Similar presentations:
Fundamentals of the theory of aerodynamic calculations of rockets
1.
Samara National Research UniversityFundamentals of the theory of
aerodynamic calculations of
rockets
Vladimir Frolov
E-mail: frolov_va_ssau@mail.ru
Winter School, 2022
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
1
2.
OutlineForces acting on a rocket
Rocket motion equation
General Formula for Rocket Drag Coefficient
Area calculation
Total friction drag coefficient of the body
Conclusions
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
2
3.
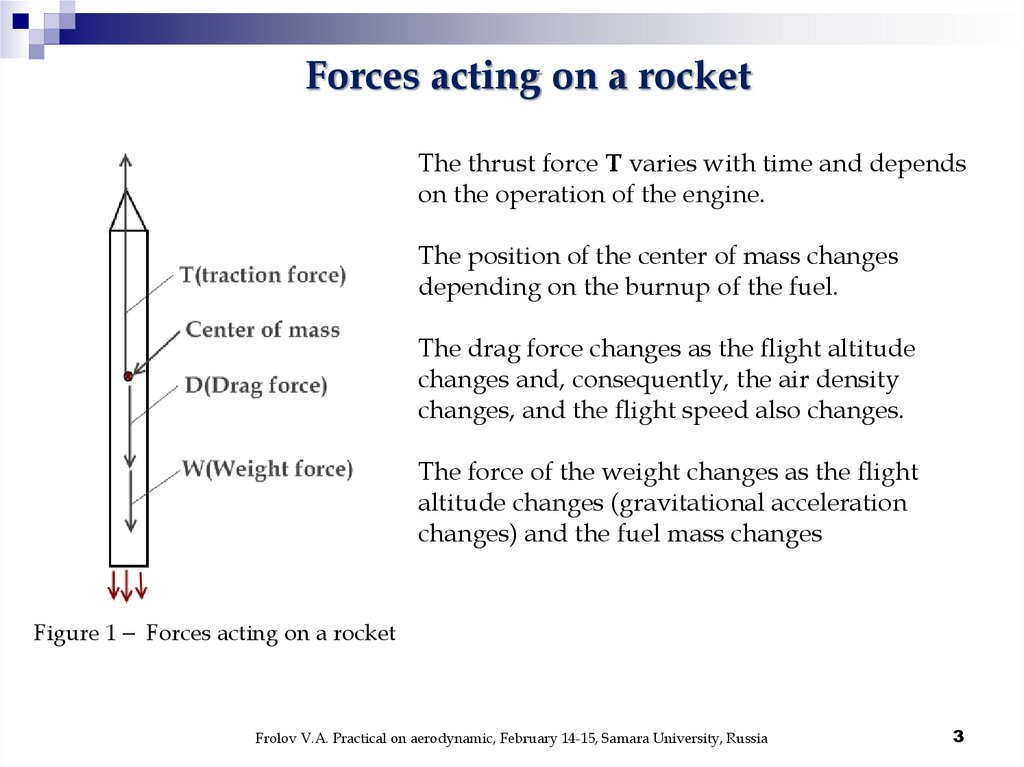
Forces acting on a rocketThe thrust force T varies with time and depends
on the operation of the engine.
The position of the center of mass changes
depending on the burnup of the fuel.
The drag force changes as the flight altitude
changes and, consequently, the air density
changes, and the flight speed also changes.
The force of the weight changes as the flight
altitude changes (gravitational acceleration
changes) and the fuel mass changes
Figure 1 Forces acting on a rocket
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
3
4.
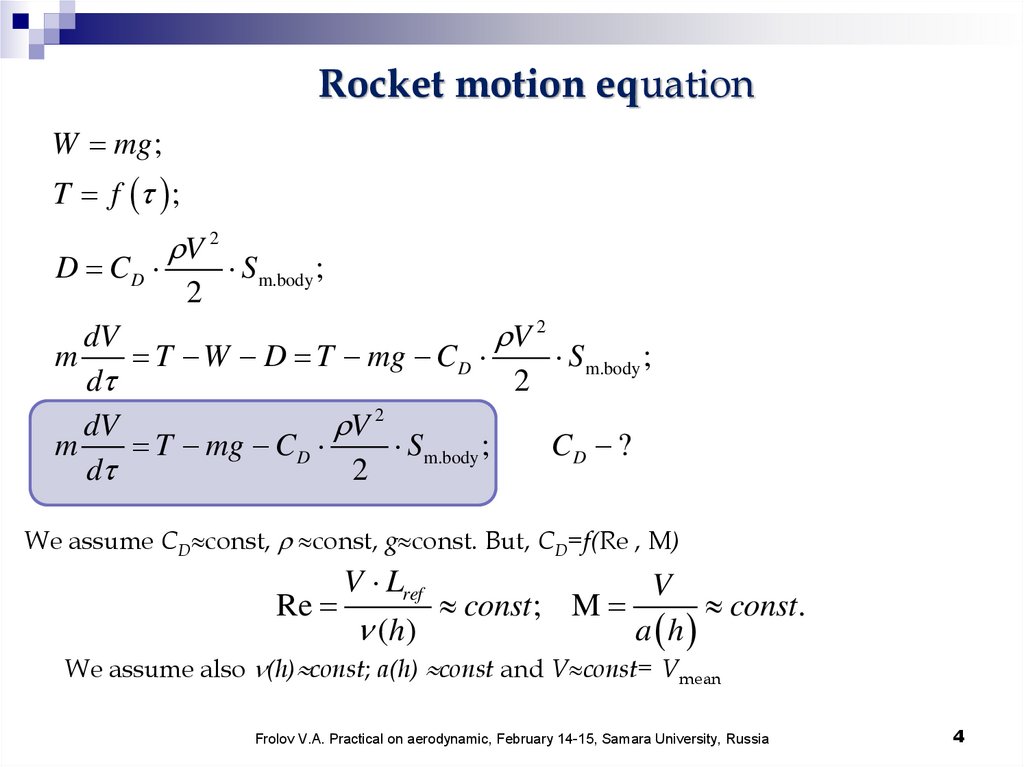
Rocket motion equationW mg ;
T f ;
D CD
V 2
2
Sm.body ;
dV
V 2
m
T W D T mg CD
S m.body ;
d
2
dV
V 2
m
T mg CD
S m.body ;
CD ?
d
2
We assume CD const, const, g const. But, CD=f(Re , M)
V Lref
V
Re
const ; M
const.
( h)
a h
We assume also (h) const; a(h) const and V const= Vmean
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
4
5.
