Similar presentations:
The Fascinating World of Lasers
1.
The FascinatingWorld of Lasers
Valentyn Peshnei
2.
Gain Medium: The Heart of a LaserSolid State Gain Medium
Gas Gain Medium
Liquid Gain Medium
3.
Population Inversion and StimulatedEmission
1
Energy Absorption
The gain medium absorbs pump energy, exciting electrons to higher
energy states.
2
Population Inversion
More particles exist in excited states than in lower energy states.
3
Stimulated Emission
Excited particles emit photons in the same direction as passing light.
4
Light Amplification
The emitted light is amplified as it passes through the gain medium.
4.
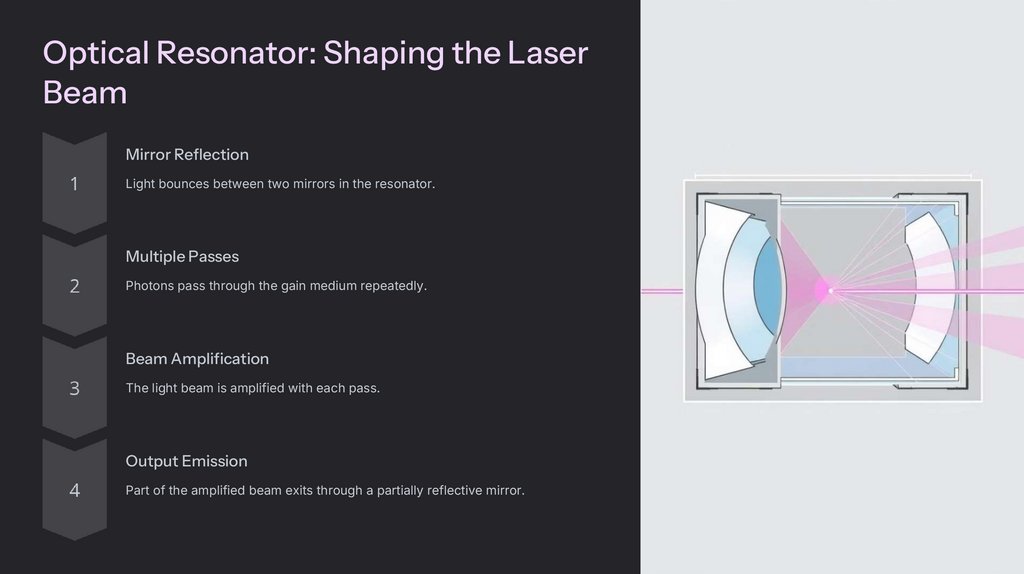
Optical Resonator: Shaping the LaserBeam
Mirror Reflection
Light bounces between two mirrors in the resonator.
Multiple Passes
Photons pass through the gain medium repeatedly.
Beam Amplification
The light beam is amplified with each pass.
Output Emission
Part of the amplified beam exits through a partially reflective mirror.
5.
Laser Beam CharacteristicsCoherence
Directionality
Monochromaticity
Laser light maintains a consistent
The beam is highly collimated,
Laser light often consists of a
phase relationship, resulting in a
with minimal divergence over
single wavelength or a very
highly organized wave pattern.
long distances.
narrow range of wavelengths.
6.
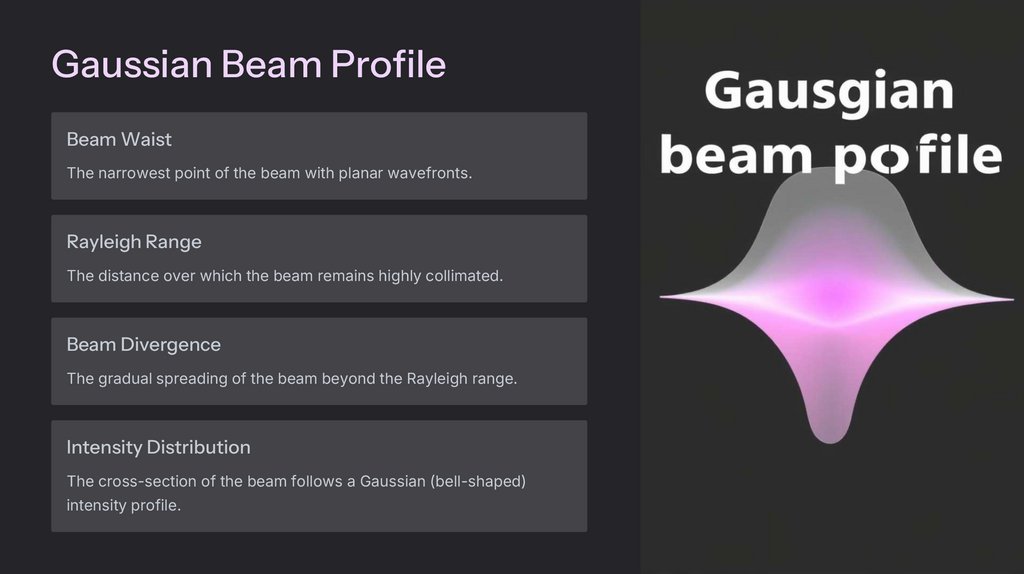
Gaussian Beam ProfileBeam Waist
The narrowest point of the beam with planar wavefronts.
Rayleigh Range
The distance over which the beam remains highly collimated.
Beam Divergence
The gradual spreading of the beam beyond the Rayleigh range.
Intensity Distribution
The cross-section of the beam follows a Gaussian (bell-shaped)
intensity profile.
7.
Types of LasersGas Lasers
Helium-neon lasers produce a characteristic red beam.
Solid-State Lasers
Ruby and Nd:YAG lasers use crystal or glass hosts.
Semiconductor Lasers
Compact diode lasers used in various applications.
Dye Lasers
Tunable lasers using organic dye solutions.
8.
Laser ApplicationsField
Application
Medicine
Surgery, eye treatments
Industry
Cutting, welding, 3D
printing
Communications
Fiber optic data
transmission
Science
Spectroscopy, holography
Consumer Electronics
Barcode scanners, optical
drives






 physics
physics








