Similar presentations:
Organic synthesis
1.
ORGANICSYNTHESIS
KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING
2015
SPECIFICATIONS
2.
Objective2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
2
3.
OBJECTIVES:Learners will
• explain the usefulness of some reactions for the
characterisation of organic compounds or specific
functional groups
• identify compounds containing specific functional
groups and identify compounds by means of chemical
and physical tests.
• discuss the importance of synthesis in organic
chemistry and recognise synthetically useful reactions
• create spider diagrams of synthetically useful reactions
• solve problems in synthesis using a synoptic knowledge
of the organic chemistry learned in the whole course
2/27/2023
4.
Feedbacking on theFormative
Assesment on the
Chemistry of Life
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
4
5.
6.
REVIEW ACTIVITY:VIDEO ON
ISOLATION OF DNA
FROM BANANAS
AND ONIONS
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
6
7.
REVIEW ACTIVITY: VIDEO ON ISOLATION OF DNAFROM BANANAS AND ONIONS
-
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
7
2/27/2023
8.
REVIEW ACTIVITY: VIDEO ON ISOLATION OF DNAFROM BANANAS AND ONIONS
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
8
2/27/2023
9.
STARTERACTIVITY:
ORGANIC
SYNTHESIS MAP
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
9
10.
ORGANICSYNTHESIS
KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING
11.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISCONTENTS
• Introduction
• Functional groups
• Extending a carbon chain
• Chiral synthesis - introduction
• Nucleophilic addition
• Nucleophilic substitution
• Synthetic methods
12.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
13.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
14.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
When planning a synthetic route, chemists must consider...
15.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
When planning a synthetic route, chemists must consider...
• the reagents required to convert one functional group into another
• the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react
16.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
When planning a synthetic route, chemists must consider...
• the reagents required to convert one functional group into another
• the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react
• the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst
• the rate of the reaction
• the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions
• atom economy
17.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
When planning a synthetic route, chemists must consider...
• the reagents required to convert one functional group into another
• the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react
• the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst
• the rate of the reaction
• the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions
• atom economy
• safety - toxicity and flammability of reactants and products
• financial economy - cost of chemicals, demand for product
• problems of purification
• possibility of optically active products
18.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others.
Many industrial processes involve a multi stage process where functional
groups are converted into other functional groups.
When planning a synthetic route, chemists must consider...
• the reagents required to convert one functional group into another
• the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react
• the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst
• the rate of the reaction
• the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions
• atom economy
• safety - toxicity and flammability of reactants and products
• financial economy - cost of chemicals, demand for product
• problems of purification
• possibility of optically active products
19.
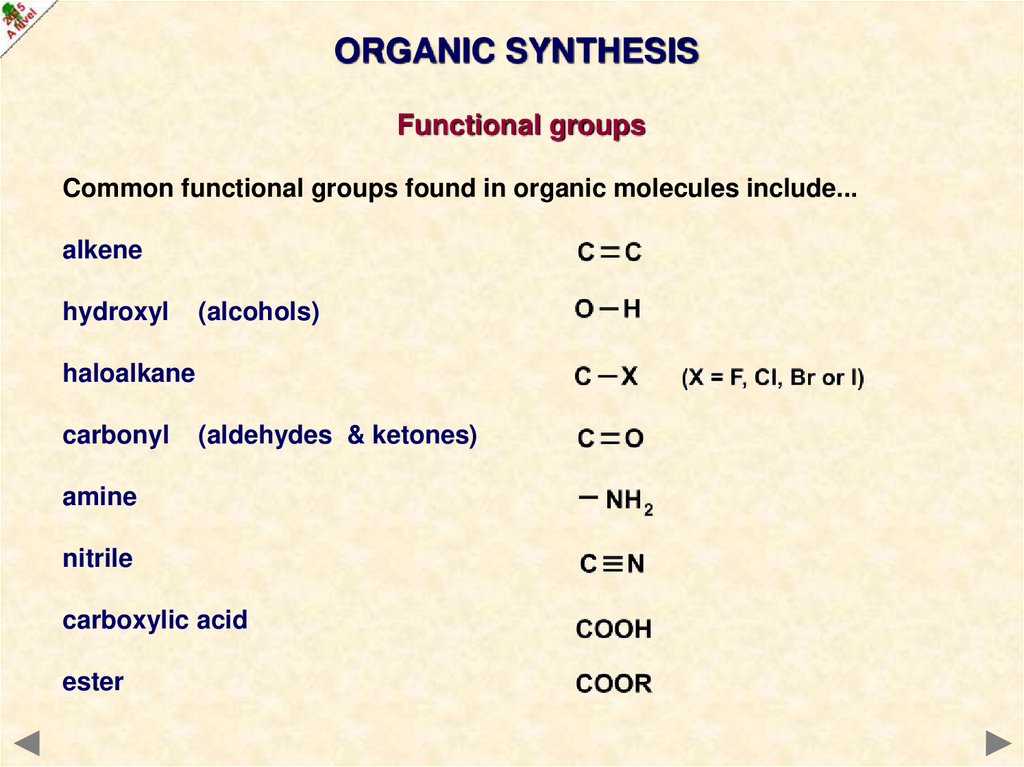
ORGANIC SYNTHESISFunctional groups
Common functional groups found in organic molecules include...