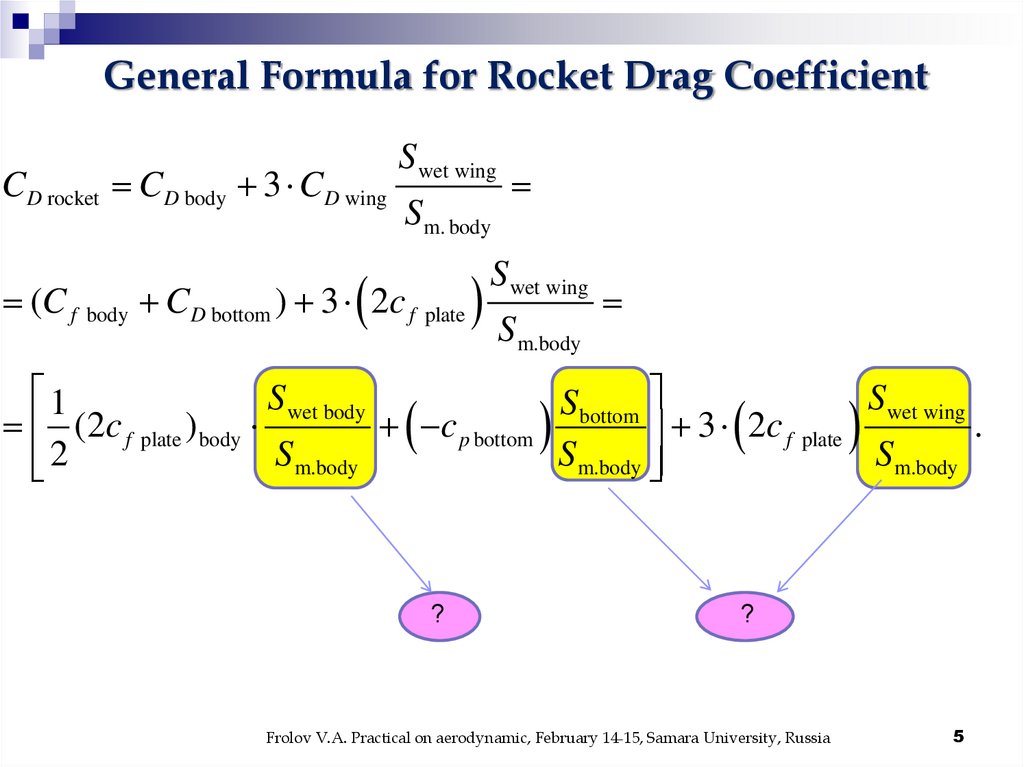
General Formula for Rocket Drag CoefficientCD rocket CD body 3 CD wing
S wet wing
Sm. body
(C f body CD bottom ) 3 2c f plate
S wet wing
Sm.body
1
S wet body
S wet wing
Sbottom
(2c f plate ) body
c p bottom
.
3 2c f plate
Sm.body
Sm.body
Sm.body
2
?
?
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
5
6.
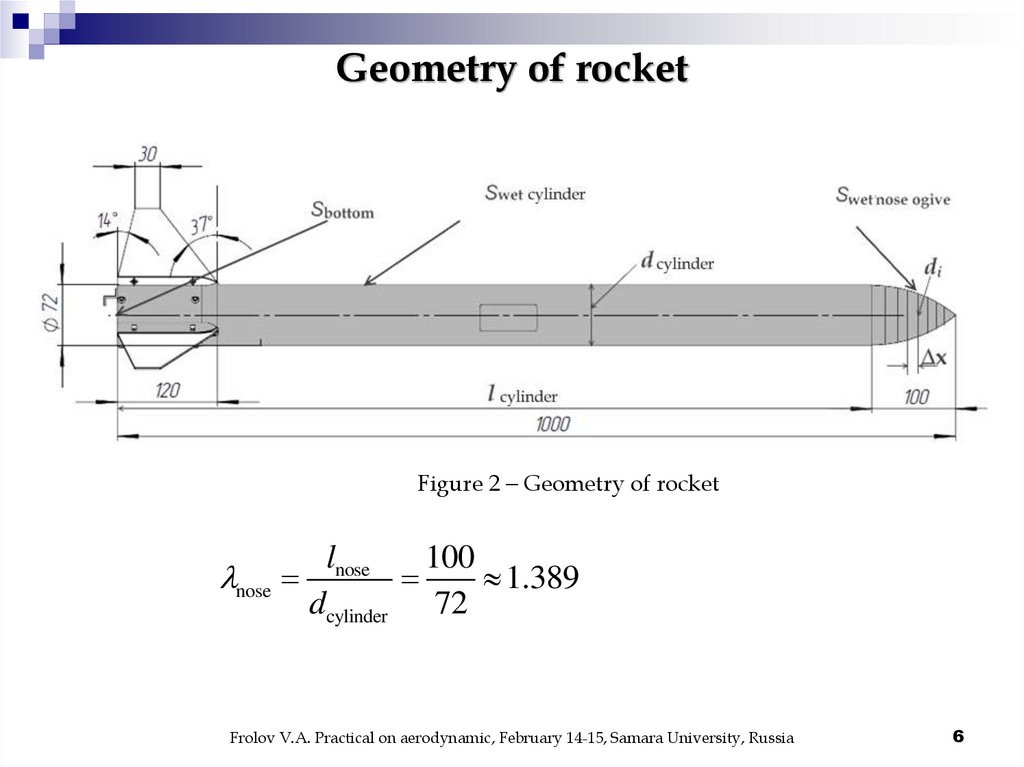
Geometry of rocketFigure 2 Geometry of rocket
lnose
100
nose
1.389
dcylinder 72
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
6
7.
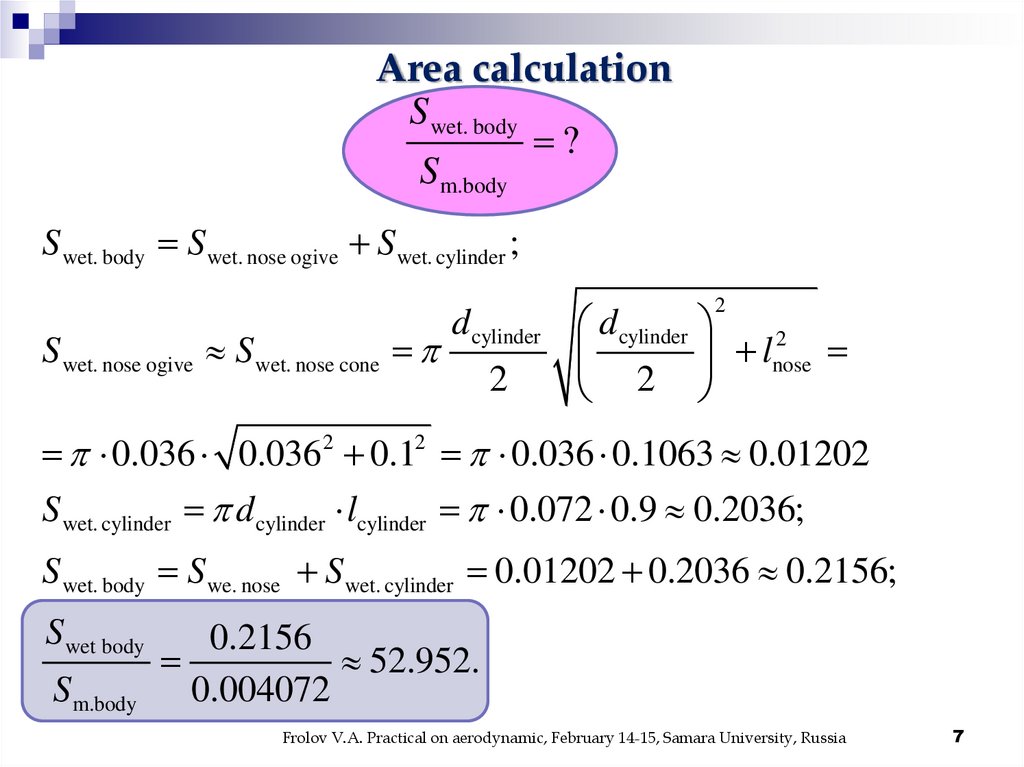
Area calculationS wet. body
?
