Similar presentations:
Carbohydrate metabolism
1. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
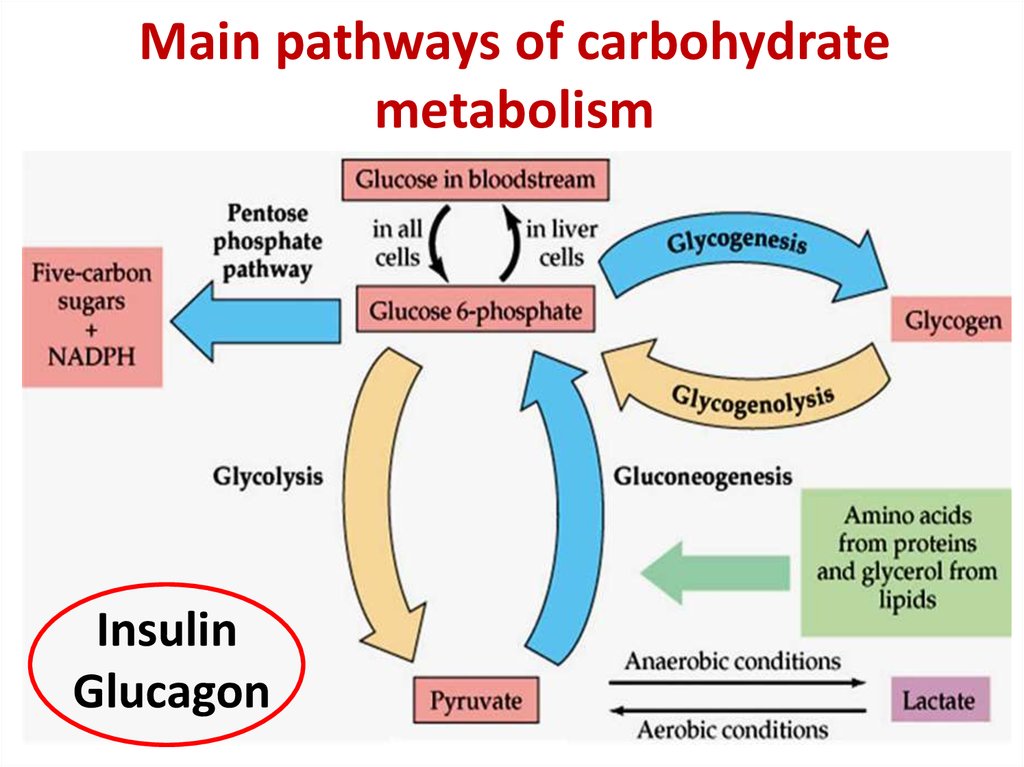
2. Main pathways of carbohydrate metabolism
InsulinGlucagon
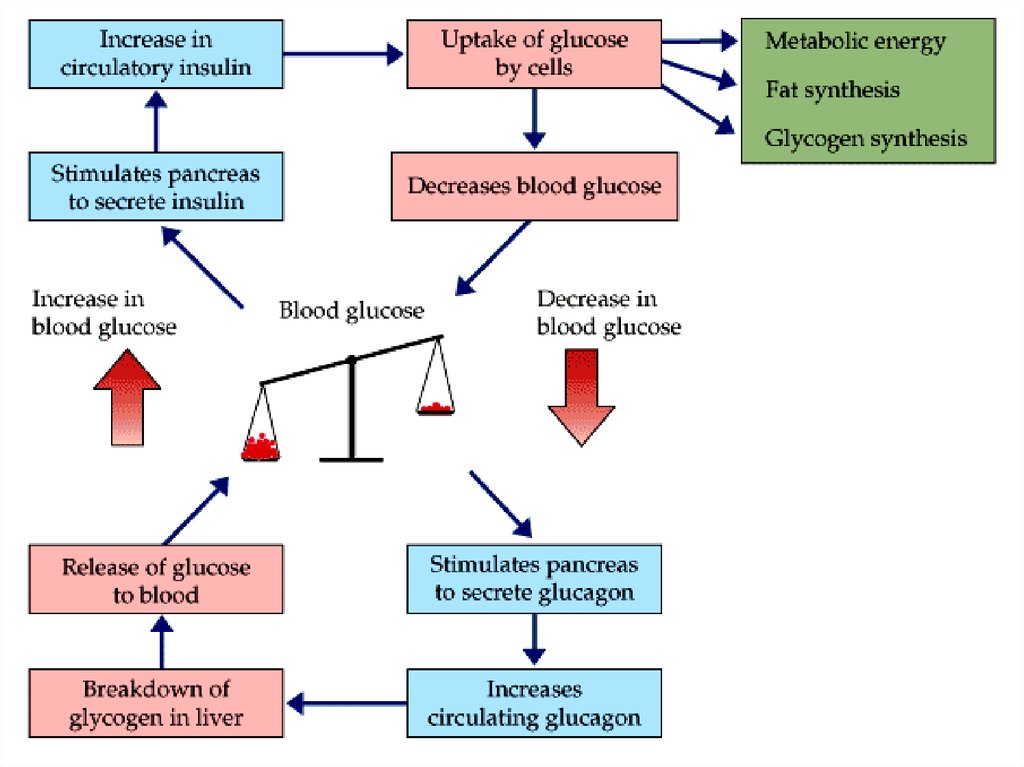
3.
