Similar presentations:
Provide an introduction to sales management. Lecture 1
1. TEACHING WEEK 1
Sales Management2. Objectives
Provide an introduction to sales managementWho does a sales manager manage?
Where does sales management fit into the integrated marketing communication process
Dr. Anil Kumar
2
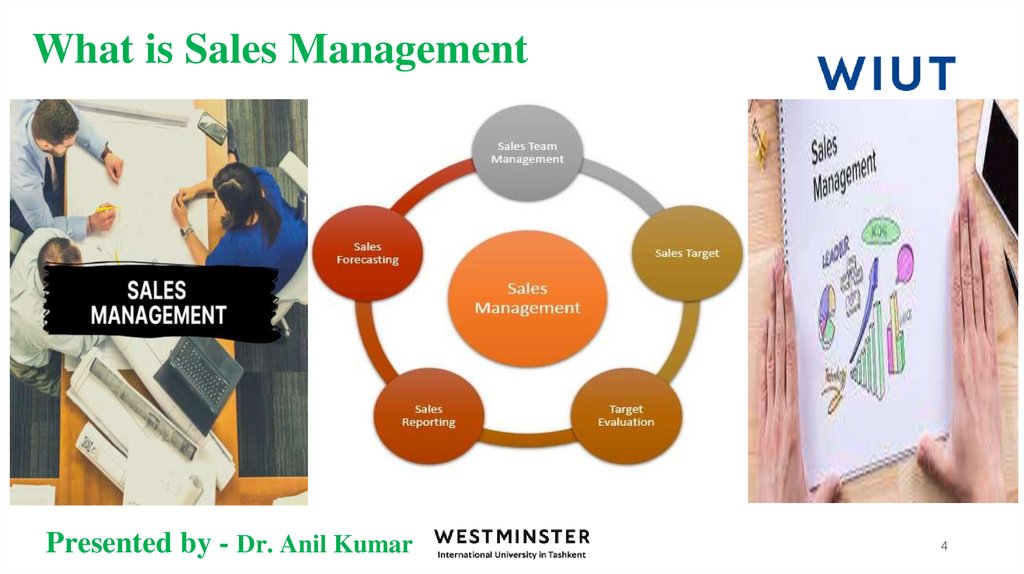
3. What is Sales Management
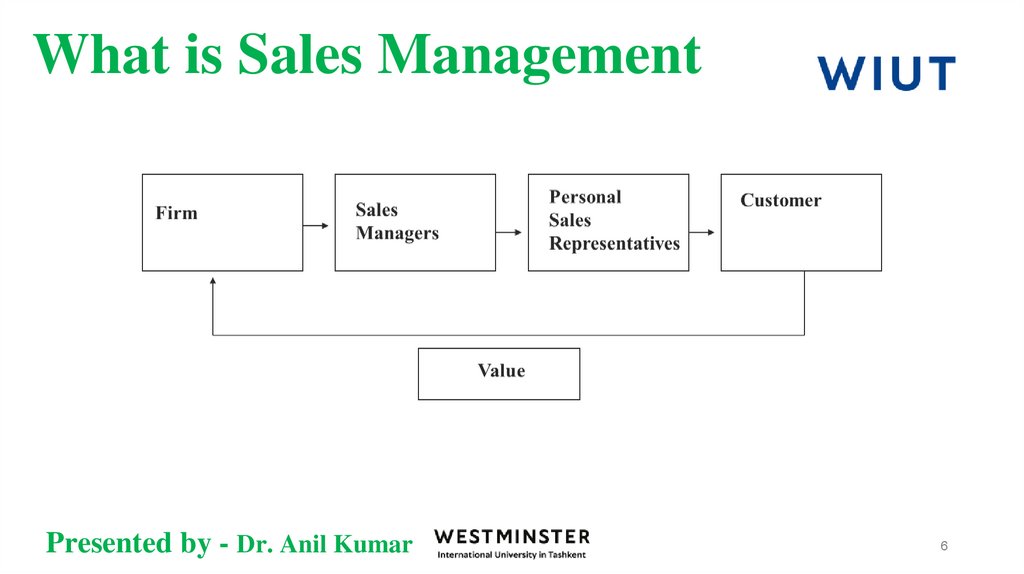
Sales Management- is the attainment of sales force goals in an effective and
efficient manner through planning, staffing, training, leading, and controlling
organizational resources (Futrell1998)
Managing a sales force involves recruiting, hiring, training, supervising,
compensating salespeople, motivating them to become problem solvers, and
providing the proper planning and backup support so they can perform their
jobs properly.
