Similar presentations:
Protein synthesis
1.
2. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
2PROTEIN
SYNTHESIS
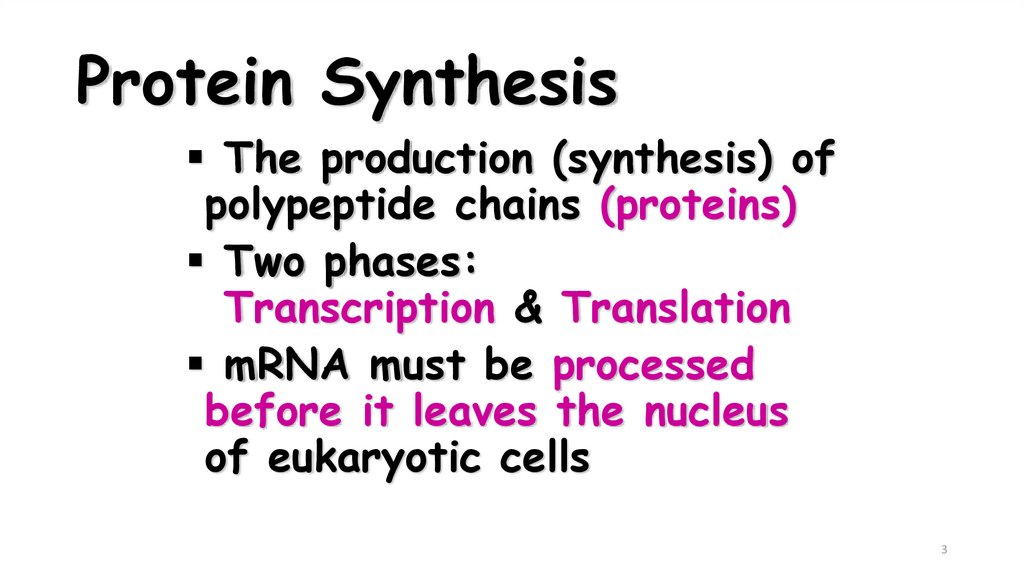
3. Protein Synthesis
The production (synthesis) ofpolypeptide chains (proteins)
Two phases:
Transcription & Translation
mRNA must be processed
before it leaves the nucleus
of eukaryotic cells
3
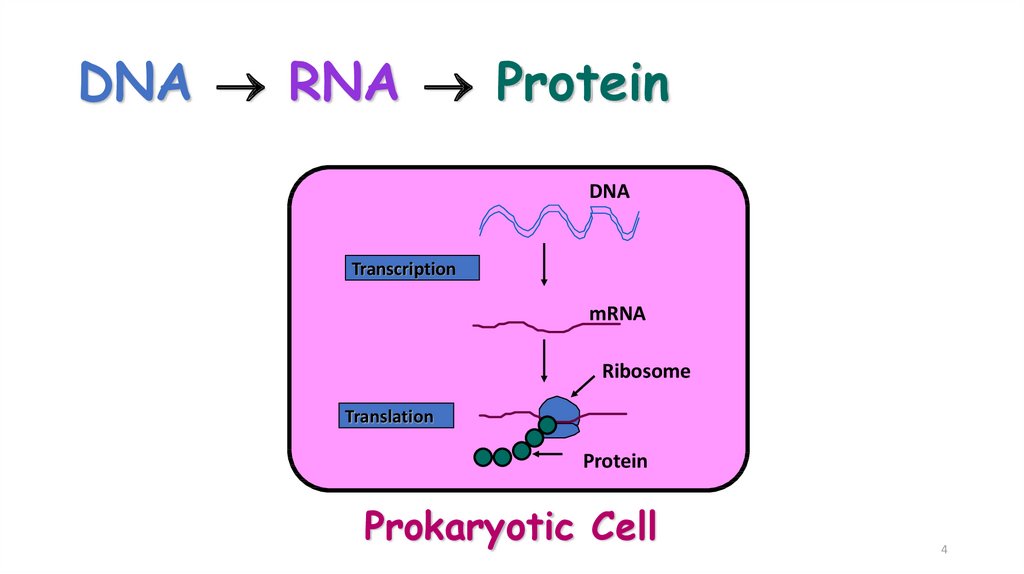
4. DNA RNA Protein
DNA RNA ProteinDNA
Transcription
mRNA
Ribosome
Translation
Protein
Prokaryotic Cell
4
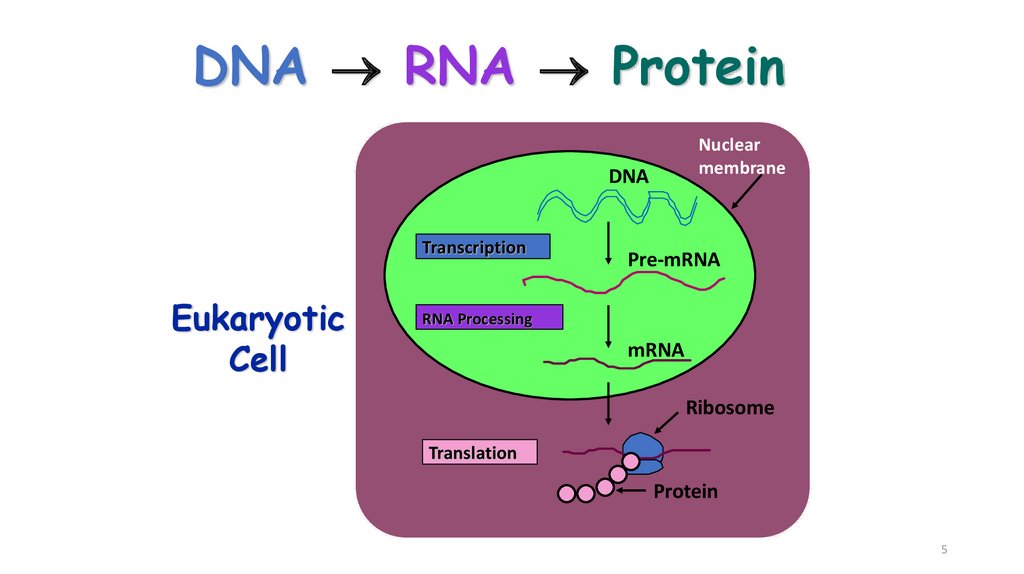
5. DNA RNA Protein
DNA RNA ProteinNuclear
membrane
DNA
Transcription
Eukaryotic
Cell
Pre-mRNA
RNA Processing
mRNA
Ribosome
Translation
Protein
5
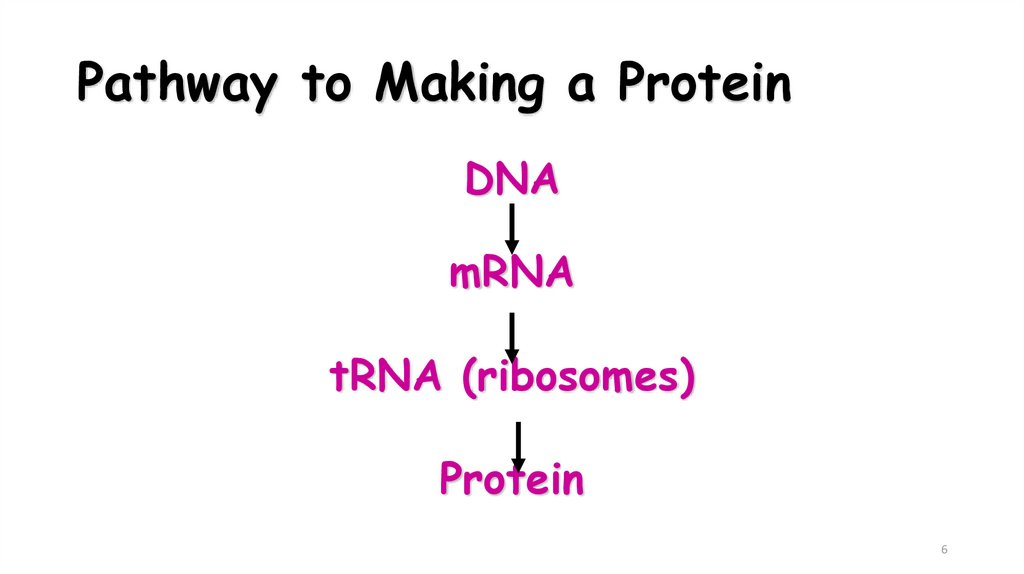
6. Pathway to Making a Protein
DNAmRNA
tRNA (ribosomes)
