Similar presentations:
Enlargement and similarity exemplar questions and answers
1.
©White Rose Maths2.
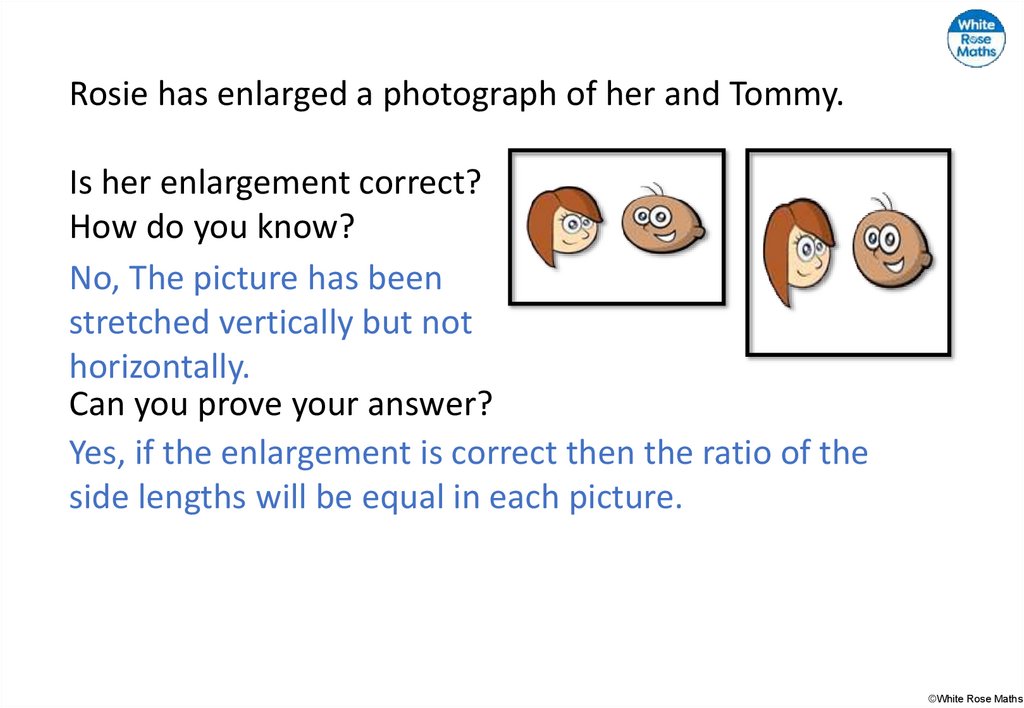
Rosie has enlarged a photograph of her and Tommy.Is her enlargement correct?
How do you know?
Can you prove your answer?
©White Rose Maths
3.
Rosie has enlarged a photograph of her and Tommy.Is her enlargement correct?
How do you know?
No, The picture has been
stretched vertically but not
horizontally.
Can you prove your answer?
Yes, if the enlargement is correct then the ratio of the
side lengths will be equal in each picture.
©White Rose Maths
4.
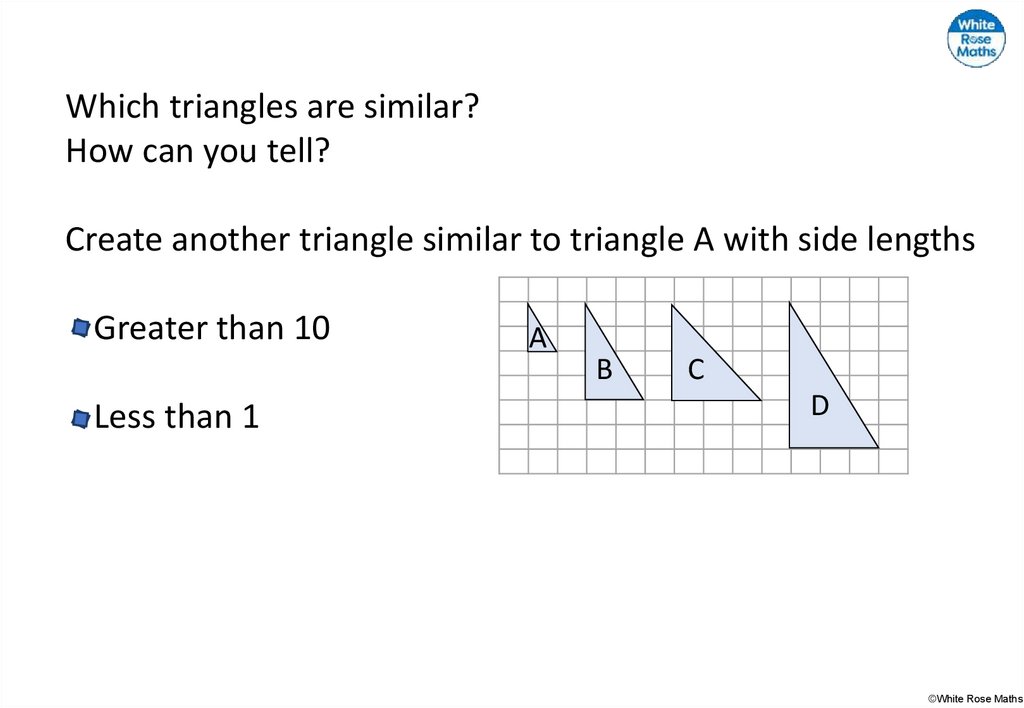
Which triangles are similar?How can you tell?
Create another triangle similar to triangle A with side lengths
Greater than 10
Less than 1
A
B
C
D
©White Rose Maths
5.
Which triangles are similar? A, B and DHow can you tell?
Corresponding sides are the in the same ratio.
Create another triangle similar to triangle A with side lengths
Greater than 10
Less than 1
A
B
C
D
Compare examples as a class.
©White Rose Maths
6.
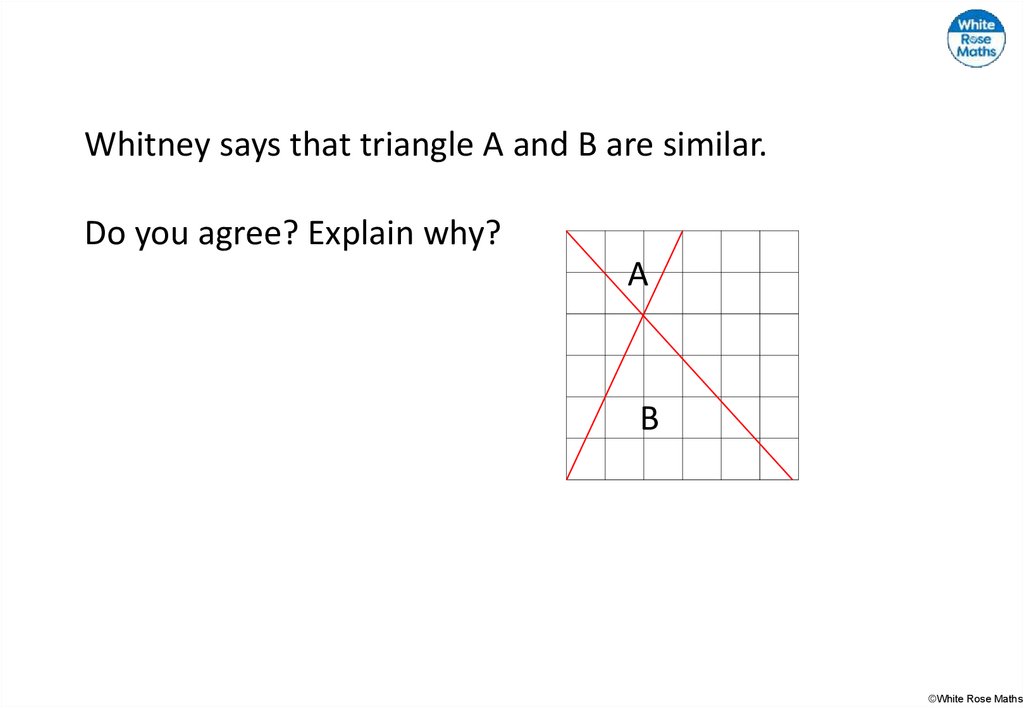
Whitney says that triangle A and B are similar.Do you agree? Explain why?
A
B
©White Rose Maths
7.
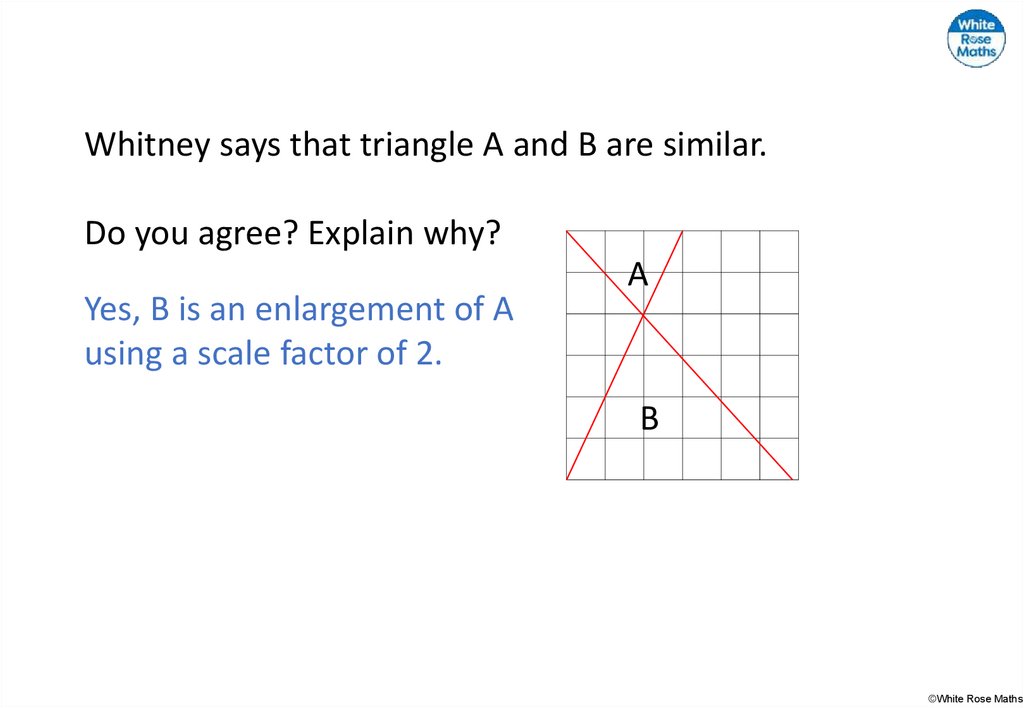
Whitney says that triangle A and B are similar.Do you agree? Explain why?
