Similar presentations:
Categorization. Lecture 3
1.
Lecture 3Categorization
1 The importance of categorization.
2 The theory of categorization.
3 The classic theory of categorization.
4 Word meanings: classic categories.
5 Limitations of the classic theory.
2.
• “If linguistics can be said to be any onething, it is the study of categories”
• William Labov
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
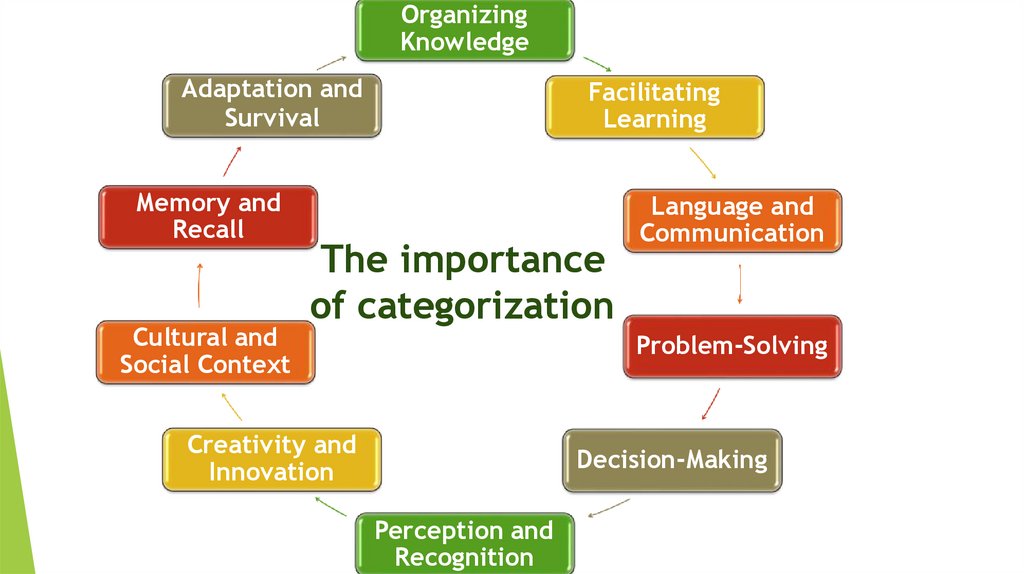
OrganizingKnowledge
Adaptation and
Survival
Memory and
Recall
Cultural and
Social Context
Facilitating
Learning
The importance
of categorization
Language and
Communication
Problem-Solving
Creativity and
Innovation
Decision-Making
Perception and
Recognition
27.
1) Organizing Knowledge:
2) Facilitating Learning:
3) Language and Communication:
4) Problem-Solving:
5) Decision-Making:
6) Perception and Recognition:
7) Creativity and Innovation:
8) Cultural and Social Context:
9) Memory and Recall:
10) Adaptation and Survival:
28.
A) Categorization aids memory and recall. When we organize information into meaningfulcategories, it becomes easier to remember related details. Retrieving information from memory often
involves accessing relevant categories.
B) Categorization helps us organize and structure our knowledge. By grouping similar objects,
concepts, or experiences into categories, we can more efficiently store and retrieve information. This
process simplifies complex realities, making them easier to understand and remember.
C) Categorization is influenced by culture and society. It shapes our social identities, group
memberships, and cultural norms. Understanding categorization processes can shed light on social issues
related to identity, bias, and discrimination.
D) Categorization has evolutionary significance. Early humans needed to categorize threats,
resources, and environmental cues for survival. The ability to categorize and respond to different situations
contributed to our species' adaptability.
E) While categorization provides structure and order, it also plays a role in creativity and
innovation. Creative thinking often involves breaking traditional category boundaries or merging existing
categories to generate novel ideas and solutions.
F) Language heavily relies on categorization. Words and phrases are used to label categories and
convey meaning. Effective communication depends on shared categories and the ability to convey complex
ideas by referencing familiar categories.
G) Categorization aids in the learning process. When we learn new information, we often relate it
to existing categories in our mental schema. This connection helps us grasp new concepts more readily and
build upon our existing knowledge.
H) Categorization is crucial for problem-solving. When faced with a new situation, we often draw
on past experiences and knowledge to identify relevant categories and apply appropriate solutions. It helps
us recognize patterns and similarities, leading to more effective problem-solving.
I) Decision-making involves evaluating options and selecting the best course of action.
Categorization helps us compare alternatives by considering their attributes and similarities within relevant
categories. It simplifies complex decision-making processes.
J) Categorization influences how we perceive and recognize objects and patterns in our
environment. Our brains quickly categorize visual and sensory input to make sense of our surroundings and
identify familiar or novel elements.
29.