Protein
6
7. Nucleic Acids
7Nucleic Acids
8. DNA or Protein?
Walter Sutton discoveredchromosomes were made of
DNA and Protein
However, scientists were
NOT sure which one (protein
or DNA) was the actual
genetic material of the cell
8
9. DNA!
Frederick Griffith in1928 showed the
DNA was the cell’s
genetic material
Watson & Crick in
the 1950’s built the
1st model of DNA
9
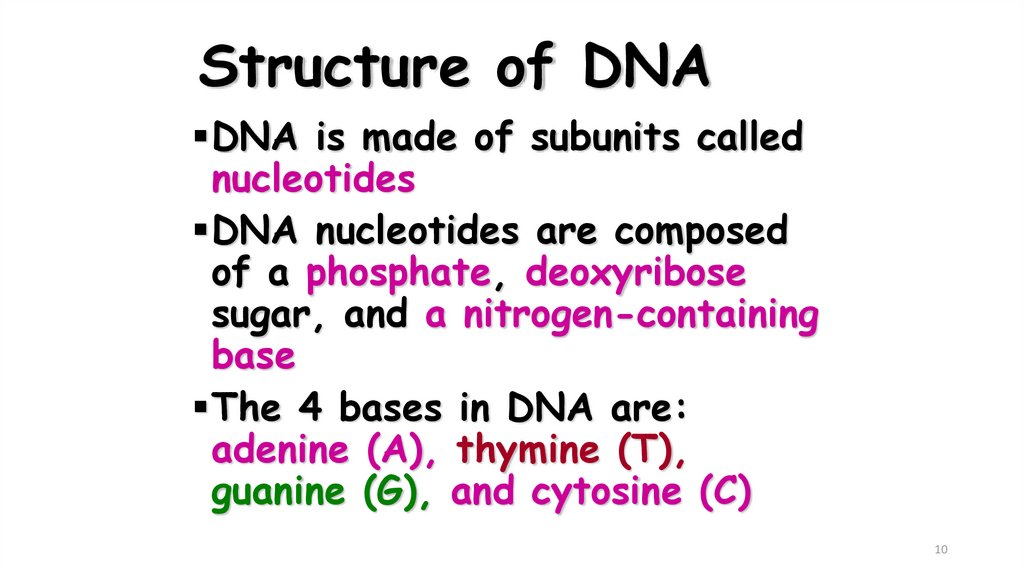
10. Structure of DNA
DNA is made of subunits callednucleotides
DNA nucleotides are composed
of a phosphate, deoxyribose
sugar, and a nitrogen-containing
base
The 4 bases in DNA are:
adenine (A), thymine (T),
guanine (G), and cytosine (C)
10
11.
DNA Nucleotide11
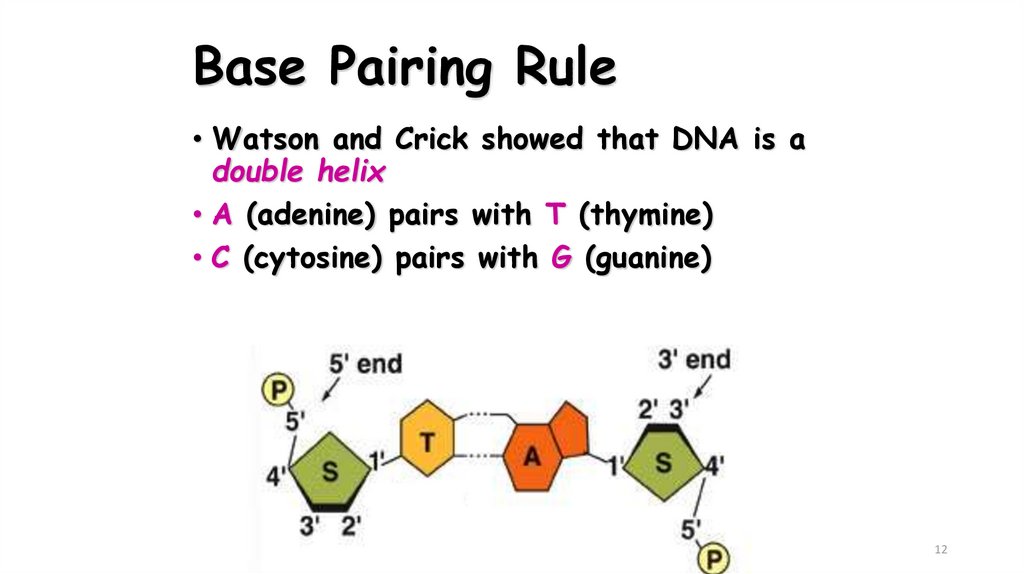
12. Base Pairing Rule
• Watson and Crick showed that DNA is adouble helix
• A (adenine) pairs with T (thymine)
• C (cytosine) pairs with G (guanine)
12
13.
AntiParallelStrands
of DNA
13
14. RNA
14RNA
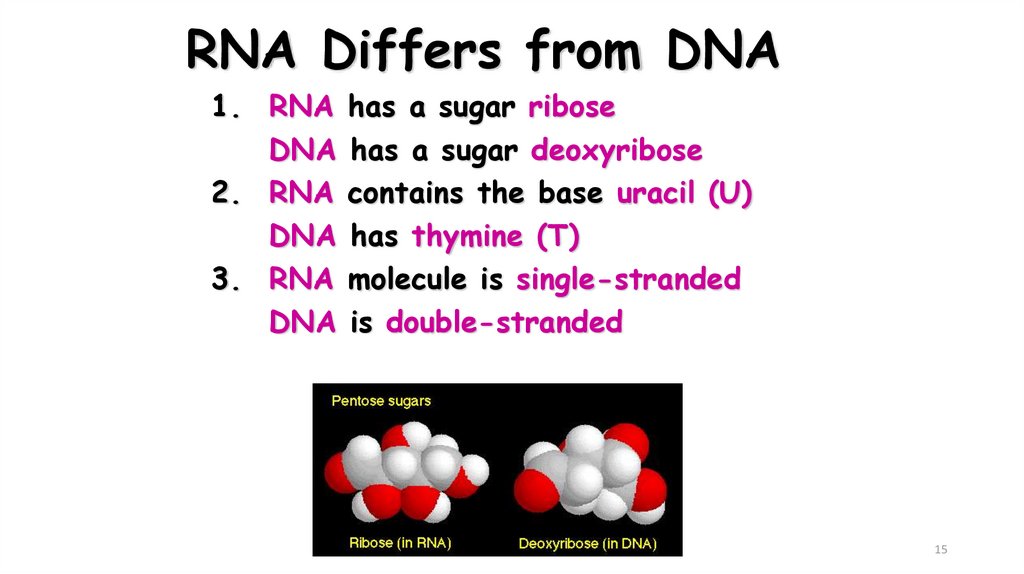
15. RNA Differs from DNA
1. RNADNA
2. RNA
DNA
3. RNA
DNA
has a sugar ribose
has a sugar deoxyribose
contains the base uracil (U)
has thymine (T)
molecule is single-stranded
is double-stranded
15
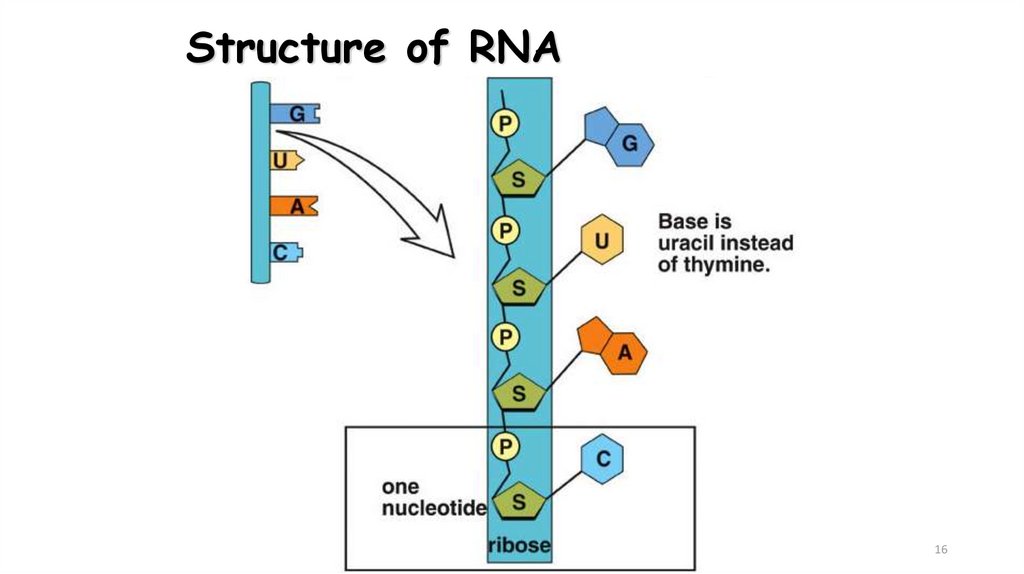
16. Structure of RNA
1617. Three Types of RNA
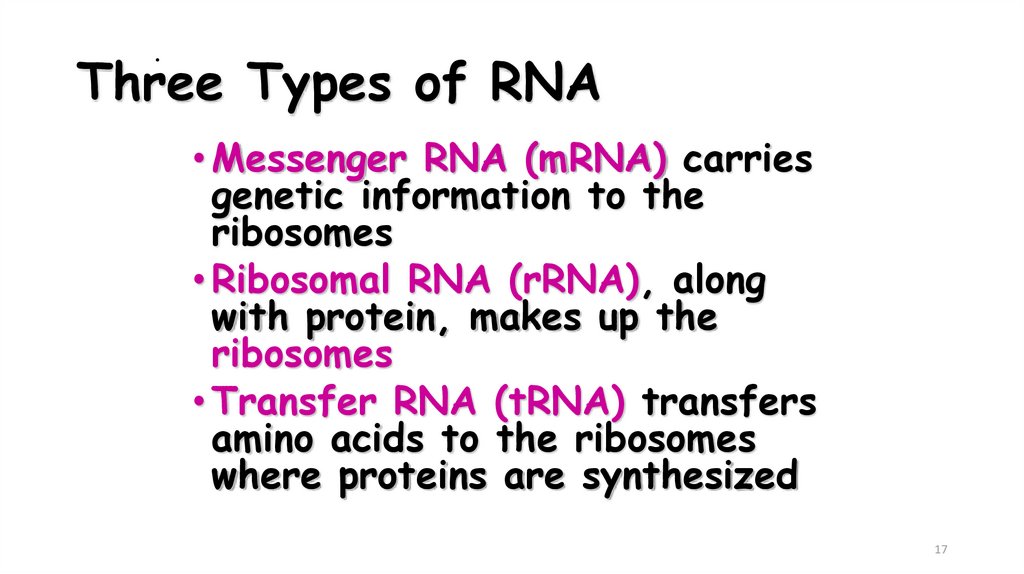
.Three Types of RNA
• Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries
genetic information to the
ribosomes
• Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along
with protein, makes up the
ribosomes
• Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers
amino acids to the ribosomes
where proteins are synthesized
17
18. Making a Protein
18Making a
Protein
19. Genes & Proteins
Genes & ProteinsProteins are made of amino
acids linked together by peptide
bonds
20 different amino acids exist
Amino acids chains are called
polypeptides
Segment of DNA that codes for
the amino acid sequence in a
protein are called genes
19
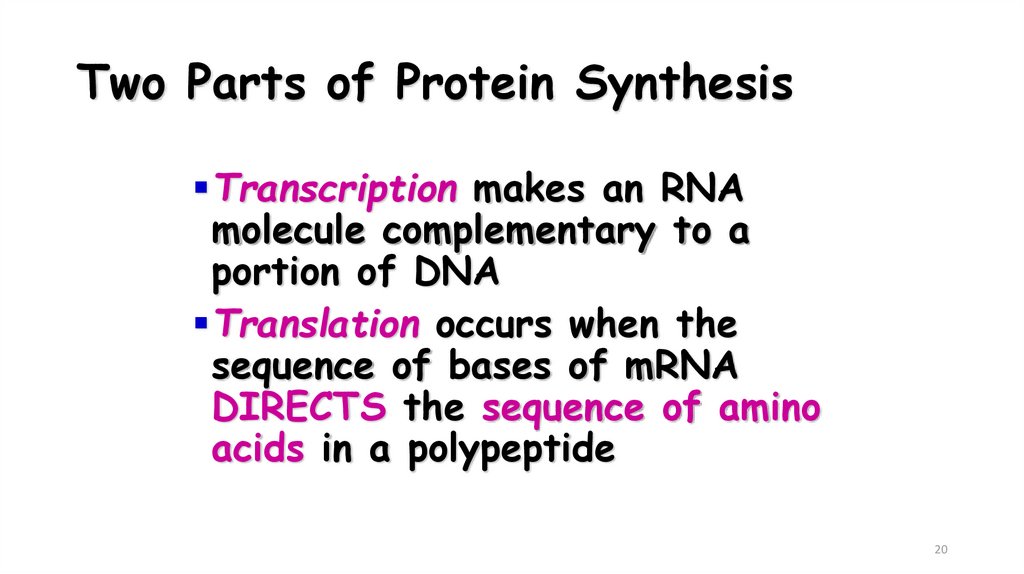
20. Two Parts of Protein Synthesis
Transcription makes an RNAmolecule complementary to a
portion of DNA
Translation occurs when the
sequence of bases of mRNA
DIRECTS the sequence of amino
acids in a polypeptide
20
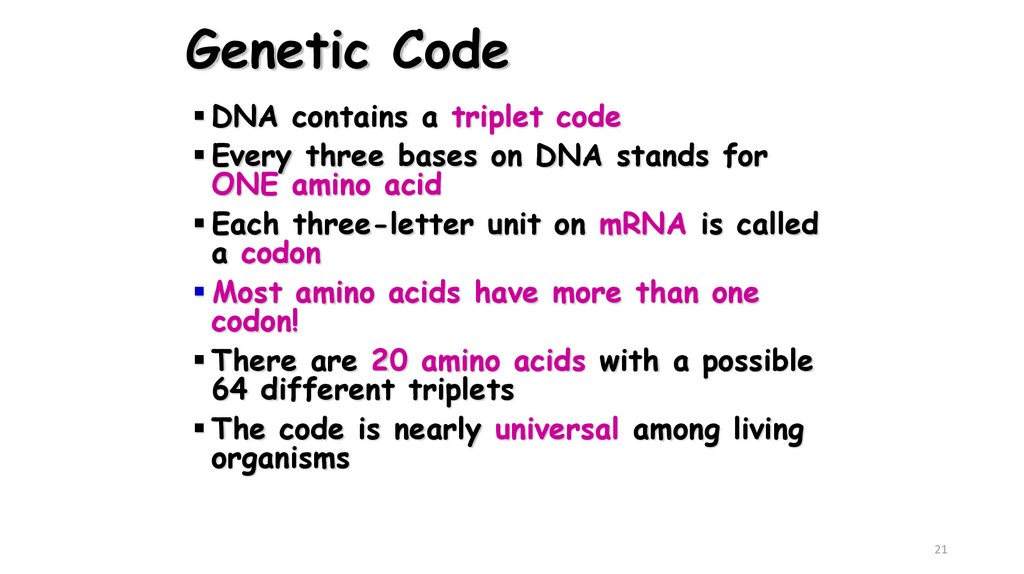
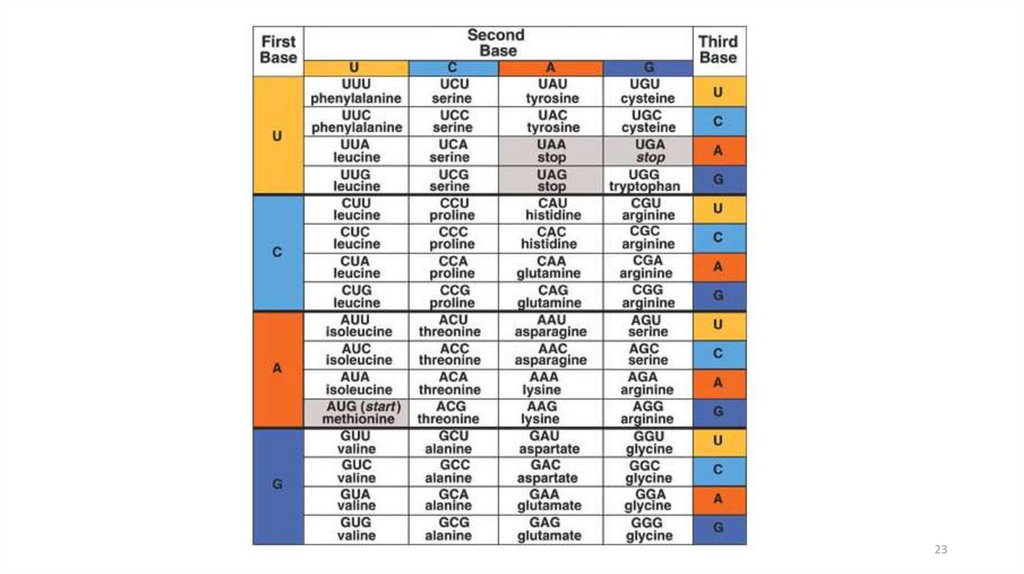
21. Genetic Code
DNA contains a triplet codeEvery three bases on DNA stands for
ONE amino acid
Each three-letter unit on mRNA is called
a codon
Most amino acids have more than one
codon!
There are 20 amino acids with a possible
64 different triplets
The code is nearly universal among living
organisms
21
22.
TranscriptionTranslation
22
23.