Yes, B is an enlargement of A
using a scale factor of 2.
A
B
©White Rose Maths
8.
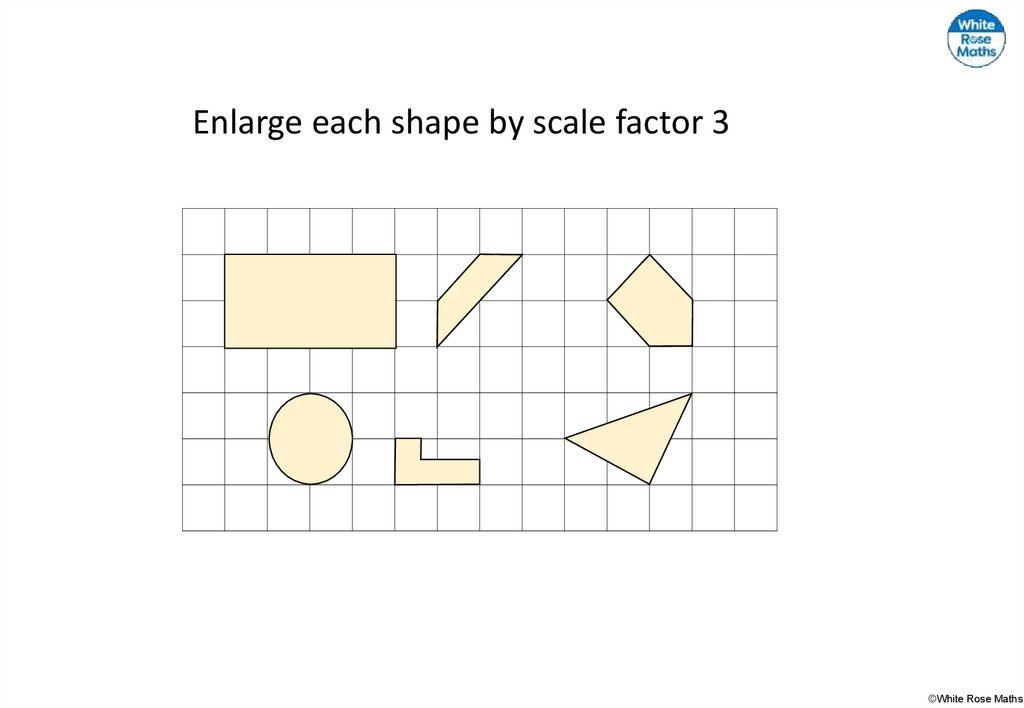
Enlarge each shape by scale factor 3©White Rose Maths
9.
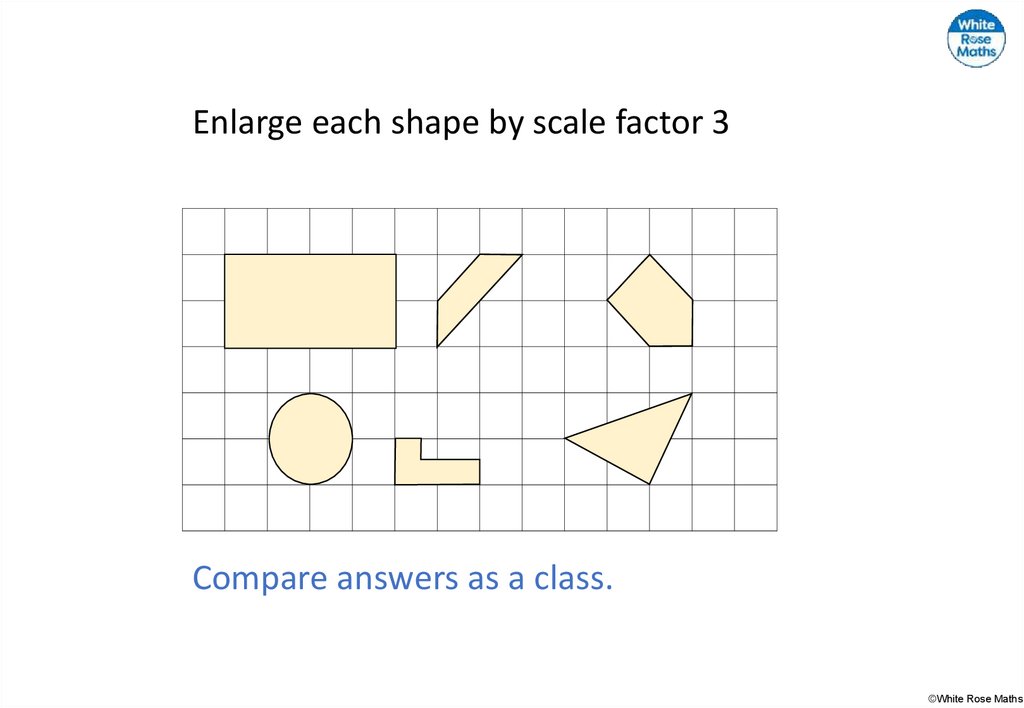
Enlarge each shape by scale factor 3Compare answers as a class.
©White Rose Maths
10.
What is the greatest integer scale factor that shape Acan be enlarged by so that it fits on the grid?
A
©White Rose Maths
11.
What is the greatest integer scale factor that shape Acan be enlarged by so that it fits on the grid?
A
Greatest integer scale factor is 2
©White Rose Maths
12.
A regular hexagon has been enlarged by scale factor 4The image has a perimeter of 36 cm.
What is the length of each side of the object?
©White Rose Maths
13.
A regular hexagon has been enlarged by scale factor 4The image has a perimeter of 36 cm.
What is the length of each side of the object?
Side length = 24 cm
©White Rose Maths
14.
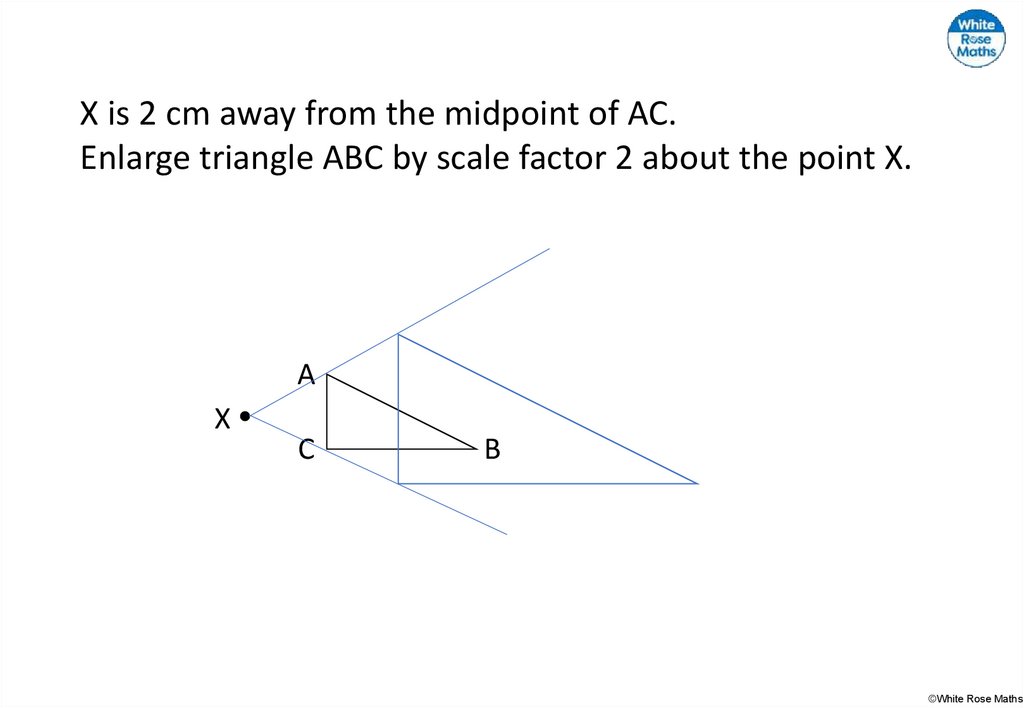
X is 2 cm away from the midpoint of AC.Enlarge triangle ABC by scale factor 2 about the point X.
A
X
C
B
©White Rose Maths
15.
X is 2 cm away from the midpoint of AC.Enlarge triangle ABC by scale factor 2 about the point X.
A
X
C
B
©White Rose Maths
16.