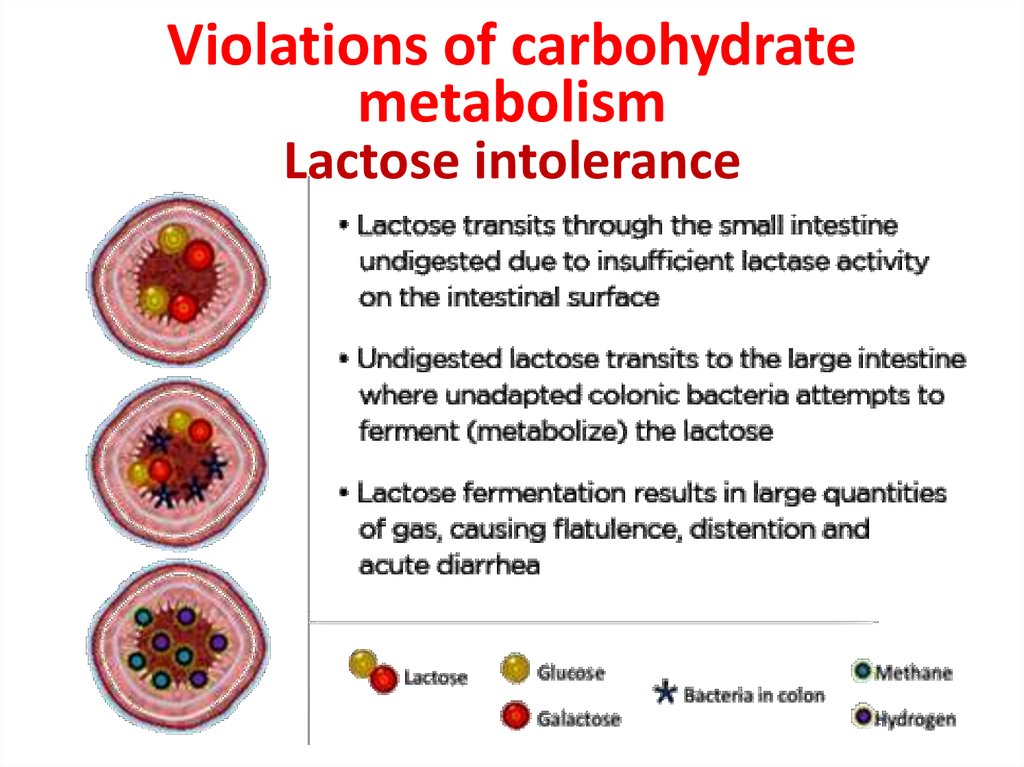
4. Violations of carbohydrate metabolism Lactose intolerance
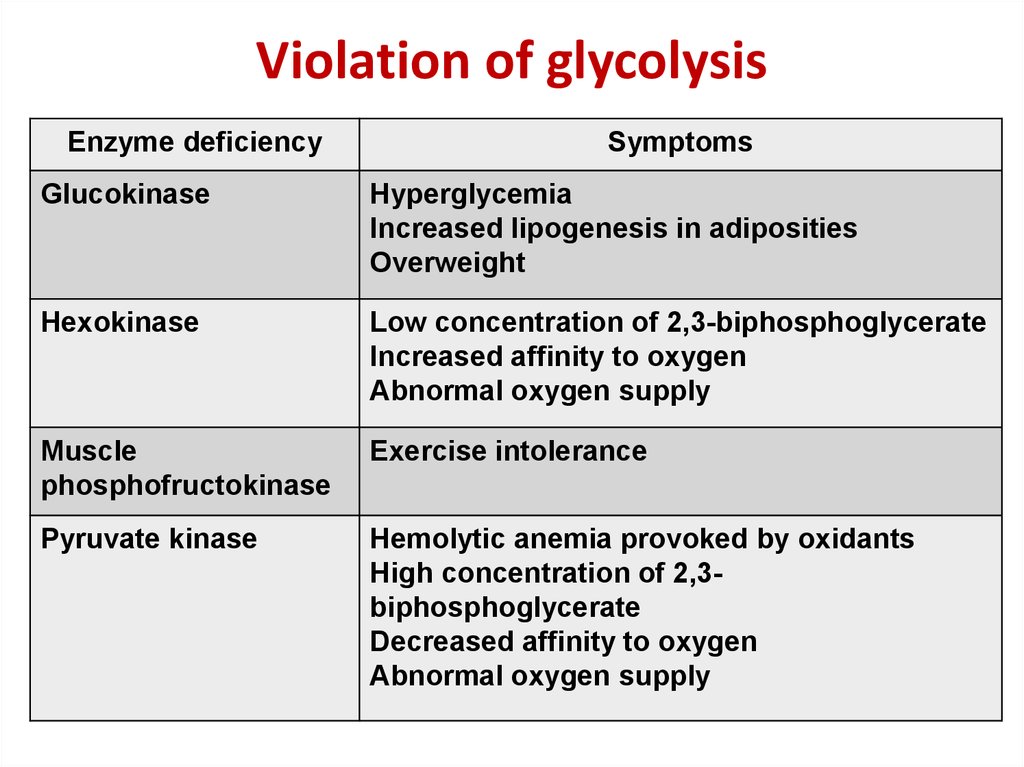
5. Violation of glycolysis
Enzyme deficiencySymptoms
Glucokinase
Hyperglycemia
Increased lipogenesis in adiposities
Overweight
Hexokinase
Low concentration of 2,3-biphosphoglycerate
Increased affinity to oxygen
