Similar presentations:
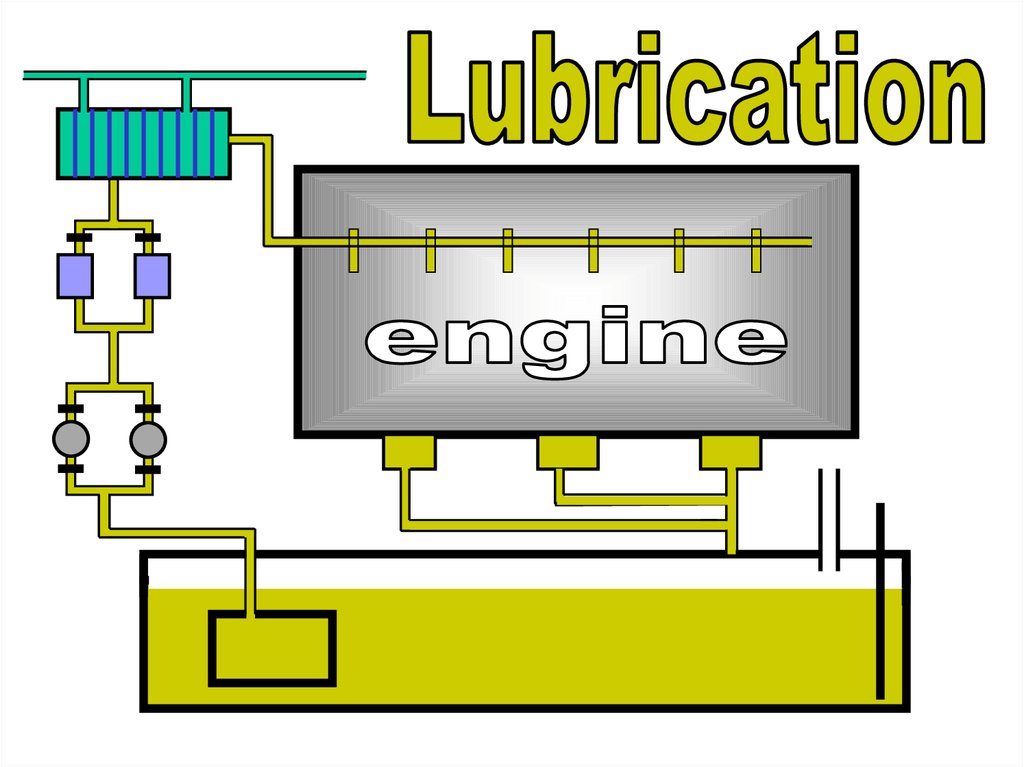
Lubrication engine
1. Dia 1
sound2
2. Dia 2
The position of the drain tankis often in the double bottom.
Drain tank (or sump) with lubricant
2
3. Dia 3
Pumpsdraw the lubricant
from the drain tank.
