Similar presentations:
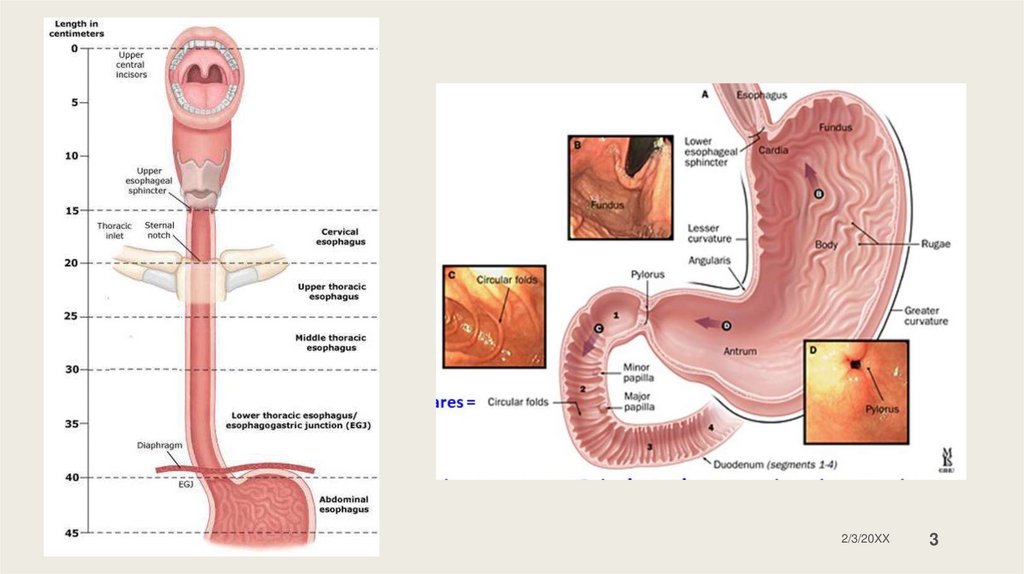
Esophagus stomach duodenum
1.
Esophagusstomach
duodenum
GI system
2.
TopicsEsophageal cancer
Esophageal perforation
Achalasia
Esophageal diverticula
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Peptic ulcer disease
Atrophic gastritis
Gastrinome (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
Gastric cancer
Boerhaave syndrome
2/3/20XX
2
3.
Sample Footer Text2/3/20XX
3
4.
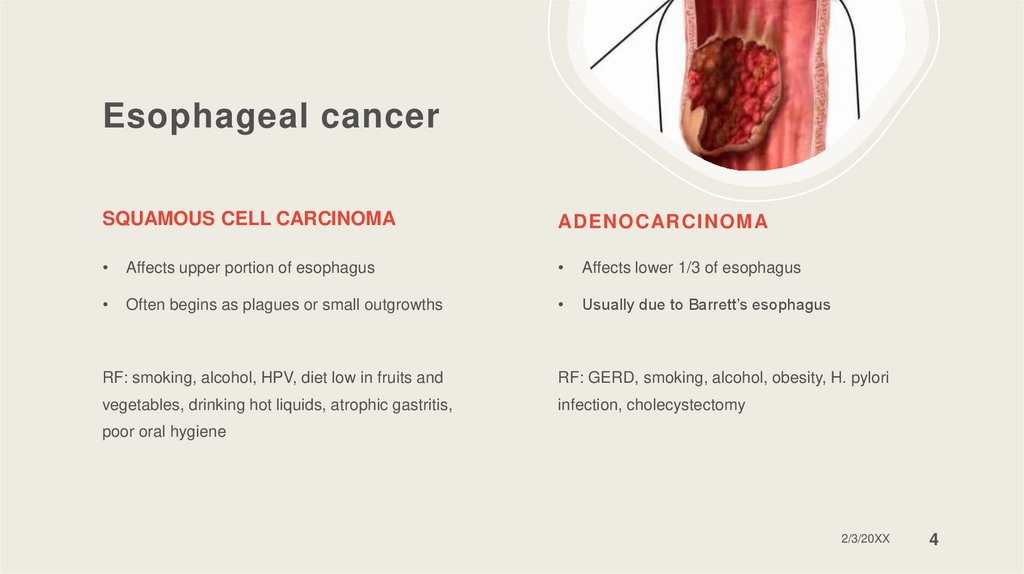
Esophageal cancerSQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
ADENOCARCINOMA
Affects upper portion of esophagus
Affects lower 1/3 of esophagus
Often begins as plagues or small outgrowths
Usually due to Barrett’s esophagus
RF: smoking, alcohol, HPV, diet low in fruits and
RF: GERD, smoking, alcohol, obesity, H. pylori
vegetables, drinking hot liquids, atrophic gastritis,
infection, cholecystectomy
poor oral hygiene
2/3/20XX
4
5.
