Similar presentations:
Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor and Metal-Insulator-Metal Structures. Heterogeneous Structures. Diodes
1. Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor and Metal-Insulator-Metal Structures. Part II. Heterogeneous Structures. Diodes
Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor and MetalInsulator-Metal Structures. Part II.Heterogeneous Structures. Diodes
Alexander Gabovich, KPI,
Lecture 9
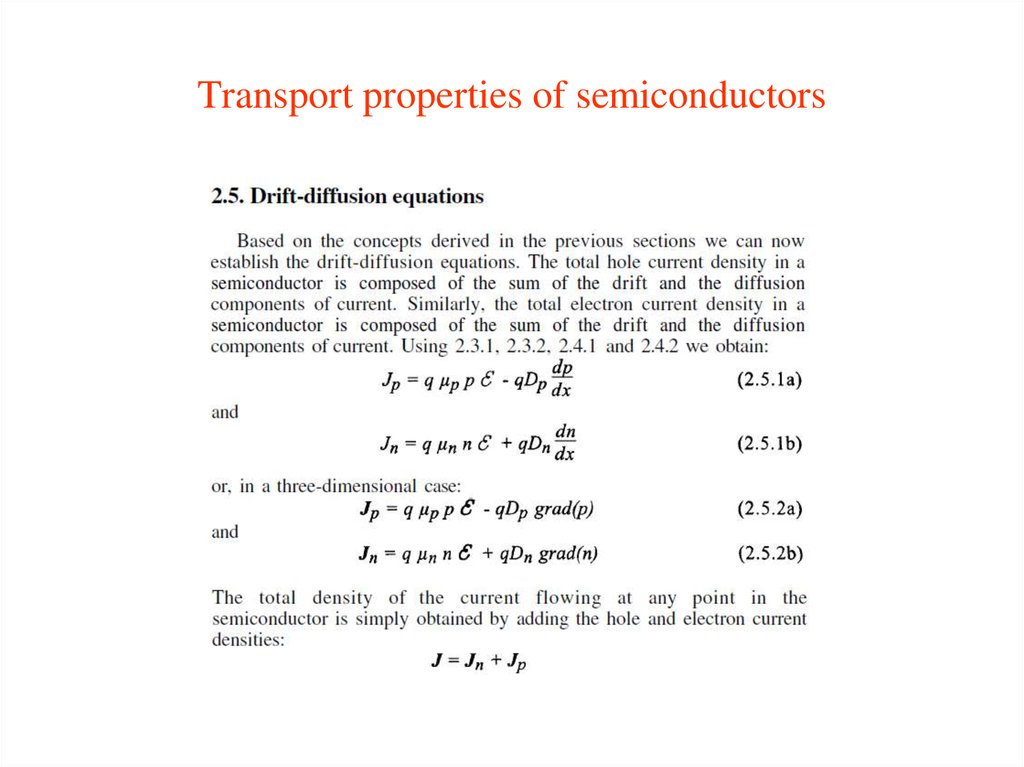