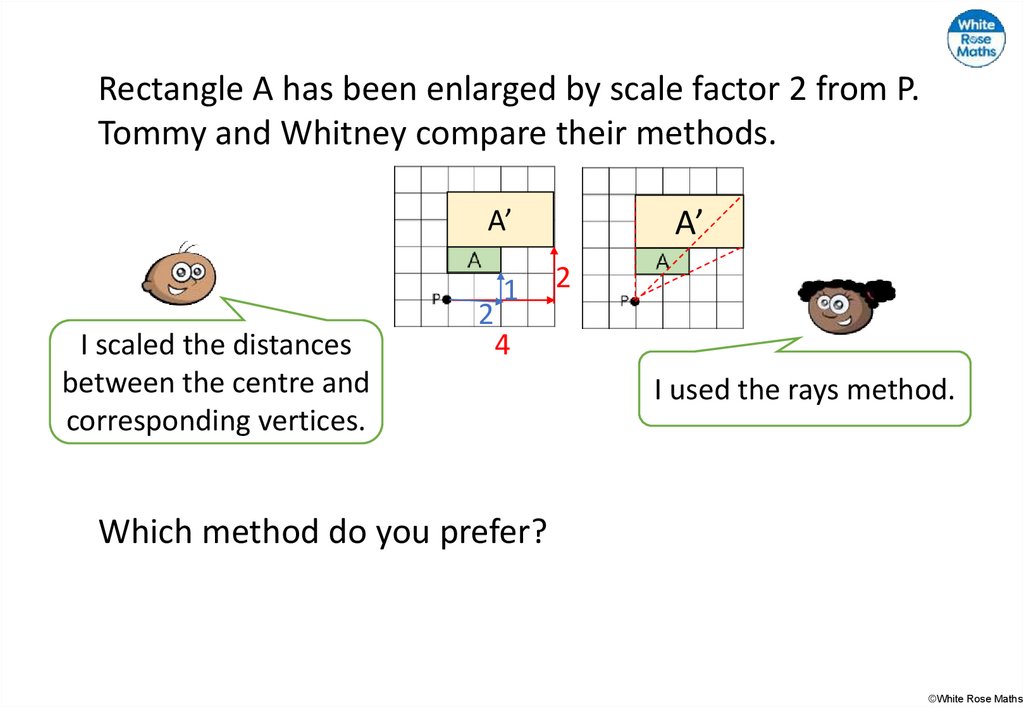
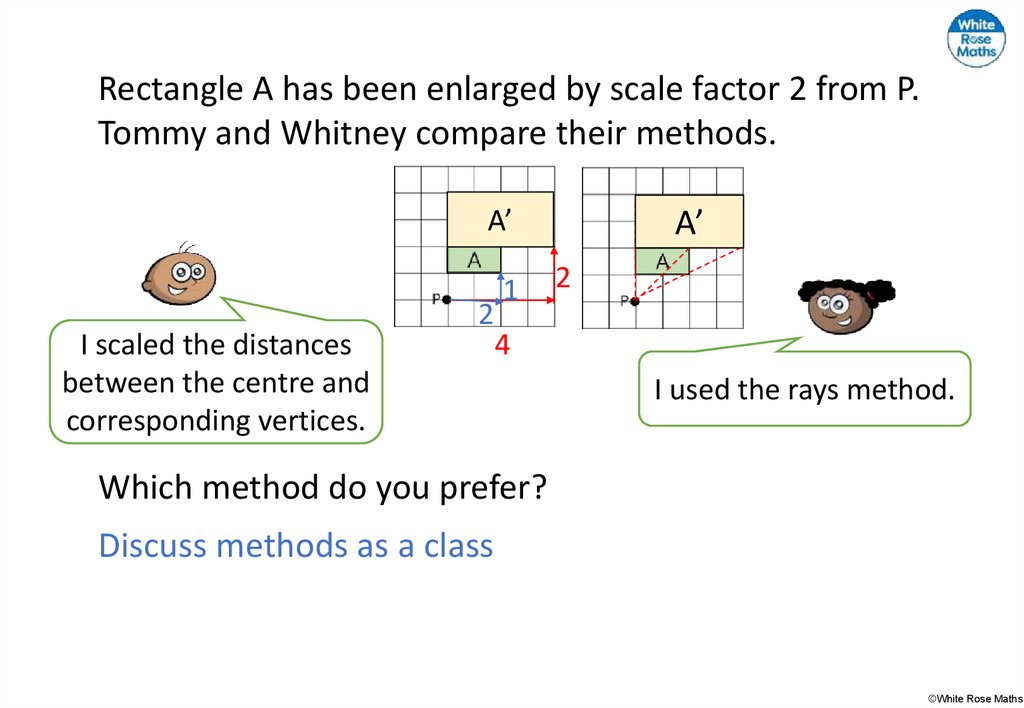
Rectangle A has been enlarged by scale factor 2 from P.Tommy and Whitney compare their methods.
A’
A’
I scaled the distances
between the centre and
corresponding vertices.
2
1
2
4
I used the rays method.
Which method do you prefer?
©White Rose Maths
17.
Rectangle A has been enlarged by scale factor 2 from P.Tommy and Whitney compare their methods.
A’
A’
I scaled the distances
between the centre and
corresponding vertices.
2
1
2
4
I used the rays method.
Which method do you prefer?
Discuss methods as a class
©White Rose Maths
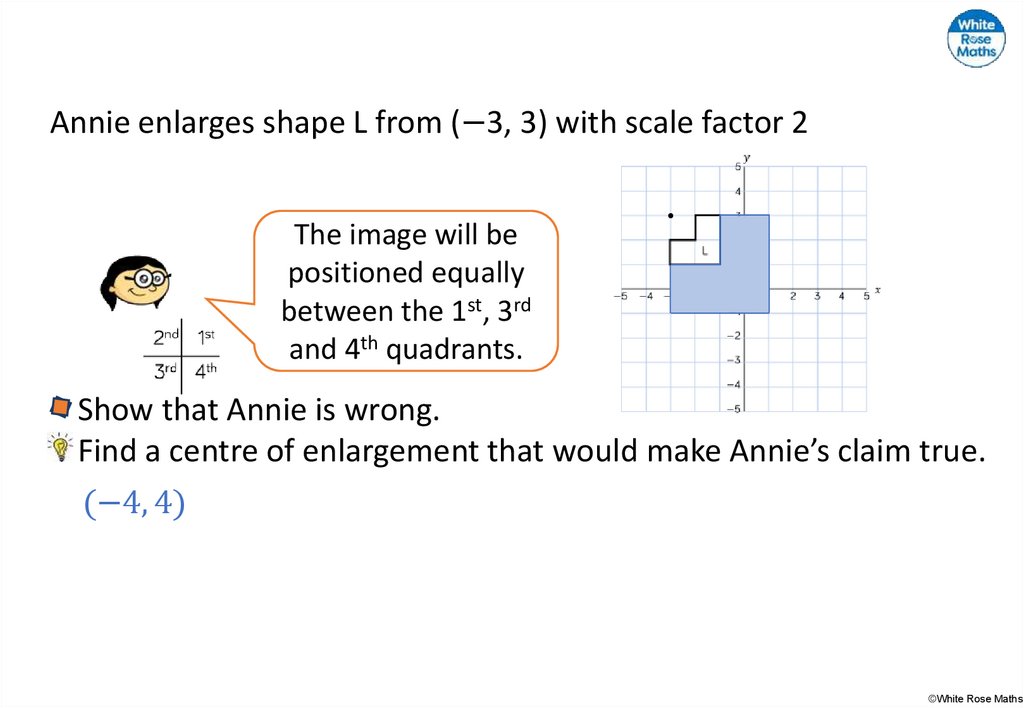
18.
Annie enlarges shape L from (−3, 3) with scale factor 2The image will be
positioned equally
between the 1st, 3rd
and 4th quadrants.
Show that Annie is wrong.
Find a centre of enlargement that would make Annie’s claim true.
©White Rose Maths
19.
Annie enlarges shape L from (−3, 3) with scale factor 2The image will be
positioned equally
between the 1st, 3rd
and 4th quadrants.
Show that Annie is wrong.
Find a centre of enlargement that would make Annie’s claim true.
(−4, 4)
©White Rose Maths
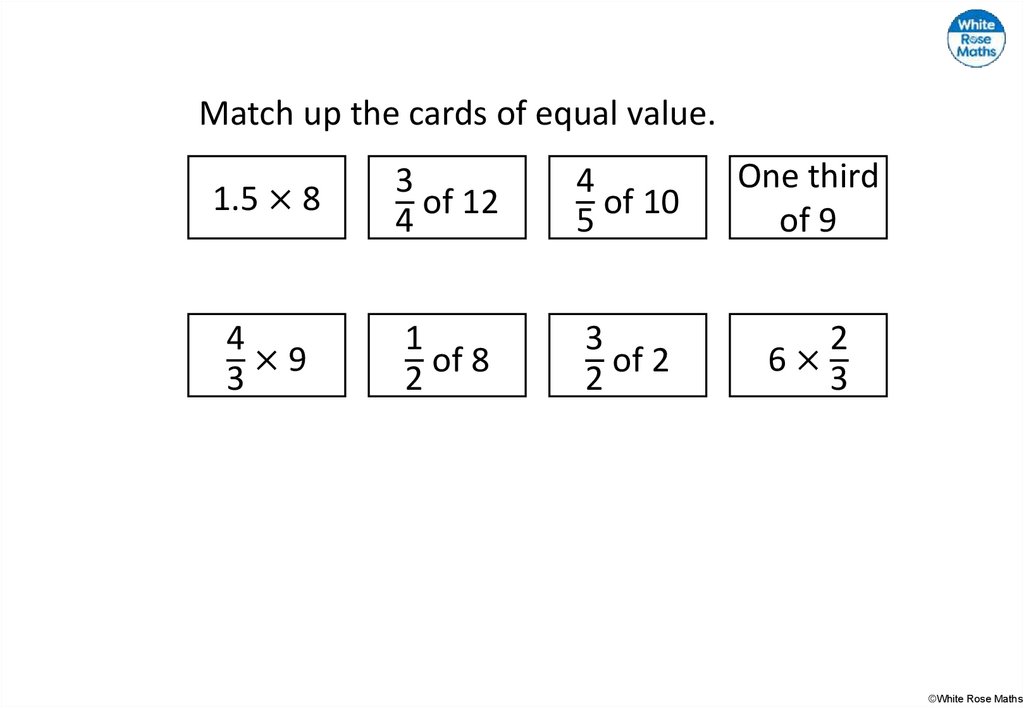
20.
Match up the cards of equal value.1.5 × 8
3
of 12
4
4
of 10
5
One third
of 9
4
×9
3
1
of 8
2
3
of 2
2
2
6×
3
©White Rose Maths
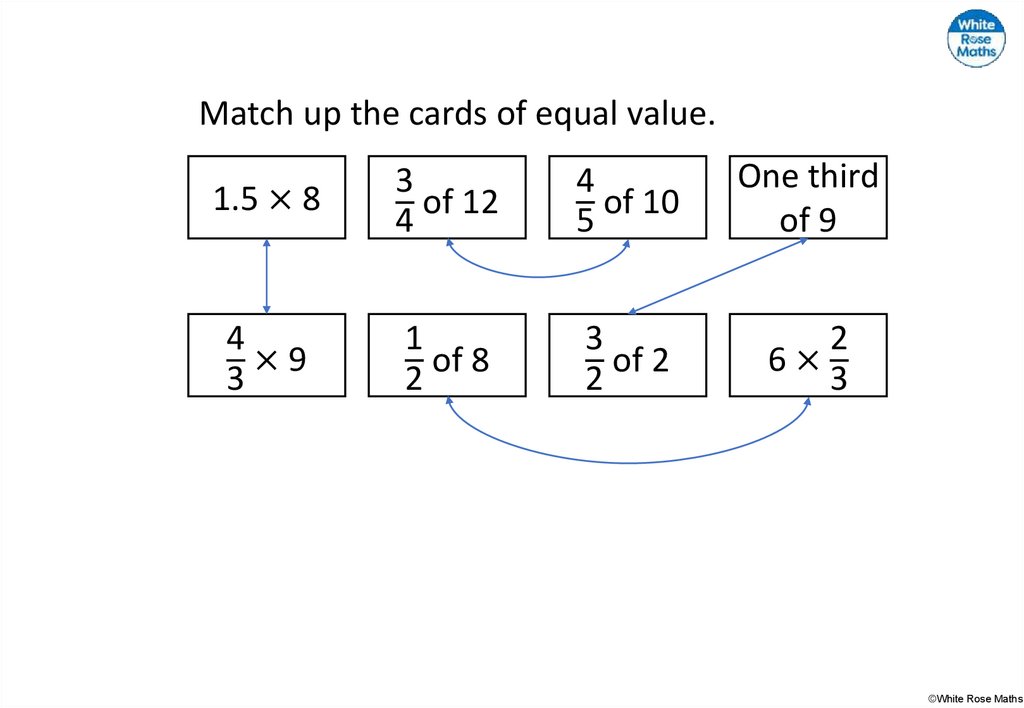
21.