S m.body
S wet. body S wet. nose ogive S wet. cylinder ;
2
d cylinder d cylinder
2
S wet. nose ogive S wet. nose cone
l
nose
2
2
0.036 0.0362 0.12 0.036 0.1063 0.01202
S wet. cylinder d cylinder lcylinder 0.072 0.9 0.2036;
S wet. body S we. nose S wet. cylinder 0.01202 0.2036 0.2156;
S wet body
0.2156
52.952.
S m.body 0.004072
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
7
8.
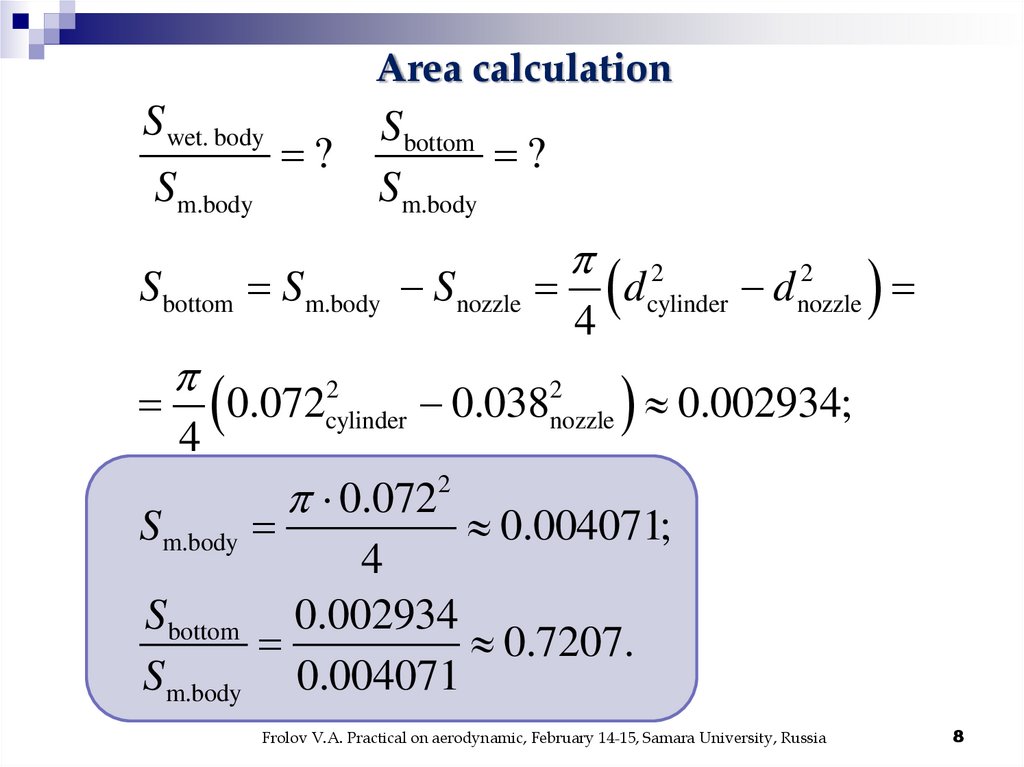
Area calculationS wet. body
Sm.body
?
Sbottom
?
Sm.body
Sbottom Sm.body Snozzle
0.072
4
Sm.body
2
cylinder
0.038
0.0722
4
2
2
d
d
cylinder nozzle
2
nozzle
0.002934;
0.004071;
4
Sbottom 0.002934
0.7207.
Sm.body 0.004071
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
8
9.
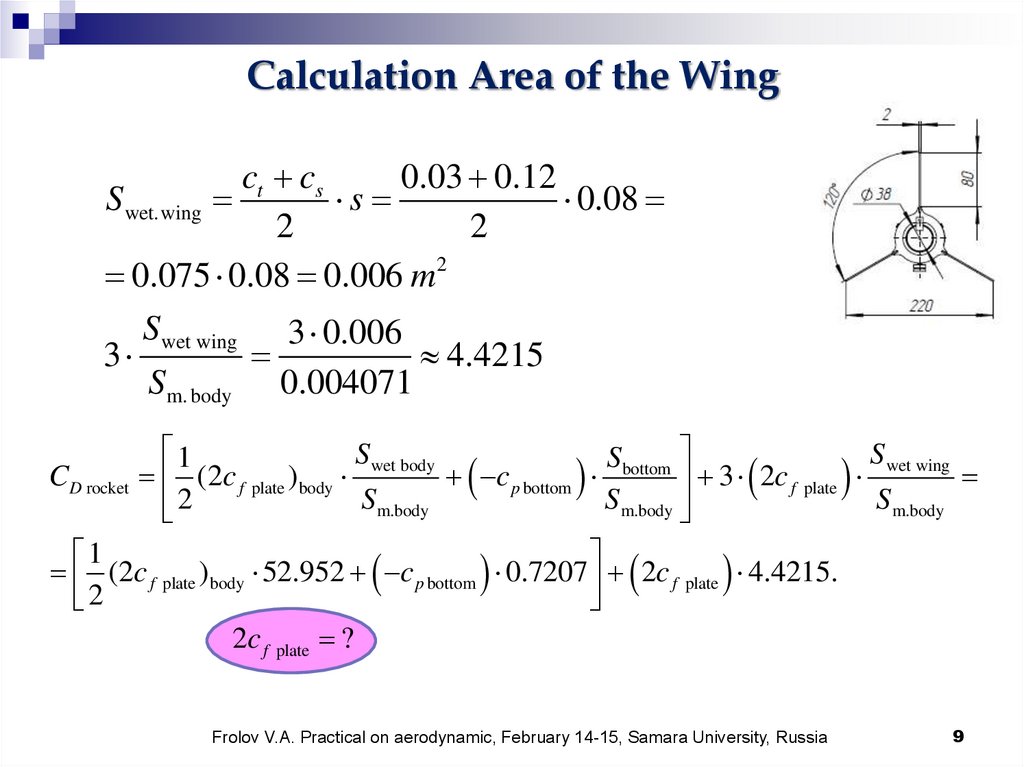
Calculation Area of the Wingct cs
0.03 0.12
S wet.wing
s
0.08
2
2
0.075 0.08 0.006 m 2
S wet wing 3 0.006
3
4.4215
Sm. body 0.004071
1
S wet body
S wet wing
Sbottom
CD rocket (2c f plate ) body
c p bottom
3 2c f plate
Sm.body
Sm.body
S m.body
2
1
(2c f plate ) body 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 2c f plate 4.4215.
2
2c f plate ?
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
9
10.
