Similar presentations:
Achieving equivalence in the translation of texts of English-language feature films
1. Ministry of education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan Buketov Karaganda University Achieving equivalence in the
translation of texts ofEnglish-language feature films.
Diploma work
Speciality 5B020700 – «Translation studies»
Performed by: student of REI-43 group Shpak V.D.
Scientific advisor: senior lecturer, master of humanities
Klunnaya V.O.
2. Relevance
The relevance of the research isdue to the need for high-quality
translation of foreign audiovisual
works and the growing interest of
linguists and translators in film
translation and film production.
3. Aim
To identify translation techniquesthat contribute to the most
complete
achievement
of
equivalence when translating films
from English into Russian.
4. Object and subject
O The object of the research is the audiovisualtext of the movie «Gone in 60 seconds» and
its translation into Russian.
O The subject is translation strategies that are
used to achieve equivalence and adequacy of
the translation of the movie text.
5. Tasks
O To define the concepts of equivalence andadequacy and highlight the main features;
O To provide ways to translate the movie text
from one language to another;
O To consider ways to achieve equivalence
when translating the film «Gone in 60
seconds» from English into Russian;
O To analyze the translation decisions made.
6. Equivalence and Adequacy as a basic concepts of theory translation
O According to V.N. Komissarov, "an adequatetranslation is a translation during which the
pragmatic tasks of the translation act are
carried out at the highest possible level of
equivalence, without violating any norms of the
translation language.
O Equivalence means that the translation text
should completely imitate the original text and
cause the reader to have a similar
communicative reaction, as it was intended by
the author.
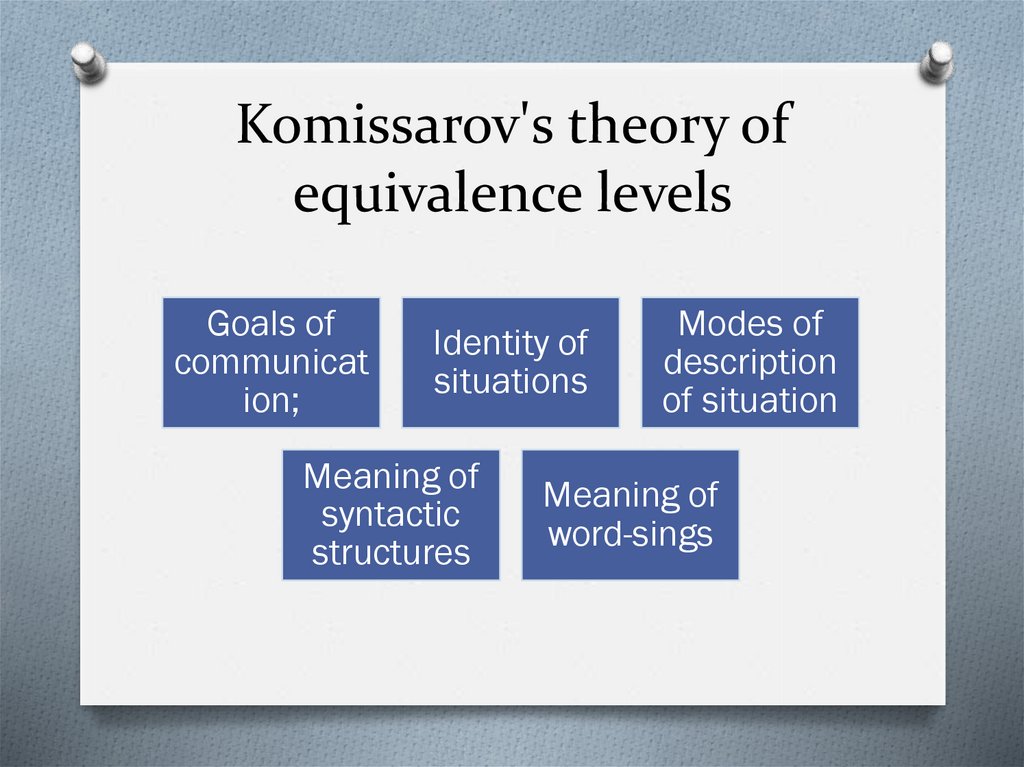
7. Komissarov's theory of equivalence levels
Goals ofcommunicat
ion;
Identity of
situations
Meaning of
syntactic
structures
Modes of
description
of situation
Meaning of
word-sings
8. Types of movie translation
•Dubbing•Subtitling
•Voice over
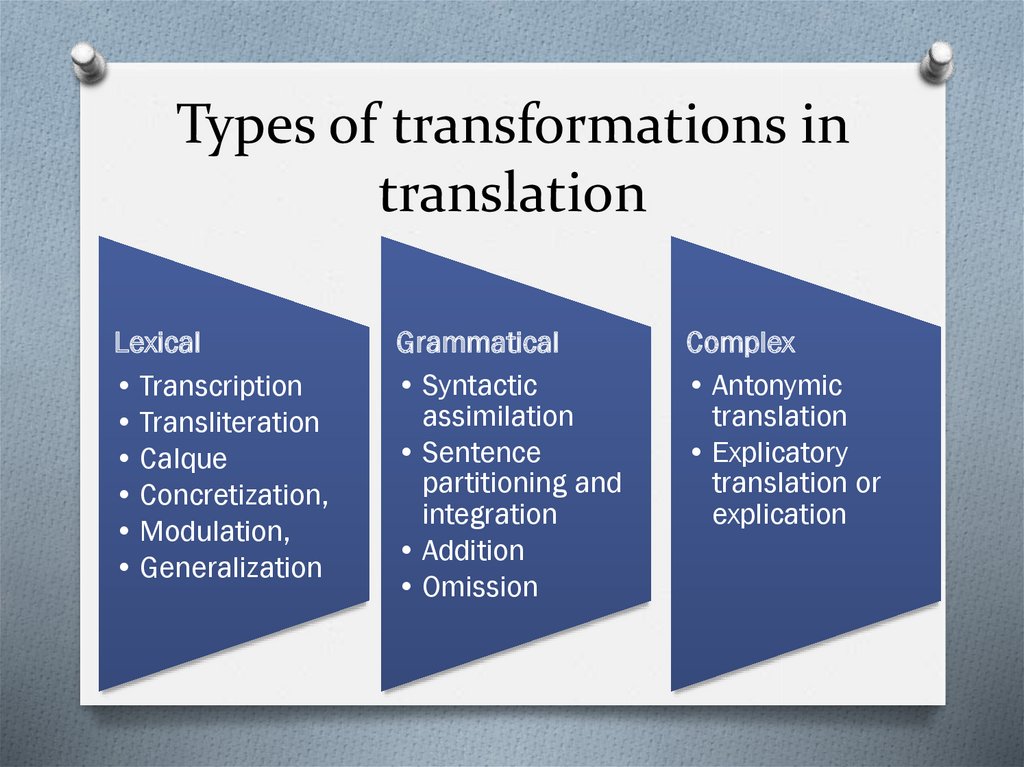
9. Types of transformations in translation
Lexical• Transcription
• Transliteration
• Calque
• Concretization,
• Modulation,
• Generalization
Grammatical
• Syntactic
assimilation
• Sentence
partitioning and
integration
• Addition
• Omission
Complex
• Antonymic
translation
• Explicatory
translation or
explication
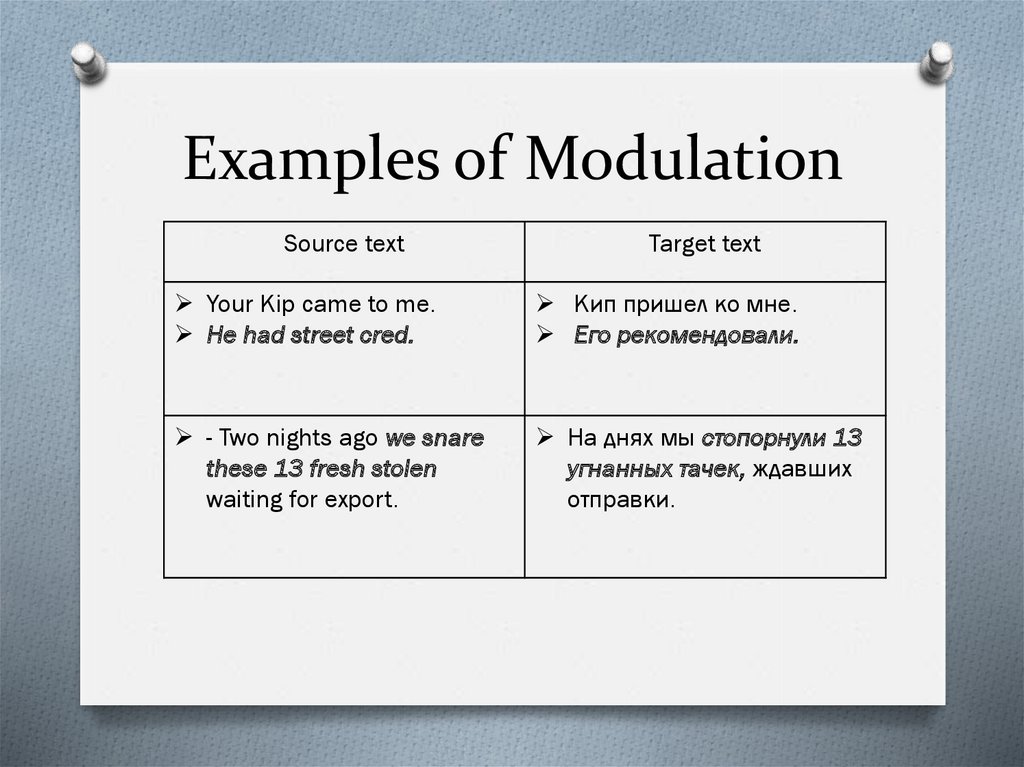
10. Examples of Modulation
Source textTarget text
Your Kip came to me.
