Similar presentations:
Healthy unhealthy food
1.
2.
3.
So, what are we discussing about today?4.
Theme:5.
Интеграция дисциплин: английскийязык, биология, химия и экология
Цель урока:
формирование понятия о ценности
пищевых
продуктов,
закрепление,
осмысление изученного материала по
английскому языку, биологии и экологии,
химии.
6.
The Problem:Genetically Modified Food:
Good or Bad?
7.
broader endeavor – всеобъемлющее усилиеdrought - засуха
trait – признак
recombinant - искусственно созданный
sources – источники
can be expressed – может
быть выражен
multiplying – размножаясь
harvest – результат
deoxyribonucleic diˈɒksɪˈraɪboʊnuˈkliɪk acid дезоксирибонуклеиновая кислота
nucleotide |ˈnjuːklɪətʌɪd| - нуклеотид
nitrogen – азотный
determine – определять, ограничивать
sequence – последовательность
proponent – сторонник
assist – помочь воздействовать
crops – зерновые
resist – сопротивляться
depleted – истощенные
excess - избыток
8.
Аутентичный текст из учебника “Biology ofHuman”, Person International, USA, 2007
“Genetically Modified Food and Social concerns”
From dinner tables to diplomatic circle, people are now discussing
genetically modified (GM) food. What is Genetically Modified Food?
Genetically modified (GM) food is a result of genetic engineering.
Genetic engineering is part of the broader endeavor of
biotechnology, a field in which scientists make controlled use of
living cells to perform specific tasks. So, the basic idea behind
genetic engineering is to put a gene of interest, one that produces a
useful protein or trait, into another piece of DNA to create
recombinant DNA, which is DNA combined from two or more
sources. The recombinant DNA (segments of DNA from two sources
that have been combined in vitro and transferred to cells in which
their information can be expressed), carrying the gene of interest, is
then placed into a rapidly multiplying cell that quickly produces
many copies of the gene.
9.