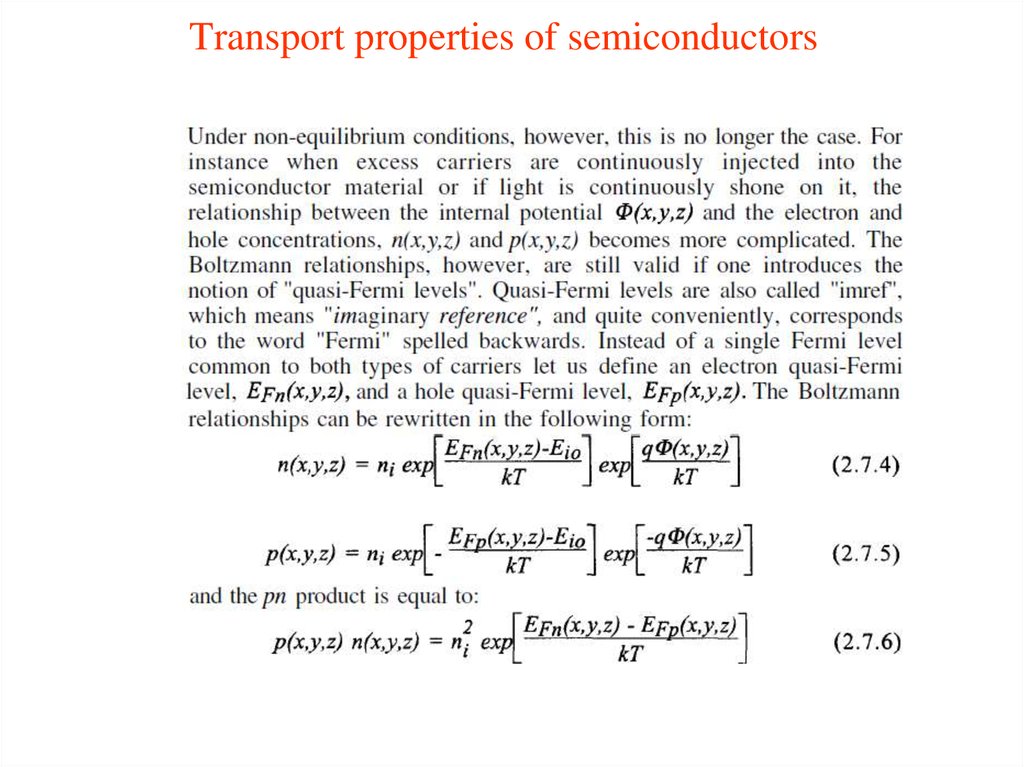
2. Transport properties of semiconductors
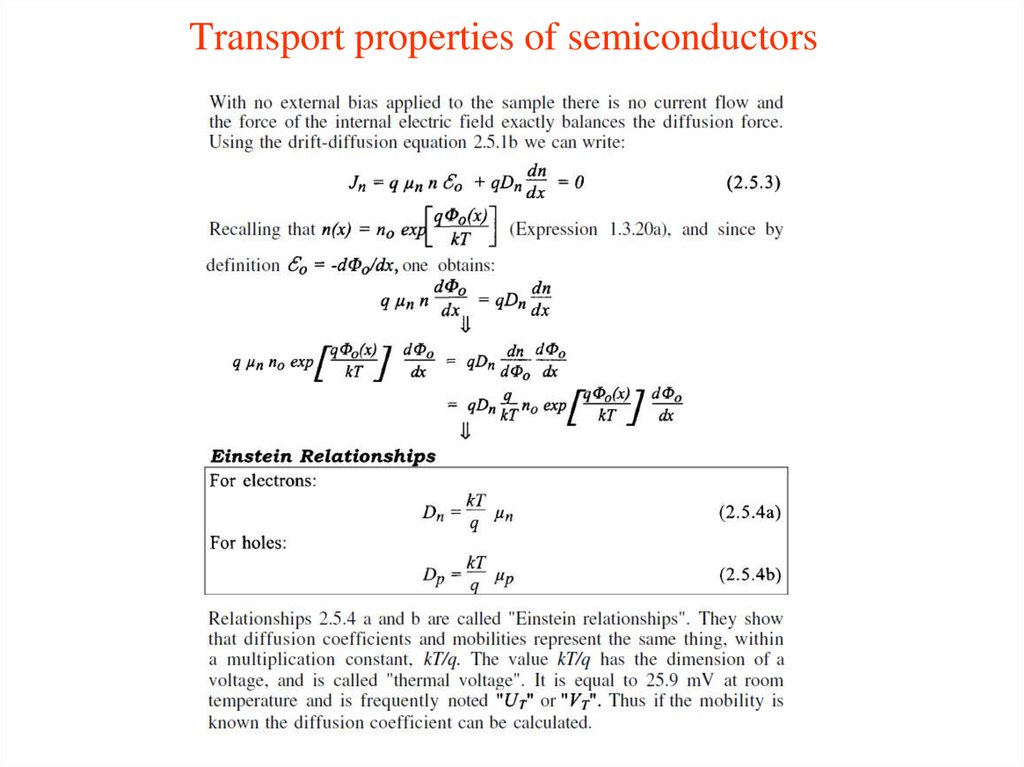
3. Transport properties of semiconductors
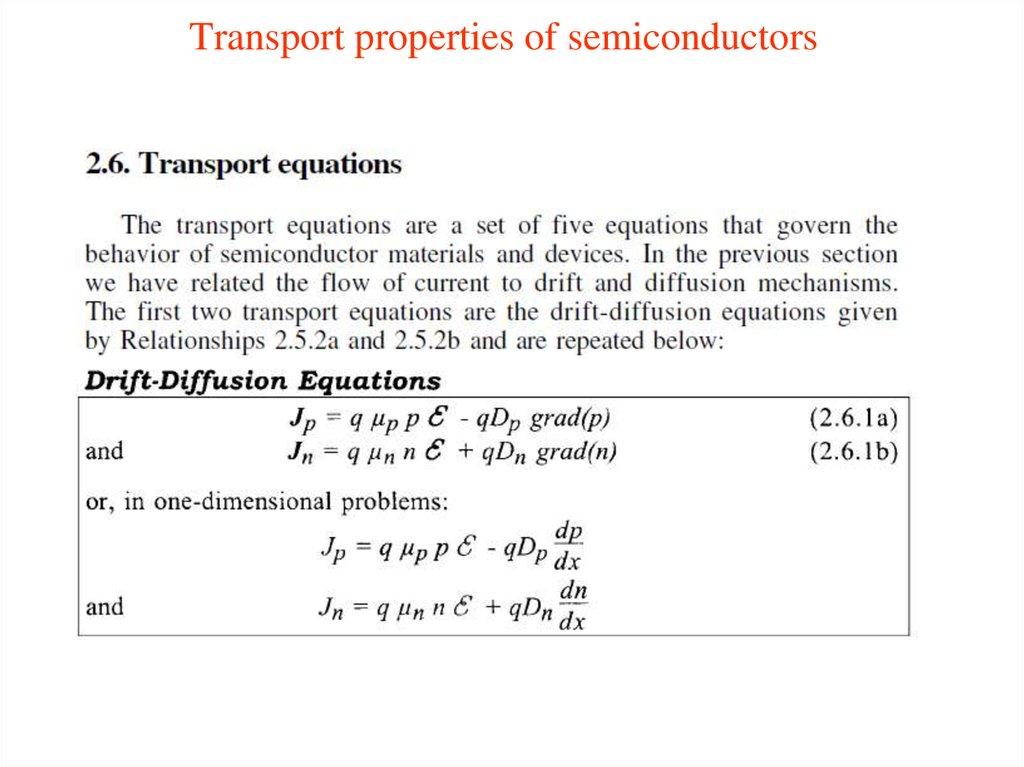
4. Transport properties of semiconductors
