Similar presentations:
Subject: The use of high-strength
1. Subject: The use of high-strength
SUBJECT: THE USE OF HIGH-STRENGTH2. CONTENTS: INTRODUCTION CHAPTER I . THEORETICAL ASPECTS OF HIGH-STRENGTH STEEL IN CONSTRUCTION High-strength building steels
Classification of high-strength steels for building structuresCHAPTER II . STEEL FOR METAL STRUCTURES SUPPLIED IN HOT-ROLLED STATE
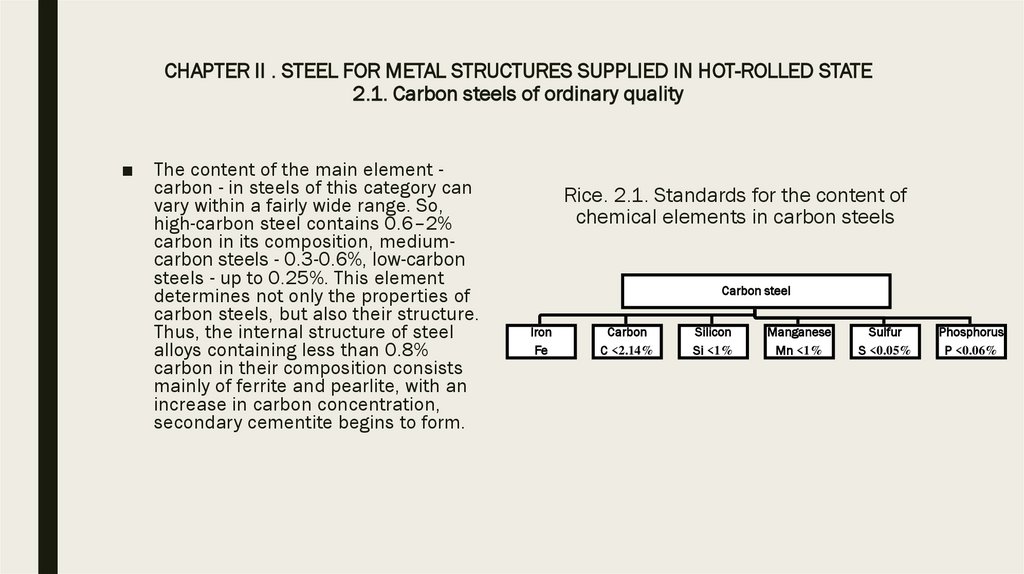
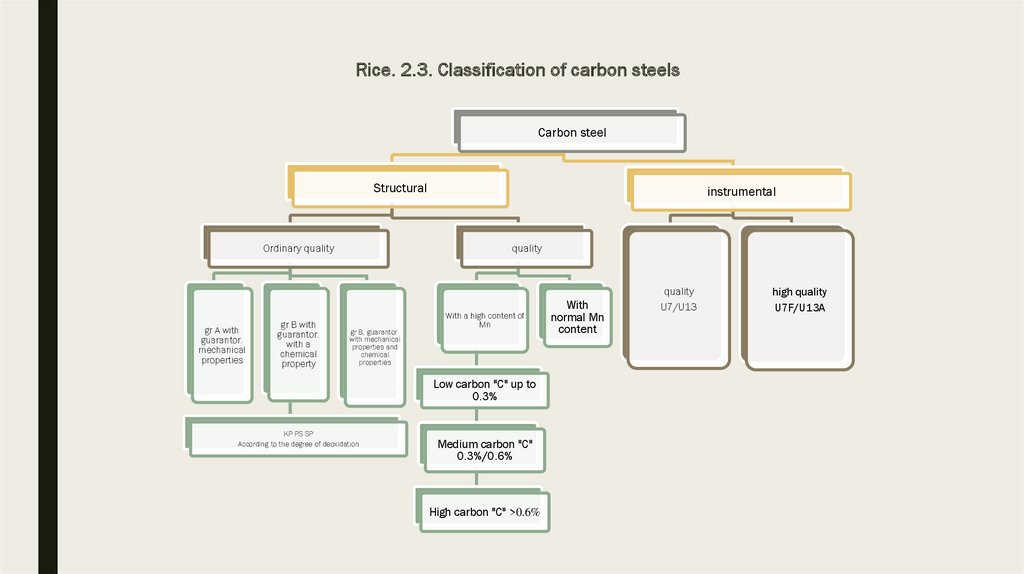
2.1. Carbon steels of ordinary quality (common strength)
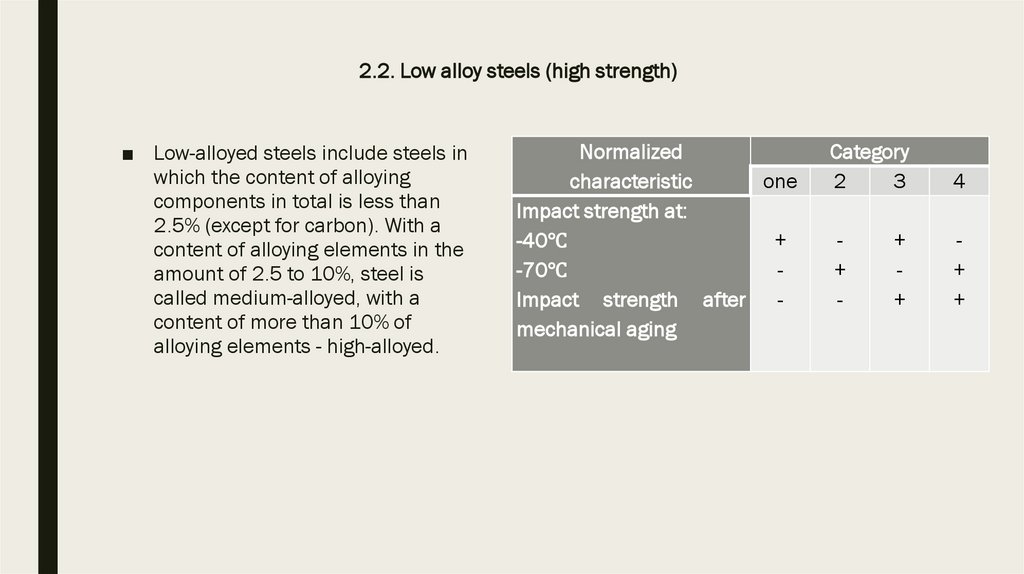