Abnormal oxygen supply
Muscle
phosphofructokinase
Exercise intolerance
Pyruvate kinase
Hemolytic anemia provoked by oxidants
High concentration of 2,3biphosphoglycerate
Decreased affinity to oxygen
Abnormal oxygen supply
6. Fructose intolerance
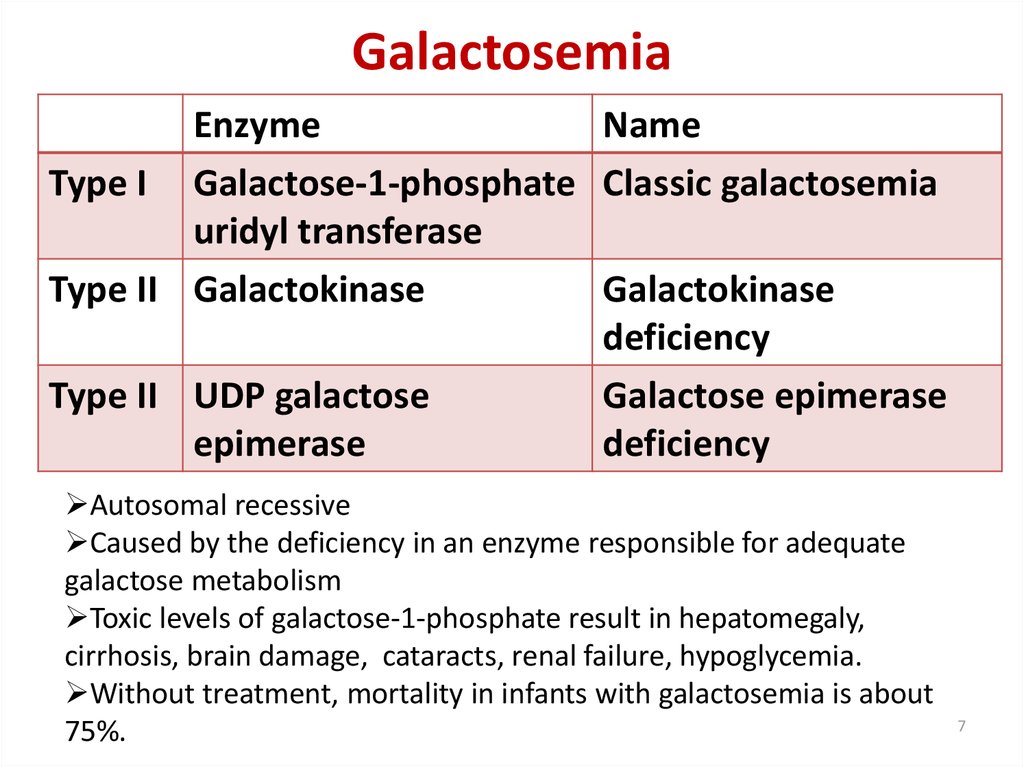
7. Galactosemia
EnzymeName
Type I Galactose-1-phosphate Classic galactosemia
uridyl transferase
