Similar presentations:
What is B2B Sales?
1. TEACHING WEEK 5
Sales Management2. Objectives
After finishing this lecture student will be able to answerfollowing questions -:
• Why salespeople had a negative reputation
• B2B sales
• B2C sales
• Modern sales
• The New ABC of sales
• Impact of B2B and B2C to contemporary business activities
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
2
3. What is B2B Sales?
Organisational buyer behaviour has usefully been broken down into three elementsStructure. The ‘who’ factor – who participates in the decision-making process
and their particular roles
Process. The ‘how’ factor – the pattern of information getting, analysis, evaluation and
decision-making which takes place as the purchasing organisation moves towards a
decision.
Content. The ‘what’ factor – the choice criteria used at different stages of the process
and by different members of the decision-making unit.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
3
4. B2B Sales
B2B, short for Business to Business, refers to companies that sell their productsmainly to other businesses, rather than consumers. B2B sales also includes
services such as accounting firms which represent major corporations.
There are mainly three types of B2B sales: supply sales, distribution sales, and service sales.
Supply sales - In this scenario, a business provides another with products such as
office supplies, equipment etc. The companies usually provide these orders in bulk
and require authorization from management.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
4
5. B2B Sales
Distribution sales – In the distribution B2B sales, a wholesaler sellsproducts in large quantities to another company, which in turn sells to
consumers. A good example is the relationship between a
manufacturing company and a supermarket.
Service sales - In this case, instead of a physical product, one
business provides a service to another. Examples include
software, legal counsel.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
5
6. Why salespeople had a negative reputation in the past?
Whysalespeople
had
a
Focused
negative
reputation
on moving product rather
Customer.
in
the
past?
than understanding the needs of the
Unequal balance of power—they had more information than their customers.
Because of the two items above, there was often a sense of manipulation.
The old ABCs of selling: Always Be Closing
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
6
7. B-C sales
B2C sales (Business to Consumer) is when a business sells its products directly to the individualconsumer.
It refers to any sales process that sells directly to consumers, e.g GAP outfitters. These include
direct sellers, online intermediaries, advertising, and subscription models. Direct Sellers such as
Amazon and Zappos. Online Intermediaries such as Amazon who act as a go between between
retailers and customers Advertising sales model where websites are created to generate more
traffic by creating targeted ads for users. Subscription fee-based models such as Netflix which
offers content to users on demand at a price.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
7
8.
In B2B selling, customers make buying decisions based on rational and strategic considerations.These include how a product or service can generate value for the company (e.g., improve
process efficiencies, upgrade services to its own customers, improve profit margins, drive
revenue, etc.).
If a B2B seller successfully demonstrates that the value generated by a product or service far
exceeds the cost of acquisition, then the prospective buyer will be more inclined to opt-in.
On the other hand, B2C audiences tend to make purchases based on how a brand establishes an
emotional connection.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
8
9. Difference between B2B & B2C sales
Differencebetween
