Similar presentations:
Organic Compounds
1.
Chemistry2. Session
Organic CompoundsContaining Oxygen - III
3. Session Objectives
1. Properties of phenols2. Reaction of phenols
3. Preparation of ethers
4. Properties and reactions of ethers
5. Some useful ethers
6. Crown ethers
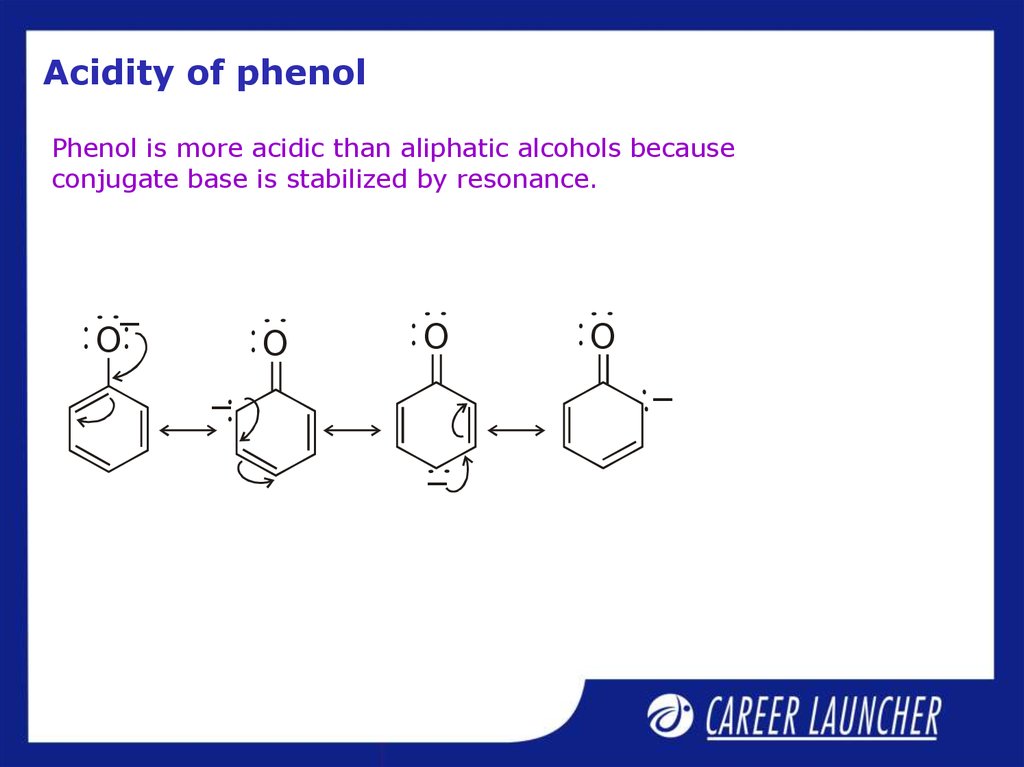
4. Acidity of phenol
Phenol is more acidic than aliphatic alcohols becauseconjugate base is stabilized by resonance.
O
O
O
O–
–
–
–
5. Reactions of phenol
Electrophilic aromatic substitution—OH group is ortho, para- directing group and
activates the benzene rings.
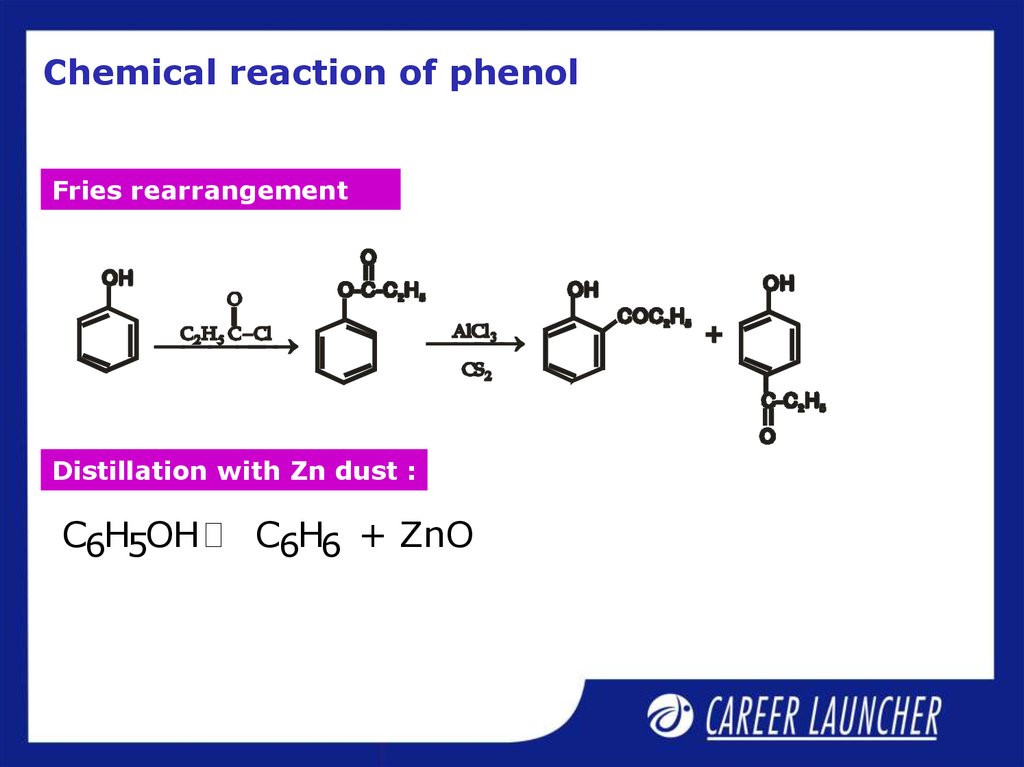
6. Chemical reaction of phenol
Fries rearrangementDistillation with Zn dust :
C6H5OH
C6H6 + ZnO
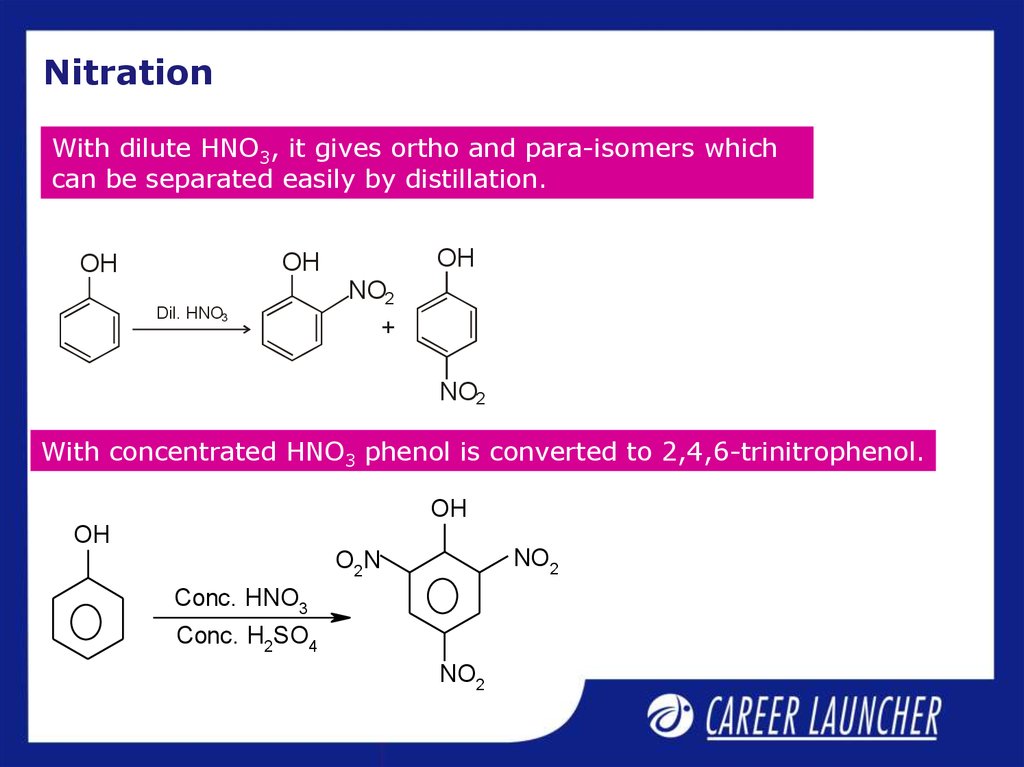
7. Nitration
With dilute HNO3, it gives ortho and para-isomers whichcan be separated easily by distillation.
OH
OH
OH
Dil. HNO3
NO2
+
NO2
With concentrated HNO3 phenol is converted to 2,4,6-trinitrophenol.
