Similar presentations:
Buffer solutions
1. BUFFER SOLUTIONS
2. Buffer solutions
solution which can resist the addition of a strongacid or a strong base or water. Its’ pH changes
very slightly.
+
• + 1 drop of base
[H ] in 1000 000 times
+
• + 1 drop of acid
[H ] in 5000 times
-4
-7
(from 10 tо 5 х10 )
-7
In buffer solution from 1.00х10
-7
to 1.01х10
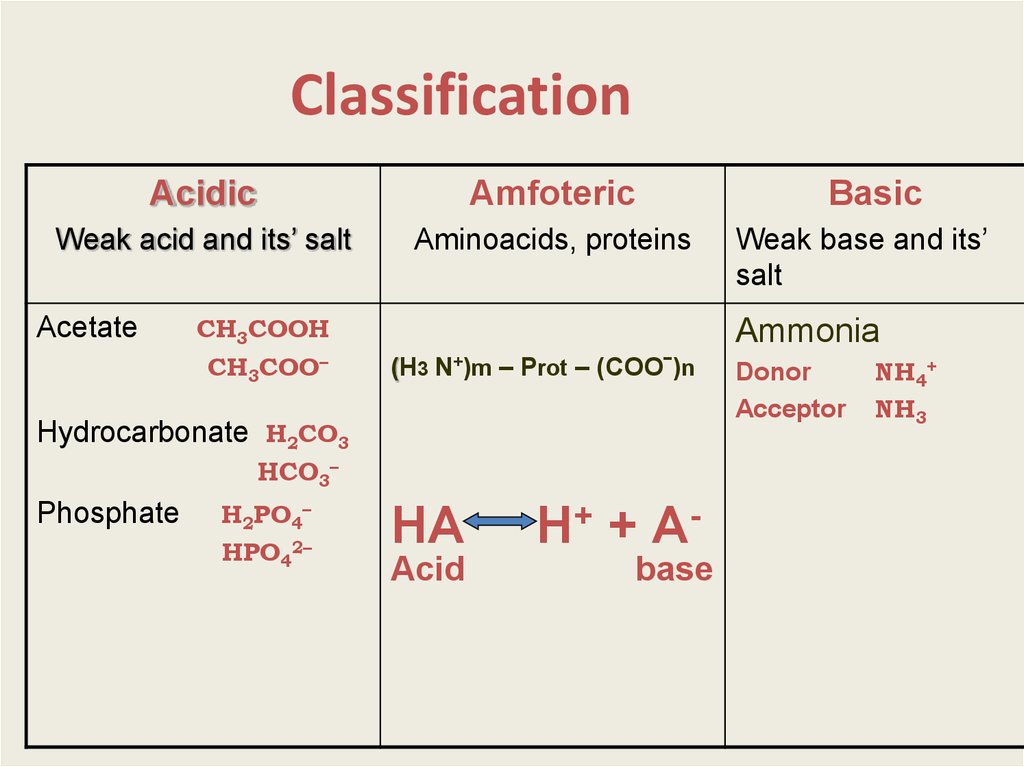
3. Classification
AcidicAmfoteric
Weak acid and its’ salt
Aminoacids, proteins
Acetate