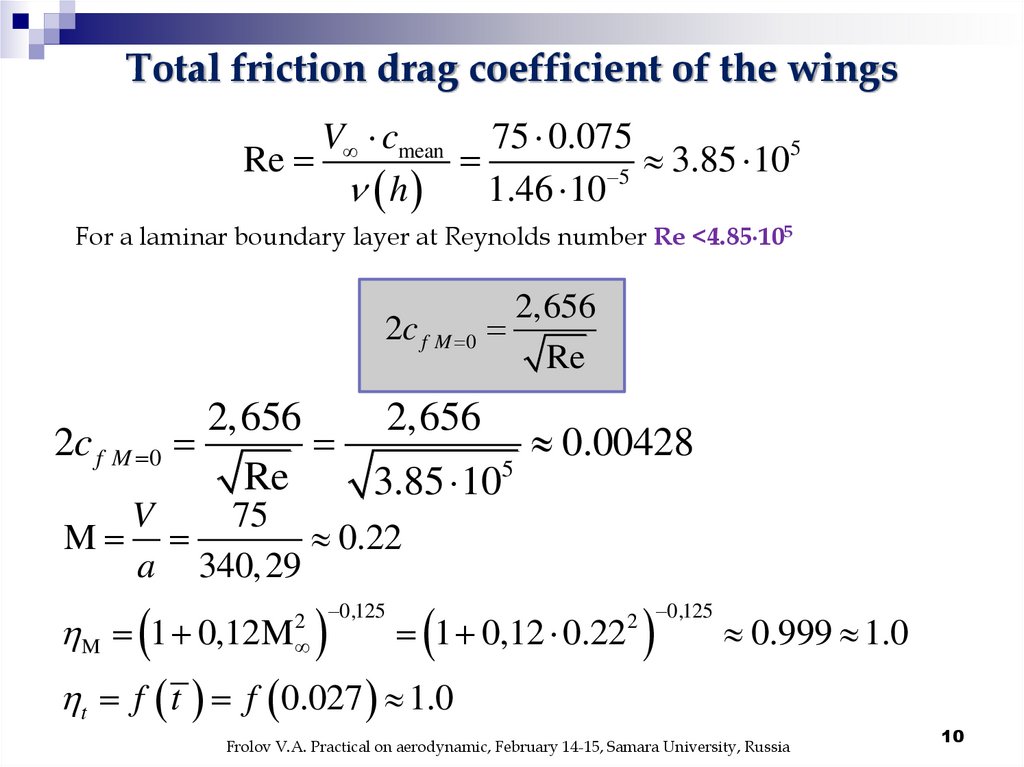
Total friction drag coefficient of the wingsV cmean 75 0.075
5
Re
3.85
10
h
1.46 10 5
For a laminar boundary layer at Reynolds number Re <4.85 105
2,656
2c f M 0
Re
2,656
2,656
2c f M 0
0.00428
5
Re
3.85 10
V
75
M
0.22
a 340,29
M 1 0,12M
2 0,125
1 0,12 0.22
2 0,125
0.999 1.0
t f t f 0.027 1.0
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
10
11.
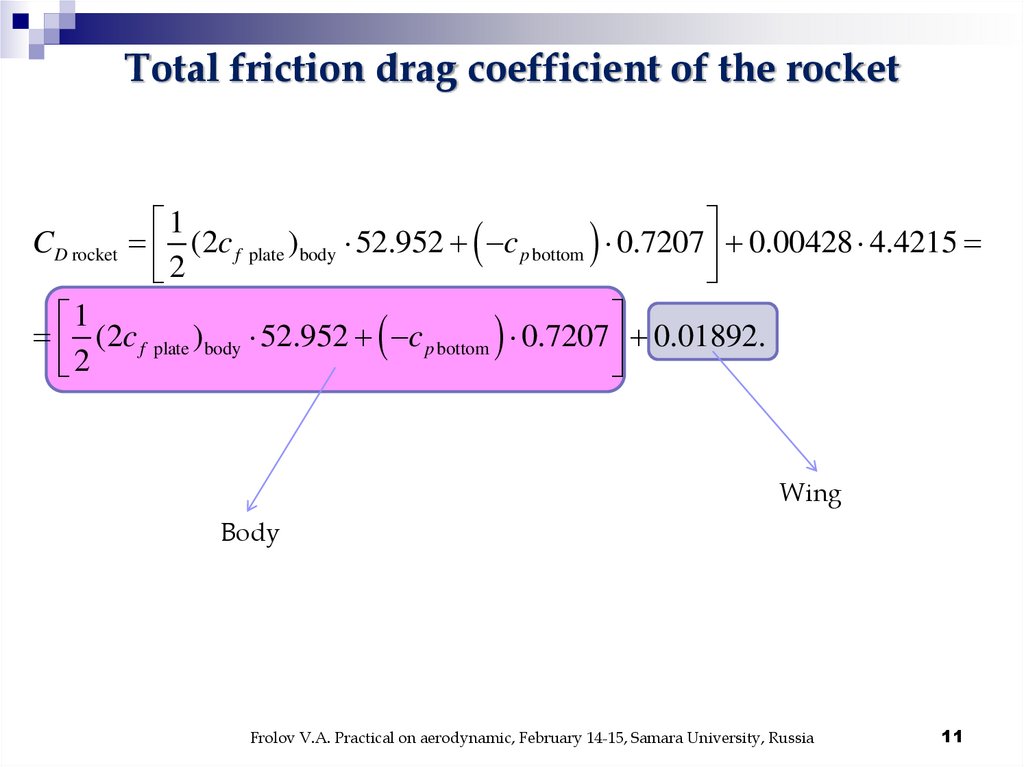
Total friction drag coefficient of the rocket1
CD rocket (2c f plate )body 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.00428 4.4215
2
1
(2c f plate )body 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892.
2
Wing
Body
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
11
12.
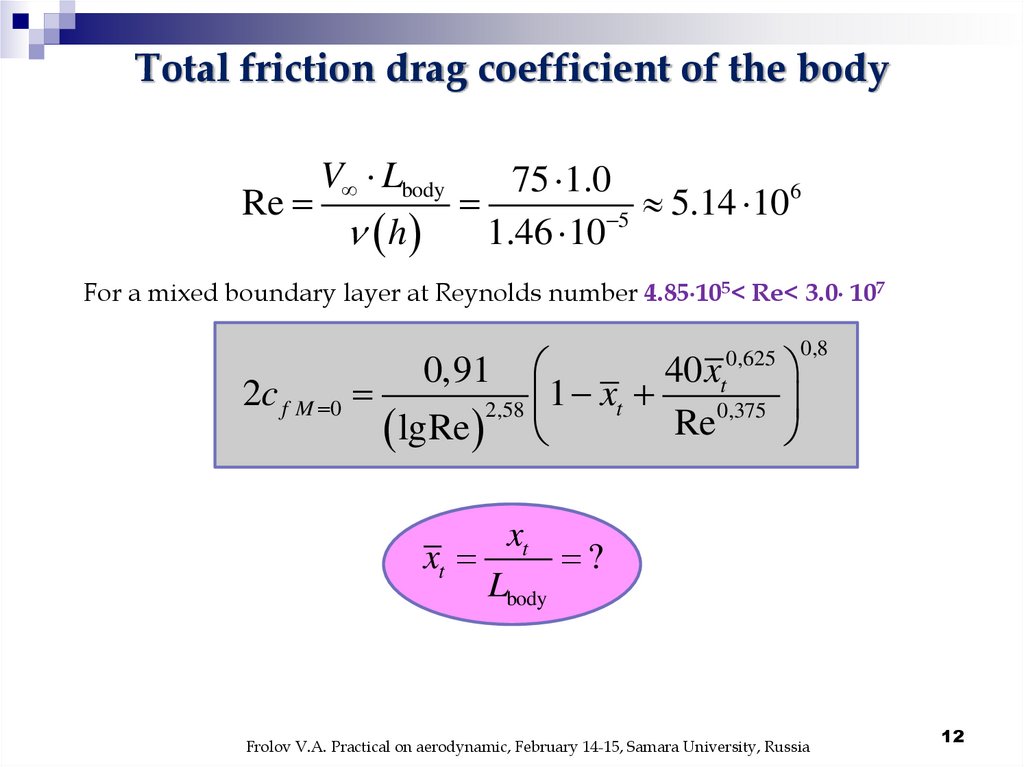
Total friction drag coefficient of the bodyRe
V Lbody
h
75 1.0
6
5.14
10
1.46 10 5
For a mixed boundary layer at Reynolds number 4.85 105< Re< 3.0 107
40 x
2c f M 0
1 xt
2,58
Re
lgRe
0,91
0,625
t
0,375
0,8
xt
xt
?