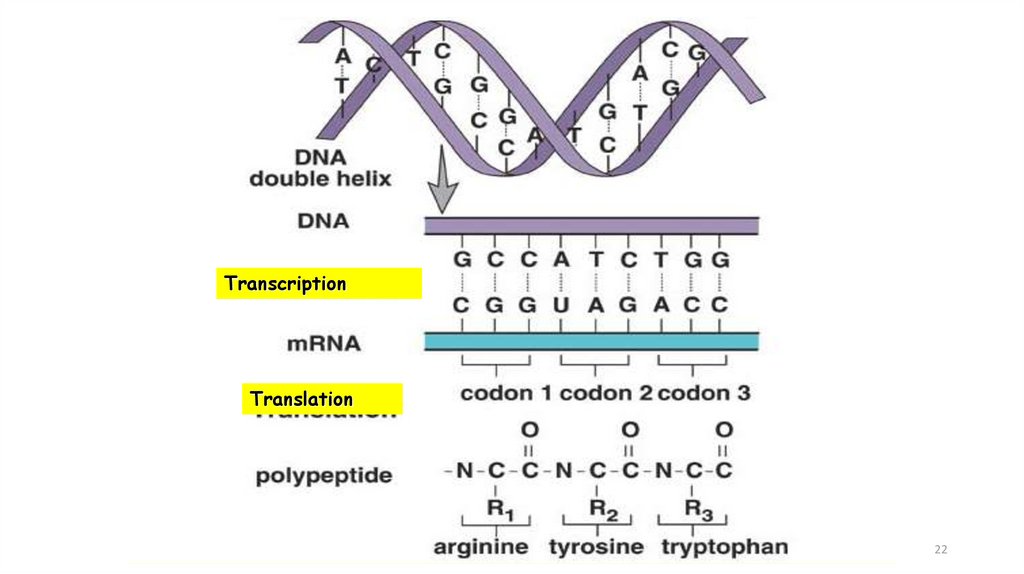
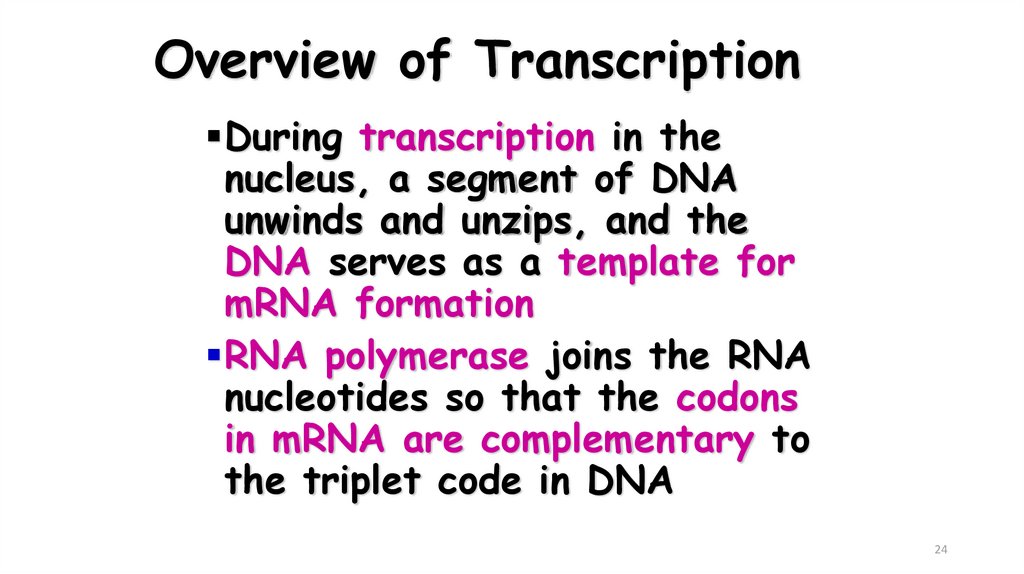
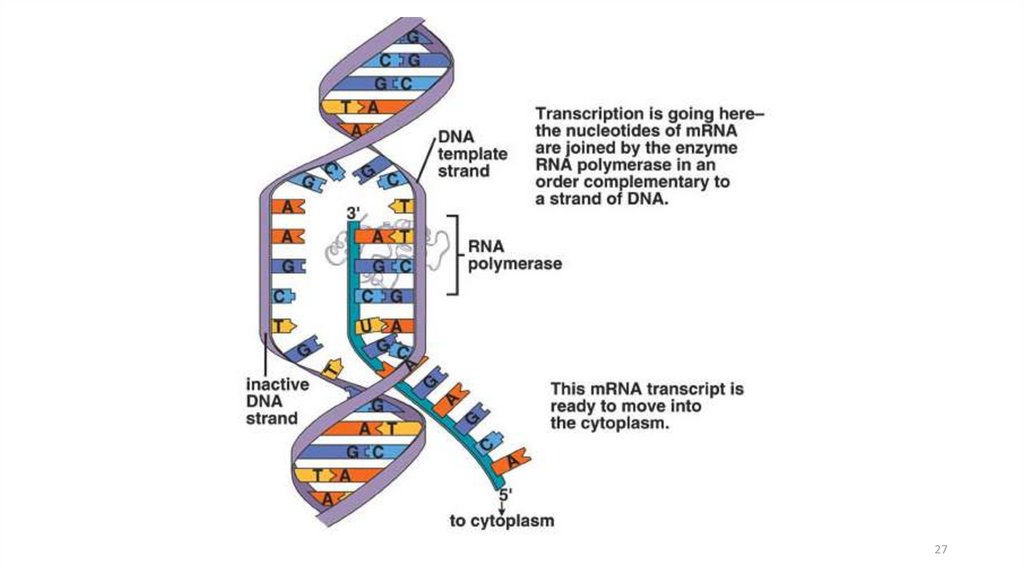
2324. Overview of Transcription
During transcription in thenucleus, a segment of DNA
unwinds and unzips, and the
DNA serves as a template for
mRNA formation
RNA polymerase joins the RNA
nucleotides so that the codons
in mRNA are complementary to
the triplet code in DNA
24
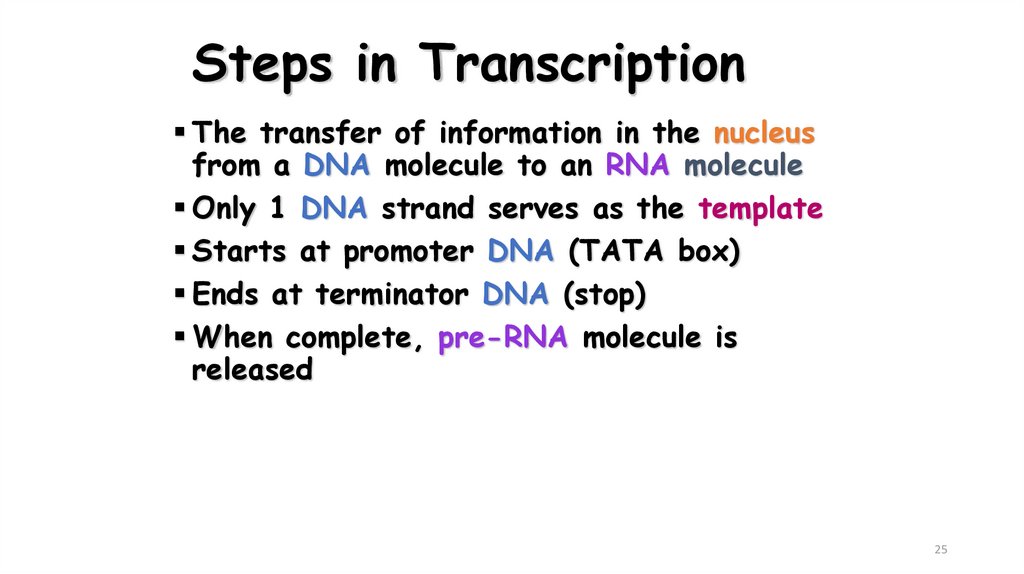
25. Steps in Transcription
The transfer of information in the nucleusfrom a DNA molecule to an RNA molecule
Only 1 DNA strand serves as the template
Starts at promoter DNA (TATA box)
Ends at terminator DNA (stop)
When complete, pre-RNA molecule is
released
25
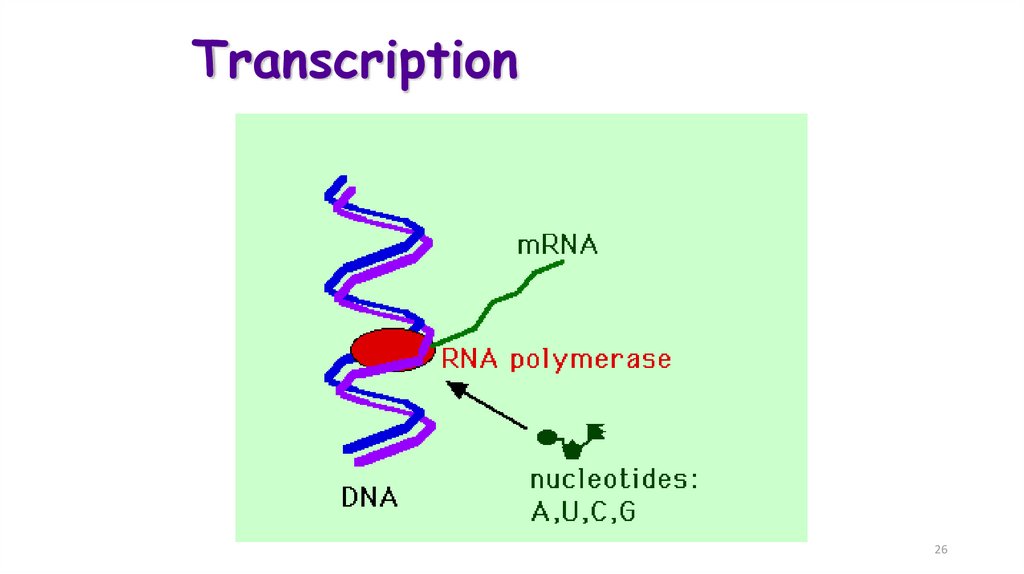
26. Transcription
2627.
2728.
What is the enzymeresponsible for the
production of the
mRNA molecule?