2.2. Low-alloy steels (increased strength)
CHAPTER III . EXAMPLES OF APPLICATION OF HIGH STRENGTH STEELS IN BUILDING
METAL STRUCTURES
3.1. The choice of steel for building steel structures
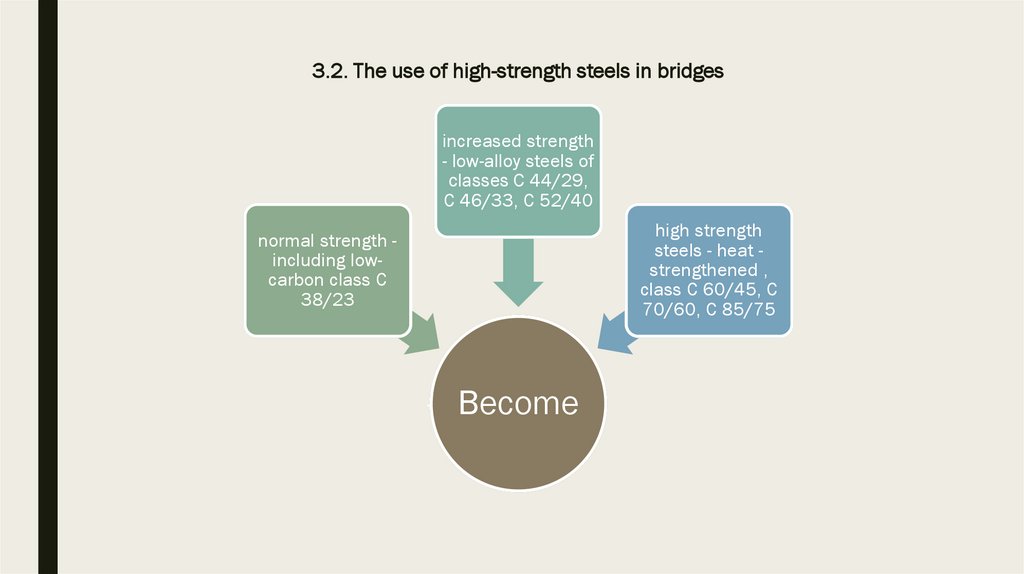
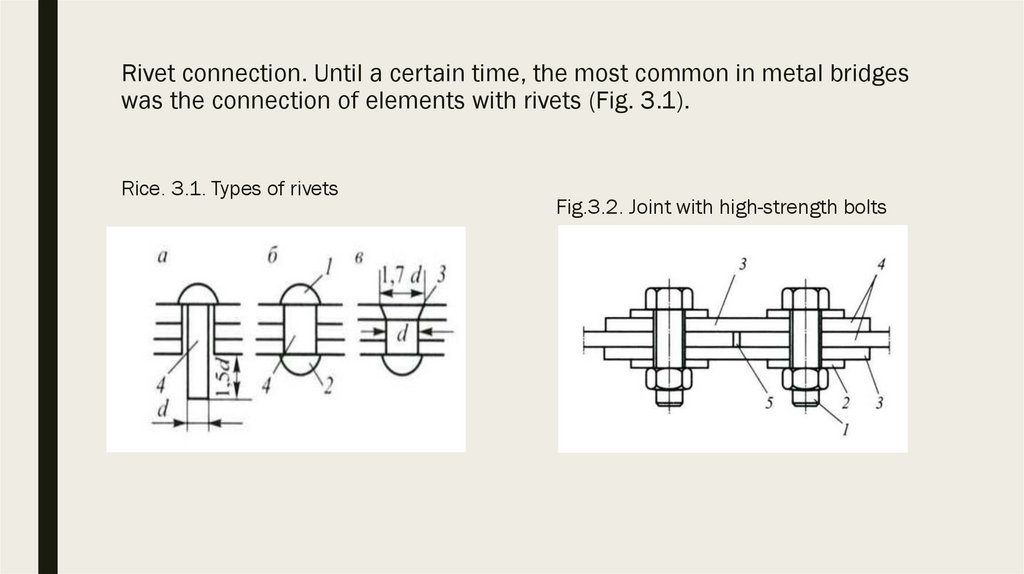
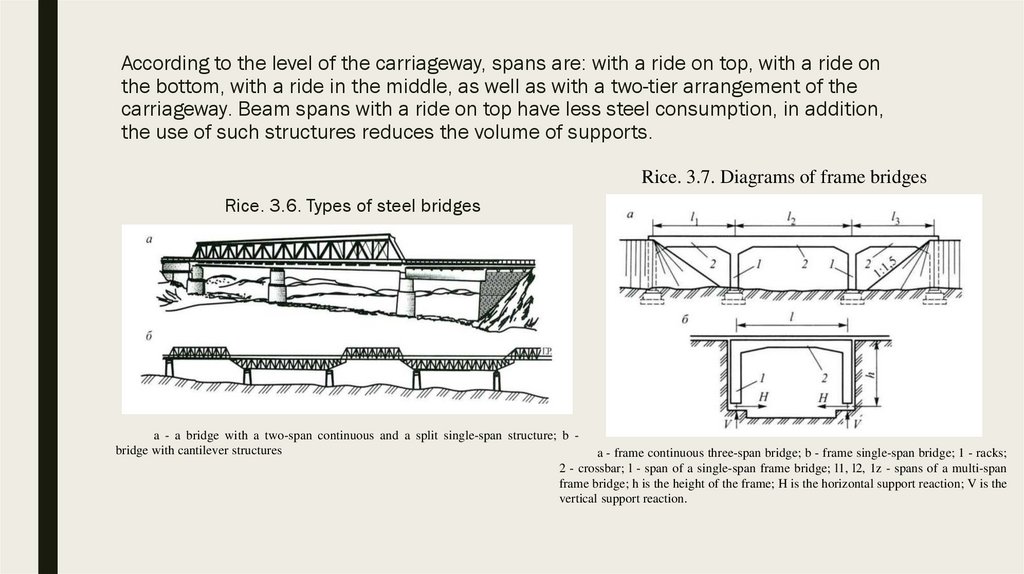
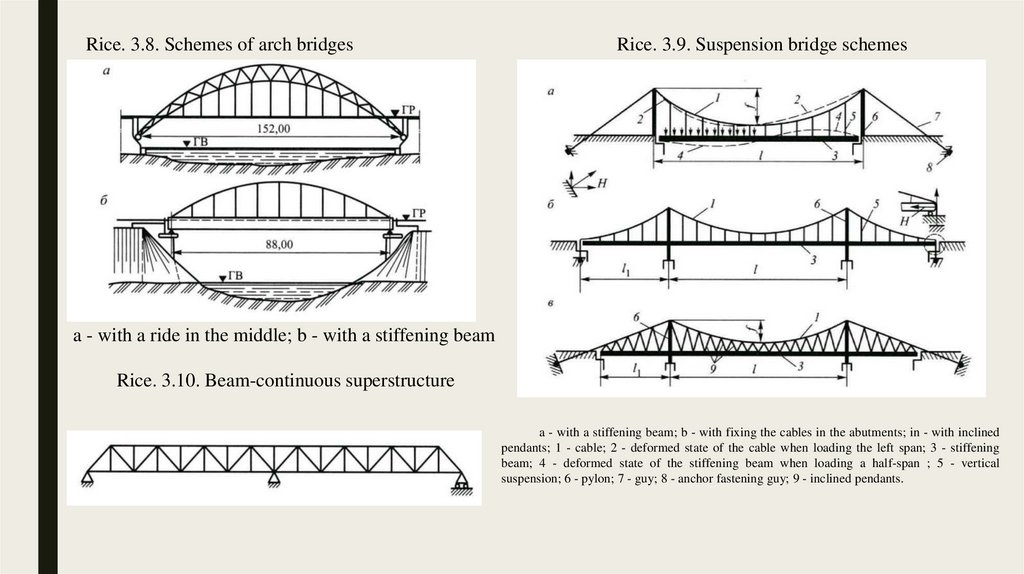
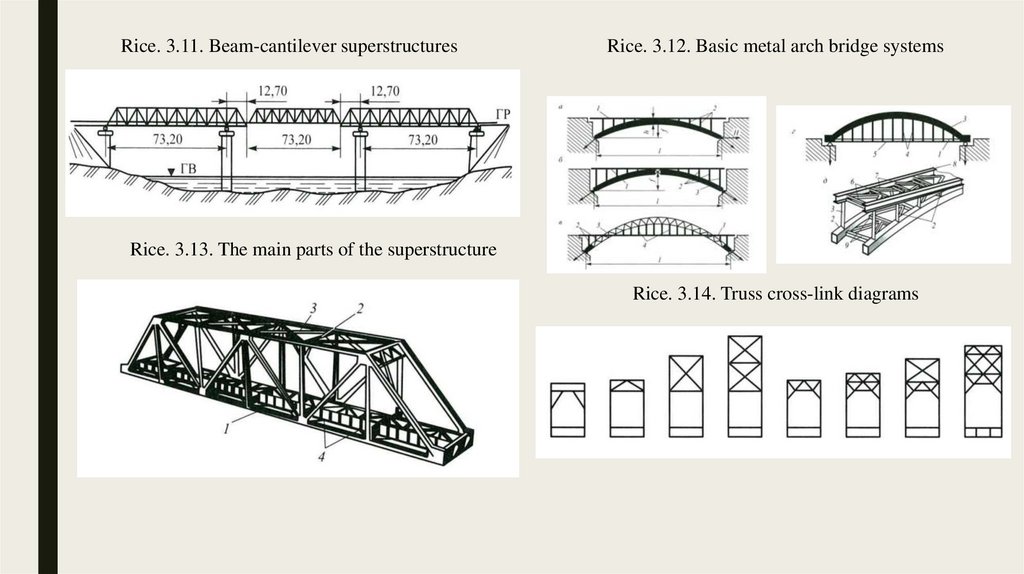
3.2. Application of high-strength steels in bridges
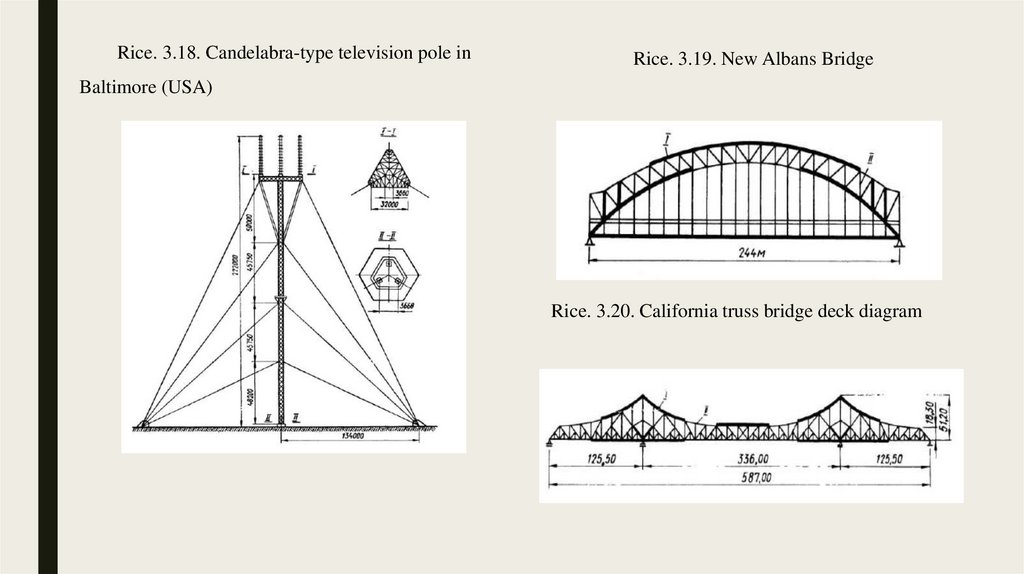
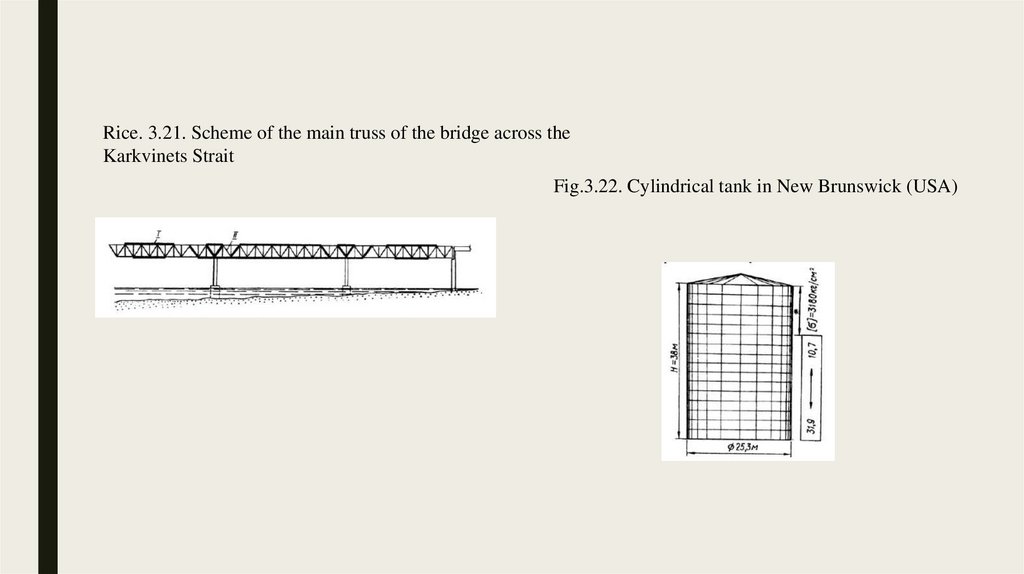
3.3. Examples of the use of high-strength steels abroad
CONCLUSION