Esophageal cancerSymptoms & signs:
o Progressive dysphagia
Diagnosis: barium swallow, endoscopic with
biopsy, endoscopic US, CT scan, PET scan
o Pain with swallowing
o Regurgitation
o Aspiration
o Reflux
o Hematemesis
o Melena
Treatment:
Endoscopic resection
Esophagectomy with lymphadenectomy
Resection with chemo
Palliative and esophageal stent
o Anemia
2/3/20XX
5
6.
Esophageal cancerSample Footer Text
2/3/20XX
6
7.
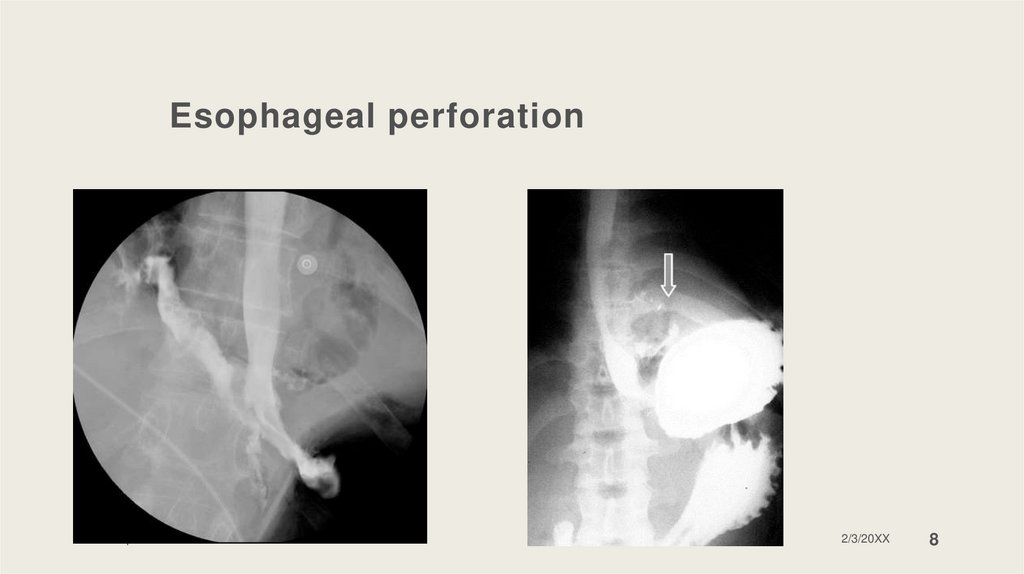
Esophageal perforationCauses: endoscopic treatment, ingested foreign bodies,
Boerhaave’s syndrome, trauma, cancer.
Treatment:
Non-operative:
Symptoms & signs:
Conservative management, Stenting, Endo VAC therapy,
Endo Clip
Pain, dyspnea, fever, nausea or vomiting, dysphagia;
Boerhaave’s triad: vomiting, thoracic pain, subcutaneous
emphysema
Primary closure: pleural flap, pericardial fat pad,
omentum onlay graft, intercostal muscle flap
Diagnosis: X-ray, CT scan, barium swallow
Operative:
T-tube drainage, esophagectomy, exclusion and
diversion
Hybrid procedure: endoscopic and thorascopia.