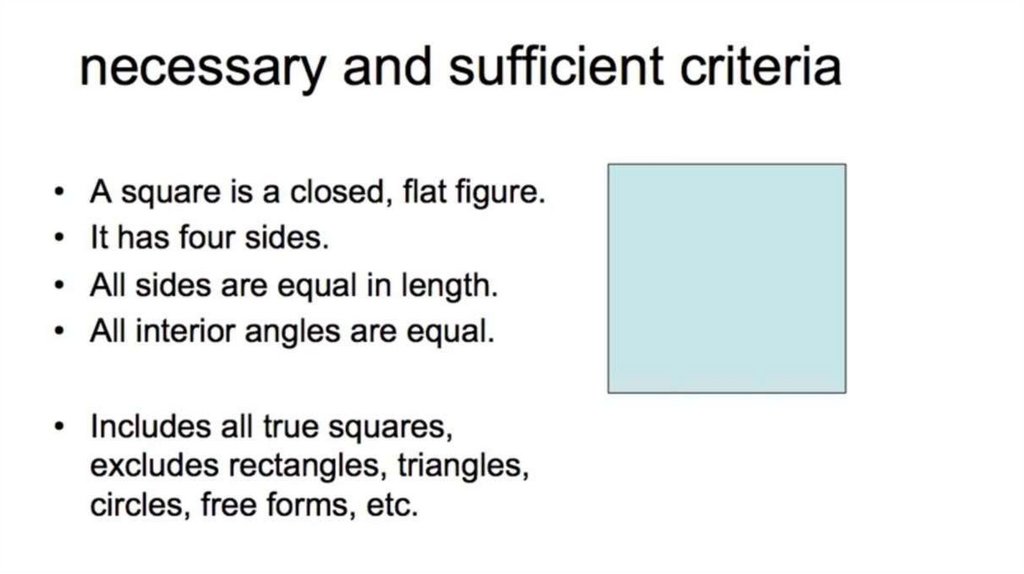
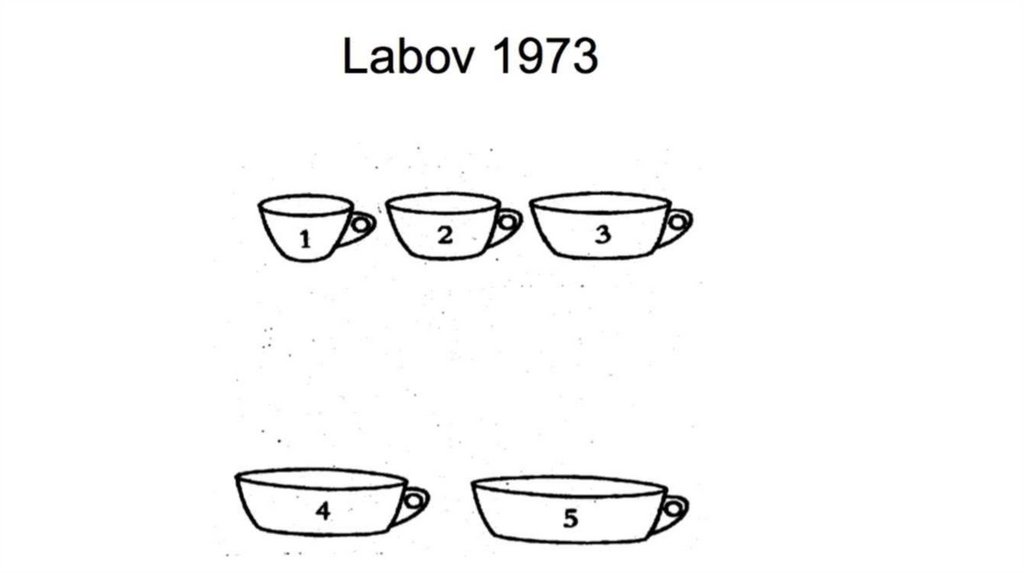
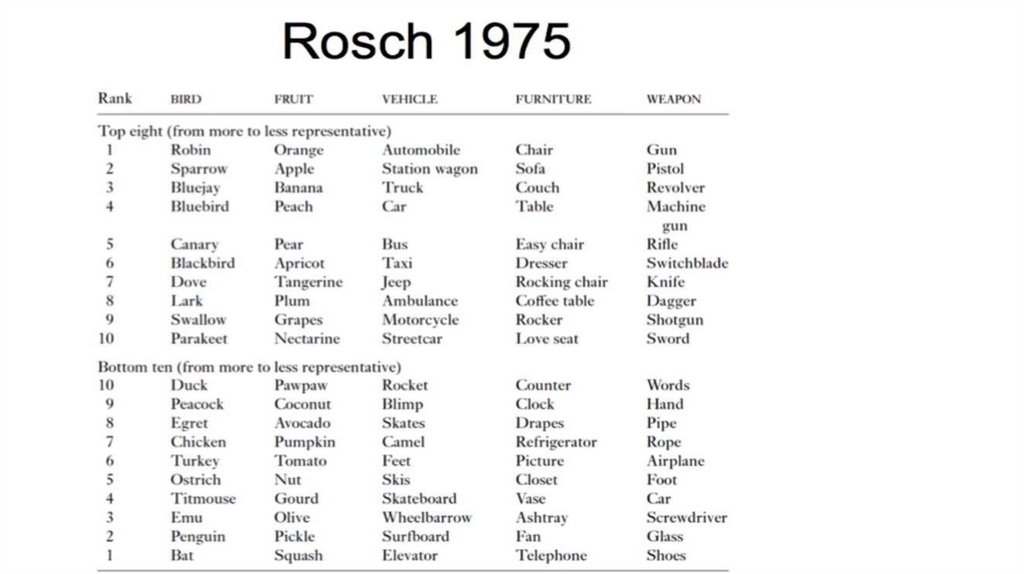
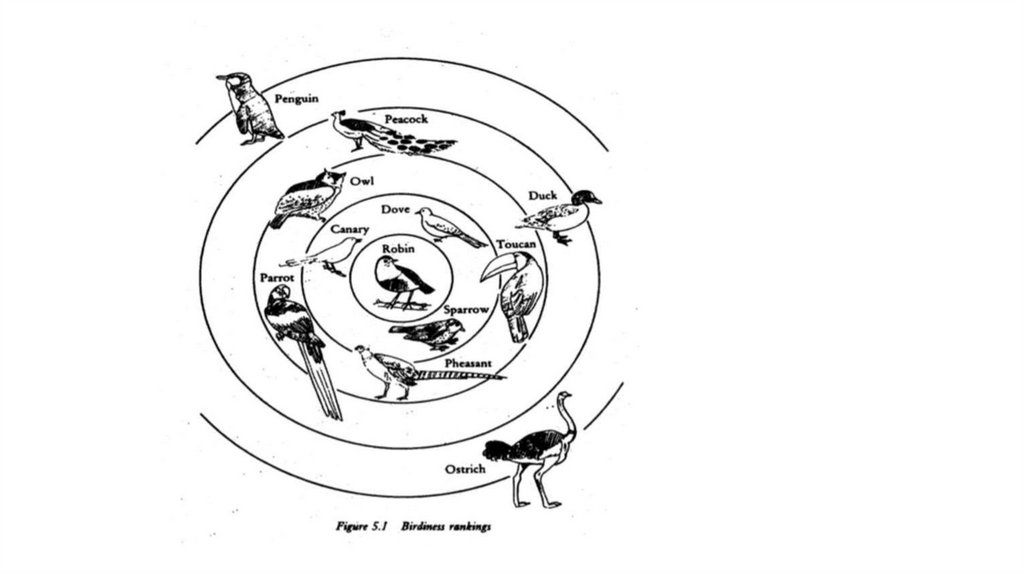
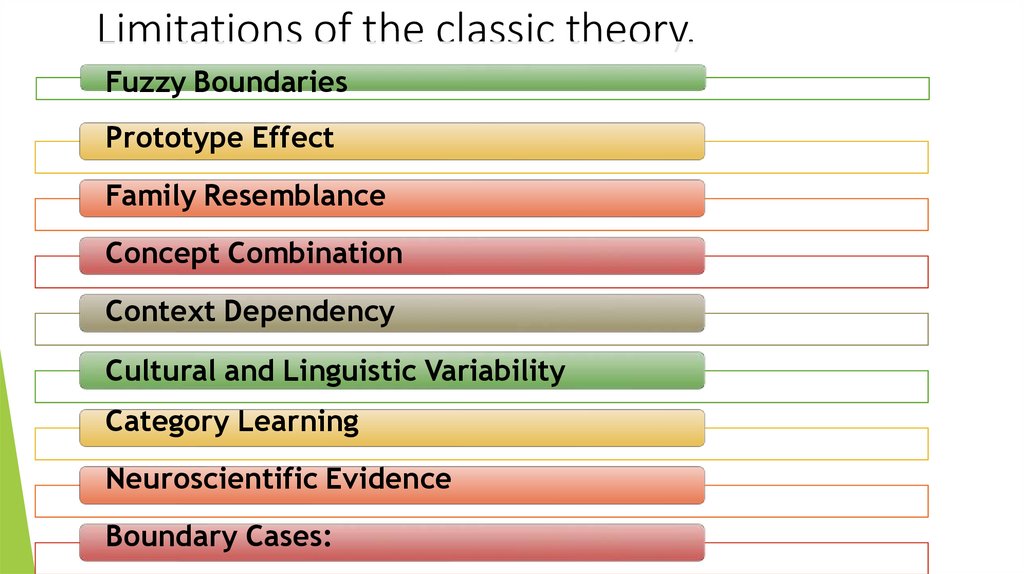
Limitations of the classic theory.Fuzzy Boundaries
Prototype Effect
Family Resemblance
Concept Combination
Context Dependency
Cultural and Linguistic Variability
Category Learning
Neuroscientific Evidence
Boundary Cases:























 english
english








