Similar presentations:
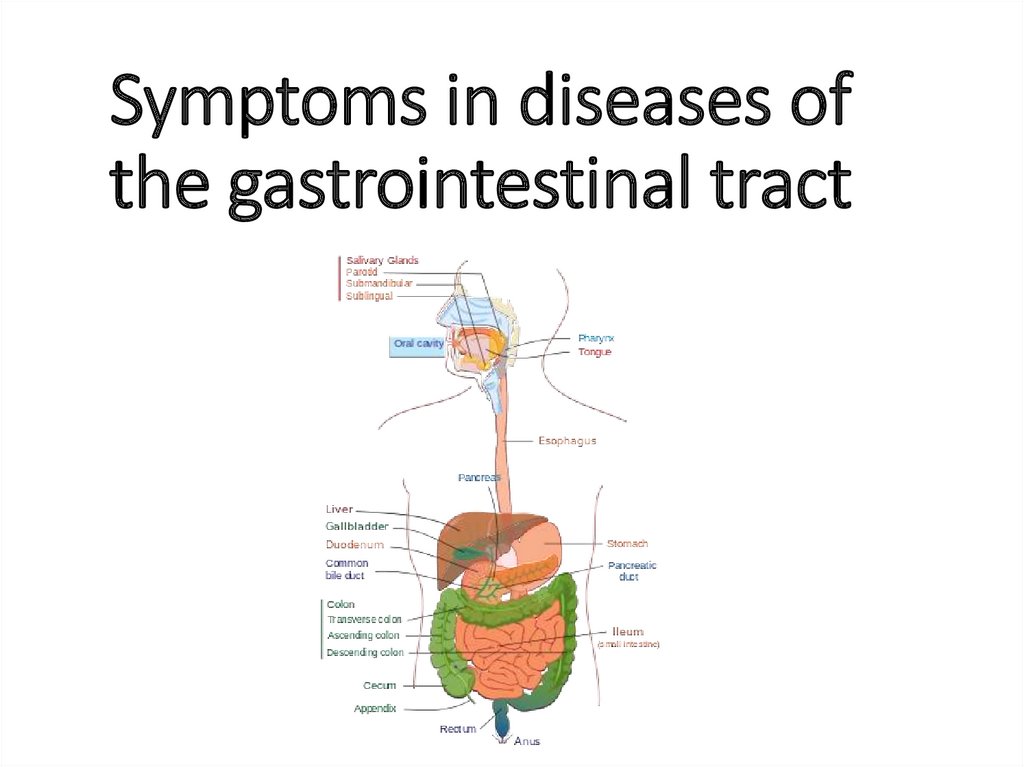
Symptoms in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
1. Symptoms in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
2.
The main manifestations ofgastrointestinal diseases:
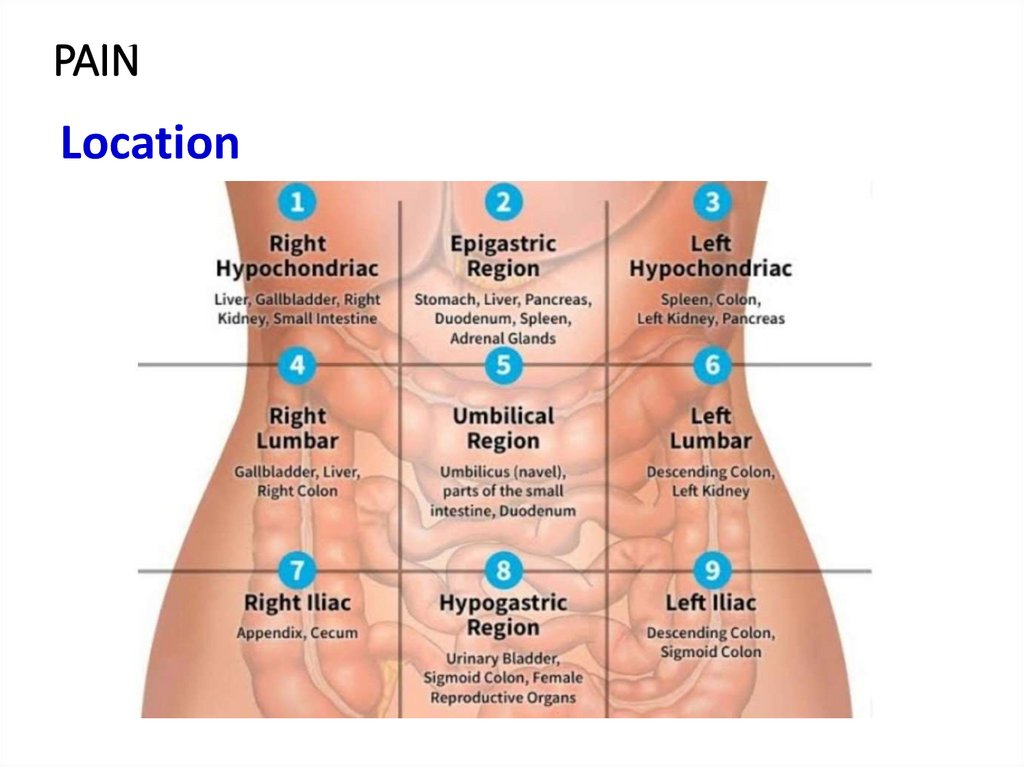
PAIN
Dysphagia
Dyspepsia
Diarrhea
3. PAIN
Location4.
