Similar presentations:
WTE project based on plasma technology
1.
WTE PROJECTbased on
PLASMA TECHNOLOGY
IRINA KUMKOVA
Institute for Electrophysics and Electric Power RAS
18, Dvortsovaya nab., Saint-Petersburg , 191186, Phone +7 (812)-315-1757
E-mail: rc@iperas.nw.ru
2.
INSTITUTE FOR ELECTROPHYSICS AND ELECTRICPOWER OF RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
• performs fundamental and applied research in
electrophysics. plasma physics. power engineering and
electrical power engineering
• was established in 1992
• comprises 17 laboratories
• has a staff of 140 people. of which 70 are scientists
• is located in Saint-Petersburg, Russia
• has a central office in town and test benches in
suburbs
2
3.
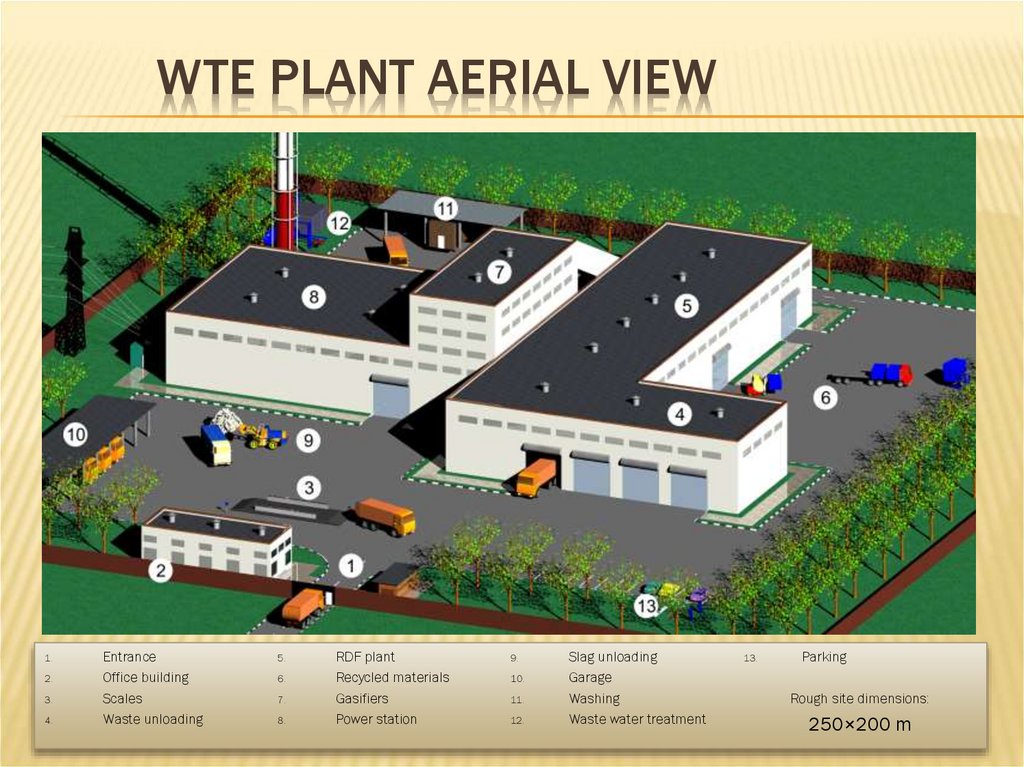
WTE PLANT AERIAL VIEW1.
2.
3.
4.
Entrance
Office building
Scales
Waste unloading
5.
6.
7.
8.
RDF plant
Recycled materials
Gasifiers
Power station
9.
10.
11.
12.
Slag unloading
Garage
Washing
Waste water treatment
13.