Match up the cards of equal value.1.5 × 8
3
of 12
4
4
of 10
5
One third
of 9
4
×9
3
1
of 8
2
3
of 2
2
2
6×
3
©White Rose Maths
22.
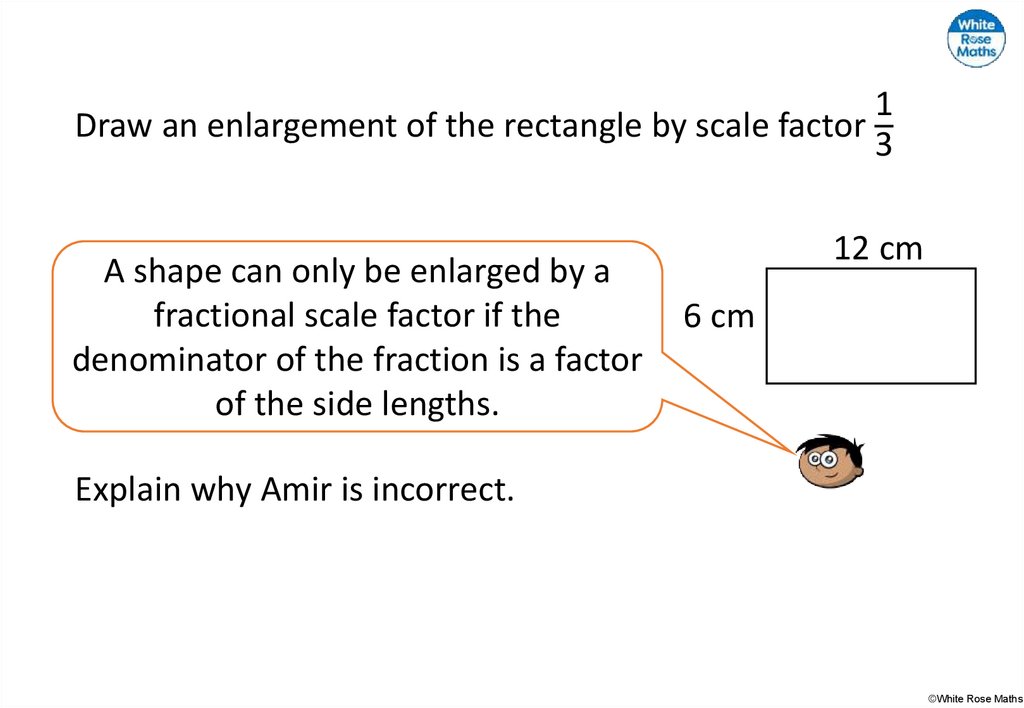
1Draw an enlargement of the rectangle by scale factor
3
A shape can only be enlarged by a
fractional scale factor if the
denominator of the fraction is a factor
of the side lengths.
12 cm
6 cm
Explain why Amir is incorrect.
©White Rose Maths
23.
1Draw an enlargement of the rectangle by scale factor
3
4 cm
2 cm
12 cm
A shape can only be enlarged by a
fractional scale factor if the
6 cm
denominator of the fraction is a factor
of the side lengths.
Explain why Amir is incorrect.
The rectangle may have non-integer lengths but still be
an enlargement.
©White Rose Maths
24.
A triangle has vertices (2, 4), (10, 2) and (8, 0).1
Enlarge the triangle by scale factor
2
about the origin
about the point (8, 2)
about the point (−2, −2)
©White Rose Maths
25.
A triangle has vertices (2, 4), (10, 2) and (8, 0).1
Enlarge the triangle by scale factor
2
Vertices - (1, 2), (5, 1), (4,0)
about the origin
about the point (8, 2)
Vertices - (5, 3), (9, 2), (8,1)
about the point (−2, −2) Vertices - (0, 1), (4, 0), (3,−1)
Compare accuracy of answers as a class.
©White Rose Maths
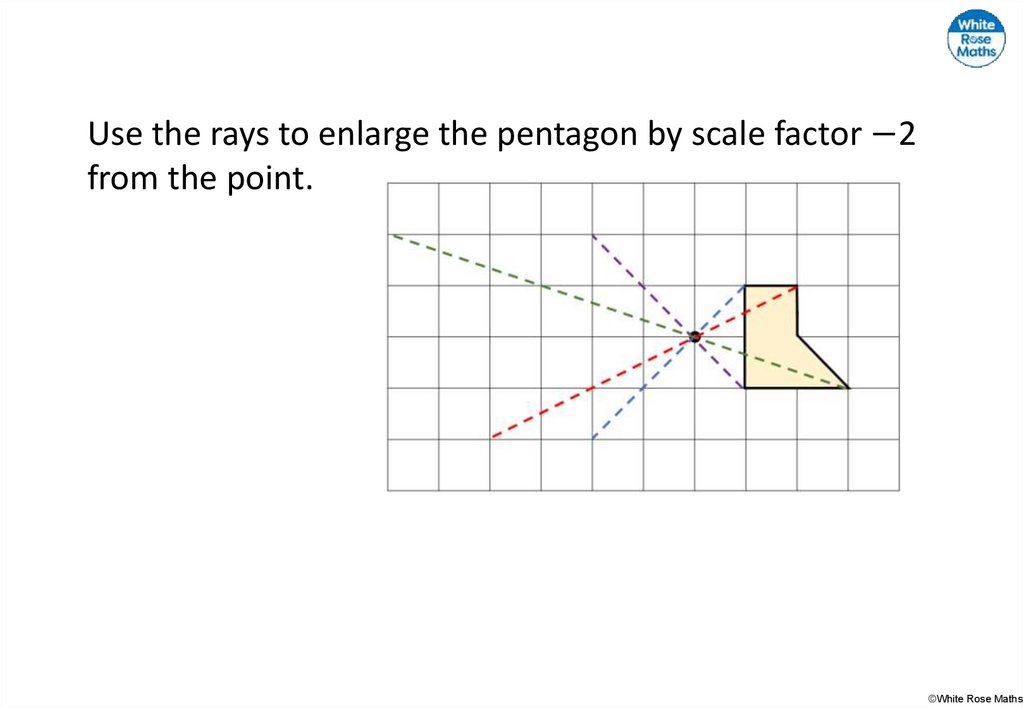
26.
Use the rays to enlarge the pentagon by scale factor −2from the point.
©White Rose Maths
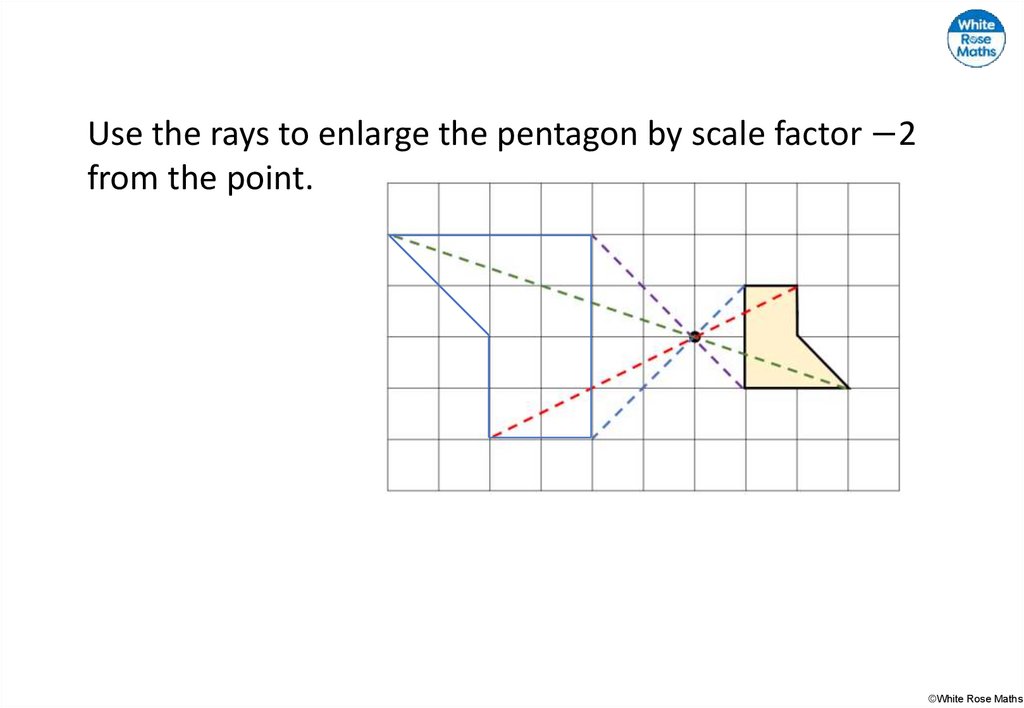
27.
Use the rays to enlarge the pentagon by scale factor −2from the point.
©White Rose Maths
28.
Enlargements by a positive scalefactor are larger than those by a
negative scale factor.
Is Dexter’s claim always, sometimes or never true?
Justify your answer
©White Rose Maths
29.
Enlargements by a positive scalefactor are larger than those by a
negative scale factor.
