Similar presentations:
Organic chemistry
1.
CHEMISTRYSarybaev Mirlan
2.
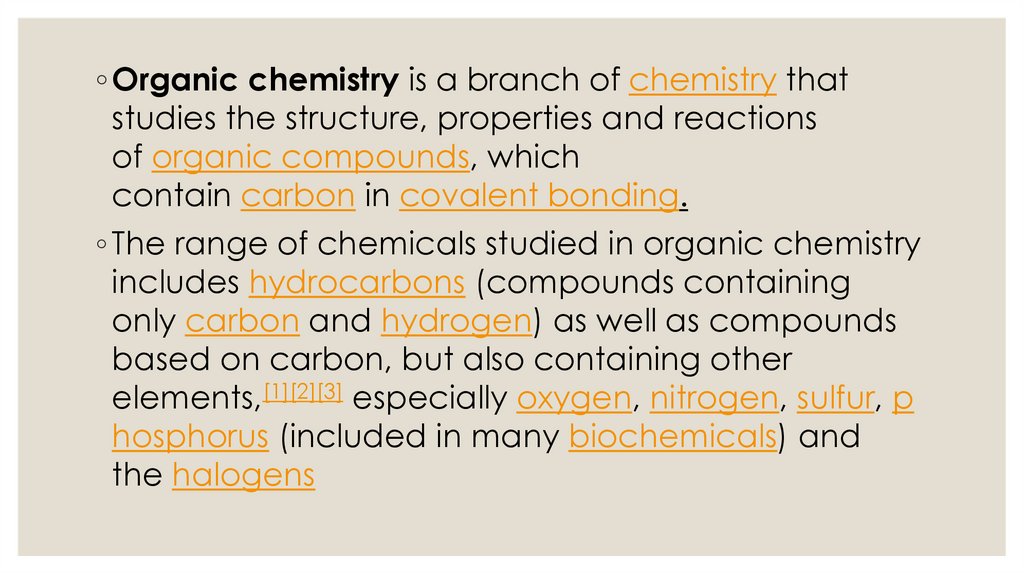
◦ Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry thatstudies the structure, properties and reactions
of organic compounds, which
contain carbon in covalent bonding.
◦ The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry
includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing
only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds
based on carbon, but also containing other
elements,[1][2][3] especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, p
hosphorus (included in many biochemicals) and
the halogens
3.
◦Organic chemistry is the chemistry of paints, plastics, drugs,
dyes, paper, ink,gasoline and rubbers.
4.
Most of the medicines that we useare also organic. Almost all of our
food and many food additives are
organic and all polymers we use in
our life such as polyethylene,
polypropylene, teflon, polystyrene
etc. are organic.
5.
The most commonelements in
organic
compounds are
carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen and
nitrogen. These
four elements
form 95% of the
human body.
Organic compounds are generally not
soluble in water
6.
7.
8.
CHEMICAL BOND◦What are the reasons that cause iron to be solid,
water to be liquid and hydrogen
to be a gas at room temperature?
• Why is diamond hard while wax is soft?
◦Why do some solids melt at low temperatures
while others melt at high temperatures?
9.
The force of attraction thatholds atoms or ions together is called
a chemical bond.
10.