Parking
Rough site dimensions:
250×200 m
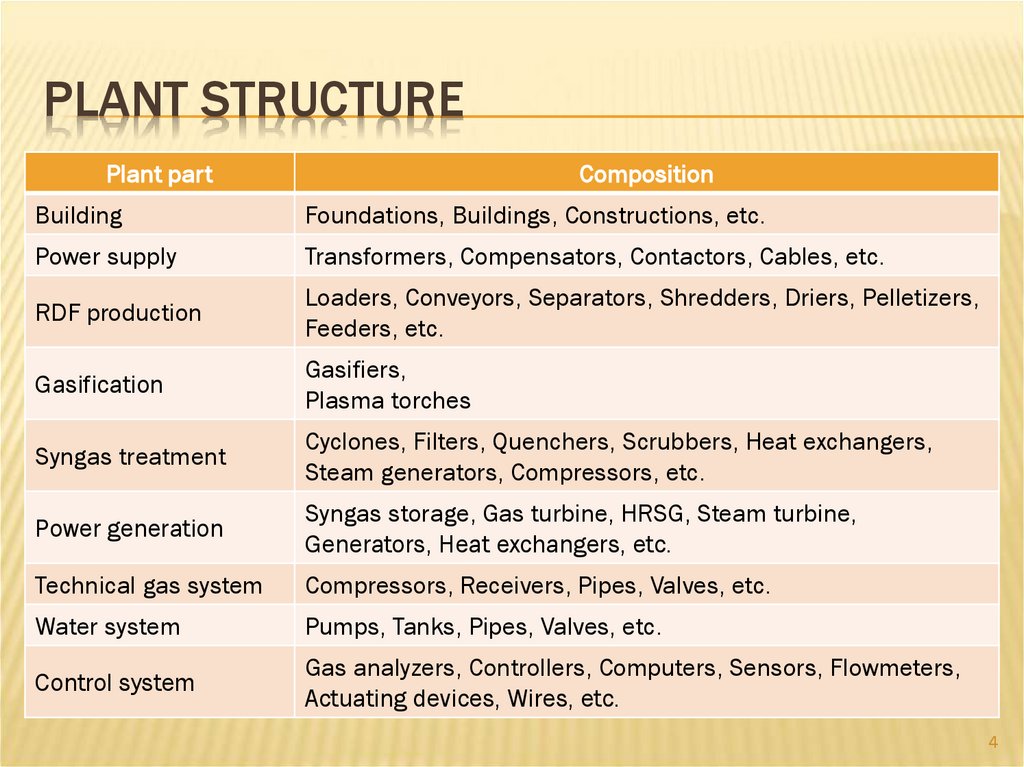
4.
PLANT STRUCTUREPlant part
Composition
Building
Foundations, Buildings, Constructions, etc.
Power supply
Transformers, Compensators, Contactors, Cables, etc.
RDF production
Loaders, Conveyors, Separators, Shredders, Driers, Pelletizers,
Feeders, etc.
Gasification
Gasifiers,
Plasma torches
Syngas treatment
Cyclones, Filters, Quenchers, Scrubbers, Heat exchangers,
Steam generators, Compressors, etc.
Power generation
Syngas storage, Gas turbine, HRSG, Steam turbine,
Generators, Heat exchangers, etc.
Technical gas system
Compressors, Receivers, Pipes, Valves, etc.
Water system
Pumps, Tanks, Pipes, Valves, etc.
Control system
Gas analyzers, Controllers, Computers, Sensors, Flowmeters,
Actuating devices, Wires, etc.
4
5.
WTE PLANT PRINCIPAL DIAGRAMRDF production
1. Waste bags destroyer
2. Drum separator
3. Materials recycling
4. Metals separator
5. Crusher
6. Dryer
7. Pelletizer
8. RDF storage
Syngas production
9. Bucket elevator
10.Feeder
11.Gasifier
12.Plasma torch
13.Hot cyclone
14.Quencher
15.Syngas cooling and
treatment
Power production
16.Compressor
17.Syngas storage
18.Gas turbine
19.HRSG
20.Stack
21.Steam turbine
22.Heat exchanger
23.Water system
Electricity production
24.Generator
25.Transformer
26.Power line
5
6.
WTE PLANT RAW MATERIALSMunicipal solid waste
Also it is possible to treat:
Industrial waste (except dangerous)
Sludge
Biomass
Used car tyres
Coals
6
7. WTE PLANT PRODUCTS
Recycled materialsSlag
Metals
Glass
Paper
Plastics
Syngas
Syngas itself
Electricity, heat, steam
Liquid fuels
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Vitrified neutralized
Constructional materials
Mineral heat insulator
((Plasma Rock analog)
Low- potential heat
Heating
Pure water production
Gardening of
vegetables and fruits
Fish breeding
8.