2/3/20XX
7
8.
Esophageal perforationSample Footer Text
2/3/20XX
8
9.
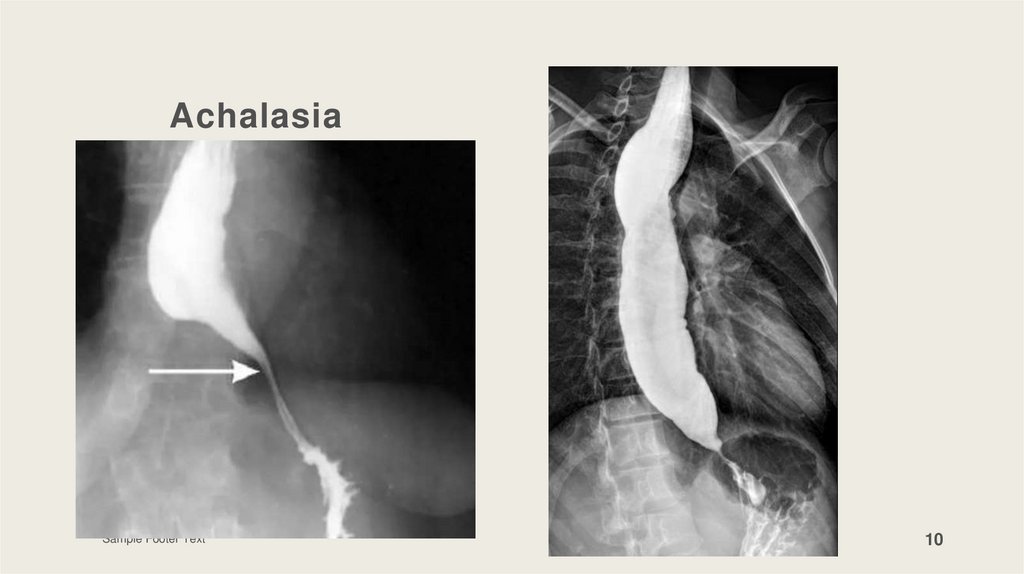
AchalasiaEtiology: denervation of esophageal muscle ->
increase pressure of LES
Symptoms: dysphagia, night regurgitation of food,
cough, pulmonary aspiration, weight loss
Diagnosis: esophageal manometry, barium swallow
Treatment:
• Conservative in the elderly (e.g.
nifedipine/or endoscopic botulinum
toxin injection into the sphincter)
• Pneumatic dilatation of lower
esophageal sphincter or surgical
myotomy
• Note: Prokinetic drugs have no place
in treatment.
2/3/20XX
9
10.
AchalasiaSample Footer Text
10
11.
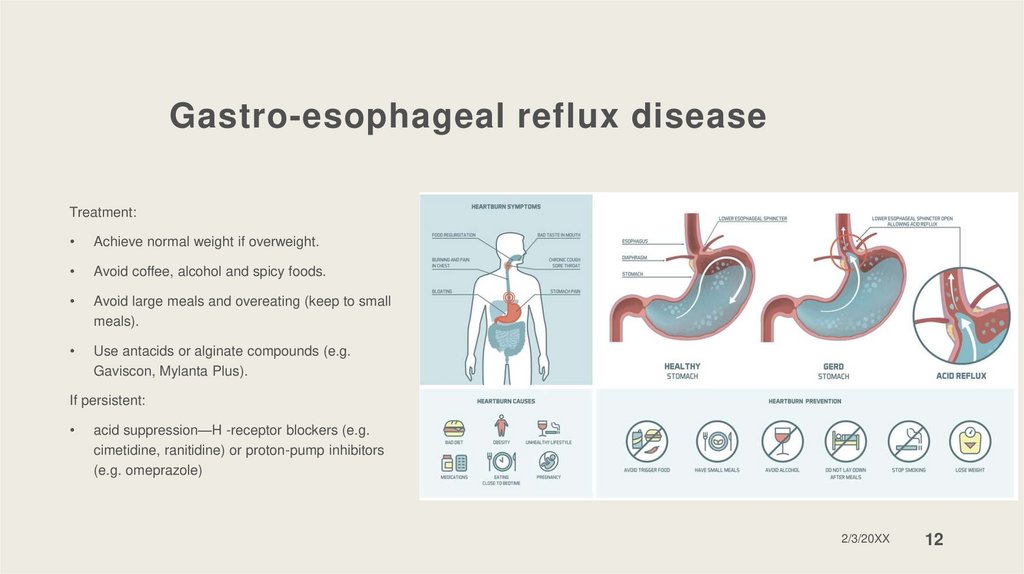
Gastro-esophageal reflux diseaseStomach acid flows back into the esophagus
Symptoms:
o
Complications: esophagitis, esophageal stenosis, Barrett’s
esophagus, adenocarcinoma, laryngitis and asthma.
