Similar presentations:
Great_Britain. Geography
1. Great Britain Physical Background
2.
• The United Kingdom of Great Britain anNorthern Ireland (since 1922)
• The UK
• Britain (Latin from Greek, around 320 B.C)
• Great Britain (1474)
• England (around 1st century A.D)
• Albion (around 6th century B.C.)
• Britannia
3. Britannia
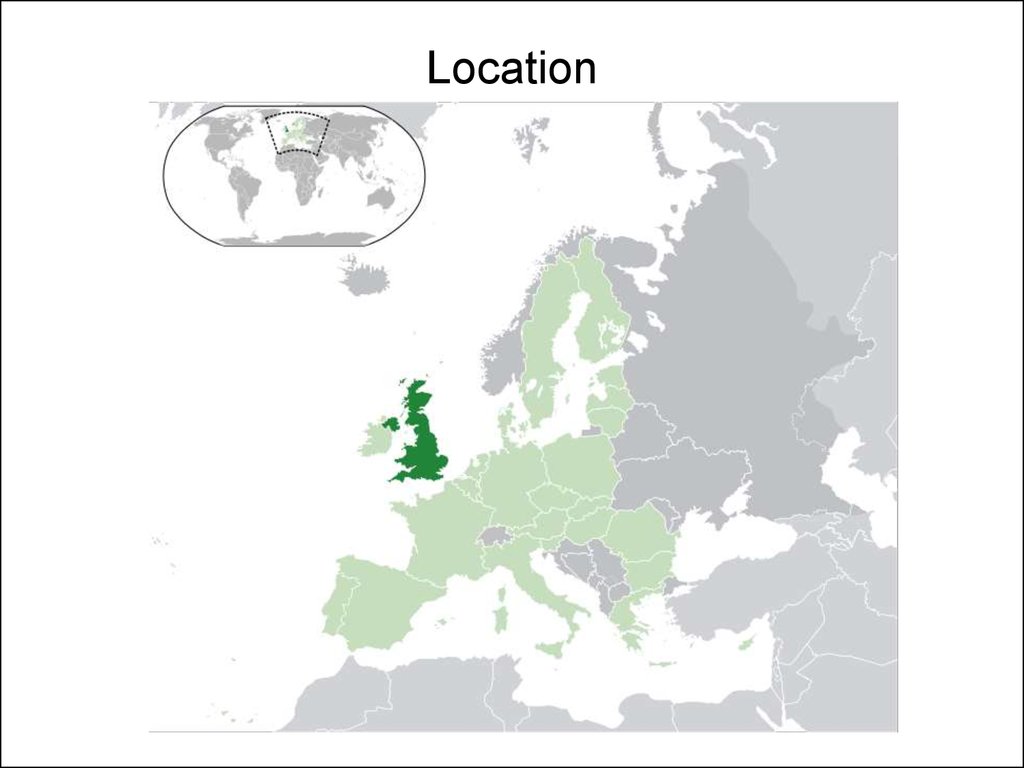
4. Location
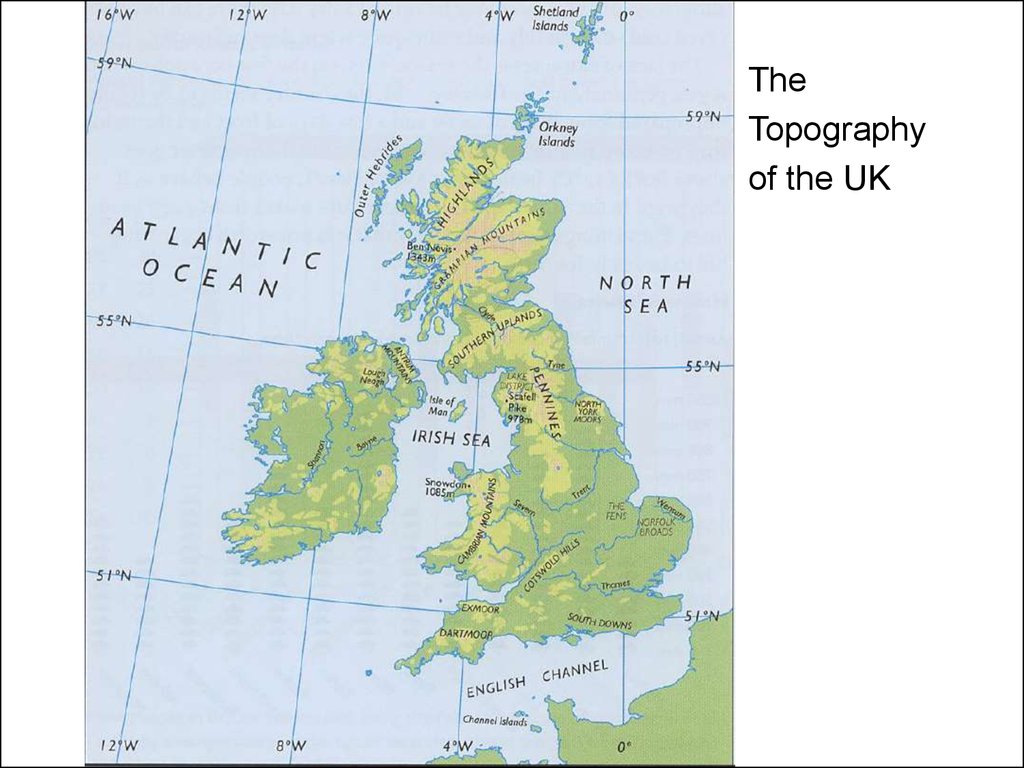
5.
TheTopography
of the UK
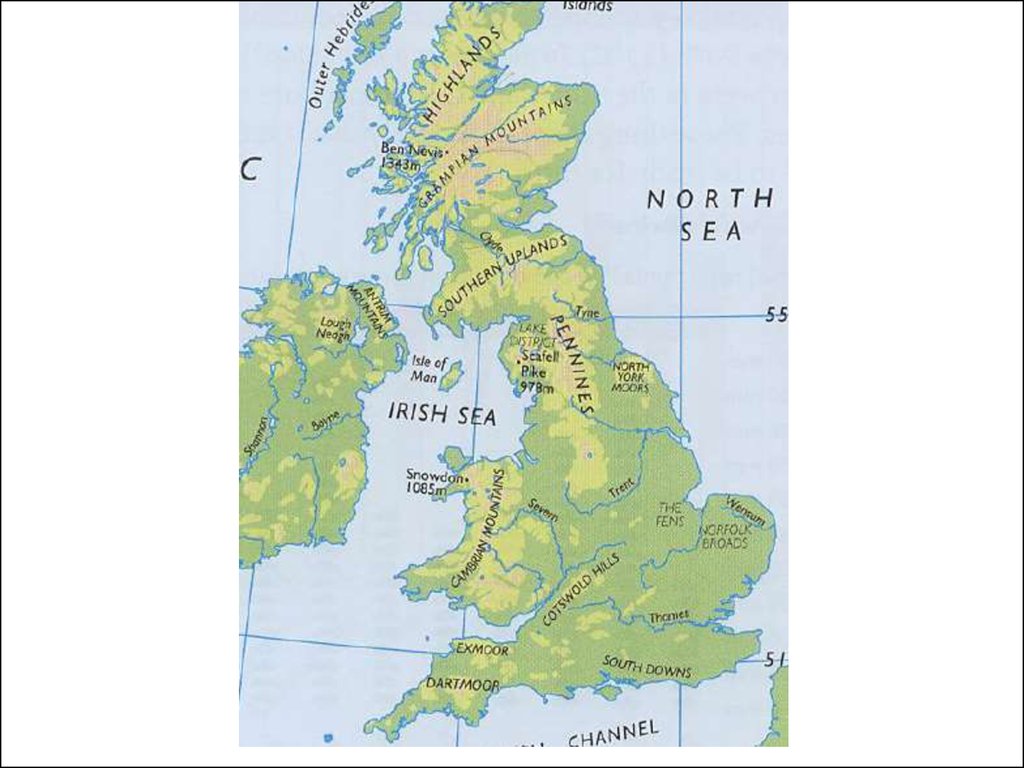
6. Islands
• Great Britain• Ireland
Smaller Islands
the Isle of Wight
the Channel Islands
the Isles of Scilly
Anglesey
the Isle of Man
The Hebrides
the Orkneys
the Shetlands.