Type II Galactokinase
Galactokinase
deficiency
Type II UDP galactose
Galactose epimerase
epimerase
deficiency
Autosomal recessive
Caused by the deficiency in an enzyme responsible for adequate
galactose metabolism
Toxic levels of galactose-1-phosphate result in hepatomegaly,
cirrhosis, brain damage, cataracts, renal failure, hypoglycemia.
Without treatment, mortality in infants with galactosemia is about
75%.
7
8. Violation of pentose phosphate pathway
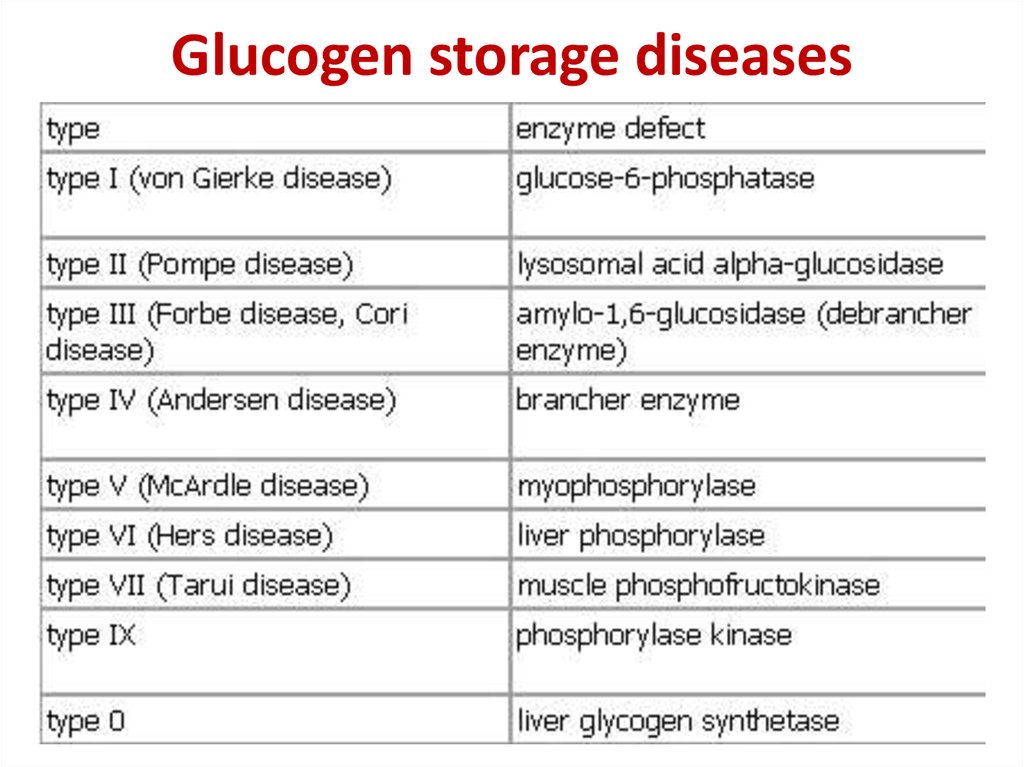
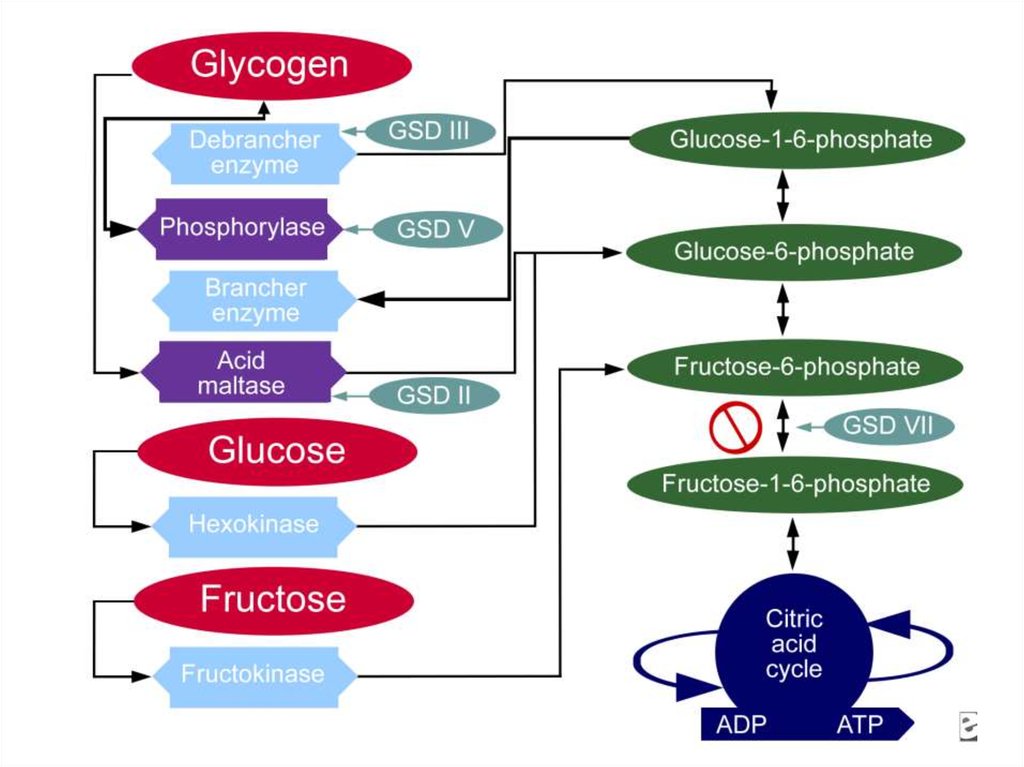
9. Glucogen storage diseases
10.
11. Ethanol metabolism
12.
13.
14.
15. Ethanol metabolism in the human body
16. Ethanol metabolism
17. Ethanol metabolism Acetate is used as a source of energy
