Similar presentations:
Vitamin like substances
1.
Vitaminlike
substances
Made by student of GM21-18 group:Algabayev Yeldos
2.
Vitamin like substancesare a large group of biologically active substances that have
some of the properties of vitamins, but do not meet all the
parameters characteristic of vitamins. Sometimes such
substances are called pseudovitamins.
3.
Vitamin like substancesWhat they include ?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Choline
Myo-inositol
Para-amino benzoic acid
Carnitine
Lipoic acid
Bioflavinoids
Taurine
Coenzyme Q
4.
01.Choline
source of methyl groups needed for many steps in
metabolism
5.
CholineSources
Egg yolk is especially rich in choline. Good sources are liver, kidneys, unrefined
vegetable oils, legumes, some vegetables (cabbage, spinach).
Daily requirement
250-600 mg.Choline
The structure of choline
By structure, it is 2-hydroxy-ethyl (trimethyl) ammonium.
Biochemical and other functions
Choline plays a role in the normal functioning of the nervous system and other
cells:component of phosphatidylcholine - the main phospholipid of cell
membranes,participates in the formation of a protective myelin sheath of
nerves,precursor of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
6.
02.Myo-inositol
might balance certain chemicals in the body to
help with mental conditions such as panic
disorder, depression, and obsessive-compulsive
disorder
7.
Myo inositolVitamin B8 (inositol, inositol, myo-inositol) Sources The best food source of inositol is sesame seed
oil. Also found in beef heart, whole grains, soybeans, beans, grapefruit, fish roe. Approximately 75%
of the daily requirement of inositol is synthesized by cells.
Daily requirement 500 mg.
Inositol Myo-inositol
The structure of inositol Structure Inositol is a cyclic hexahydric alcohol of cyclohexane.
Biochemical and other functions
Inositol is part of the plasma membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol and its phosphorylated
derivatives, which are found in all tissues, especially nervous tissue is rich in them. Phosphorylated
forms of inositol, primarily inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate, mediate the action of a number of hormones.
It promotes the release of calcium ions from its intracellular depots. As a consequence of this
function, inositol is required for a number of systems:
Vascular system
Inositol is involved in the regulation of fat metabolism, helps to reduce blood cholesterol levels,
improves blood rheology, which prevents the formation of blood clots, and also contributes to the
elasticity of artery walls.
8.
Affects of myo-inositolNervous system
Inositol improves the transmission of nerve signals, it is effectively used in the treatment
of diabetic neuropathy and diseases with impaired nerve sensitivity, in violation of the
quality of sleep. Vitamin B8 is absolutely essential for the proper development and
function of spinal cord cells.
Mental activity
By participating in the processes of signal transmission, inositol improves concentration
and memory ability.
Growth
By normalizing hormonal signaling, inositol promotes bone growth and muscle mass.
reproductive system Vitamin B8 deficiency can lead to infertility in both sexes. It is
believed that inositol is necessary for the reproduction of spermatozoa, and it is also
assigned a central role in the trigger mechanism for egg division.
Vision
The lens and tear fluid contain a high concentration of inositol. Its additional
introduction into the diet improves the condition of the visual system and prevents eye
fatigue, visual impairment.
Hypovitaminosis
Symptoms of inositol deficiency are stress, insomnia, high blood cholesterol, impaired
vision, skin rashes, hair loss.
9.
PABA(B10)para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), also called aminobenzoic acid, a vitaminlike substance and a growth factor required by several types of
microorganisms. In bacteria, PABA is used in the synthesis of
the vitamin folic acid. The drug sulfanilamide is effective in treating
some bacterial diseases because it prevents the bacterial utilization
of PABA in the synthesis of folic acid.
PABA is not an essential nutrient for vertebrates, since they do not
synthesize their own folic acid. PABA is present in high
concentrations in brewer’s yeast, and it is perhaps best-known as an
ultraviolet screen and as an active ingredient of some sun lotions.
10.
Coenzyme QThe name comes from the Latin word
ubique - everywhere, everywhere and
quinone. In 1978, for the development of the
theory of the action of coenzyme Q10, an
indispensable cellular component involved
in the synthesis of ATP, the American
scientist P. Mitchell received a Nobel trip. By
structure, these are derivatives of 2,3dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone with
an isoprene chain in the C6 position:
11.
Coenzyme QUbiquinones are capable of reversible redox transformations and are localized in
the cytoplasmic membranes of mitochondria. Their main function of ubiquinones is
coenzymatic and is associated with the transfer of electrons and protons during
respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. Since coenzyme Q10 is involved in
providing energy to cells, in humans, the largest amount of coenzyme Q10 is
concentrated in the mitochondria of the cells of the most energy-consuming organs
- the heart, liver, pancreas. Another important function of ubiquinones is antioxidant.
