Similar presentations:
Internet Technologies
1.
Lection 9INTERNET
TECHNOLOGIES
Senior Lecturer – KURMANBEKKYZY NURGUL
Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences,
Associate Professor
2.
CONTENTSBasic concepts Internet.
The universal identifier of resources (URI), its
assignment and components.
Service DNS.
Web technologies: HTTP, DHTML,
CSS, and JavaScript.
E-mail. Message format.
SMTP, POP3, IMAP protocols.
3.
INTERNETa world system of interconnected
computer networks, built on the
use of IP Protocol and routing of
data packets
4.
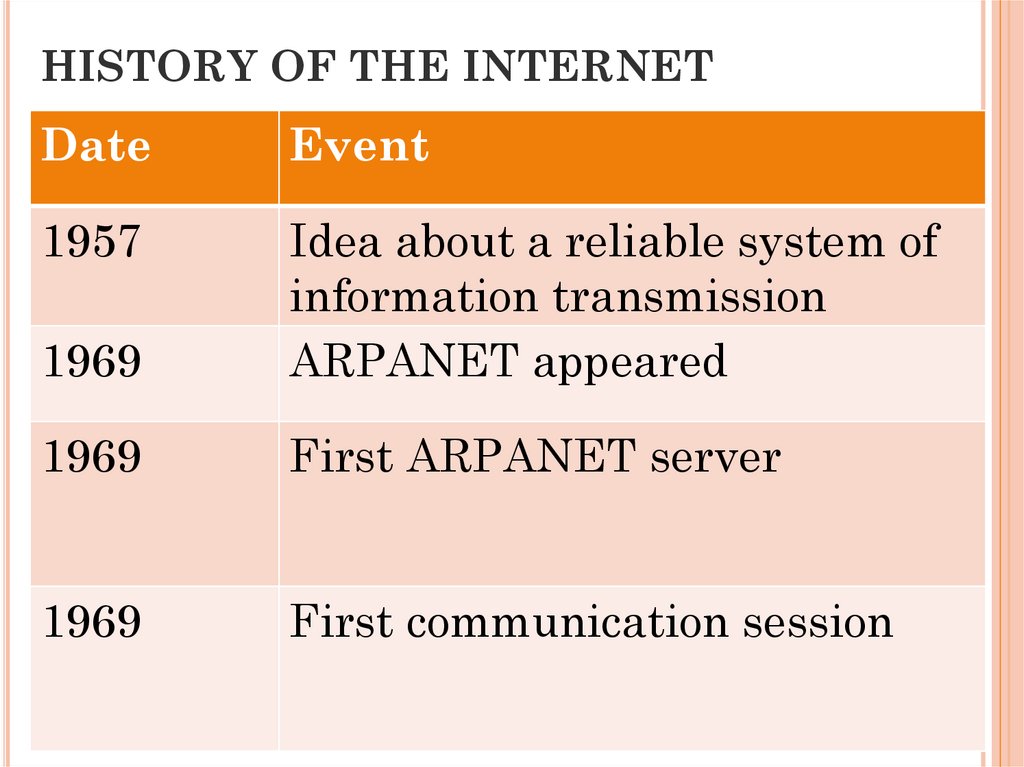
HISTORY OF THE INTERNETDate
Event
1957
1969
Idea about a reliable system of
information transmission
ARPANET appeared
1969
First ARPANET server
1969
First communication session
5.
