Similar presentations:
Ent. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
1.
zENT
2.
zCaused allergens: hay, pollen, dust,
animal hair, mold spores
Symptoms: nasal congestion and red, itchy,
swollen eyes with frequent bouts of
sneezing
Begin after exposure to allergen
Allergic Rhinitis
Diagnosis: patch test, scratch test
Treatment:
Avoid triggering allergen
Antihistamine medication
Nasal irrigation
Micro-dose of allergen to full dose
3.
zIt’s inflammation of the paranasal
sinuses
Causes: viral (Rhinovirus,
Parainfluenza virus, Influenza
virus) bacterial (Streptococcus
Pneumoniae, Haemophilus
Influenzae, Moraxella Catarrhalis)
Sinusitis
Diagnosis: Cl, CT scan, rhinoscopy
Symptoms: facial pain, pressure in
face, headache, fever, changes in
voice, sense of smell, cough
Treatment: Bacterial: antibiotics, decongestants
Allergy or polyps: steroids and antihistamines
Chronic: sinus surgery
4.
zInflammation of the tonsils
Causes: virus, bacteria (Strep. Pyogenes
and pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenza
and Staph)
Symptoms: sore throat, fever, pain on
swallowing, anterior cervical
lymphadenopathy
Tonsillitis
Diagnosis: Cl
Treatment
Simple analgesia
(paracetamol, ibuprofen)
Antibiotics (penicillin V,
clarithromycin)
5.
zTonsillitis
Tonsils
Red
Inflamed
Enlarged
Exudates (white patches of
pus)
6.
zComplications
Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy)
Otitis media
Scarlet fever
Rheumatic fever
Post- streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Post-streptococcal reactive arthritis
Tonsillitis
7.
zEpistaxis
Anterior bleeding
More common
Young patient
Mucosal dryness/ foreign /picking
Symptoms
Blood coming out of the nostrils/
the lacrimal ducts/the mouth
(vomiting)/the anus (dark blood)
Age
Posterior bleeding
Less common
Older patients
HTN
Younger than 10
Older then 50
8.
zCauses
Epistaxis
Jeuvenile nasopharyngeal
angiofibroma – surgical
resection
Elderly hypertension – (huge
amount of bleeding) BP
control, posterior packing and
vessel ligation
Most commons: nose picking,
foreign object, blunt trauma, RTIs
Treatment
Picking the nose – local pressure
and phenylephrine spray
9.
zNasal papilloma
Uncommon tumor
Symptoms
Associated with HPV 11,16,18
Nasal obstruction
Lateral wall of nose in the middle
meatus
Nasal discharge
Epistaxis
Headache due to sinus
involvement
Proptosis, lacrimation and
diplopia due to orbital
involvement
Almost always unilateral
Can invade sinus or orbit
10.
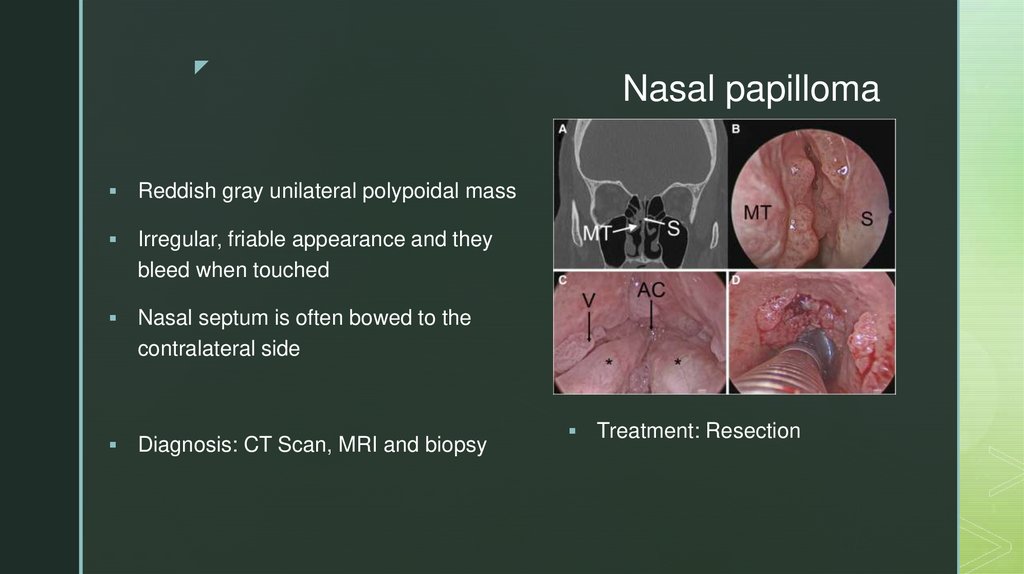
zReddish gray unilateral polypoidal mass
Irregular, friable appearance and they
bleed when touched
Nasal septum is often bowed to the
contralateral side
Diagnosis: CT Scan, MRI and biopsy
Nasal papilloma
Treatment: Resection
11.