28
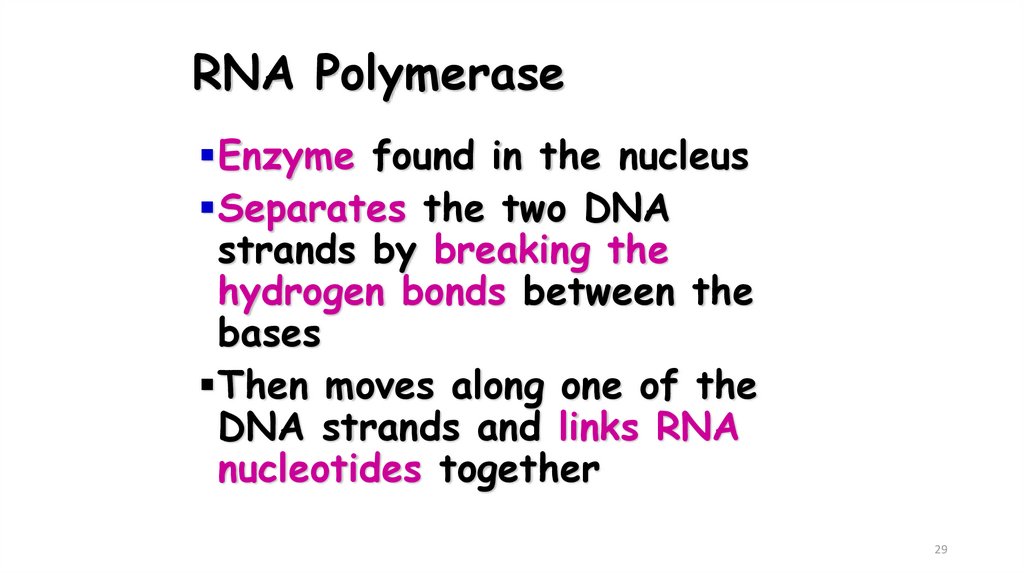
29. RNA Polymerase
Enzyme found in the nucleusSeparates the two DNA
strands by breaking the
hydrogen bonds between the
bases
Then moves along one of the
DNA strands and links RNA
nucleotides together
29
30. Question:
What would be thecomplementary RNA strand
for the following DNA
sequence?
DNA 5’-GCGTATG-3’
30
31. Answer:
•DNA 5’-GCGTATG-3’•RNA 3’-CGCAUAC-5’
31
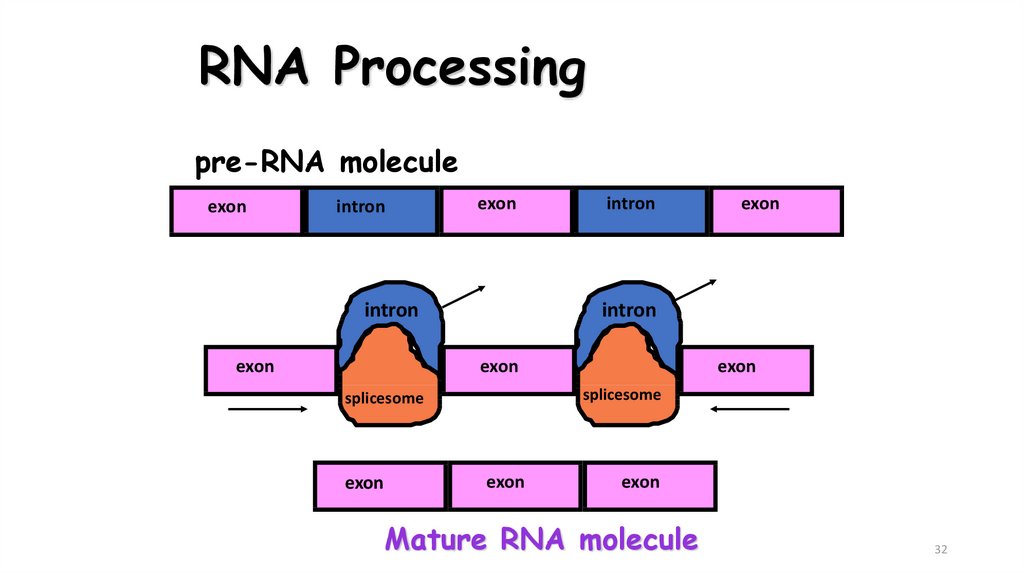
32. RNA Processing
pre-RNA moleculeexon
intron
exon
intron
exon
intron
intron
exon
exon
splicesome
splicesome
exon
exon
exon
exon
Mature RNA molecule
32
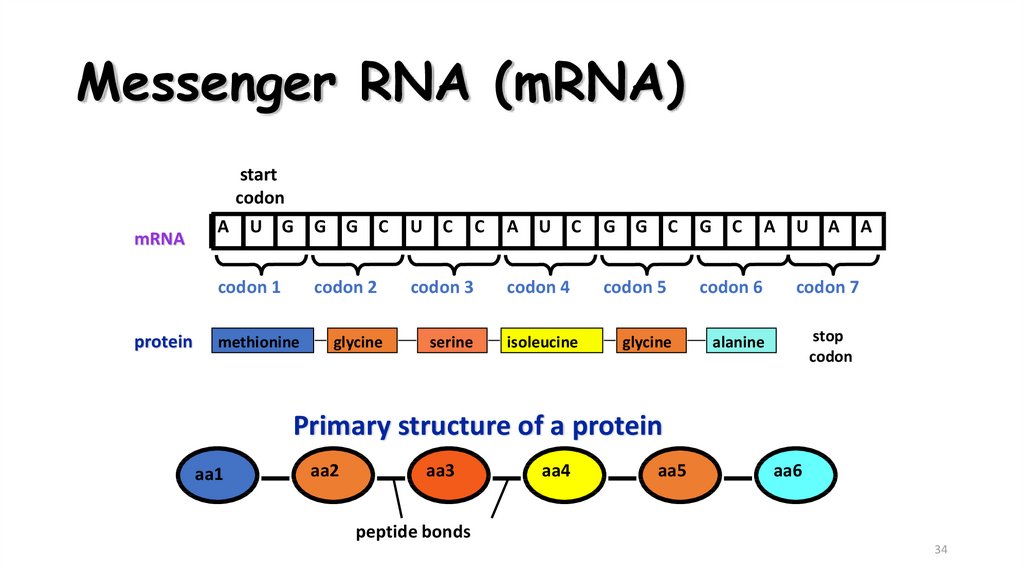
33. Messenger RNA (mRNA)
• Carries the information for aspecific protein
• Made up of 500 to 1000
nucleotides long
• Sequence of 3 bases called codon
• AUG – methionine or start codon
• UAA, UAG, or UGA – stop codons
33
34. Messenger RNA (mRNA)
mRNAprotein
start
codon
A U G
G
codon 1
codon 2
methionine
G
C
glycine
U
C
codon 3
serine
C
A
U
C
codon 4
isoleucine
G
G
C
codon 5
glycine
G
C
A
codon 6
U
A
A
codon 7
stop
codon
alanine
Primary structure of a protein
aa1
aa2
aa3
aa4
aa5
aa6
peptide bonds
34
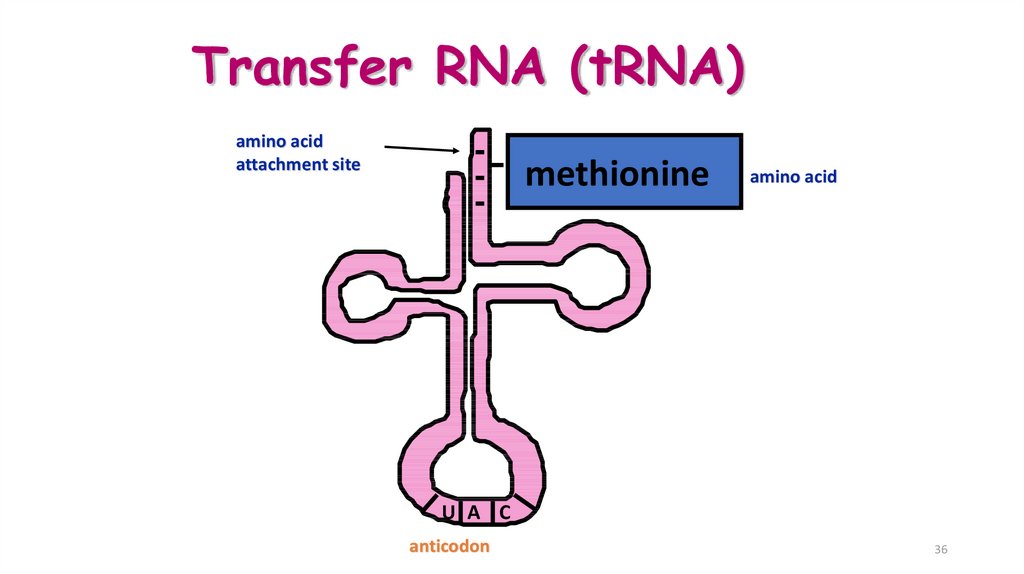
35. Transfer RNA (tRNA)