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
3
4. What is Sales Management
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar4
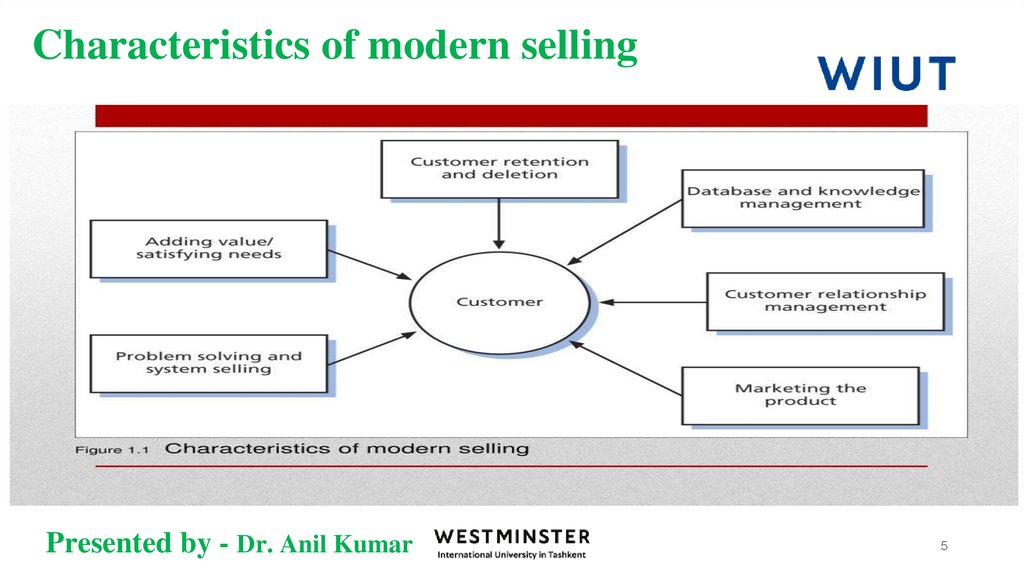
5. Characteristics of modern selling
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar5
6. What is Sales Management
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar6
7. What is Sales Management
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar7
8. What are the sales managers goals?
Sales• Revenues
• Profits
• Market Share
• Controlling internal costs
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
8
9. How do they obtain their goals?
Knowledge of the sales environment• Planning for sales
• Recruiting the sales force
• Training the sales force
• Motivating the sales force
• Supervising the sales force
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
9
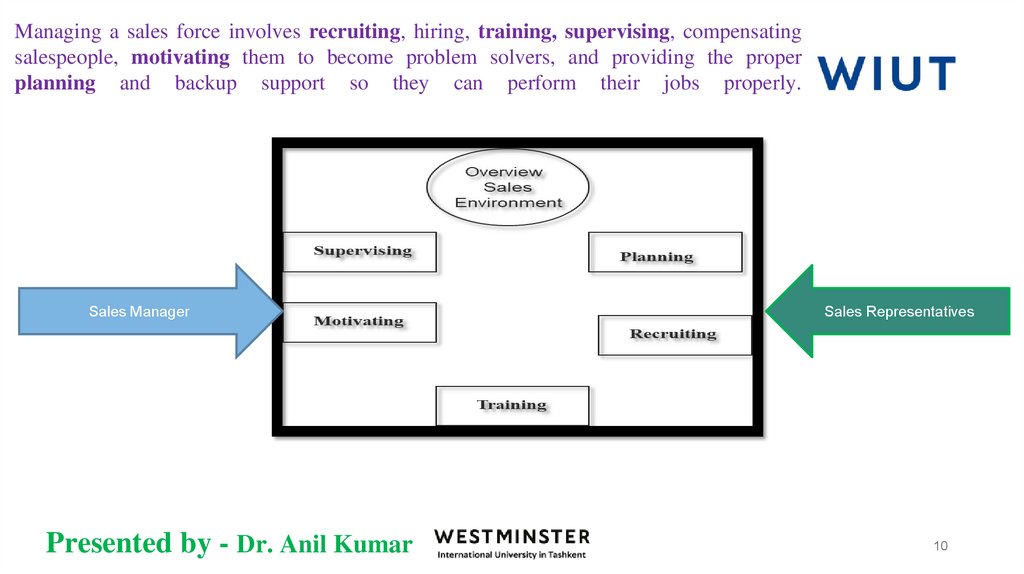
10. Managing a sales force involves recruiting, hiring, training, supervising, compensating salespeople, motivating them to become
problem solvers, and providing the properplanning and backup support so they can perform their jobs properly.