Whyplasma ?
9.
Novel technologies based on plasmatreatment are the most progressive
Provide unique solutions to critical
global environmental issues
The basis of these technologies is
powerful and reliable plasma
generators
9
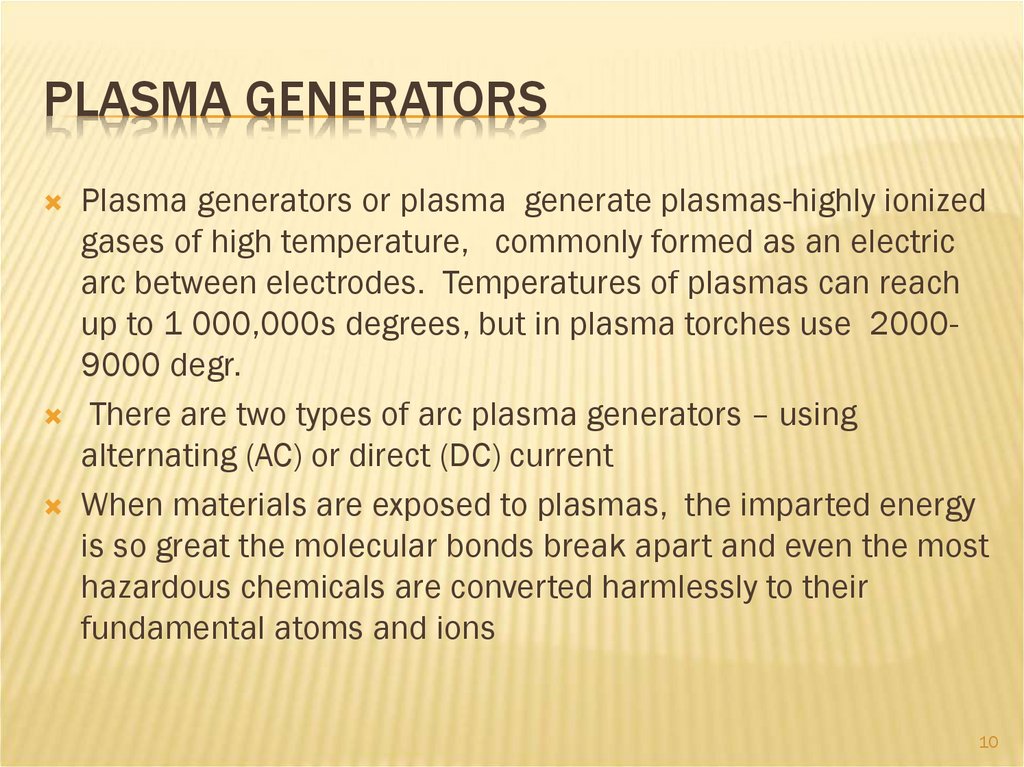
10.
PLASMA GENERATORSPlasma generators or plasma generate plasmas-highly ionized
gases of high temperature, commonly formed as an electric
arc between electrodes. Temperatures of plasmas can reach
up to 1 000,000s degrees, but in plasma torches use 20009000 degr.
There are two types of arc plasma generators – using
alternating (AC) or direct (DC) current
When materials are exposed to plasmas, the imparted energy
is so great the molecular bonds break apart and even the most
hazardous chemicals are converted harmlessly to their
fundamental atoms and ions
10
11.
IEE RAS PLASMA GENERATORSUse alternating current (AC)
Have very high efficiency (~ 94%)
May operate with various gases, air and
steam as the plasma forming medium
Use ordinary tap-water for cooling
Have significant lower operating costs
then for DC
11
12.
AC PLASMA GENERATORS12
13.