Lbody
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
12
13.
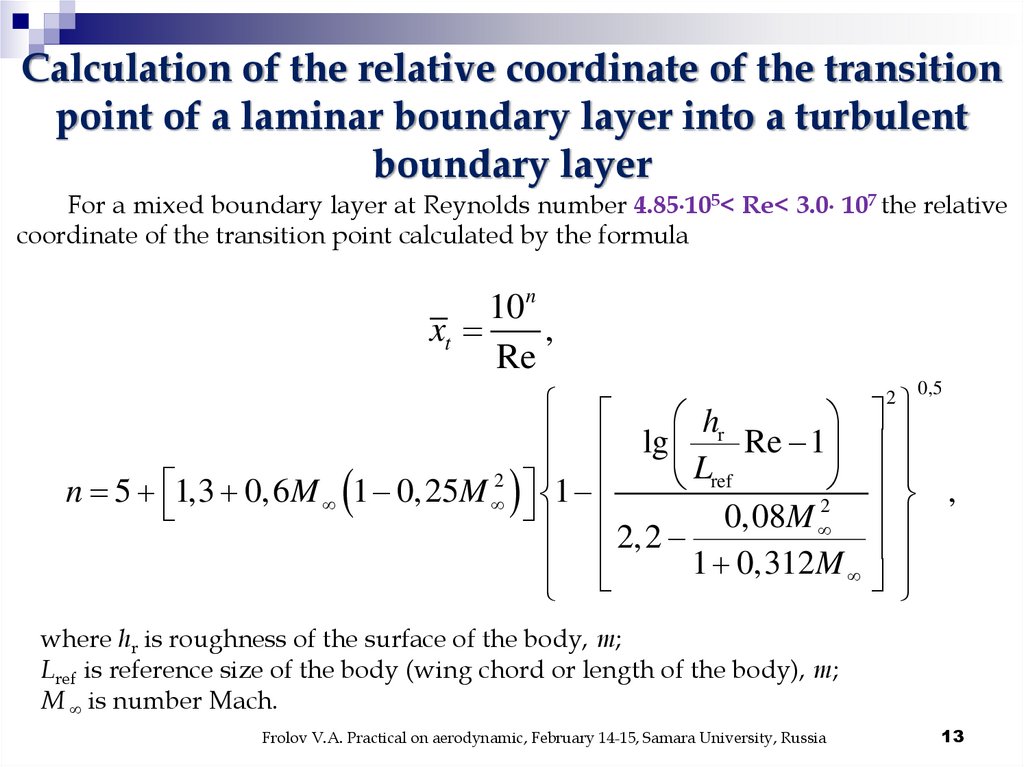
Calculation of the relative coordinate of the transitionpoint of a laminar boundary layer into a turbulent
boundary layer
For a mixed boundary layer at Reynolds number 4.85 105< Re< 3.0 107 the relative
coordinate of the transition point calculated by the formula
10n
xt
,
Re
0,5
hr
lg
Re 1
Lref
2
n 5 1,3 0,6 M 1 0,25M 1
,
2
2,2 0,08M
1 0,312 M
2
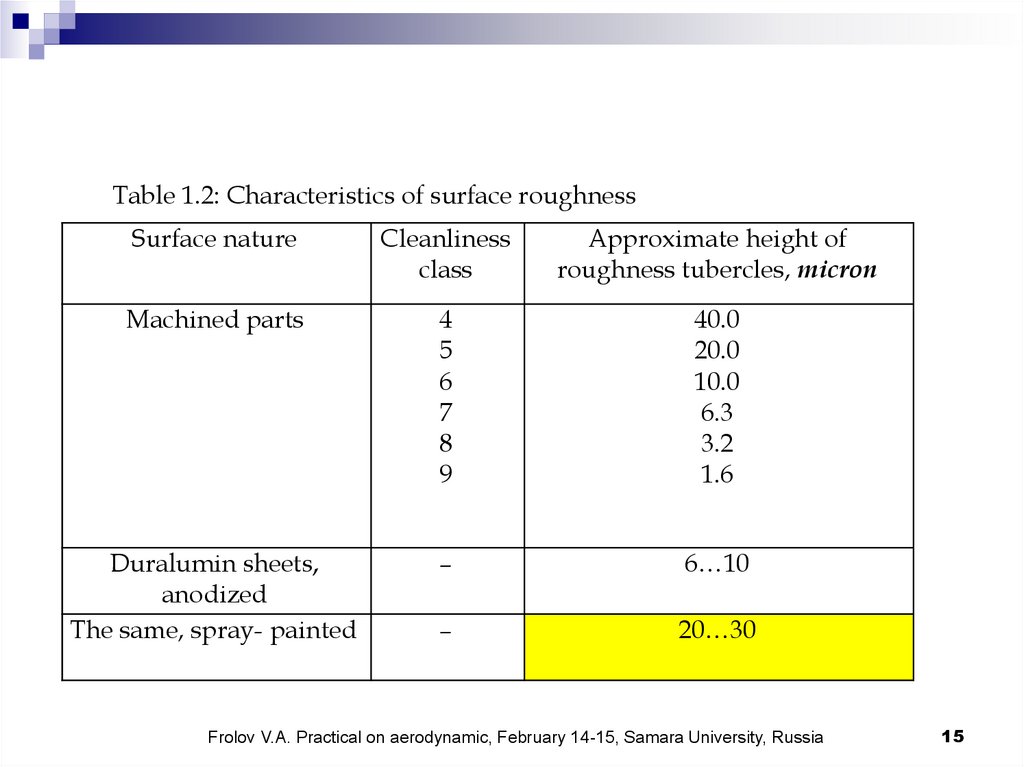
where hr is roughness of the surface of the body, m;
Lref is reference size of the body (wing chord or length of the body), m;
M is number Mach.
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
13
14.