5.
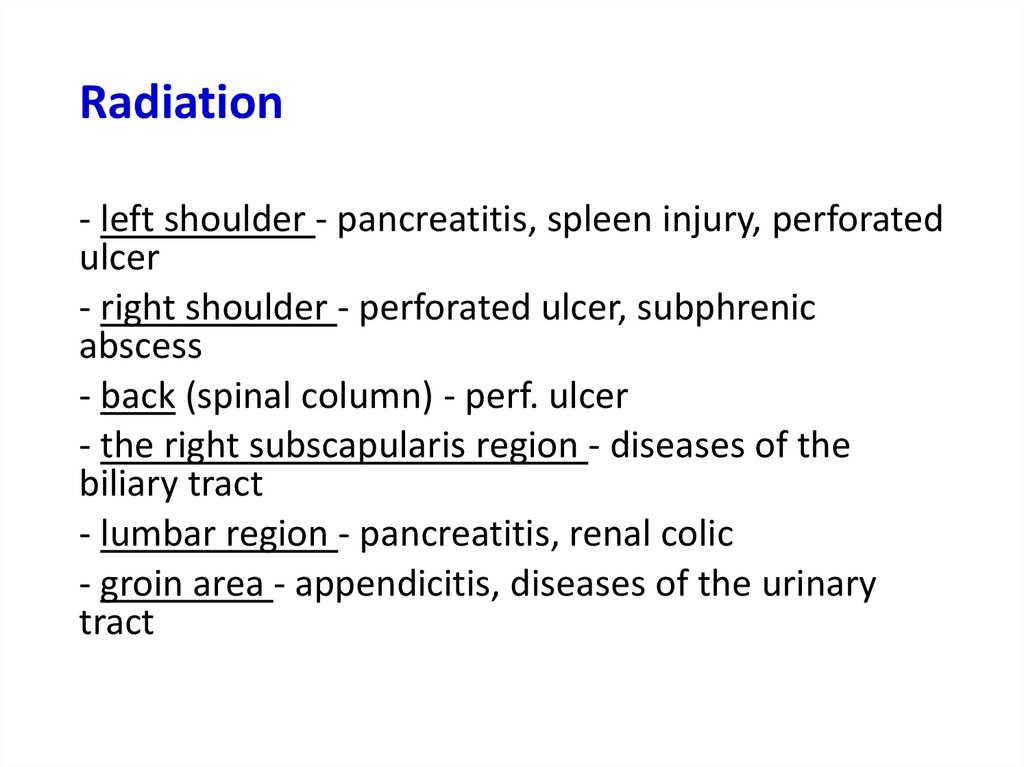
Radiation- left shoulder - pancreatitis, spleen injury, perforated
ulcer
- right shoulder - perforated ulcer, subphrenic
abscess
- back (spinal column) - perf. ulcer
- the right subscapularis region - diseases of the
biliary tract
- lumbar region - pancreatitis, renal colic
- groin area - appendicitis, diseases of the urinary
tract
6.
Onset of painAcute (sudden) within seconds or minutes :
- perforated ulcer,
- rupture of the esophagus,
- impaired ectopic pregnancy,
- ureteral stone,
- rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm
7.
Gradual within minutes, hours, days:- acute cholecystitis,
- pancreatitis,
- appendicitis,
- pyelonephritis,
- exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease,
- acute gastritis,
- intra-abdominal abscesses,
- intestinal obstruction,
- strangulated hernia
8.
Slowly developing pain (within days,weeks) :
-neoplasms of internal organs,
- chronic inflammatory bowel diseases
(Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn`s Disease),
- irritable bowel syndrome
9.
Pain intensityThe pattern of the pain (cramping, dull ...)