СН3СООН
СН3СОО–
(H3 N+)m – Prot – (COOˉ)n
НСО3–
Н2РО4–
НРO42–
Weak base and its’
salt
Ammonia
Hydrocarbonate Н2СО3
Phosphate
Basic
НА
Acid
Н+ + Аbase
Donor
Аcceptor
NH4+
NH3
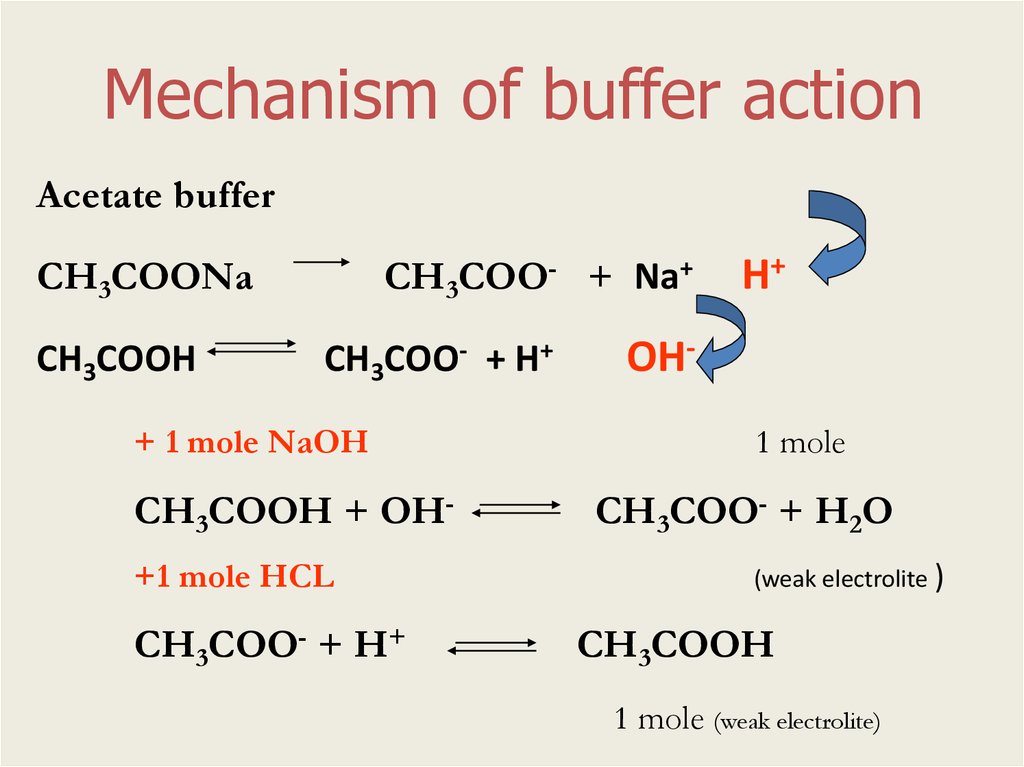
4.
Mechanism of buffer actionAcetate buffer
СН3СОО- + Na+
СН3СООNa
СН3СООН
СН3СОО- + Н+
+ 1 mole NaOH
СН3СООН + ОН+1 mole HCL
СН3СОО- + Н+
Н+
ОН1 mole
СН3СОО- + Н2О
(weak electrolite )
СН3СООН
1 mole (weak electrolite)
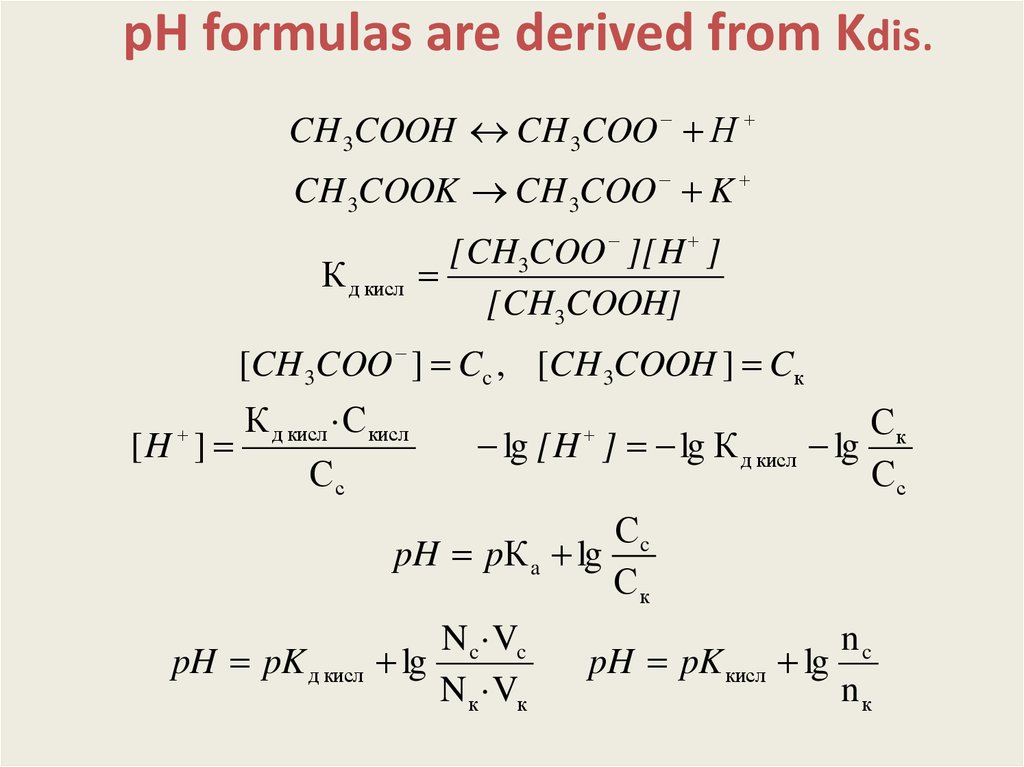
5.