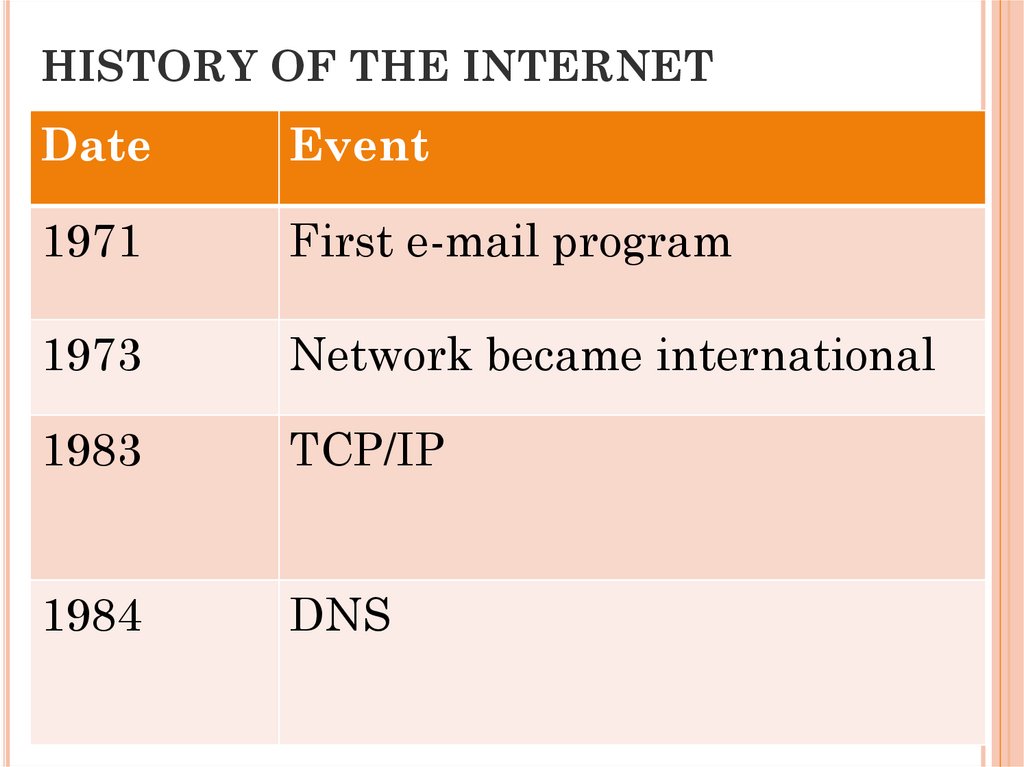
HISTORY OF THE INTERNETDate
Event
1971
First e-mail program
1973
Network became international
1983
TCP/IP
1984
DNS
6.
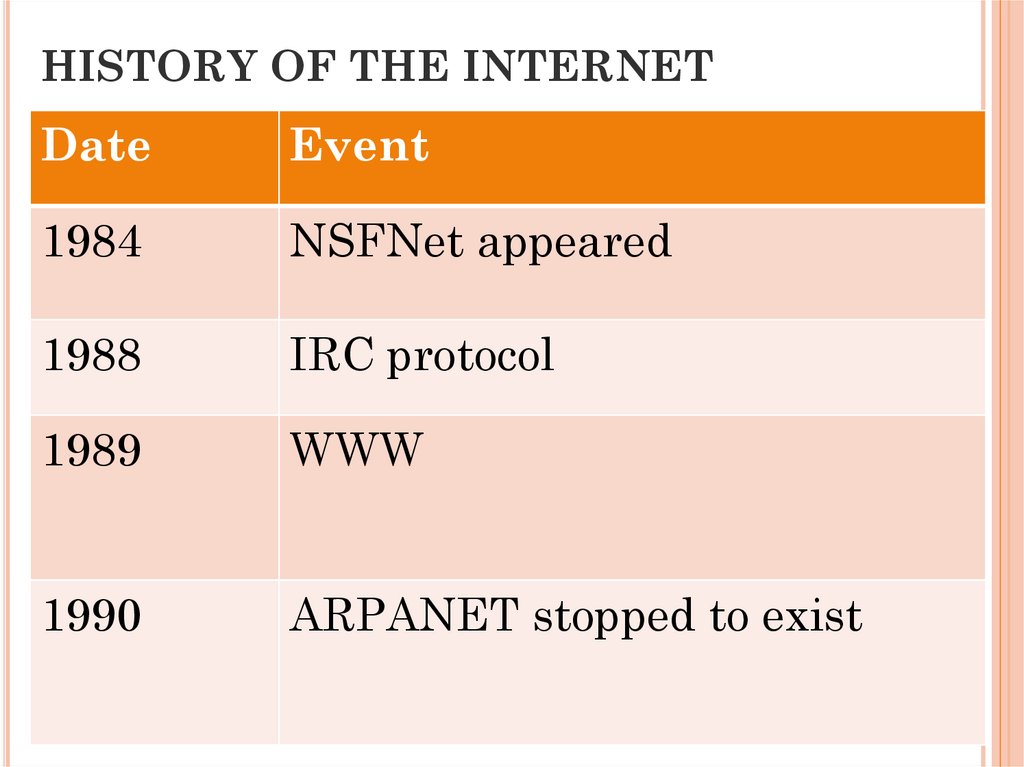
HISTORY OF THE INTERNETDate
Event
1984
NSFNet appeared
1988
IRC protocol
1989
WWW
1990
ARPANET stopped to exist
7.