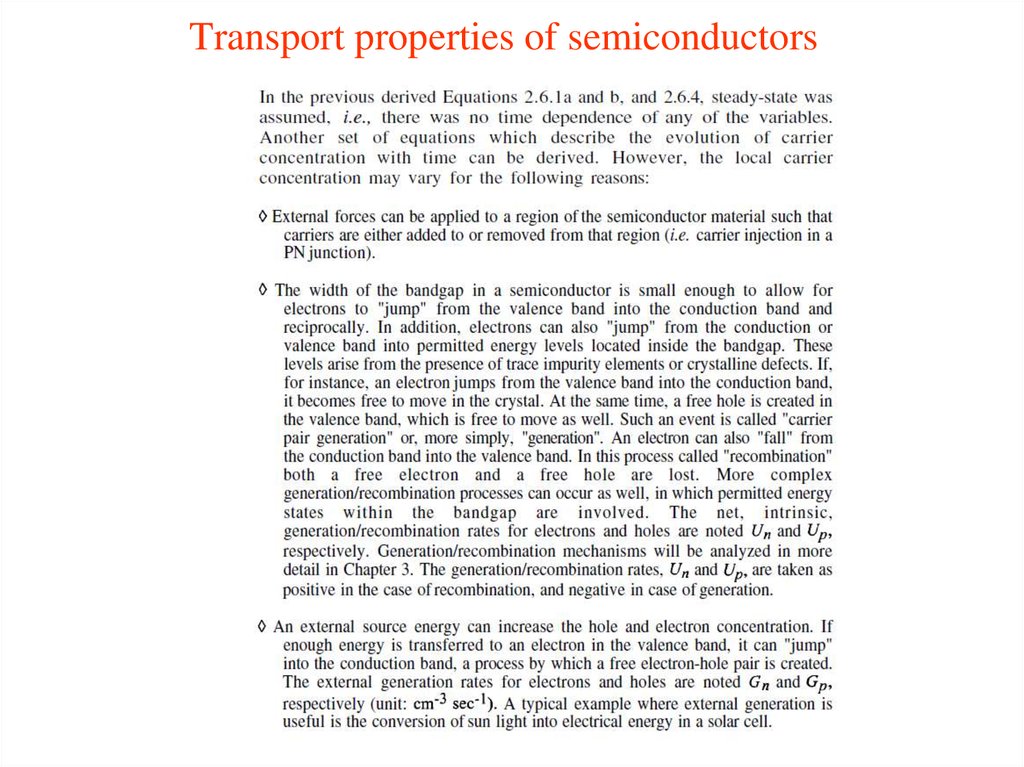
5. Transport properties of semiconductors
6. Transport properties of semiconductors
7. Transport properties of semiconductors
8. Transport properties of semiconductors
9. Transport properties of semiconductors