рН formulas are derived from Kdis.CH 3COOH CH 3COO Н
CH 3COOK CH 3COO K
К д кисл
[CH3COO ][H ]
[CH3COOH]
[CH 3COO ] Cc , [CH 3COOH ] Cк
К д кисл ·С кисл
[H ]
Сс
lg [H ] lg К д кисл
Ск
lg
Сс
Сc
pH pК a lg
Ск
pH pK д кисл
N c ·Vc
lg
N к ·Vк
pH pK кисл
nc
lg
nк
6. HOW TO PREPARE BUFFER
1. Mixingthe components:
-for acidic buffer
pH = pKa + lg Ns·Vs/Na·Va
-for basic buffer
pH = 14 – pKв – lg Ns·Vs/Nb·Vb
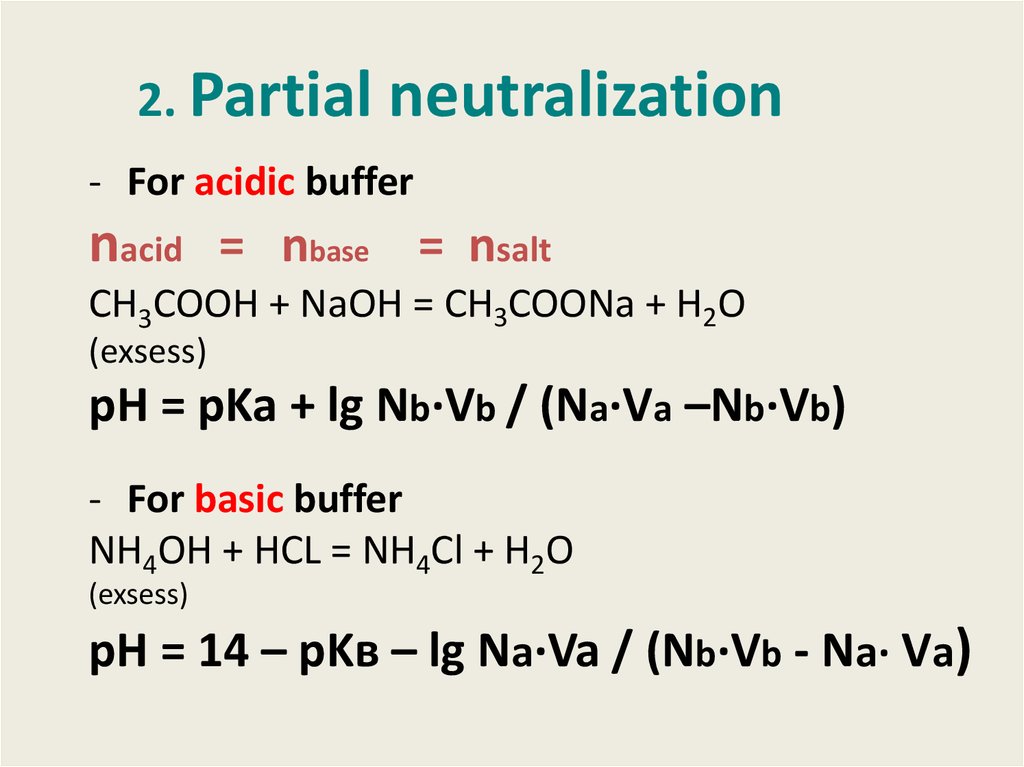
7. 2. Partial neutralization
- For acidic buffernacid = nbase = nsalt
СН3СООН + NaOH = CH3COONa + H2O
