Similar presentations:
Хранение данных
1.
ЧТО ВЫ ВИДИТЕ?2.
NISХРАНЕНИЕ
ДАННЫХ
3.
ЦЕЛИ ОБУЧЕНИЯ01
- К ЛАССИФ ИЦИРОВАТЬ ВИД Ы П АМЯТИ
02
- с ра внива ть ха ра ктеристики жес тких дис ков и твердотельных
на копителей
4.
ГЛОССАРИЙMain memory
RAM(random ac c ess memory)
ROM (read onl y memory)
Primary memory
Secondary memor y
Stores program instructions and frequently used data
a fast temporary type of memory
a memory that cannot be changed by a program or user.
a synonym for Main memory
the external memory and stores data permanently.
5.
ХРАНЕНИЕ ДАННЫХэто важный аспект информационн ы х технологий , и д ля понимания
этой темы , давайте начнем с к лассификации различн ы х видов
памяти и затем сравним характеристики жестких дисков и
твердоте льн ы х накопителей .
• К лассификация вид ов памяти :
⚬ Оперативная память (RAM - Random Acce ss Me mo ry):
⚬ П остоянная память ( R O M - Re ad - Only Me mo ry):
⚬ Жесткие д иски (H DD - H ard D isk D rive s):
⚬ Тверд отельные накопители (SSD - So lid State Drive s):
6.
RAMRAM ( R A M - R a n d o m A c c e s s M e m o r y ) представляет собой
"рабочую " память компьютера , которая используется д ля
временного хранения данных , когда компьютер работает .
Эта память быстро дост упна , но не сохраняет данные при
вык лючении компьютера .
7.
ROMПостоянная память (ROM - Read -Only Memory):
ROM - это память , которая содержит постоянные данные ,
которые не могу т быть изменены . Это, например , BIOS на
материнской плате компьютера .
Эта память дост упна при вк лючении компьютера и не теряется
после его вык лючения .
8.
HDDЖесткие диски (HDD - Hard Disk Drives):
HDD - это механические устройства , используемые д ля хранения
данных на магнитных дисках .
Они пред лагают большой объем хранения данных , но мед леннее
в сравнении с твердотельными накопителями .
9.
SSDТвердотельные накопители (SSD - Solid State Drives):
SSD - это устройства без подвижных частей , используемые д ля
хранения данных на микрочипах .
Они обычно быстрее по сравнению с HDD и обладают высокой
надежностью .
10.
GROUP WORKСДЕЛАТЬ ПОСТЕР (ОПИШИТЕ
ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ, КАЧЕСТВО И ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ)
Group 1
Характеристики
HDD
Group 2
Хар актер истики
SSD
Group 3
ГИБ РИДНЫЙ
SSHD
11.
ДЛЯ ЧЕГО ИСПОЛЬЗУЕТЬСЯHDD
SSD
12.
REFLECTION"What did you
find most
interesting or
engaging about
today's lesson?"
"Is there
something you
still don't
understand or
need further
clarification on?"
"Do you have
any suggestions
for improving
future lessons
on this topic?"
13.
ДОП ИНФОРМАЦИИ14.
TYPES OF COMPUTERR MEMORY15.
Memory is an essential part of a computer. It stores data and instructions.We have divided the whole memory system of a computer into 4 different
categories.
01
02
03
04
CPU REGISTER
CACHE
PRIMARY
SECONDARY
ar e smal l , high - speed
sto r age l o cations
within the CPU of a
co mp uter or
micr o p r o cessor.
T hese r egisters are
used to sto r e and
manip ulate data
temporarily during
p r o gr am ex ecution
is a s mall, high -s peed
data s torage layer
that s its between a
s lower, larger, and
more -distant RAM
and a fas ter, s maller,
and clos er proces s or
or CPU .
is a crucial component
of a computer's
architecture. It is a
type of volatile
memory that s erves as
the primary works pace
for a computer's
operating s ys tem,
applications , and data
during active us e.
is a type of non volatile memory
used in computing
to store data and
programs for long term or persistent
storage.
16.
MEMORY HIERARCHY17.
Memory can beeither volatile and
non-volatile
memory.
COMPUTER MEMORY
Volatile memory is
a memory that loses
its contents when
the computer or
hardware
device
loses power.
Non-volatile is the
opposite,
the
content is not lost
when the computer
is turned off I.e
operating
system
memory.
Note: Hard-Disk, CD,
DVD,
Floppy-Disk,
Magnetic Tape are
18.
READ -ONLY MEMORY (ROM):Read-Only Memory (ROM):
• ROM is non-volatile memory that contains firmware or software
instructions essential for booting and initializing hardware
components.
• It retains its data even when the computer is powered off.
• Examples of ROM include BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) in PCs and
firmware in game consoles.
19.
HARD DISK DRIVE (HDD):• HDDs are non-volatile storage devices used for long-term data
storage.
• They use spinning disks to read and write data magnetically.
• HDDs have larger storage capacities but are slower than solidstate drives (SSDs).
20.
VIRTUAL MEMORY:- Purpose: Virtual memory is a memory management
technique used by operating systems to provide the
illusion of having more physical RAM than is actually
installed in the computer.
- How it works: When the physical RAM is fully utilized,
the operating system moves less frequently used data from
RAM to a portion of the hard drive or SSD called the "page
file" or "swap space." This frees up space in physical RAM for
more important and active processes.
- Benefits: Virtual memory helps prevent the system from
running out of memory and crashing. It allows multitasking
and running larger applications by using a combination of
physical RAM and disk storage for data storage.
