Similar presentations:
Nuclear R eactions: Understanding the Power of the Atom
1.
Nuclear R eactions:Understanding the Power of
the Atom
Welcome! Let's explore the fundamental principles of nuclear reactions,
their implications, and their impact on our world. We will delve into the
structure of the atom, the different types of reactions, and the applications
of nuclear technology.
2.
Introduction to Nuclear ReactionsThe Realm of the Nucleus
A World of Energy
Nuclear reactions involve changes within the nucleus of an
These reactions release or absorb tremendous amounts of
atom, affecting its composition and energy levels.
energy, driving various phenomena in the universe, from the
sun's brilliance to the power of nuclear weapons.
3.
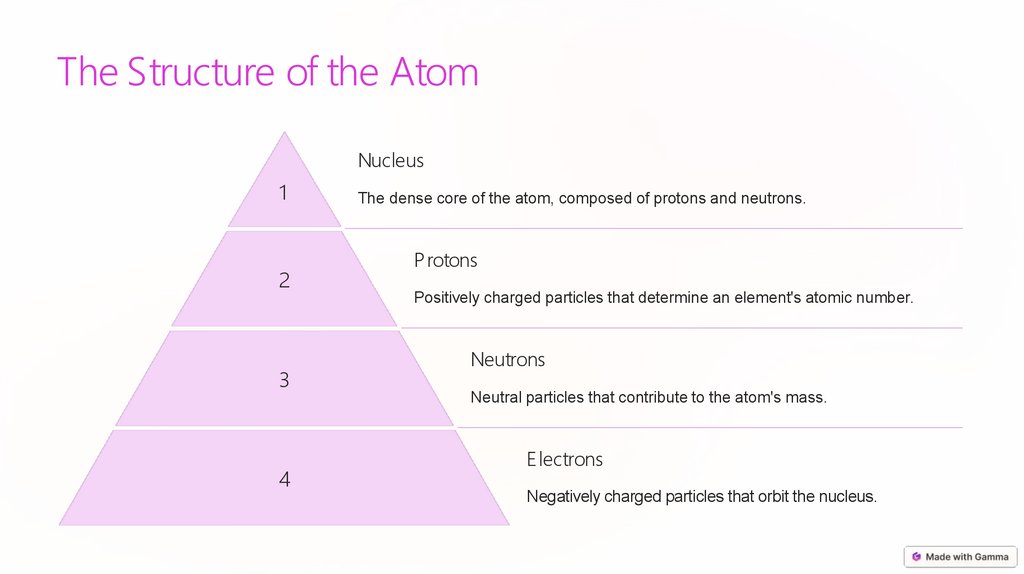
The Structure of the AtomNucleus
1
2
3
4
The dense core of the atom, composed of protons and neutrons.
Protons
Positively charged particles that determine an element's atomic number.
Neutrons
Neutral particles that contribute to the atom's mass.
E lectrons
Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
4.
R adioactivity and IsotopesR adioactive Decay
Isotopes
Unstable isotopes release
Atoms of the same element
energy and particles in an effort
with different numbers of
to achieve stability.
neutrons, resulting in varying
stability.
Half-Life
The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay, crucial
for understanding decay rates.
5.
Fission and Fusion ReactionsFission
Fusion
A heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei, releasing enormous
Light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing even
energy, as seen in nuclear power plants.
more energy, as in the sun and hydrogen bombs.
6.
Nuclear Stability and Instability1
Strong Force
The fundamental force holding the nucleus together,
overcoming electrostatic repulsion between protons.
2
Nuclear Binding E nergy
The energy required to break apart a nucleus, a measure of its
stability.
3
R adioactive Decay
The process by which unstable nuclei transform to achieve stability.
7.
Applications of Nuclear ReactionsNuclear Power
Generating electricity through fission reactions, providing a clean and reliable energy source.
Medical Imaging
Using radioactive isotopes to diagnose and treat diseases, from cancer therapy to bone scans.
Scientific R esearch
Radioactive isotopes act as tracers, revealing the mechanisms of biological and chemical
processes.
8.
Nuclear Safety and WasteManagement
R adiation Shielding
Using concrete and lead barriers to protect personnel and the
environment from harmful radiation.
Waste Storage
Managing radioactive waste through secure underground
disposal and advanced technologies.
Safety Protocols
Strict regulations and procedures to prevent accidents and
ensure responsible operation of nuclear facilities.
9.
The Future of Nuclear Technology1
2
3
Fusion Power
Advanced Reactors
Medical Isotopes
Harnessing the power of fusion to create
Developing safer and more efficient
Expanding the use of radioactive
a clean and nearly inexhaustible energy
reactor designs, addressing concerns
isotopes for targeted cancer treatment
source.
about waste and accidents.
and advanced medical imaging.
10.
Conclusion: The Significance ofNuclear R eactions
Nuclear reactions play a vital role in our world, from the creation of energy
to the development of groundbreaking medical technologies.
Understanding these reactions is key to harnessing their power safely and
ethically, shaping a brighter future for humanity.







 chemistry
chemistry