(exsess)
pH = pKa + lg Nb·Vb / (Na·Va –Nb·Vb)
- For basic buffer
NH4OH + HCL = NH4Cl + H2O
(exsess)
pH = 14 – pKв – lg Na·Va / (Nb·Vb - Na· Va)
8. Buffer capacity
.Н|
Ba = nacid / |∆р
Vbuf.sol
Вb = nbase/ |∆р Н|. Vbuf.sol
n
– mole equivalents
of a strong acid or a strong base
Vbuf.sol - volume of a buffer solution
∆рН – pH change as a result of acid or base addition
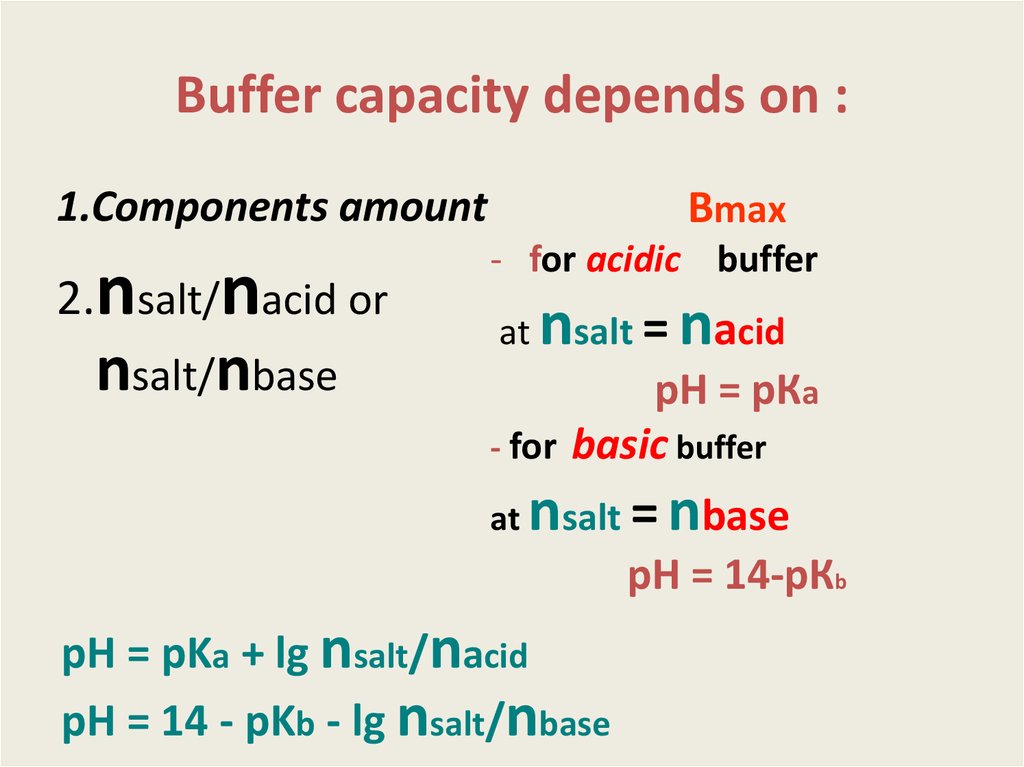
9. Buffer capacity depends on :
1.Components amount2.nsalt/nacid or
nsalt/nbase
Вmax
- for acidic buffer
at
nsalt = nacid
