Similar presentations:
After finishing this lecture student will be able to answer following questions
1. TEACHING WEEK 2
Sales Management2. After finishing this lecture student will be able to answer following questions -:
Need, Want, Demand of the buyersSales Process
Organisational Sales Structure
How sales manager will get more?
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
2
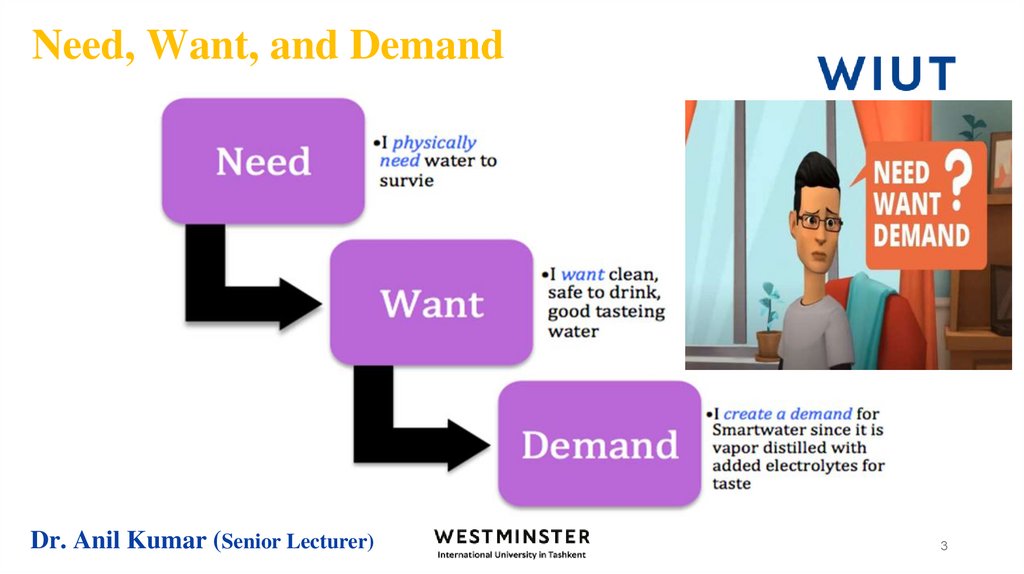
3. Need, Want, and Demand
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)3
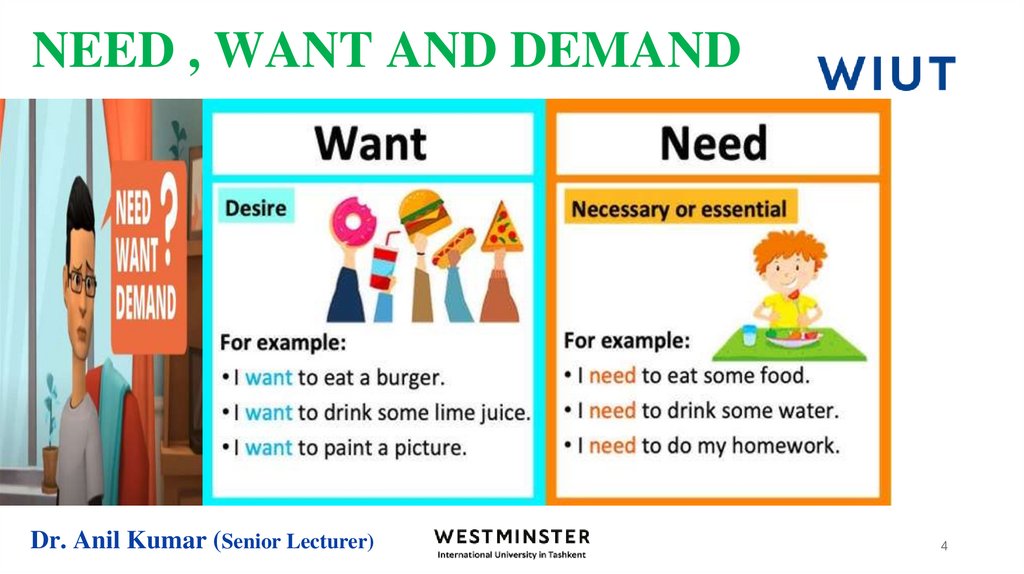
4. NEED , WANT AND DEMAND
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)4
5. Need, Want, Demand of the buyers
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)5
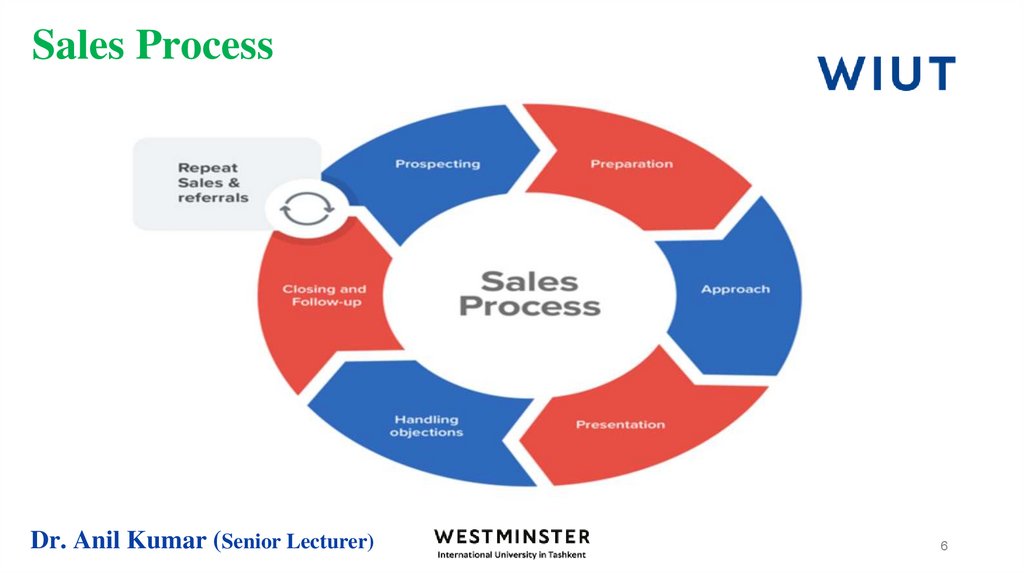
6. Sales Process
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)6
7. Sales Process
Professional salespeople go through seven steps when helping a customer make a purchase.Prospecting
Preparation
Approach
Presentation
Addressing Objections
Closing
Follow up
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
7
8. Life doesn’t always go as planned. We need to react to new circumstances and adapt to them.
The most commonmistake many sales
men make is that
they start with telling
the client about all
the advantages of
the product or service
They think they
don’t have anything
else to talk about with their clients except for that.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
8
9. Prospecting
The first thing a perfect salesperson must do is pinpoint the client’s needs (i.e., their painpoints). So, the salesperson just asks leading questions and listens to the client’s answers.
Consequently, the more information you get from the client during such a conversation, the
more likely you are to close the deal.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
9
10. Prospecting
When a company is looking for new customers 1.) follow employer leads and suggestions2.) search in telephone directories
3.) search trade and professional directories
4.) Search newspapers
5.) Look through commercial lists
6.) Use customer referrals
7.) Use cold canvassing – which means contacting clients “coldly”
meaning without any previous contact. The potential customer may
or may not be interested, but it is the sales representative's job to
inform the potential customer about the company and products as
much as possible during the interaction.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
10
11. Preparation
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)11
12. Preparation
Preparing for initial contact with a potential customer, researching the market andcollecting all relevant information regarding your product or service. Develop
your sales presentation and tailor it to your potential client’s particular needs.
Preparation is key to setting you up for success. The better you understand your
prospect and their needs, the better you can address their objections and set
yourself apart from the competition.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
12
13. Preparation
Analyze past sales records.
View notes about the personal aspects of the customer.
Revisiting previous customers; selling add-ons.
Inquire with other salespeople of non-competing lines.
Ask questions in a pre-visit phone call.