Pyrosis, regurgitation, dysphagia, chronic
cough, hoarseness
o
Symptoms worsen when lying down
Risk factors:
Diagnosis:
o
o
24 HR pH monitoring in the lower esophagus
o
X-Ray with barium contrast;
o
Endoscopy with biopsy
o
Obesity, fat-rich diet, caffeine, alcohol, smoking,
antihistamines, CCB, antidepressants, benzodiazepines and
glucocorticoids
Hiatal hernia, scleroderma, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
2/3/20XX
11
12.
Gastro-esophageal reflux diseaseTreatment:
Achieve normal weight if overweight.
Avoid coffee, alcohol and spicy foods.
Avoid large meals and overeating (keep to small
meals).
Use antacids or alginate compounds (e.g.
Gaviscon, Mylanta Plus).
If persistent:
acid suppression—H -receptor blockers (e.g.
cimetidine, ranitidine) or proton-pump inhibitors
(e.g. omeprazole)
2/3/20XX
12
13.
Peptic ulcerSymptoms: epigastric pain, bloating, belching, vomiting
Gastric ulcer – pain
Having one or more sores in the stomach or in
while eating
Duodenum ulcer – pain
while eating
the duodenum
Diagnosis: EGD, biopsy
Causes: H. Pylori infection, NSAIDs, Zollinger-
Ellison syndrome
Complications: bleeding, perforation,
Treatment:
depends on underlying cause
Diet
Severe cases – surgery
obstruction of pyloric sphincter
2/3/20XX
13
14.
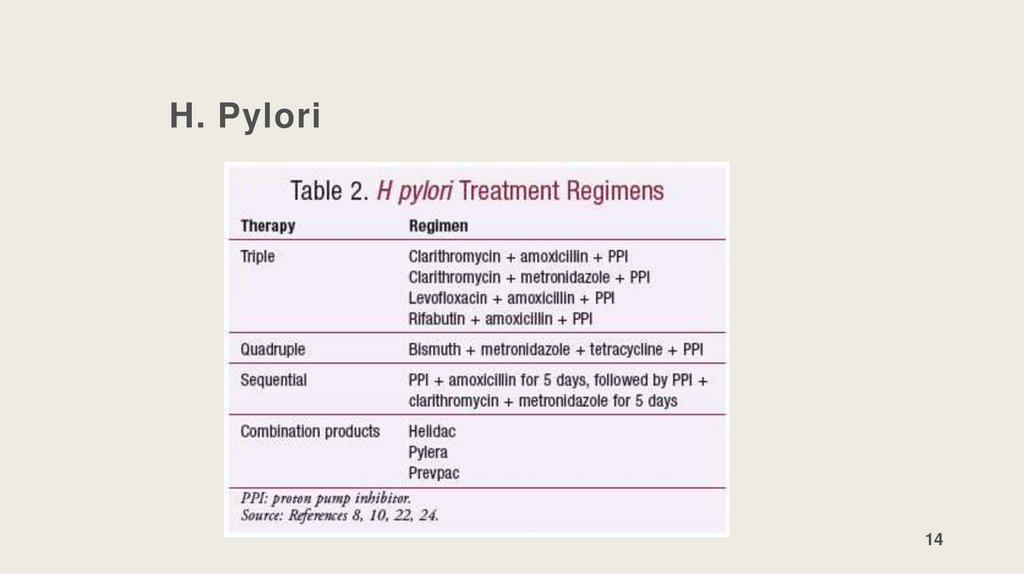
H. Pylori14
15.