• Made up of 75 to 80 nucleotides long• Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating
in the cytoplasm
• Transports amino acids to the mRNA
• Have anticodons that are complementary to
mRNA codons
• Recognizes the appropriate codons on the
mRNA and bonds to them with H-bonds
35
36. Transfer RNA (tRNA)
amino acidattachment site
methionine
amino acid
U A C
anticodon
36
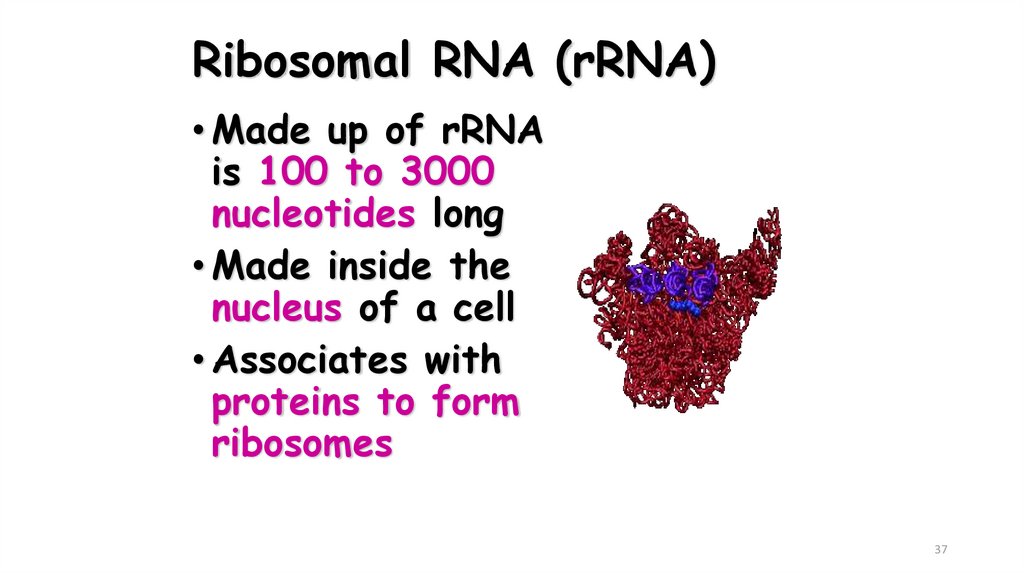
37. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
• Made up of rRNAis 100 to 3000
nucleotides long
• Made inside the
nucleus of a cell
• Associates with
proteins to form
ribosomes
37
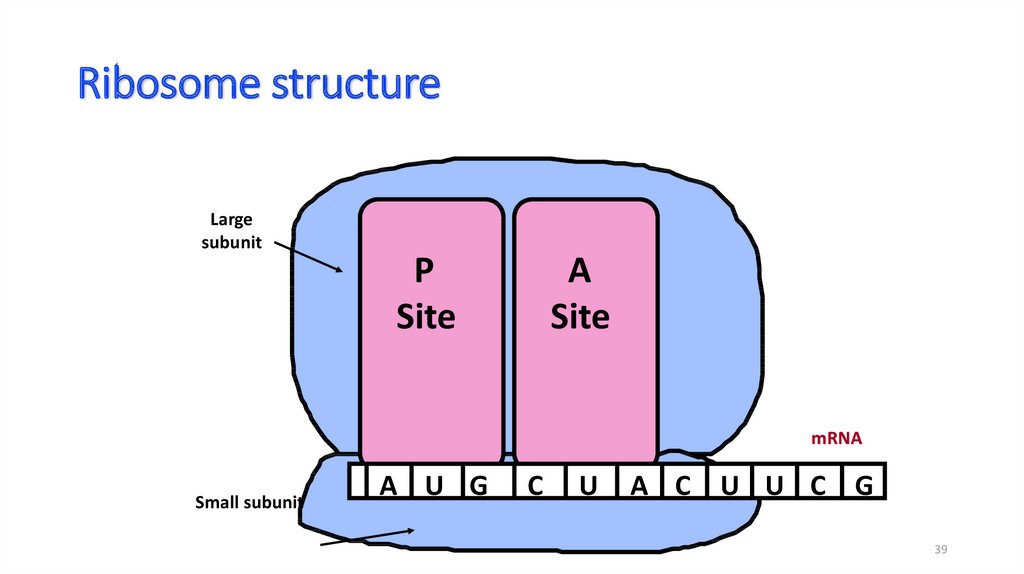
38. Ribosomes
• Made of a large and smallsubunit
• Composed of rRNA (40%) and
proteins (60%)
• Have two sites for tRNA
attachment --- P and A
38
39. Ribosome structure
Largesubunit
P
Site
A
Site
mRNA
Small subunit
A U G
C
U
A C U U C G
39
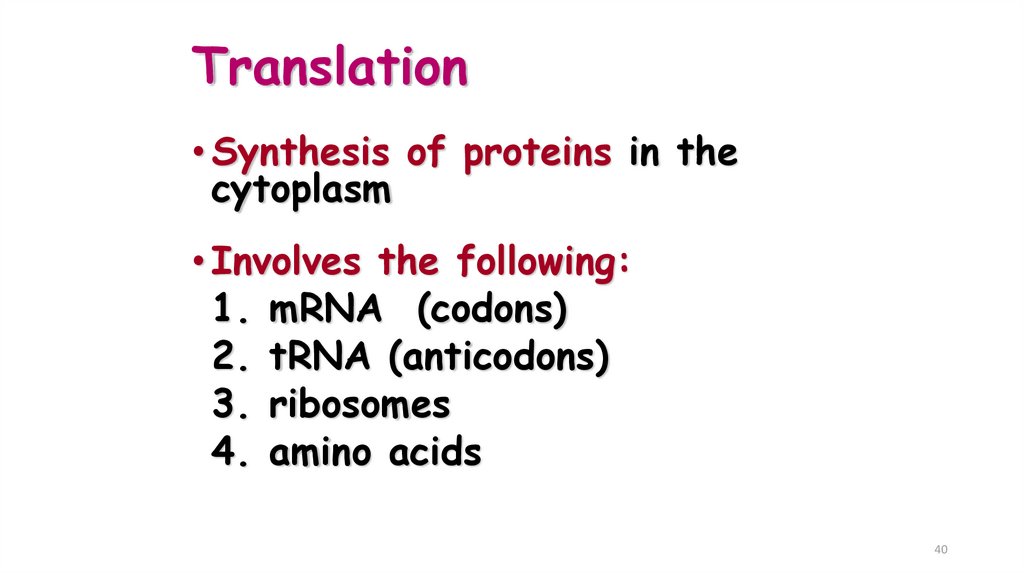
40. Translation
• Synthesis of proteins in thecytoplasm
• Involves the following:
1. mRNA (codons)
2. tRNA (anticodons)
3. ribosomes
4. amino acids
40
41. Translation
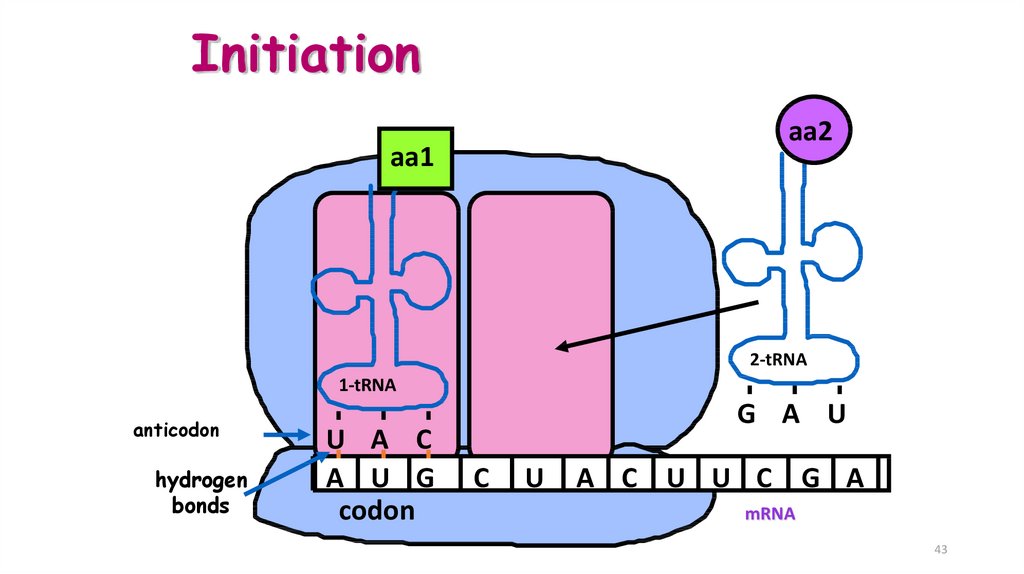
• Three steps:1. initiation: start codon (AUG)
2. elongation: amino acids linked
3. termination: stop codon
(UAG, UAA, or UGA).
Let’s Make a Protein !