Sales Manager
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
Sales Representatives
10
11. Sales Environment
• Industrial Revolution• After WWI the need for mass distribution became evident
• 1950s and the marketing concept
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
11
12. Sales Environment
Organizing the Sales ForceOrganizing- the assignment of tasks, the grouping of task into
departments, and the allocation of resources to departments
Structure of the sales managers job
Chain of command
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
12
13. Sales Environment
Legal Issues
Consumer protection laws
Antitrust laws
Unfair trade practices
Fraud and misrepresentation
Uniform Commercial Code
Direct-to-consumer sales
Antidiscrimination laws
Ethical Issues
Creating ethical corporate structures
Relationships with customers
Relationships with competitors
Relationships with the firm
Relationships with society
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
13
14. Sales Environment
Internationalization
• Ethnic composition
• Religious orientation
• Social class environment
• Education
• Gender bias
• Differences in negotiating styles
• Differences in decision making
• Job status and company protocol
• Social aspects
• Perceptions of time
• Personal relationships
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
14
15. Sales Person Motivation
The most commonly used definitions of salesperson motivation include three dimensions:
(1) intensity, referring to the amount of mental and physical effort put forth by salespeople,
(2) persistence, describing the salesperson’s choice to expend effort over a period of time,
and
(3) direction, implying that salespeople choose where their efforts will be spent among
various activities.
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
15
16. Sales Person Motivation
Motivating can be done-
• Recognition
• Awards
• Special communications
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
16
17. Sales Person Motivation
Motivation can be done by compensating • Salary
• Commission
• Bonus
• Combinations
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
17
18. Sales Person Motivation
To motivate today’s salespeople, sales managers need to treat them like seven Rolls Royces! (VII RR):Valued – the ‘feel good’ factor
Involved in the business as much as possible
Informed regularly on People, Policies, Performance and Points that interest them
Rewarded fairly related to achievement and the financial means of the company
Recognised with thanks and ‘by catching them doing something right’
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
18
19. BENEFITS OF SELLING ACTIVITIES
Benefits to the society
Benefits to consumers
Benefits to business firms; their sales-persons and customers
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
19
20. Staff motivation
In today’s business world,sales managers will get more from their staff if they A.G.R.E.EAgree targets and objectives whenever possible, rather than impose
Give time and help to each of their people
Review progress on a regular basis
Empower sales people to act on their own initiative within agreed guidelines
Encourage by recognition, motivation and helping them to learn from mistakes.
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
20
21. B-B & B-C Selling
B-B&
B-C
Selling
The term business-to-consumer (B2C) refers to the process of selling products and services
directly between a business and consumers who are the endusers of its products or services.
Most companies that sell directly to consumers can be referred to as B2C companies. An
example of B2C includes retail sales, as the items sold are directly targeted and consumed
by one individual person.
Business-to-business (B2B) describes a relationship, situation, or marketplace between one
business entity and another. A B2B company is one sells to other businesses. Common
examples of B2B sales include: Organizations that provide professional services (e.g.
market research) to companies.
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar
21
22. QUESTIONS PLEASE IF ANY……………….
Presented by - Dr. Anil Kumar22


















 english
english