18.
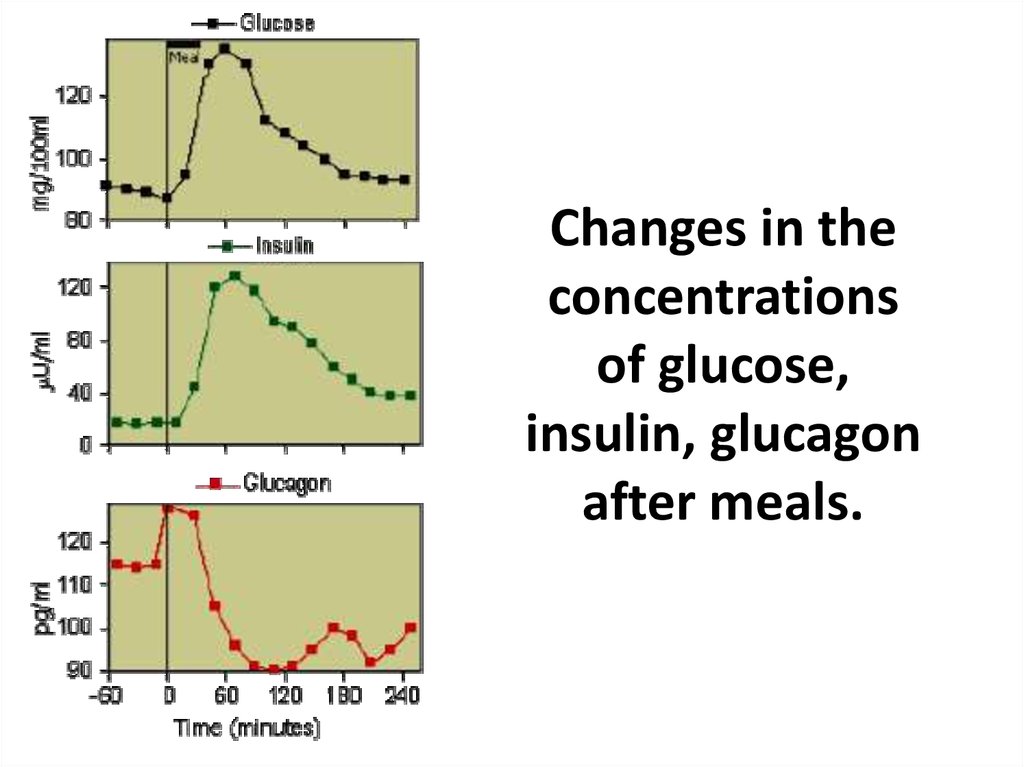
19. Changes in the concentrations of glucose, insulin, glucagon after meals.
Changes in theconcentrations
of glucose,
insulin, glucagon
after meals.
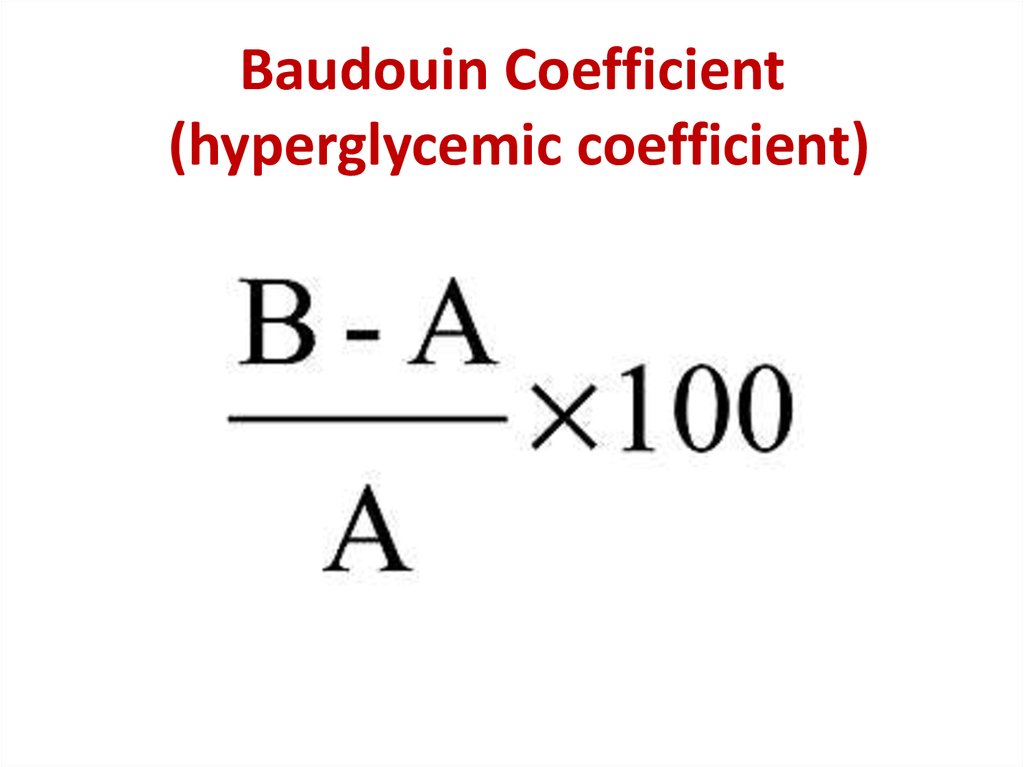
20. Baudouin Coefficient (hyperglycemic coefficient)
21.
Glycemic index graph in norm (1)and diabetes (2)
22.
23.
