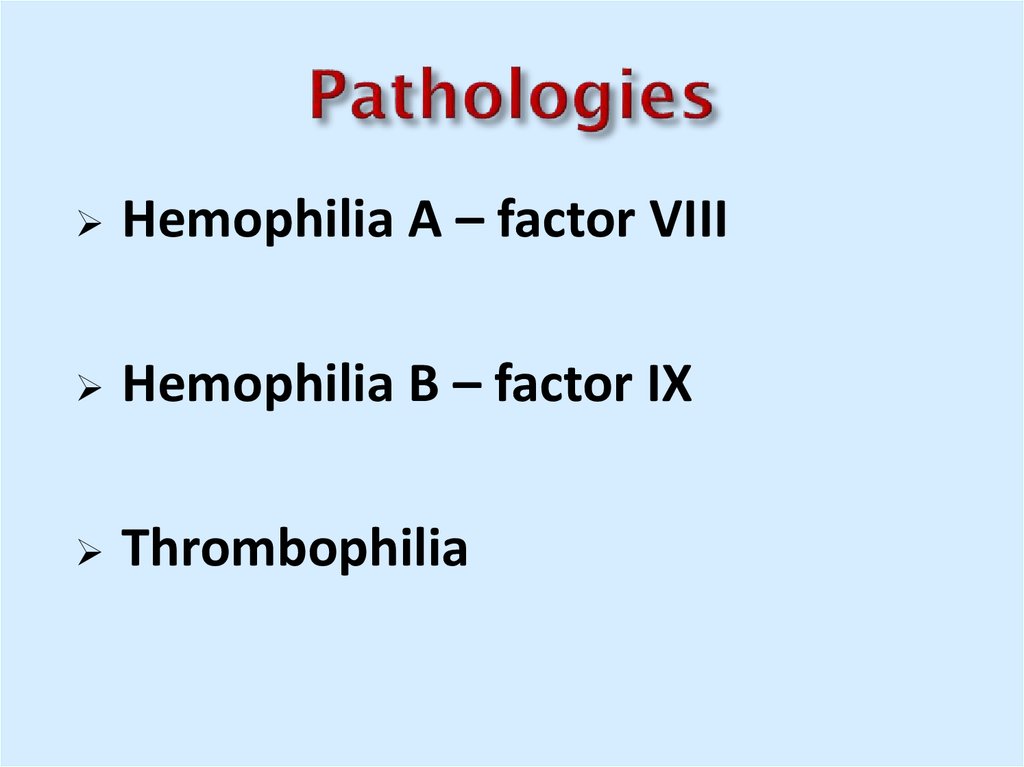
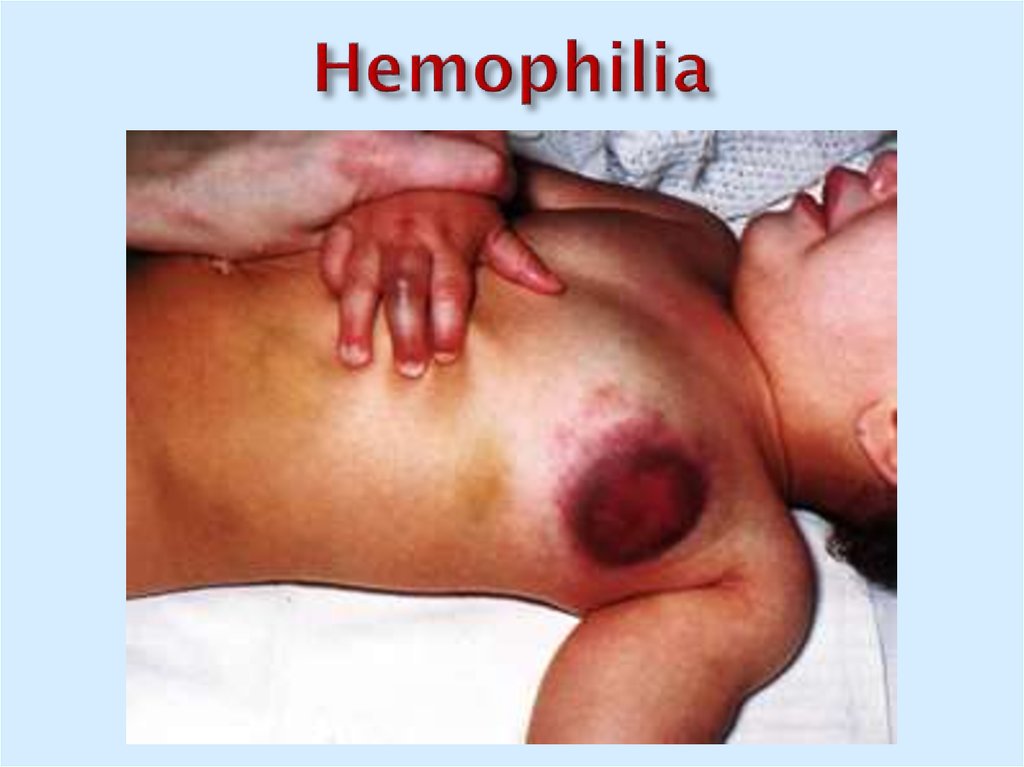
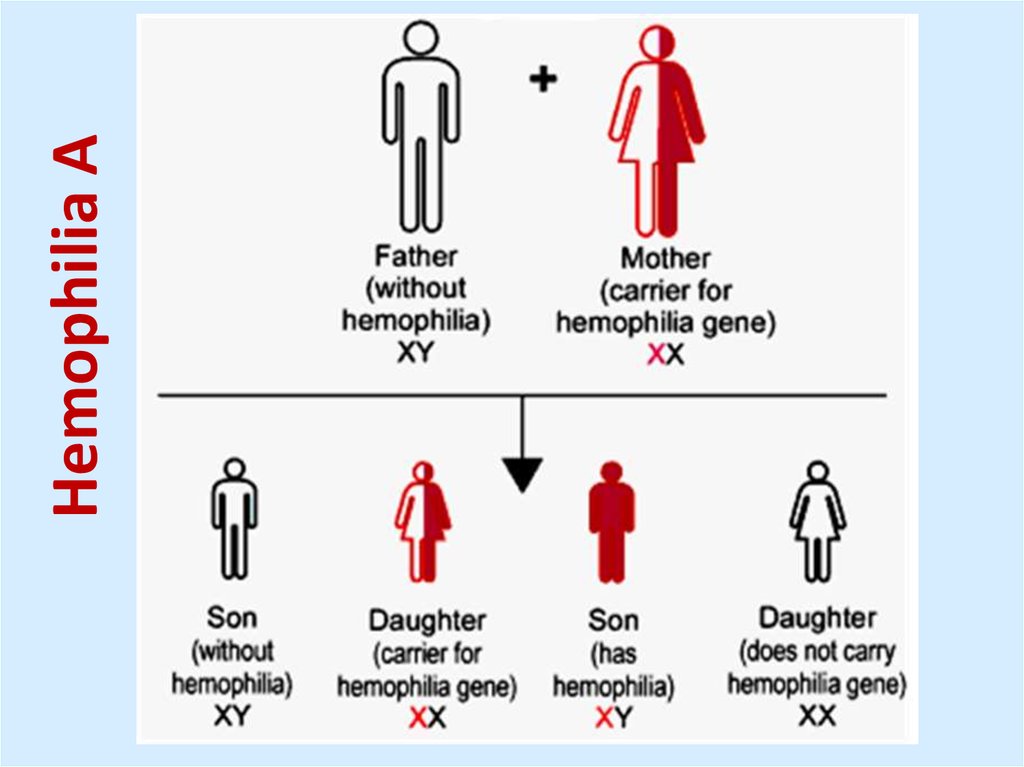
34. Pathologies
Hemophilia A – factor VIIIHemophilia B – factor IX
Thrombophilia







 medicine
medicine