OH
OH
NO2
O2N
Conc. HNO3
Conc. H2SO4
NO2
8. Bromination of phenol
OH3 Br2
Br
Br
+ 3HBr
aqueous medium
OH
Br
2, 4, 6 tribromophenol
OH
OH
Br2
Br
+
CHCl3/CCl4
o-Bromophenol
(minor product)
Br
p-Bromophenol
(major product)
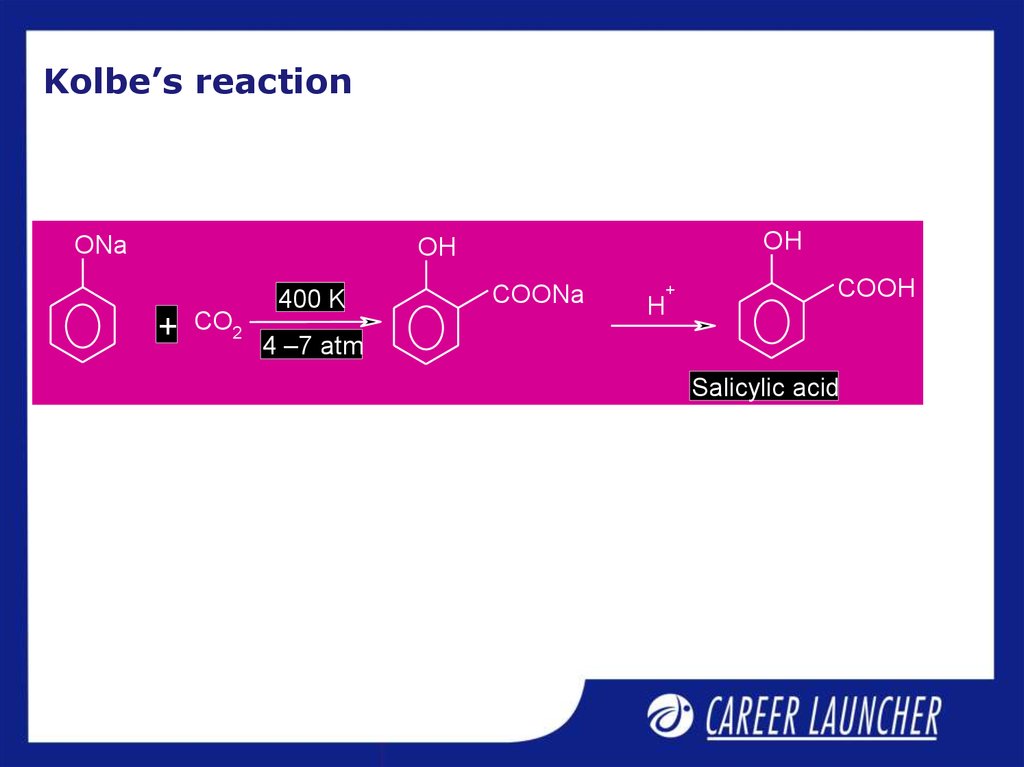
9. Kolbe’s reaction
ONaOH
OH
+
CO2
400 K
COONa
+
H
COOH
4 –7 atm
Salicylic acid
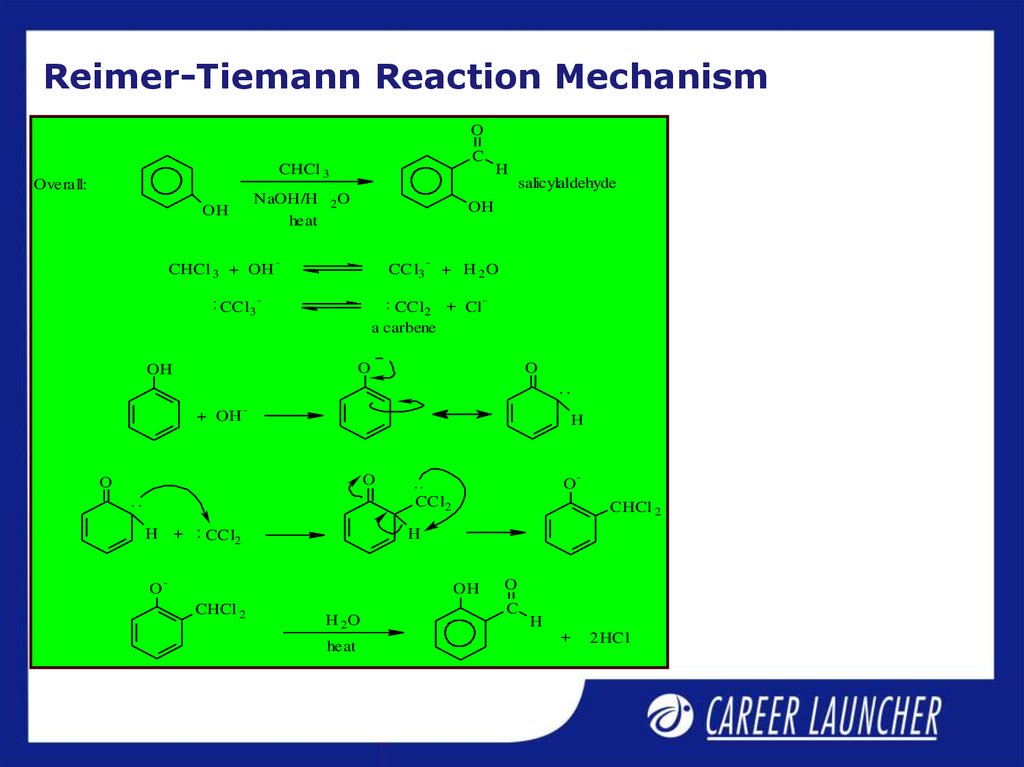
10. Reimer-Tiemann Reaction Mechanism
OC
CHCl 3
Overall:
NaOH/H
heat
OH
CHCl 3 + OH
CCl3
H
salicylaldehyde
2O
OH
-
CCl3
-
-
+ H 2O
CCl2 + Cl
a carbene
O
OH
+ OH
O
-
H
O
O
O
CCl2
H +
O
CHCl 2
H
CCl2
-
OH
CHCl 2
-
H 2O
heat
O
C
H
+
2 HCl
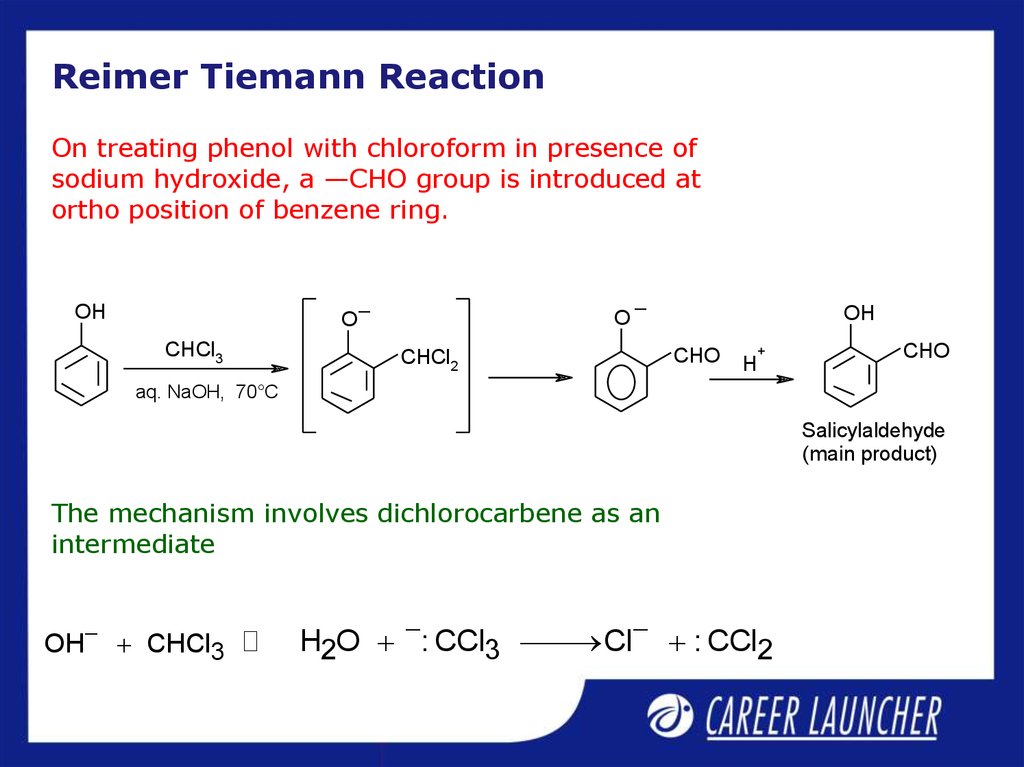
11. Reimer Tiemann Reaction
On treating phenol with chloroform in presence ofsodium hydroxide, a —CHO group is introduced at
ortho position of benzene ring.
O
O
OH
CHCl3
CHCl2
OH
CHO
+
H
CHO
aq. NaOH, 70°C
Salicylaldehyde
(main product)
The mechanism involves dichlorocarbene as an
intermediate
OH CHCl3
H2O : CCl3 Cl : CCl2
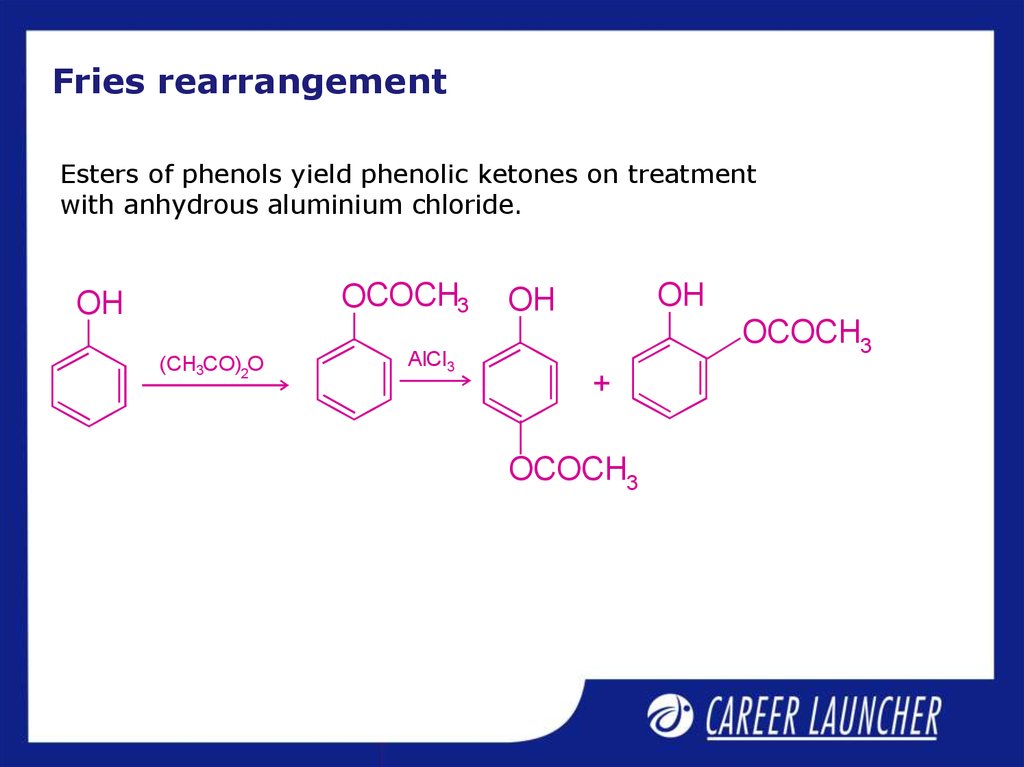
12. Fries rearrangement
Esters of phenols yield phenolic ketones on treatmentwith anhydrous aluminium chloride.