10. Transport properties of semiconductors
11. Transport properties of semiconductors
12. Transport properties of semiconductors
13. Transport properties of semiconductors
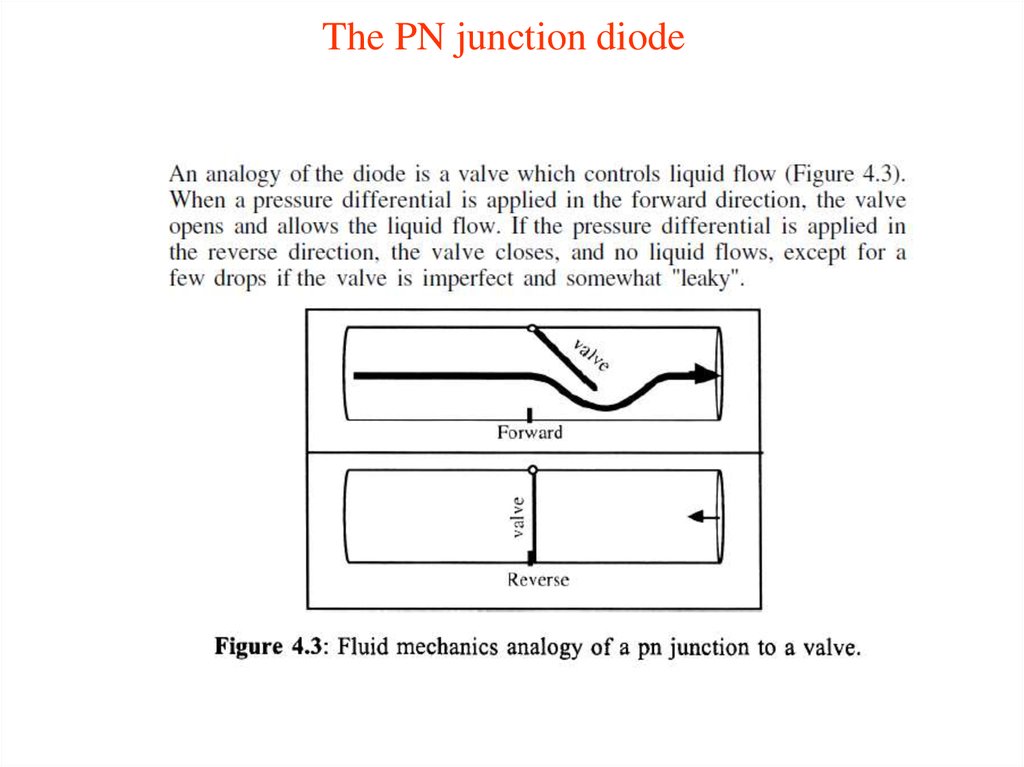
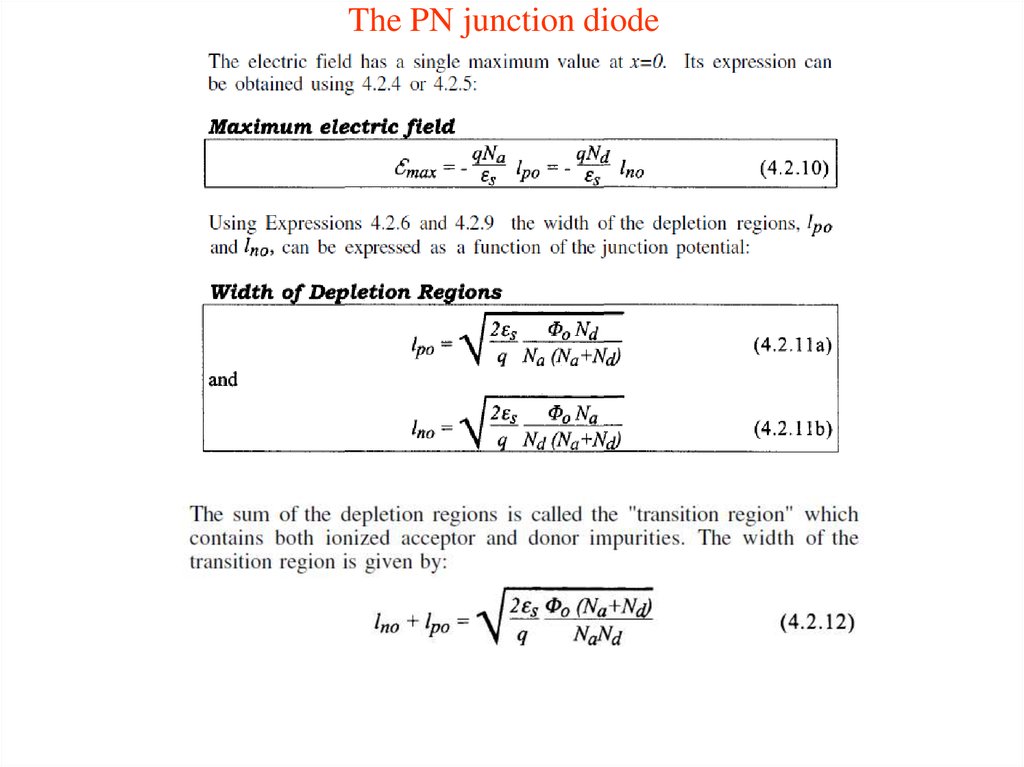