The final harvest may consist of large amounts of the gene productor many copies of the gene itself.
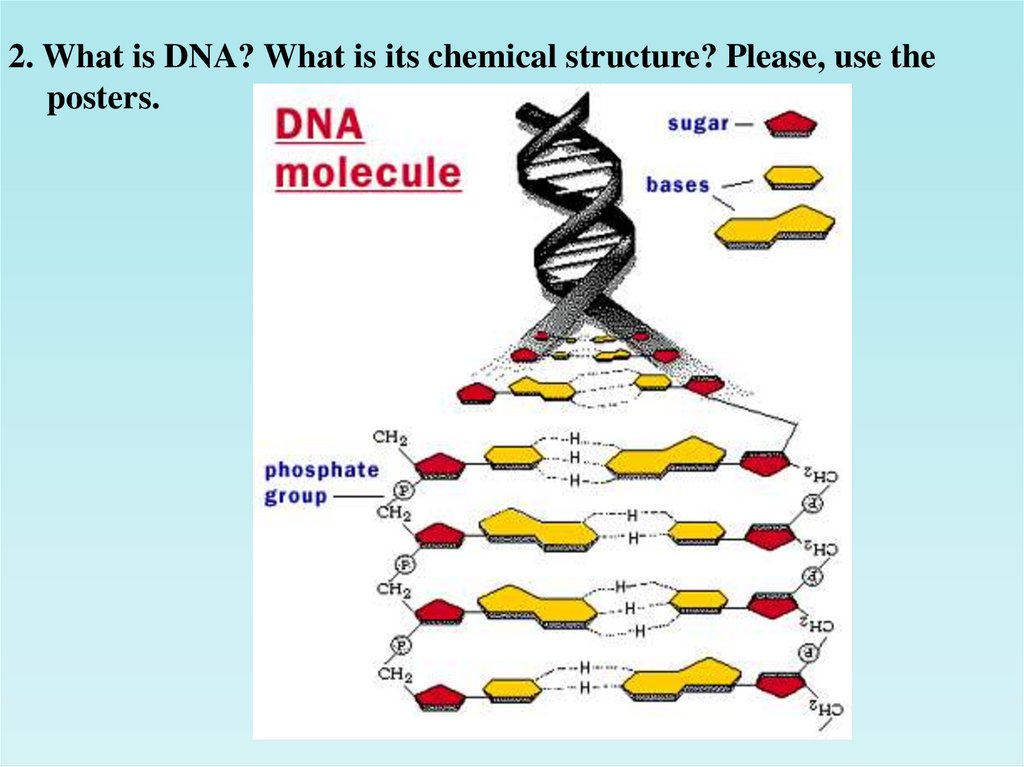
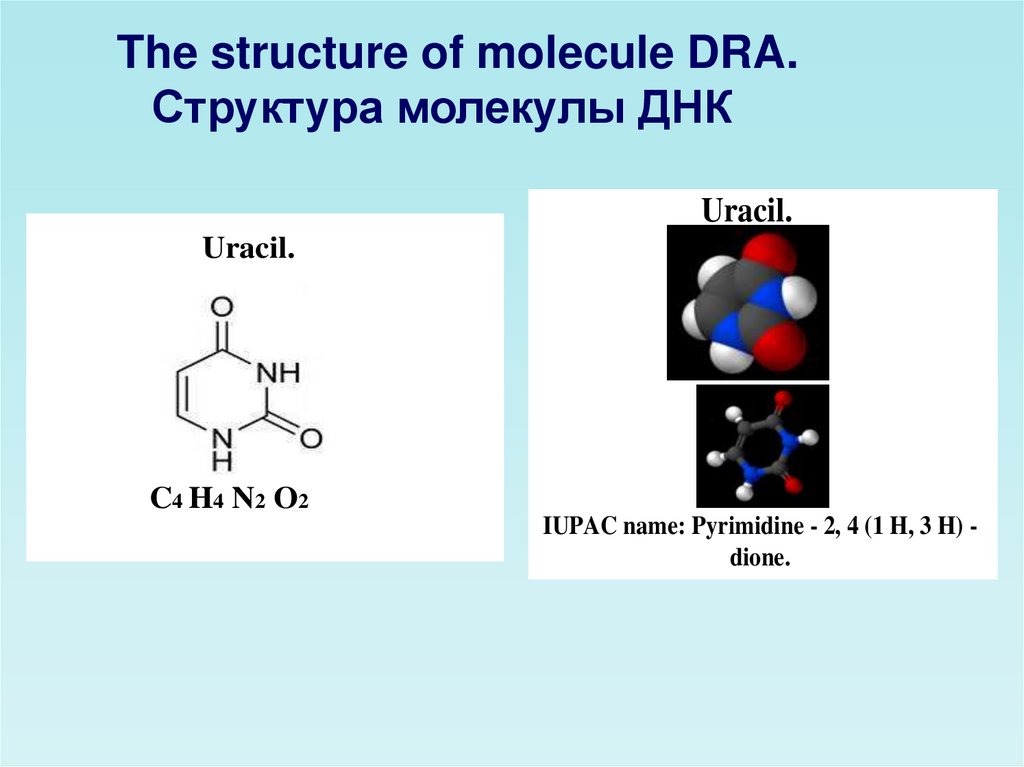
What is DNA? DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is one of the two types
of nucleic acids. It has smaller units called nucleotides, joined into
chains through dehydration synthesis.
Every nucleotide monomer consists of a five-carbon (pentose) sugar
bonded to one of five nitrogen-containing bases and at least one
phosphate group. The five nitrogen-containing bases are adenine,
guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Some of the bases (cytosine,
thymine, and uracil) have a single ring made of carbon and nitrogen
atoms. The other (adenine and guanine) have two such rings. The
sequence of bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in
a protein. DNA, as we said above, is the nucleic said found in genes.
10.
Proponents of GM food claim that GM food can assist in thebattle against world hunger. We have seen that genetic
engineering can produce crops that resist pests and
disease. It can also produce crops with greater yields and
crops that will grow in spite of drought, depleted soil, or
excess salt, aluminum, or iron. Foods can also be genetically
modified to contain higher amounts of specific nutrients.
One example is the “golden rice” mentioned in this chapter.
More than 100 million children worldwide suffer from
vitamin A. A deficiency, and 500,000 of them go blind every
year because of that deficiency.
11.
Although golden rice cannot supply a completerecommended daily dose of vitamin A, the amount it
contains could be helpful to a person whose diet is very low
in vitamin A.
Critics of using GM food to battle world hunger
argue that the problem of hunger has nothing to do with an
inability to produce enough food. The problem, they say, is
a social one of distributing food so that it is available to the
people who need it.