OCOCH3
OH
(CH3CO)2O
AlCl3
OH
OH
OCOCH3
+
OCOCH3
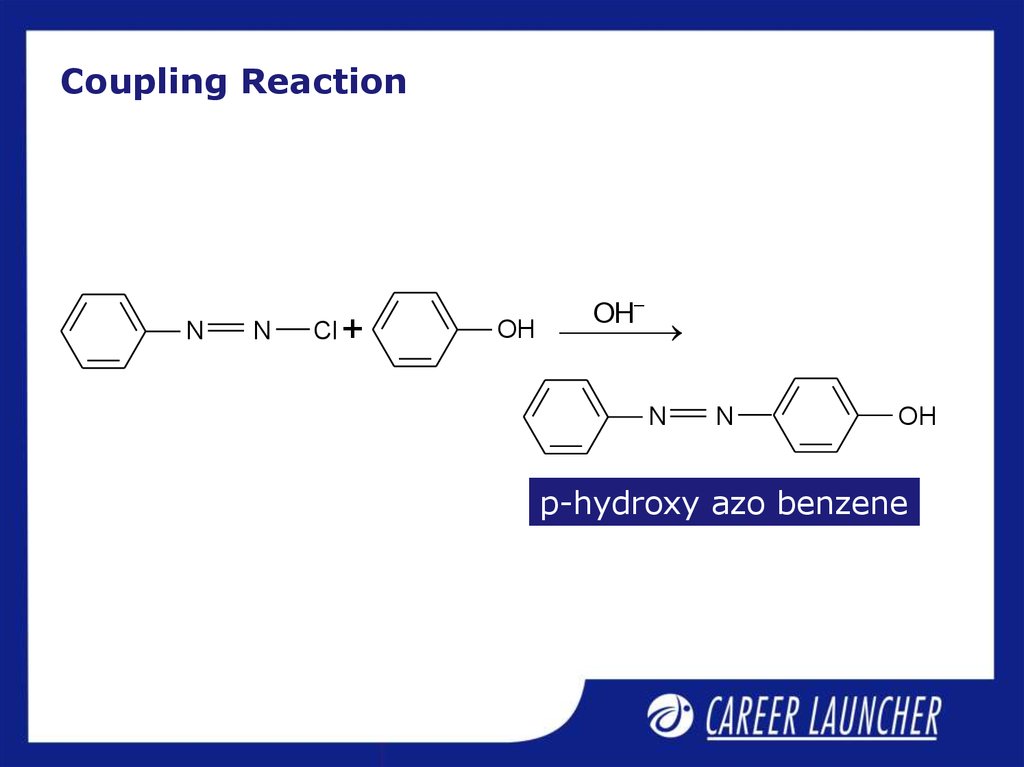
13. Coupling Reaction
NN
Cl +
OH–
OH
N
N
OH
p-hydroxy azo benzene
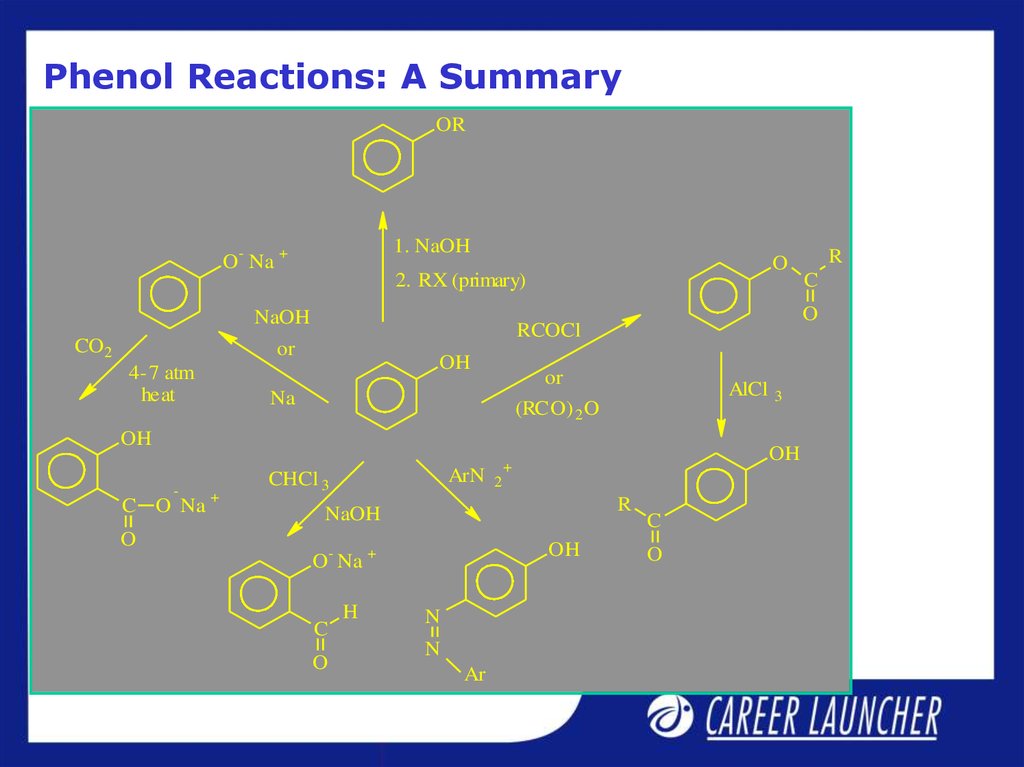
14. Phenol Reactions: A Summary
OR1. NaOH
O- Na +
O
2. RX (primary)
NaOH
CO2
4-7 atm
heat
OH
or
Na
AlCl
(RCO) 2 O
OH
-
C O Na
+
ArN
CHCl 3
O
-
O Na
2
R
C
O
H
OH
+
N
N
Ar
3
OH
+
NaOH
C
O
RCOCl
or
R
C
O
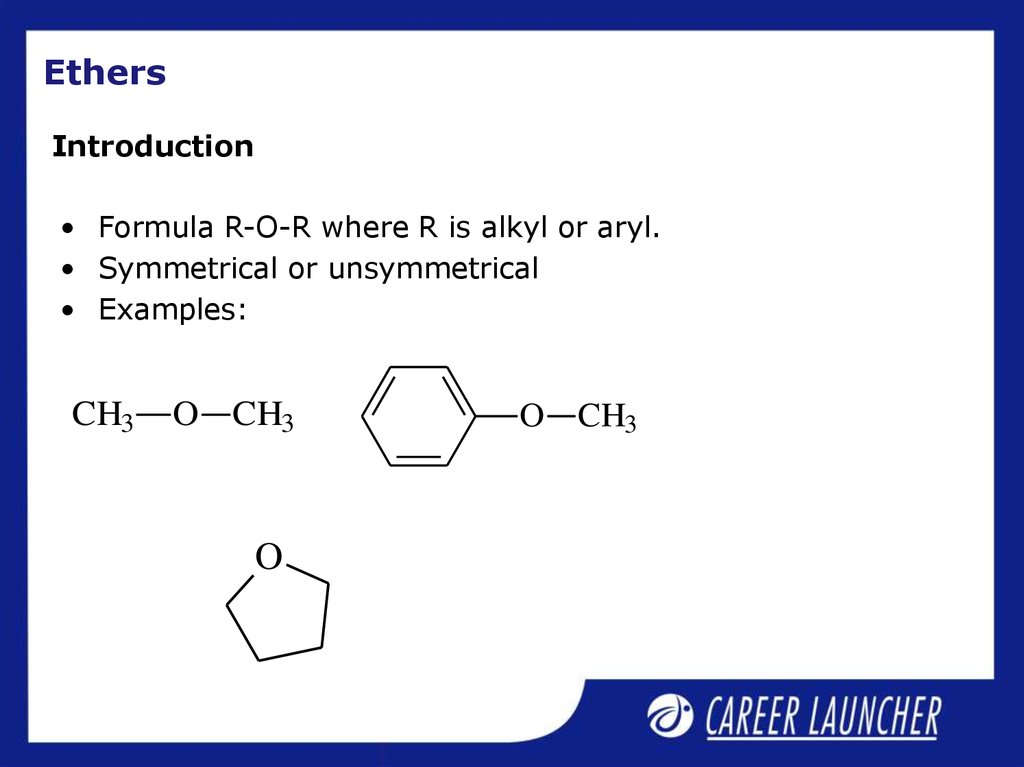
15. Ethers
Introduction• Formula R-O-R where R is alkyl or aryl.