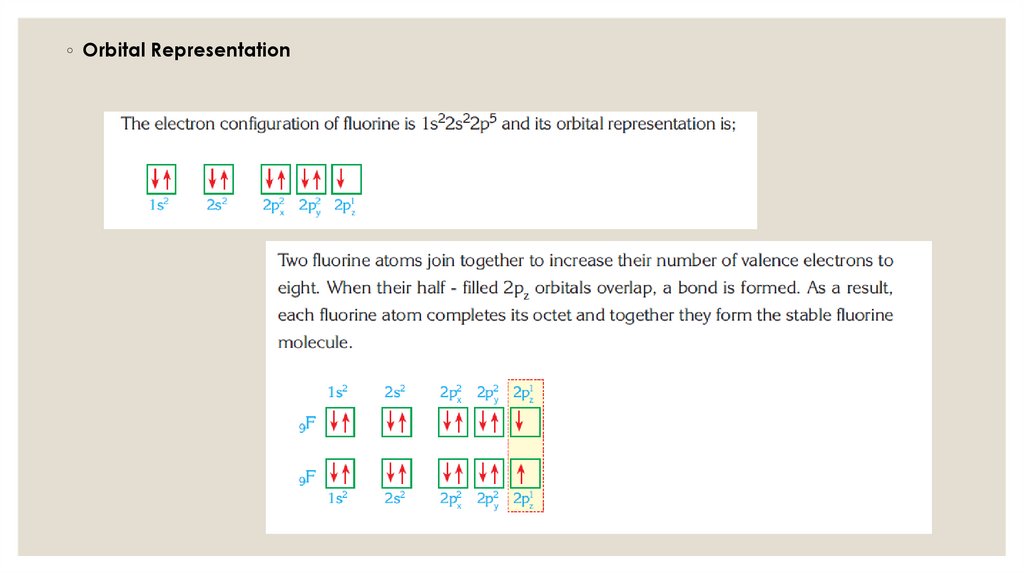
◦ Orbital Representation11.
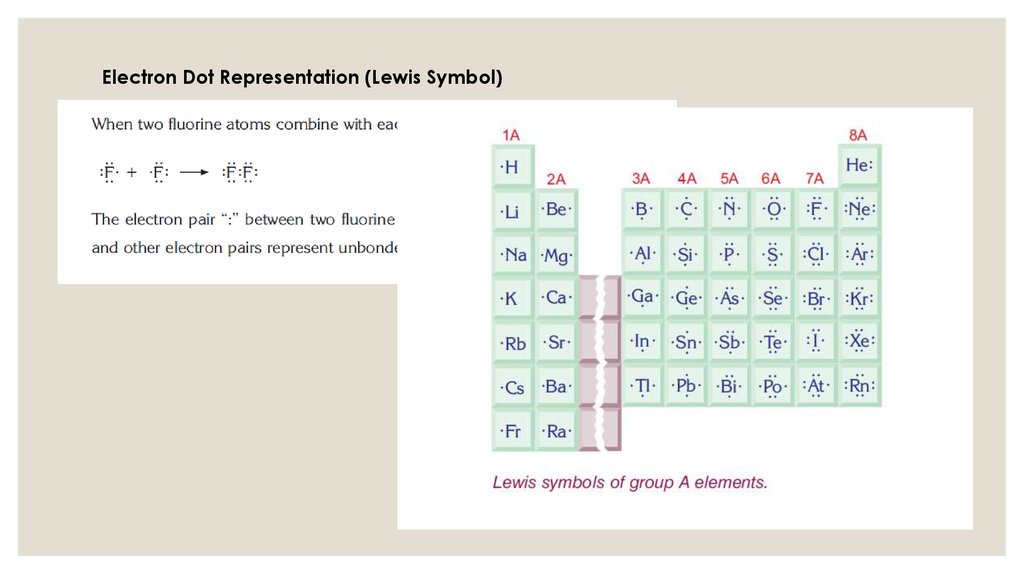
Electron Dot Representation (Lewis Symbol)12.
IONIC BONDSIonic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one
atom to another.
After the transfer of electrons, the atom that lost electrons
becomes positively
charged and the atom that gained electrons becomes
negatively charged. The
force of attraction that holds these atoms together is the
electrostatic force
between their opposite charges.
13.
14.