Duration
Daily rhythm
Provocation and strengthening, incl. connection
with food intake
Relief and reduction of pain
Concomitant symptoms
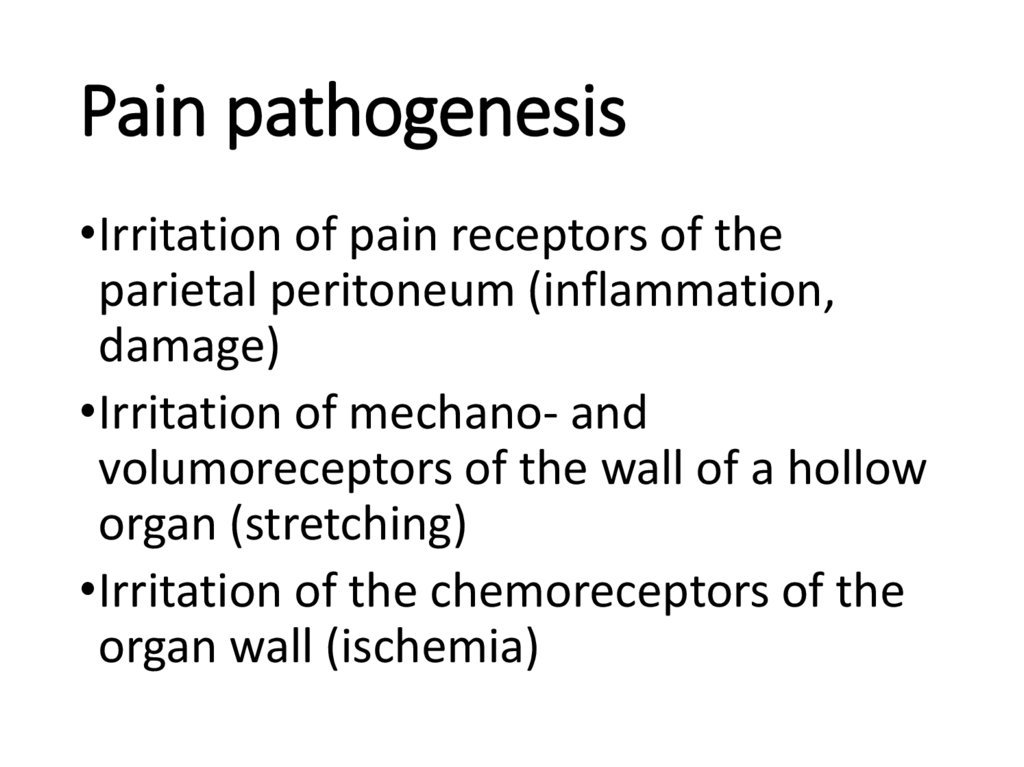
10. Pain pathogenesis
•Irritation of pain receptors of theparietal peritoneum (inflammation,
damage)
•Irritation of mechano- and
volumoreceptors of the wall of a hollow
organ (stretching)
•Irritation of the chemoreceptors of the
organ wall (ischemia)
11. 2 main types of the pain
•Parietal -is a well-localized, acute,intense, positive rebound
symptom. Requires surgical
treatment
•Visceral pain -broad, dull, negative
rebound tenderness symptom.
Does not require urgent surgical
treatment
12. Gastric dyspepsia
(nausea, vomiting, feeling of overflow,belching sour)
- by the type of acidism
- by the type of delayed evacuation
Regurgitation symptoms:
- gastric contents - heartburn,
- bile contents -bitterness in the mouth,
belching bitter
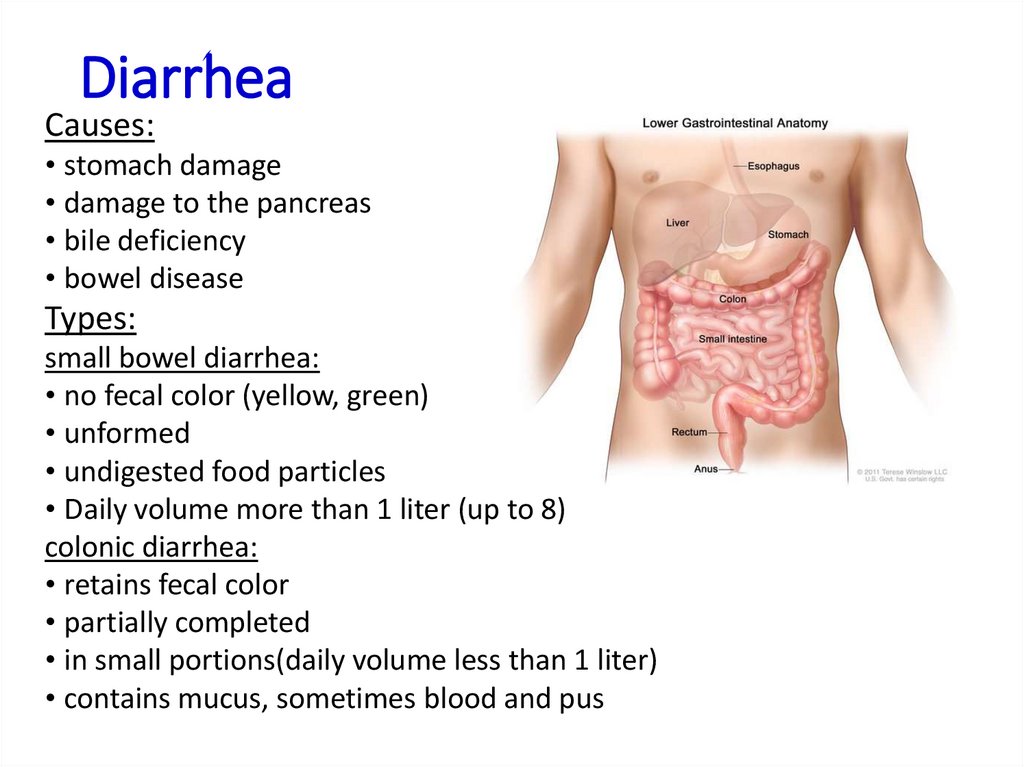
13. Diarrhea
Causes:• stomach damage
• damage to the pancreas
• bile deficiency
• bowel disease
Types:
small bowel diarrhea:
• no fecal color (yellow, green)
• unformed
• undigested food particles
• Daily volume more than 1 liter (up to 8)
colonic diarrhea:
• retains fecal color
• partially completed
• in small portions(daily volume less than 1 liter)
• contains mucus, sometimes blood and pus
14. Malabsorption syndrome
• Syndrome of Metabolic Disorder - diarrhea +loss of weight due to impaired absorption of
proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins,
microelements
•Where are they absorbed?