• Symmetrical or unsymmetrical
• Examples:
CH3
O CH3
O
O CH3
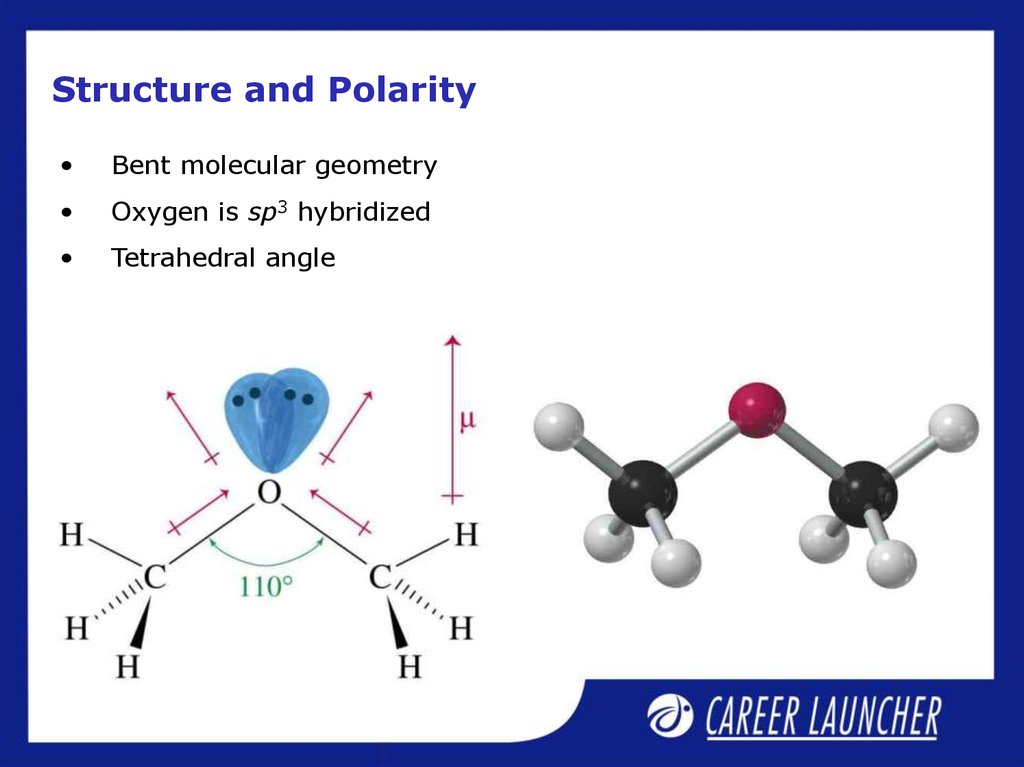
16. Structure and Polarity
Bent molecular geometry
Oxygen is sp3 hybridized
Tetrahedral angle
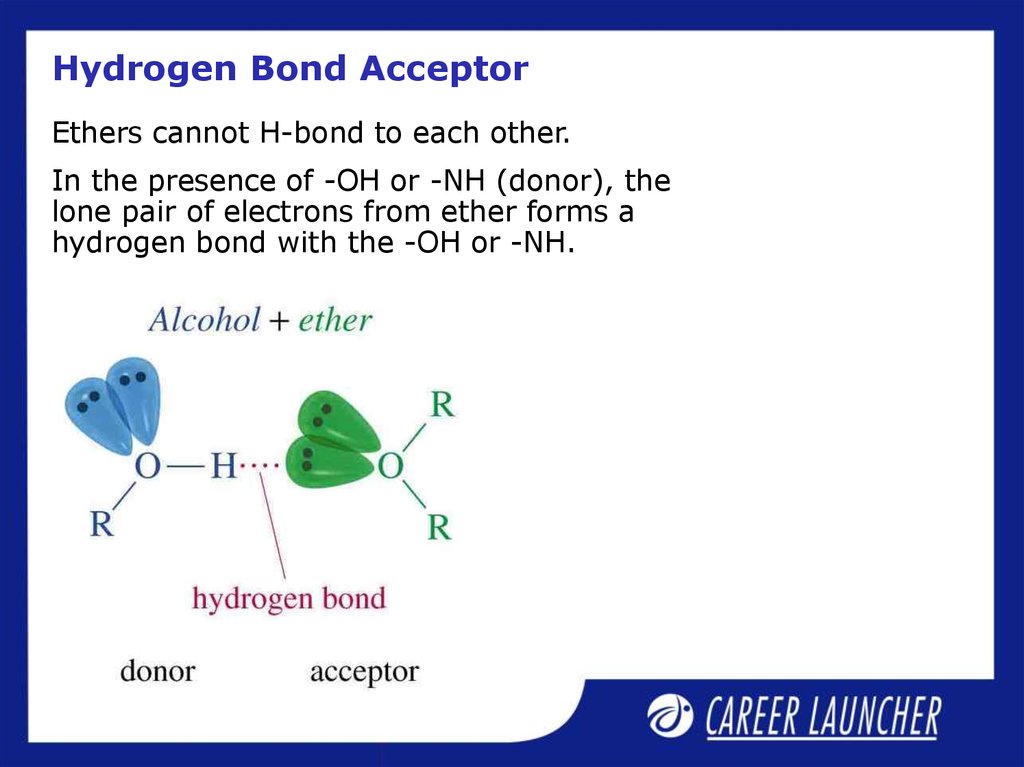
17. Hydrogen Bond Acceptor
Ethers cannot H-bond to each other.In the presence of -OH or -NH (donor), the
lone pair of electrons from ether forms a
hydrogen bond with the -OH or -NH.
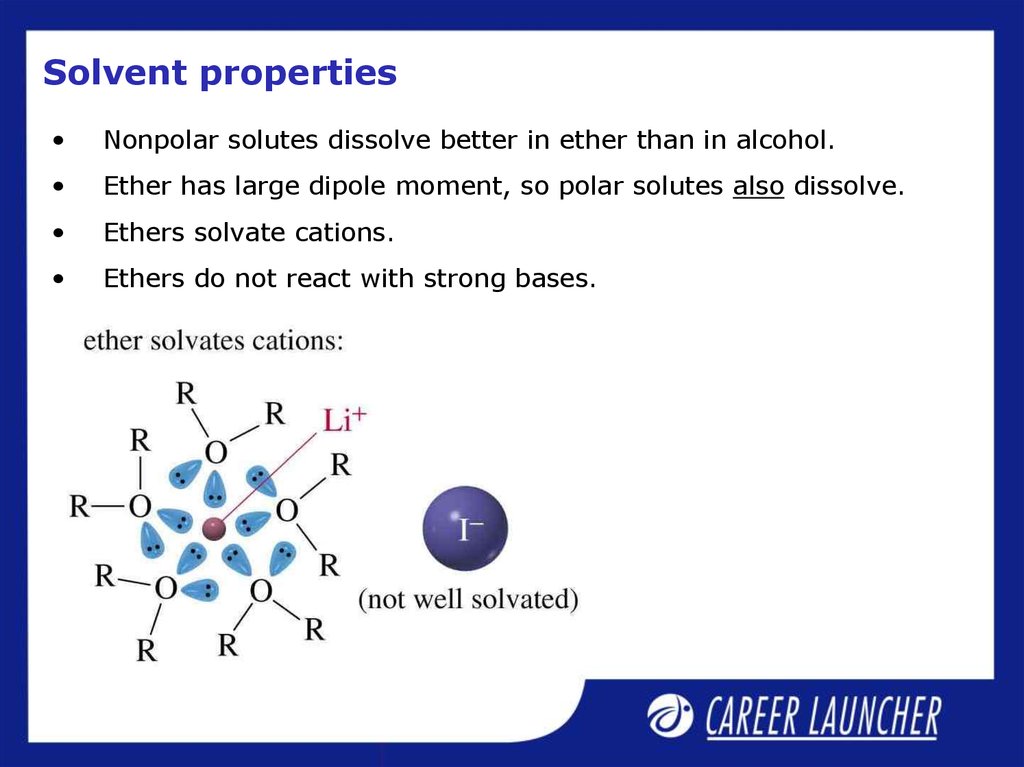
18. Solvent properties
Nonpolar solutes dissolve better in ether than in alcohol.
Ether has large dipole moment, so polar solutes also dissolve.
Ethers solvate cations.
Ethers do not react with strong bases.