Is Dexter’s claim always, sometimes or never true?
Justify your answer
Dexter claim is sometimes true. It depends on the
magnitude of the scale factor, for example:
• Scale factors of −5 and 3. The scale factor −5
produces a larger enlargement
• Scale factors of 5 and −3. The scale factor 5
produces a larger enlargement
• Scale factors of −3 and3. Both produce the same
sized enlargement
©White Rose Maths
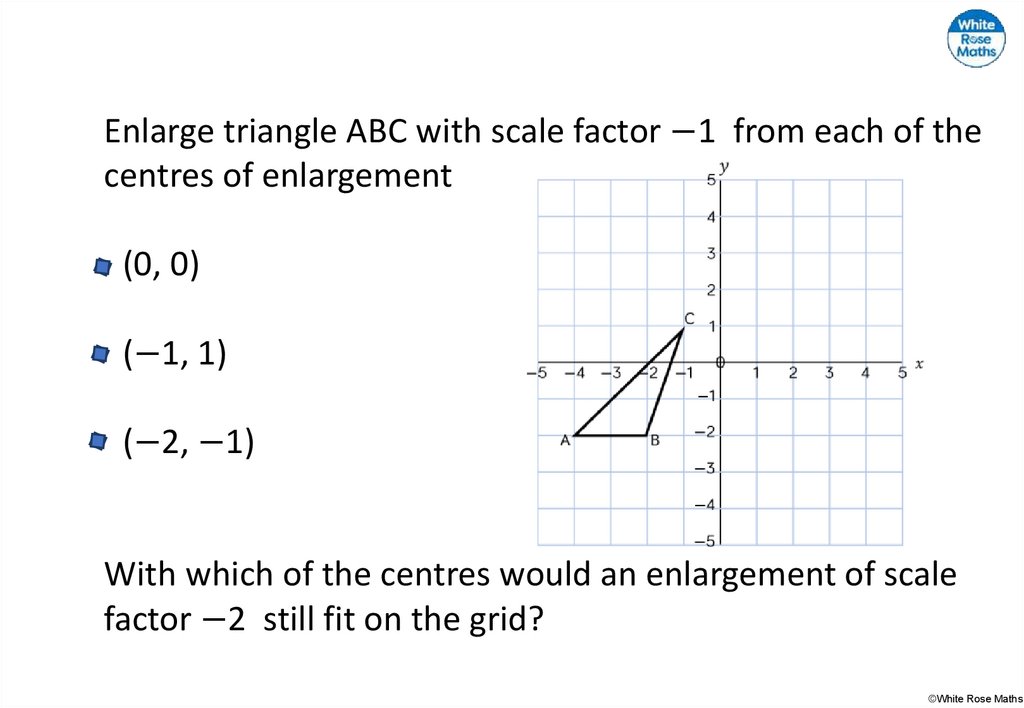
30.
Enlarge triangle ABC with scale factor −1 from each of thecentres of enlargement
(0, 0)
(−1, 1)
(−2, −1)
With which of the centres would an enlargement of scale
factor −2 still fit on the grid?
©White Rose Maths
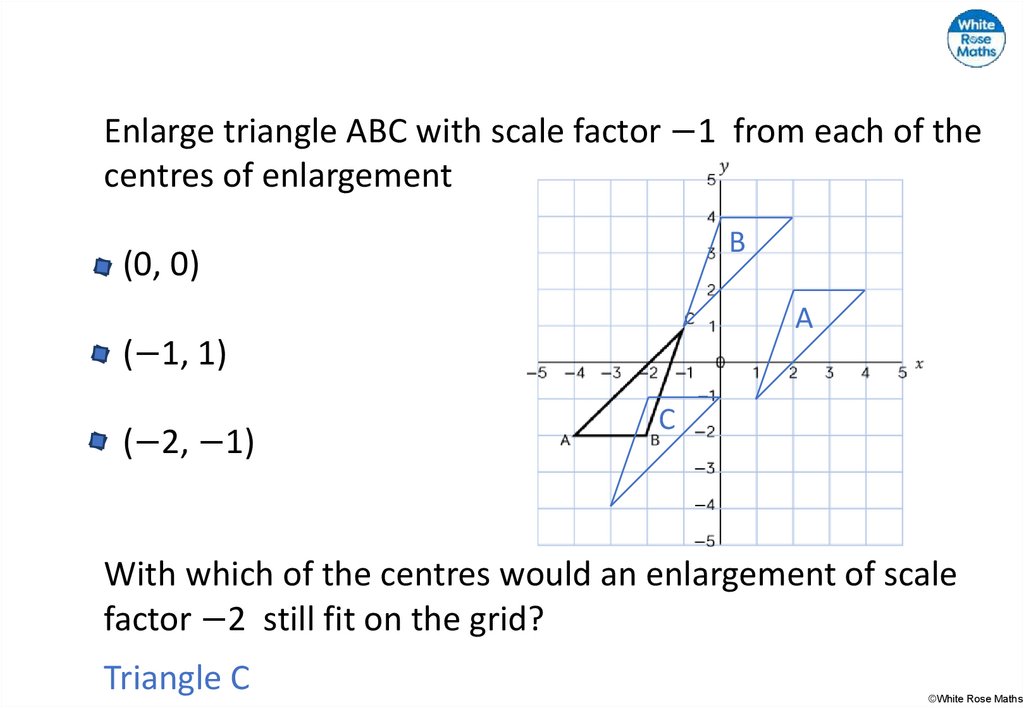
31.
Enlarge triangle ABC with scale factor −1 from each of thecentres of enlargement
B
(0, 0)
A
(−1, 1)
(−2, −1)
C
With which of the centres would an enlargement of scale
factor −2 still fit on the grid?
Triangle C
©White Rose Maths
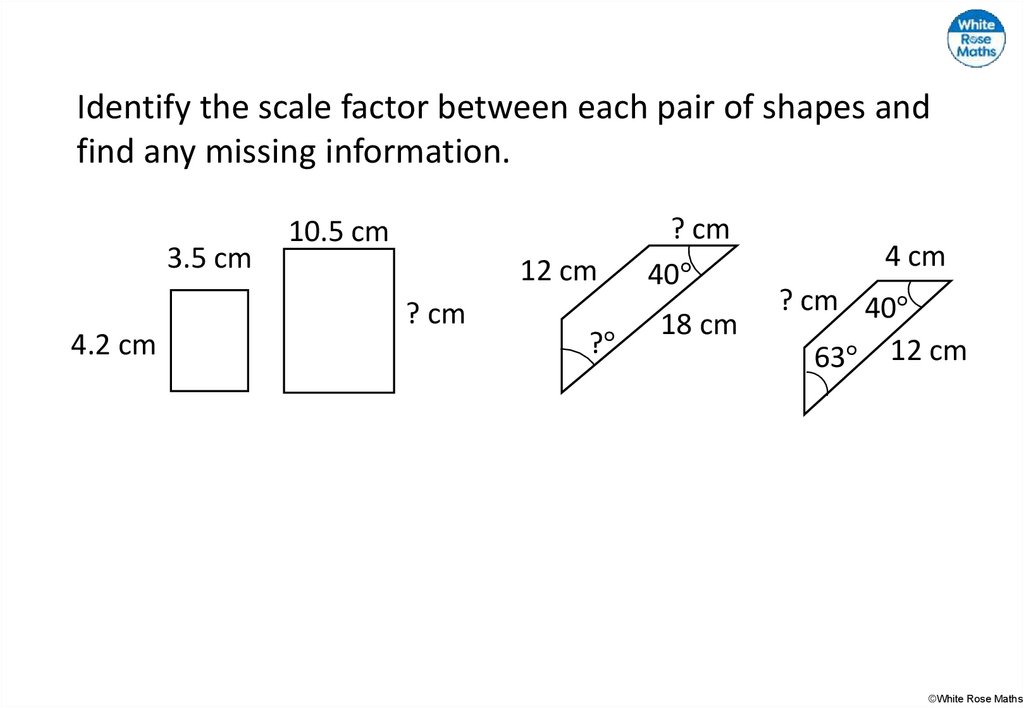
32.
Identify the scale factor between each pair of shapes andfind any missing information.
3.5 cm
4.2 cm
10.5 cm
12 cm
? cm
?°
? cm
40°
18 cm
4 cm
? cm 40°
63° 12 cm
©White Rose Maths
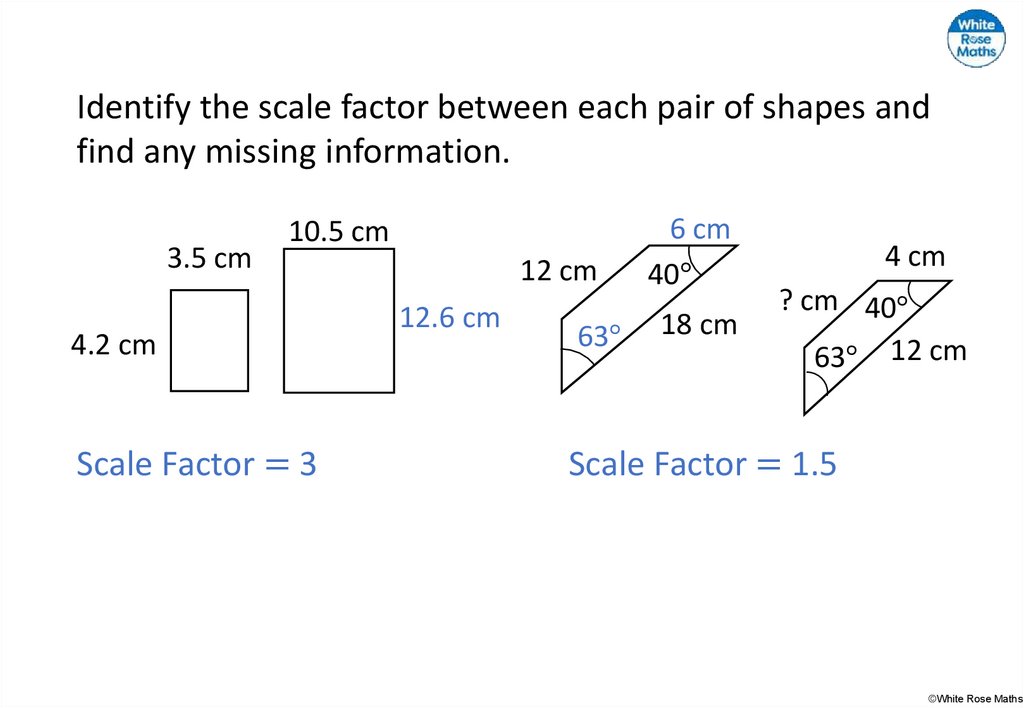
33.