He had street cred.
Кип пришел ко мне.
Его рекомендовали.
- Two nights ago we snare
these 13 fresh stolen
waiting for export.
На днях мы стопорнули 13
угнанных тачек, ждавших
отправки.
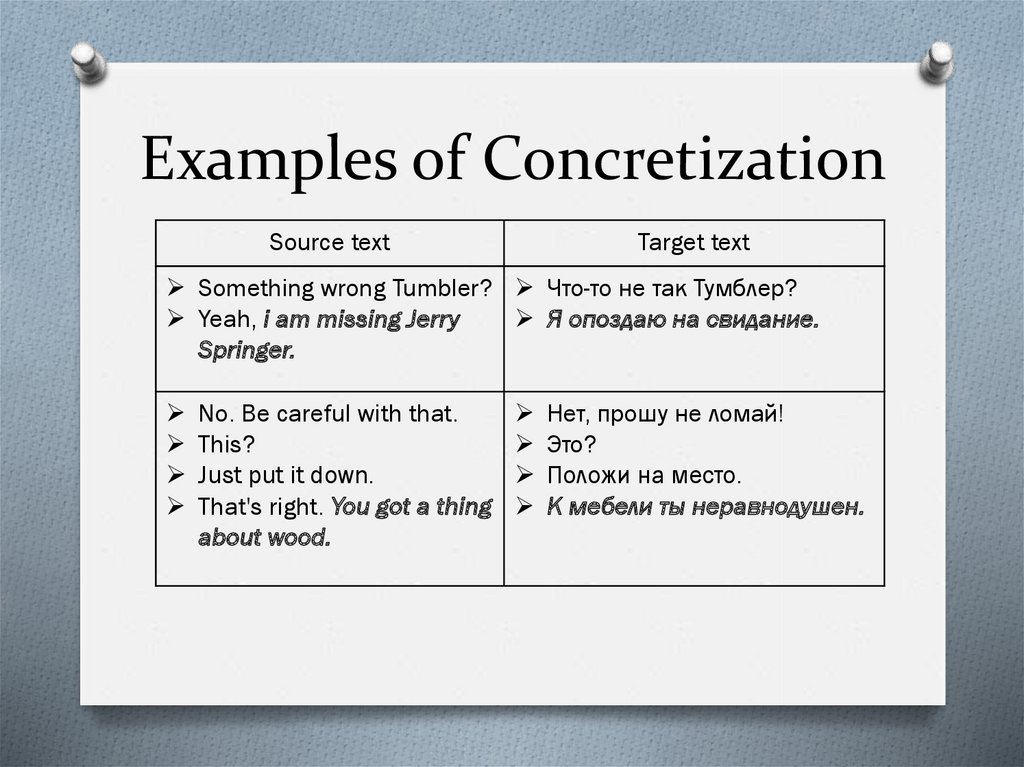
11. Examples of Concretization
Source textTarget text
Something wrong Tumbler? Что-то не так Тумблер?
Yeah, i am missing Jerry
Я опоздаю на свидание.
Springer.
No. Be careful with that.
This?
Just put it down.
That's right. You got a thing
about wood.
Нет, прошу не ломай!
Это?
Положи на место.
К мебели ты неравнодушен.
12. Examples of Generalization
Source textTarget text
Suspect has increased
speed to 120.
Maintain visual, Air One.
140 miles an hour!
Do not lose him!
This is an A-Star, is, not an
Apache.
Подозреваемый разогнался
до 120.
Ведите наблюдение!
140 миль в час.
Не упустите его!
У меня гражданский
вертолет, а не военный.
He's pulling something out
of his pocket.It's a camera.
Looks like he's just doing
some homework.
Он что-то достал из
кармана.
Фотоаппарат. Похоже он
еще на стадии подготовки.
13. Conclusion
In the course of the study, we examined the main typesand features of film translation, considered the concept of
equivalence proposed by V.N. Komissarov and its levels,
and also identified strategies used to achieve equivalent
translation.
First, the translator tries to convey all the content of the
original text, including its syntactic structure. However, in
the process of translation, he chooses the best option,
preserving text invariants as much as possible in this
situation.
This process represents a series of transformations
during which the translator can abandon equivalence at a
lower level in favor of equivalence at a higher level.









 english
english