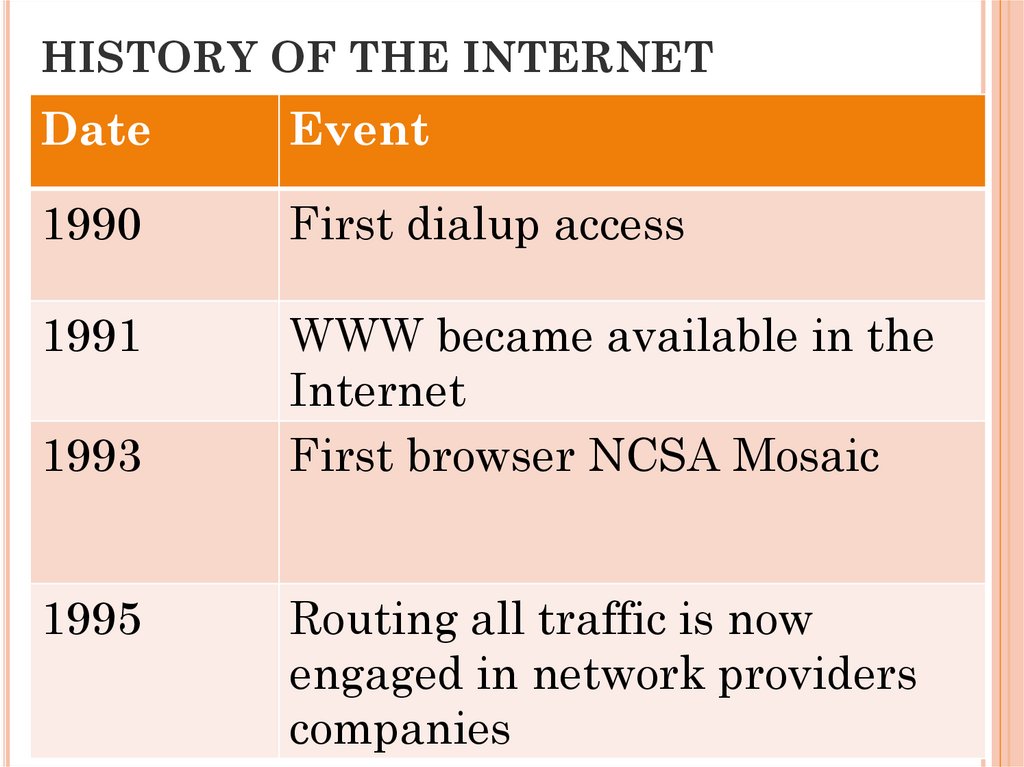
HISTORY OF THE INTERNETDate
Event
1990
First dialup access
1991
WWW became available in the
Internet
First browser NCSA Mosaic
1993
1995
Routing all traffic is now
engaged in network providers
companies
8.
WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW)a distributed system that provides access
to related documents located on different
computers connected to the Internet
9.
HYPERLINKsome of the file element of the web
page usually allocated by color or by
underlining, which is the starting
point to navigate to the another web
pages.
10.
WEB-PAGEa computer file created using a
special hypertext markup
language HTML
11.
WEB-SITEcollection of web pages, which
are united by some principle
12.
WEB-SERVERserver that accepts HTTP requests
from clients, typically web browsers,
and issues them HTTP responses,
usually together with an HTML page
13.
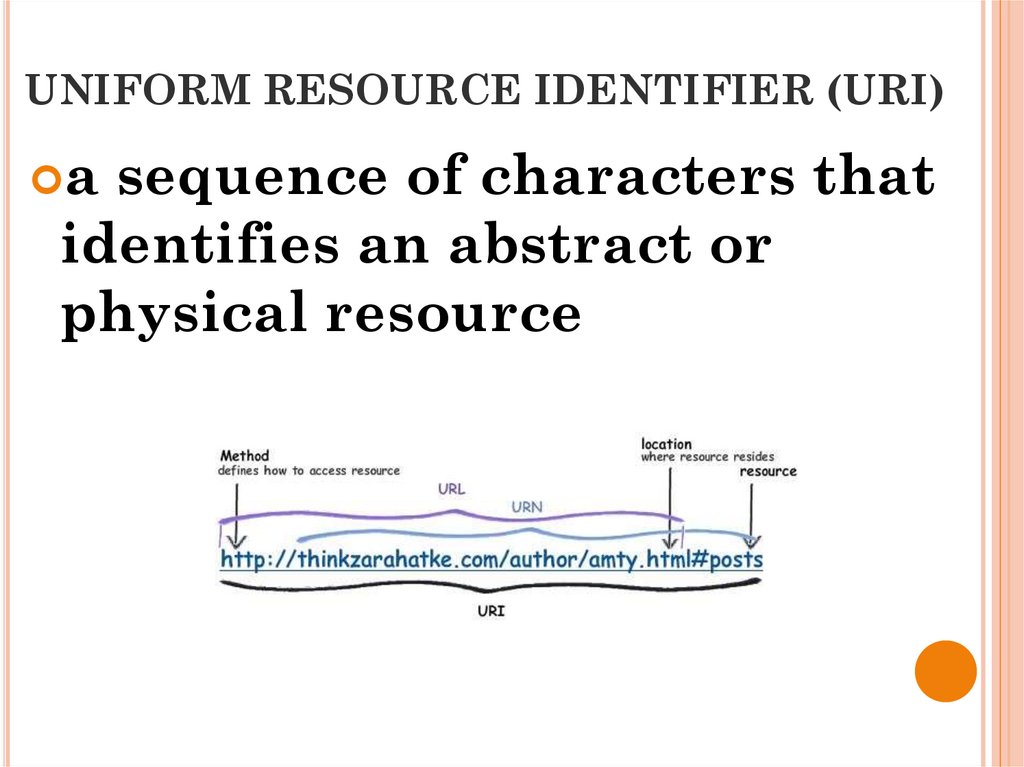
UNIFORM RESOURCE IDENTIFIER (URI)a sequence of characters that
identifies an abstract or
physical resource
14.
UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR (URL)URI that, in addition to identifying a
resource, provides information on the
location of this resource
15.
UNIFORM RESOURCE NAME (URN)URI, that only
identify a
resource in a certain namespace
16.
DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM, DNSa centralized service based on
distributed database of mappings
«domain name – IP address»
17.
DNS SERVERspecial software for DNS service
18.
DNS CLIENTspecial library (or program) for
work with DNS
19.
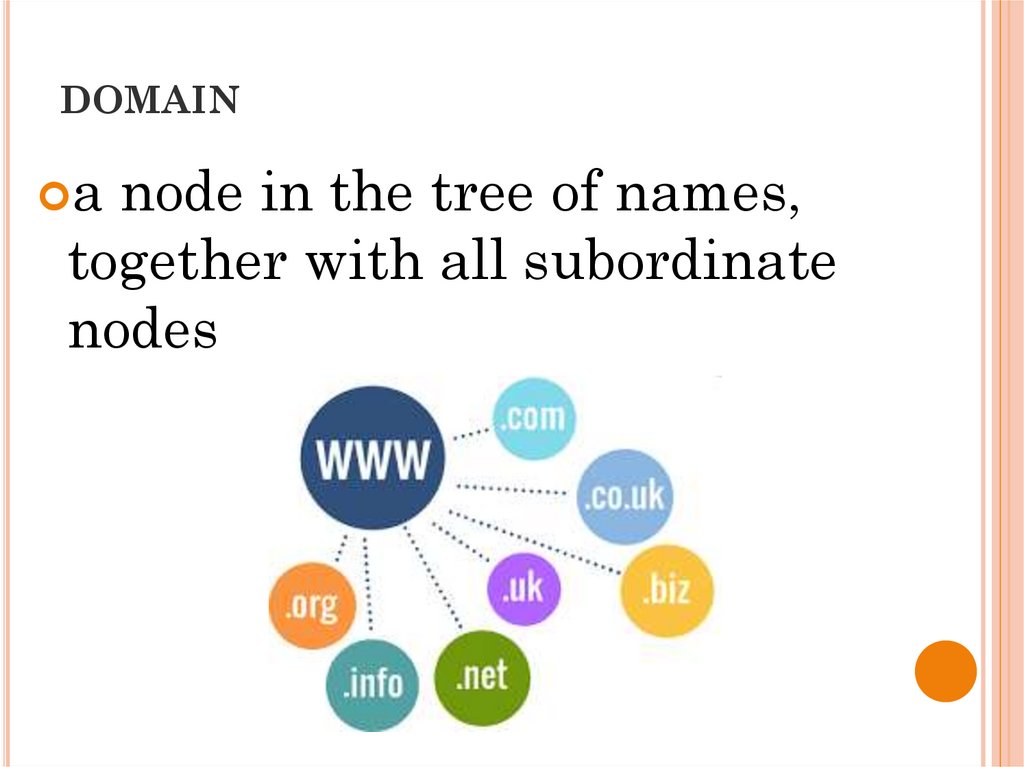
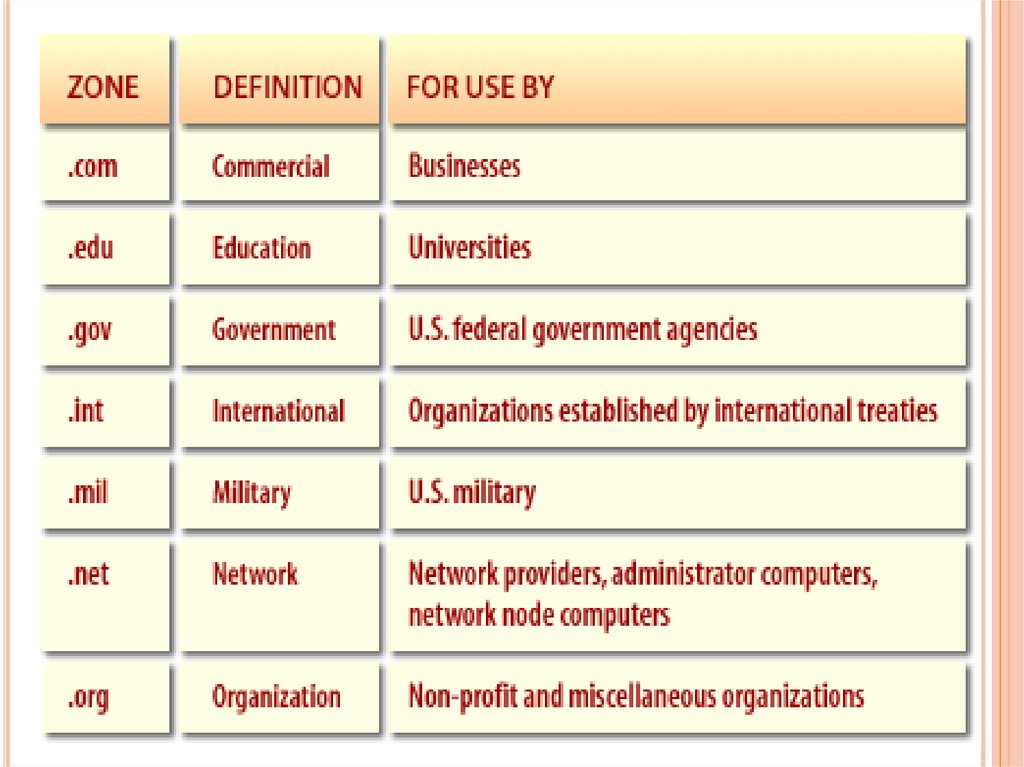
DOMAINa node in the tree of names,
together with all subordinate
nodes
20.
21.
HYPERTEXT TRANSFER PROTOCOLapplication layer protocol
of data transmission
22.
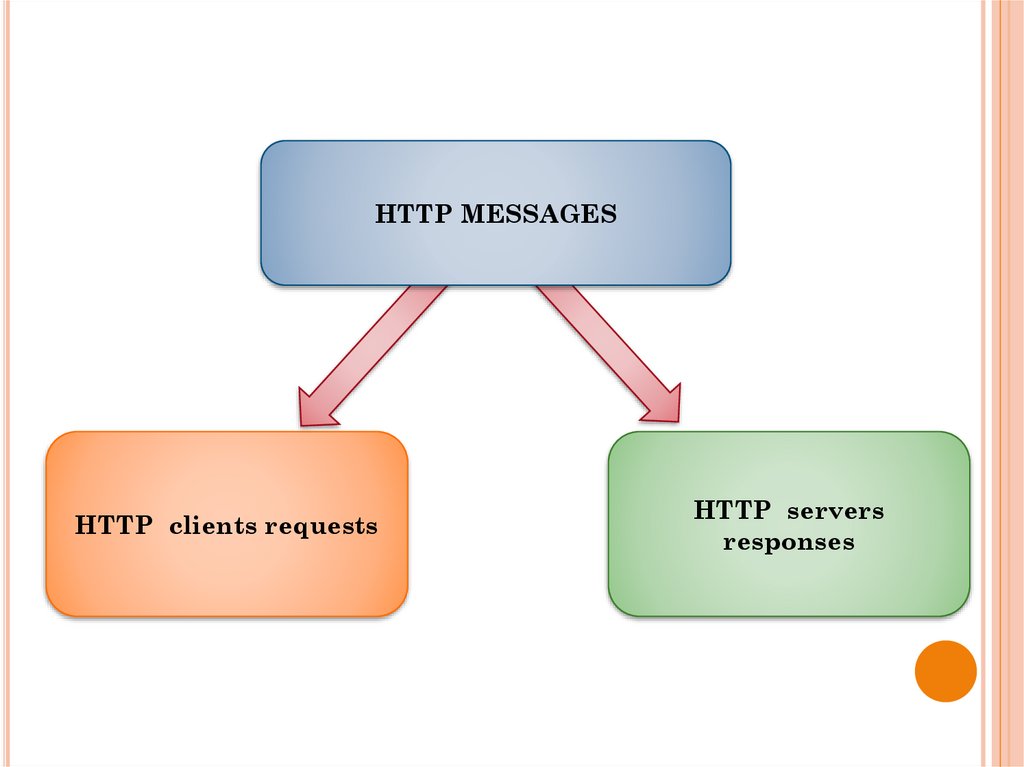
HTTP MESSAGESHTTP clients requests
HTTP servers
responses
23.