рН = рКа
- for basic buffer
at
nsalt = nbase
рН = 14-рКb
pH = pKa + lg nsalt/nacid
pH = 14 - pKb - lg nsalt/nbase
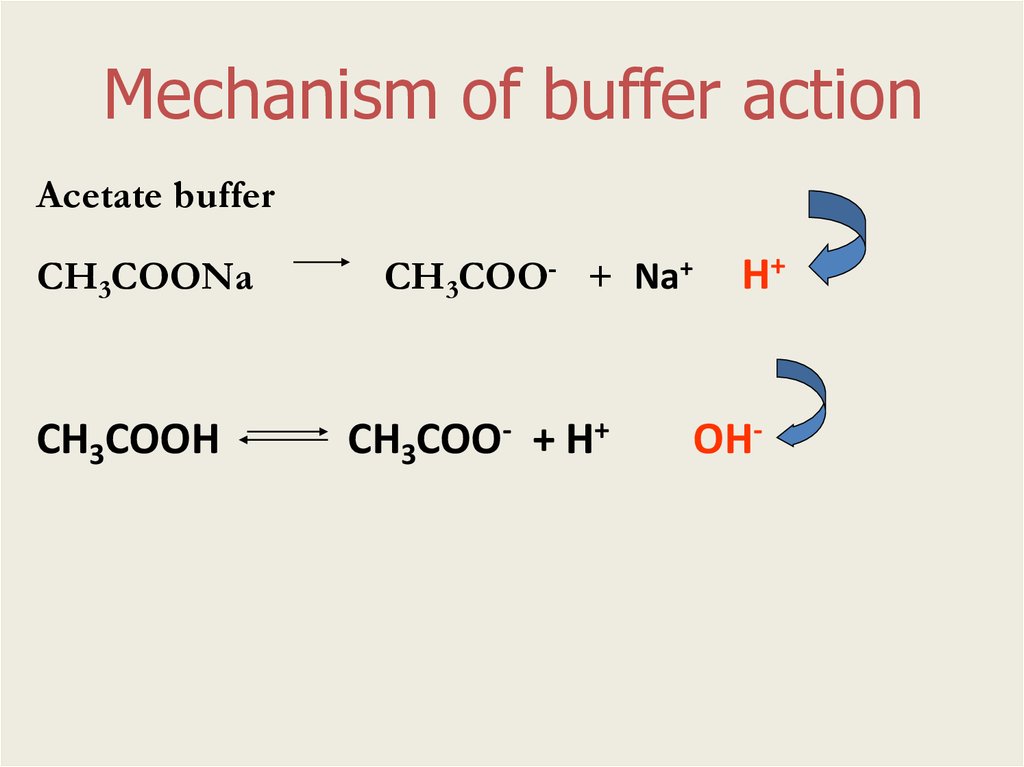
10.
Mechanism of buffer actionAcetate buffer
СН3СООNa
СН3СООН
СН3СОО- + Na+
СН3СОО- + Н+
Н+
ОН-
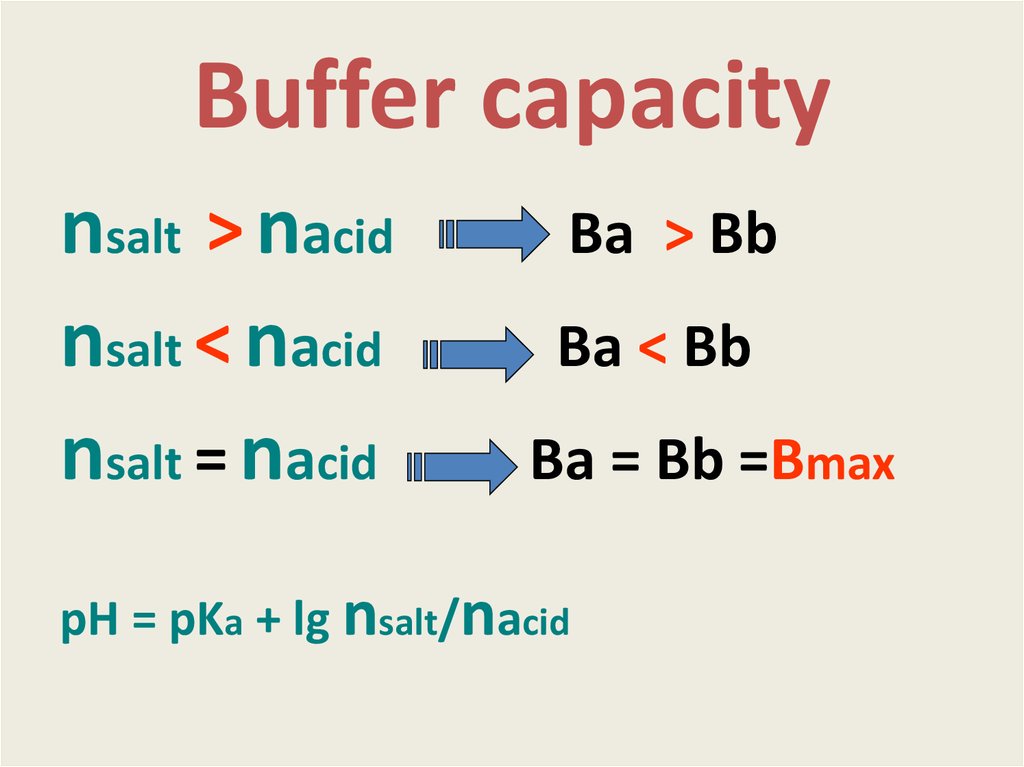
11. Buffer capacity
nsalt > nacidnsalt < nacid
nsalt = nacid
Вa > Вb
Вa < Вb
Вa = Вb =Вmax
pH = pKa + lg nsalt/nacid
12.
• Choose the buffer with maximumcapacity and рН = 7.36 :
1) acetic
рК = 4.75;
2) phosphate рК = 7.21;
3) hydrocarbonate рК = 6.37.