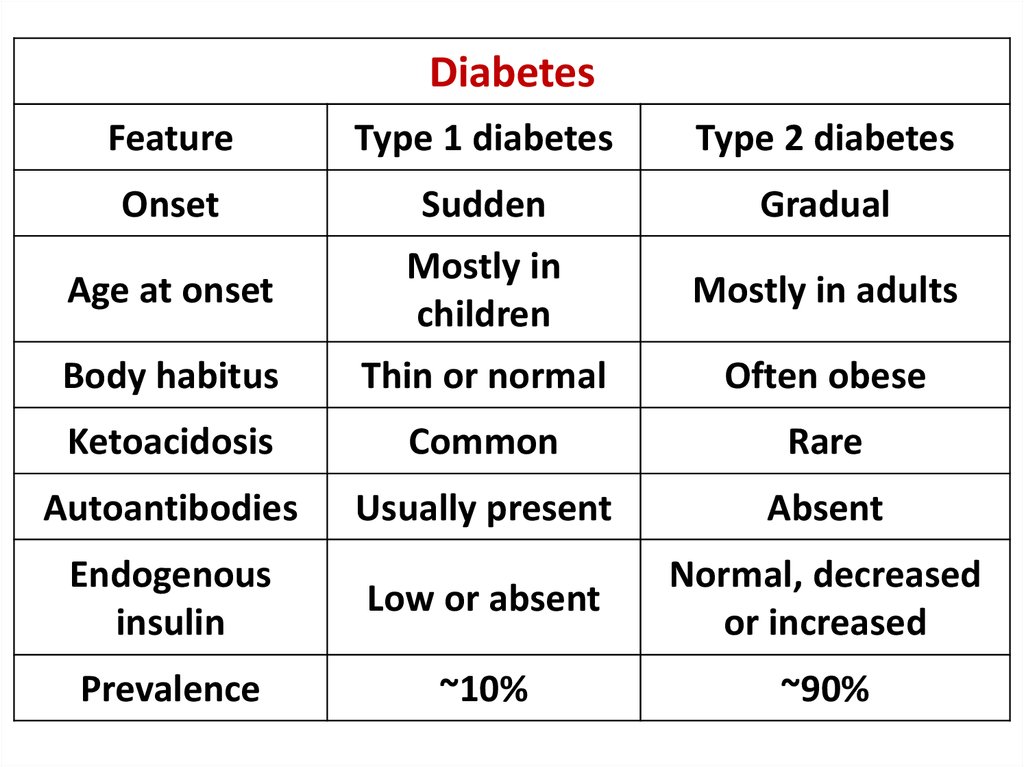
DiabetesFeature
Type 1 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
Onset
Sudden
Gradual
Age at onset
Mostly in
children
Mostly in adults
Body habitus
Thin or normal
Often obese
Ketoacidosis
Common
Rare
Autoantibodies
Usually present
Absent
Endogenous
insulin
Low or absent
Normal, decreased