Identify the scale factor between each pair of shapes andfind any missing information.
3.5 cm
10.5 cm
4.2 cm
Scale Factor = 3
12 cm
12.6 cm
63°
6 cm
40°
18 cm
4 cm
? cm 40°
63° 12 cm
Scale Factor = 1.5
©White Rose Maths
34.
Rectangles G and H are similar.Eva thinks the missing length in H is 9
Do you agree? Justify your answer
?
3 cm
4 cm
G
12 cm
H
©White Rose Maths
35.
Rectangles G and H are similar.Eva thinks the missing length in H is 9
Do you agree? Justify your answer
?
3 cm
4 cm
G
12 cm
H
No, the corresponding side length on G is 4 cm
because the rectangle has been rotated.
The missing side length is 16 cm
©White Rose Maths
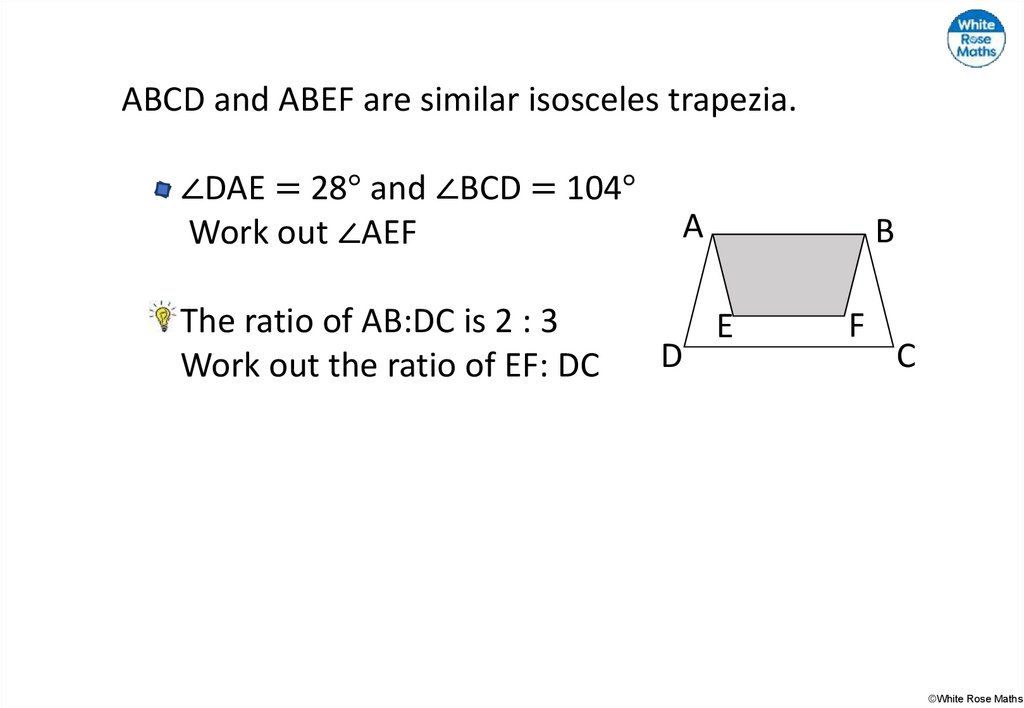
36.
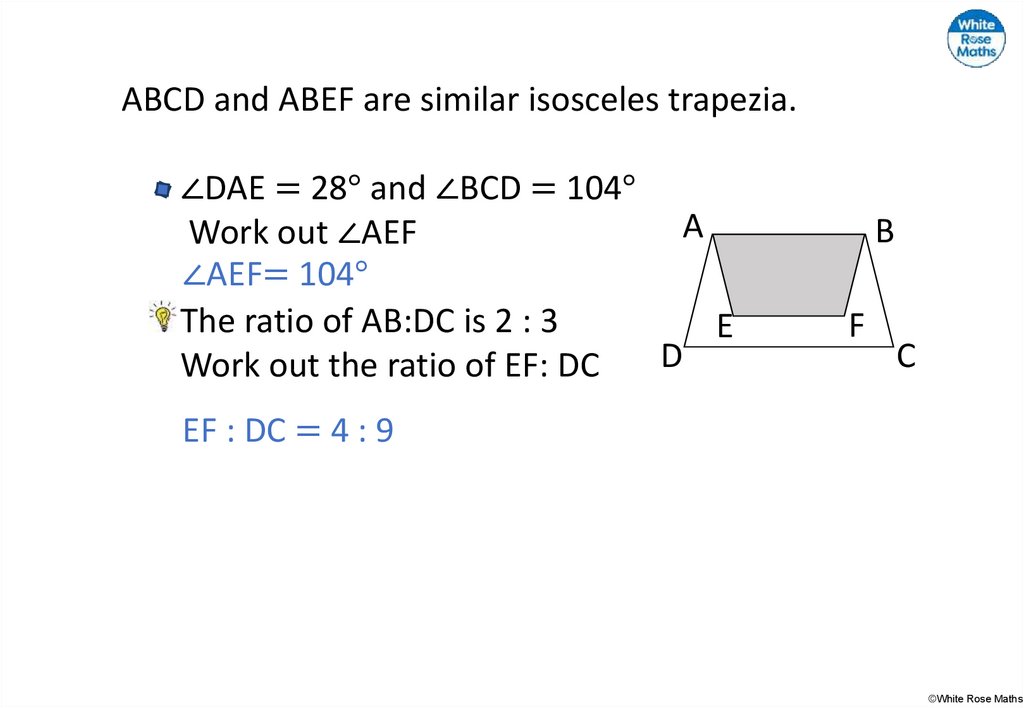
ABCD and ABEF are similar isosceles trapezia.∠DAE = 28° and ∠BCD = 104°
Work out ∠AEF
The ratio of AB:DC is 2 : 3
Work out the ratio of EF: DC
A
D
B
E
F
C
©White Rose Maths
37.
ABCD and ABEF are similar isosceles trapezia.∠DAE = 28° and ∠BCD = 104°
A
Work out ∠AEF
∠AEF= 104°
The ratio of AB:DC is 2 : 3
E
D
Work out the ratio of EF: DC
B
F
C
EF : DC = 4 : 9
©White Rose Maths
38.
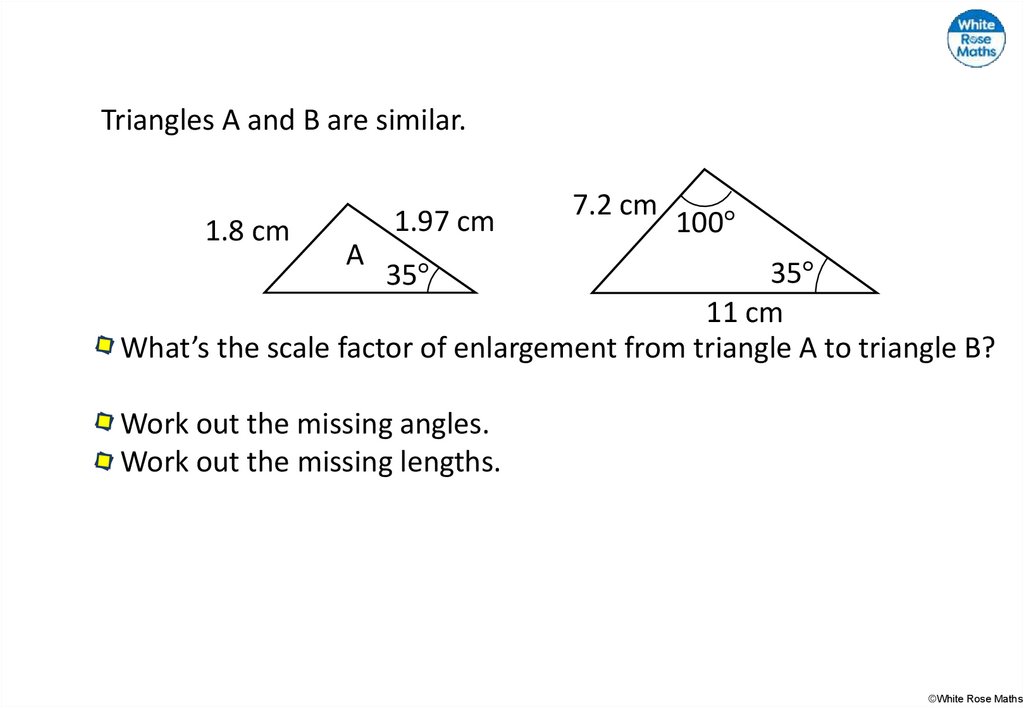
Triangles A and B are similar.1.8 cm
1.97 cm
A
7.2 cm
100°
35°
11 cm
What’s the scale factor of enlargement from triangle A to triangle B?
35°
Work out the missing angles.
Work out the missing lengths.
©White Rose Maths
39.