12.
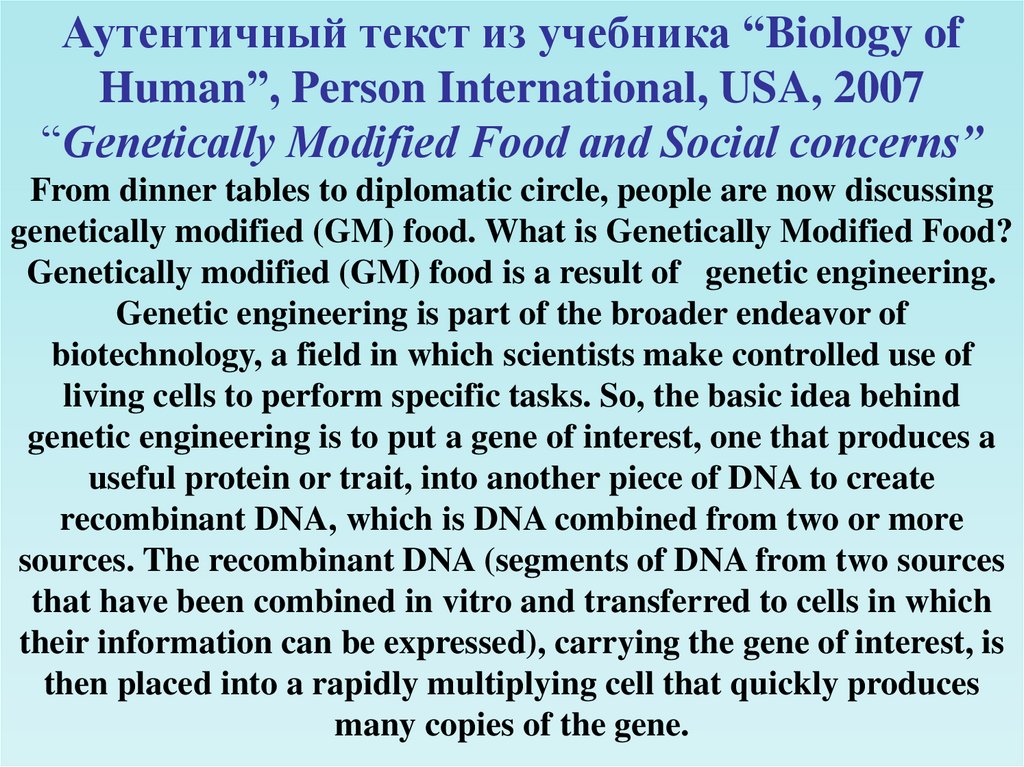
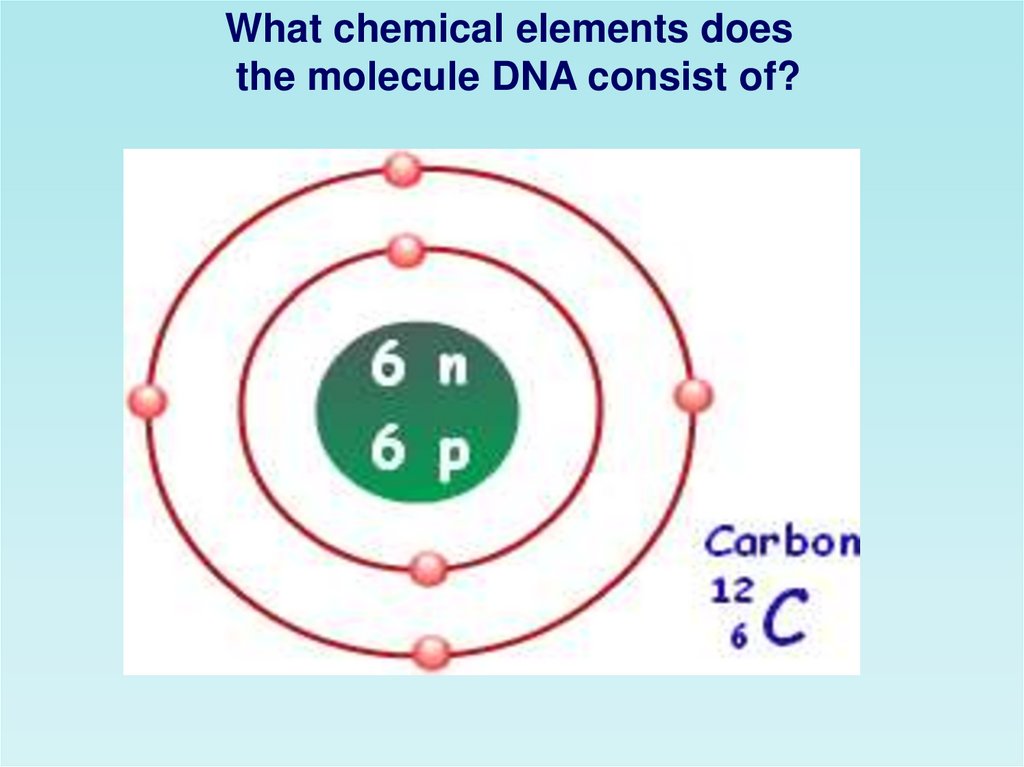
What chemical elements doesthe molecule DNA consist of?