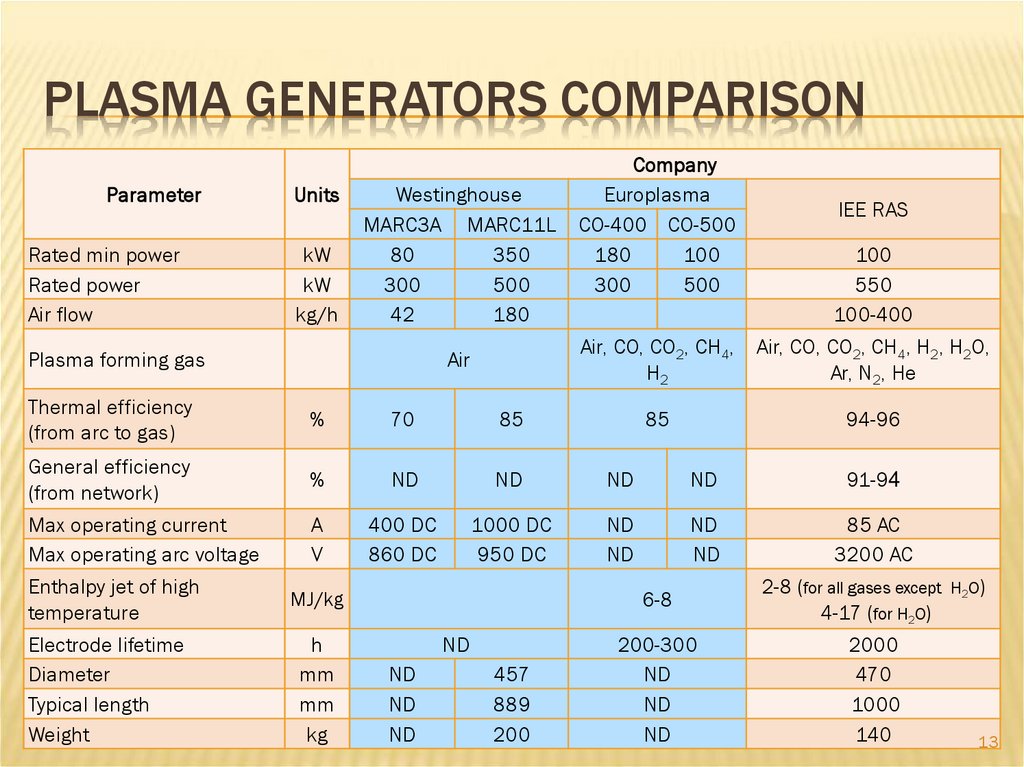
PLASMA GENERATORS COMPARISONParameter
Rated min power
Rated power
Air flow
Units
kW
kW
kg/h
Westinghouse
MARC3A MARC11L
80
350
300
500
42
180
Plasma forming gas
Air
Company
Europlasma
CO-400 CO-500
180
100
300
500
IEE RAS
Air, CO, CO2, CH4,
H2
100
550
100-400
Air, CO, CO2, CH4, H2, H2O,
Ar, N2, He
85
94-96
Thermal efficiency
(from arc to gas)
%
70
85
General efficiency
(from network)
%
ND
ND
ND
ND
91-94
Max operating current
Max operating arc voltage
A
V
400 DC
860 DC
1000 DC
950 DC
ND
ND
ND
ND
85 AC
3200 AC
Enthalpy jet of high
temperature
MJ/kg
Electrode lifetime
Diameter
Typical length
Weight
h
mm
mm
kg
ND
ND
ND
ND
457
889
200
6-8
2-8 (for all gases except H2O)
4-17 (for H2O)
200-300
ND
ND
ND
2000
470
1000
140
13
14.