41
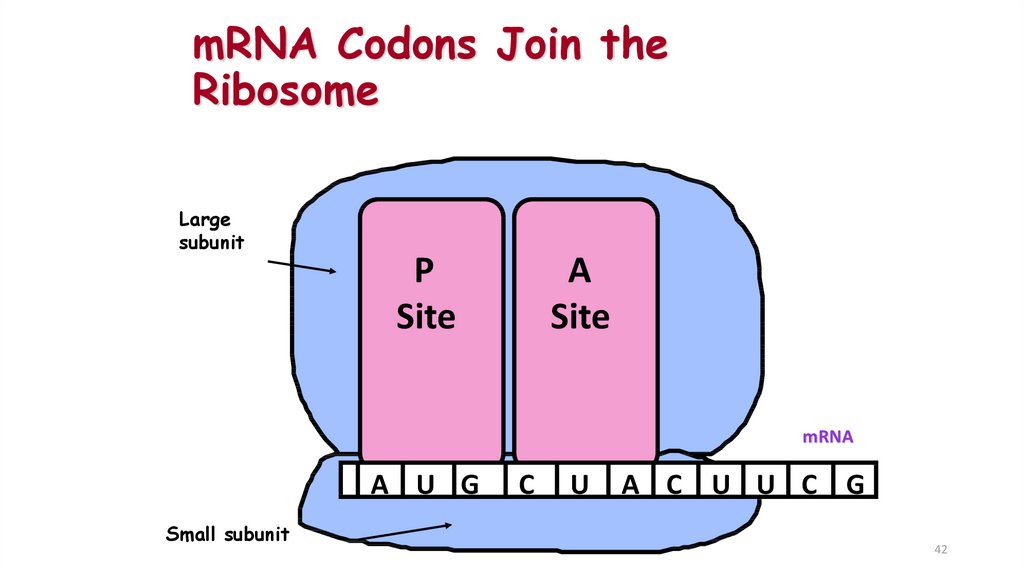
42. mRNA Codons Join the Ribosome
Largesubunit
P
Site
A
Site
mRNA
A U G
Small subunit
C
U
A C U U C G
42
43. Initiation
aa2aa1
2-tRNA
1-tRNA
anticodon
hydrogen
bonds
U A C
A U G
codon
G A U
C
U
A C U U C G A
mRNA
43
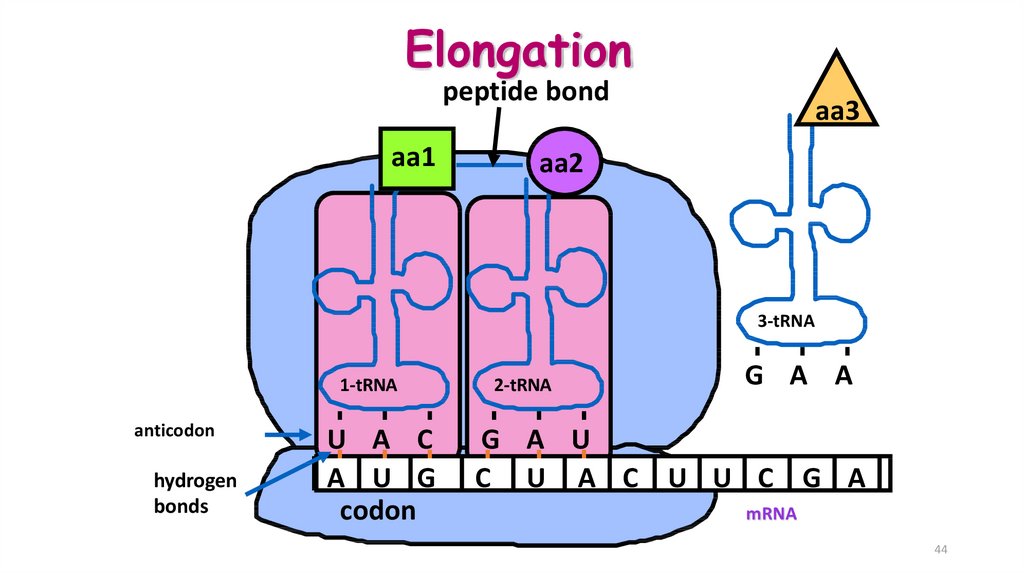
44.
Elongationpeptide bond
aa1
aa3
aa2
3-tRNA
1-tRNA
anticodon
hydrogen
bonds
U A C
A U G
codon
2-tRNA
G A A
G A U
C U A C U U C G A
mRNA
44
45.
aa1peptide bond
aa3
aa2
1-tRNA
3-tRNA
U A C
(leaves)
2-tRNA
A U G
G A A
G A U
C U A C U U C G A
mRNA
Ribosomes move over one codon
45
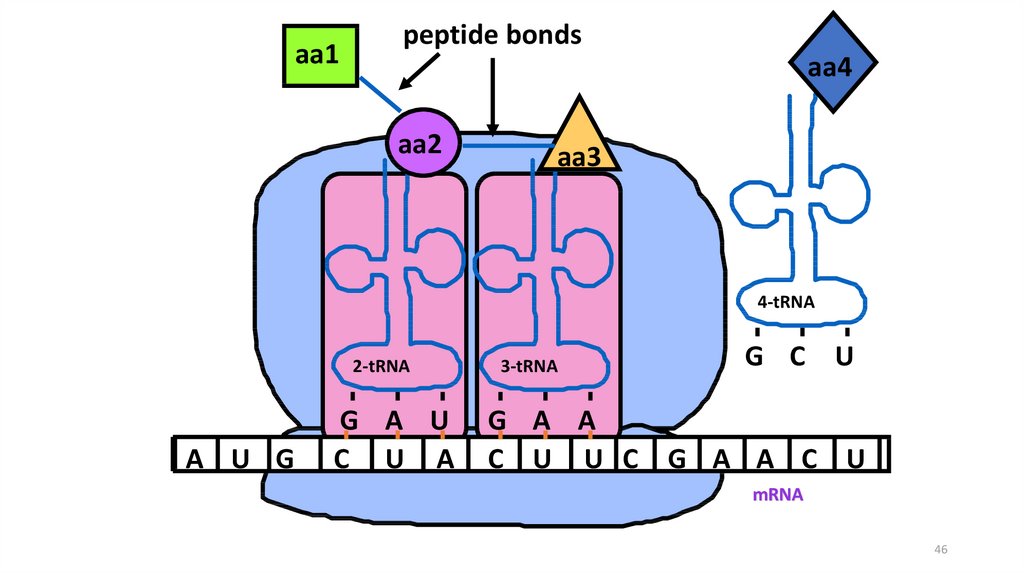
46.
aa1peptide bonds
aa4
aa2
aa3
4-tRNA
2-tRNA
A U G
G A U
C U A
3-tRNA
G C U
G A A
C U U C G A A C U
mRNA
46
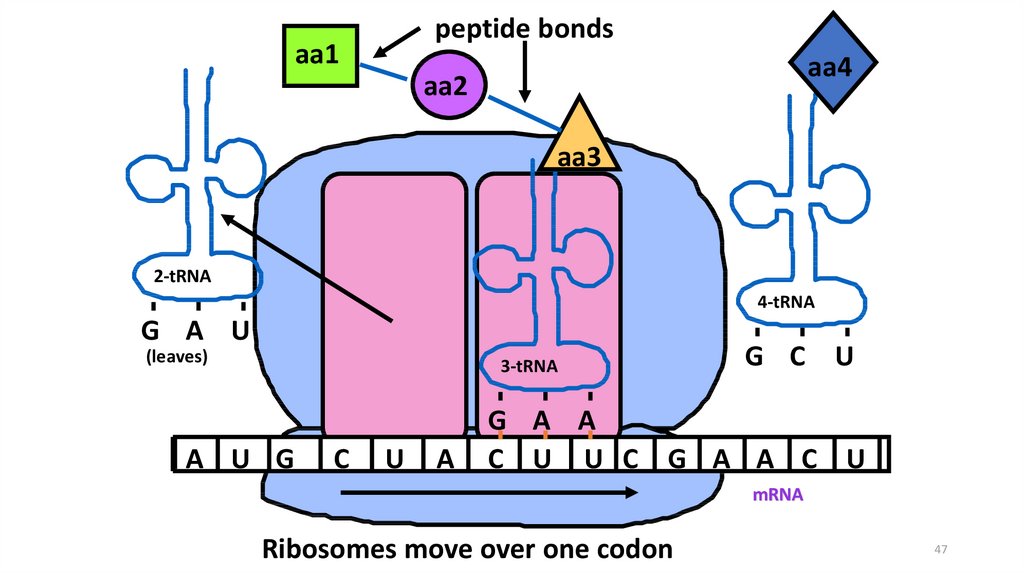
47.
peptide bondsaa1
aa4
aa2
aa3
2-tRNA
4-tRNA
G A U
(leaves)
3-tRNA
A U G
C
U
A
G C U
G A A
C U U C G A A C U
mRNA
Ribosomes move over one codon
47
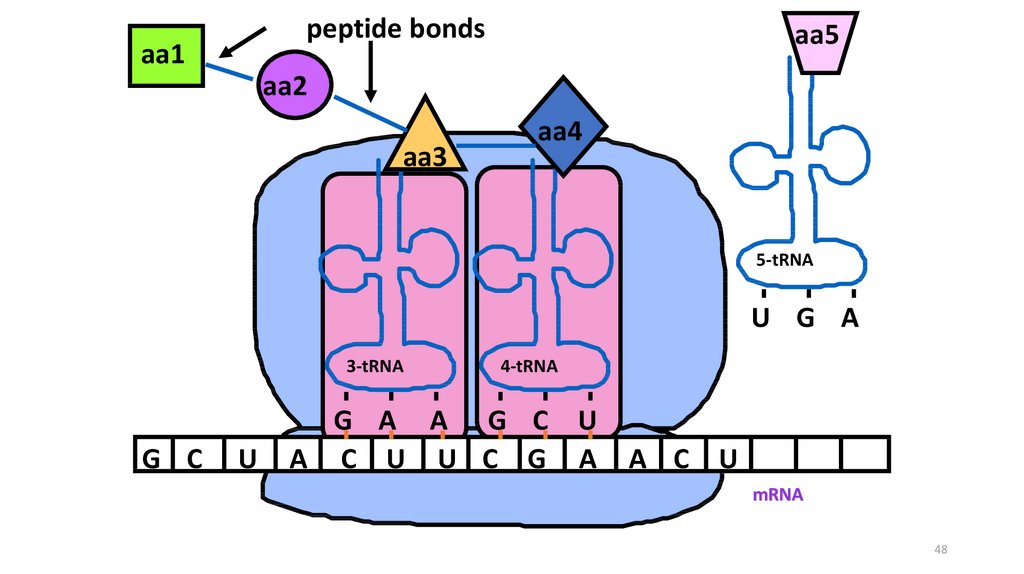
48.