zCause: viral (Rhinovirus, Parainfluenza
viruses, Adenovirus, Influenza viruses),
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Symptoms: hoarseness, sore throat,
cough, rhinorrhea, postnasal discharge,
fatigue, malaise
Laryngitis
Treatment
Humidified air and vocal rest
Mucolytics (guaifenesin)
12.
zLocated behind the nasal passage at
the roof of the mouth
Symptoms: nasal blockage, mouth
breathing, bad breath, nasal tone
when speaking, chronic running nose
Complications: temporary hearing loss
(fluid accumulation in the middle ear),
frequent ear infection, snoring,
obstructive sleep apnea
Adenoid hypertrophy
13.
zAdenoid hypertrophy
Diagnosis: X-ray
Treatment
They usually shrink as the child
gets older and disappear by
puberty
Bacterial infection: antibiotics
Allergy: steroidal nasal spray
Surgical removal (if no
improvement with the above
medications)
14.
zSunken eyes
Narrow pinched nostrils
Open mouth
High-arched palate
Crowded teeth
Dull mask-like face
Drooling saliva
Everted upper lip
Rhinorrhoea
Adenoid Facies
15.
zRisk factors: cigarette smoking, alcohol,
squamos papillomass and
papillomatosis, HPV 6 and 11
The most common:
SCC on the true vocal cords
Hoarsness of voice, cervical
lymphadenopathy
Laryngeal carcinoma
Treatment:
Radiation
Partial or total laryngectomy
Chemoradiation therapy
16.
zNasopharyngeal cancer
SCC
In the posterior-lateral nasopharynx
or pharyngeal recess
Causes: Epstein-Barr virus, genetic
susceptibility, consumption of food
(salted fish)
Symptoms:
nasal discharge, epistaxis
5th cranial nerve: neurokeratitis,
loss of facial sensation,
weakness of jaw muscles
6th cranial nerve: diplopia
Cavernous sinus syndrome
Painless lymphadenopathy
(cervical lymph nodes)
17.
zNasopharyngeal cancer
Diagnosis: histopathology,
physical exam and CT/PET
scan
Treatment
Resection
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
18.
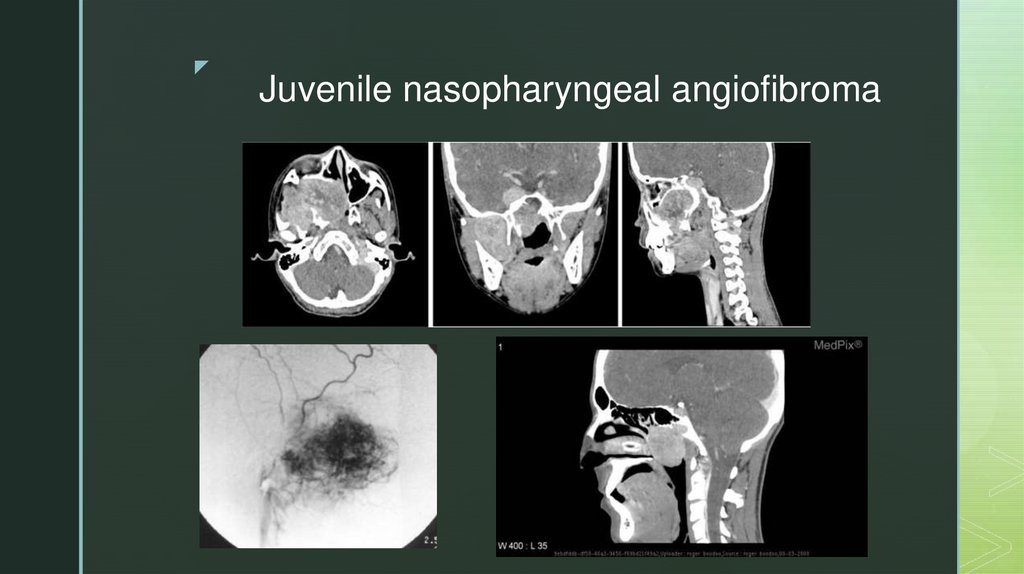
zJuvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Benign tumor
Treatment:
Onset is most commonly in
the second decade
Hormonal therapy
Symptoms: nasal obstruction,
epistaxis, headache, facial
swelling
Diagnosis: CT scan, MRI,
angiography
testosterone receptor
blocker flutamide
Radiotherapy
Surgical therapy
19.
zJuvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma

















 medicine
medicine