alkene
hydroxyl
(alcohols)
haloalkane
carbonyl
(aldehydes & ketones)
amine
nitrile
carboxylic acid
ester
20.
ORGANIC SYNTHESISInvolves the preparation of new compounds from others, for example…
POLYMERS
ALKANES
DIBROMOALKANES
ALKENES
KETONES
ALCOHOLS
ALDEHYDES
HALOGENOALKANES
AMINES
ESTERS
NITRILES
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
21.
ACTIVITY 1:GROUP ACTIVITY
ON ORGANIC
SYNTHESIS AND
ANALYSIS
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
21
22.
HAND-OUThttp://www.a-levelchemistry.co.uk/410organic-synthesis-and-analysis.html
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
22
2/27/2023
23.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
23
2/27/2023
24.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
24
2/27/2023
25.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
25
2/27/2023
26.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
26
2/27/2023
27.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
27
2/27/2023
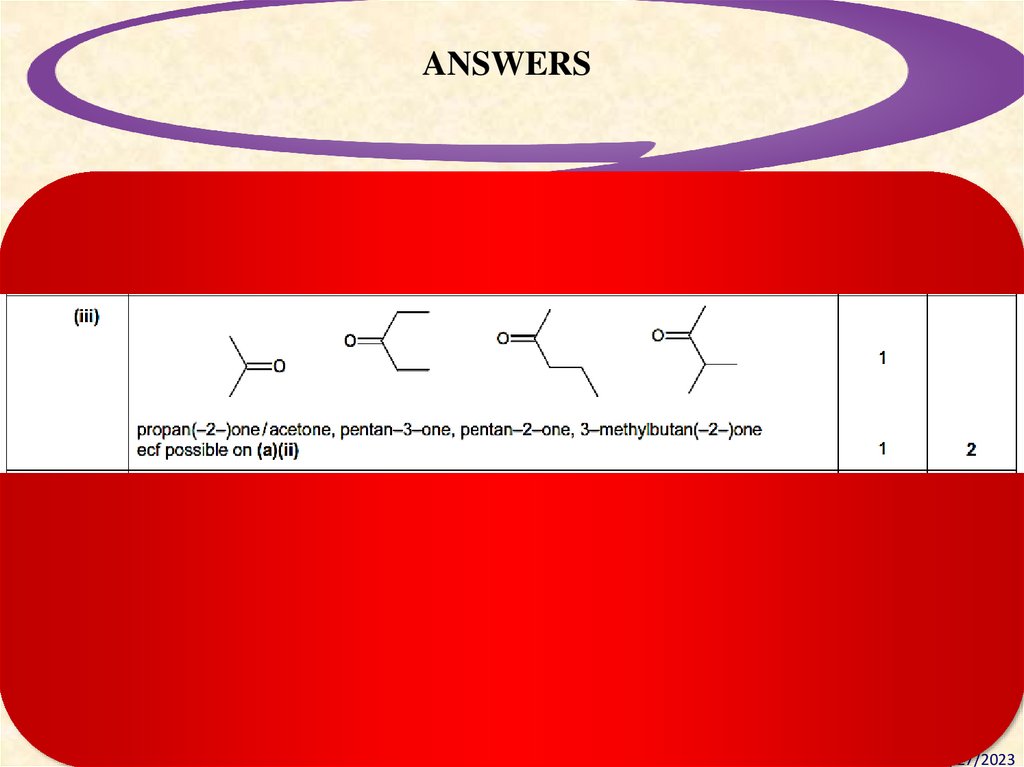
28.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
28
2/27/2023
29.
