Similar presentations:
Kazakh labour market
1.
21/05/2017Sonali
1
2. Testing Previous Knowledge
The concepts/terms learnt:•Factors of production
•Factor Incomes
•Derived demand
•Employer/ Firm
21/05/2017
Sonali
2
3. Lesson Objectives
The students will be able toUnderstand the nature of factors of production
Analyse the incomes earned by factors of production.
21/05/2017
Sonali
3
4. Activity 1
21/05/2017Sonali
(5.51 min)
4
5. Class Discussion
Nature of Factors of Production.Income earned by each factor
21/05/2017
Sonali
5
6. Reflection
1. What did you learn today?2. Where are you going to use the information you learnt
today?
21/05/2017
Sonali
6
7.
21/05/2017Sonali
7
8. Lesson Objectives
The students will be able toExplain the peculiarity of resource markets,
particularly the labour market
Apply to real world situation.
21/05/2017
Sonali
8
9.
Group DivisionGROUP 1:
KAZAKH LABOUR MARKET
GROUP 2:
MINING
GROUP 3:
GROUP 4:
10.
Activity 2-Critical Thinking(25 min)
Preparation Time: 10 min
Presentation: 15 min
Evaluate the present scenario about the type of
labour market given to you.
Тақырыпты ашу шеберлігі
2 балл
Уақытты ұтымды пайдалануы
(2 минут)
Креативтілігі
1 балл
2 балл
11. Class Discussion
Nature of Kazakhstan’s Labour markets21/05/2017
Sonali
11
12.
ReflectionWhat did you learn today ?
Чему вы научились сегодня?
13.
21/05/2017Sonali
13
14. Lesson Objectives
The students will be able toAnalyse the factors affecting the demand for labour.
Analyse the factors affecting the supply of labour.
Explain with the help of a diagram how wage is
determined.
Apply to real world situation.
21/05/2017
Sonali
14
15.
21/05/2017Sonali
15
16. Labour Force/Supply
21/05/2017Sonali
16
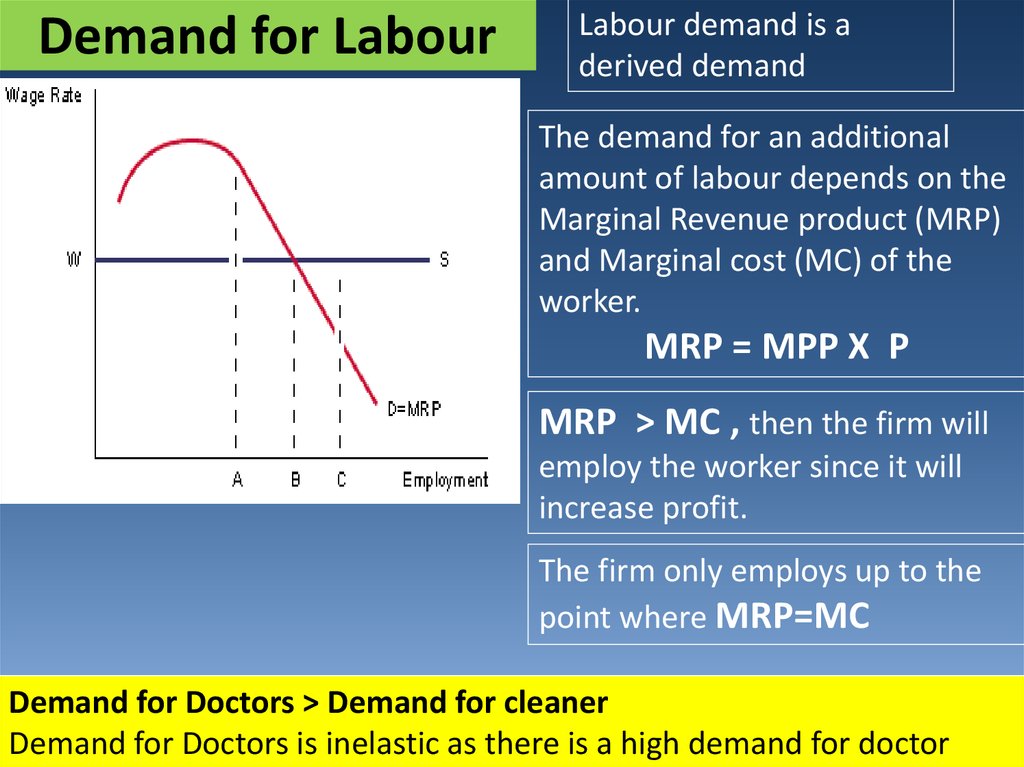
17. Demand for Labour
Labour demand is aderived demand
The demand for an additional
amount of labour depends on the
Marginal Revenue product (MRP)
and Marginal cost (MC) of the
worker.