2
4. Dia 4
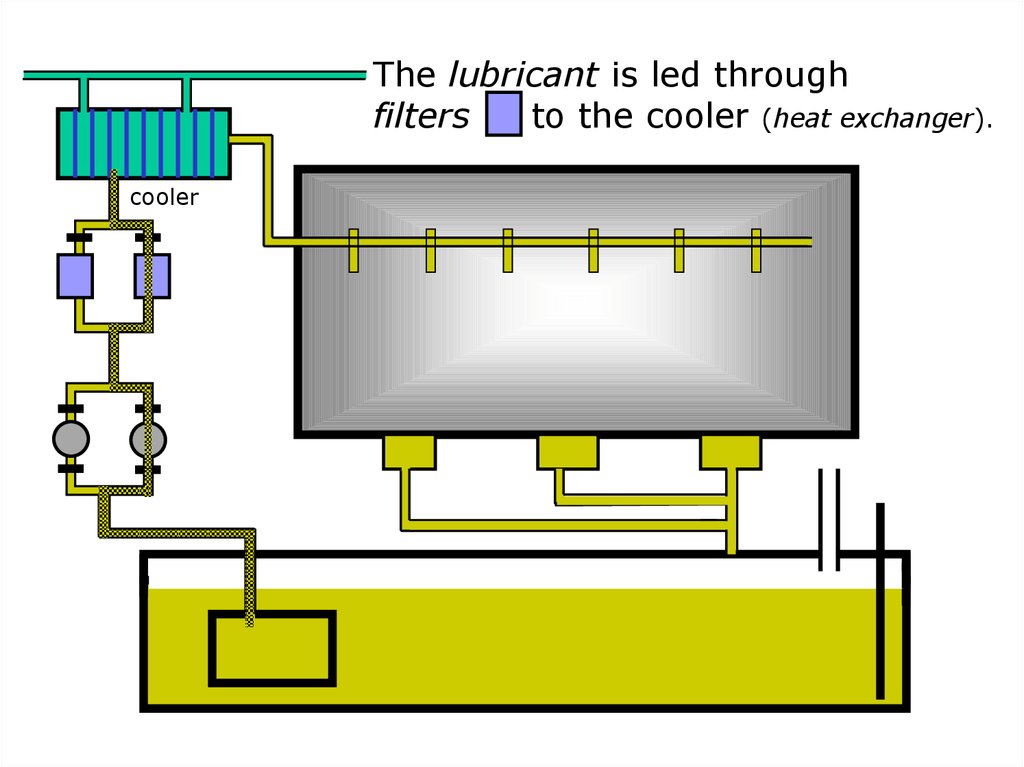
The lubricant is led throughfilters
to the cooler (heat exchanger).
cooler
2
5. Dia 5
In the cooler the lubricant iscooled by fresh water or sea water.
cooler
sound
2
6. Dia 6
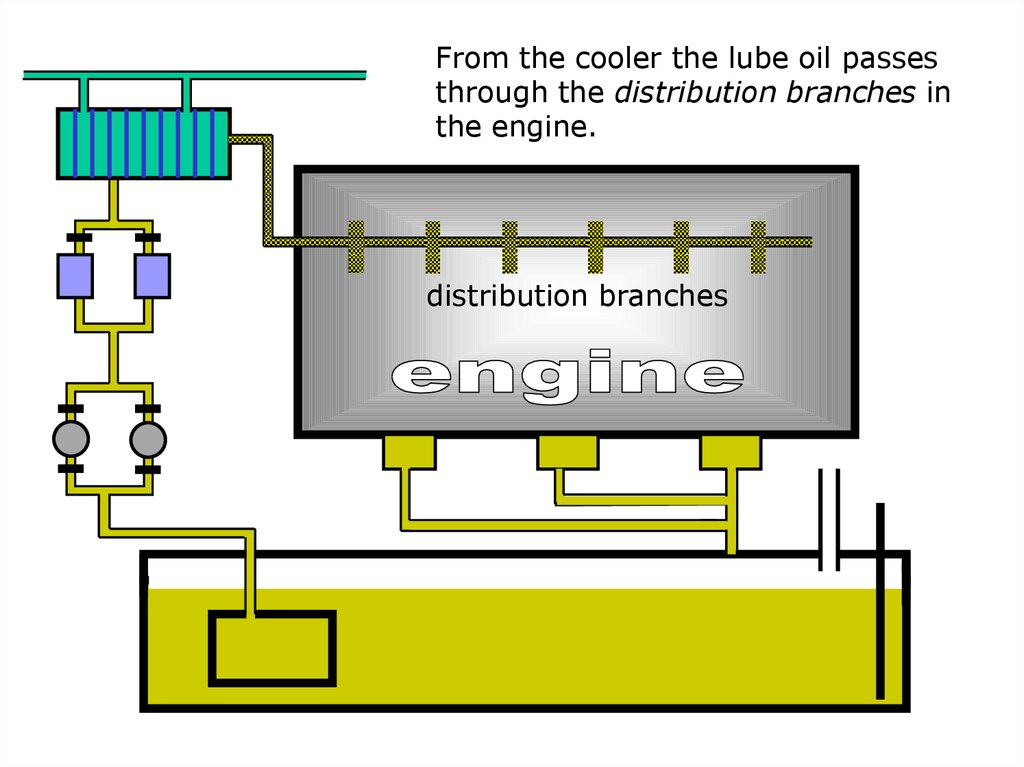
From the cooler the lube oil passesthrough the distribution branches in
the engine.