ACTIVITY 2: CLASSDISCUSSION OF A
SAMPLE A LEVEL ON
ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
29
30.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
30
2/27/2023
31.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
31
2/27/2023
32.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
32
2/27/2023
33.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
33
2/27/2023
34.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
34
2/27/2023
35.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
35
2/27/2023
36.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
36
2/27/2023
37.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
37
2/27/2023
38.
ACTIVITY 3:INDIVIDUAL
SEATWORK ON SAMPLE
A LEVEL EXAMINATION
ON ORGANIC
SYNTHESIS
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
38
39.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
39
2/27/2023
40.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
40
2/27/2023
41.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
41
2/27/2023
42.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
42
2/27/2023
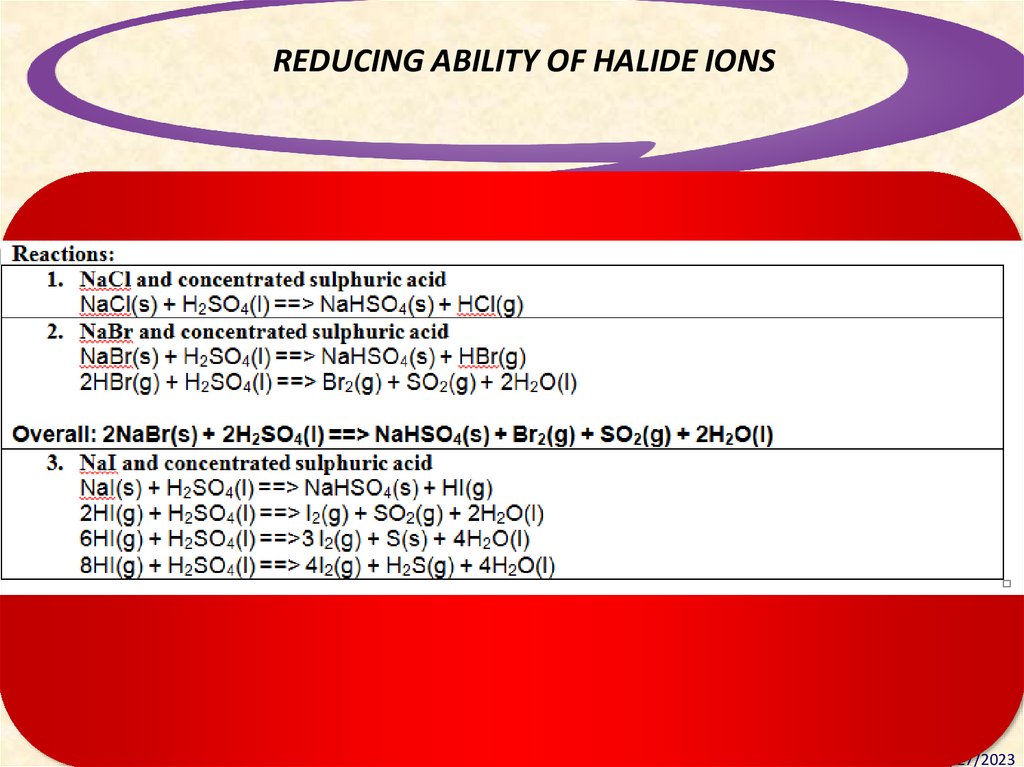
43.
REDUCING ABILITY OF HALIDE IONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
43
2/27/2023
44.