B2B
&
B2C
sales
B2B: Longer sales cycles involve multiple decision makers.
B2C: Brand matters as a driving factor for purchases.
B2B: More stakeholders
B2C: Less stake holders
B2B: Market size is niche and small
B2C: Market size is big
B2B: Sales cycle Long
B2C: sales cycle short
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
9
10. B-B sales (Characteristics)
Organisational selling/buying may be more risky
Organisational buying is more complex
Negotiation is often important in organisational buying
Fewer customers
Concentrated markets
Complex purchasing decisions
Long-term relationships
Reciprocal trading
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
10
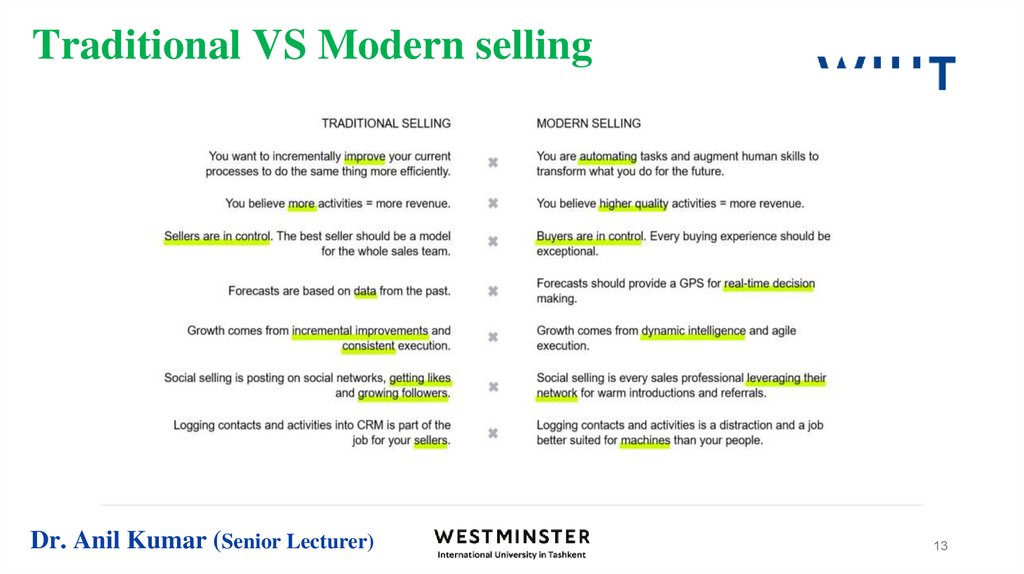
11. Traditional VS Modern selling
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)11
12. Traditional VS Modern selling
The traditional sales model focuses on acquiring prospects and customers, while themodern model relies on retaining existing customers and building long-term
relationships. By focusing on customer retention, companies can increase customer
loyalty and generate recurring revenue over time.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
12
13. Traditional VS Modern selling
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)13
14.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)14
15. B2B sales techniques
Solution selling: This involves gaining a deep understanding of the buyer’s business, needs, andproblems, and offering a tailored, holistic solution in response, rather than pushing one-size-fits-all
products. Solution sellers almost never offer products off-the-shelf. Solution selling might incur
higher sales costs, but the solution’s suitability usually results in a higher rate of closing.
Account-based sales: This method focuses on premium customers, offering them end-to-end,
highly tailored experiences. Each account, with all its shareholders, is treated as a complete market.
A host of resources that would otherwise be put into full market segments is allocated to each
account. This helps grow revenues from each key account through more targeted cross- and
upselling.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
15
16. B2B sales techniques
Challenger sale: In this method, salespeople educate and inform the customer about theirneeds in response to market trends, risks, and opportunities. The salesperson takes on a more
active role here, helping customers realise a need in the first place.
Sandler selling system: The system places greater emphasis on the buyer-seller relationship.
Salespeople need to establish themselves as trusted advisors to clients, inspiring mutual
confidence to work towards shared success. This system leverages human psychology and the
buyer-seller dynamic to accelerate the sales cycle.
Value selling: Value selling instructs salespeople to emphasise and establish the value addition
their products or services can make to the buyer’s business. The value additions presented need
to be concrete and measurable, such as cost savings, revenue increments, or productivity
improvements.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
16
17. The New ABCs of Selling The only thing you got in this world is what you can sell. And the funny thing is, you’re a salesman,
and you don’t know that.”— Arthur Miller, Death of a Salesman
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
17
18. ABCs of Selling
Daniel Pink takes one of the old adages of sales ABC — “Always Be Closing” and proposesa new ABC — “Attunement, Buoyancy, and Clarity.”
Attunement
Buoyancy
Clarity
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
18
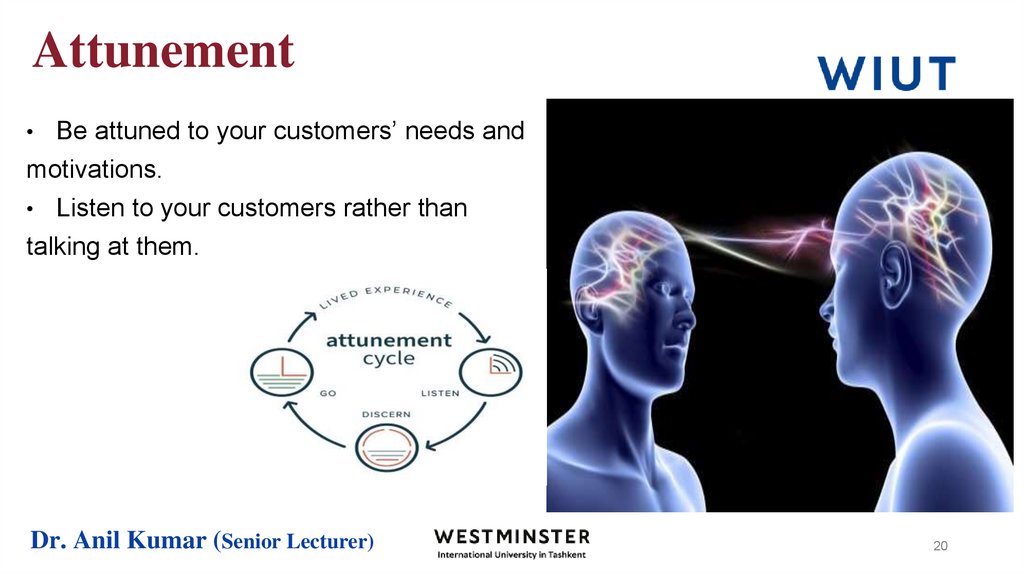
19. Attunement
Attunement - Attunement “is the ability to bring one’s actions and outlook
into harmony with other people and with the context you’re in,” It hinges on
three principles.