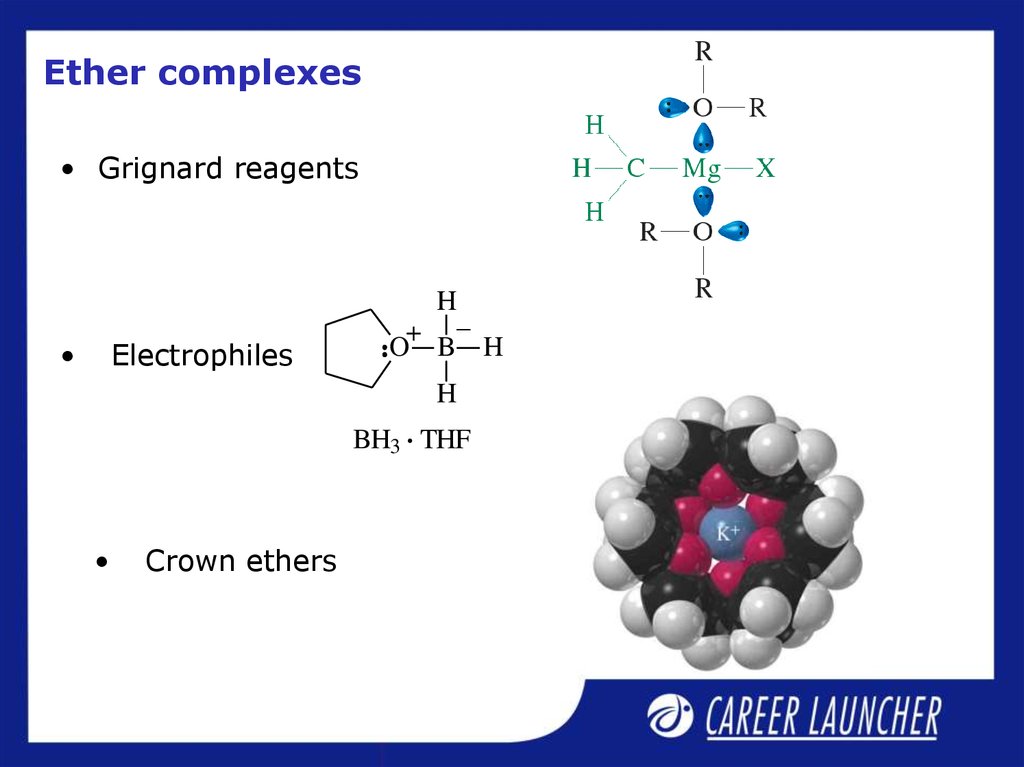
19. Ether complexes
• Grignard reagentsElectrophiles
H
_
+
O B H
H
BH3 THF
Crown ethers
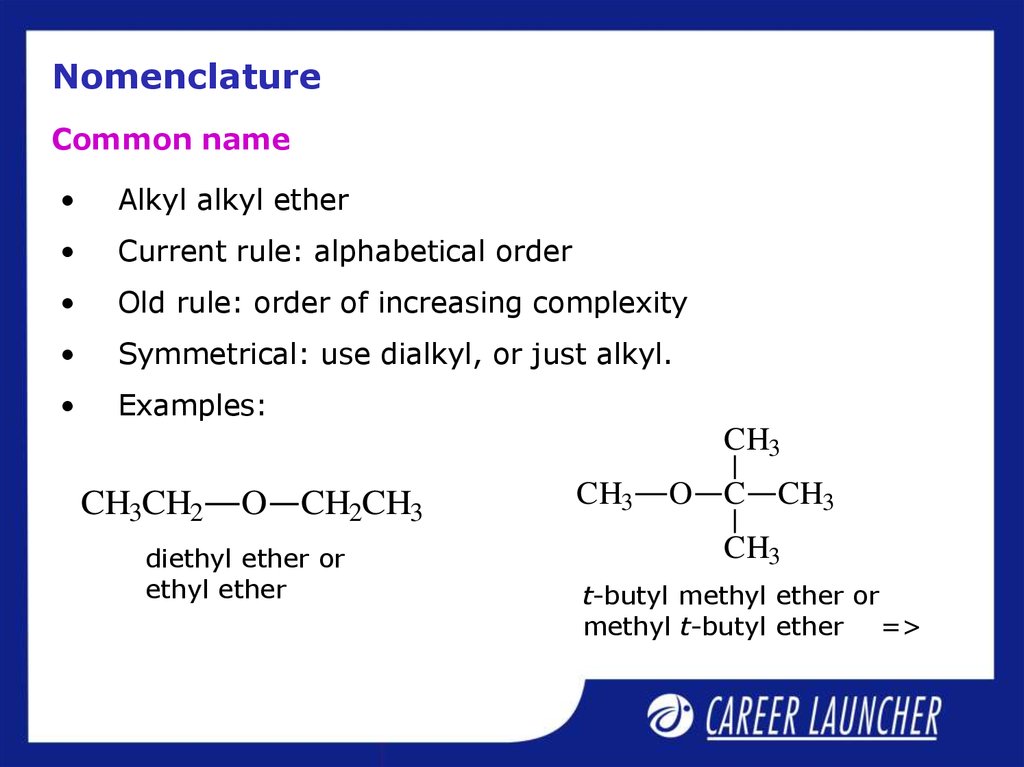
20. Nomenclature
Common nameAlkyl alkyl ether
Current rule: alphabetical order
Old rule: order of increasing complexity
Symmetrical: use dialkyl, or just alkyl.
Examples:
CH3
CH3CH2
O CH2CH3
diethyl ether or
ethyl ether
CH3
O C CH3
CH3
t-butyl methyl ether or
methyl t-butyl ether =>
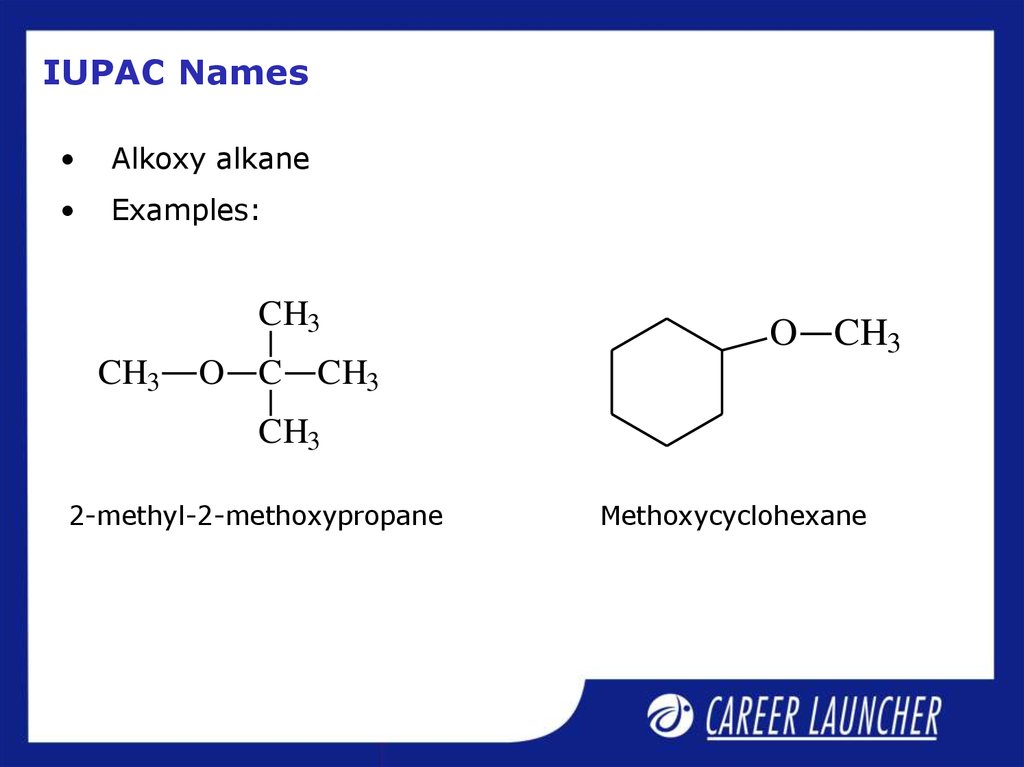
21. IUPAC Names
Alkoxy alkane
Examples:
CH3
CH3
O CH3
O C CH3
CH3
2-methyl-2-methoxypropane
Methoxycyclohexane
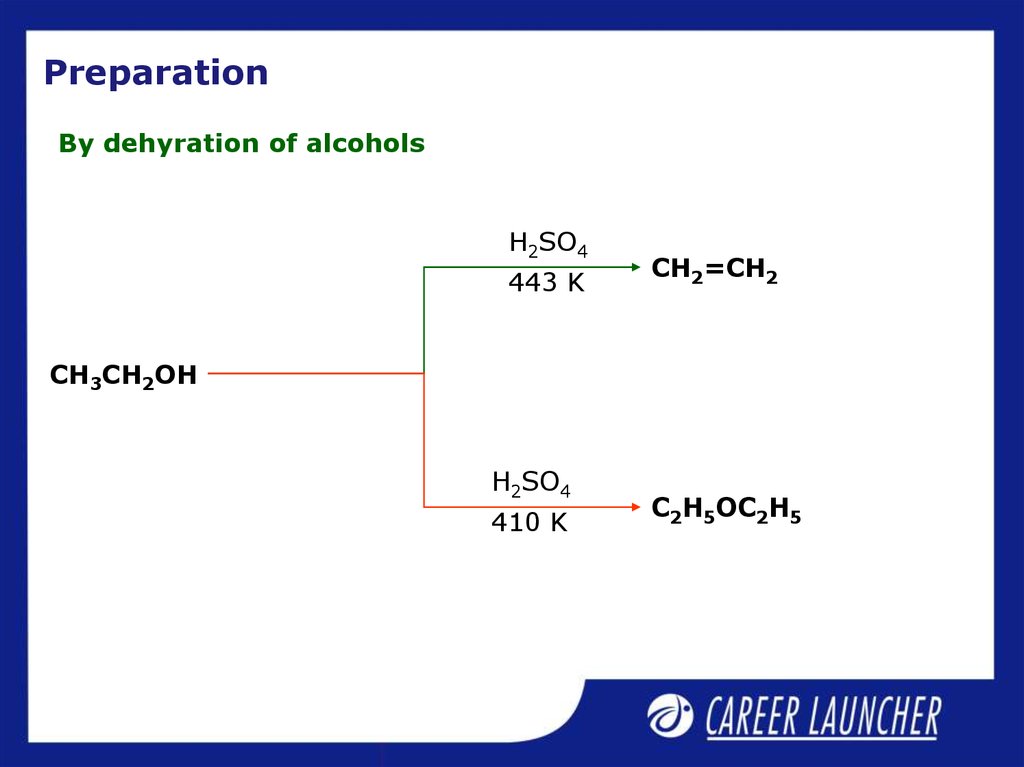
22. Preparation
By dehyration of alcoholsH2SO4
443 K
CH2=CH2
CH3CH2OH
H2SO4
410 K
C2H5OC2H5
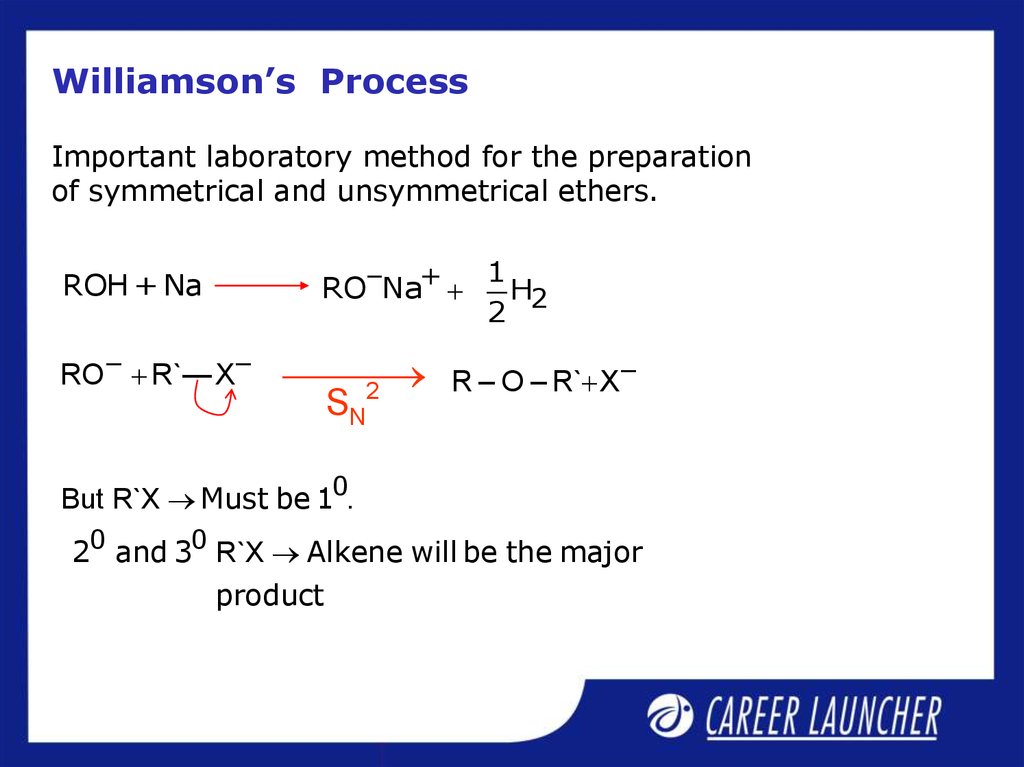
23. Williamson’s Process
Important laboratory method for the preparationof symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
RO–Na+
ROH + Na
RO – R`—X –
2
SN
1
H2
2
R – O – R` X –
But R`X Must be 10.