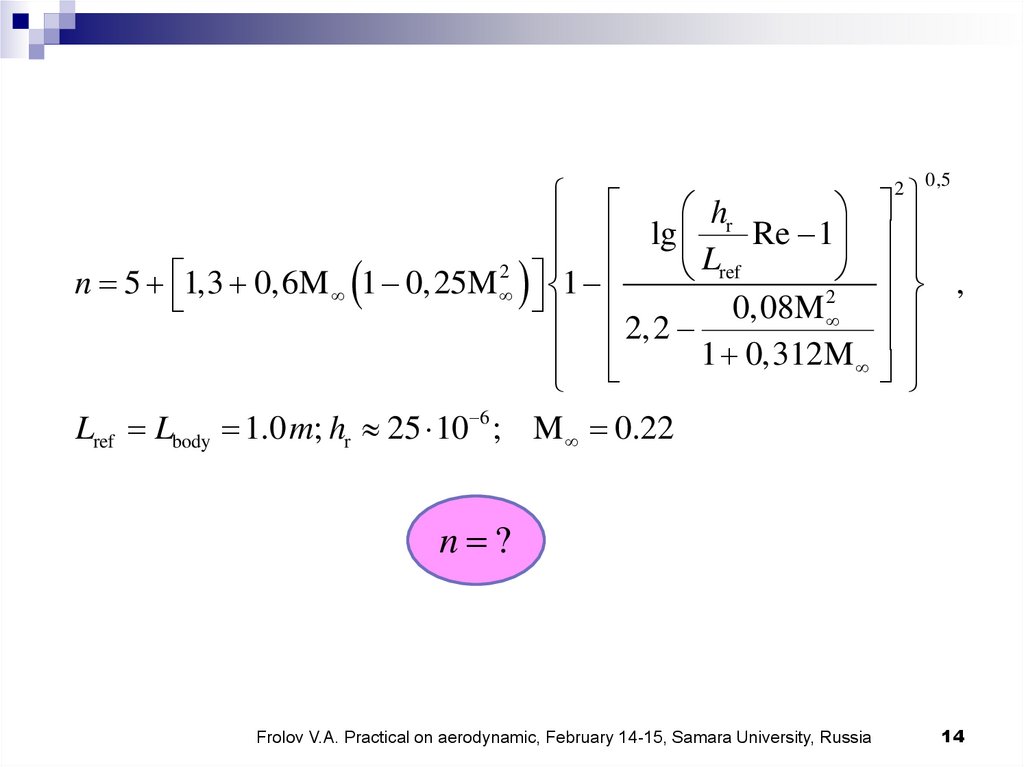
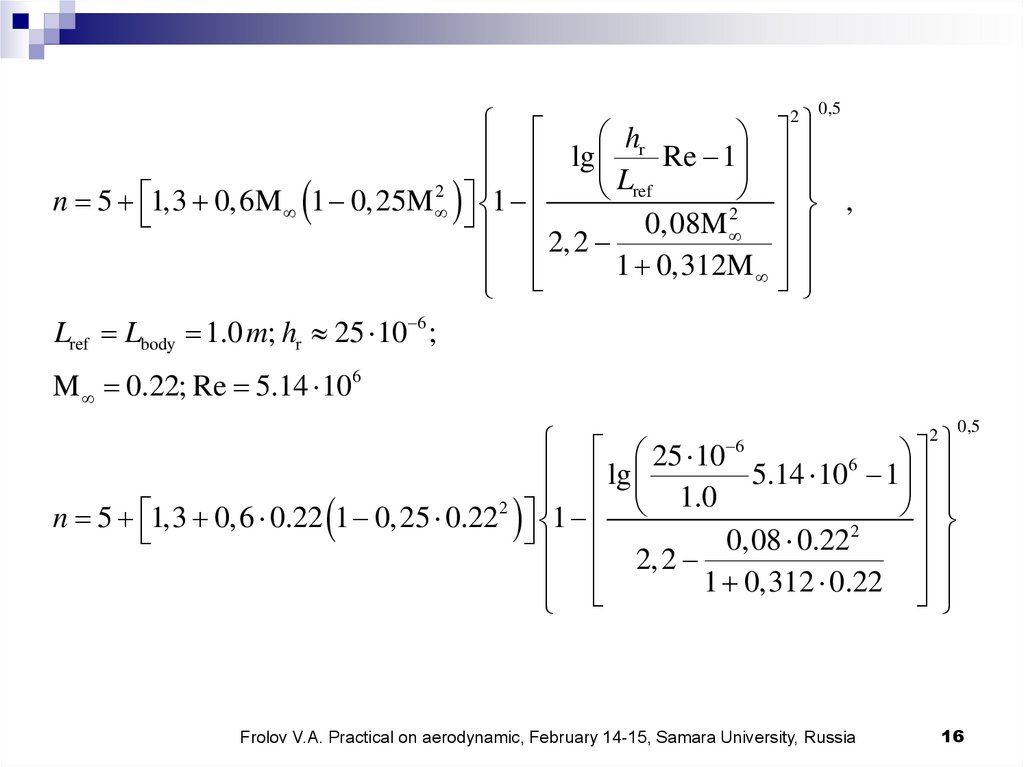
0,5hr
lg
Re 1
Lref
2
,
n 5 1,3 0,6M 1 0,25M 1
2
2,2 0,08M
1 0,312M
Lref Lbody 1.0 m; hr 25 10 6 ; M 0.22
2
n ?
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
14
15.
Table 1.2: Characteristics of surface roughnessSurface nature
Cleanliness
class
Approximate height of
roughness tubercles, micron
Machined parts
4
5
6
7
8
9
40.0
20.0
10.0
6.3
3.2
1.6
Duralumin sheets,
anodized
The same, spray- painted
–
6…10
–
20…30
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
15
16.
0,52
hr
lg
Re 1
Lref
2
,
n 5 1,3 0,6M 1 0,25M 1
2
0,08M
2,2
1 0,312M
Lref Lbody 1.0 m; hr 25 10 6 ;
M 0.22; Re 5.14 106
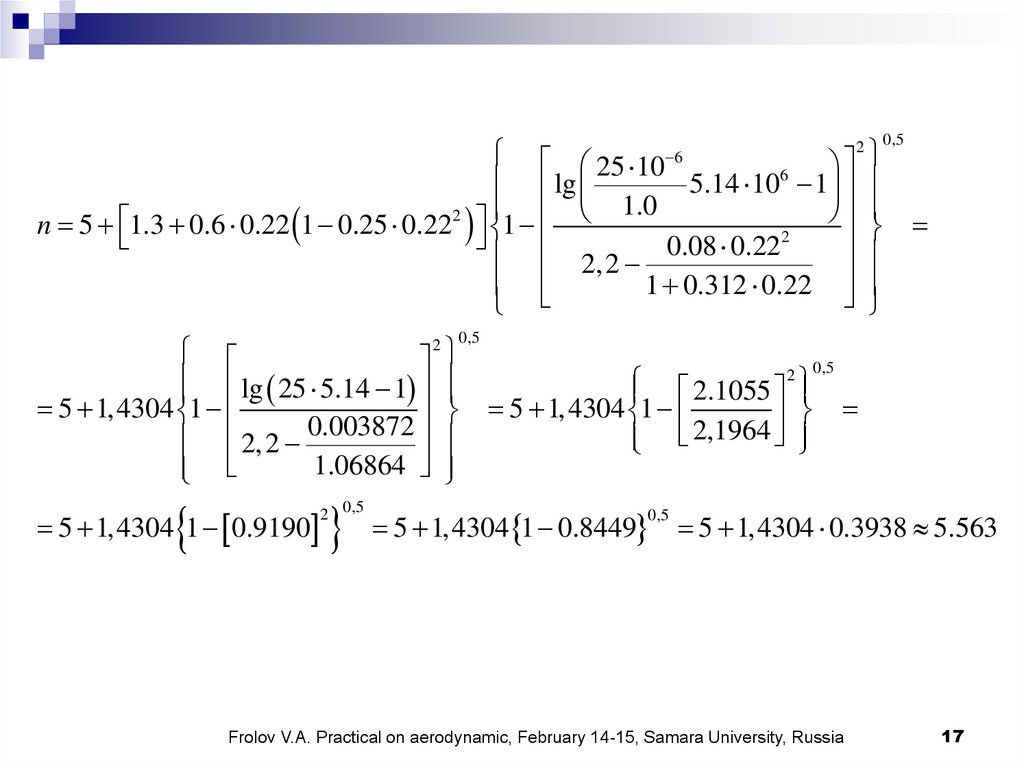
2
25 10 6
6
lg
5.14 10 1
1.0
n 5 1,3 0,6 0.22 1 0,25 0.222 1
2
0,08
0.22
2,2
1 0,312 0.22
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
0,5
16
17.