Atrophic gastritisLoss of the gastric glandular cells
Symptoms: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting,
anorexia or significant weight loss
Causes: H. Pylori infection, autoimmune gastritis
Diagnosis: endoscopy + biopsy
Complications:
H. Pylori –gastric ulcers, gastric adenocarcinoma
Treatment: to treat H. Pylori or correct
complication
Autoimmune gastritis: pernicious anemia, gastric
polyps, gastric adenocarcinoma
2/3/20XX
15
16.
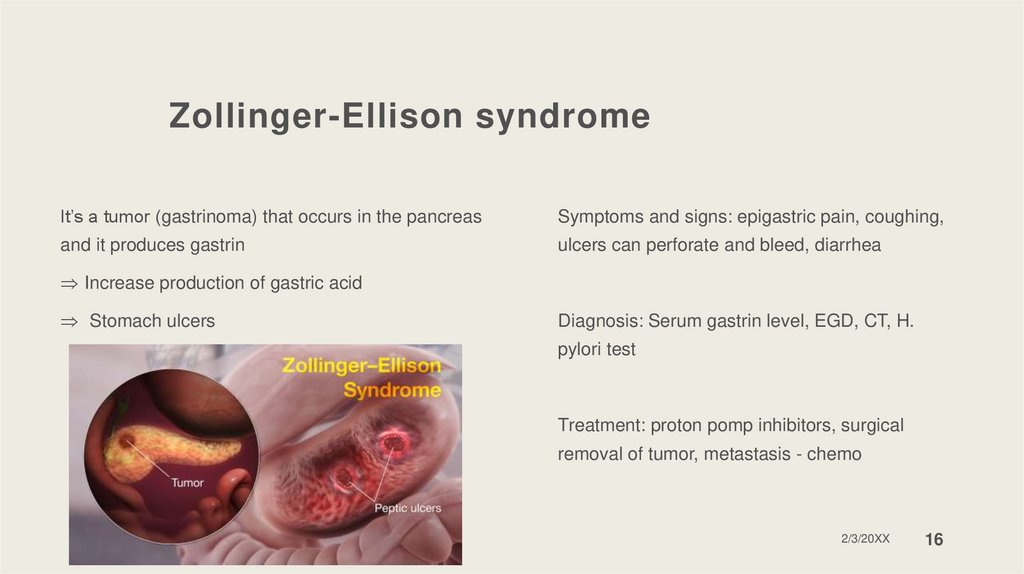
Zollinger-Ellison syndromeIt’s a tumor (gastrinoma) that occurs in the pancreas
Symptoms and signs: epigastric pain, coughing,
and it produces gastrin
ulcers can perforate and bleed, diarrhea
Increase production of gastric acid
Stomach ulcers
Diagnosis: Serum gastrin level, EGD, CT, H.
pylori test
Treatment: proton pomp inhibitors, surgical
removal of tumor, metastasis - chemo
Sample Footer Text
2/3/20XX
16
17.
Esophageal diverticulaOutpouching of mucosa through the muscular layer
Diagnosis: barium swallow, esophageal
of the esophagus
manometry, Ambulatory pH monitoring,
endoscopy
Symptoms: dysphagia, regurgitation, aspiration,
pneumonia halitosis, gurling sound in the neck
Treatment: excision of the diverticulum and
myotomy
2/3/20XX
17
18.