distribution branches
sound
2
7. Dia 7
sDistribution branches
8. Dia 8
In a crosshead engine oil bores run through thecrankshaft, crankwebs and crankpins,
9. Dia 9
so that the oil can flowfrom the main bearing to
the crank,
connecting rod,
crosshead,
crosshead guide shoes and
crosshead guides.
S
sound
10. Dia 10
The oil passes through the main lube-oil supply lineto the bearings.
11. Dia 11
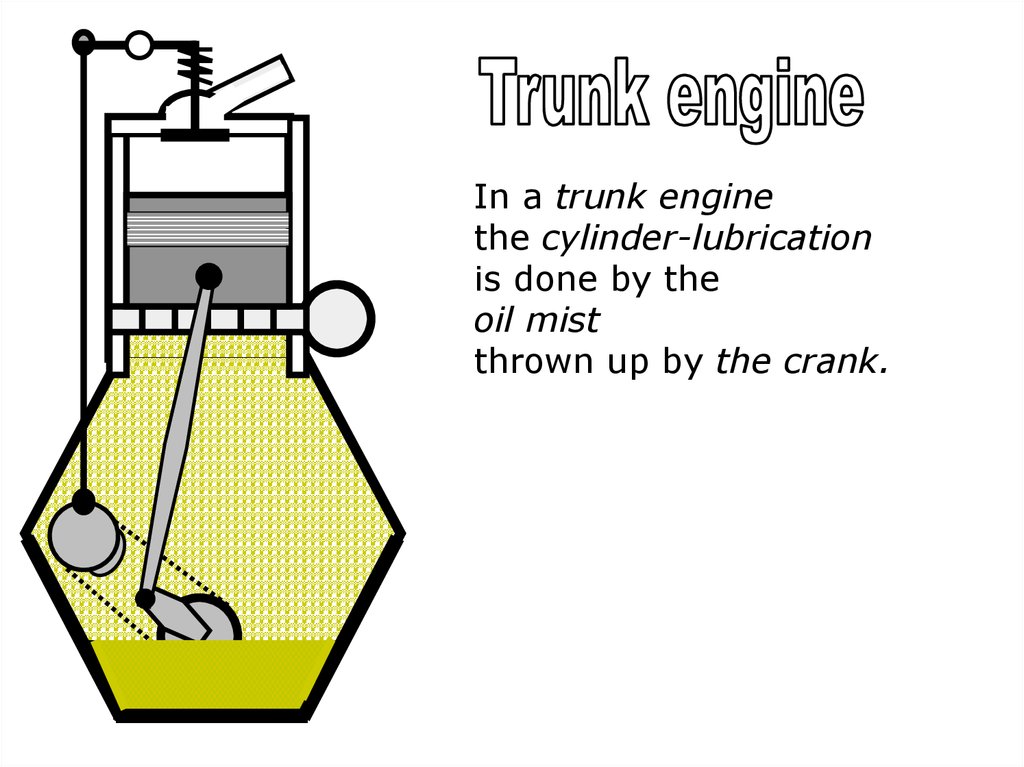
In a trunk enginethe cylinder-lubrication
is done by the
oil mist
thrown up by the crank.