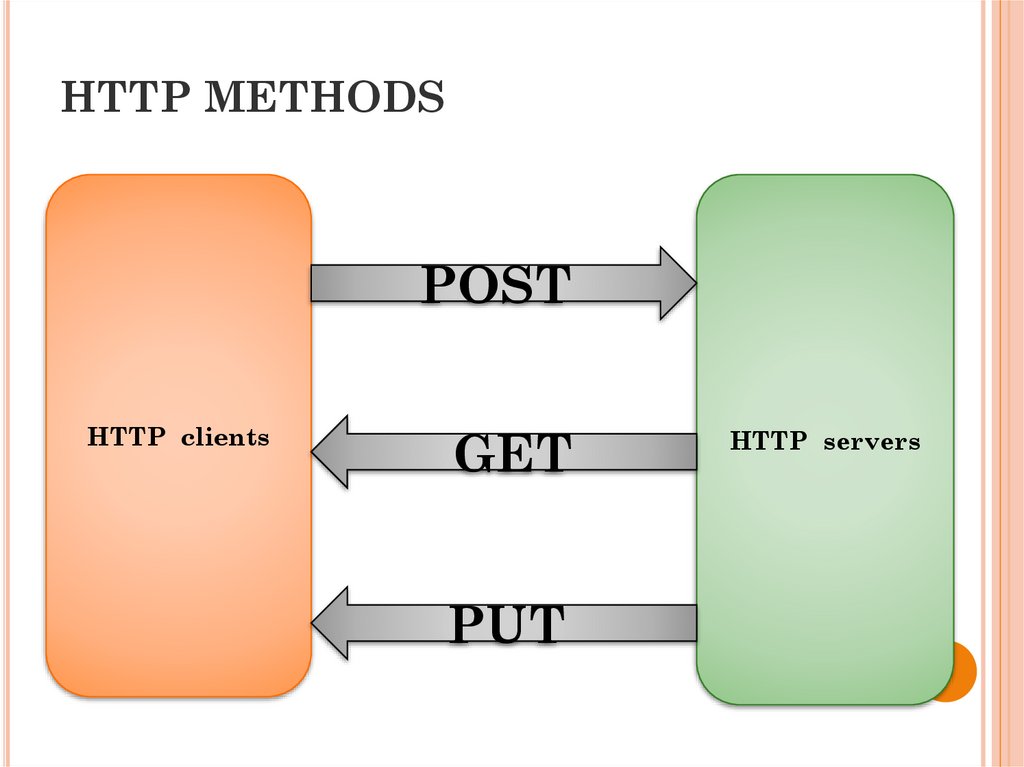
HTTP METHODSPOST
HTTP clients
GET
PUT
HTTP servers
24.
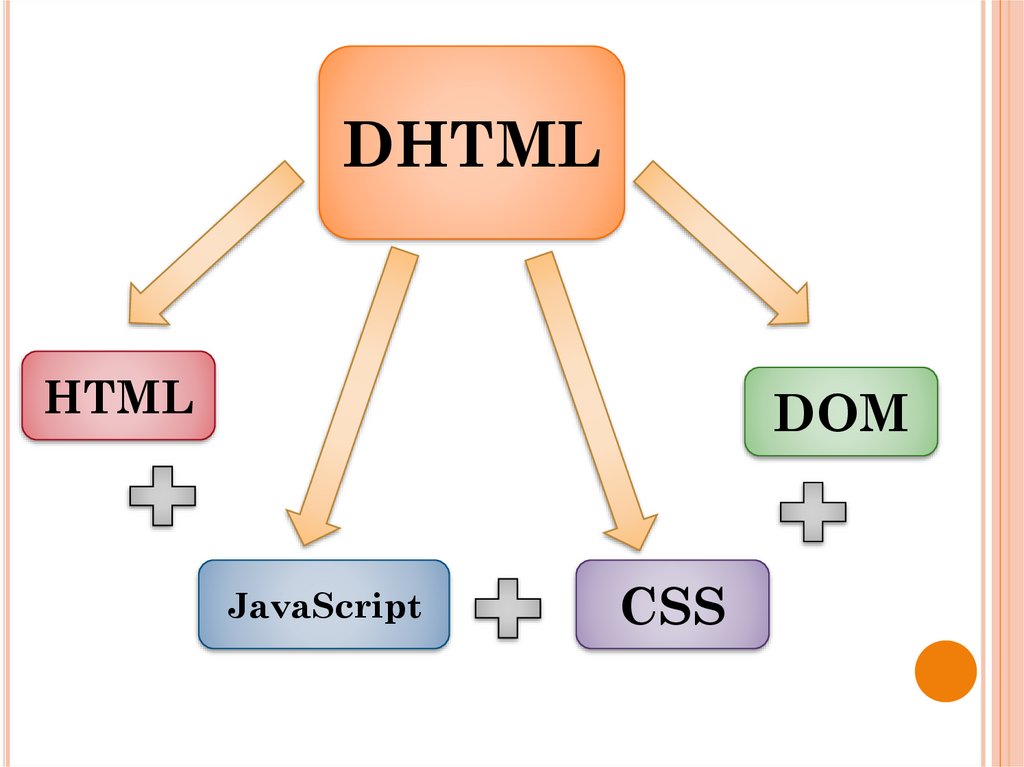
DHTMLHTML
DOM
JavaScript
CSS
25.
HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE (HTML)standardized markup language for
documents on the world wide web.
26.
JAVASCRIPTprogramming language that adds
interactivity to the web site
27.
AJAXapproach to building interactive user
interfaces of web applications, based on the
"background" data-sharing between browser
and web server.
28.
CASCADING STYLE SHEETS (CSS)technology of description of the
appearance of a document executed
by the markup language
29.
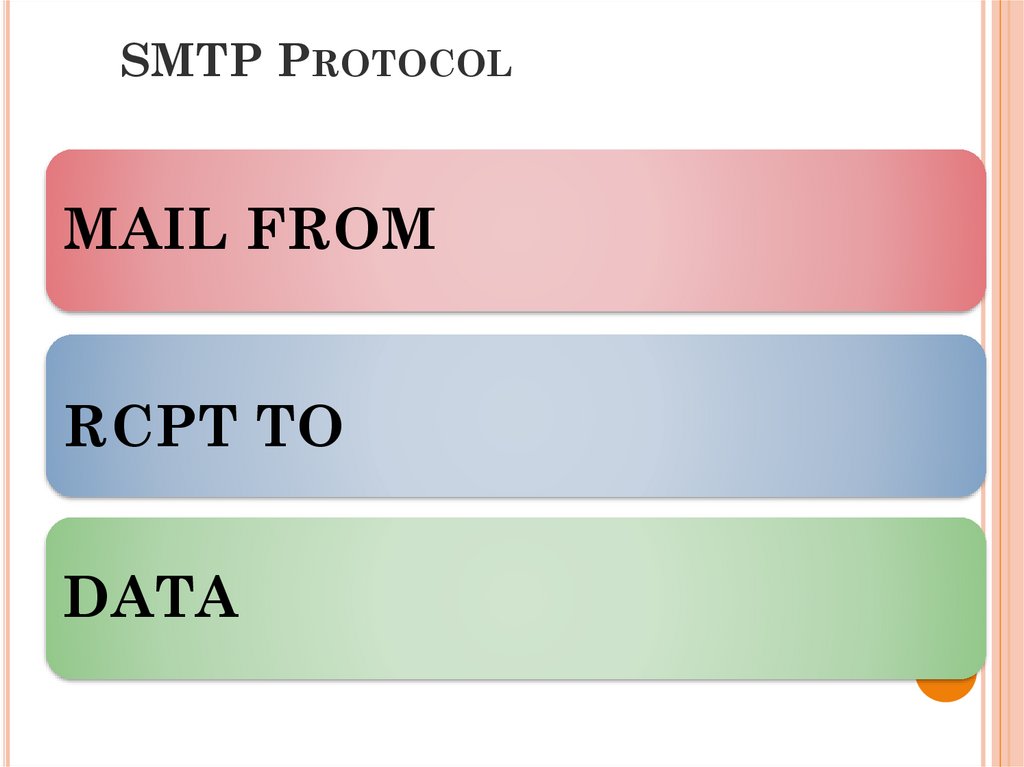
SMTP PROTOCOLMAIL FROM
RCPT TO
DATA
30.