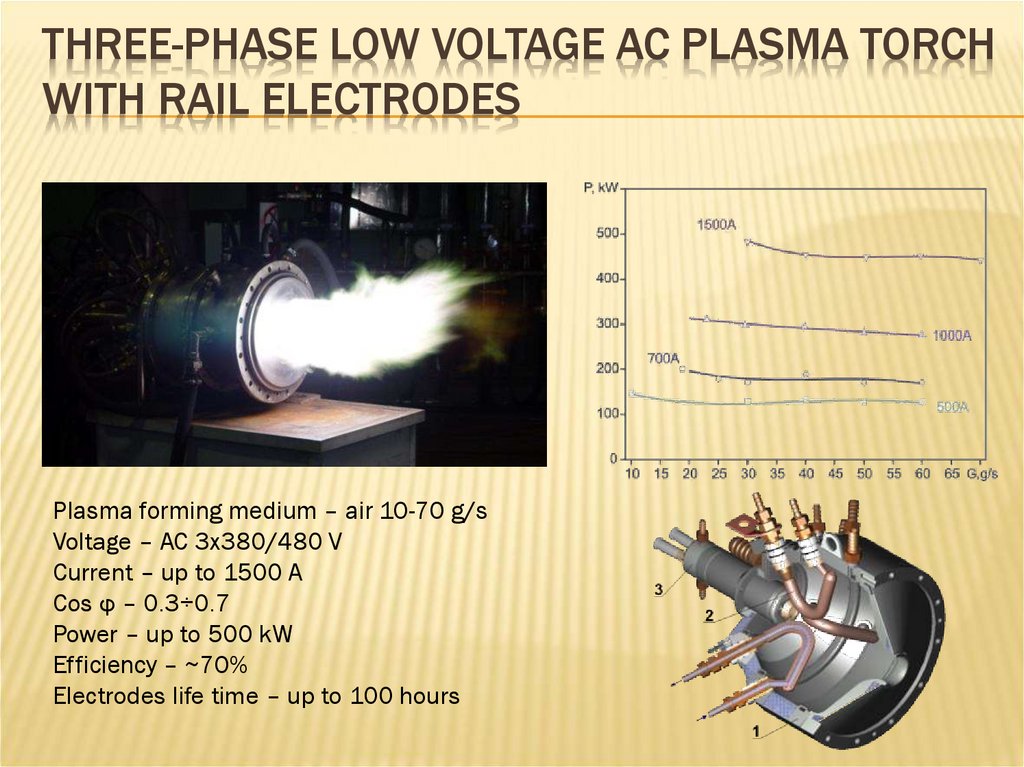
THREE-PHASE LOW VOLTAGE AC PLASMA TORCHWITH RAIL ELECTRODES
Plasma forming medium – air 10-70 g/s
Voltage – AC 3x380/480 V
Current – up to 1500 A
Cos φ – 0.3÷0.7
Power – up to 500 kW
Efficiency – ~70%
Electrodes life time – up to 100 hours
15.
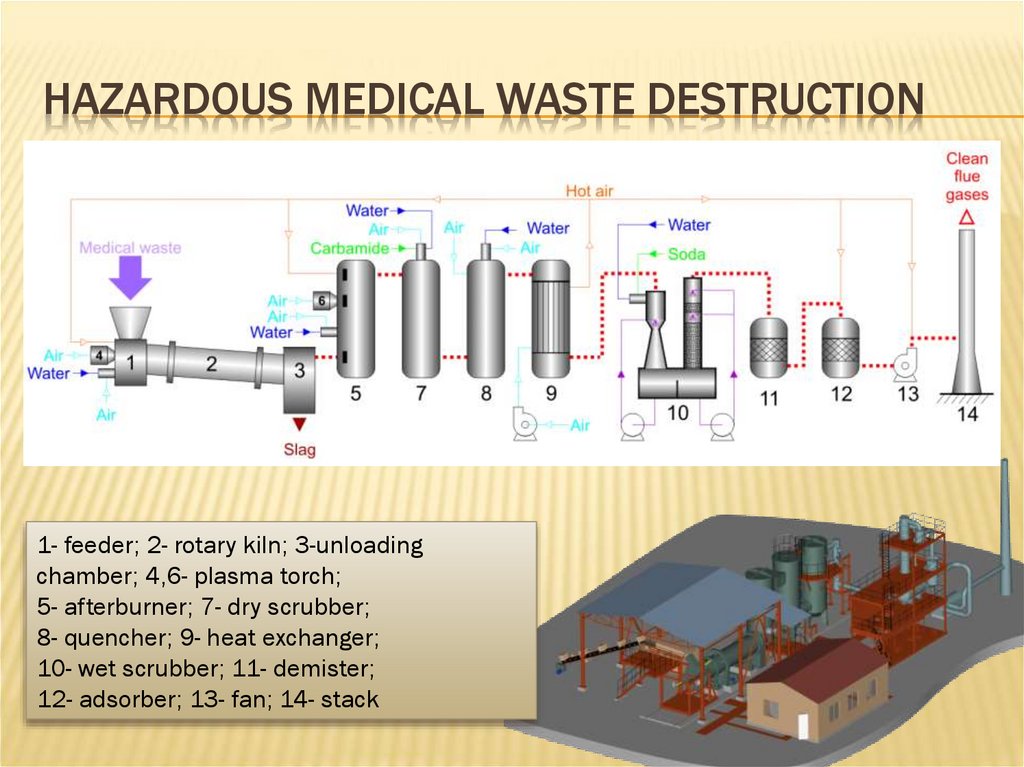
HAZARDOUS MEDICAL WASTE DESTRUCTION1- feeder; 2- rotary kiln; 3-unloading
chamber; 4,6- plasma torch;
5- afterburner; 7- dry scrubber;
8- quencher; 9- heat exchanger;
10- wet scrubber; 11- demister;
12- adsorber; 13- fan; 14- stack
16.