H
Nitrogen.
Hydrogen.
13.
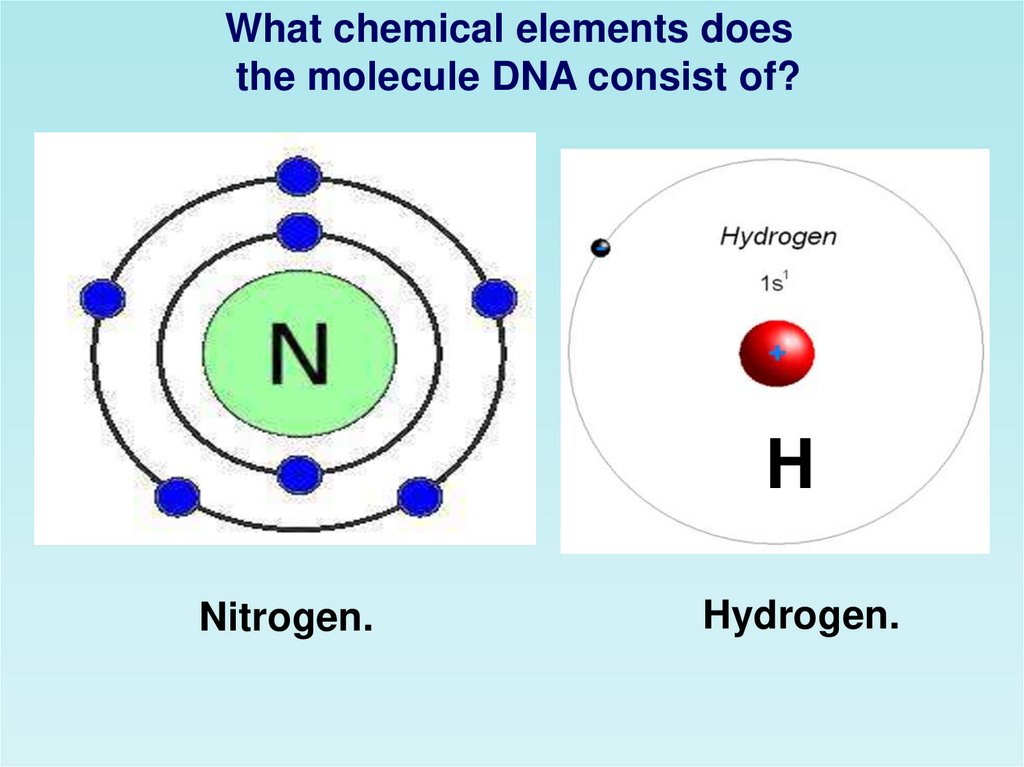
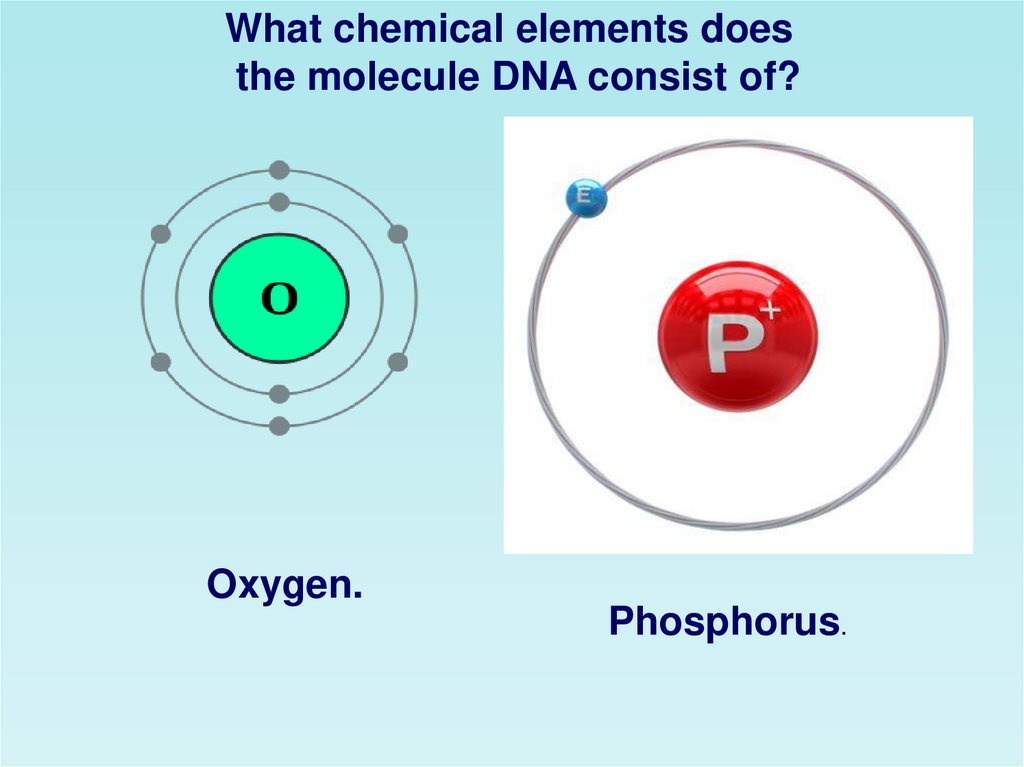
What chemical elements doesthe molecule DNA consist of?
Oxygen.
Phosphorus.
14.
What chemical elements doesthe molecule DNA consist of?
carbonium
15.
Аутентичный текст из учебника “Biology of Human”,Person International, USA, 2007 “Genetically Modified