20 and 30 R`X Alkene will be the major
product
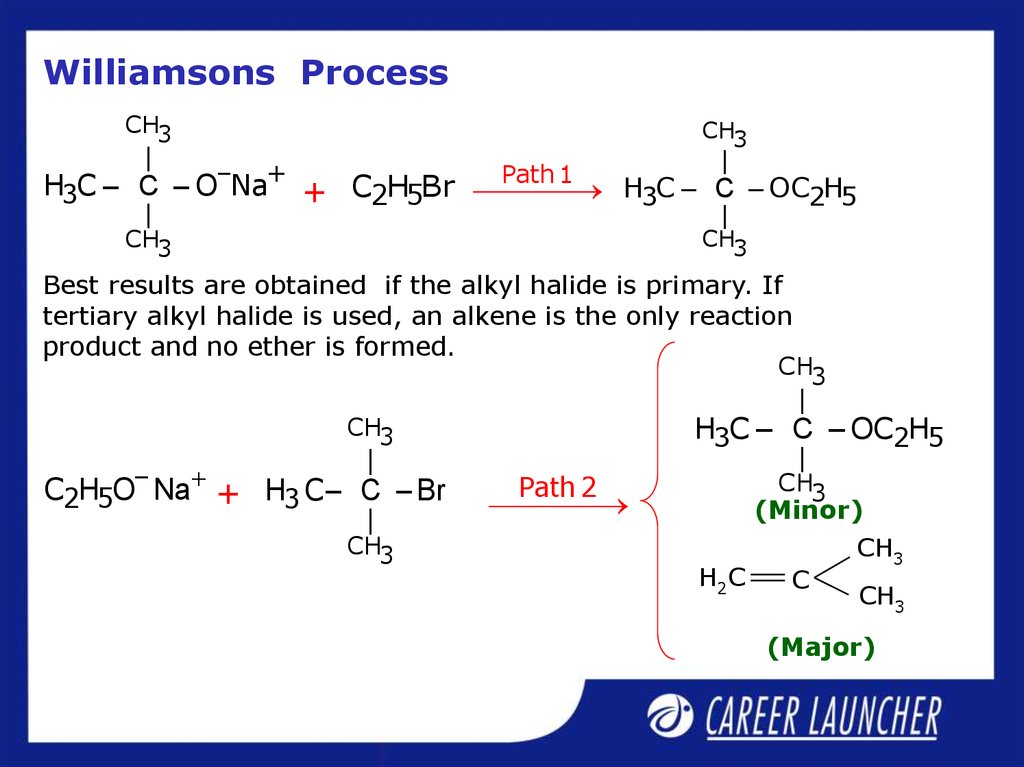
24. Williamsons Process
CH3|
CH3
|
–
+
Path
1
H3C – C – O Na + C2H5Br H3C – C – OC2H5
|
|
CH3
CH3
Best results are obtained if the alkyl halide is primary. If
tertiary alkyl halide is used, an alkene is the only reaction
product and no ether is formed.
CH3
|
CH3
H3C – C – OC2H5
|
|
CH3
Path 2
C2H5O– Na + H3 C – C – Br
(Minor)
|
CH3
CH3
H2C
C
CH3
(Major)
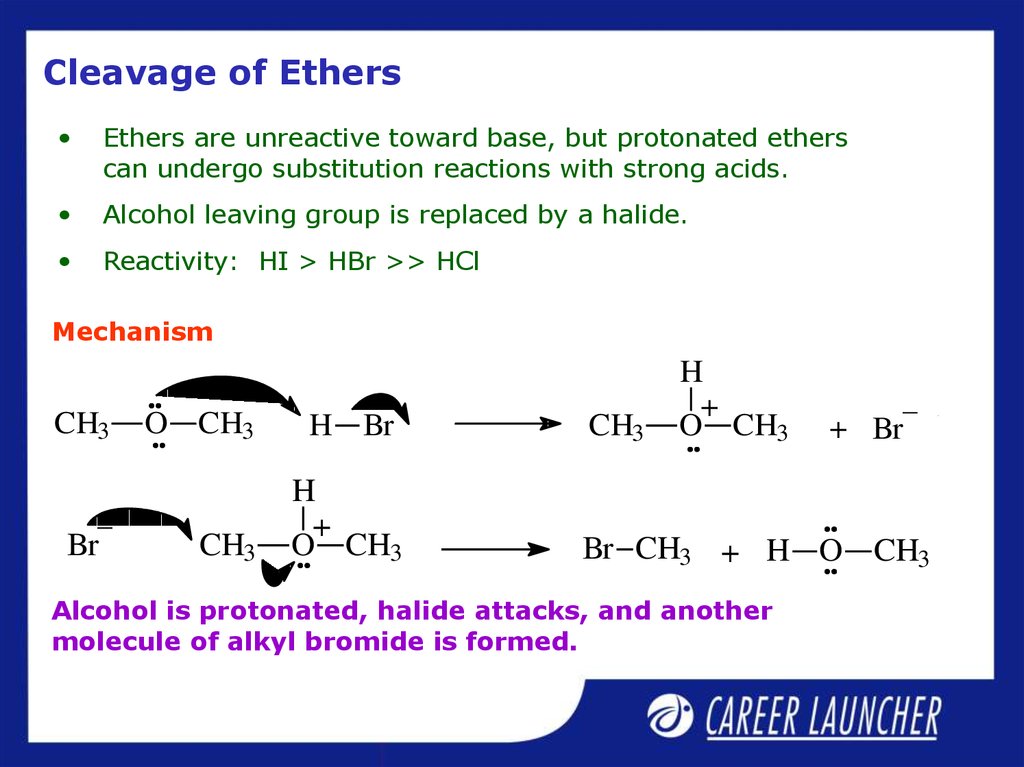
25. Cleavage of Ethers
Ethers are unreactive toward base, but protonated ethers
can undergo substitution reactions with strong acids.
Alcohol leaving group is replaced by a halide.
Reactivity: HI > HBr >> HCl
Mechanism
CH3
O CH3
H Br
CH3
H
+
O CH3
_
Br
CH3
H
+
O CH3
_
+ Br
Br CH3 + H O CH3
Alcohol is protonated, halide attacks, and another
molecule of alkyl bromide is formed.
_
26. Phenyl Ether Cleavage
Alkyl aryl ethers are cleaved at the alkyl oxygen bonddue to the low reactivity of aryl-oxygen bond.
Phenol cannot react further to become halide.