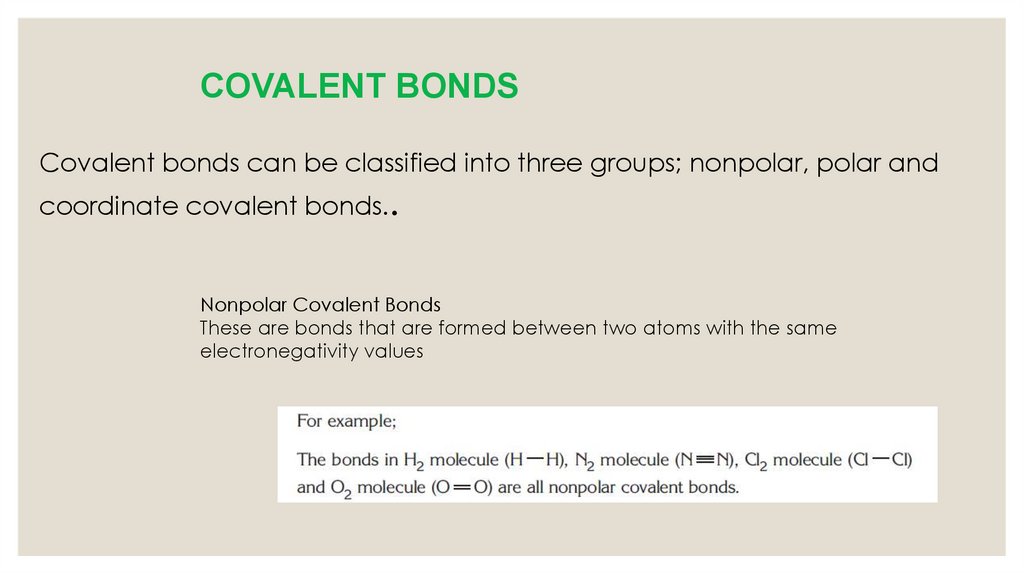
COVALENT BONDSCovalent bonds can be classified into three groups; nonpolar, polar and
coordinate covalent bonds..
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
These are bonds that are formed between two atoms with the same
electronegativity values
15.
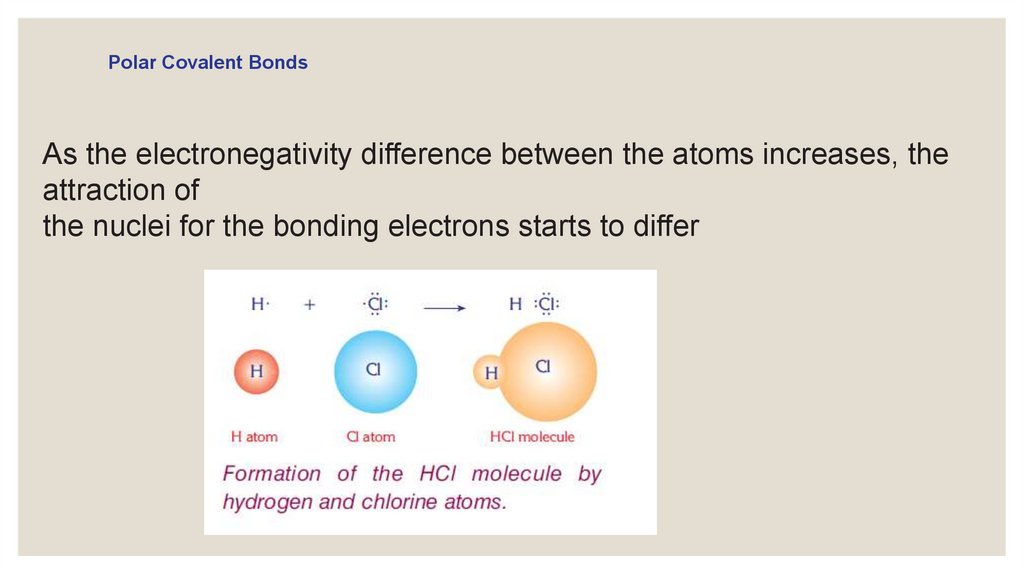
Polar Covalent BondsAs the electronegativity difference between the atoms increases, the
attraction of
the nuclei for the bonding electrons starts to differ
16.