25 106
lg
5.14 10 1
1.0
2
n 5 1.3 0.6 0.22 1 0.25 0.22 1
2
0.08
0.22
2,2
1 0.312 0.22
2
6
2
lg 25 5.14 1
5 1,4304 1
0.003872
2,2
1.06864
5 1,4304 1 0.9190
2 0,5
0,5
0,5
2.1055
5 1,4304 1
2,1964
2
5 1,4304 1 0.8449
0,5
0,5
5 1,4304 0.3938 5.563
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
17
18.
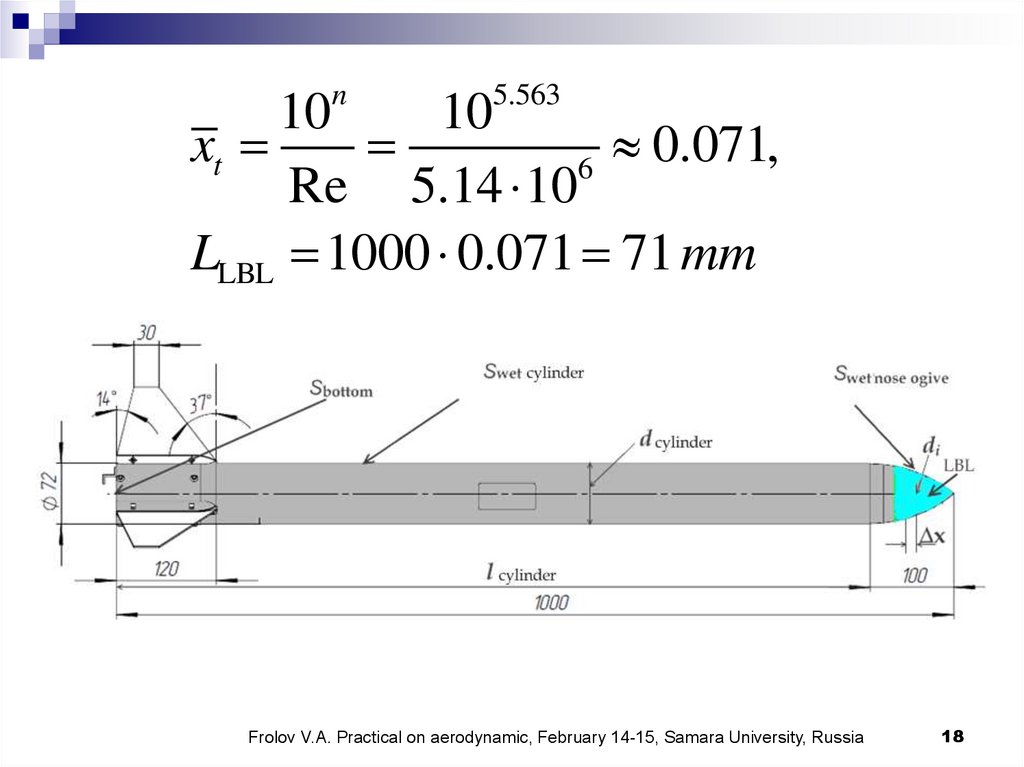
n5.563
10
10
xt
0.071,
6
Re 5.14 10
LLBL 1000 0.071 71 mm
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
18
19.
40 x2c f M 0
1 xt
2,58
Re
lgRe
0,91
0,625
t
0,375
0,8
40 0.071
1 0.071
2,58
6 0,375
6
(5.14
10
)
lg(5.14 10 )
0,625
0,91
7.6577
0.006698 0.929
328.557
0,8
0.8
0.00644
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
19
20.
1CD rocket (2c f plate )body 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.00428 4.4215
2
1
0.00644 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892
2
1
0.00644 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892
2
0.00322 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892
0.00322 52.952 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892
0.1705 c p bottom 0.7207 0.01892 .
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
20
21.
SbCd b c p b
,
Smax
0.0155
0.0155
0.0733
c p b C 1000
b D f body
0.00322
72
CD rocket 0.1705 0.0733 0.7207 0.01892
0.1705 0.0528 0.01892 0.2233 0.01892 0.2422.
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
21
22.
We will perform all the necessary calculations of thedrag coefficient in subsequent practical exercises.
Thanks for attention!
I will be glad
to answer any questions.
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
22
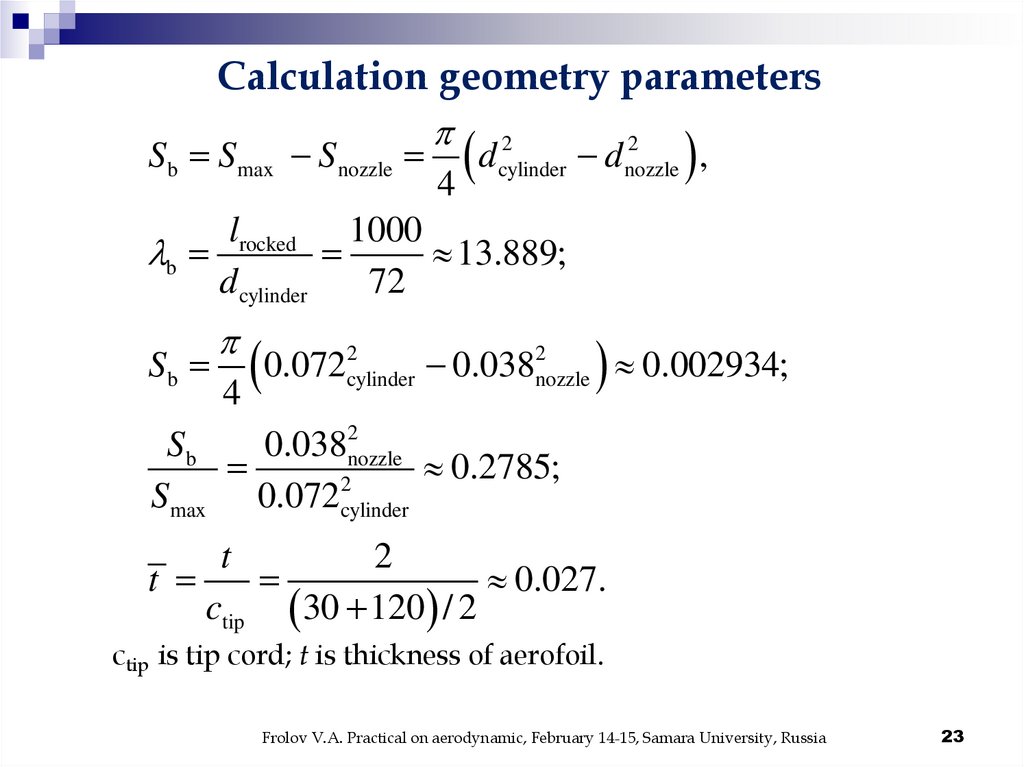
23.