7. Under constant attack from the sea
8. Land’s End (the extreme southwest point of England)
9.
10. Lowland Britain
11. Lowland Britain
South and South-East EnglandLondon, Bristol, Bath, Brighton
East Anglia. The Fens.
Kent County - “the garden of England”
The hills: the South Downs and the North
Downs, the Cotswolds, the Chilterns.
• The Midlands
• Birmingham, “the Black Country”, “the Potteries”
• Stratford-upon-Avon, Nottingham – tourist
attractions
12. The Highland Zone
• Northern England
The Cheviot Hills, The Pennines – “the
backbone of England”
Manchester, Liverpool, Sheffield, Newcastle –
industrial centers
The Lake District, the Cumbrian Mountains,
Scafell Pike (978 meters)
• Wales
. The Cambrian Mountains, Snowdon (Yr
Wyddfa Fawr in Welsh) (1,085 m)
the Brecon Beacons (southern Wales)
13. The Lake District
14. Snowdonia National Park
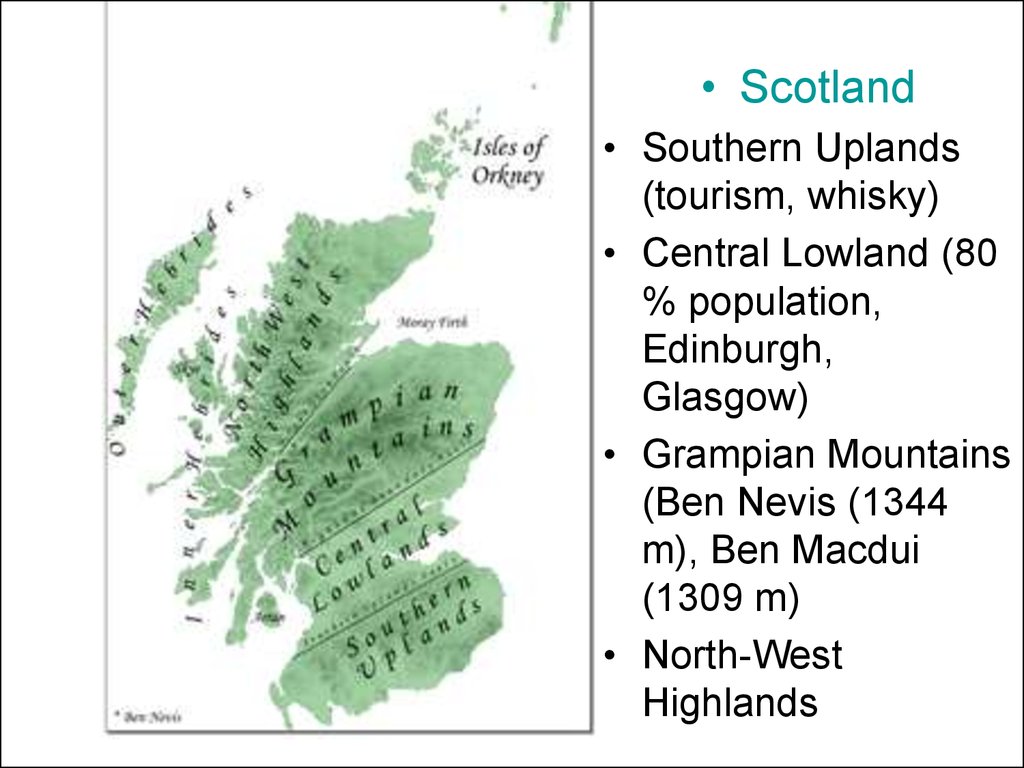
15.
• Scotland• Southern Uplands
(tourism, whisky)
• Central Lowland (80
% population,
Edinburgh,
Glasgow)
• Grampian Mountains
(Ben Nevis (1344
m), Ben Macdui
(1309 m)
• North-West
Highlands
16. The Grampian Mountains
17. Ben Nevis
18. Cornwall
• Exmoor,Dartmoor
• Cornish
Riviera
• Tintagel
Castle,
birthplace of
King Arthur
19. Rivers in Britain
• EnglandThe Thames
the Severn
the Mersey
the River Humber with the Tyne River
• Scotland
the Tay
the Clyde
the Forth
the Tweed
20. Rivers in Britain
• Northern Ireland• the Bann
• the Lagan
• the Foyle.