sound
12. Dia 12
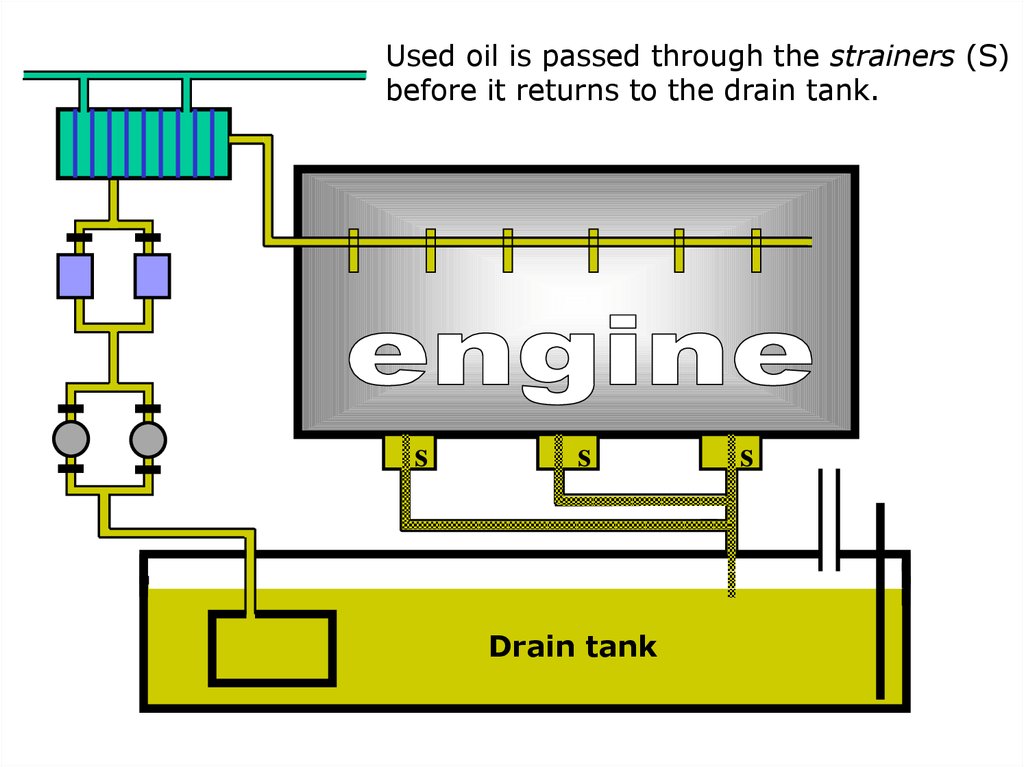
Used oil is passed through the strainers (S)before it returns to the drain tank.
s
s
s
Drain tank
sound
2
13. Dia 13
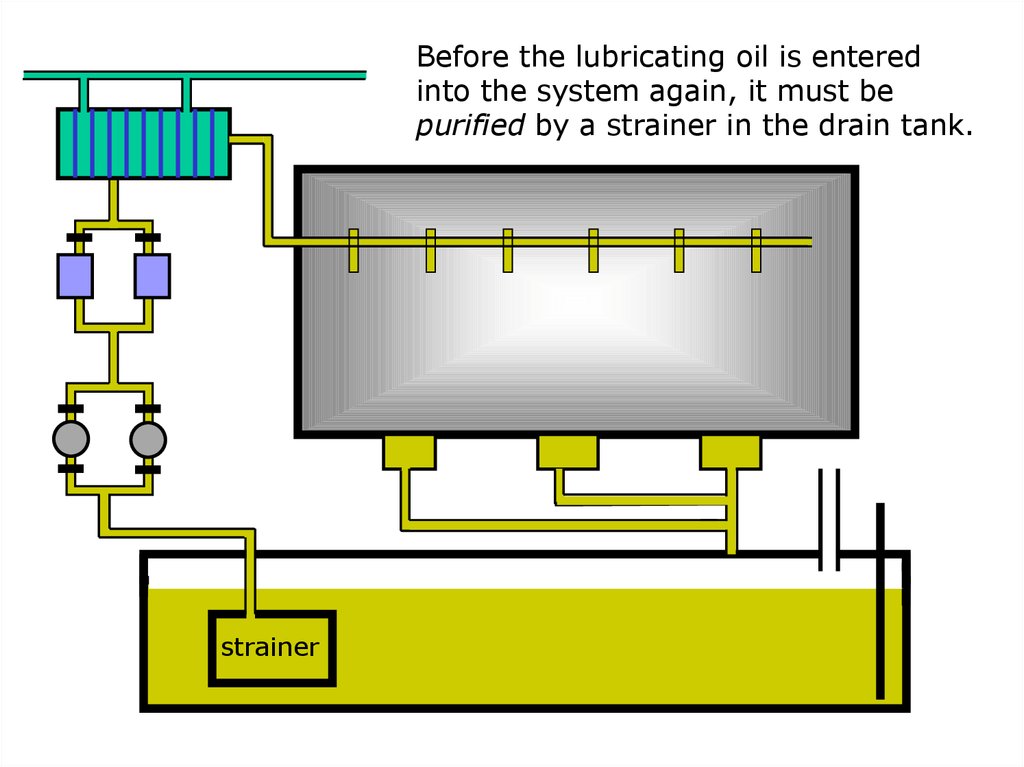
Before the lubricating oil is enteredinto the system again, it must be
purified by a strainer in the drain tank.