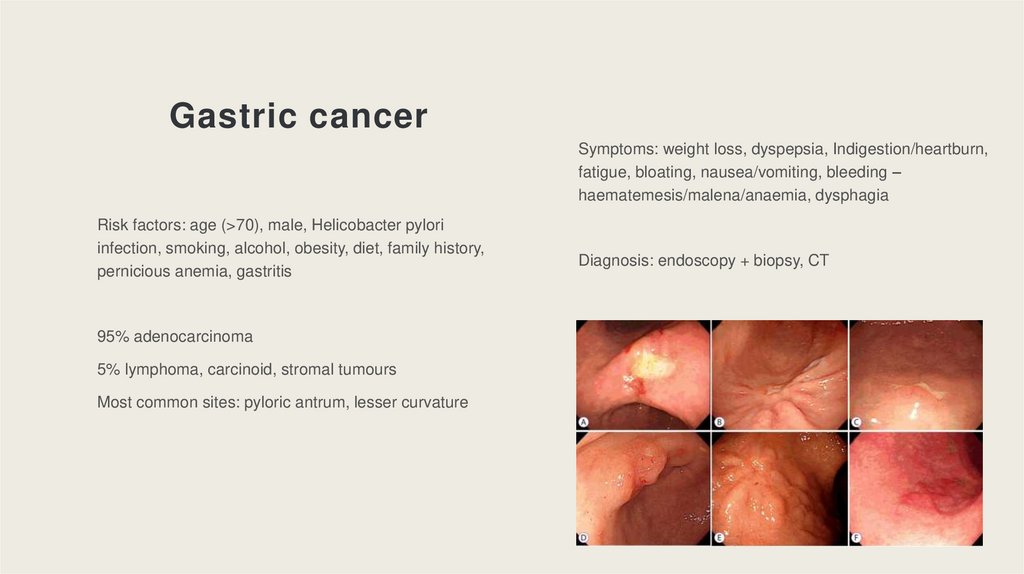
Gastric cancerSymptoms: weight loss, dyspepsia, Indigestion/heartburn,
fatigue, bloating, nausea/vomiting, bleeding –
haematemesis/malena/anaemia, dysphagia
Risk factors: age (>70), male, Helicobacter pylori
infection, smoking, alcohol, obesity, diet, family history,
pernicious anemia, gastritis
Diagnosis: endoscopy + biopsy, CT
95% adenocarcinoma
5% lymphoma, carcinoid, stromal tumours
Most common sites: pyloric antrum, lesser curvature
2/3/20XX
18
19.
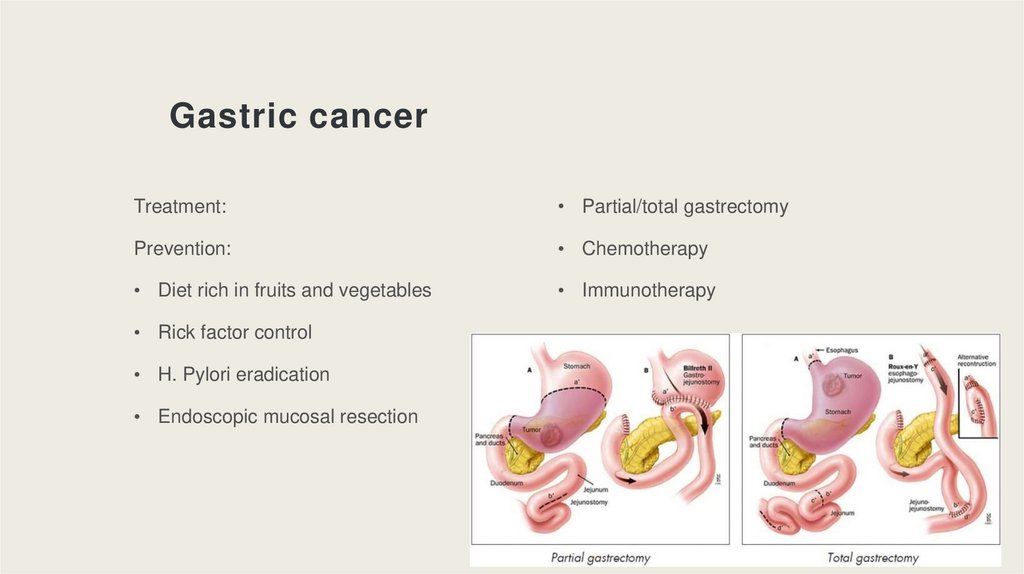
Gastric cancerTreatment:
• Partial/total gastrectomy
Prevention:
• Chemotherapy
• Diet rich in fruits and vegetables
• Immunotherapy
• Rick factor control
• H. Pylori eradication
• Endoscopic mucosal resection
2/3/20XX
19
20.