Food and Social concerns”
The questions:
1. What is Genetically Modified Food? What is genetic engineering?
16.
2. What is DNA? What is its chemical structure? Please, use theposters.
17.
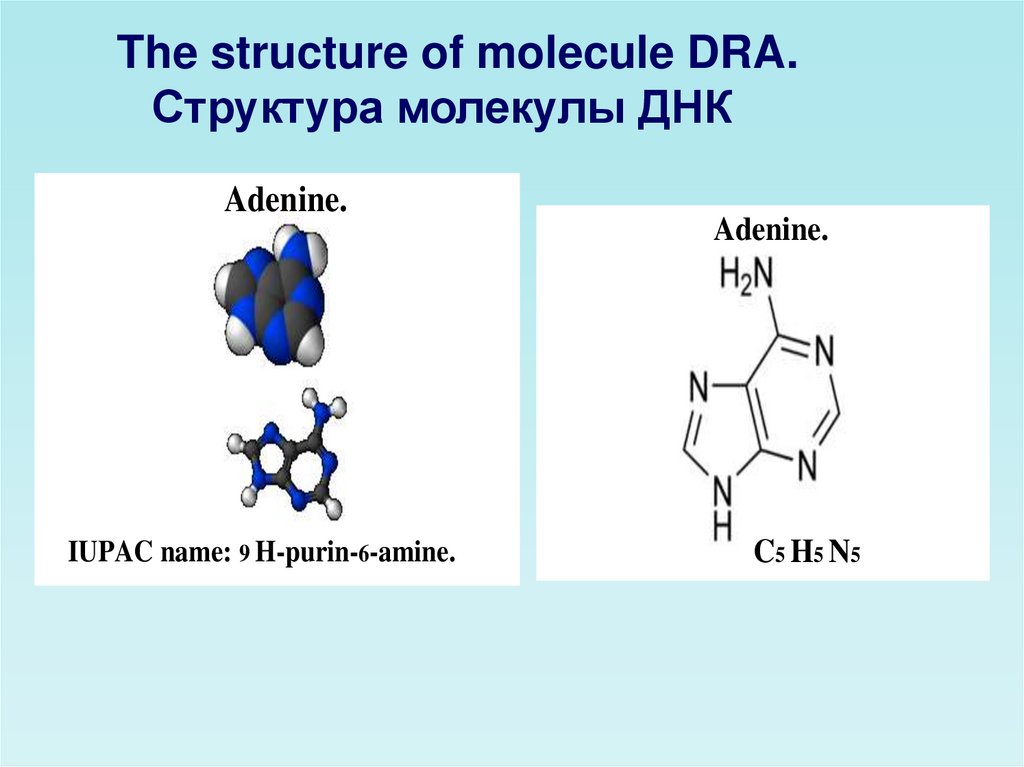
The structure of molecule DRA.Структура молекулы ДНК
Adenine.