Example:
OH
O CH2CH3
HBr
+ CH3CH2
Br
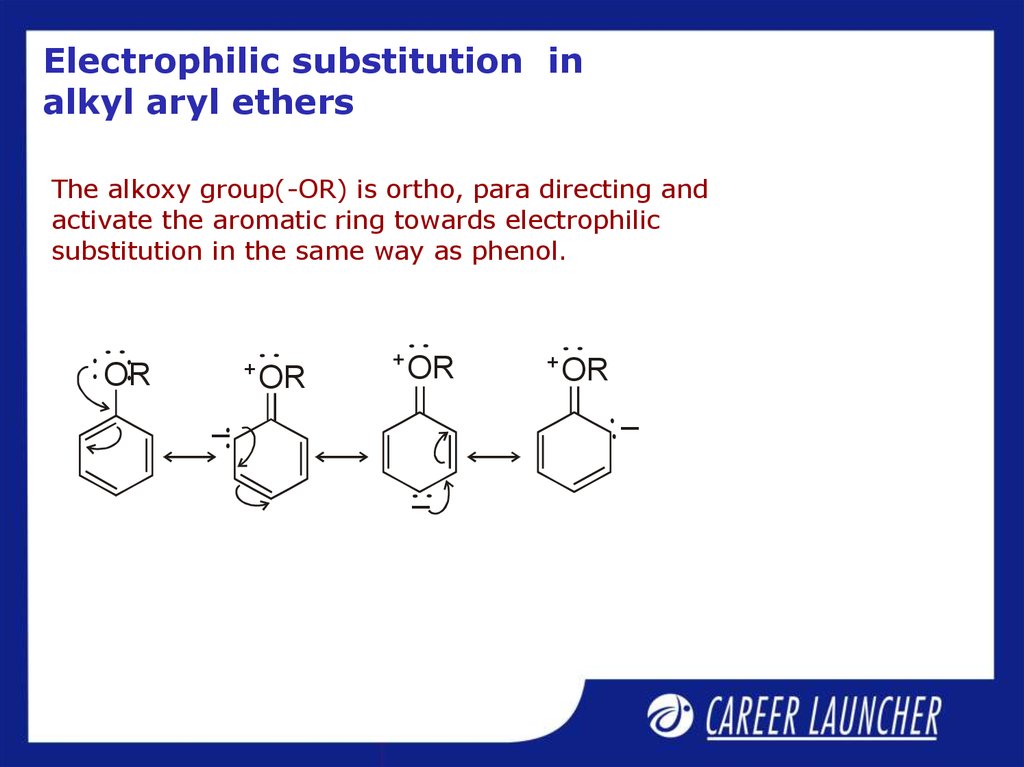
27. Electrophilic substitution in alkyl aryl ethers
The alkoxy group(-OR) is ortho, para directing andactivate the aromatic ring towards electrophilic
substitution in the same way as phenol.
+
OR
+
OR
OR
+
OR
–
–
–
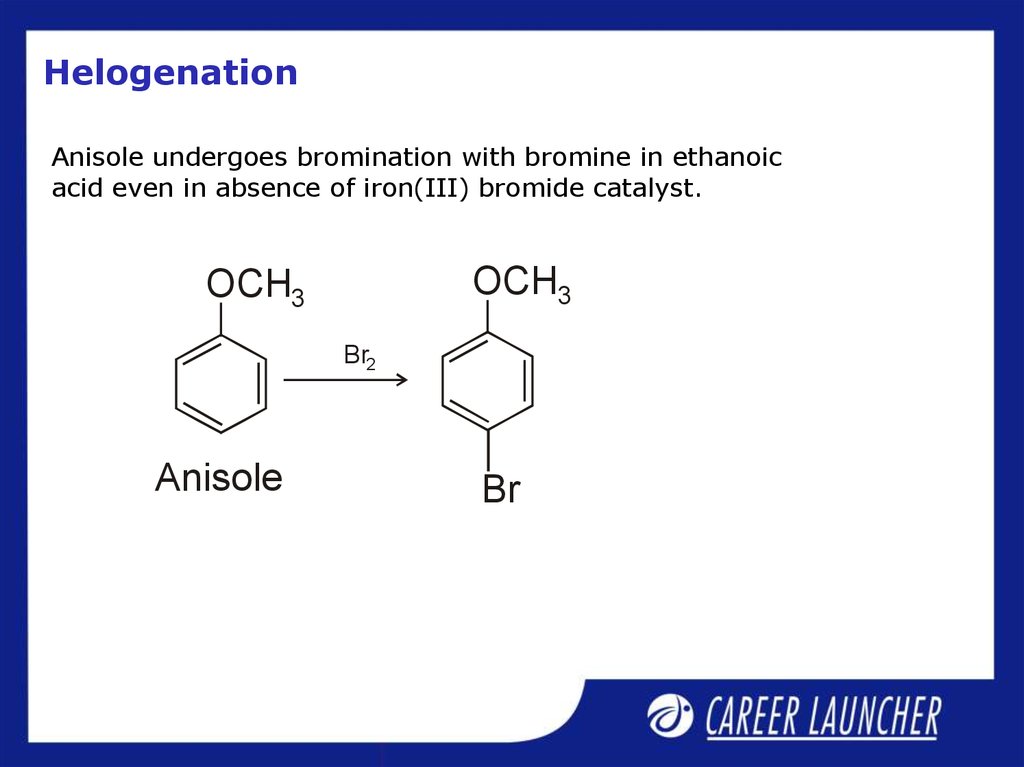
28. Helogenation
Anisole undergoes bromination with bromine in ethanoicacid even in absence of iron(III) bromide catalyst.
OCH3
OCH3
Br2
Anisole
Br
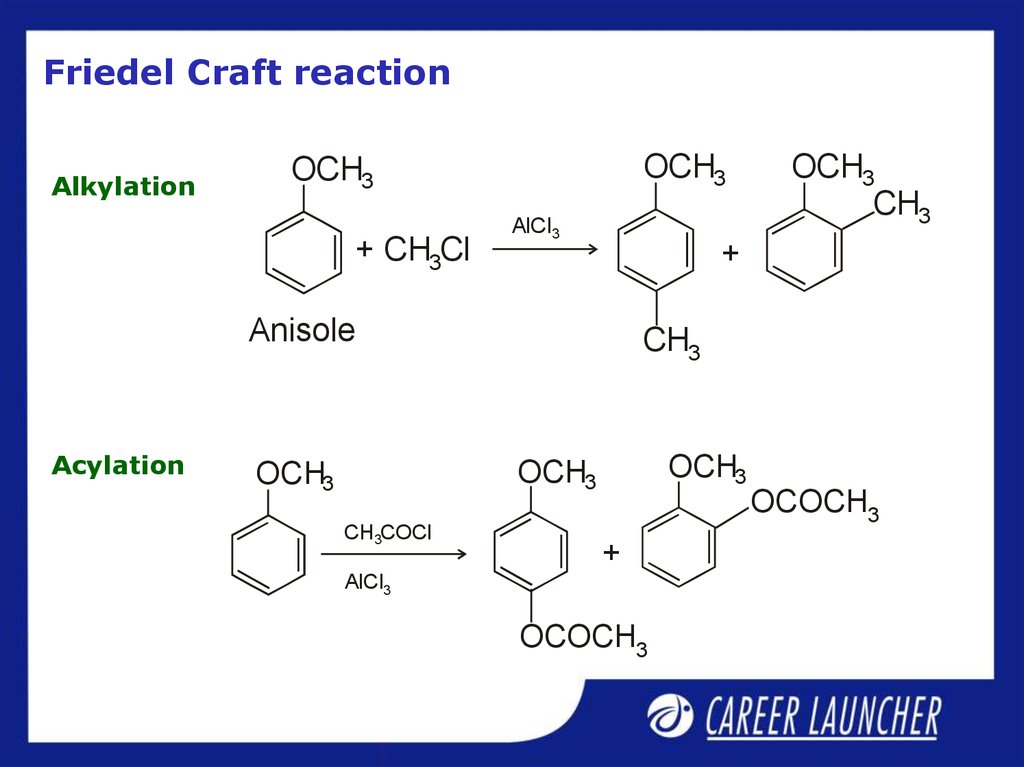
29. Friedel Craft reaction
AlkylationOCH3
OCH3
+ CH3Cl
AlCl3
+
Anisole
Acylation
CH3
OCH3
OCH3
OCH3
CH3COCl
OCH3
CH3
OCOCH3
+
AlCl3
OCOCH3
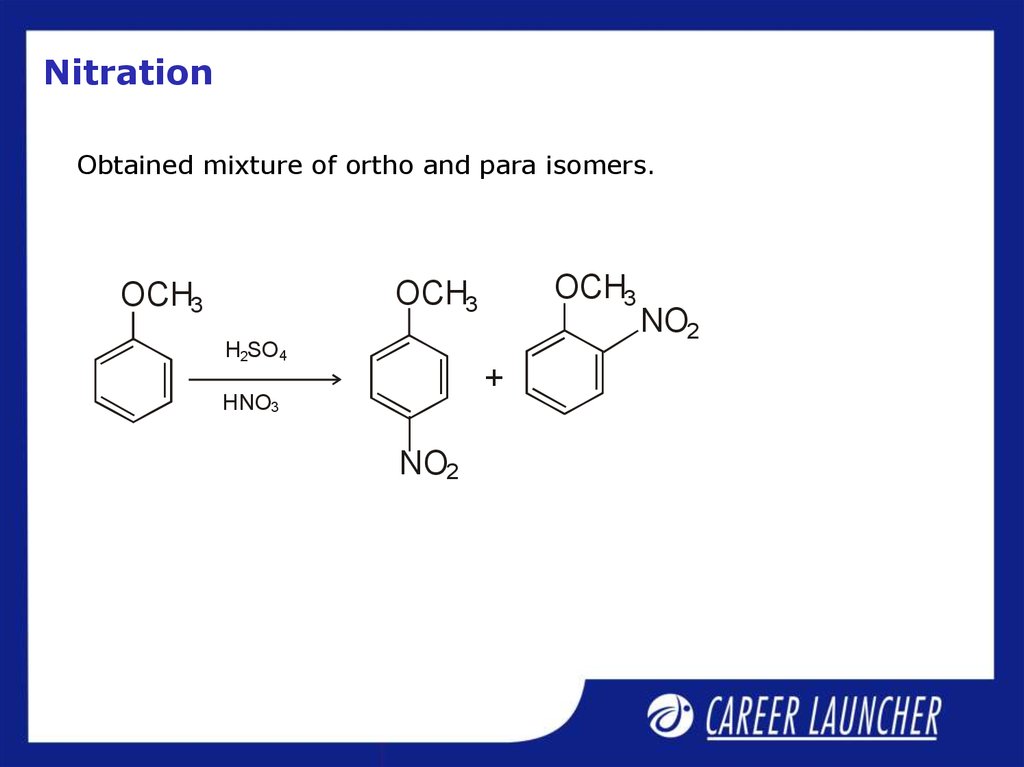
30. Nitration
Obtained mixture of ortho and para isomers.OCH3
OCH3
OCH3
H2SO4
+
HNO3
NO2
NO2
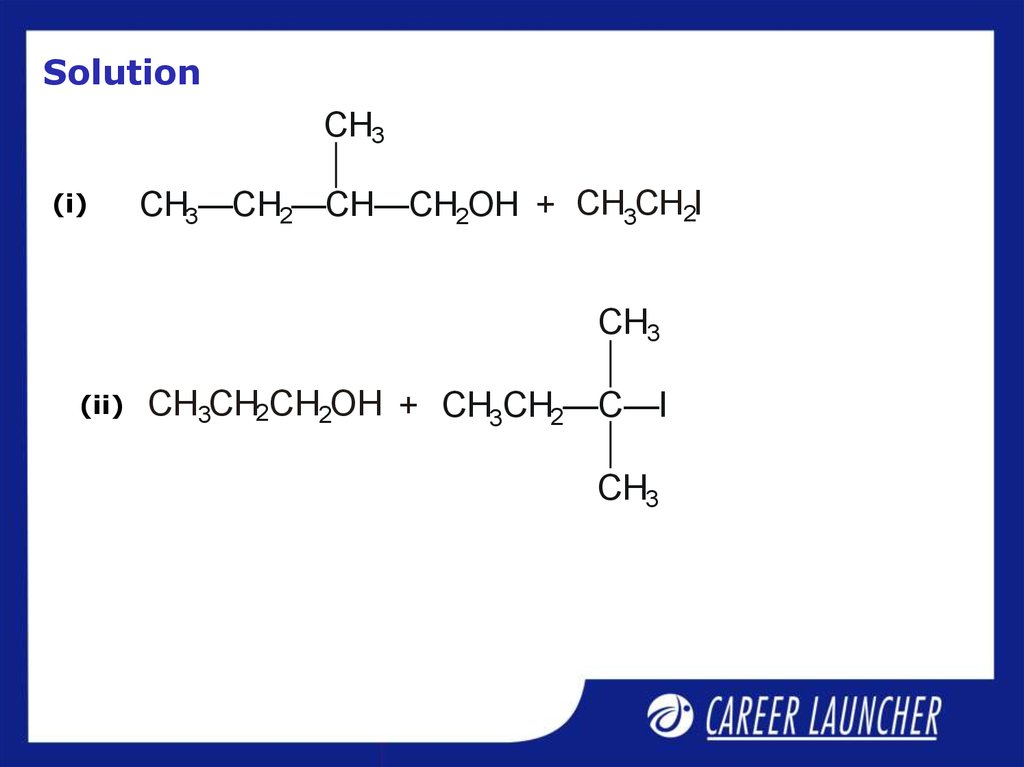
31. Illustrative Example
Give the major products that are formed by heating each ofthe following ethers with HI.