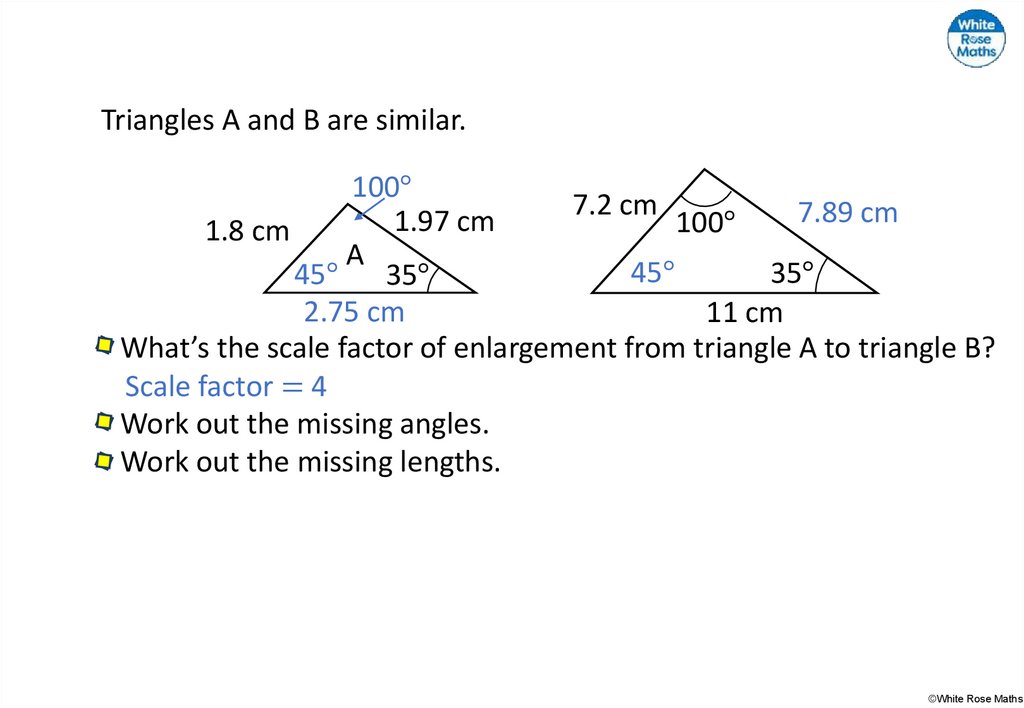
Triangles A and B are similar.100°
7.2 cm
7.89 cm
1.97
cm
100°
1.8 cm
A
45°
35°
45°
35°
2.75 cm
11 cm
What’s the scale factor of enlargement from triangle A to triangle B?
Scale factor = 4
Work out the missing angles.
Work out the missing lengths.
©White Rose Maths
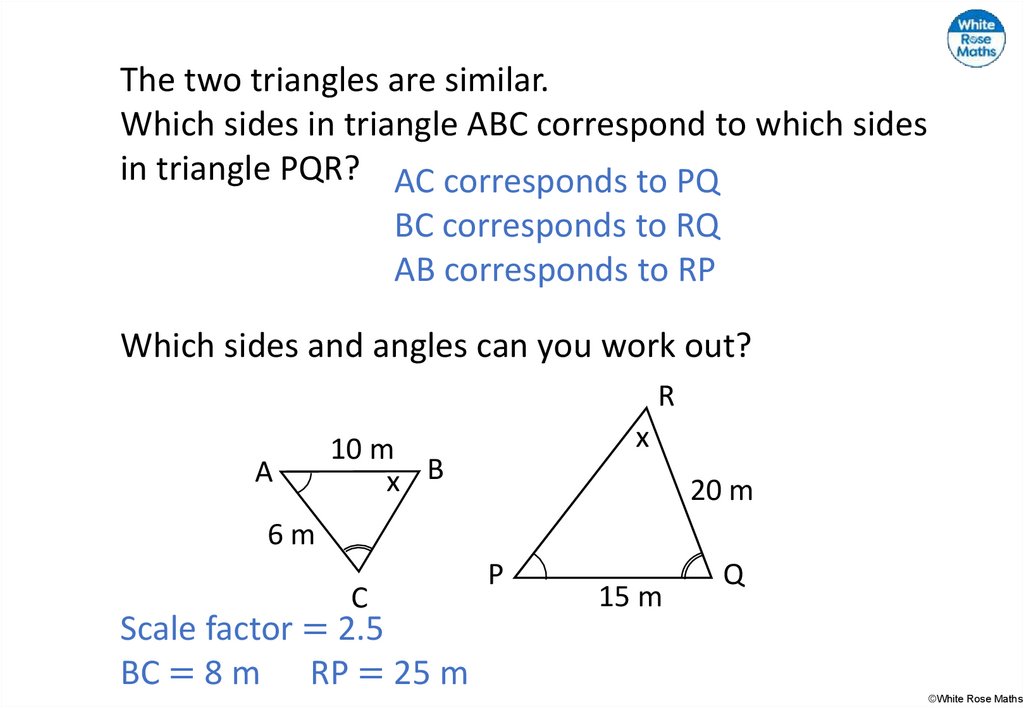
40.
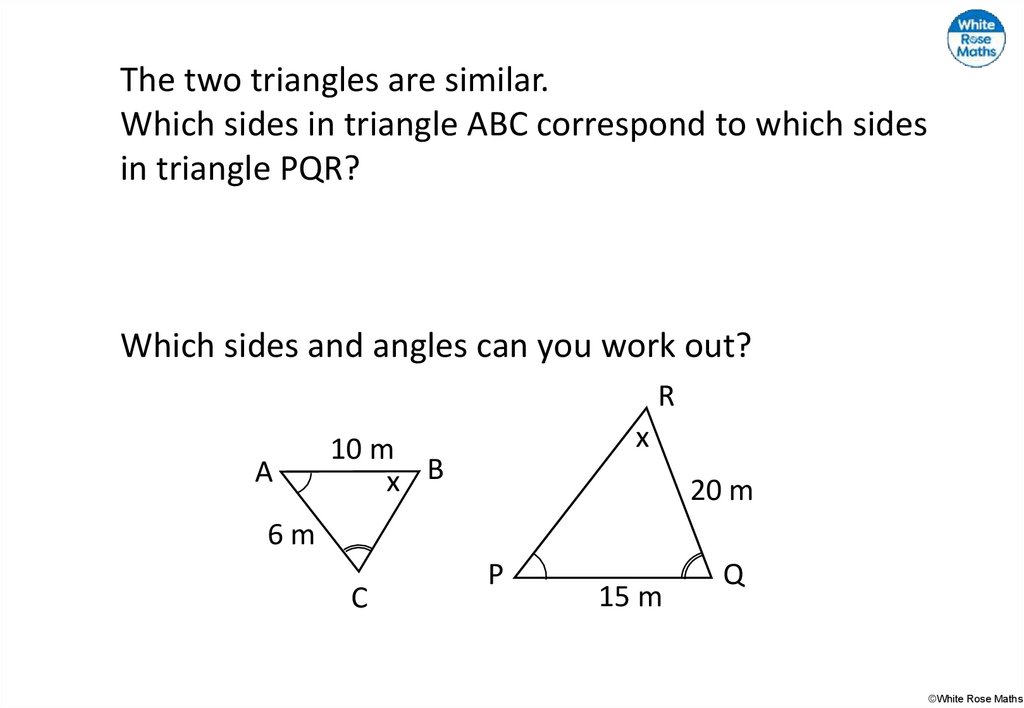
The two triangles are similar.Which sides in triangle ABC correspond to which sides
in triangle PQR?
Which sides and angles can you work out?
R
A
x
10 m
x B
20 m
6m
C
P
15 m
Q
©White Rose Maths
41.
The two triangles are similar.Which sides in triangle ABC correspond to which sides
in triangle PQR? AC corresponds to PQ
BC corresponds to RQ
AB corresponds to RP
Which sides and angles can you work out?
R
A
x
10 m
x B
20 m
6m
C
Scale factor = 2.5
BC = 8 m RP = 25 m
P
15 m
Q
©White Rose Maths
42.
Show that triangles ABC and CDE are similar.The perimeter of ABC is 36 m.
Find the missing lengths in ABC and CDE.
A
12 m
C
B
6m
D
8m
E
©White Rose Maths
43.
Show that triangles ABC and CDE are similar.The perimeter of ABC is 36 m.
Find the missing lengths in ABC and CDE.
A
12 m
C
B
6m
D
8m
E
12
Scale factor = = 1.5
8
BC = 6 × 1.5 = 9 m
AB = 36 − 21 = 15 m
DE = 15 ÷ 1.5 = 10 m
©White Rose Maths
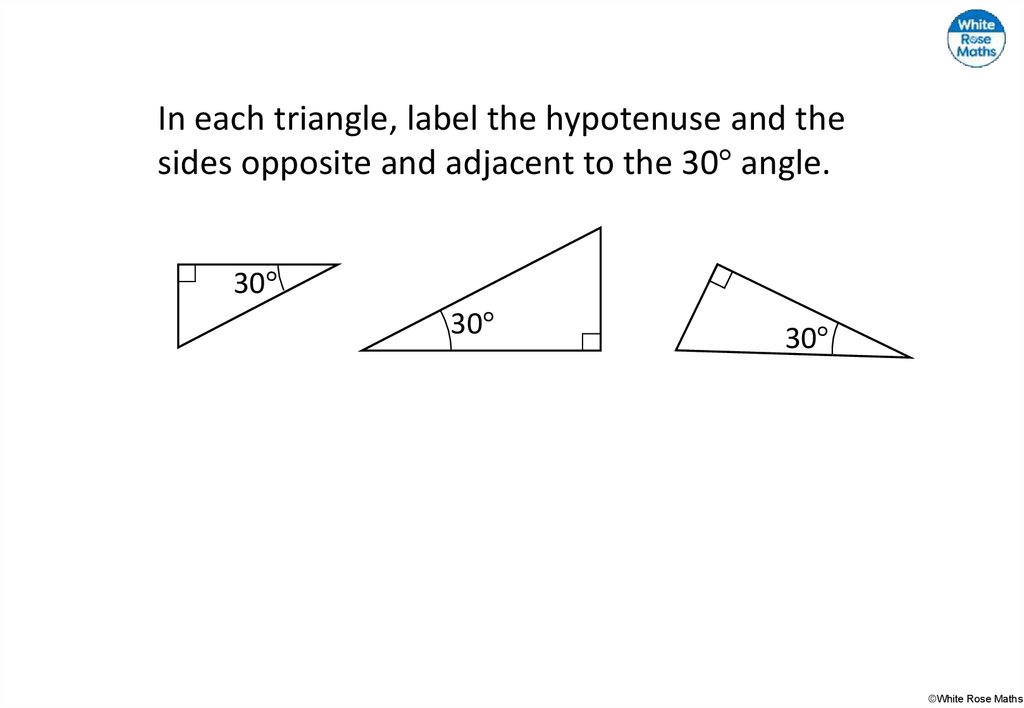
44.
In each triangle, label the hypotenuse and thesides opposite and adjacent to the 30° angle.