ONE-PHASE HIGH VOLTAGE AC PLASMA TORCHWITH ROD ELECTRODES
Plasma forming medium – air 1-4 g/s
Voltage – AC 6 kV
Current – up to 14 A
Power – up to 15 kW
Efficiency – ~95%
Electrodes life time – up to 300 hours
17.
THREE-PHASE HIGH VOLTAGE AC PLASMATORCH WITH ROD ELECTRODES
Plasma forming medium – air up to 35 g/s
Voltage – AC 3x6/10 kV
Current – up to 100 A
Power – up to 75 kW
Efficiency – up to 95%
Electrodes life time – up to 200 hours
18.
PILOT INSTALLATION FOR PLASMADESTRUCTION OF LIQUID TOXIC WASTE
19.
THREE-PHASE HIGH VOLTAGE AC PLASMATORCH WITH ROD ELECTRODES
Plasma forming medium – steam + air
Voltage – AC 3x10 kV
Current – up to 50 A
Power – up to 105 kW
Efficiency – ~95%
Electrodes life time – up to 2000 hours
20.
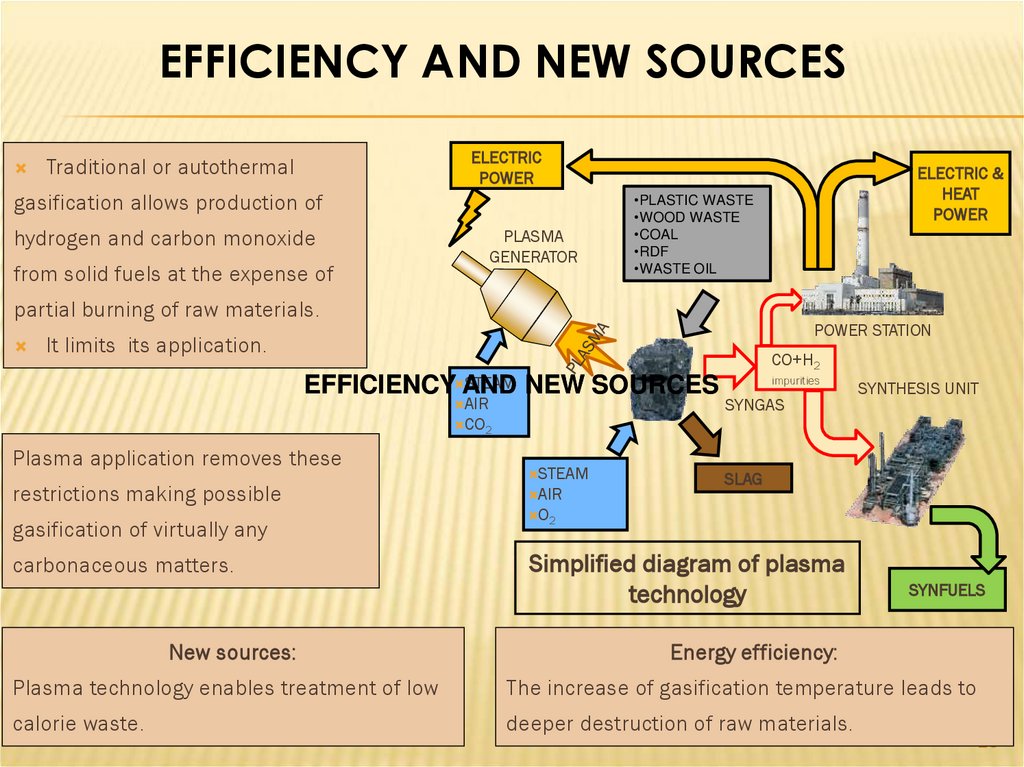
EFFICIENCY AND NEW SOURCESELECTRIC
POWER
Traditional or autothermal
gasification allows production of
hydrogen and carbon monoxide
PLASMA
GENERATOR
from solid fuels at the expense of
ELECTRIC &
HEAT
POWER
•PLASTIC WASTE
•WOOD WASTE
•COAL
•RDF
•WASTE OIL
partial burning of raw materials.