21.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.HOW DOES A COMPUTER WORK WITH
MEMORY?
22.
CACHE MEMORY:- Purpose: Cache memory is a small, high-speed volatile memory located between the CPU and main
memory (RAM). Its primary purpose is to provide faster data access to the CPU.
- How it works: Cache memory stores frequently accessed data and instructions from RAM. When
the CPU needs data, it checks the cache first. If the required data is found in the cache (a cache hit), it
can be accessed much more quickly than if it had to be retrieved from the slower RAM (a cache miss).
- Benefits: Cache memory significantly improves CPU performance by reducing the time it takes to
access frequently used data. There are different levels of cache (L1, L2, L3) with varying sizes and
speeds, with L1 being the fastest but smallest and closest to the CPU.
23.
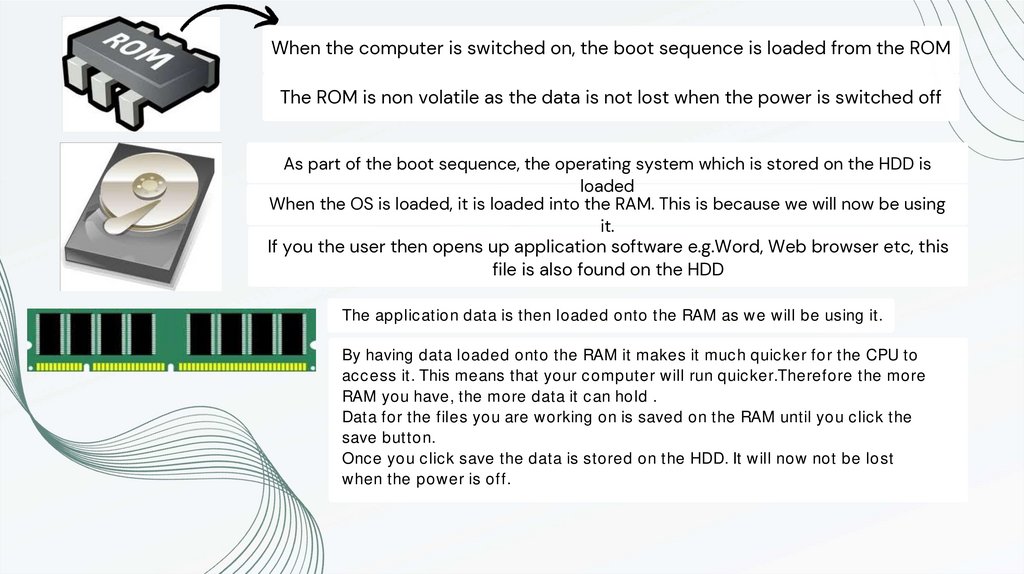
When the computer is switched on, the boot sequence is loaded from the ROMThe ROM is non volatile as the data is not lost when the power is switched off
As part of the boot sequence, the operating system which is stored on the HDD is
loaded
When the OS is loaded, it is loaded into the RAM. This is because we will now be using
it.
If you the user then opens up application software e.g.Word, Web browser etc, this
file is also found on the HDD
The application data is then loaded onto the RAM as we will be using it.
By having data loaded onto the RAM it makes it much quicker for the CPU to
access it. This means that your computer will run quicker.Therefore the more
RAM you have, the more data it can hold .
Data for the files you are working on is saved on the RAM until you click the
save button.
Once you click save the data is stored on the HDD. It will now not be lost
when the power is off.
24.
So why do we not just store data straight away on the HDD andforget about the RAM?
It takes a lot longer for the data to be retrieved and stored on the HDD
than the RAM so saving it on the HDD all the time would slow down
your computer a lot
So now data is in the RAM this means that we are using it. Therefore this
also means that the CPU is going to want to access it.
The CPU could get the data from the RAM each time it needs to
complete a process but even this would still take too long
There is another type of memory called cache. This is often built into the CPU.
Data stored on the cache is very quick for the CPU to access. Therefore data that the
CPU is going to process is taken from the RAM and put onto the cache .
A computer will only have a small amount of cache but the more it has, the quicker the
CPU can process data and the quicker your computer will run
25.
Secondary Storage: e.g. hard drive, USB, SD Card, CD etc will have alarge amount of storage for a relatively cheap price. For example a
typical computer will now have a build in hard drive of around 1TB. All
of this type of storage is non volatile
Primary Storage: You will have less RAM and it can be quite expensive.
A typical computer may now have around 8Gb of RAM built in. This
type of storage is volatile
Primary Storage: The cache memory is often built into the CPU and
only has a small amount of memory. This can be very expensive. This
type of storage is volatile
26.
Non Volatile so stores data when power is turned off.Stores Operating system, application software and all data files.
When required by the computer they are found on the HDD and
moved to the RAM
The data held here is what is being worked on. When it is going to be
needed by the CPU it is moved to the Cache. When it needs to be
permanently saved or not used anymore it is moved back to the HDD
When the CPU needs data to process it first looks at the Cache. If it is
not there it requests the data from the RAM which may then request
it from the HDD. The data on the CPU can be processed quickly.
27.
QUIZLEThttps ://quizlet.com/266600675/learn
80%
28.
GOALS01
T H E DIFFER ENCES BET WEEN R AM AND R O M MEMO R Y
02
T H E P UR P O SE O F VIR T UAL MEMO R Y
03
T H E P UR P O SE O F CACH E MEMO R Y
29.
THANK'S FORWATCHING
NIS



























 informatics
informatics