MRP = MPP X P
MRP > MC , then the firm will
employ the worker since it will
increase profit.
The firm only employs up to the
point where MRP=MC
Demand for Doctors > Demand for cleaner
21/05/2017
Sonali
Demand
for Doctors is inelastic as there
is a high demand for doctor17
18.
21/05/2017Sonali
18
19. Supply for Labour
The total number of hours that labour is willingand able to supply at a given wage rate.
Labour force
Participation rate =
Population of working age
Employment rate =
unemployment rate =
unemployment
21/05/2017
number of people
currently employed
population of
working age
Labour force
The Supply curve for Labour tends to be
upwardly sloping
Substitution effect of a rise in wages: E to F
Workers will tend to substitute income for
leisure as leisure now has a higher
opportunity cost. This effect leads to more
hours being worked as wages rise
Income effect of a rise in wages: F to G
This occurs when an increase in wages causes
workers to work fewer hours.
This is because workers can get a higher
income by working less hours. Therefore they
Sonali
19
may work less.
20. WAGE RATE DETERMINATION
Equilibrium Wage RateNew Equilibrium Wage Rate
Demand for Labour = Supply of Labour
Demand for Labour = New Supply of
Labour
(Wage rate decrease)
21/05/2017
Sonali
20
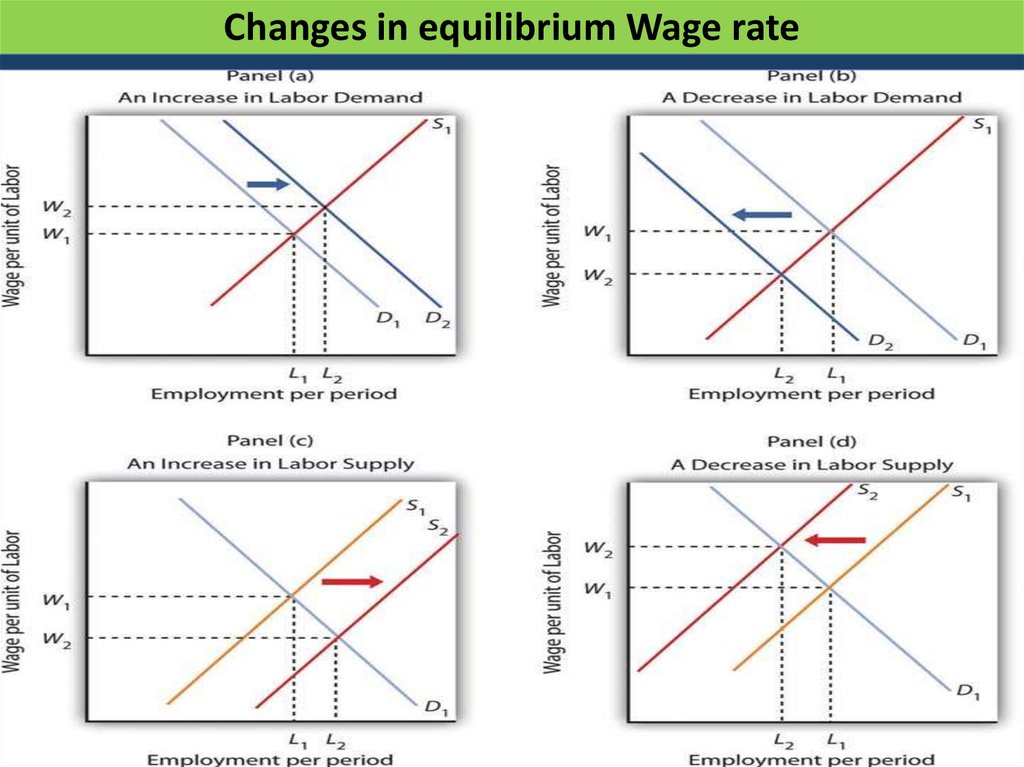
21. Changes in equilibrium Wage rate
21/05/2017Sonali
21
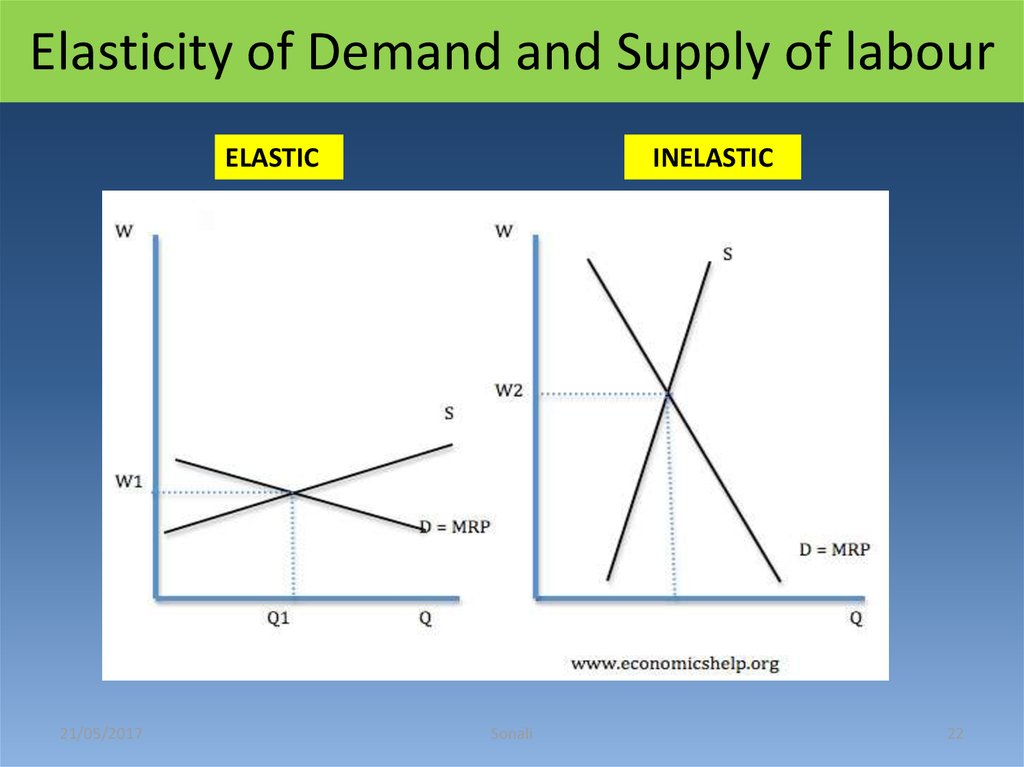
22. Elasticity of Demand and Supply of labour
ELASTIC21/05/2017
INELASTIC
Sonali
22
23.
21/05/2017Sonali
23
24.
ReflectionWhat did you learn today ?
How are you going to transfer this
knowledge to next level?





















 economics
economics