POWER STATION
It limits its application.
CO+H2
STEAM NEW SOURCES
EFFICIENCY AND
AIR
CO2
Plasma application removes these
restrictions making possible
gasification of virtually any
carbonaceous matters.
STEAM
AIR
impurities
SYNGAS
SYNTHESIS UNIT
SLAG
O2
Simplified diagram of plasma
technology
SYNFUELS
New sources:
Energy efficiency:
Plasma technology enables treatment of low
The increase of gasification temperature leads to
calorie waste.
deeper destruction of raw materials.
20
21.
PLASMA GASIFICATION ADVANTAGESAllothermal gasification
High temperatures
High efficiency of the process
Ecological sustainability, no hamfull emission, no ahes,
no tars….
Reactions equilibrium displace to increase CO and H2
production
Increase of capacity
Decrease of dimensions and weigh.
Possibility of full conversion of raw material energy to
syngas energy
Possibility to process different types of biomass and
wastes
21
22.
PLASMA TECHNOLOGY IS ENVIRONMENT FRIENDLYDIOXINS and FURANS
are not forming due to
the temperature and process organization
Obtained syngas contains:
o Combustible components CO and H2 ~ 63%
o Nitrogen ~ 32%
o Admixtures (CO2 and others) ~ 5%
Admixtures contents in flue gases − under EPA
regulations
Contributes to solving climate change problem
22
23. IEE INSTALLATION, St.Petersburg, Russia
24.
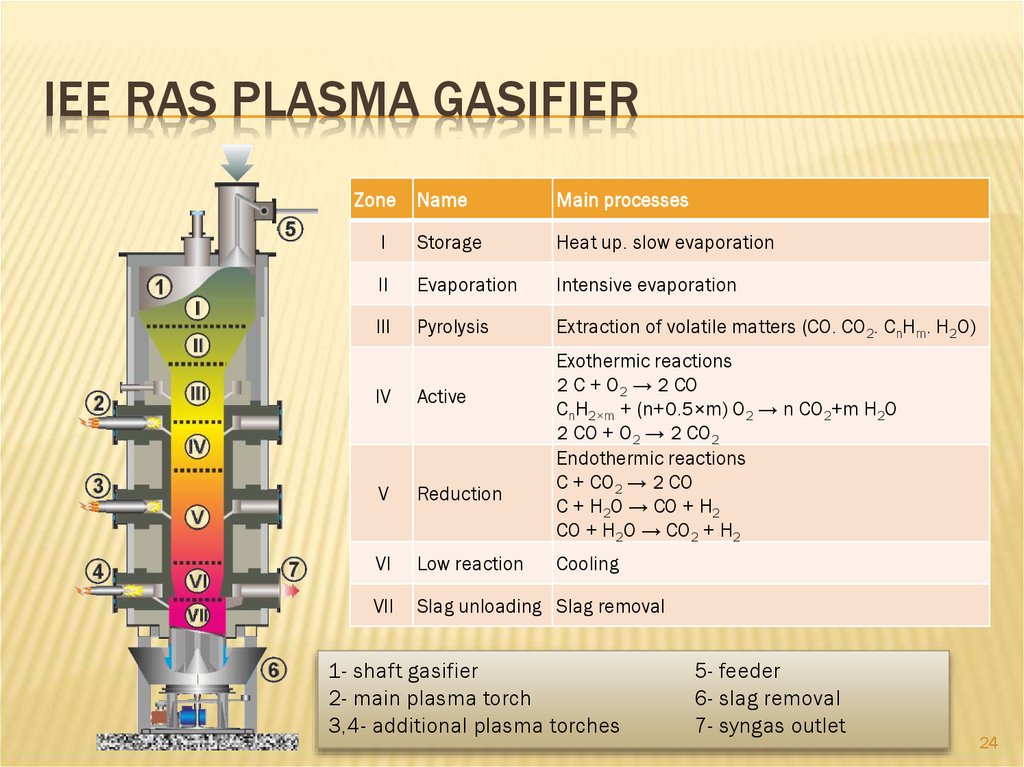
IEE RAS PLASMA GASIFIERZone
Name
Main processes
I
Storage
Heat up. slow evaporation
II
Evaporation
Intensive evaporation
III
Pyrolysis
Extraction of volatile matters (CO. CO2. CnHm. H2O)
Exothermic reactions
2 C + O2 → 2 CO
CnH2×m + (n+0.5×m) O2 → n CO2+m H2O
2 CO + O2 → 2 CO2
Endothermic reactions
C + CO2 → 2 CO
C + H2O → CO + H2
CO + H2O → CO2 + H2
IV
Active
V
Reduction
VI
Low reaction
VII
Slag unloading Slag removal
Cooling
1- shaft gasifier
2- main plasma torch
3,4- additional plasma torches
5- feeder
6- slag removal
7- syngas outlet
24
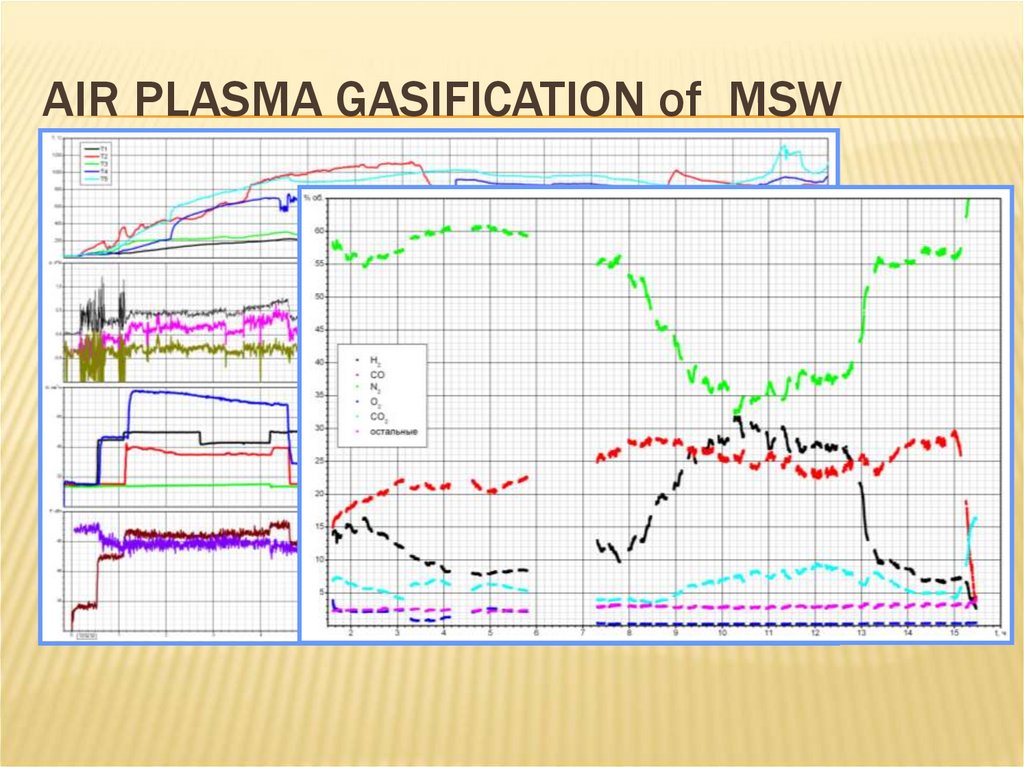
25. AIR PLASMA GASIFICATION of MSW
26.
THREE-PHASE HIGH VOLTAGE AC PLASMATORCH WITH HOLLOW ELECTRODES
Plasma forming medium – air up to 100 g/s
Voltage – AC 3x10 kV
Current – up to 100 A
Power – up to 500 kW
Efficiency – ~95%
Electrodes life time – up to 2000 hours

















 industry
industry








