Similar presentations:
Diesel engine. Cooling. The coolants
1. Dia 1
mu2. Dia 2
In a Diesel enginethe pistons and the cylinders
must be cooled by coolants.
Sea water
cools theoil,
coolants
Fresh
water,
air.
sound
3. Dia 3
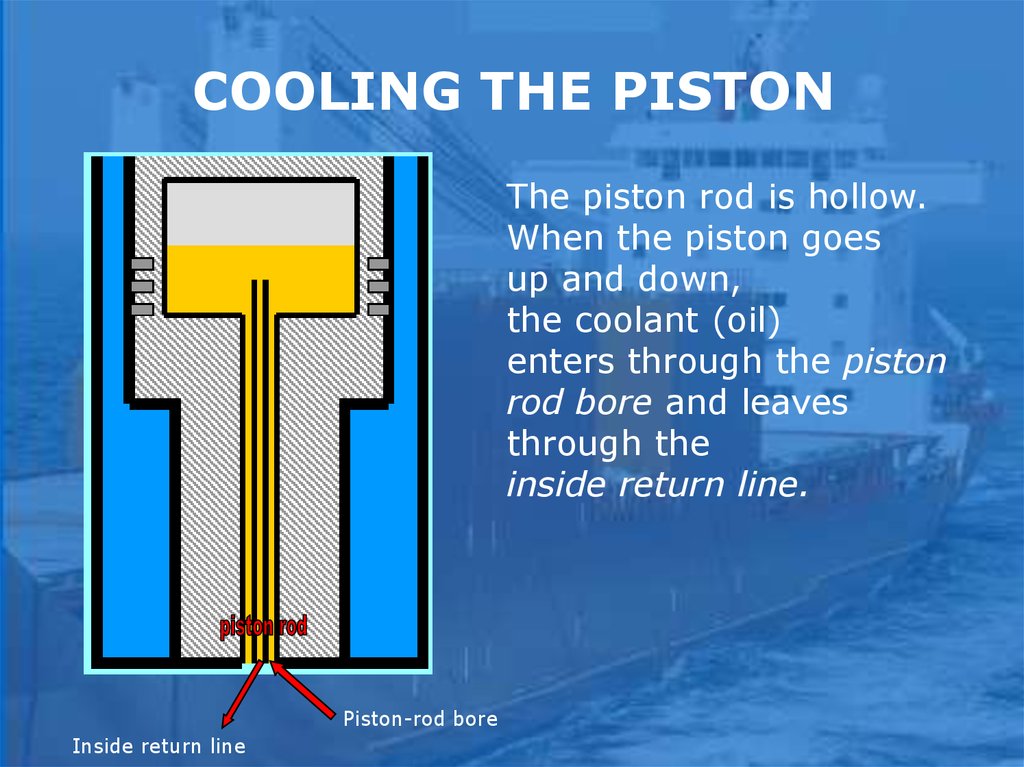
COOLING THE PISTONThe piston rod is hollow.
When the piston goes
up and down,
the coolant (oil)
enters through the piston
rod bore and leaves
through the
inside return line.
Piston-rod bore
Inside return line
4. Dia 4
COOLING THE PISTONThe piston is cooled by oil.
The advantages of oil as
a coolant are:
. it reduces noise;
. it purifies;
. it forms a seal;
. it lubricates;
. it is anti-corrosive;
. it has a higher resistance
to heat.
5. Dia 5
COOLING THE CYLINDERThe cylinder is cooled by
injecting the
coolant between the
cylinder liner and
the cylinder jacket.
The most common coolant
is fresh water.
S
Liner
Jacket
6. Dia 6
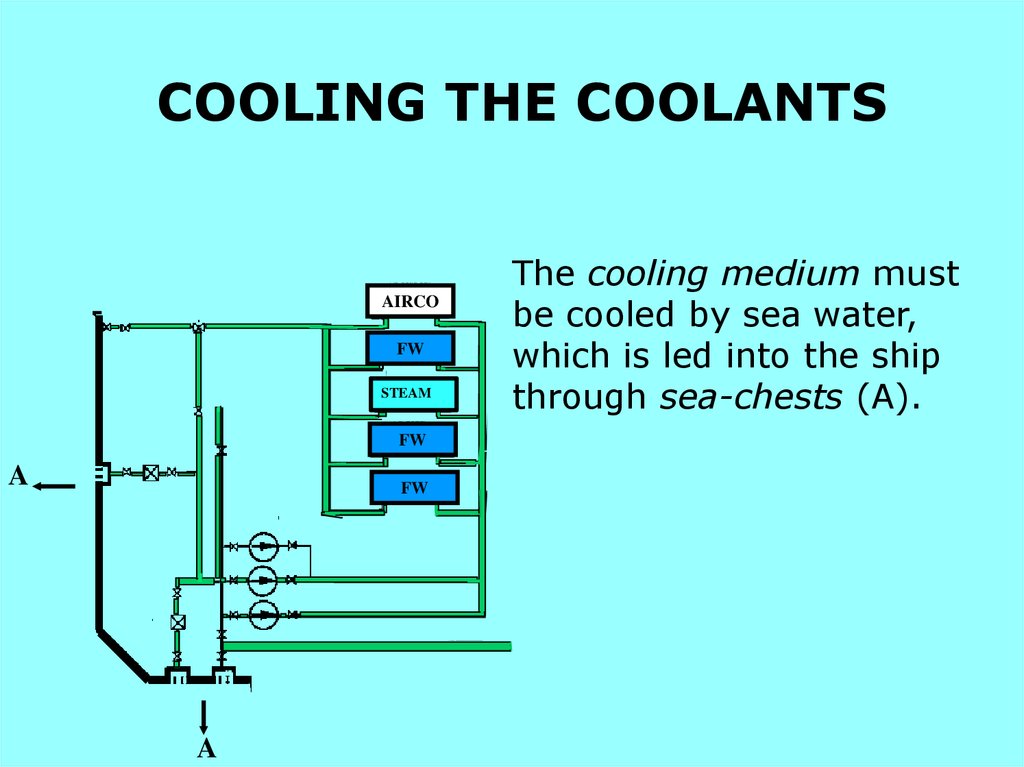
COOLING THE COOLANTSAIRCO
FW
STEAM
FW
A
FW
A
The cooling medium must
be cooled by sea water,
which is led into the ship
through sea-chests (A).
7. Dia 7
HEAT EXCHANGERSIn a heat exchanger the
hot coolant is cooled by
sea water.
SOUND
8. Dia 8
TheInternational Maritime Language Programme – IMLP
C
The IMLP is an IMO-standard.
P.C. van Kluijven






 mechanics
mechanics