Adenine.
IUPAC name: 9 H-purin-6-amine.
C5H5N5
C5 H5 N5
18.
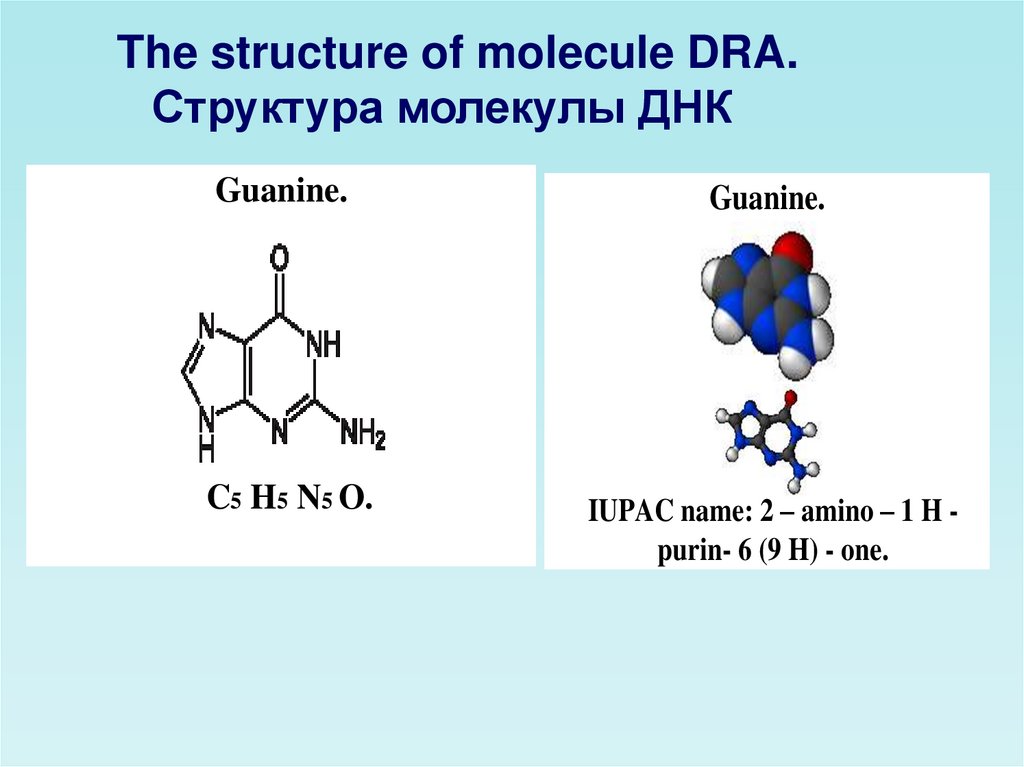
The structure of molecule DRA.Структура молекулы ДНК
Guanine.
Guanine.
C5 H5 N5 O.
IUPAC name: 2 – amino – 1 H purin- 6 (9 H) - one.
19.
The structure of molecule DRA.Структура молекулы ДНК
Uracil.
Uracil.
C4 H4 N2 O2
IUPAC name: Pyrimidine - 2, 4 (1 H, 3 H) dione.
20.