• Wales
• The Severn
• The Towy
• The Wye
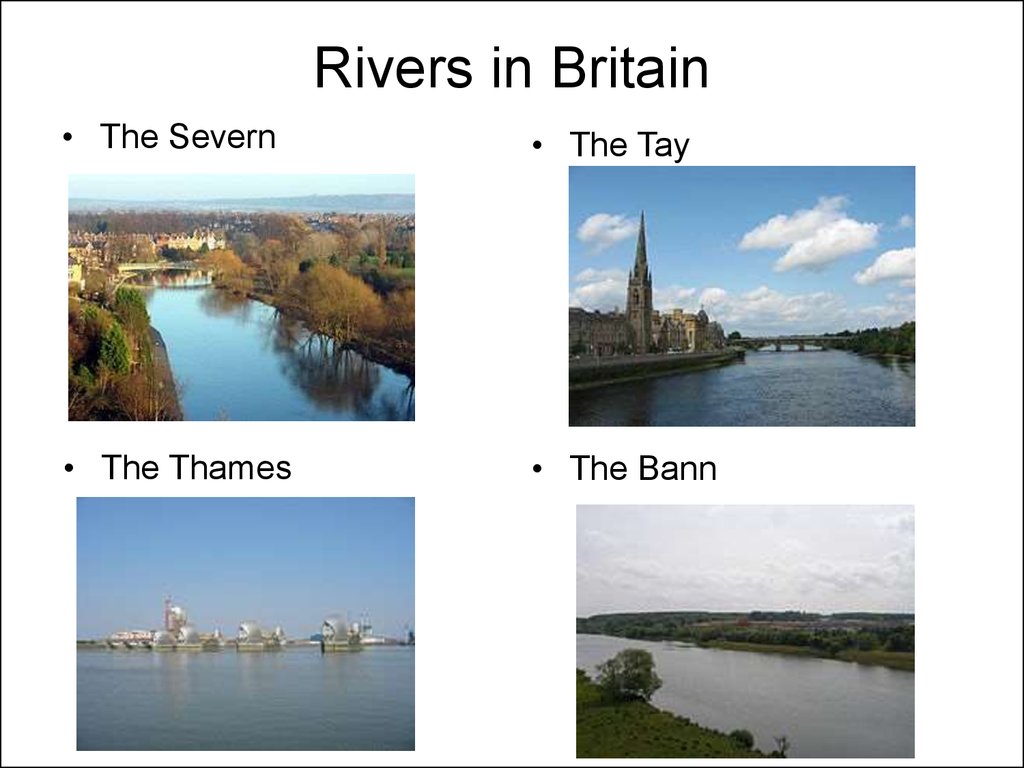
21. Rivers in Britain
• The Severn• The Tay
• The Thames
• The Bann
22. Lakes
Lough Neagh (Northern Ireland) – 382 km²
Loch Lomond (Scotland) - 71 km²
Loch Morar (Scotland) – 309 m deep
Loch Ness (Scotland) – 229 m deep
The Lake District (England) – Lake
Windermere, Lake Derwentwater – “the
Queen of lakes”, the Brothers Water
23. Lough Neagh
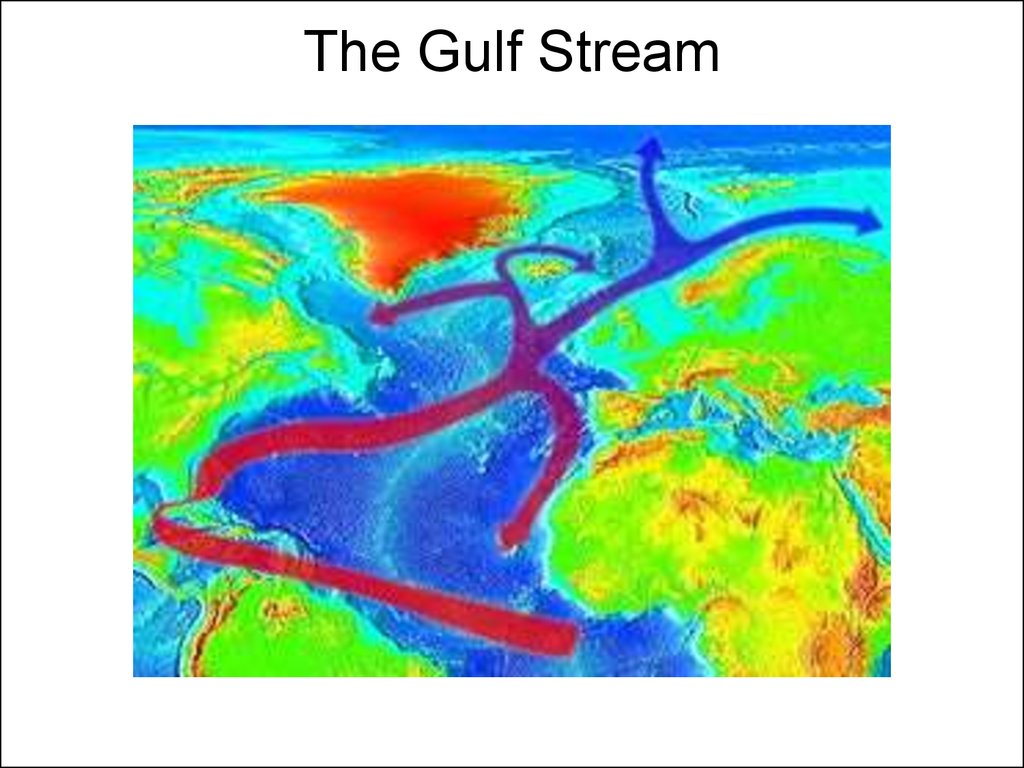
24. The Gulf Stream
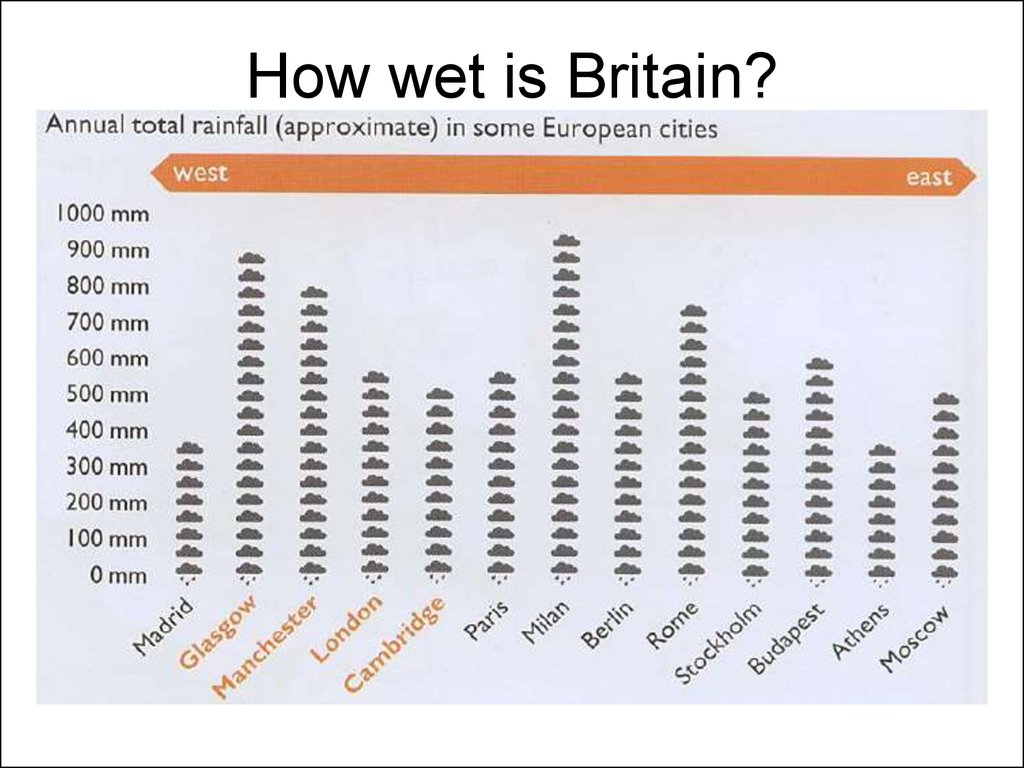
25. How wet is Britain?
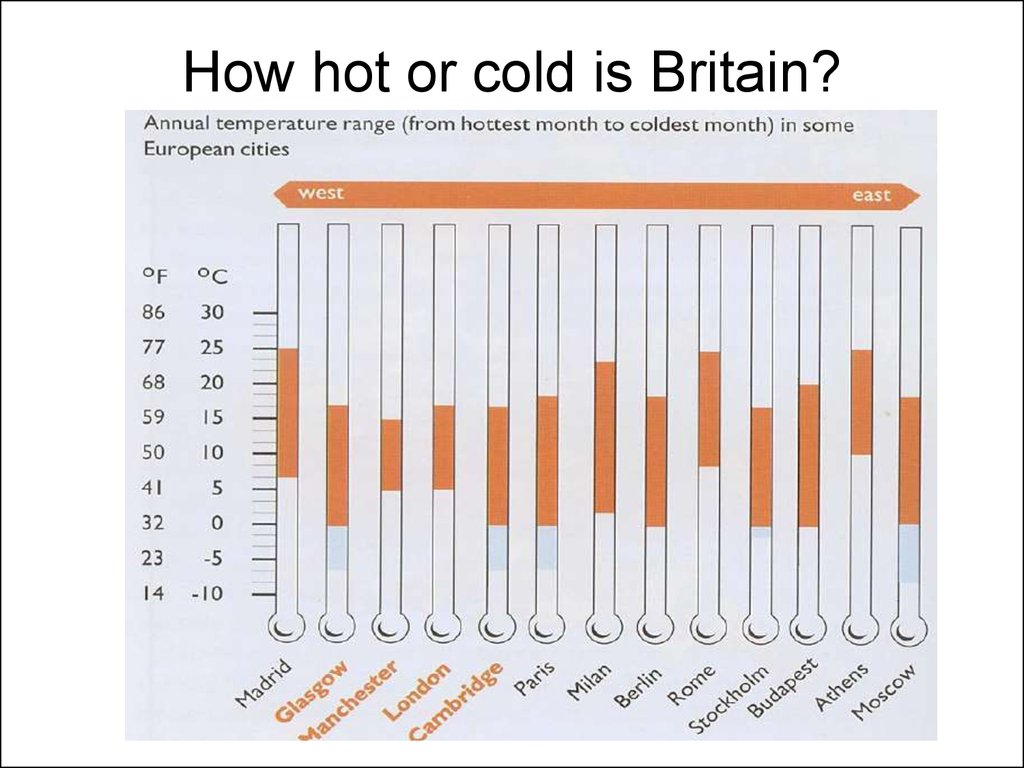
26. How hot or cold is Britain?
27. National and Forest Parks
• National Parks• Lake District, Peak District, Border
Country, Yorkshire Dales, Yorkshire Moors
Dartmoor and Exmoor)
• Forest Parks
• Snowdonia in Wales; Queen Elizabeth and
Argyll in Scotland; Dean, Border, and New
Forest in England.
28. Chief Industries
• service sector ( around 78% of GDP)including financial service industry
• aerospace industry
• pharmaceutical industry
• automotive industry
• North Sea oil and gas production
29. Agriculture
About 1.6% of the labour force
Covers 60% of the national food needs
2/3-ds –livestock, 1/3-d – growing crops
Fishing industry
30. Natural resources
Coal
Oil
natural gas
Tin
Limestone
iron ore
salt
Clay
Chalk
gypsum
Lead
silica
31. Pound sterling
• Symbol: £ (лат. Libra —фунт), banking code:
GBP (Great Britain
Pounds),
32. The UK is a member of
Commonwealth of Nations
the European Union
the G7
the G8
the G20
the International Monetary Fund
the Organisation for Economic Co-operation
and Development
• the World Bank
• the World Trade Organisation
• the United Nations.
























 geography
geography








