Similar presentations:
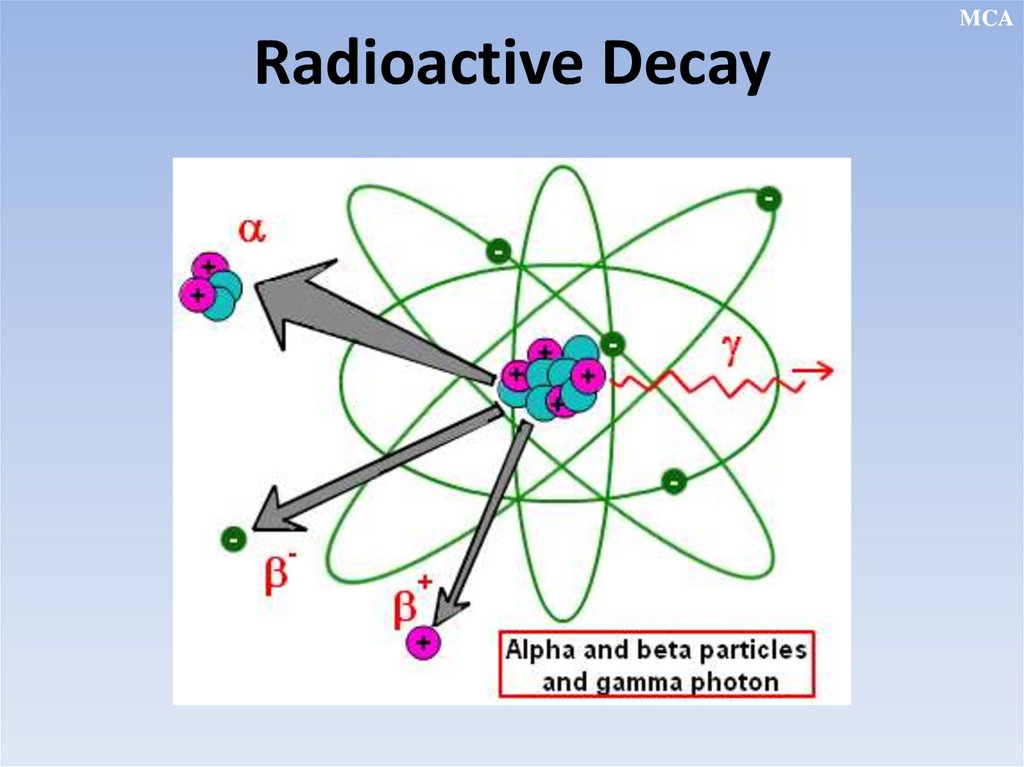
Radioactive Decay
1.
MCARadioactive Decay
2.
Topics / Key WordsNuclear reactions Vs chemical reactions
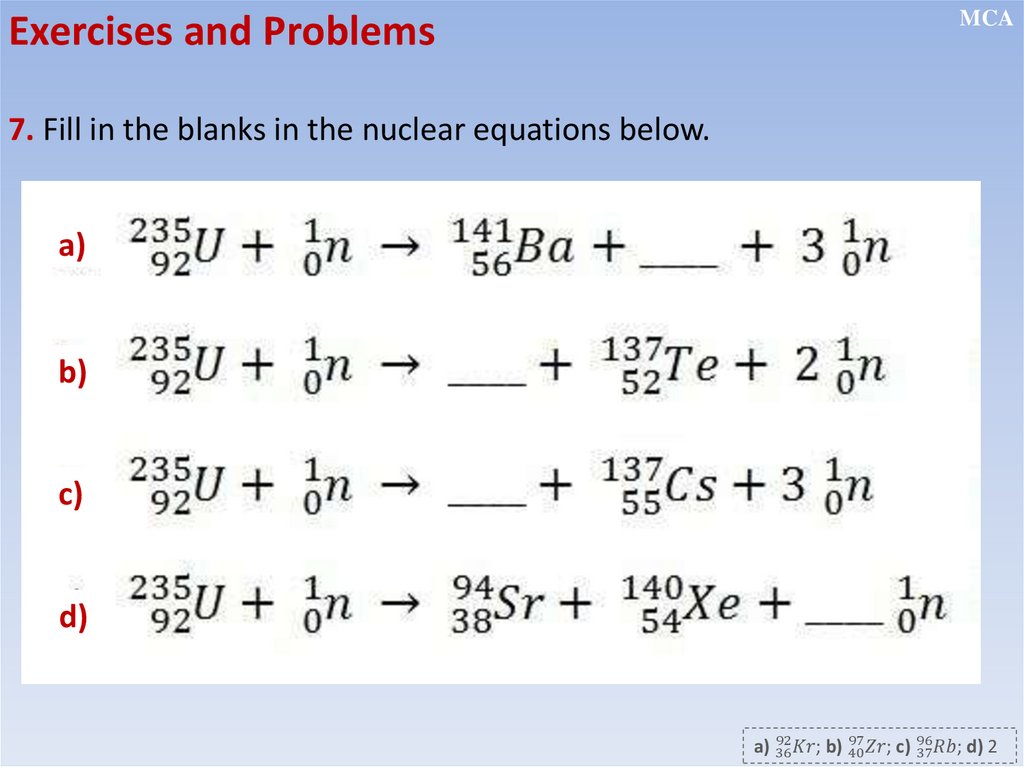