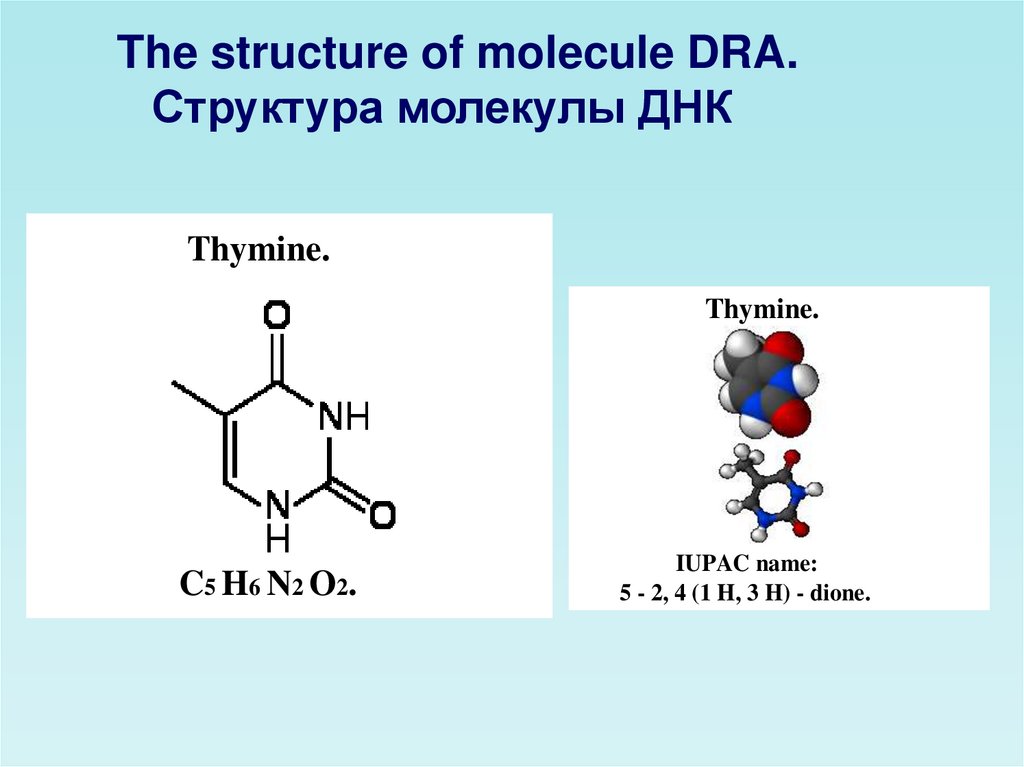
The structure of molecule DRA.Структура молекулы ДНК
Thymine.
Thymine.
C5 H6 N2 O2.
IUPAC name:
5 - 2, 4 (1 H, 3 H) - dione.
21.
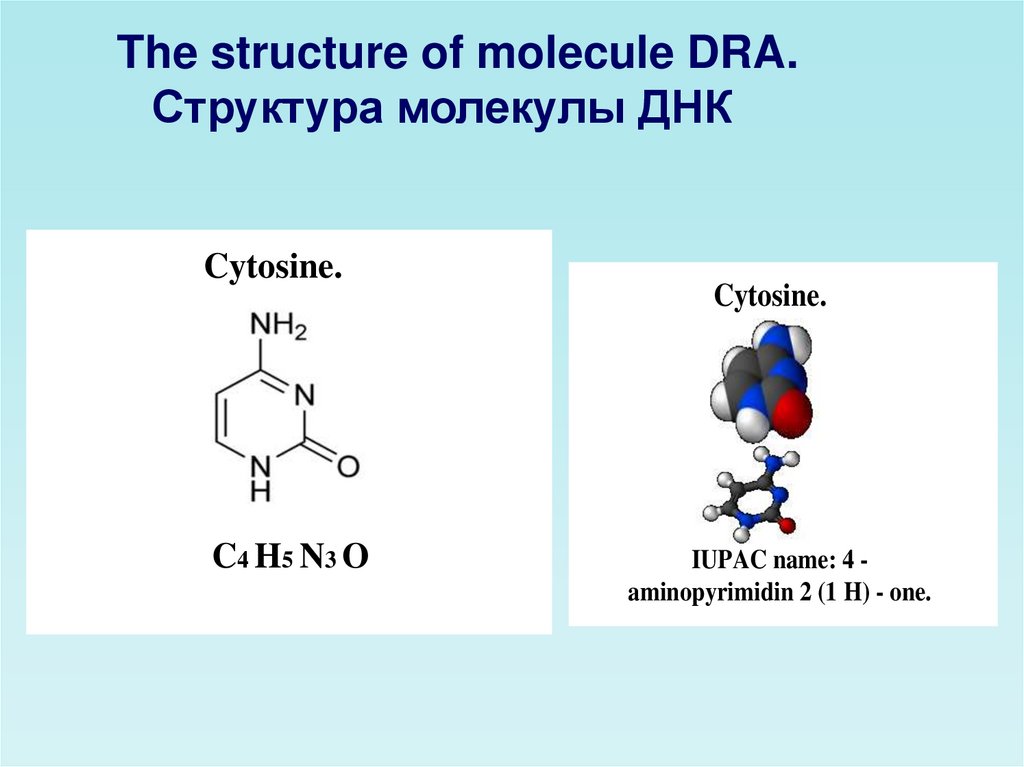
The structure of molecule DRA.Структура молекулы ДНК
Cytosine.