peptide bondsaa1
aa5
aa2
aa3
aa4
5-tRNA
U G A
3-tRNA
G C
U
4-tRNA
G A A G C U
A C U U C G A
A C U
mRNA
48
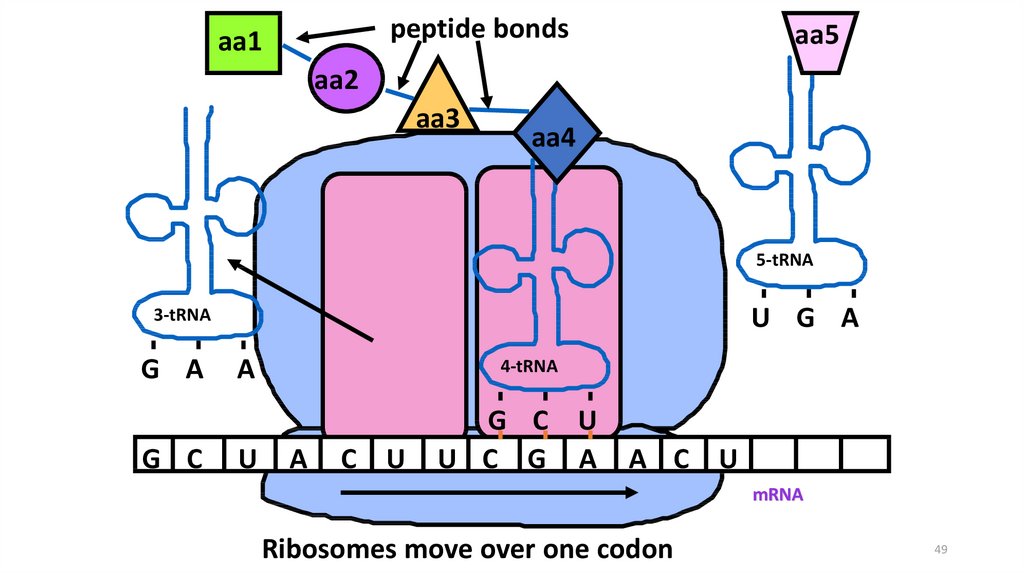
49.
peptide bondsaa1
aa5
aa2
aa3
aa4
5-tRNA
U G A
3-tRNA
G A
G C
A
U
4-tRNA
A
C U
G C U
U C G A
A C U
mRNA
Ribosomes move over one codon
49
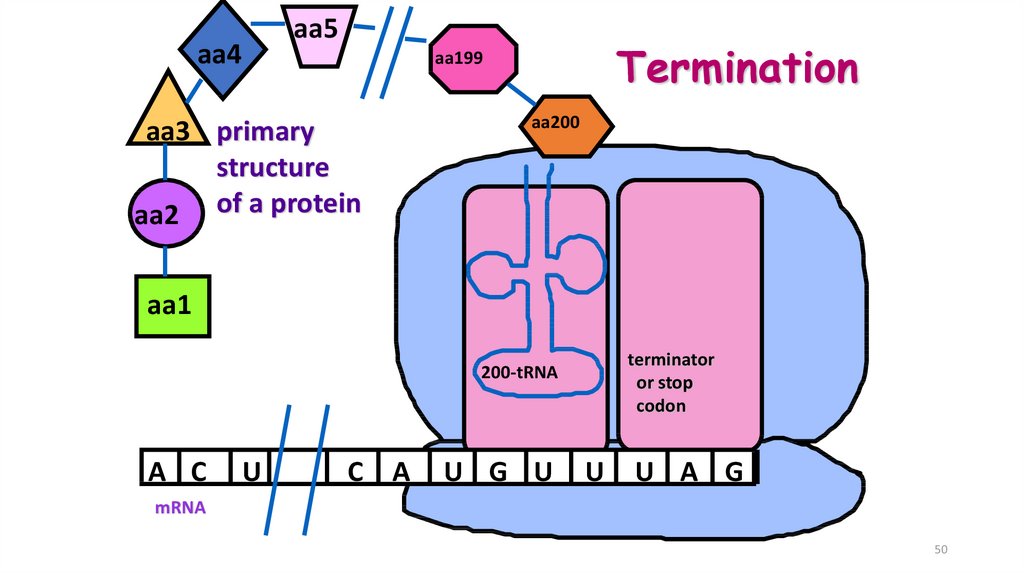
50.
aa5aa4
Termination
aa199
aa3 primary
structure
aa2 of a protein
aa200
aa1
terminator
or stop
codon
200-tRNA
A C
U
C A
U G U
U
U A G
mRNA
50
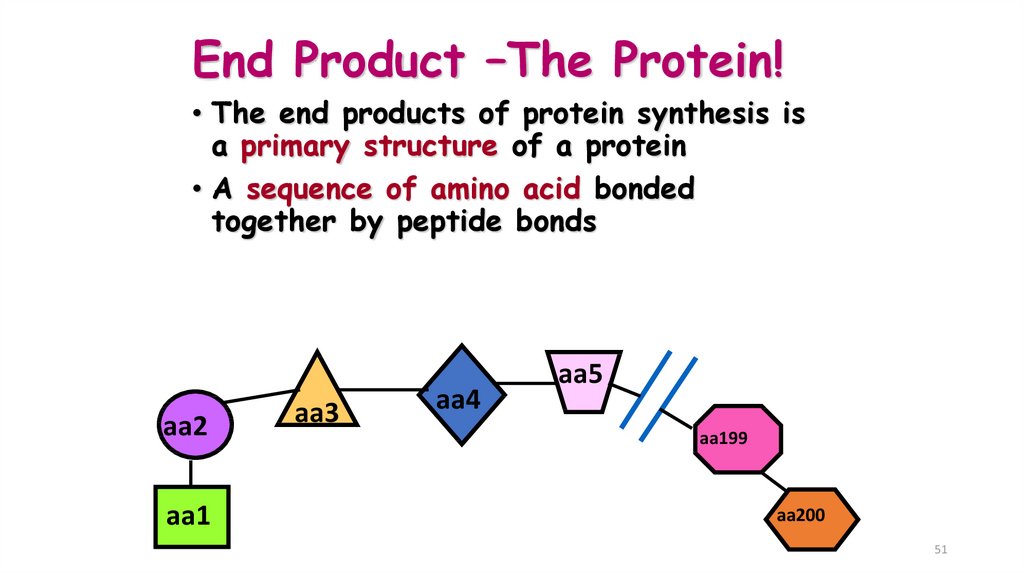
51. End Product –The Protein!
• The end products of protein synthesis isa primary structure of a protein
• A sequence of amino acid bonded
together by peptide bonds
aa2
aa1
aa3
aa4
aa5
aa199
aa200
51












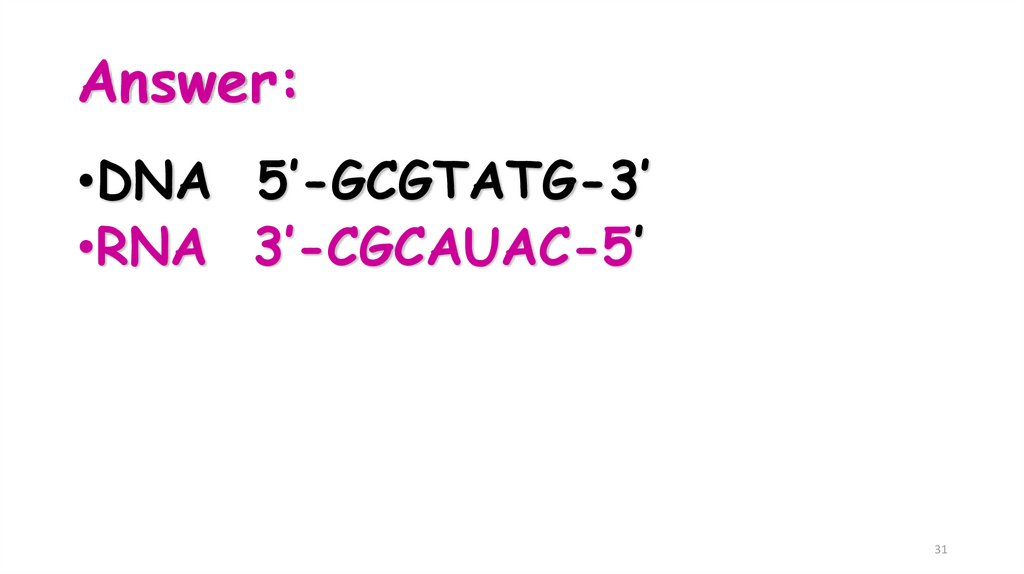





 biology
biology