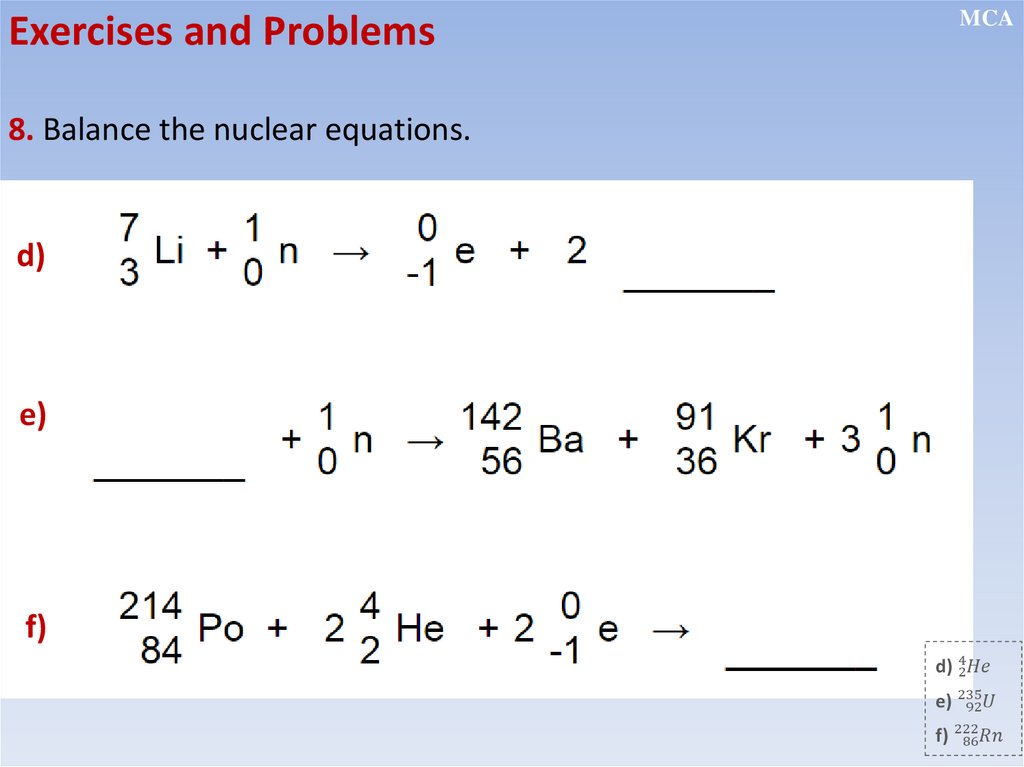
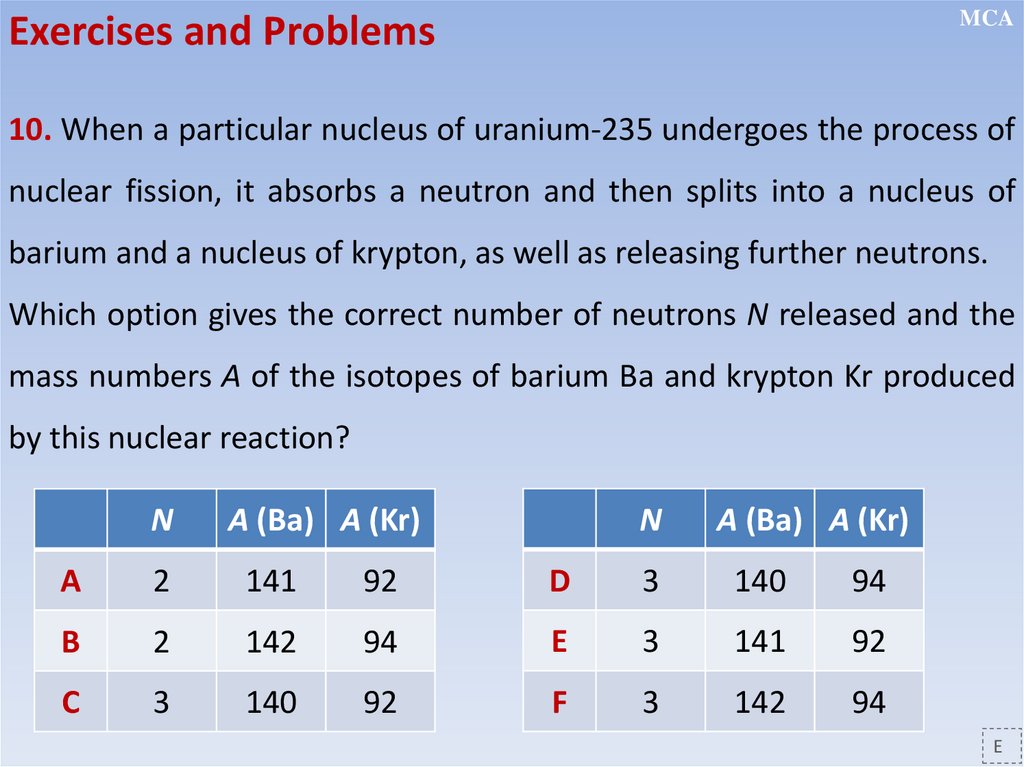
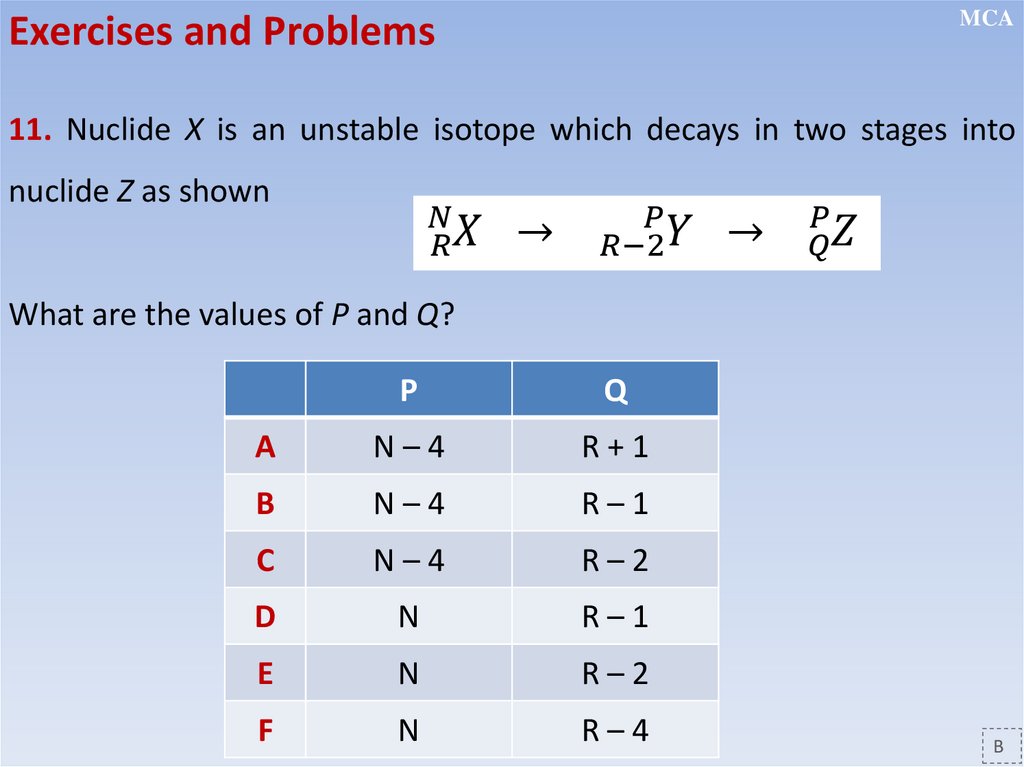
Nuclear transformation equations