C4 H5 N3 O
Cytosine.
IUPAC name: 4 aminopyrimidin 2 (1 H) - one.
22.
3. What are the recombinant DNA and its role for geneticengineering?
23.
4. What do proponents of GM food claim?24.
5. Why do critics of using GM food confirm their theory of uselessGM food production?
25.
26.
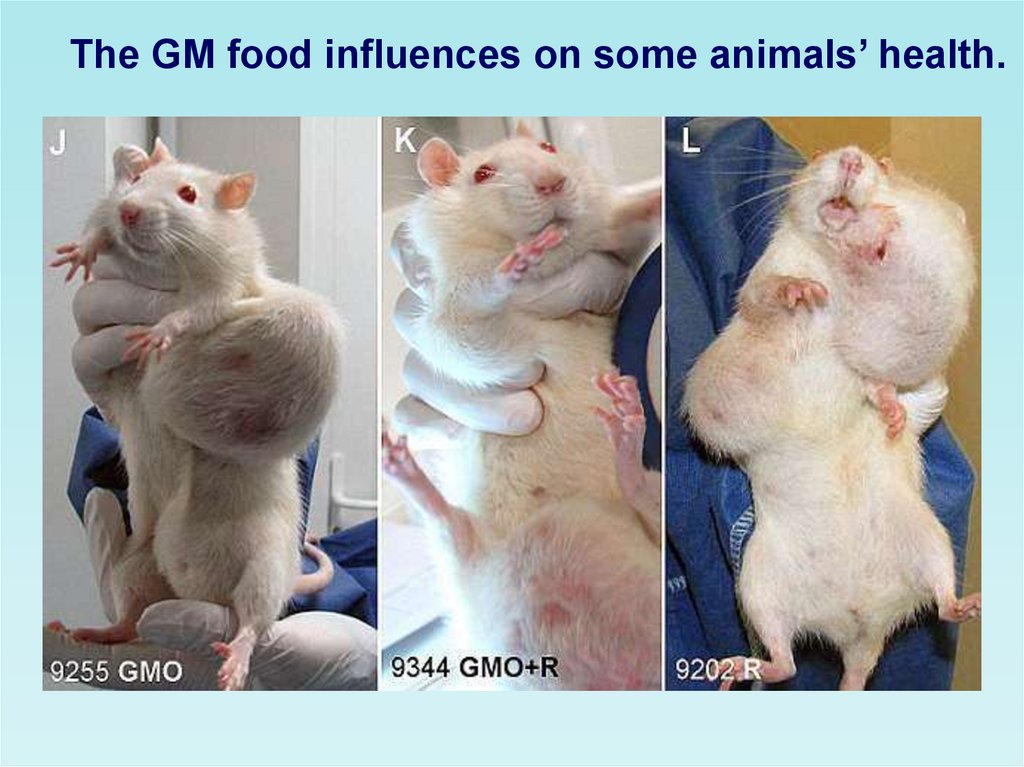
The GM food influences on some animals’ health.27.
The Result: We would like to give you thefollowing advice:
1. Be more careful about buying food and pay attention
to the food ingredients.
2. You shouldn’t trust the sign GM free and check up
the food ingredients more
attentively.
3. Remember: most Russian food producers encode
GM food ingredients.
4. Toy should find out more information of GM Food
influence on living organisms.
5. Remember: GM food can be allergenic for some
people.
28.
Thanks foryour
attention!

















 biology
biology