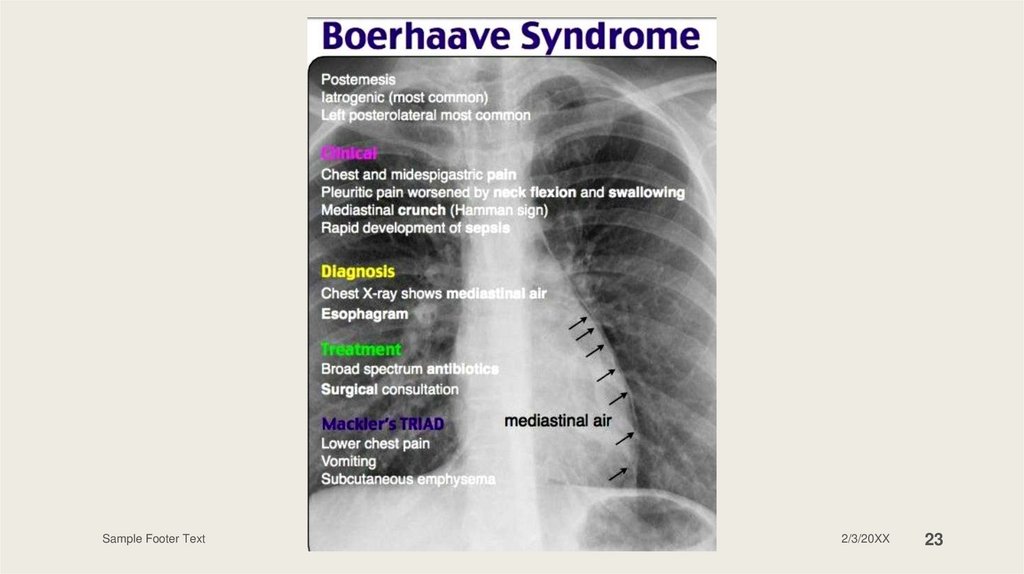
Boerhaave syndromeIt’s due to a transmural tear in the esophageal wall
Risk factors: alcohol, diet
Causes by rapid increases in intra-abdominal pressure
Symptoms and signs:
Complications: sepsis, pneumomediastinum, mediastinitis,
o
emesis
mediastinal abscess, subcutaneous emphysema,
o
odynophagia
empyema
o
fever
o
dyspnea
o
Chest and epigastric pain
o
crepitus
o
Hamman sign
o
septic shock
Most common places: left posterior lateral aspect of the
distal esophagus and subdiaphragmatic area in the
thoracic esophagus
2/3/20XX
20
21.