LIST OF USED LITERATURE
3. INTRODUCTION Building steels of various grades are widely used in the metal structures of industrial buildings, bridges, towers
and masts, in the frames of high-rise civil and public buildings, in a number of special structures, aswell as in load-bearing welded metal frames of heavy equipment in the metallurgical, mining and other
industries. Due to the general trend towards greater use in construction of welded steel structures, the
consumption of structural steels is steadily increasing. Therefore, finding ways to radically reduce the cost of
steel in metal structures is very important and represents a major national economic task. Therefore, the
relevance of the topic of this work is not in doubt.
The purpose of this work is to consider the use of high-strength steel in construction.
To achieve the goal, the following tasks were set :
to give the concept of high-strength steels;
consider the classification of high-strength steels used in construction;
to study the use of high-strength steels in building metal structures.
The subject of this work is the theory and methodological foundations of the use of high-strength steels in
construction.
The object of research is high-strength steels in construction.
The theoretical and methodological basis was the theoretical provisions set forth in the works of domestic
and foreign authors on the issues under study, the Internet information network.
The structure of the work is determined by the subject, purpose and objectives of the study. The work
consists of an introduction, three chapters and a conclusion. The introduction reveals the relevance of the
topic, the purpose of the study, the theoretical and practical significance of the work.