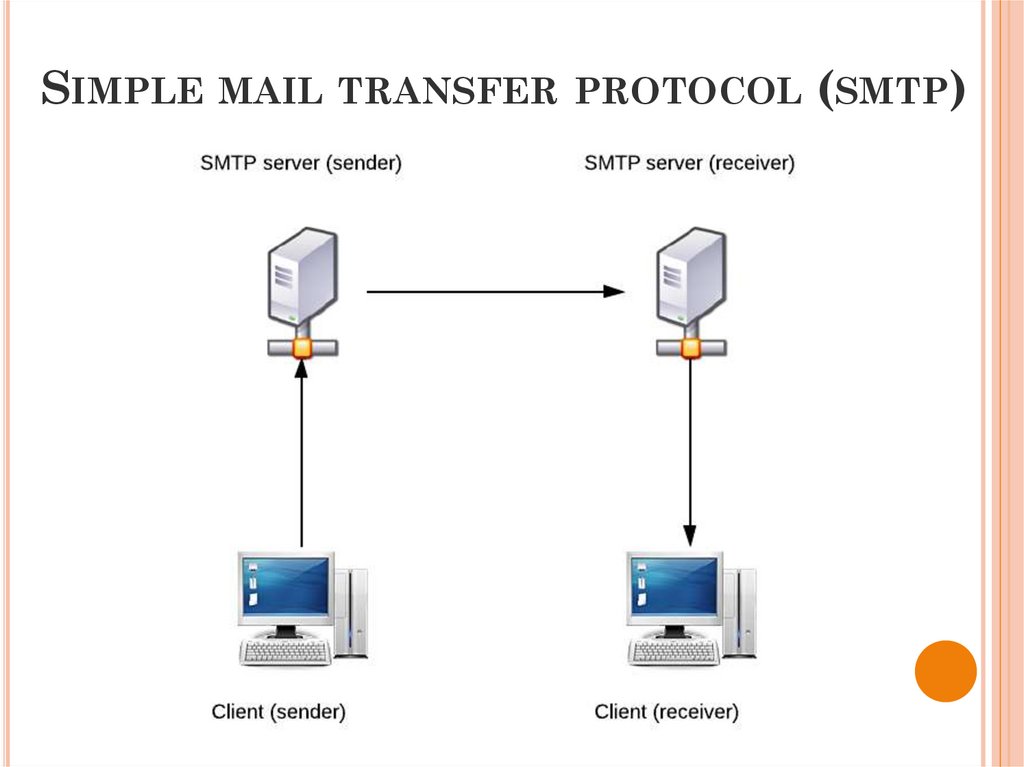
SIMPLE MAIL TRANSFER PROTOCOL (SMTP)31.
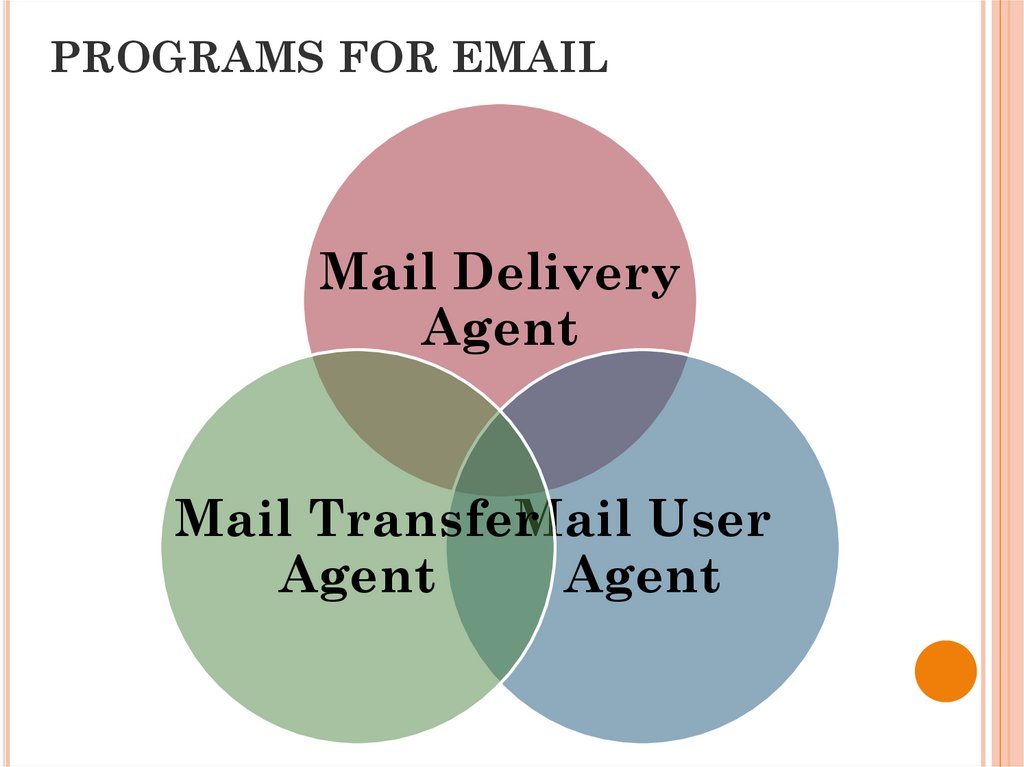
PROGRAMS FOR EMAILMail Delivery
Agent
Mail Transfer
Mail User
Agent
Agent
32.
CONCLUSIONURI
for identification of the web
resources
CSS for style of HTML documents
JavaScript for interaction of user and
web-srever
IMAP, POP3 protocols for receiving

















 internet
internet