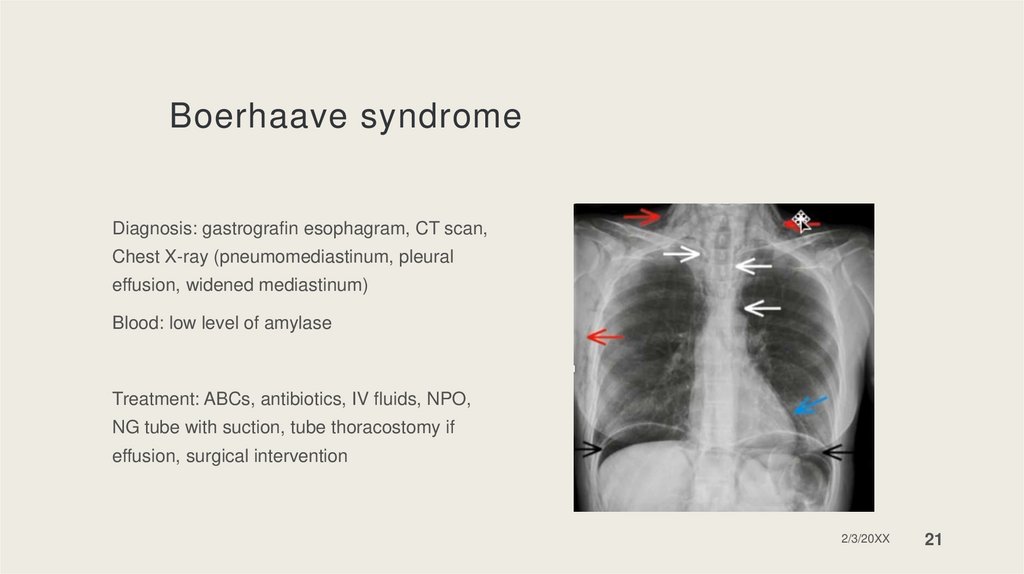
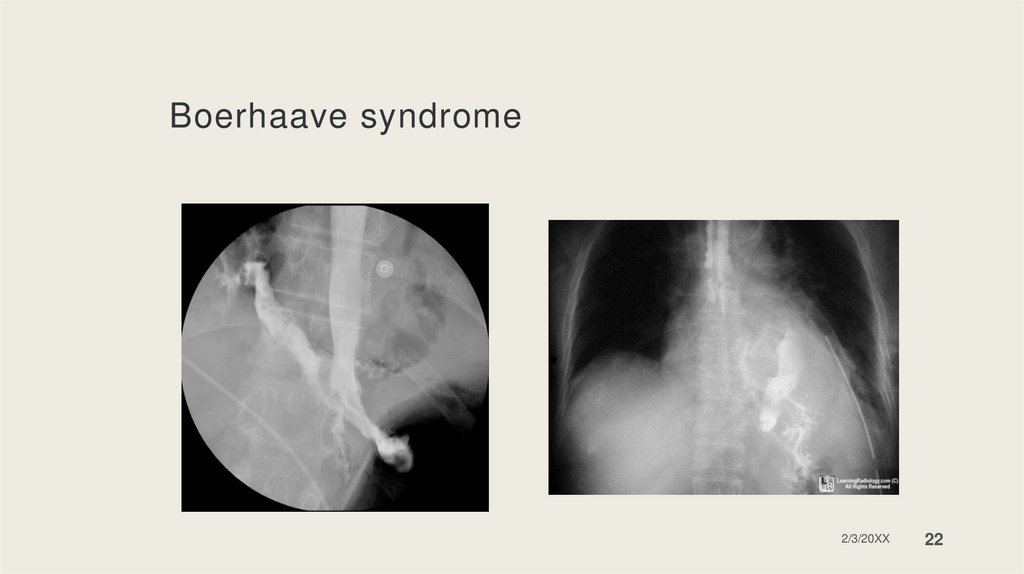
Boerhaave syndromeDiagnosis: gastrografin esophagram, CT scan,
Chest X-ray (pneumomediastinum, pleural
effusion, widened mediastinum)
Blood: low level of amylase
Treatment: ABCs, antibiotics, IV fluids, NPO,
NG tube with suction, tube thoracostomy if
effusion, surgical intervention
2/3/20XX
21
22.
Boerhaave syndrome2/3/20XX
22
23.
Sample Footer Text2/3/20XX
23









 medicine
medicine