•Only digested foods are absorbed !!!
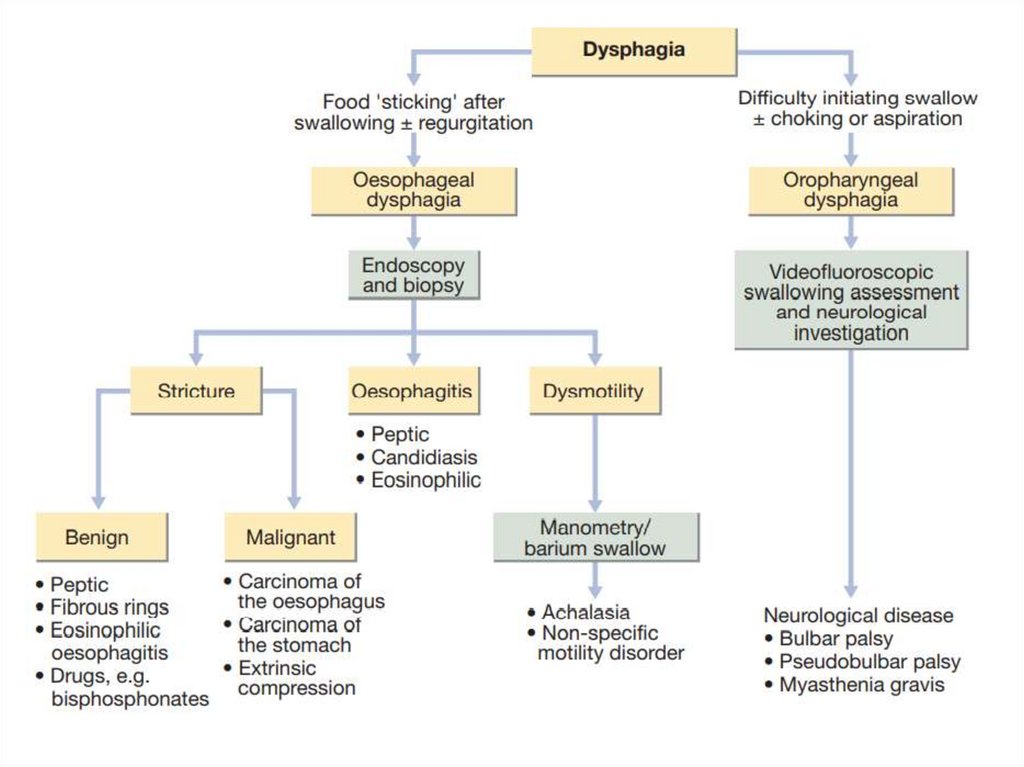
15. Dysphagia- difficulty in swallowing
Violation of the passage of food, it should bedistinguished from both globus sensation (in
which anxious people feel a lump in the throat
without organic cause) and odynophagia (pain
during swallowing, usually from gastrooesophageal reflux or candidiasis).
2 types:
- Pharyngeal (oropharyngeal)
- Esophageal dysphagia
16.
17. Other symptoms
• Bloating (flatulence) - excess gassing• Excessive salivation - hypersalivation
• Odinophagy
• Sitophobia
• Hypo- and anorexia
• Rumination with chewing
• Borborism
• Signs of bleeding: vomiting blood ("coffee
grounds"), tarry stools (melena), weakness,
dizziness










 medicine
medicine