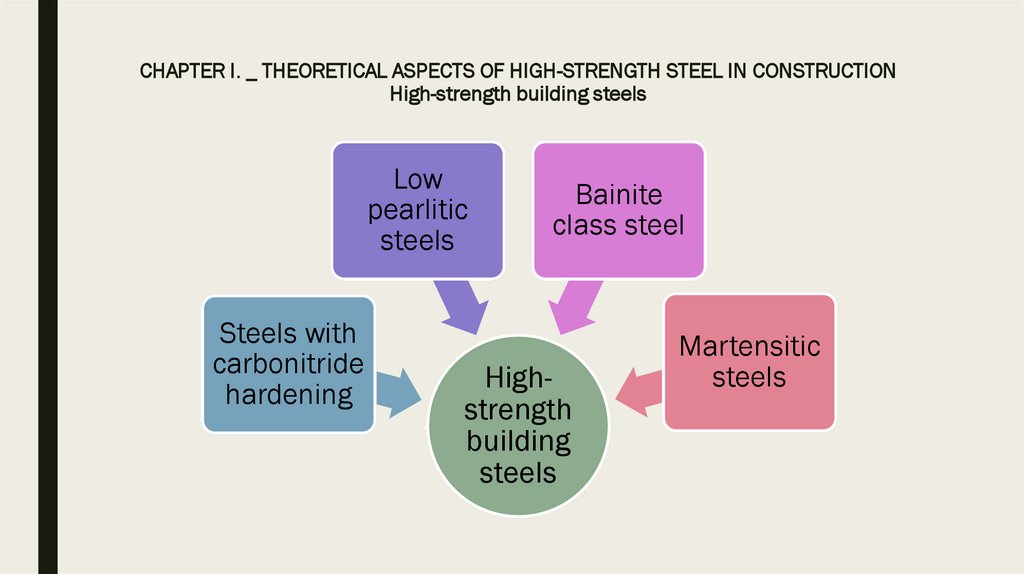
4. CHAPTER I. _ THEORETICAL ASPECTS OF HIGH-STRENGTH STEEL IN CONSTRUCTION High-strength building steels
Lowpearlitic
steels
Steels with
carbonitride
hardening
Bainite
class steel
Highstrength
building
steels
Martensitic
steels
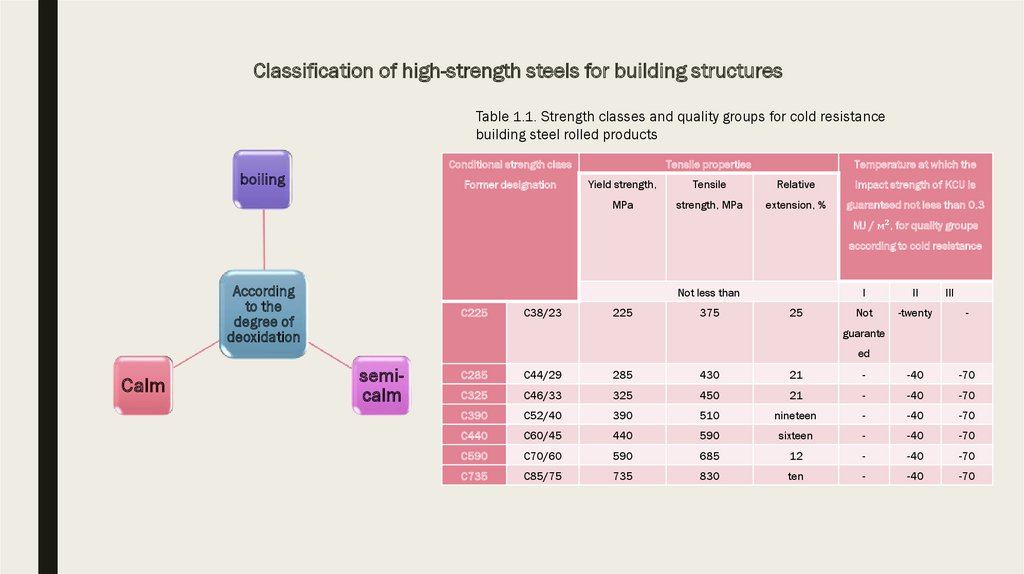
5. Classification of high-strength steels for building structures
Table 1.1. Strength classes and quality groups for cold resistancebuilding steel rolled products
Conditional strength class
boiling
Former designation
Tensile properties
Temperature at which the
Yield strength,
Tensile
Relative
impact strength of KCU is
MPa
strength, MPa
extension, %
guaranteed not less than 0.3
MJ / м