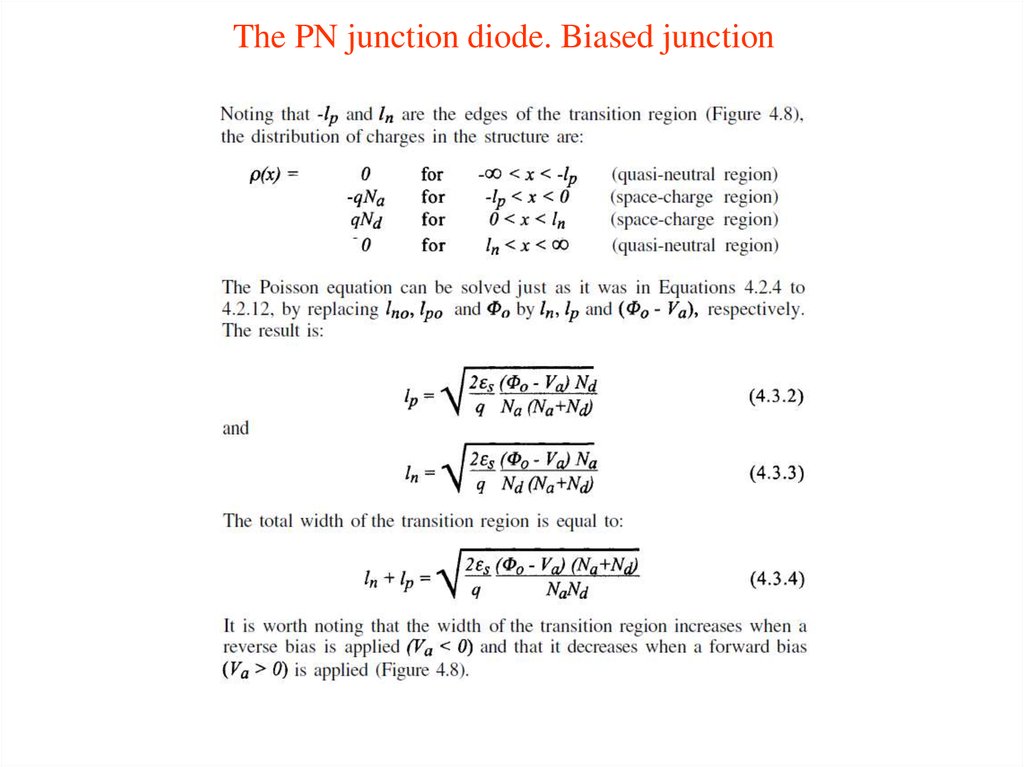
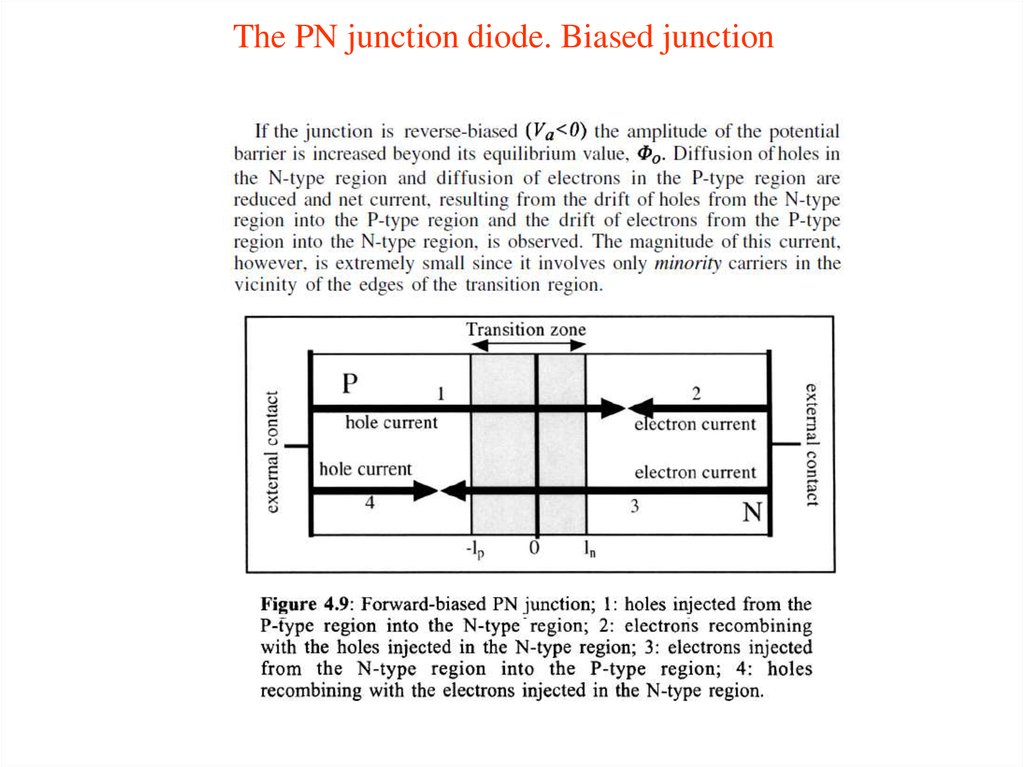
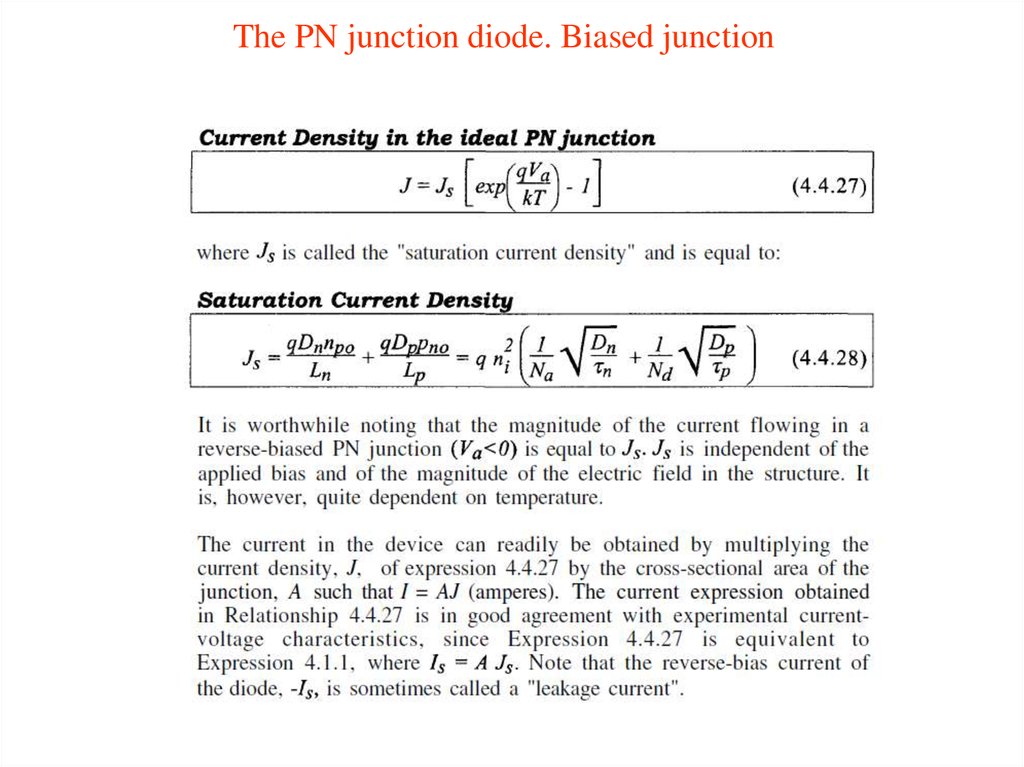
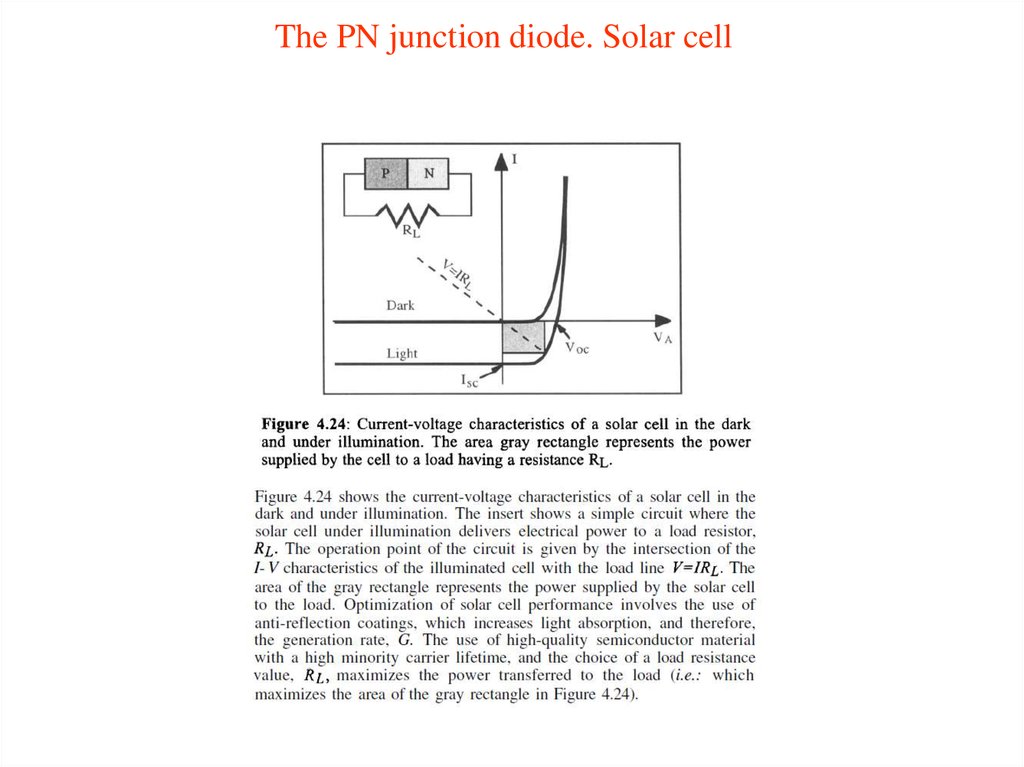
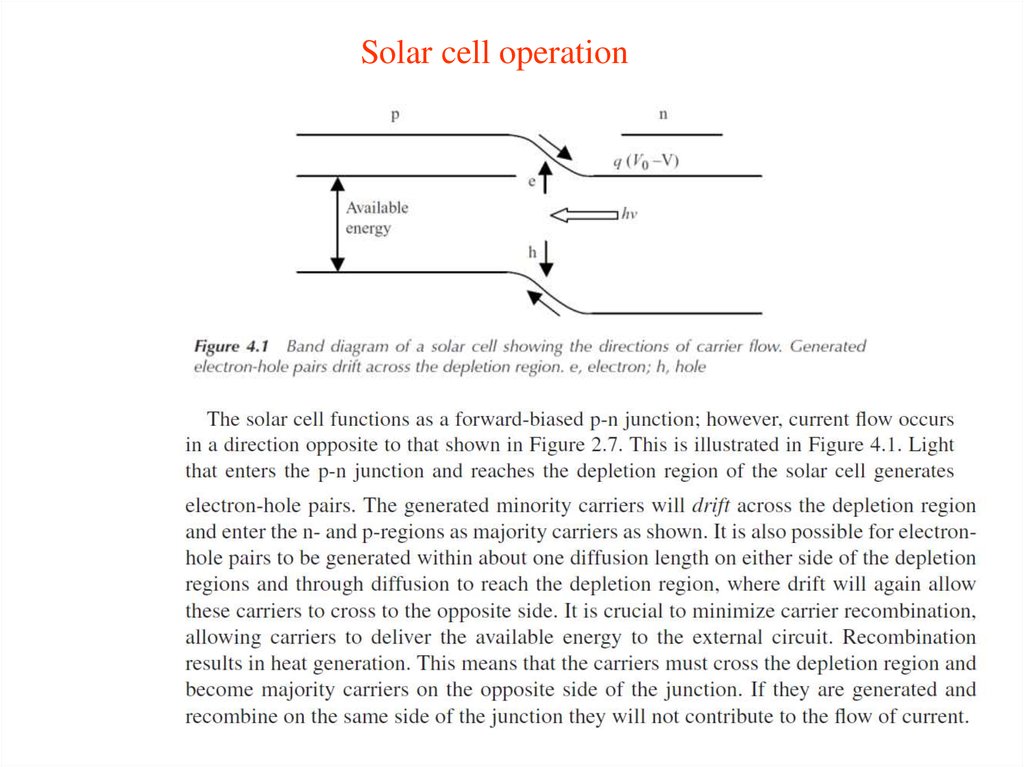
14. The PN junction diode
15. The PN junction diode
16. The PN junction diode
17. The PN junction diode
18. The PN junction diode
19. The PN junction diode
20. The PN junction diode
21. The PN junction diode
22. The PN junction diode
23. The PN junction diode
24. The PN junction diode
Actually, the electromagnetic induction D rather than the field E should becontinuous. However, here it does not matter because the dielectric constant
ε is the same in the whole area.


























 physics
physics








