Similar presentations:
Participles
1. Participles
Types of participlesFunctions
Constructions
2. Types
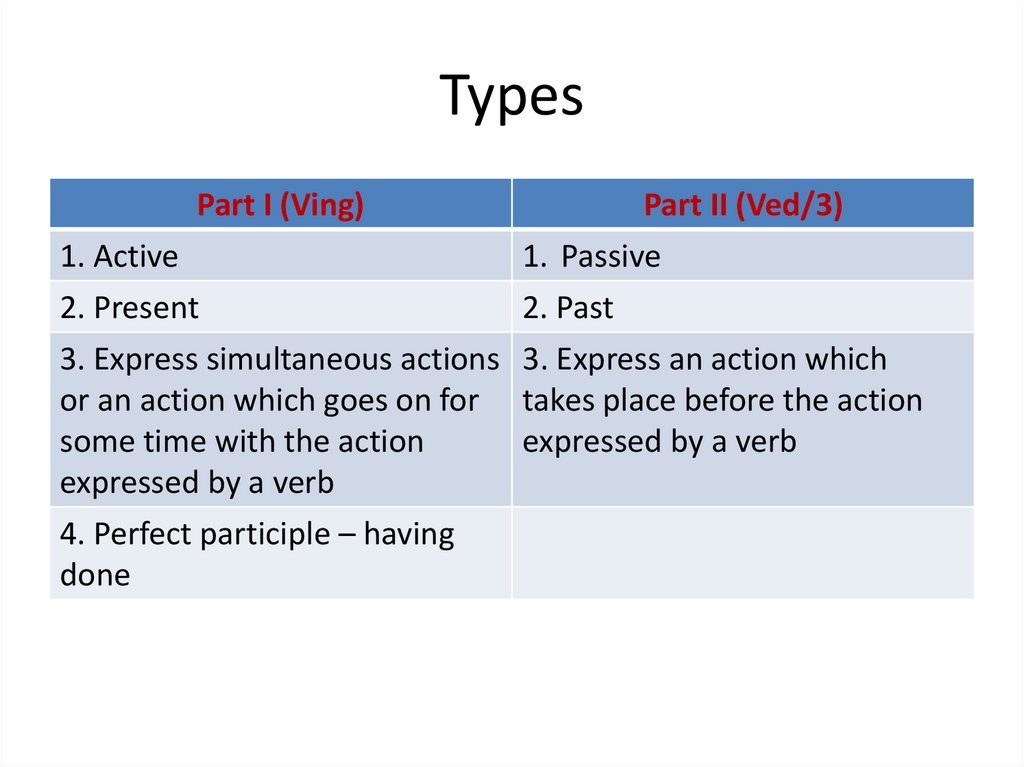
Part I (Ving)Part II (Ved/3)
1. Active
1. Passive
2. Present
2. Past
3. Express simultaneous actions 3. Express an action which
or an action which goes on for takes place before the action
some time with the action
expressed by a verb
expressed by a verb
4. Perfect participle – having
done
3. Functions
• An attribute. He came up to the cryingchildren.
• An adverbial modifier:
Of time (with “when” or “while”). When
listening to her I understood that she was
upset.
Of cause. Not knowing his new telephone I
couldn’t get in touch with him.
4. An adverbial modifier
Of manner and attending circumstances. He ran upto her, smiling happily
Of comparison (with “as if”, “as though”). He peering
at me, as if not recognizing.
Of concession (with “though”). He couldn’t catch up
with them though working very hard.
Of condition. Driving at this speed, we will be there in
time.
• A parenthesis. Frankly speaking, taking into
consideration.
5. Uses
• Instead of relative pronouns and full verb. The womanwaving at me is my aunt.
• To express reason. Feeling shy, she didn’t talk to him
• To express time. (After) taking degree, he applied for a
job
• Instead of Past Simple for description actions happening
immediately one after the other. Hearing the news, she
fainted.
• To avoid repeating Past Continuous in the same sentence.
He was walking down the street whistling a tune.
6. Constructions
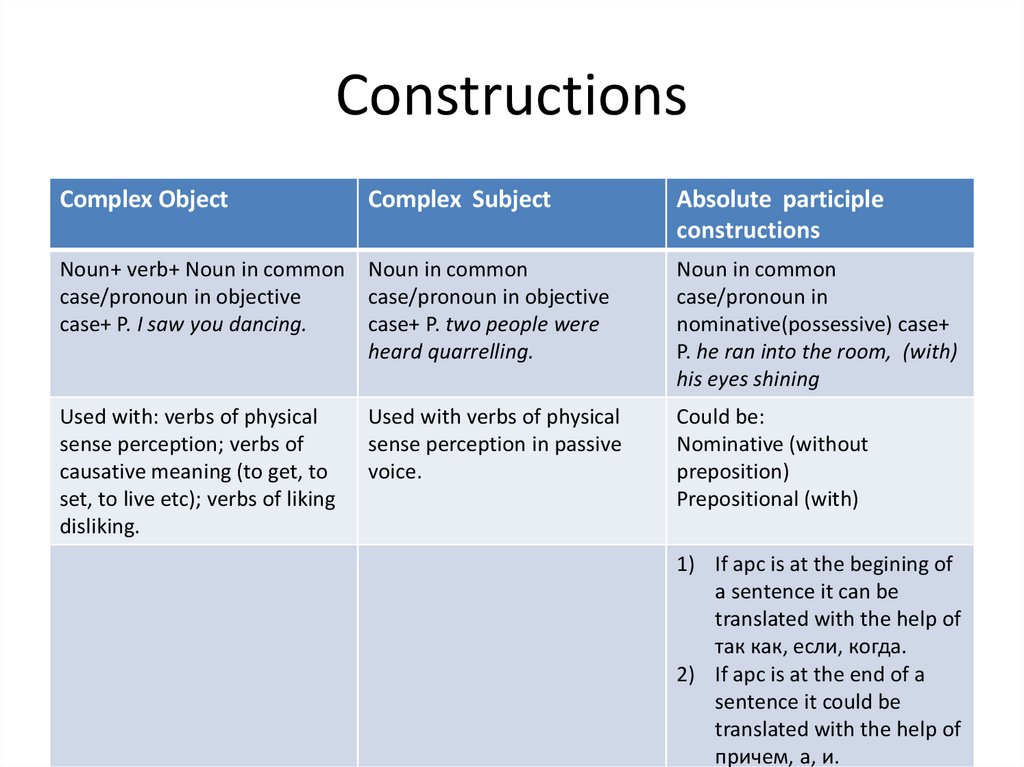
Complex ObjectComplex Subject
Absolute participle
constructions
Noun+ verb+ Noun in common
case/pronoun in objective
case+ P. I saw you dancing.
Noun in common
case/pronoun in objective
case+ P. two people were
heard quarrelling.
Noun in common
case/pronoun in
nominative(possessive) case+
P. he ran into the room, (with)
his eyes shining
Used with: verbs of physical
sense perception; verbs of
causative meaning (to get, to
set, to live etc); verbs of liking
disliking.
Used with verbs of physical
sense perception in passive
voice.
Could be:
Nominative (without
preposition)
Prepositional (with)
1) If apc is at the begining of
a sentence it can be
translated with the help of
так как, если, когда.
2) If apc is at the end of a
sentence it could be
translated with the help of
причем, а, и.



 english
english