CH3
(i)
CH3—CH2—CH—CH2—O—CH2CH3
C
H
3
(ii)
C
H
C
H
C
H
O
C
C
H
C
H
2
3
2
2
3
32. Solution
CH3(i)
CH3—CH2—CH—CH2OH + CH3CH2I
CH3
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2OH + CH3CH2—C—I
CH3
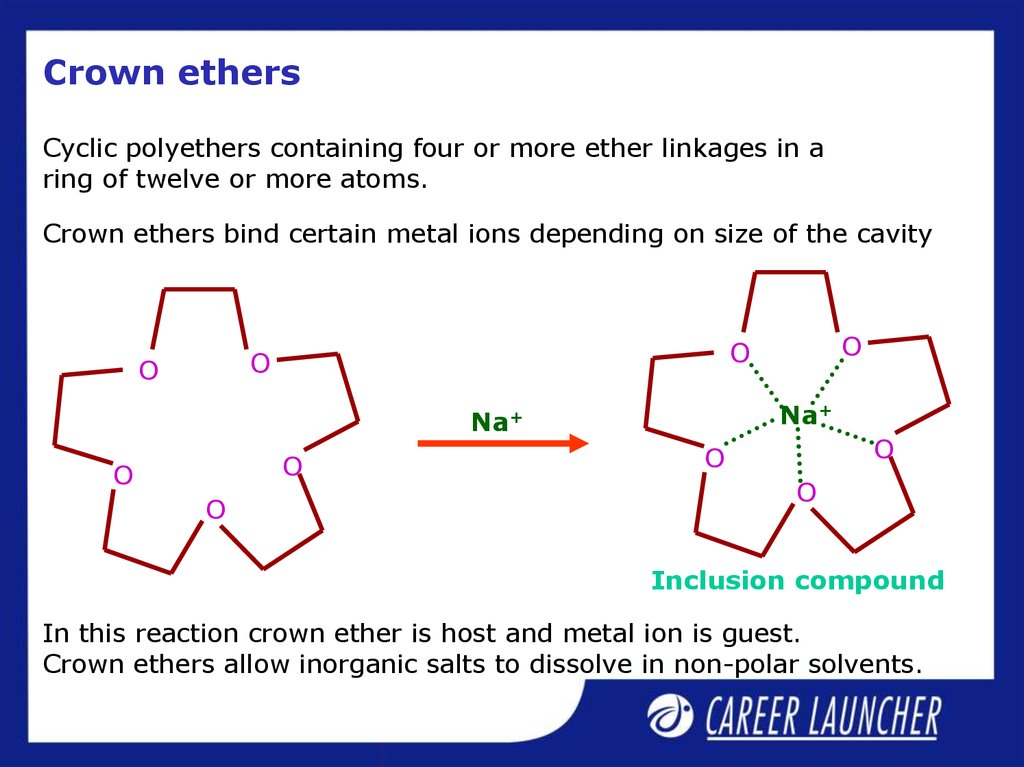
33. Crown ethers
Cyclic polyethers containing four or more ether linkages in aring of twelve or more atoms.
Crown ethers bind certain metal ions depending on size of the cavity
O
Na+
Na+
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Inclusion compound
In this reaction crown ether is host and metal ion is guest.
Crown ethers allow inorganic salts to dissolve in non-polar solvents.
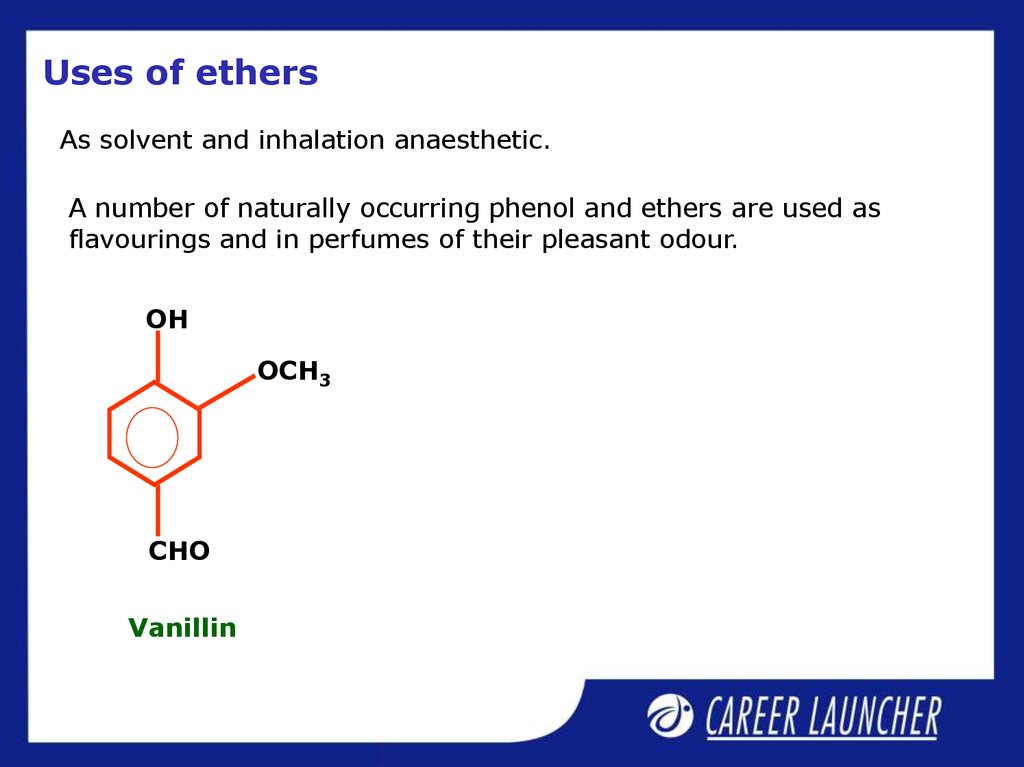
34. Uses of ethers
As solvent and inhalation anaesthetic.A number of naturally occurring phenol and ethers are used as
flavourings and in perfumes of their pleasant odour.
OH
OCH3
CHO
Vanillin








 chemistry
chemistry