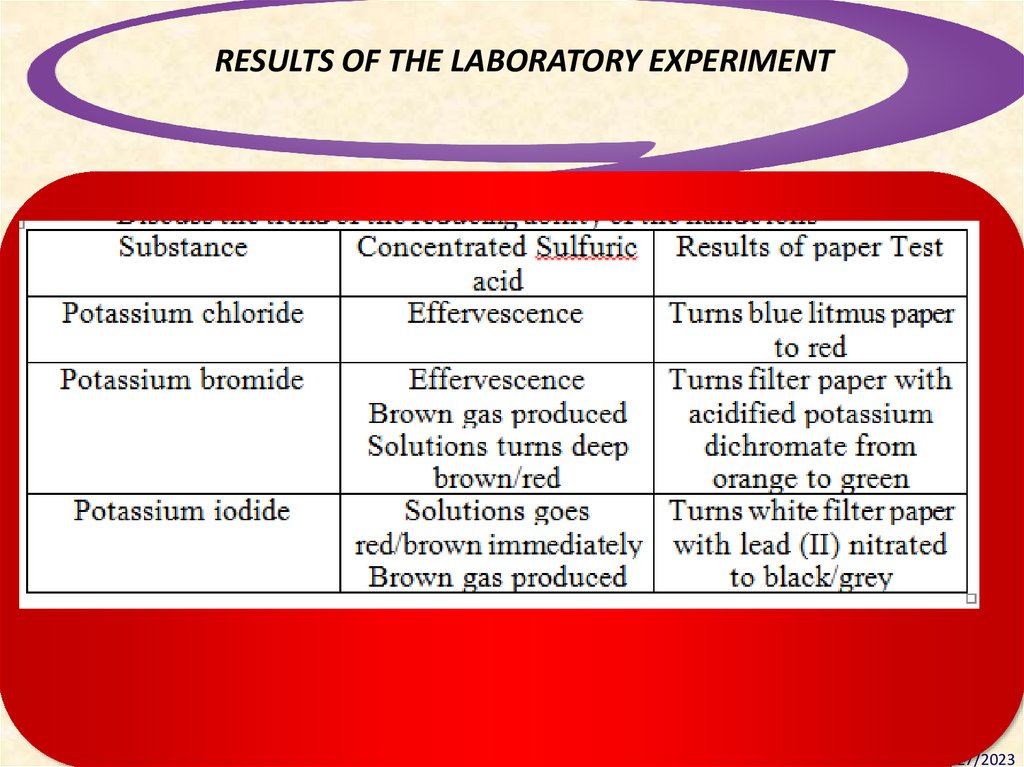
TESTING FOR HALIDES – Conc. H2SO4Summary
Halide
Observation(s)
Product
O.S.
Reaction type
NaCl
misty fumes
HCl
-1
Displacement of Cl¯
NaBr
misty fumes
brown vapour
colourless gas
HBr
Br2
SO2
-1
0
+4
Displacement of Br¯
Oxidation of Br¯
Reduction of H2SO4
NaI
misty fumes
purple vapour
colourless gas
yellow solid
bad egg smell
HI
I2
SO2
S
H2S
-1
0
+4
0
-2
Displacement of I¯
Oxidation of I¯
Reduction of H2SO4
Reduction of H2SO4
Reduction of H2SO4
45.
RESULTS OF THE LABORATORY EXPERIMENTDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
45
2/27/2023
46.
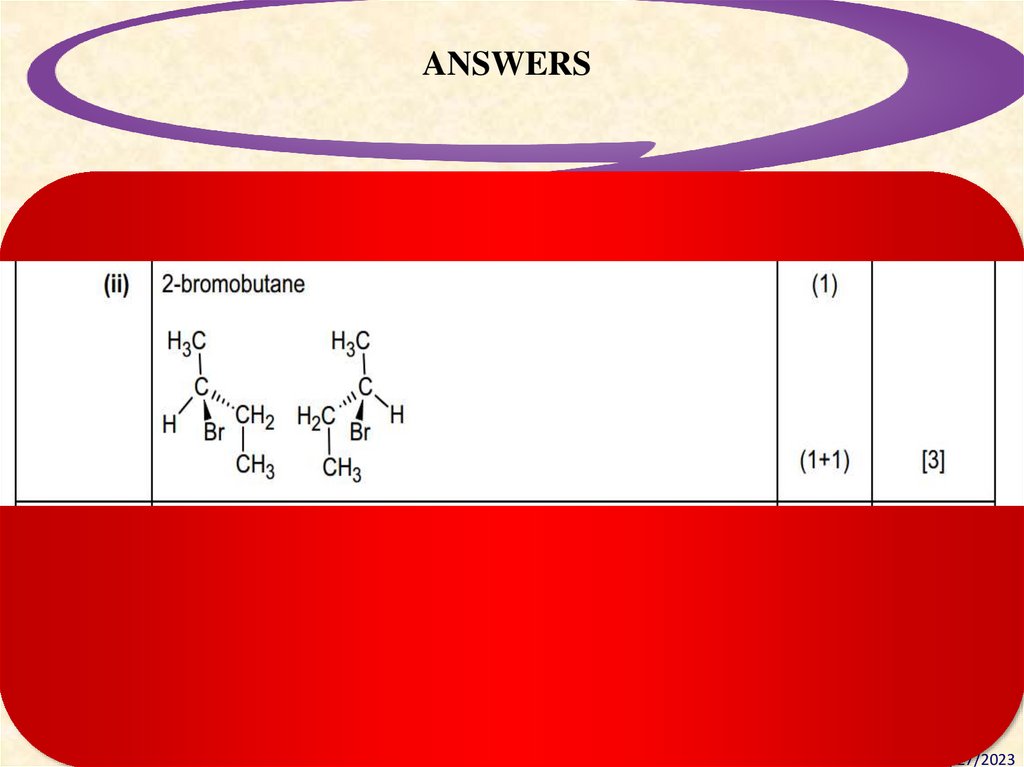
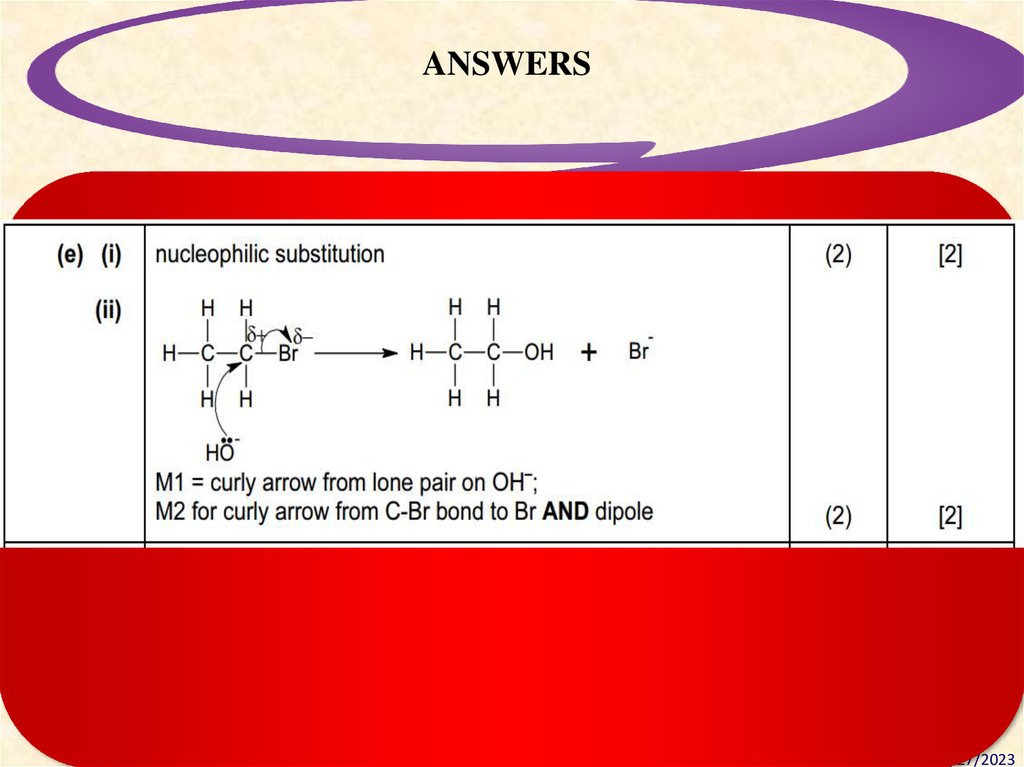
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
46
2/27/2023
47.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
47
2/27/2023
48.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
48
2/27/2023
49.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
49
2/27/2023
50.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
50
2/27/2023
51.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
51
2/27/2023
52.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
52
2/27/2023
53.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
53
2/27/2023
54.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
54
2/27/2023
55.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
55
2/27/2023
56.
ANSWERSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
56
2/27/2023
57.
ORGANIC ANALYSIS TESTHOMETASK: DETERMINING
ORGANIC ANALYSIS TESTS
2/27/2023
Designing Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
57
58.
QUESTIONSDesigning Standards-Based Learning
Modules for Understanding
58
2/27/2023
59.
OBJECTIVES:Return to goals of the lesson: Learners will
• explain the usefulness of some reactions for the
characterisation of organic compounds or specific
functional groups
• identify compounds containing specific functional
groups and identify compounds by means of chemical
and physical tests.
• discuss the importance of synthesis in organic
chemistry and recognise synthetically useful reactions
• create spider diagrams of synthetically useful reactions
• solve problems in synthesis using a synoptic knowledge
of the organic chemistry learned in the whole course
2/27/2023
60.
ORGANICSYNTHESIS
KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING
2015
SPECIFICATIONS






















































 chemistry
chemistry