strainer
sound
2
14. Dia 14
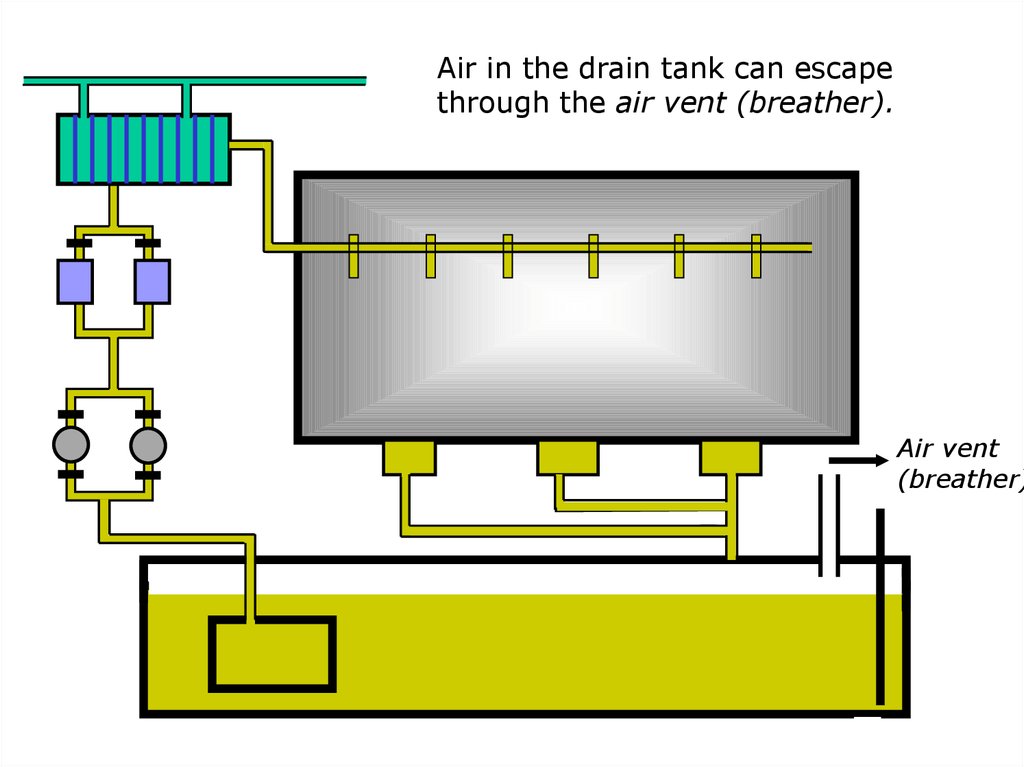
Air in the drain tank can escapethrough the air vent (breather).
Air vent
(breather)
sound
2
15. Dia 15
The oil-level is indicated with a level gaugeand is measured through a sounding pipe.
Level gauge
Sounding
pipe
sound
2
16. Dia 16
TheInternational Maritime Language Programme – IMLP
C
The IMLP is an IMO-standard.
P.C. van Kluijven









 mechanics
mechanics