Calculation geometry parameters2
2
Sb Smax Snozzle
d
4
cylinder
d nozzle ,
lrocked 1000
b
13.889;
d cylinder
72
Sb
4
2
2
0.072
0.038
cylinder
nozzle 0.002934;
Sb
0.0382nozzle
0.2785;
2
Smax 0.072cylinder
t
2
t
0.027.
ctip 30 120 / 2
ctip is tip cord; t is thickness of aerofoil.
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University, Russia
23
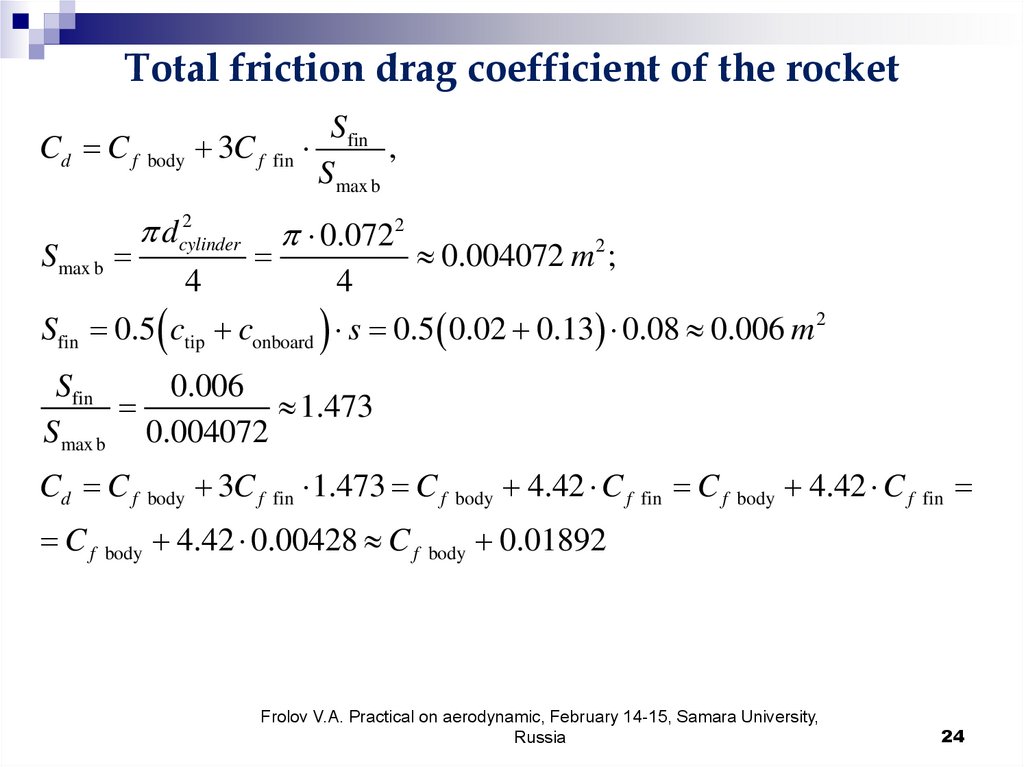
24.
Total friction drag coefficient of the rocketCd C f body 3C f fin
Smax b
2
dcylinder
4
Sfin
,
Smax b
0.0722
0.004072 m 2 ;
4
Sfin 0.5 ctip conboard s 0.5 0.02 0.13 0.08 0.006 m 2
Sfin
0.006
1.473
Smax b 0.004072
Cd C f body 3C f fin 1.473 C f body 4.42 C f fin C f body 4.42 C f fin
C f body 4.42 0.00428 C f body 0.01892
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University,
Russia
24
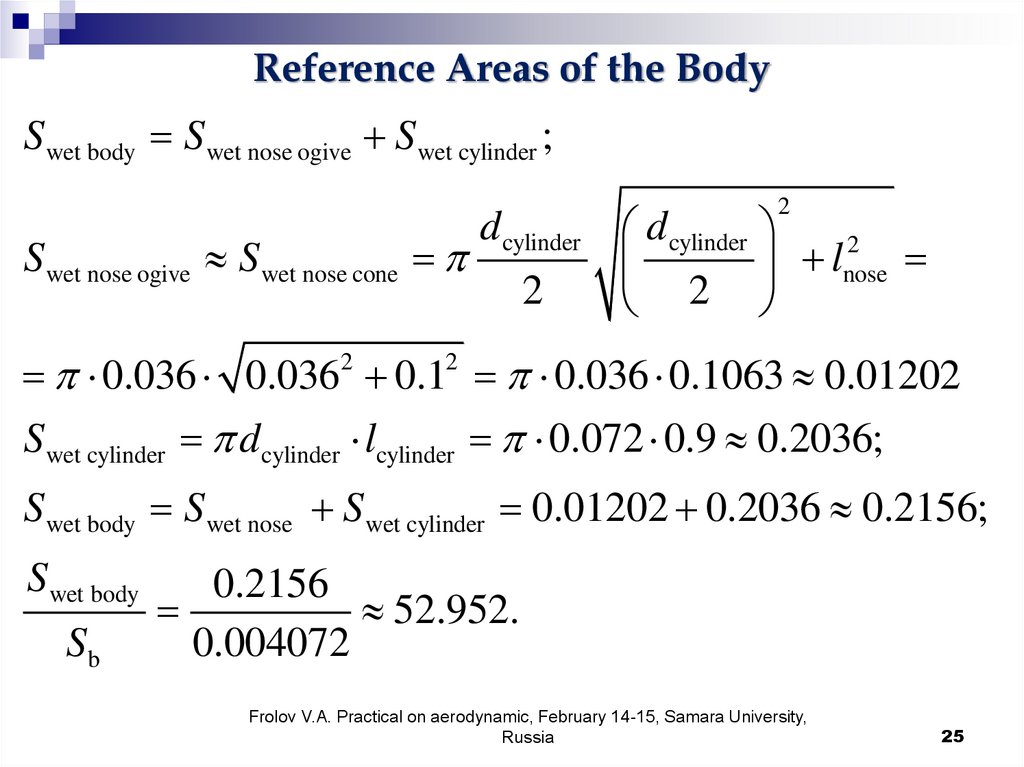
25.
Reference Areas of the BodyS wet body S wet nose ogive S wet cylinder ;
2
d cylinder d cylinder
2
S wet nose ogive S wet nose cone
l
nose
2
2
0.036 0.0362 0.12 0.036 0.1063 0.01202
S wet cylinder d cylinder lcylinder 0.072 0.9 0.2036;
S wet body S wet nose S wet cylinder 0.01202 0.2036 0.2156;
S wet body
Sb
0.2156
52.952.
0.004072
Frolov V.A. Practical on aerodynamic, February 14-15, Samara University,
Russia
25






 mathematics
mathematics