Make appointments to see the prospective customers in order to have time to explain
the features of the product.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
13
14. Approaching
Make first contact with your client. This is called the approach.Sometimes this is a face-to-face meeting, sometimes it’s over the
phone. There are three common approach methods.
Premium approach: Presenting your potential client with a gift at the
beginning of your interaction
Question approach: Asking a question to get the prospect interested
Product approach: Giving the prospect a sample or a free trial to
review and evaluate your service
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
14
15. Approaching
The approach is the first face-to-face contact with the customer. The approach sets the mood oratmosphere for the other steps of the sale. It has three purposes:
• To begin conversation
• To establish a relationship with the customer
• To focus on the merchandise
When approaching the customer, follow these rules:
• Treat the customer as an individual.
• Be perceptive about the customer’s buying style.
• Be enthusiastic, courteous, and respectful
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
15
16.
PresentationDr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
16
17.
PresentationIn the presentation phase, you actively demonstrate how your product or service meets
the needs of your potential customer
you must determine the customers needs. You can do this by asking questions and
actively listening to customers. Sometimes customers are unsure of their needs and you,
as the sales person, should be able to direct them towards the best product for them.
Then you must present the product to the customers. Speak honestly while telling the
customer the benefits and disadvantages of purchasing the product. Often, customers
appreciate honesty
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
17
18. Addressing Objections
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)18
19. Addressing Objections
Most underrated step of the sales process is handling objections. This is where you listen toyour prospect’s concerns and address them. It’s also where many unsuccessful salespeople
drop out of the process—44% of salespeople abandoning pursuit after one rejection, 22% after
two rejections, 14% after three, and 12% after four, even though 80% of sales require at least
five follow-ups to convert. Successfully handling objections and alleviating concerns separates
good salespeople from bad and great from good.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
19
20. Addressing Objections
Listen Fully to the Objection. Your first reaction when you hear an objection
may be to jump right in and respond immediately. ...
Understand the Objection Completely. Many objections hide underlying issues
that the buyer can't or isn't ready to articulate. ...
Respond Properly. ...
Confirm You've Satisfied the Objection.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
20
21. Addressing Objections
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)21
22. Closing
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)22
23. Closing
Closing a sale occurs when the seller and buyer agree to the conditions of thesale and the buyer makes a firm commitment to the transaction. Closing the sale
should not be seen as a transactional event, but rather as the natural ending of the
sales process.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
23
24. Closing
In the closing stage, you get the decision from the client to move forward.Depending on your business, you might try one of these three closing techniques.
Alternative choice close: Assuming the sale and offering the prospect a choice,
where both options close the sale—for example, “Will you be paying the whole
fee up front or in installments?” or “Will that be cash or charge?”
Extra inducement close: Offering something extra to get the prospect to close,
such as a free month of service or a discount
Standing room only close: Creating urgency by expressing that time is of the
essence—for example, “The price will be going up after this month” or “We only
have six spots left”
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
24
25. Follow up
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)25
26. Follow up
This final stage in the sales process is necessary toensure that the customer is satisfied with the purchase
and no problems with factors such as delivery,
installation, product use and training have arisen.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
26
27. Follow up Once you have closed the sale, your job is not done. The follow-up stage keeps you in contact with customers you have
closed, not only for potential repeat business but for referrals aswell. And since retaining current customers is six to seven
times less costly than acquiring new ones, maintaining
relationships is key.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
27
28. Concluding Remarks……..
The best sales systems should follow the KlSS principle – Keep It Short and Simple!To motivate today’s salespeople, sales managers need to treat them like seven Rolls Royces!
(VII RR):
• Valued – the ‘feel good’ factor
• I nvolved in the business as much as possible
• I nformed regularly on People, Policies, Performance and Points that interest them
• R ewarded fairly related to achievement and the financial means of the company
• R ecognised with thanks and ‘by catching them doing something right’
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
28
29.
Dr. Anil Kumar(Senior Lecturer)29

























 english
english