or increased
Prevalence
~10%
~90%
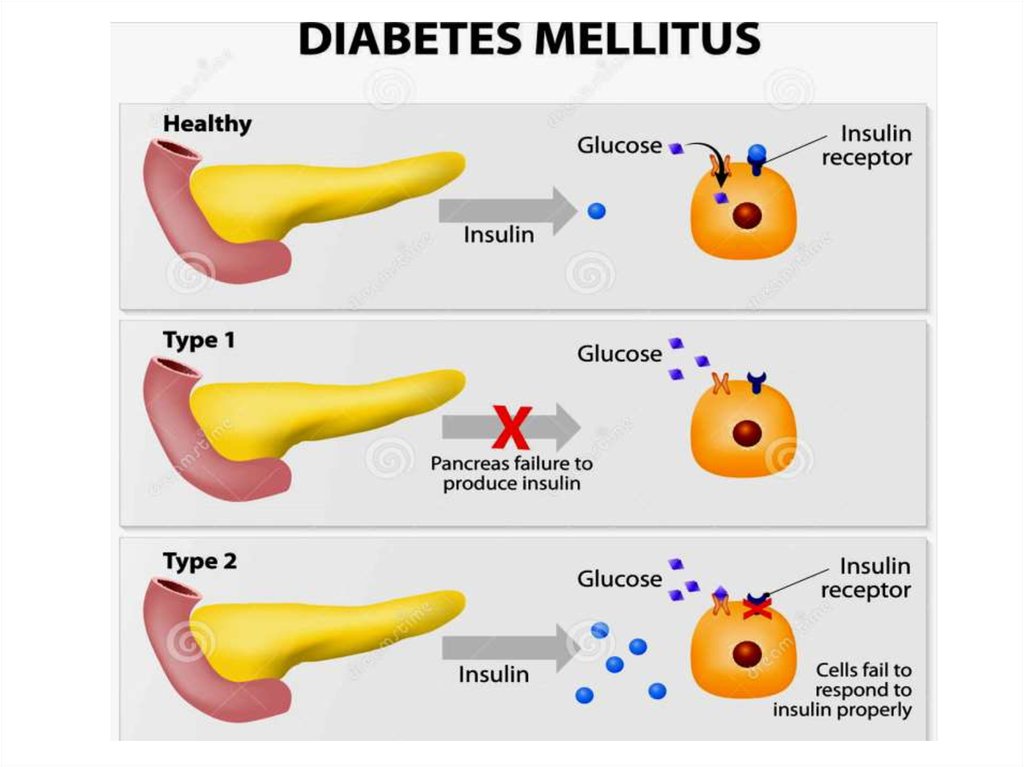
24. The main manifestations of diabetes
• Decreased synthesis and depositionof glycogen and fat
• Hyperglycemia
• Hyperlipoproteinemia
• Ketonemia
• Azotemia and azoturia
• Polyuria and polydipsia













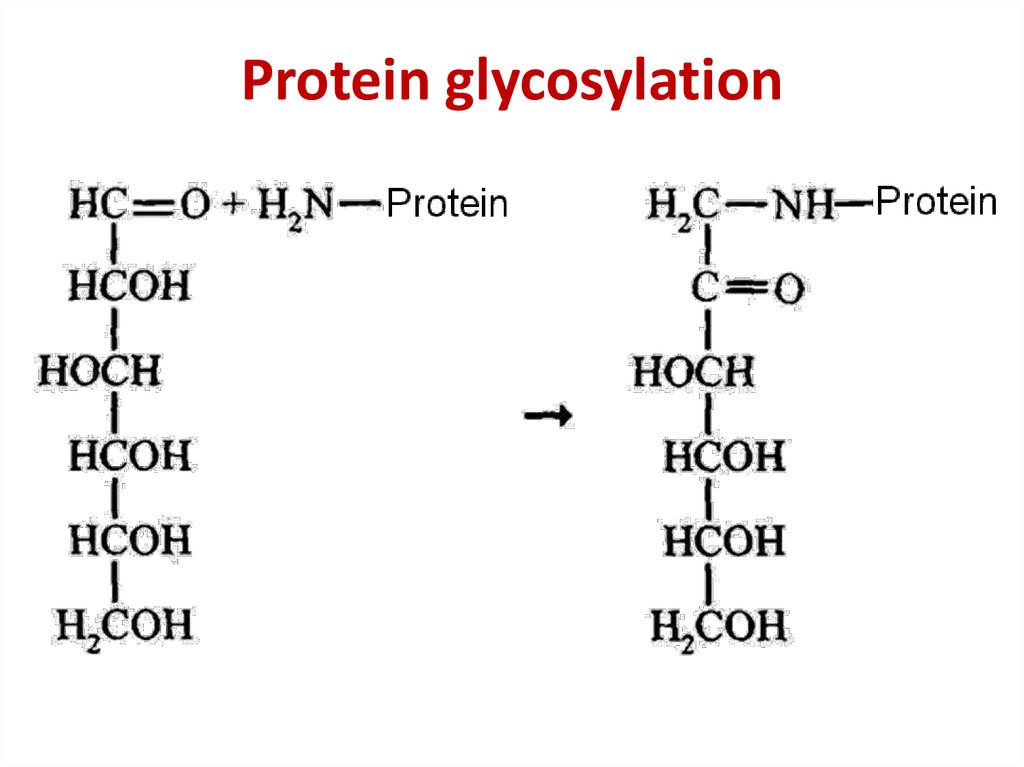


 medicine
medicine