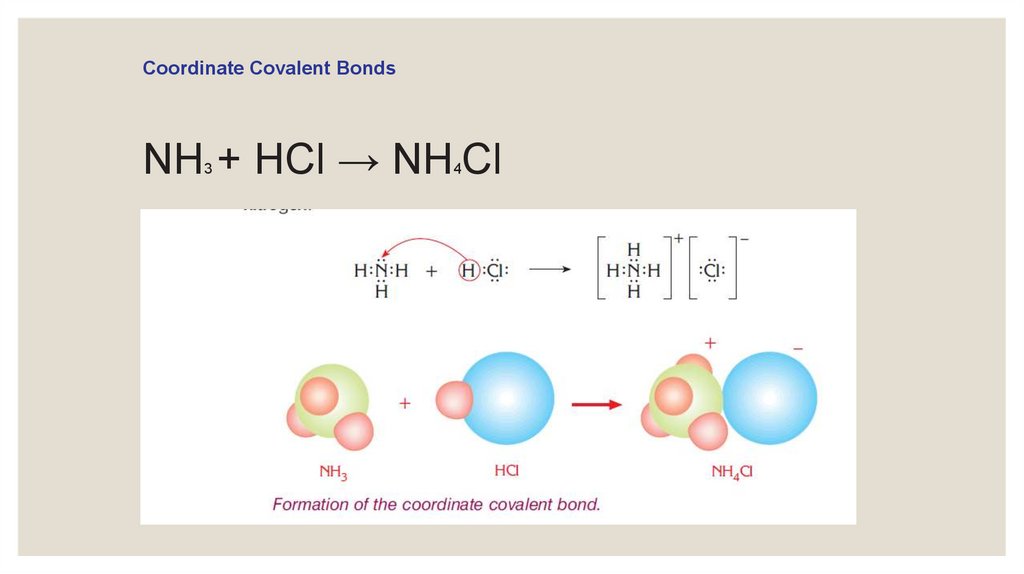
Coordinate Covalent BondsNH + HCl → NH Cl
3
4
17.
18.
19.
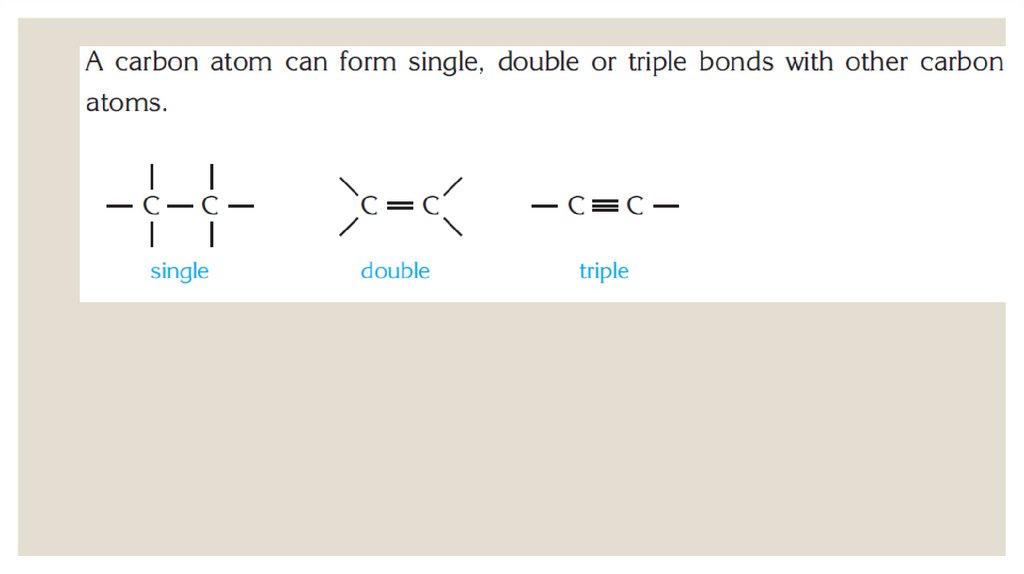
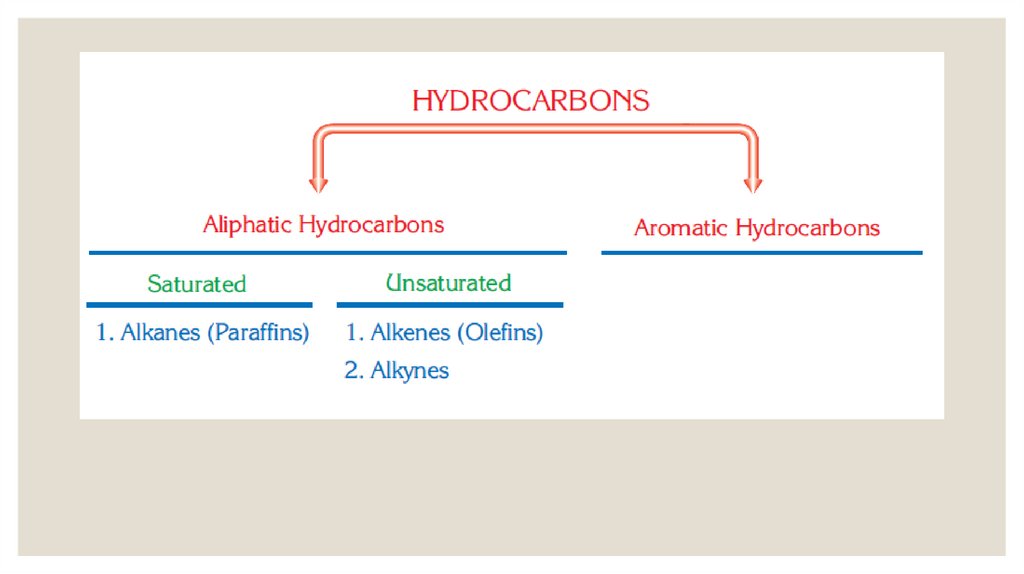
ALKANES◦ In alkanes or saturated hydrocarbons, each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds.
These bonds are C C and C H sigma bonds.
CnH2n+2 , where n is an integer and
◦ The general formula of the alkanes is
indicates the number of carbon atoms.
20.
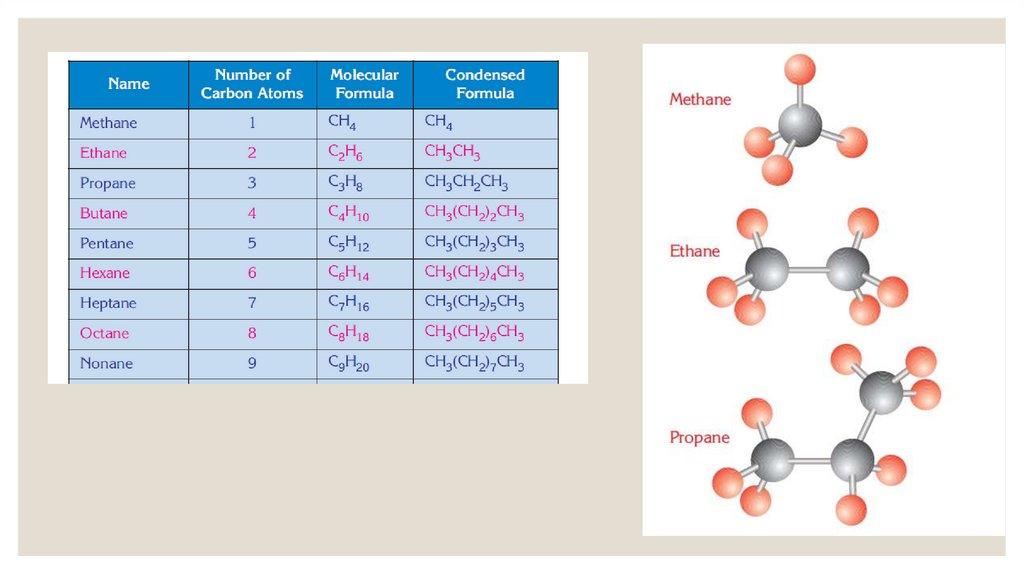
◦ The first four members of the alkanes have common names: methane (CH4),ethane(C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10). After the fourth carbon, Latin numbers are
used to name alkanes.
◦ For example: Five is penta in Latin.C5H12 is named penta + ane = pentane.
21.
22.
EXAMPLE:◦ What is the molecular formula of a saturated hydrocarbon if 0.05 moles of
the compound has a mass of 3.6 grams? (C:12, H:1)
◦ SOLUTION:












 chemistry
chemistry