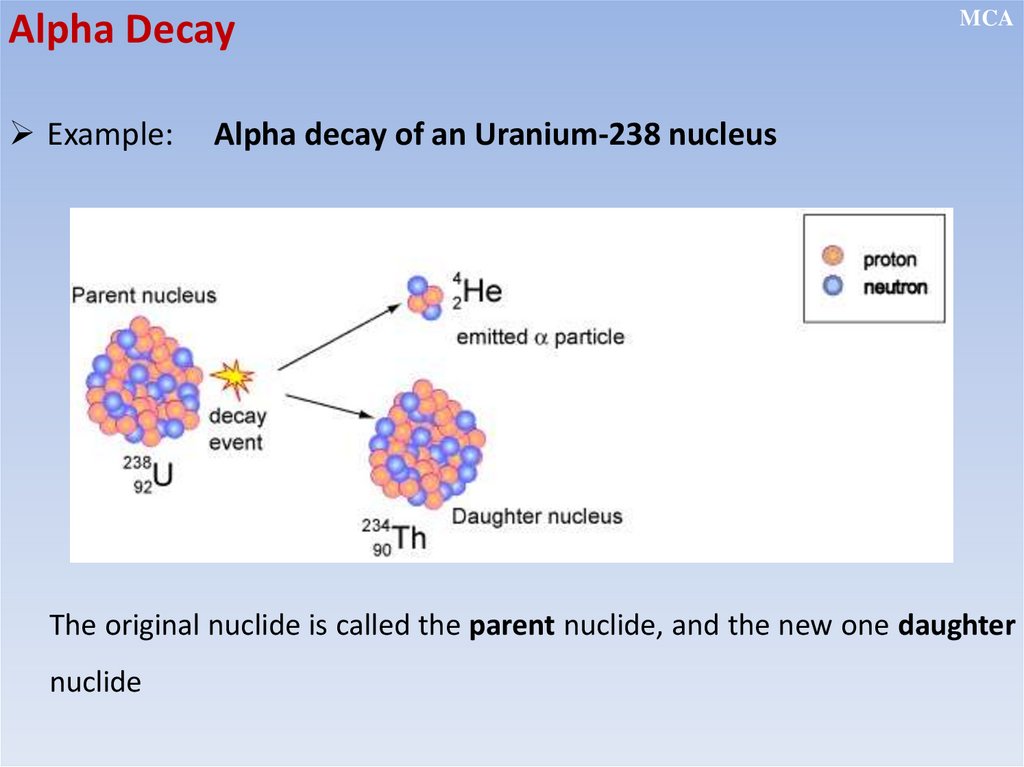
Radioactive decay
Alpha, beta and gamma decay
Conservation of charge and nucleon number
Detectors and background radiation
Properties of radioactive emissions
MCA
3.