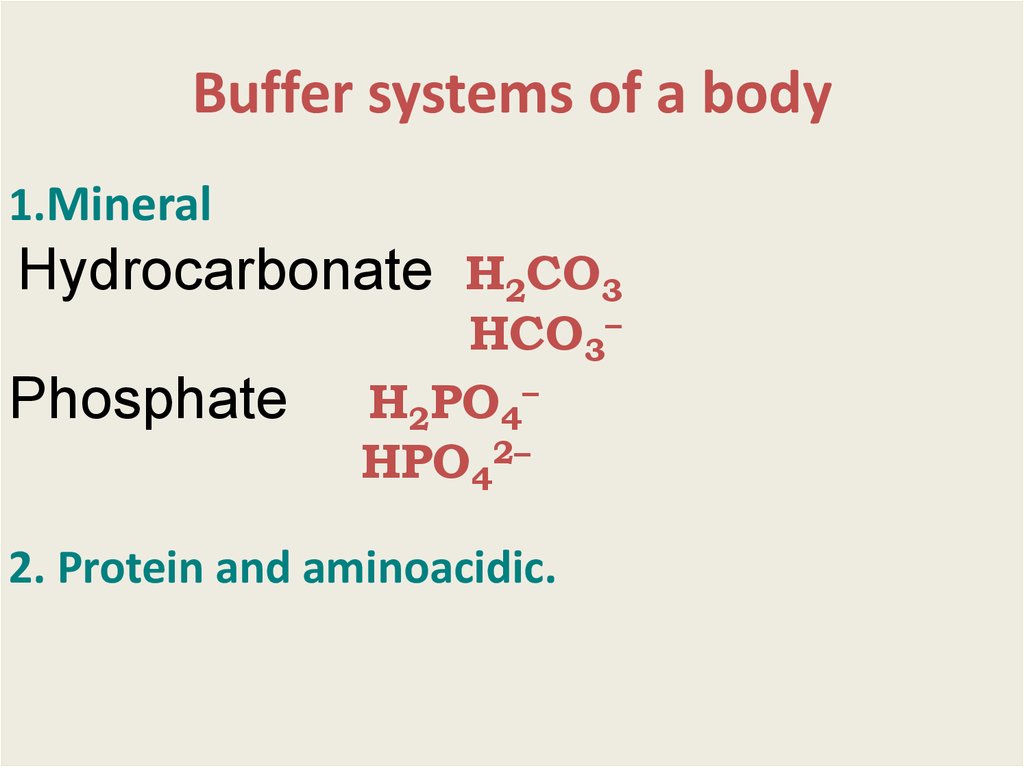
13. Buffer systems of a body
1.MineralHydrocarbonate Н2СО3
Phosphate
НСО3–
Н2РО4–
НРO42–
2. Protein and aminoacidic.
14.
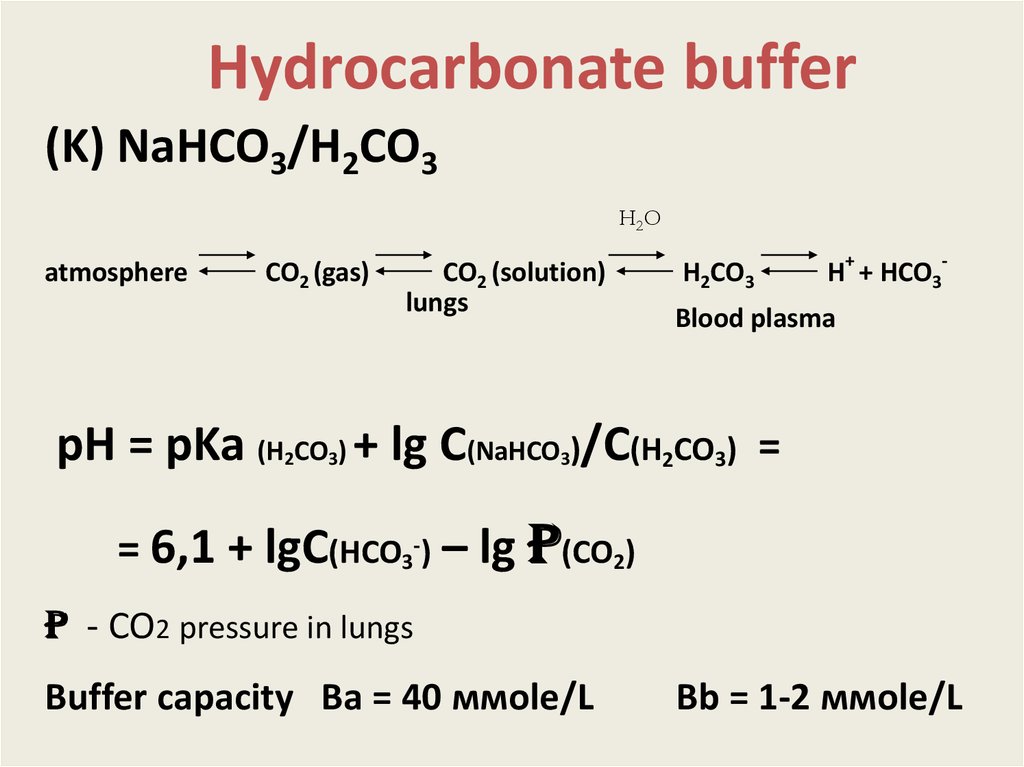
Hydrocarbonate buffer(K) NaHCO3/H2CO3
H2 O
atmosphere
СO2 (gas)
СO2 (solution)
lungs
H2СO3
H+ + HСO3-
Blood plasma
рН = pKa (H СO ) + lg C(NaHCO )/C(H2CO3) =
2
3
3
= 6,1 + lgC(HCO3-) – lg p(CO2)
p - CO2 pressure in lungs
Buffer capacity Вa = 40 ммole/L
Вb = 1-2 ммоle/L
15.