1.
Increase your power by reducing it.
2.
Use your head as much as your heart.
3.
Mimic Strategically
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
19
20. Attunement
Be attuned to your customers’ needs andmotivations.
• Listen to your customers rather than
talking at them.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
20
21. Buoyancy Buoyancy is the capacity to stay afloat on what one salesman calls an “ocean of rejection.”
BuoyancyBuoyancy is the capacity to stay afloat on what one salesman calls an
“ocean of rejection.”
Leads: There will be a lot of people
you assume will be interested.
Prospects: Test your assumptions
by interacting with leads.
Customers: Convert prospects
to customers by answering
all their questions.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
21
22. Clarity
Clarify who you are selling to, and it will become much easier to refine your salesapproach.
Business to business (B2B)
Selling to organizations
Outbound sales
Goal: Secure bulk orders from a few large clientsClarify who you are selling to, and it
will become much easier to refine your sales approach.
Business to customer (B2C)
Selling to individuals
Inbound sales
Goal: Attract large numbers of individual customers
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
22
23. Impact of B2B and B2C to contemporary business activities
First, B2B sales performance improves in proportion to sales calls. When salescalls serve as the means to provide product information, they help client
companies understand product benefits and make purchases accordingly.
Second, B2B sales performance increases as B2C markets become more
commercialized, but the effect of sales calls on B2B sales declines.
Commercialized markets are more attractive to individual consumers and thus,
lead to greater sales in the consumer market. However, the role of sales calls as
information sources weakens as B2C companies share product information
themselves and develop expertise in commercialized markets.
Finally, B2B sales are greater in urban markets compared to suburbs. However,
the effect of sales calls on B2B sales increases in suburban markets compared to
the
urban counterpart.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
23
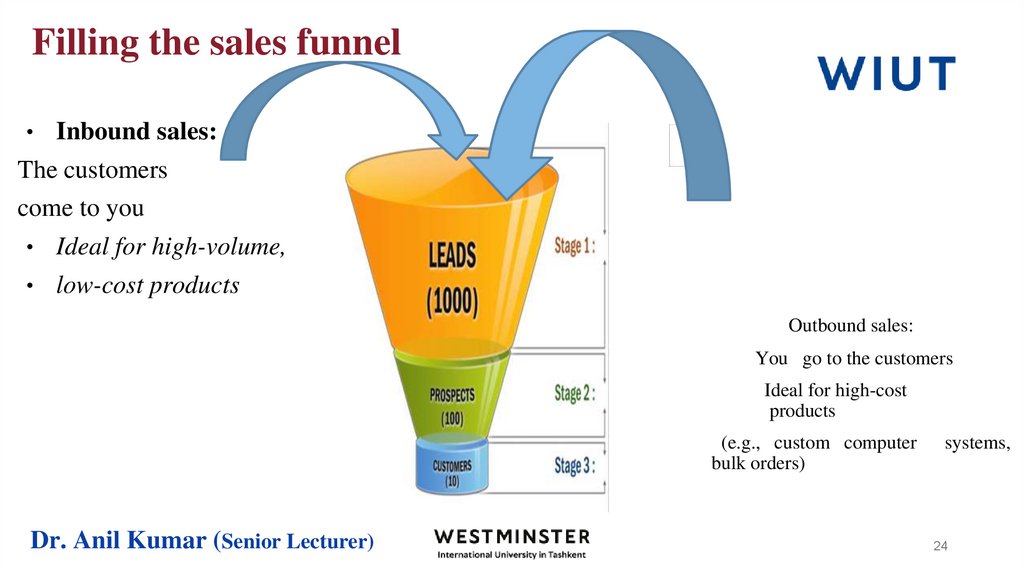
24. Filling the sales funnel
Inbound sales:
The customers
come to you
• Ideal for high-volume,
• low-cost products
Outbound sales:
You go to the customers
Ideal for high-cost
products
(e.g., custom computer
bulk orders)
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
systems,
24
25.
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar25






















 english
english