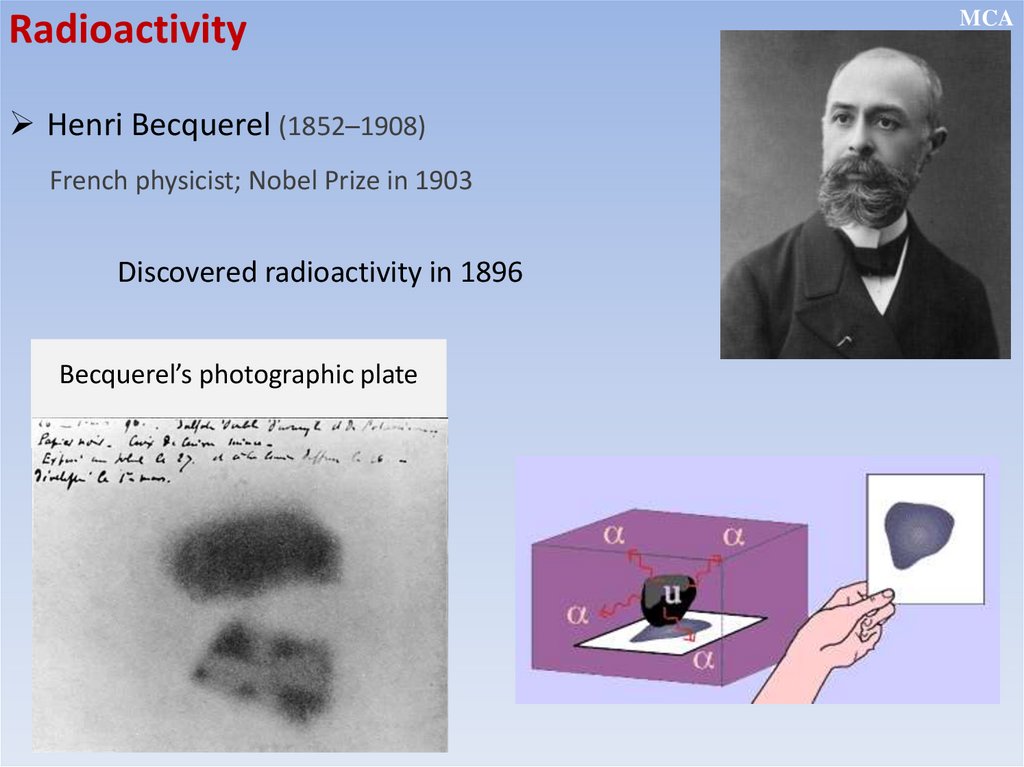
RadioactivityHenri Becquerel (1852–1908)
French physicist; Nobel Prize in 1903
Discovered radioactivity in 1896
Becquerel’s photographic plate
MCA
4.