рН of blood plasma7.4 = 6.1 + lg
–
[НСО3 ]/ [СО2]
[НСО3–]:[СО2] = 20:1
Вa > В b
Н2СО3 – 13 моle/ day
Other acids – from 0.03 to 0.08 моle/ day
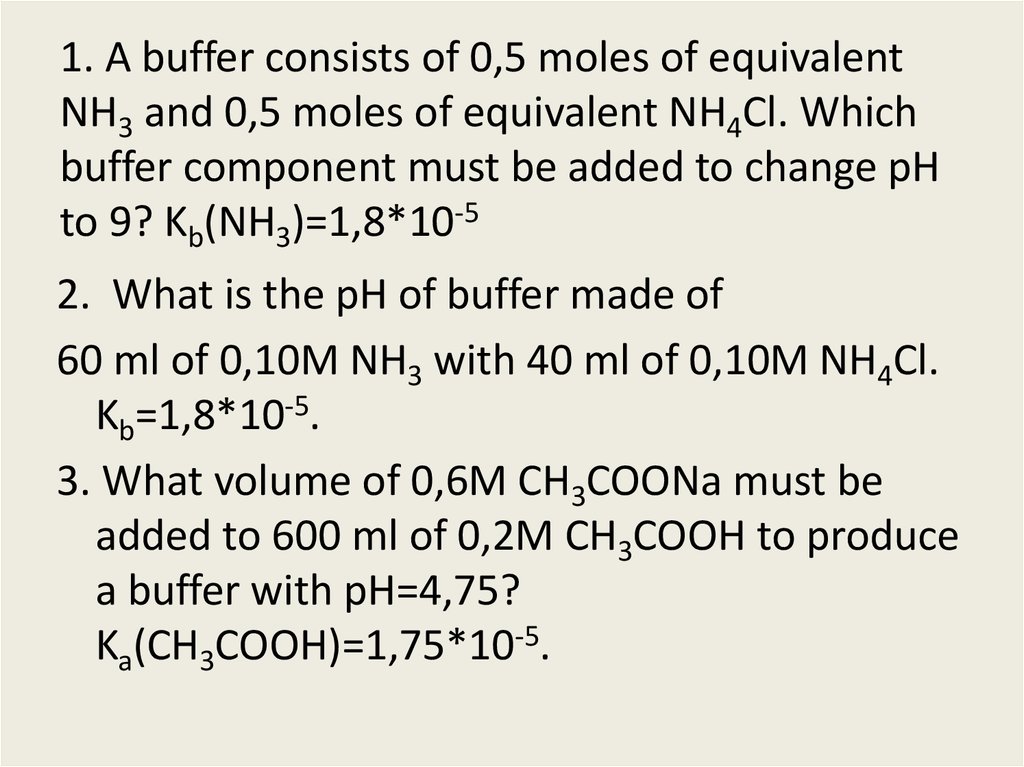
16. 1. A buffer consists of 0,5 moles of equivalent NH3 and 0,5 moles of equivalent NH4Cl. Which buffer component must be added to
change pHto 9? Kb(NH3)=1,8*10-5
2. What is the pH of buffer made of
60 ml of 0,10M NH3 with 40 ml of 0,10M NH4Cl.
Kb=1,8*10-5.
3. What volume of 0,6M CH3COONa must be
added to 600 ml of 0,2M CH3COOH to produce
a buffer with pH=4,75?
Ka(CH3COOH)=1,75*10-5.
17. 4. What volume of 0,01M NaOH should be added to 100 ml of 0,5M CH3COOH solution to produce a buffer with pH 4,75?
pKa(CH3COOH)=4,755. A buffer was prepared of 500 ml NaН2РО4 and
500 ml Na2НРO4 . After addition of 1 ml 0.1N HCl
the change of buffer pH = 0.03. Calculate buffer
capacity Ba.
6. Choose a buffer with Вa > Вb:
a). 100 ml 0.2M NaHCO3 + 100ml 0.4M H2CO3
b). 100 ml 0.4M NaHCO3 + 100ml 0.2M H2CO3
c). 100 ml 0.2M NaHCO3 + 100ml 0.2M H2CO3








 chemistry
chemistry