30°
30°
30°
©White Rose Maths
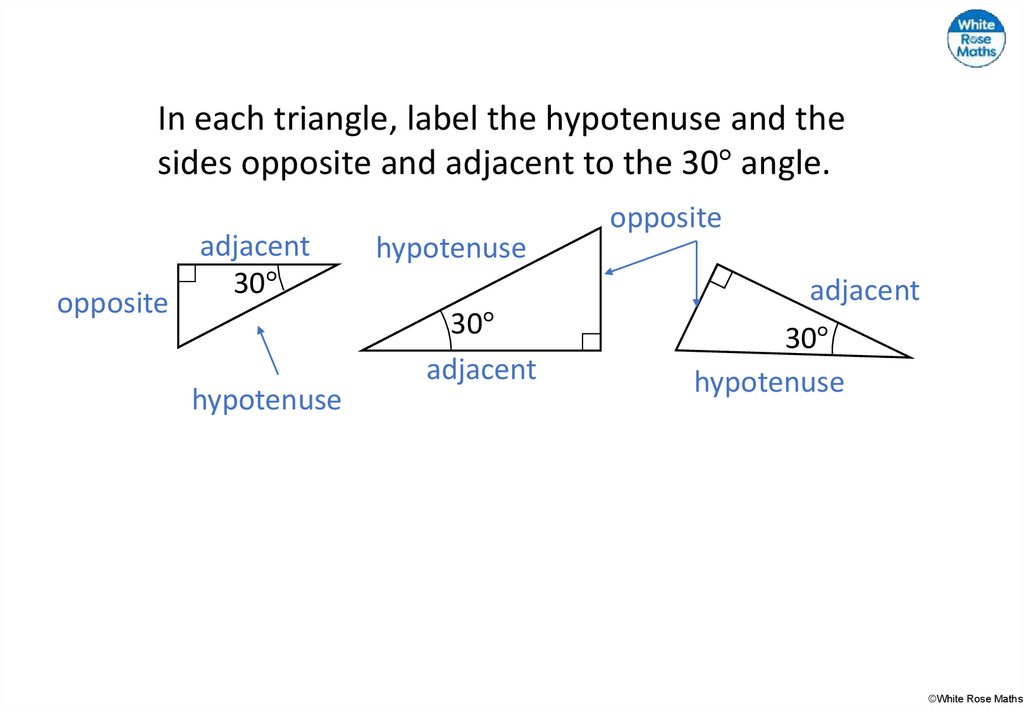
45.
In each triangle, label the hypotenuse and thesides opposite and adjacent to the 30° angle.
opposite
adjacent
30°
hypotenuse
hypotenuse
opposite
adjacent
30°
adjacent
30°
hypotenuse
©White Rose Maths
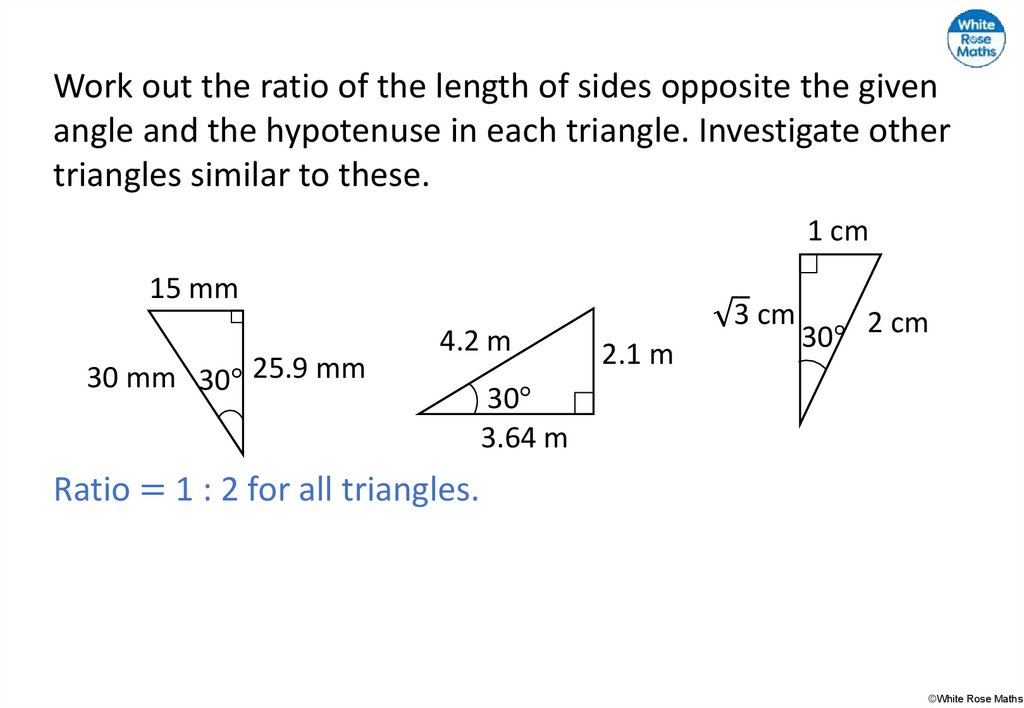
46.
Work out the ratio of the length of sides opposite the givenangle and the hypotenuse in each triangle. Investigate other
triangles similar to these.
1 cm
15 mm
30 mm 30° 25.9 mm
4.2 m
3 cm
2.1 m
30° 2 cm
30°
3.64 m
©White Rose Maths
47.
Work out the ratio of the length of sides opposite the givenangle and the hypotenuse in each triangle. Investigate other
triangles similar to these.
1 cm
15 mm
30 mm 30° 25.9 mm
4.2 m
3 cm
2.1 m
30° 2 cm
30°
3.64 m
Ratio = 1 : 2 for all triangles.
©White Rose Maths



















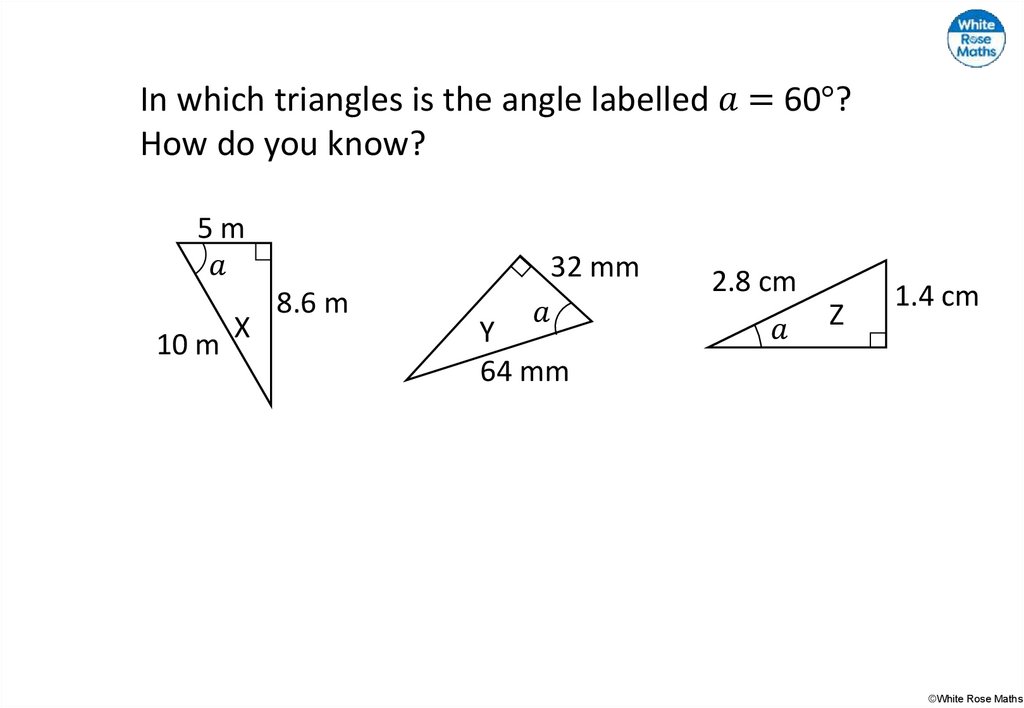
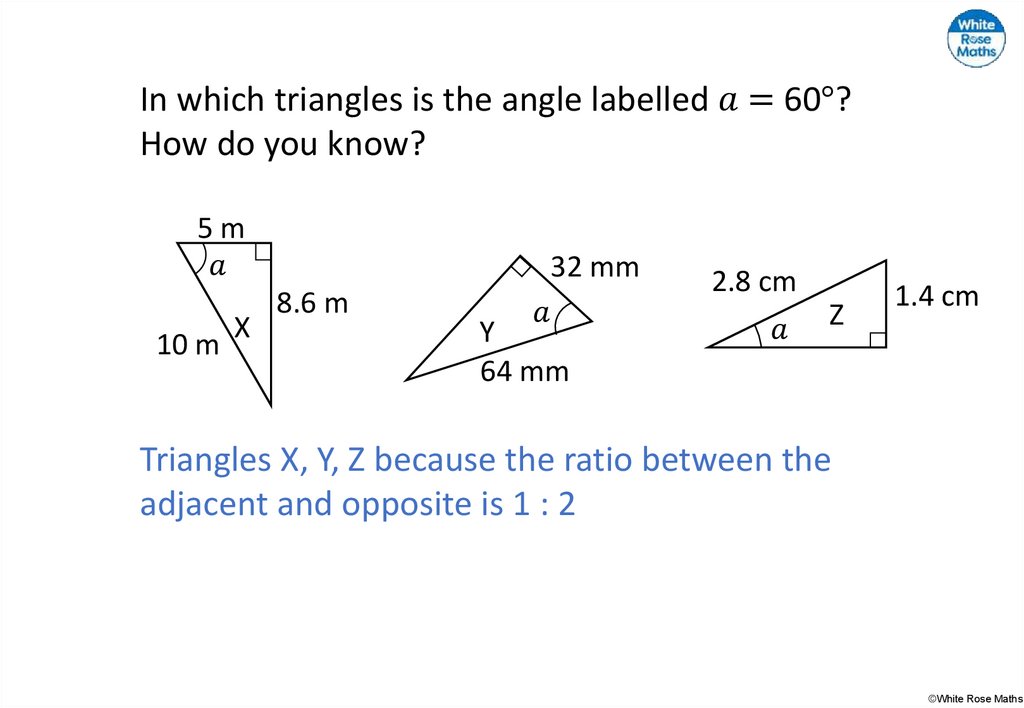


 mathematics
mathematics