MCARadioactivity
Marie Curie (1867–1934) and Pierre Curie (1859–1906)
A (very) Brief History
of Radioactivity
Radioactivity
Henri Becquerel, Marie &
Polish-French physicist and
chemist; Nobel Prize in 1903
French physicist;
Nobel Prize in 1903
Pierre Curie
Marie Curie was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize; The first person and only
woman to win it twice; The only person to win twice in multiple sciences (Physics and
Chemistry); First woman to become a professor at the University of Paris
5.
RadioactivityMCA
Radioactivity or radioactive decay is the spontaneous emission of
particles and electromagnetic radiation by unstable nuclides
Radioactive decay is a random process
Chemical elements that spontaneously emit such radiation are called radioactive
Rutherford used the radioactive
element Radium (Ra) as a source
of alpha particles
6.
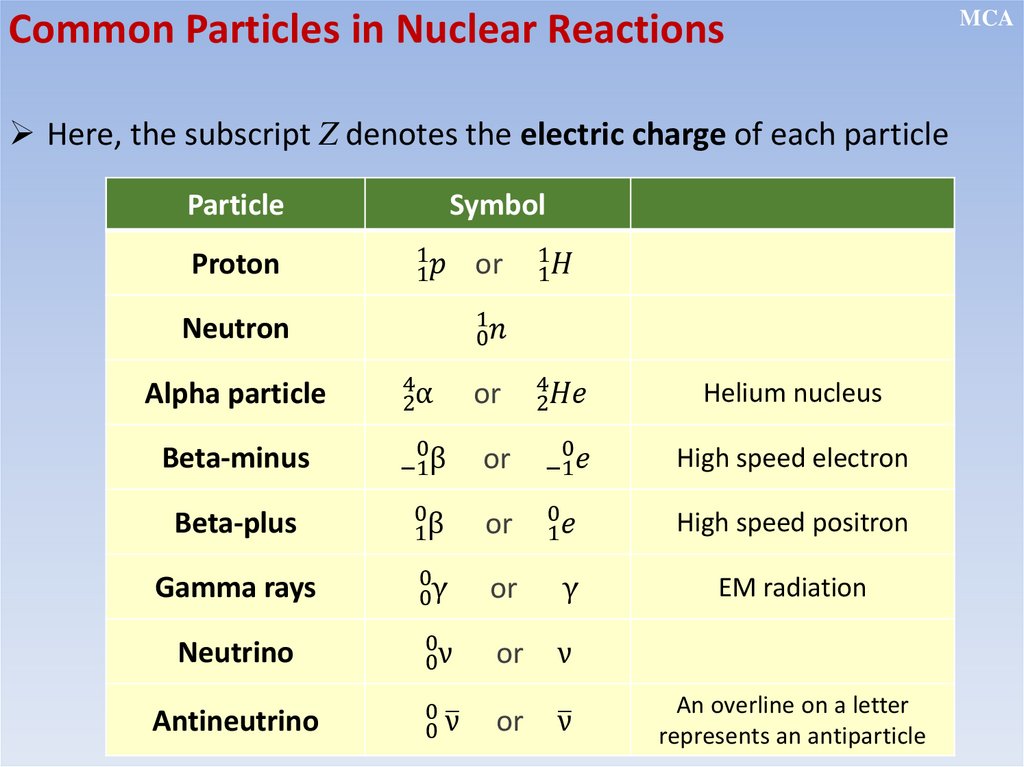
Common Particles in Nuclear ReactionsHere, the subscript Z denotes the electric charge of each particle
Particle
Proton
Symbol
1
1





























 chemistry
chemistry