They, along with a-tocopherol, b-carotene and selenium, are powerful antioxidants
and are the first to be consumed. Unlike the above antioxidants, ubiquinones are
synthesized in the human body itself and have the ability to constantly restore their
antioxidant activity, passing from the oxidized form (ubiquinol) to the reduced form
(ubiquinone). According to some reports, they play an important role in protecting
low density lipoproteins from oxidation. In heart cells, Q10, by reducing the level of
free radicals, slows down the development of atherosclerosis.
12.
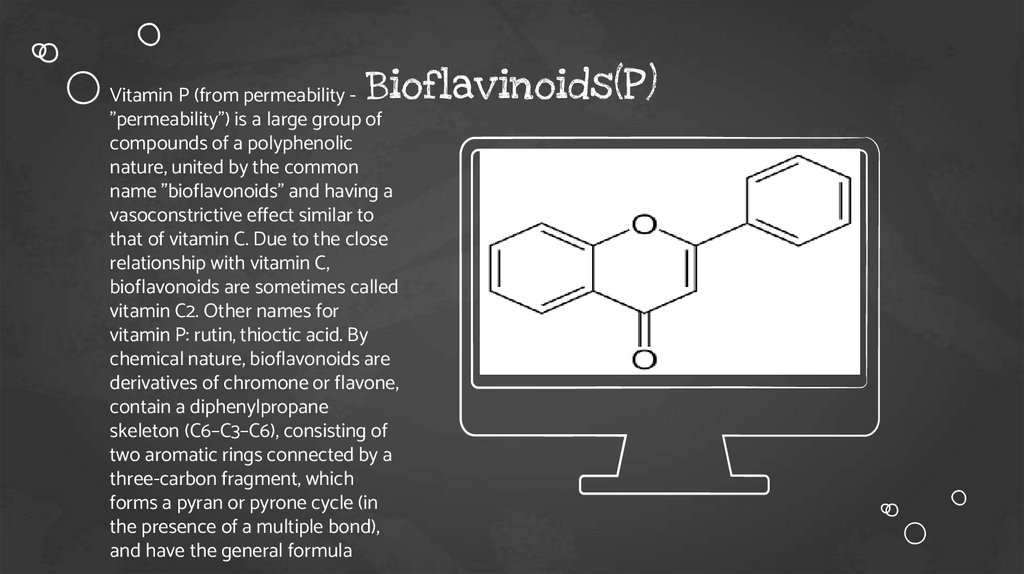
Bioflavinoids(P)Vitamin P (from permeability "permeability") is a large group of
compounds of a polyphenolic
nature, united by the common
name "bioflavonoids" and having a
vasoconstrictive effect similar to
that of vitamin C. Due to the close
relationship with vitamin C,
bioflavonoids are sometimes called
vitamin C2. Other names for
vitamin P: rutin, thioctic acid. By
chemical nature, bioflavonoids are
derivatives of chromone or flavone,
contain a diphenylpropane
skeleton (C6–C3–C6), consisting of
two aromatic rings connected by a
three-carbon fragment, which
forms a pyran or pyrone cycle (in
the presence of a multiple bond),
and have the general formula
13.
AssignmentThe main dietary sources of flavonoids are fruits, vegetables, and beverages (tea,
juice, wine). For example, the content of flavonoids in red wine is higher than in grape
juice, the reason for this is the microorganisms involved in the production of wine. In
foods, flavonoids can be present in monomeric, dimeric, and polymeric forms, the
latter being called tannins. The biological role of flavonoids is to stabilize the
intercellular matrix of connective tissue and reduce capillary permeability. The strength
of the walls of the blood capillaries is directly controlled by the hormones of the adrenal
cortex, the role of P-vitamin substances is that they protect the adrenal medulla
hormone adrenaline from oxidation, prolonging its action. P-vitamin activity is
manifested by influencing some of the body's enzyme systems that regulate vascular
permeability. For example, bioflavonoids, along with vitamin C, inactivate the action of
the enzyme hyaluronidase, which catalyzes the breakdown of heteropolysaccharide hyaluronic acid - the main substance of connective tissue.
14.
Daily requirementCoenzyme q
Myo inositol
PAMB(B10)
The daily requirement for
ubiquinone has not been
determined.
Mercury is the closest
planet to the Sun and the
smallest one
The daily requirement for
para-aminobenzoic acid
has not been established.
Choline
The estimated daily
requirement for choline is
150-1000 mg (average
500 mg) and is usually
easily achieved through
nutrition.
15.
Thanksfor your
attention!
CREDITS: This presentation template was created
by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, and
infographics & images by Freepik.













 chemistry
chemistry








